Small Nucleolar Derived RNAs as Regulators of Human Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
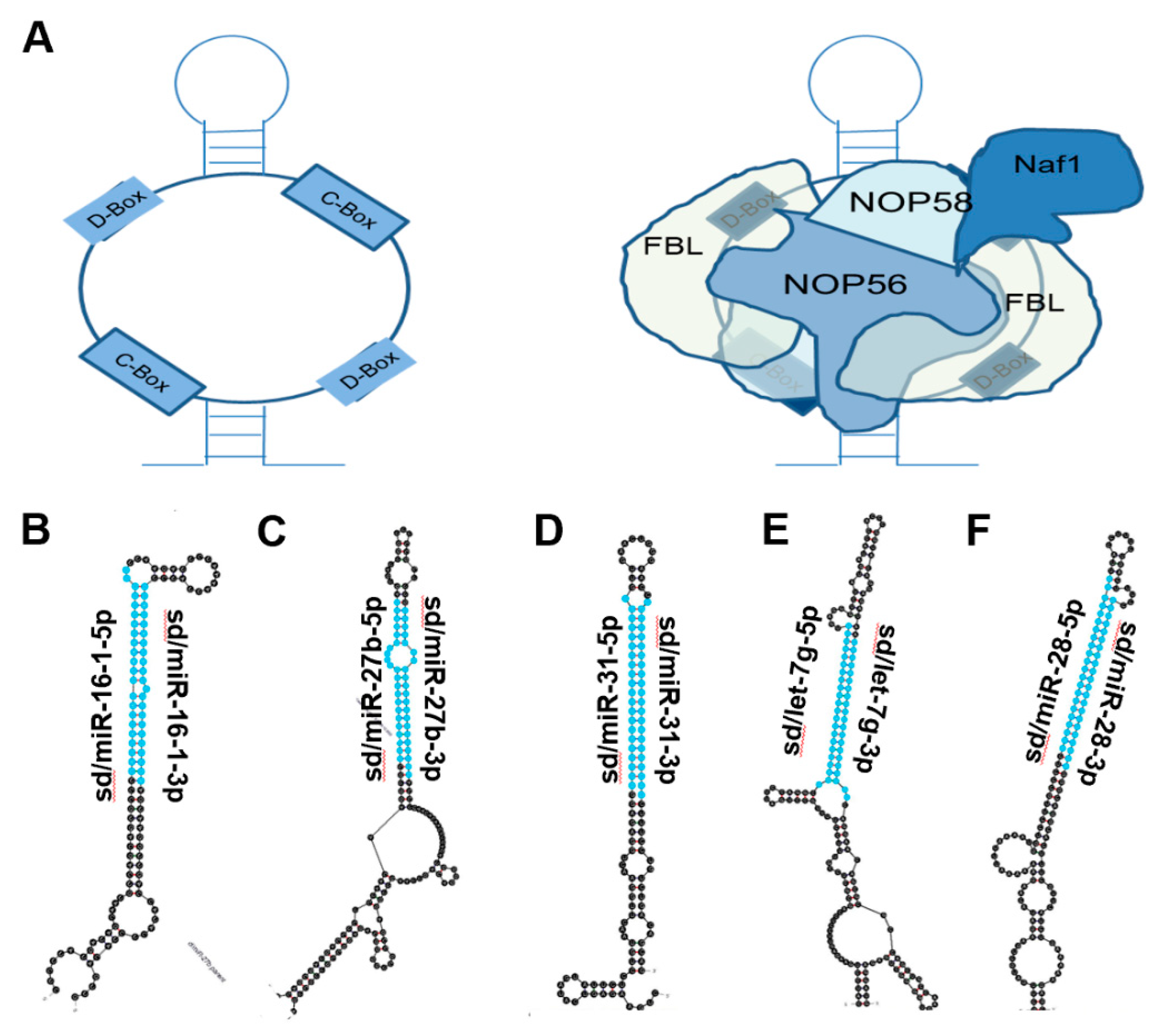
2. snoRNA Structure and Function
3. sdRNA Biogenesis
3.1. miRNA-Like Biogenesis of sdRNAs
3.2. Non-miRNA-Like Biogenesis of sdRNAs
4. sdRNAs in Cancer
4.1. sd/miR-664
4.2. Sd/miR-1291
4.3. Sd/miR-3651
4.4. sd/miR-768
4.5. sd/miR-1248
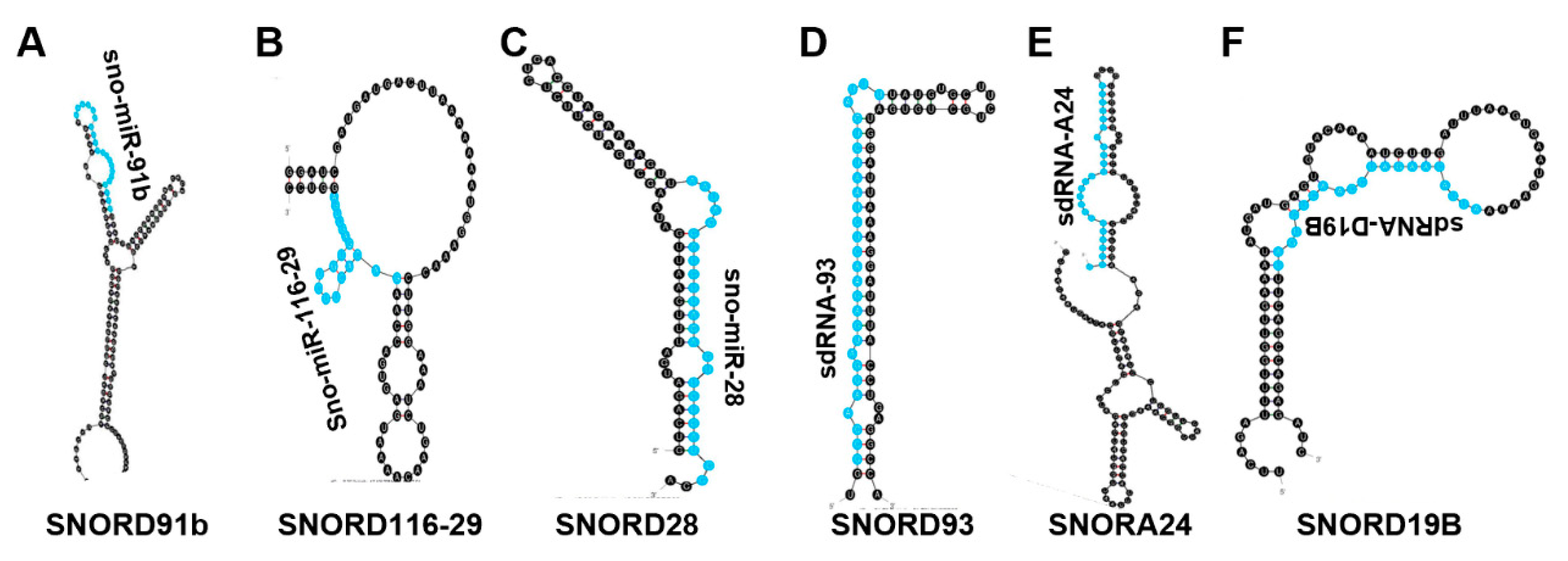
4.6. hsa-sno-HBII-296B and hsa-sno-HBII-85-29
4.7. Sno-miR-28
4.8. sdRNA-93
4.9. sdRNA-D19b and sdRNA-A24
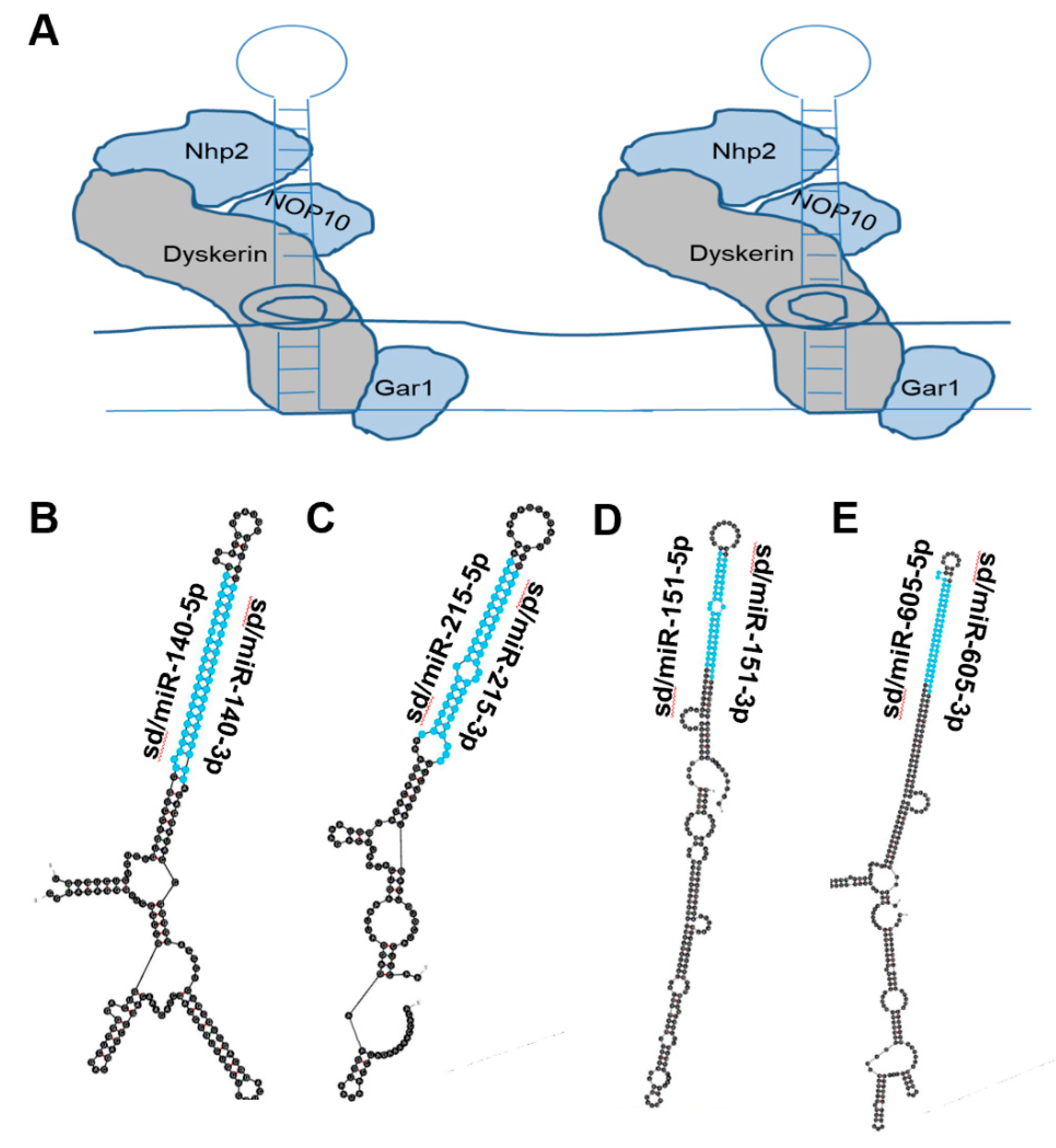
4.10. Sd/miR-140
4.11. Sd/miR-151
4.12. Sd/miR-215
4.13. Sd/miR-605
4.14. Sd/miR-16-1
4.15. Sd/miR-27b
4.16. Sd/miR-31
4.17. Sd/let-7g
4.18. Sd/miR-28
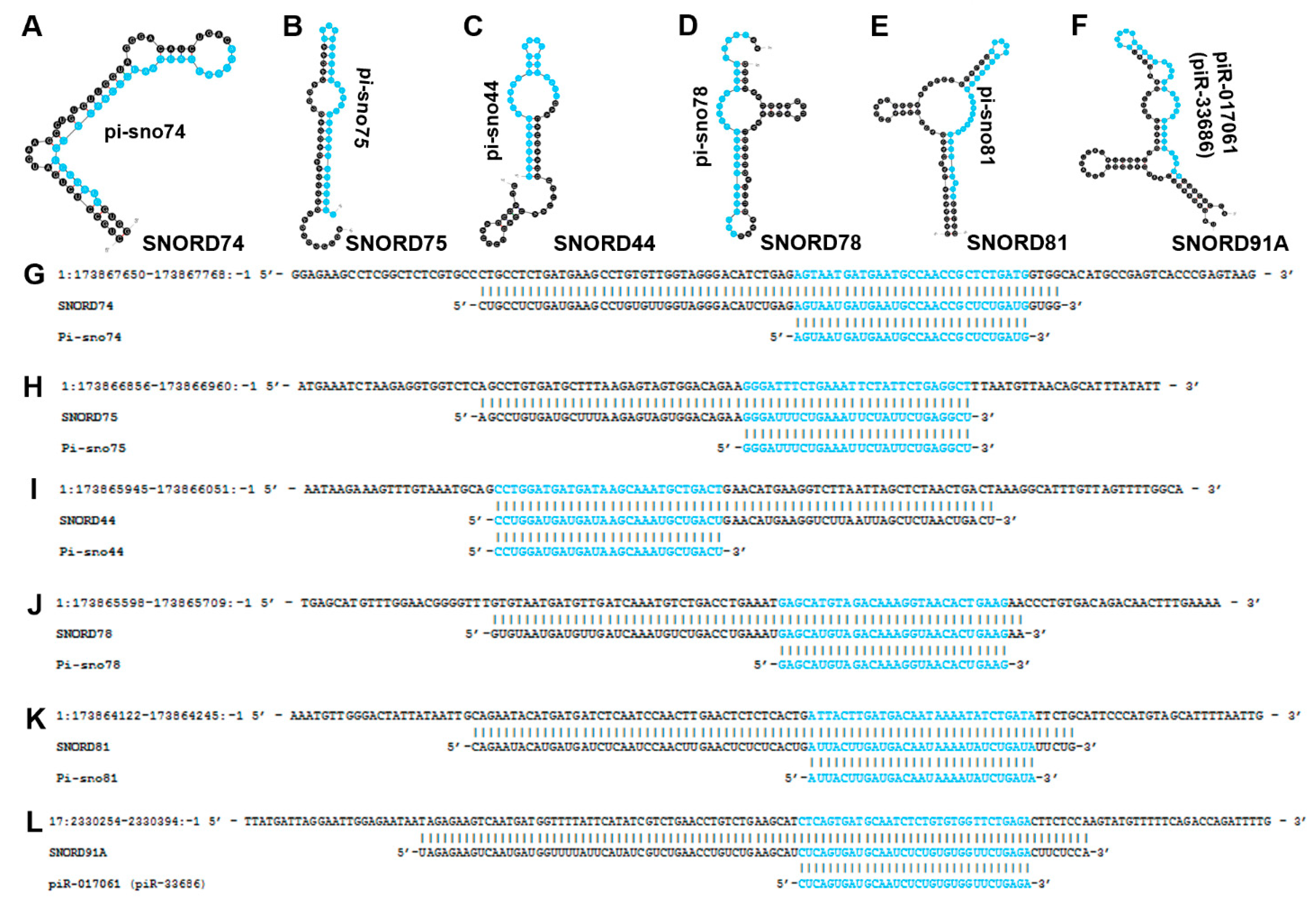
4.19. pi-sno74, pi-sno75, pi-sno44, pi-sno78, and pi-sno81
4.20. pi-sno78 (Sd78-3′)
4.21. piR-017061
5. SdRNAomes
6. Discussion/Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Calin, G.A.; Dumitru, C.D.; Shimizu, M.; Bichi, R.; Zupo, S.; Noch, E.; Alder, H.; Rattan, S.; Keating, M.; Rai, K.; et al. Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro- RNA genes miR15 and miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 15524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawaji, H.; Nakamura, M.; Takahashi, Y.; Sandelin, A.; Katayama, S.; Fukuda, S.; O Daub, C.; Kai, C.; Kawai, J.; Yasuda, J.; et al. Hidden layers of human small RNAs. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balakin, A.G.; Smith, L.; Fournier, M.J. The RNA world of the nucleolus: Two major families of small RNAs defined by different box elements with related functions. Cell 1996, 86, 823–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss-László, Z.; Henry, Y.; Kiss, T. Sequence and structural elements of methylation guide snoRNAs essential for site-specific ribose methylation of pre-rRNA. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 797–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaille, J.; Nicoloso, M.; Bachellerie, J.P. Targeted ribose methylation of RNA in vivo directed by tailored antisense RNA guides. Nature 1996, 383, 732–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss-László, Z.; Henry, Y.; Bachellerie, J.P.; Caizergues-Ferrer, M.; Kiss, T. Site-specific ribose methylation of preribosomal RNA: A novel function for small nucleolar RNAs. Cell 1996, 85, 1077–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganot, P.; Bortolin, M.L.; Kiss, T. Site-specific pseudouridine formation in preribosomal RNA is guided by small nucleolar RNAs. Cell 1997, 89, 799–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Tien, A.L.; Fournier, M.J. Small nucleolar RNAs direct site-specific synthesis of pseudouridine in ribosomal RNA. Cell 1997, 89, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolin, M.L.; Ganot, P.; Kiss, T. Elements essential for accumulation and function of small nucleolar RNAs directing site-specific pseudouridylation of ribosomal RNAs. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, B.; Yegnasubramanian, S.; Wheelan, S.J.; Laiho, M. RNA-Seq of the Nucleolus Reveals Abundant SNORD44-Derived Small RNAs. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leverette, R.D.; Andrews, M.T.; Maxwell, E.S. Mouse U14 snRNA is a processed intron of the cognate hsc70 heat shock pre-messenger RNA. Cell 1992, 71, 1215–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragapane, P.; Prislei, S.; Michienzi, A.; Caffarelli, E.; Bozzoni, I. A novel small nucleolar RNA (U16) is encoded inside a ribosomal protein intron and originates by processing of the pre-mRNA. EMBO J. 1993, 12, 2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tycowski, K.T.; Shu MDi Steitz, J.A. A mammalian gene with introns instead of exons generating stable RNA products. Nature 1996, 379, 464–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard, P.; Kiss, A.M.; Darzacq, X.; Kiss, T. Cotranscriptional recognition of human intronic box H/ACA snoRNAs occurs in a splicing-independent manner. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 26, 2540–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ender, C.; Krek, A.; Friedländer, M.R.; Beitzinger, M.; Weinmann, L.; Chen, W.; Pfeffer, S.; Rajewsky, N.; Meister, G. A human snoRNA with MicroRNA-like functions. Mol. Cell 2008, 32, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Ben, S.; Xin, J.; Li, S.; Zheng, R.; Wang, H.; Fan, L.; Du, M.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, M. The biogenesis and biological function of PIWI-interacting RNA in cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimasu, H.; Ishizu, H.; Saito, K.; Fukuhara, S.; Kamatani, M.K.; Bonnefond, L.; Matsumoto, N.; Nishizawa, T.; Nakanaga, K.; Aoki, J.; et al. Structure and function of Zucchini endoribonuclease in piRNA biogenesis. Nature 2012, 491, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wajahat, M.; Bracken, C.P.; Orang, A. Emerging functions for snoRNAs and snoRNA-derived fragments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, M.; Scott, M.S.; Yamada, K.; Avolio, F.; Barton, G.J.; Lamond, A.I. Identification of human miRNA precursors that resemble box C/D snoRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 3879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuker, M. Mfold web server for nucleic acid folding and hybridization prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3406–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Hou, J.; Li, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Wei, J.; Song, D.; Hu, T.; Wu, Q.; Yang, J.Y.; Cai, J.C. miR-15a-3p and miR-16-1-3p Negatively Regulate Twist1 to Repress Gastric Cancer Cell Invasion and Metastasis. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 13, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qq, F.; Zq, D.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, H.; Long, C. miR-16-1-3p targets TWIST1 to inhibit cell proliferation and invasion in NSCLC. Bratisl. Lek. Listy 2018, 119, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maximov, V.V.; Akkawi, R.; Khawaled, S.; Salah, Z.; Jaber, L.; Barhoum, A.; Or, O.; Galasso, M.; Kurek, K.C.; Yavin, E.; et al. MiR-16-1-3p and miR-16-2-3p possess strong tumor suppressive and antimetastatic properties in osteosarcoma. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 145, 3052–3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, T.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, X. MicroRNA-16-1-3p Represses Breast Tumor Growth and Metastasis by Inhibiting PGK1-Mediated Warburg Effect. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 615154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishteiwy, R.A.; Ward, T.M.; Dykxhoorn, D.M.; Burnstein, K.L. The microRNA -23b/-27b cluster suppresses the metastatic phenotype of castration-resistant prostate cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e52106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, L.; Zhang, L.; Fan, K.; Wang, J. MiR-27b targets LIMK1 to inhibit growth and invasion of NSCLC cells. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2014, 390, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Duan, Q.; Gan, L.; Li, W.; Yang, J.; Huang, G. microRNA-27b inhibits cell proliferation and invasion in bladder cancer by targeting engrailed-2. Biosci. Rep. 2021, 41, BSR20201000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurila, E.M.; Kallioniemi, A. The diverse role of miR-31 in regulating cancer associated phenotypes. Genes Chromosom. Cancer 2013, 52, 1103–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Ma, P.; Wu, D.; Shu, Y.; Gao, W. Functions and mechanisms of microRNA-31 in human cancers. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 108, 1162–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandrés, E.; Cubedo, E.; Agirre, X.; Malumbres, R.; Zárate, R.; Ramirez, N.; Abajo, A.; Navarro, A.; Moreno, I.; Monzó, M.; et al. Identification by Real-time PCR of 13 mature microRNAs differentially expressed in colorectal cancer and non-tumoral tissues. Mol. Cancer. 2006, 5, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.J.; Tsai, M.M.; Hung, P.S.; Kao, S.Y.; Liu, T.Y.; Wu, K.J.; Chiou, S.H.; Lin, S.C.; Chang, K.W. miR-31 ablates expression of the HIF regulatory factor FIH to activate the HIF pathway in head and neck carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 1635–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenberg, E.; Hershkovitz, L.; Itzhaki, O.; Hajdu, S.; Nemlich, Y.; Ortenberg, R.; Gefen, N.; Edry, L.; Modai, S.; Keisari, Y.; et al. Regulation of cancer aggressive features in melanoma cells by MicroRNAs. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuse, M.; Kojima, S.; Enokida, H.; Chiyomaru, T.; Yoshino, H.; Nohata, N.; Kinoshita, T.; Sakamoto, S.; Naya, Y.; Nakagawa, M.; et al. Tumor suppressive microRNAs (miR-222 and miR-31) regulate molecular pathways based on microRNA expression signature in prostate cancer. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 57, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.S.; Erkeland, S.J.; Pester, R.E.; Chen, C.Y.; Ebert, M.S.; Sharp, P.A.; Jacks, T. Suppression of non-small cell lung tumor development by the let-7 microRNA family. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 3903–3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.M.; Wong, H.S.C.; Huang, C.Y.; Hsu, W.L.; Maio, Z.F.; Chiu, S.J.; Tsai, Y.T.; Chen, B.K.; Wan, Y.J.Y.; Wang, J.Y.; et al. Functional effects of let-7g expression in colon cancer metastasis. Cancers 2019, 11, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biamonte, F.; Santamaria, G.; Sacco, A.; Perrone, F.M.; Di Cello, A.; Battaglia, A.M.; Salatino, A.; Di Vito, A.; Aversa, I.; Venturella, R.; et al. MicroRNA let-7g acts as tumor suppressor and predictive biomarker for chemoresistance in human epithelial ovarian cancer. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, C.; Setty, M.; Holmes, A.B.; Maute, R.L.; Leslie, C.S.; Mussolin, L.; Rosolen, A.; Dalla-Favera, R.; Bassoa, K. microRNA 28 controls cell proliferation and is down-regulated in B-cell lymphomas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 8185–8190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazio, S.; Berti, G.; Russo, F.; Evangelista, M.; D’Aurizio, R.; Mercatanti, A.; Pellegrini, M.; Rizzo, M. The miR-28-5p targetome discovery identified SREBF2 as one of the mediators of the miR-28-5p tumor suppressor activity in prostate cancer cells. Cells 2020, 9, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, F. miR-28-5p inhibits the migration of breast cancer by regulating WSB2. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 46, 1562–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, M.S.; Avolio, F.; Ono, M.; Lamond, A.I.; Barton, G.J. Human miRNA precursors with Box H/ACA snoRNA features. PLOS Comput. Biol. 2009, 5, e1000507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, T.; Wang, Z.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Shang, Y.; Sun, J. MALAT1 knockdown inhibits prostate cancer progression by regulating miR-140/BIRC6 axis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 123, 109666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, G.; Zhang, W.; Niu, L.; Yan, Y.; REn, Y.; Zou, Y. MiR-215 functions as a tumor suppressor in epithelial ovarian cancer through regulation of the X-chromosome-linked inhibitor of apoptosis. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 35, 1816–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vychytilova-Faltejskova, P.; Merhautova, J.; Machackova, T.; Gutierrez-Garcia, I.; Garcia-Solano, J.; Radova, L.; Brchnelova, D.; Slaba, K.; Svoboda, M.; Halamkova, J.; et al. MiR-215-5p is a tumor suppressor in colorectal cancer targeting EGFR ligand epiregulin and its transcriptional inducer HOXB9. Oncogene 2017, 6, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, B.; Chen, S.; Ke, S.; Cheng, S.; Wu, T.; Yang, Y. MicroRNA-151 regulates the growth, chemosensitivity and metastasis of human prostate cancer cells by targeting PI3K/AKT. J. BUON 2020, 25, 2045–2050. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.-Y.; Xu, L.-F.; Hu, H.-L.; Wen, Y.-Q.; Chen, D.; Liu, W.-H. MiRNA-215-5p alleviates the metastasis of prostate cancer by targeting PGK1. Gene 2017, 626, 344–353. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, C.; Zhao, H.; Yang, B.; Sun, Z.; Li, X.; Hu, X. lnc-REG3G-3-1/miR-215-3p Promotes Brain Metastasis of Lung Adenocarcinoma by Regulating Leptin and SLC2A5. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.; Lin, H.; Luo, X.; Luo, X.; Wang, Z. miR-605 joins p53 network to form a p53:miR-605:Mdm2 positive feedback loop in response to stress. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 5021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.P.; Levesque, E.; Guillemette, C.; Yu, C.C.; Huang, C.Y.; Lin, V.C.; Chung, I.C.; Chen, L.C.; Laverdière, I.; Lacombe, L.; et al. Genetic variants in microRNAs and microRNA target sites predict biochemical recurrence after radical prostatectomy in localized prostate cancer. Int. J. Cancer. 2014, 135, 2661–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Cao, Y.; Rong, D.; Wang, Y.; Cao, Y. MicroRNA-605 functions as a tumor suppressor by targeting INPP4B in melanoma. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 1276–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhasan, A.H.; Scott, A.W.; Wu, J.J.; Feng, G.; Meeks, J.J.; Thaxton, C.S.; Mirkin, C.A. Circulating microRNA signature for the diagnosis of very high-risk prostate cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 10655–10660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yang, H.; Xia, W.; Cui, L.; Xu, R.; Lu, H.; Xue, Z.; Zhang, B.; Tian, Z.; Cao, Y.; et al. Down-regulation of miR-605 promotes the proliferation and invasion of prostate cancer cells by up-regulating EN2. Life Sci. 2017, 190, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, R.D.; Chen, S. Sno-derived RNAs are prevalent molecular markers of cancer immunity. Oncogene 2018, 37, 6442–6462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edoh, D.; Kiss, T.; Filipowicz, W. Activity of U-snRNA genes with modified placement of promoter elements in transfected protoplasts and stably transformed tobacco. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993, 21, 1533–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Taft, R.J.; Glazov, E.A.; Lassmann, T.; Hayashizaki, Y.; Carninci, P.; Mattick, J.S. Small RNAs derived from snoRNAs. RNA 2009, 15, 1233–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregory, R.I.; Yan, K.P.; Amuthan, G.; Chendrimada, T.; Doratotaj, B.; Cooch, N.; Shiekhattar, R. The Microprocessor complex mediates the genesis of microRNAs. Nature 2004, 432, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Guo, D.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, S.; Zhang, R. miR-664b-5p inhibits hepatocellular cancer cell proliferation through targeting oncogene AKT2. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2020, 35, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, M.; Ou, R.; Zhang, Q.; Lin, F.; Li, X.; Wang, K.; Xu, Y. MicroRNA-664 suppresses the growth of cervical cancer cells via targeting c-Kit. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2019, 13, 2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, C.; Xie, X.; Zhou, Z.; Zhou, M.; Chen, L.; Ding, Z. MicroRNA-664 functions as an oncogene in cutaneous squamous cell carcinomas (cSCC) via suppressing interferon regulatory factor 2. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2019, 94, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, M.J.; Pan, Y.Z.; Qiu, J.X.; Kim, E.J.; Yu, A.M. MicroRNA-1291 targets the FOXA2-AGR2 pathway to suppress pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and tumorigenesis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 45547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, M.J.; Duan, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, C.; Bold, R.J.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Kim, E.J.; Yu, A. MicroRNA-1291-5p sensitizes pancreatic carcinoma cells to arginine deprivation and chemotherapy through the regulation of arginolysis and glycolysis. Mol. Pharmacol. 2020, 98, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, T.; Seki, N.; Yoshino, H.; Itesako, T.; Yamada, Y.; Tatarano, S.; Hidaka, H.; Yonezawa, T.; Nakagawa, M.; Enokida, H. Tumor-suppressive microRNA-1291 directly regulates glucose transporter 1 in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2013, 104, 1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Q.; Zhao, A.; Ren, L.; Chen, J.; Liao, K.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, W. MicroRNA-1291 mediates cell proliferation and tumorigenesis by downregulating MED1 in prostate cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escuin, D.; López-Vilaró, L.; Bell, O.; Mora, J.; Moral, A.; Pérez, J.I.; Arqueros, C.; Ramón y Cajal, T.; Lerma, E.; Barnadas, A. MicroRNA-1291 is associated with locoregional metastases in patients with early-stage breast cancer. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 562114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pudova, E.A.; Krasnov, G.S.; Nyushko, K.M.; Kobelyatskaya, A.A.; Savvateeva, M.V.; Poloznikov, A.A.; Dolotkazin, D.R.; Klimina, K.M.; Guvatova, Z.G.; Simanovsky, S.A.; et al. miRNAs expression signature potentially associated with lymphatic dissemination in locally advanced prostate cancer. BMC Med. Genom. 2020, 13 (Suppl. S8), 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Ding, D.; Gao, Y.; Li, Y. MicroRNA-3651 promotes colorectal cancer cell proliferation through directly repressing T-box transcription factor 1. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 45, 956–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Guan, S.; Chen, X.; Liu, B.; Liu, F.; Han, L.; Un Nesa, E.; Song, Q.; Bao, C.; Wang, X.; et al. Clinical potential of miR-3651 as a novel prognostic biomarker for esophageal squamous cell cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 465, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blenkiron, C.; Hurley, D.G.; Fitzgerald, S.; Print, C.G.; Lasham, A. Links between the oncoprotein YB-1 and small non-coding RNAs in breast cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Ni, Z.; Wang, G.; Cui, J.; Wei, C.; Wang, J.; Yang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Li, F. Aberrant expression of microRNAs in gastric cancer and biological significance of miR-574-3p. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2012, 13, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramani, A.; Alsidawi, S.; Jagannathan, S.; Sumita, K.; Sasaki, A.T.; Aronow, B.; Warnick, R.E.; Lawler, S.; Driscoll, J.J. The brain microenvironment negatively regulates miRNA-768-3p to promote K-ras expression and lung cancer metastasis. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, S.; Raulefs, S.; Bruns, P.; Afonso-Grunz, F.; Plötner, A.; Thermann, R.; Jäger, C.; Schlitter, A.M.; Kong, B.; Regel, I.; et al. Next-generation sequencing reveals novel differentially regulated mRNAs, lncRNAs, miRNAs, sdRNAs and a piRNA in pancreatic cancer. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Bracken, C.P.; Pillman, K.A.; Lawrence, D.M.; Goodall, G.J.; Callen, D.F.; Neilsen, P.M. p53 Represses the oncogenic Sno-MiR-28 derived from a SnoRNA. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, D.G.; Roberts, J.T.; King, V.M.; Houserova, D.; Barnhill, E.C.; Crucello, A.; Polska, C.J.; Brantley, L.W.; Kaufman, G.C.; Nguyen, M.; et al. Human snoRNA-93 is processed into a microRNA-like RNA that promotes breast cancer cell invasion. NPJ Breast Cancer 2017, 3, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coley, A.B.; Stahly, A.N.; Kasukurthi, M.V.; Barchie, A.A.; Hutcheson, S.B.; Houserova, D.; Huang, Y.; Watters, B.C.; King, V.M.; Dean, M.A.; et al. MicroRNA-like snoRNA-Derived RNAs (sdRNAs) promote castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cells 2022, 11, 1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Sempere, L.F.; Ouyang, H.; Memoli, V.A.; Andrew, A.S.; Luo, Y.; Demidenko, E.; Korc, M.; Shi, W.; Preis, M.; et al. MicroRNA-31 functions as an oncogenic microRNA in mouse and human lung cancer cells by repressing specific tumor suppressors. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, D.; Ding, D.; Han, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, N.; Foltz, G.; Lan, Q.; Huang, Q.; Lin, B. Human miR-31 targets radixin and inhibits migration and invasion of glioma cells. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 27, 700–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Chen, X.; Zhang, X.; Duan, X.; Pan, T.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhong, F.; Liu, J.; Zhang, H.; et al. An Lnc RNA (GAS5)/SnoRNA-derived piRNA induces activation of TRAIL gene by site-specifically recruiting MLL/COMPASS-like complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 3712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martens-Uzunova, E.S.; Hoogstrate, Y.; Kalsbeek, A.; Pigmans, B.; Vredenbregt-van den Berg, M.; Dits, N.; Nielsen, S.J.; Baker, A.; Visakorpi, T.; Bangma, C.; et al. C/D-box snoRNA-derived RNA production is associated with malignant transformation and metastatic progression in prostate cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 17430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.M.; Liu, X.M.; Zhang, X.J.; Zheng, B.; Qian, G.R.; Ma, Z.L. MicroRNA-18a-5p functions as an oncogene by directly targeting IRF2 in lung cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.J.; Luo, S.N.; Wu, H.; Zhang, N.P.; Dong, L.; Liu, T.T.; Liang, L.; Shen, X.Z. IRF-2 inhibits cancer proliferation by promoting AMER-1 transcription in human gastric cancer. J. Transl Med. 2022, 20, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, G.; Wang, L.; Lin, Y.; Sun, F. Hsa-miR-513b-5p suppresses cell proliferation and promotes P53 expression by targeting IRF2 in testicular embryonal carcinoma cells. Gene 2017, 626, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulf, T.; Sibbritt, T.; Wiklund, E.D.; Patterson, K.; Song, J.Z.; Stirzaker, C.; Qu, W.; Nair, S.; Horvath, L.G.; Armstrong, N.J.; et al. Epigenetic-induced repression of microRNA-205 is associated with MED1 activation and a poorer prognosis in localized prostate cancer. Oncogene 2012, 32, 2891–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brameier, M.; Herwig, A.; Reinhardt, R.; Walter, L.; Gruber, J. Human box C/D snoRNAs with miRNA like functions: Expanding the range of regulatory RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aqeilan, R.I.; Calin, G.A.; Croce, C.M. miR-15a and miR-16-1 in cancer: Discovery, function and future perspectives. Cell Death Differ. 2009, 17, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Jiao, D.; Hu, H.; Song, J.; Yan, J.; Wu, L.; Xu, L.Q. Downregulation of LIMK1 level inhibits migration of lung cancer cells and enhances sensitivity to chemotherapy drugs. Oncol. Res. 2013, 20, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyerinas, B.; Park, S.M.; Hau, A.; Murmann, A.E.; Peter, M.E. The role of let-7 in cell differentiation and cancer. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2010, 17, F19–F36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Cao, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, N.; You, Y. Regulation of let-7 and its target oncogenes (Review). Oncol Lett. 2012, 3, 955–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balzeau, J.; Menezes, M.R.; Cao, S.; Hagan, J.P. The LIN28/let-7 pathway in cancer. Front. Genet. 2017, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martens-Uzunova, E.S.; Jalava, S.E.; Dits, N.F.; Van Leenders, G.J.L.H.; Møller, S.; Trapman, J.; Bangma, C.H.; Litman, T.; Visakorpi, T.; Jenster, G. Diagnostic and prognostic signatures from the small non-coding RNA transcriptome in prostate cancer. Oncogene 2011, 31, 978–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraiya, A.A.; Wang, C.C. snoRNA, a Novel precursor of microRNA in giardia lamblia. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, E.C.; Tomancak, P.; Williams, R.W.; Rubin, G.M. Computational identification of drosophila microRNA genes. Genome Biol. 2003, 4, R42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| sdRNA | Sequence (5′-sdRNA :: 3′-sdRNA) ** | Parental snoRNA | Annotated as miR? | Cancer | Expression | Phenotypic Effect | Target | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sdRNAs Misannotated as Traditional miRNAs | ||||||||
| **sd/miR-664a (ENSG00000281696) | 5′-ACUGGCUAGGGAAAAUGAUUGGAU-3′ :: 5′-UAUUCAUUUAUCCCCAGCCUACA-3′ | SNORA36B (ENSG00000222370) | Yes | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Downregulated in tumor | Tumor-suppressing | AKT2 | [56] |
| Cervical | Downregulated in tumor | Tumor-suppressing | c-Kit | [57] | ||||
| Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma | Upregulated in Tumor | Tumor-promoting | IFR2 | [58] | ||||
| sd/miR-1291 (ENSG00000281842) | 5′-UGGCCCUGACUGAAGACCAGCAGU-3′ | SNORA2C (ENSG00000221491) | Yes | Pancreatic | Downregulated in Tumor | Tumor-suppressing | FOXA2 | [59] |
| Pancreatic | UNDETERMINED | Tumor-suppressing | FOXA2 | [60] | ||||
| Renal Cell Carcinoma | Downregulated in Tumor | Tumor-suppressing | GLUT1 | [61] | ||||
| Prostate | Downregulated in Tumor | Tumor-suppressing | MED1 | [62] | ||||
| Breast | Downregulated in metastases | Tumor-suppressing | UNDETERMINED | [63] | ||||
| sd/miR-1248 (ENSG00000283958) | 5′-ACCUUCUUGUAUAAGCACUGUGCUAAA-3′ | SNORA81 (ENSG00000221420) | Yes | Prostate | Upregulated aggressive tumor | UNDETERMINED | UNDETERMINED | [64] |
| sd/miR-3651 (ENSG00000281156) | 5′-CAUAGCCCGGUCGCUGGUACAUGA-3′ | SNORA84 (ENSG00000239183) | Yes | Colorectal | Upregulated in tumor | Tumor-promoting | TBX1 | [65] |
| Esophageal | Downregulated in tumor | UNDETERMINED | UNDETERMINED | [66] | ||||
| **sd/miR-768 (ENSG00000223224) | 5′-GUUGGAGGAUGAAAGUACGGAGUGAU-3′ :: 5′-UCACAAUGCUGACACUCAAACUGCUGAC-3′ | SNORD71 (ENSG00000223224) | Yes | Breast | UNDETERMINED | UNDETERMINED | YB-1 | [67] |
| Gastric | Downregulated in tumor | UNDETERMINED | UNDETERMINED | [68] | ||||
| Lung, Breast, Ovary, Melanoma, Liver, Parotid Gland, Thyroid Gland, Large Cell | Downregulated in tumor | Tumor-suppressing, UNDETERMINED | KRAS | [69] | ||||
| sdRNAs not Previously Annotated as miRNAs | ||||||||
| sd/hsa-sno-HBII-296B | NA | SNORD91B (ENSG00000275084) | No | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Downregulated in Tumor | UNDETERMINED | UNDETERMINED | [70] |
| sd/hsa-sno-HBII-85-29 | NA | SNORD116-29 (ENSG00000207245) | No | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Downregulated in Tumor | UNDETERMINED | UNDETERMINED | [70] |
| sno-miR-28 | 5′-AAUAGCAUGUUAGAGUUCUGAUGG-3′ | SNORD28 (ENSG00000274544) | No | Breast | Upregulated in Tumor | Tumor-promoting | TAF9B | [71] |
| sdRNA-93 | 5′-GCCAAGGAUGAGAACUCUAAUCUGAUUU-3′ | SNORD93 (ENSG00000221740) | No | Breast | Upregulated in Tumor | Tumor-promoting | PIPOX | [72] |
| sdRNA-D19b | 5′-AUUACAAGAUCCAACUCUGAU-3′ | SNORD19b (ENSG00000238862) | No | Prostate | Upregulated in tumor | Tumor-promoting | CD44 | [73] |
| sdRNA-A24 | 5′-CUCCAUGUAUCUUUGGGACCUGUCA-3′ | SNORA24 (ENSG00000275994) | No | Prostate | Upregulated in tumor | Tumor-promoting | CDK12 | [73] |
| miRNAs that Bind Dyskerin | ||||||||
| **sd/miR-140 (ENSG00000208017) | 5′-CAGUGGUUUUACCCUAUGGUAG-3′ :: 5′-UACCACAGGGUAGAACCACGG-3′ | Binds Dyskerin | Yes | Prostate | Downregulated in tumor | Tumor-suppressing | BIRC1 | [41] |
| **sd/miR-151 (ENSG00000254324) | 5′-UCGAGGAGCUCACAGUCUAGU-3′ :: 5′-CUAGACUGAAGCUCCUUGAGG-3′ | Binds Dyskerin | Yes | Prostate | Downregulated in tumor | Tumor-suppressing | UNDETERMINED | [44] |
| **sd/miR-215 (ENSG00000207590) | 5′-AUGACCUAUGAAUUGACAGAC-3′ :: 5′-UCUGUCAUUUCUUUAGGCCAAUA-3′ | Binds Dyskerin | Yes | Ovary | Downregulated in Tumor | Tumor-suppressing | XIAP (not confirmed) | [42] |
| Colorectal | Downregulated in Tumor | Tumor-suppressing | EREG, HOXB9 | [43] | ||||
| Prostate | Downregulated in Tumor | Tumor-suppressing | PGK1 (not confirmed) | [45] | ||||
| Lung | Downregulated in Tumor | Tumor-suppressing | Leptin, SLC2A5 | [46] | ||||
| **sd/miR-605 (ENSG00000207813) | 5′-UAAAUCCCAUGGUGCCUUCUCCU-3′ :: 5′-AGAAGGCACUAUGAGAUUUAGA-3′ | Binds Dyskerin | Yes | Melanoma | UNDETERMINED | Tumor-suppressing | INPP4B | [49] |
| Prostate | UNDETERMINED | Tumor-suppressing | EN2 | [51] | ||||
| Colorectal, Breast Lung | UNDETERMINED | Tumor-suppressing, UNDETERMINED | Mdm2 | [47] | ||||
| Prostate | Downregulated in tumor | UNDETERMINED | UNDETERMINED | [50] | ||||
| Prostate | UNDETERMINED | UNDETERMINED | UNDETERMINED | [48] | ||||
| miRNAs that Bind Fibrillarin | ||||||||
| **sd/miR-16-1 (ENSG00000208006) | 5′-UAGCAGCACGUAAAUAUUGGCG-3′ :: 5′-CCAGUAUUAACUGUGCUGCUGA-3′ | Binds Fibrillarin | Yes | Chronic Lymphocytotic Leukemia | Downregulated in tumor | UNDETERMINED | Multiple (not confirmed) | [1] |
| Gastric | Downregulated in tumor | Tumor-suppressing | TWIST1 | [21] | ||||
| Non-small cell lung cancer | Downregulated in tumor | Tumor-suppressing | TWIST1 | [22] | ||||
| Osteosarcoma | Downregulated in tumor | Tumor-suppressing | FGFR2 | [23] | ||||
| Breast | Downregulated in tumor | Tumor-suppressing | PGK1 | [24] | ||||
| **sd/miR-27b (ENSG00000207864) | 5′-AGAGCUUAGCUGAUUGGUGAAC-3′ :: 5′-UUCACAGUGGCUAAGUUCUGC-3′ | Binds Fibrillarin | Yes | Prostate | Downregulated in tumor | Tumor-suppressing | UNDETERMINED | [25] |
| Lung | Downregulated in tumor | Tumor-suppressing | LIMK1 | [26] | ||||
| Bladder | Downregulated in tumor | Tumor-suppressing | EN2 | [27] | ||||
| **sd/miR-31 (ENSG00000199177) | 5′-AGGCAAGAUGCUGGCAUAGCU-3′ :: 5′-UGCUAUGCCAACAUAUUGCCAU-3′ | Binds Fibrillarin | Yes | Colorectal | Upregulated in tumor | Tumor-promoting | UNDETERMINED | [30] |
| Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma | Upregulated in tumor | Tumor-promoting | FIH (not confirmed) | [31] | ||||
| Lung | Upregulated in tumor | Tumor-promoting | LATS2, PP2R2A | [74] | ||||
| Glioblastoma | Downregulated in tumor | Tumor-suppressing | RDX | [75] | ||||
| Melanoma | Downregulated in tumor | Tumor-suppressing | UNDETERMINED | [32] | ||||
| Prostate | Downregulated in tumor | Tumor-suppressing | UNDETERMINED | [33] | ||||
| **sd/let-7g (ENSG00000199150) | 5′-UGAGGUAGUAGUUUGUACAGUU-3′ :: 5′-UGAGGUAGUAGUUUGUACAGUU-3′ | Binds Fibrillarin | Yes | Non-small cell lung cancer | Downregulated in tumor | Tumor-suppressing | KRAS (not confirmed) | [34] |
| Colorectal | Downregulated in tumor | Tumor-suppressing | UNDETERMINED | [35] | ||||
| Ovary | Downregulated in tumor | Tumor-suppressing | UNDETERMINED | [36] | ||||
| **sd/miR-28 (ENSG00000207651) | 5′-AAGGAGCUCACAGUCUAUUGAG-3′ :: 5′-CACUAGAUUGUGAGCUCCUGGA-3′ | Binds Fibrillarin | Yes | B-cell Lymphoma | Downregulated in tumor | Tumor-suppressing | MAD2L1, BAG1, RAP1B, RAB23 | [37] |
| Prostate | Downregulated in tumor | Tumor-suppressing | SREBF2 | [38] | ||||
| Breast | Downregulated in tumor | Tumor-suppressing | WSB2 | [39] | ||||
| Sno-Derived Piwi-interacting RNAs | ||||||||
| pi-sno75 | 5′-GGGAUUUCUGAAAUUCUAUUCUGAGGCU-3′ | SNORD75 | No | Breast | Downregulated in Tumor | Tumor-suppressing | WDR5 | [76] |
| pi-sno74 | 5′-AGUAAUGAUGAAUGCCAACCGCUCUGAUG-3′ | SNORD74 | No | Breast | Downregulated in Tumor | UNDETERMINED | UNDETERMINED | [76] |
| pi-sno44 | 5′-CCUGGAUGAUGAUAAGCAAAUGCUGACU-3′ | SNORD44 | No | Breast | Downregulated in Tumor | UNDETERMINED | UNDETERMINED | [76] |
| pi-sno78 (sd78-3′) | 5′-GAGCAUGUAGACAAAGGUAACACUGAAG-3′ | SNORD78 | No | Breast | Downregulated in Tumor | UNDETERMINED | UNDETERMINED | [76] |
| Prostate | Upregulated in metastases | UNDETERMINED | UNDETERMINED | [77] | ||||
| pi-sno81 | 5′-AUUACUUGAUGACAAUAAAAUAUCUGAUA-3′ | SNORD81 | No | Breast | Downregulated in Tumor | UNDETERMINED | UNDETERMINED | [76] |
| piR-017061 (piR-33686) | 5′-CUCAGUGAUGCAAUCUCUGUGUGGUUCUGAGA-3′ | SNORD91A (ENSG00000212163) | No | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Downregulated in Tumor | UNDETERMINED | UNDETERMINED | [70] |
| Cancer | # of sdRNAs Identified | Experimental Validation | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 32 TCGA Cancer Types | >300 | 133 sdRNAs correlate with PD-L1 expression, CD8+ T cell abundance, GZMA expression, patient survival, and copy number variation | [52] |
| Prostate | 78 | sd78-3′ was found to be overexpressed in aggressive patient tumors | [77,89] |
| Breast | 10 | sdRNA-93 was confirmed to correlate with malignant invasion in vitro and cancer type in vivo | [72] |
| Prostate | 38 | sdRNA-D19b and sdRNA-A24 were confirmed to correlate with the malignant phenotype in vitro and cancer type in vivo | [73] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Coley, A.B.; DeMeis, J.D.; Chaudhary, N.Y.; Borchert, G.M. Small Nucleolar Derived RNAs as Regulators of Human Cancer. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1819. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10081819
Coley AB, DeMeis JD, Chaudhary NY, Borchert GM. Small Nucleolar Derived RNAs as Regulators of Human Cancer. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(8):1819. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10081819
Chicago/Turabian StyleColey, Alexander Bishop, Jeffrey David DeMeis, Neil Yash Chaudhary, and Glen Mark Borchert. 2022. "Small Nucleolar Derived RNAs as Regulators of Human Cancer" Biomedicines 10, no. 8: 1819. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10081819
APA StyleColey, A. B., DeMeis, J. D., Chaudhary, N. Y., & Borchert, G. M. (2022). Small Nucleolar Derived RNAs as Regulators of Human Cancer. Biomedicines, 10(8), 1819. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10081819







