Risk of Dementia after Exposure to Contrast Media: A Nationwide, Population-Based Cohort Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Data Sources
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Definitions of Outcome, Exposure, and Covariates
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CM | Contrast medium; |
| SVD | Small vessels disease; |
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease; |
| VD | Vascular dementia; |
| NHIRD | National Health Insurance Research Database; |
| ICD-9-CM | International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision, Clinical Modification; |
| HR | Hazard ratio; |
| CI | Confidence interval. |
References
- Faucon, A.L.; Bobrie, G.; Clement, O. Nephrotoxicity of iodinated contrast media: From pathophysiology to prevention strategies. Eur. J. Radiol. 2019, 116, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehran, R.; Dangas, G.D.; Weisbord, S.D. Contrast-Associated Acute Kidney Injury. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2146–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shehadi, W.H. Contrast media adverse reactions: Occurrence, recurrence, and distribution patterns. Radiology 1982, 143, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, R.; Kiernan, M.C.; Murray, A.; Rosner, M.H.; Ronco, C. Kidney-brain crosstalk in the acute and chronic setting. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2015, 11, 707–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seliger, S.L.; Longstreth, W.T., Jr. Lessons about brain vascular disease from another pulsating organ, the kidney. Stroke 2008, 39, 5–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferri, C.P.; Prince, M.; Brayne, C.; Brodaty, H.; Fratiglioni, L.; Ganguli, M.; Hall, K.; Hasegawa, K.; Hendrie, H.; Huang, Y.; et al. Global prevalence of dementia: A Delphi consensus study. Lancet 2005, 366, 2112–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaria, R.N.; Maestre, G.E.; Arizaga, R.; Friedland, R.P.; Galasko, D.; Hall, K.; Luchsinger, J.A.; Ogunniyi, A.; Perry, E.K.; Potocnik, F.; et al. Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia in developing countries: Prevalence, management, and risk factors. Lancet Neurol. 2008, 7, 812–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKhann, G.; Drachman, D.; Folstein, M.; Katzman, R.; Price, D.; Stadlan, E.M. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: Report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurology 1984, 34, 939–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elahi, F.M.; Miller, B.L. A clinicopathological approach to the diagnosis of dementia. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2017, 13, 457–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haight, T.J.; Landau, S.M.; Carmichael, O.; Schwarz, C.; DeCarli, C.; Jagust, W.J. Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Dissociable effects of Alzheimer disease and white matter hyperintensities on brain metabolism. JAMA Neurol. 2013, 70, 1039–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalaria, R.N. Neuropathological diagnosis of vascular cognitive impairment and vascular dementia with implications for Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 659–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ter Telgte, A.; van Leijsen, E.M.C.; Wiegertjes, K.; Klijn, C.J.M.; Tuladhar, A.M.; de Leeuw, F.E. Cerebral small vessel disease: From a focal to a global perspective. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, S.; Nagasawa, T.; Abe, M.; Mori, T. Strain vessel hypothesis: A viewpoint for linkage of albuminuria and cerebro-cardiovascular risk. Hypertens. Res. 2009, 32, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyoda, K. Cerebral small vessel disease and chronic kidney disease. J. Stroke 2015, 17, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Rourke, M.F.; Safar, M.E. Relationship between aortic stiffening and microvascular disease in brain and kidney: Cause and logic of therapy. Hypertension 2005, 46, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deckers, K.; Camerino, I.; van Boxtel, M.P.; Verhey, F.R.; Irving, K.; Brayne, C.; Kivipelto, M.; Starr, J.M.; Yaffe, K.; de Leeuw, P.W.; et al. Dementia risk in renal dysfunction: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. Neurology 2017, 88, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, A.; Chung, H.; Komada, T.; Platnich, J.M.; Sandall, C.F.; Choudhury, S.R.; Chun, J.; Naumenko, V.; Surewaard, B.G.; Nelson, M.C.; et al. Renal immune surveillance and dipeptidase-1 contribute to contrast-induced acute kidney injury. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 2894–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Wang, L.; Jiang, N.; Mou, S.; Zhang, M.; Gu, L.; Shao, X.; Wang, Q.; Qi, C.; Li, S.; et al. NLRP3 inflammasome mediates contrast media-induced acute kidney injury by regulating cell apoptosis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilhus, N.E.; Deuschl, G. Neuroinflammation—A common thread in neurological disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 429–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd, A.F.; Miron, V.E. The pro-remyelination properties of microglia in the central nervous system. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, X.F.; Chen, Q.J.; Zuo, X.C.; Guo, R.; Peng, X.D.; Wang, J.L.; Yin, W.J.; Li, D.Y. Contrast Media-Induced Renal Inflammation Is Mediated Through HMGB1 and Its Receptors in Human Tubular Cells. DNA Cell Biol. 2017, 36, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singhal, G.; Jaehne, E.J.; Corrigan, F.; Toben, C.; Baune, B.T. Inflammasomes in neuroinflammation and changes in brain function: A focused review. Front. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, M.S.; Yu, J.T.; Jiang, T.; Zhu, X.C.; Tan, L. The NLRP3 inflammasome in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2013, 48, 875–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brothers, H.M.; Bardou, I.; Hopp, S.C.; Marchalant, Y.; Kaercher, R.M.; Turner, S.M.; Mitchem, M.R.; Kigerl, K.; Wenk, G.L. Time-Dependent Compensatory Responses to Chronic Neuroinflammation in Hippocampus and Brainstem: The Potential Role of Glutamate Neurotransmission. J. Alzheimers Dis. Parkinsonism 2013, 3, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



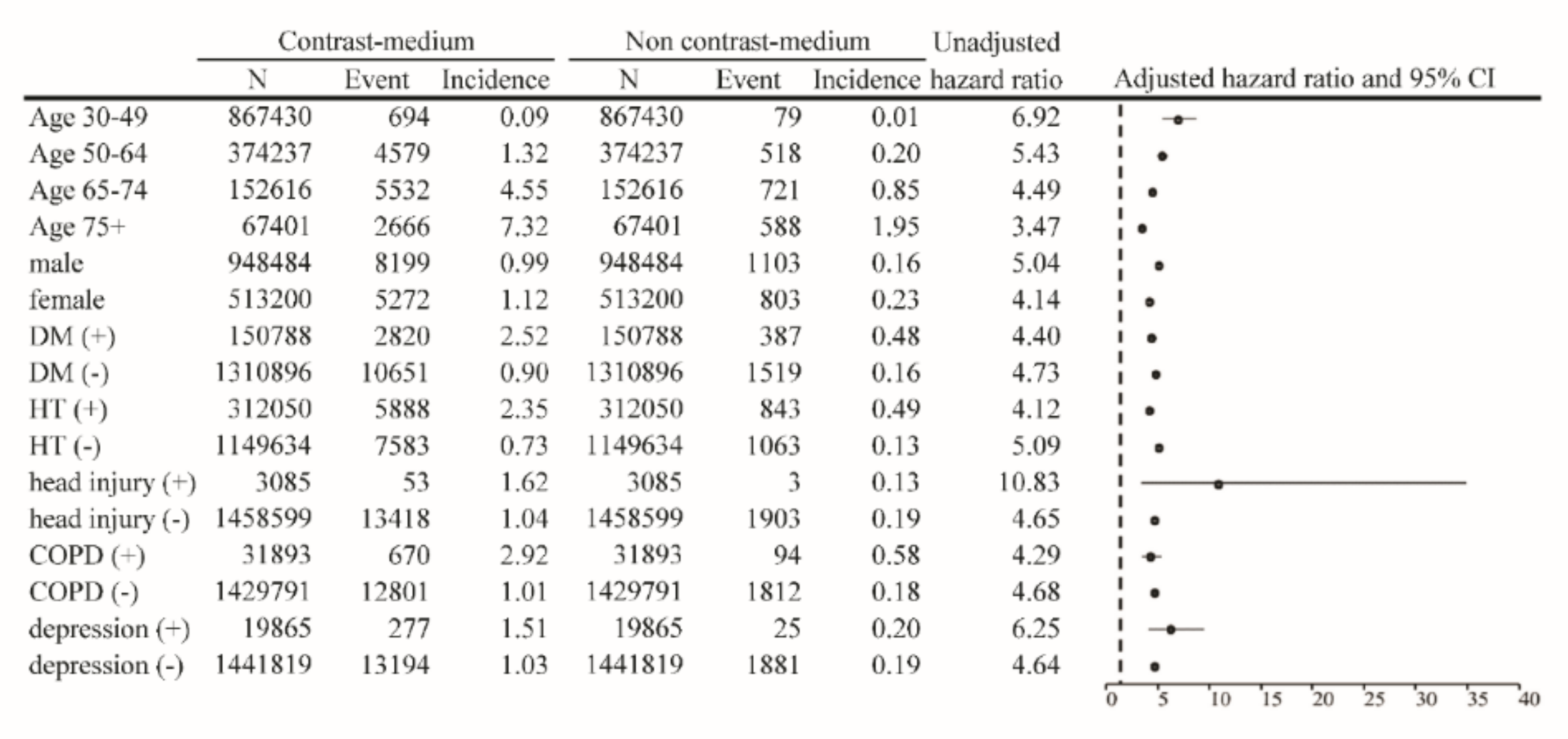
| Before Match | After Match | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contrast Medium Exposure | Contrast Medium Non-Exposure | Standard Difference | Contrast Medium Exposure | Contrast Medium Non-Exposure | Standard Difference | |||||
| N (3,993,770) | % | N (7,338,846) | % | N (1,461,684) | % | N (1,461,684) | % | |||
| Age | ||||||||||
| Mean (SD) | 51.8 | 13.8 | 45.5 | 12.8 | 0.47957 | 48.8 | 13.3 | 48.7 | 13.3 | 0.00309 |
| 30–49 | 1,970,025 | 49.3 | 5,208,013 | 70.9 | −0.45321 | 867,430 | 59.3 | 867,430 | 59.3 | 0.0000 |
| 50–64 | 1,170,274 | 29.3 | 1,400,847 | 19.1 | 0.24012 | 374,237 | 25.6 | 374,237 | 25.6 | 0.0000 |
| 65+ | 853,471 | 21.4 | 729,986 | 10.0 | 0.31819 | 220,017 | 15.1 | 220,017 | 15.1 | 0.0000 |
| Sex | ||||||||||
| Male | 2,264,465 | 56.7 | 3,500,813 | 47.7 | 0.18091 | 948,484 | 64.9 | 948,484 | 64.9 | 0.0000 |
| Female | 1,729,305 | 43.3 | 3,838,033 | 52.3 | −0.18091 | 513,200 | 35.1 | 513,200 | 35.1 | 0.0000 |
| Frequency of outpatient visits/per year, mean(SD) | 13.8 | 14.9 | 9.6 | 11.7 | 0.31432 | 14.4 | 13.7 | 14.4 | 13.7 | 0.0000 |
| Comorbidity | ||||||||||
| Hypertension | 642,508 | 16.1 | 521,842 | 7.1 | 0.28323 | 312,050 | 21.4 | 312,050 | 21.4 | 0.0000 |
| Hyperlipidemia | 212,278 | 5.3 | 172,815 | 2.4 | 0.15512 | 130,009 | 8.9 | 130,009 | 8.9 | 0.0000 |
| Diabetes | 290,025 | 7.3 | 216,803 | 3.0 | 0.19677 | 150,788 | 10.3 | 150,788 | 10.3 | 0.0000 |
| COPD | 94,784 | 2.4 | 81,458 | 1.1 | 0.09647 | 31,893 | 2.2 | 31,893 | 2.2 | 0.0000 |
| CAD | 165,821 | 4.2 | 114,257 | 1.6 | 0.15599 | 8,0411 | 5.5 | 80,411 | 5.5 | 0.0000 |
| Head injury | 22,432 | 0.6 | 29,521 | 0.4 | 0.02315 | 3085 | 0.2 | 3085 | 0.2 | 0.0000 |
| Depression | 56,470 | 1.4 | 65,324 | 0.9 | 0.04879 | 19,865 | 1.4 | 19,865 | 1.4 | 0.0000 |
| Cancer | 54,699 | 1.4 | 30,911 | 0.4 | 0.10100 | 33,023 | 2.3 | 33,023 | 2.3 | 0.0000 |
| Dementia | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Incidence | Crude | Adjusted † | Adjusted ¶ | ||||
| Variable | Rate | HR | (95% CI) | HR | (95% CI) | HR | (95% CI) |
| Exposure of contrast medium | 5.49 | 2.25 | (2.21–2.28) *** | 2.09 | (2.06–2.13) *** | 2.09 | (2.06–2.13) *** |
| Sex (Men vs. Women) | 3.58 | 0.72 | (0.71–0.73) *** | 0.84 | (0.83–0.85) *** | 0.84 | (0.83–0.85) *** |
| Age, years | |||||||
| 50–64 | 5.01 | 19.36 | (18.71–20.04) *** | 18.00 | (17.39–18.62) *** | 18.00 | (17.39–18.63) *** |
| 65–74 | 19.03 | 77.02 | (74.46–79.66) *** | 69.10 | (66.78–71.50) *** | 69.10 | (66.77–71.51) *** |
| 75+ | 36.94 | 161.81 | (156.27–167.55) *** | 149.92 | (144.72–155.31) *** | 149.92 | (144.66–155.37) *** |
| Baseline comorbidities (yes vs. no) | |||||||
| Hypertension | 8.93 | 3.11 | (3.07–3.15) *** | 1.13 | (1.12–1.18) *** | 1.13 | (1.12–1.15) *** |
| Hyperlipidemia | 5.85 | 1.55 | (1.52–1.59) *** | 0.97 | (0.95–0.99) ** | 0.97 | (0.95–0.99) ** |
| Diabetes | 8.63 | 2.48 | (2.44–2.52) *** | 1.35 | (1.32–1.37) *** | 1.35 | (1.32–1.37) *** |
| COPD | 12.93 | 3.37 | (3.27–3.47) *** | 1.13 | (1.10–1.16) *** | 1.13 | (1.10–1.17) *** |
| CAD | 10.72 | 2.91 | (2.86–2.97) *** | 0.99 | (0.97–1.01) | 0.99 | (0.97–1.01) |
| Head injury | 5.83 | 1.35 | (1.21–1.51) *** | 1.33 | (1.19–1.48) *** | 1.33 | (1.18–1.49) *** |
| Depression | 6.93 | 1.72 | (1.65–1.80) *** | 1.86 | (1.78–1.94) *** | 1.86 | (1.77–1.95) *** |
| Cancer | 6.16 | 1.51 | (1.45–1.57) *** | 0.82 | (0.79–0.85) *** | 0.82 | (0.79–0.85) *** |
| Alzheimer’s Disease | Vascular Dementia | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Incidence Rate | Crude HR | Adjusted HR † | Adjusted HR ¶ | Incidence Rate | Crude HR | Adjusted HR † | Adjusted HR ¶ | |
| Contrast medium exposure (overall) | 1.57 | 2.10(2.04–2.16) *** | 1.82(1.77–1.88) *** | 1.82(1.77–1.88) *** | 1.04 | 5.18(4.93–5.43) *** | 4.66(4.44–4.89) *** | 4.66(4.44–4.89) *** |
| PCI-unrelated contrast medium exposure | 1.55 | 2.11(2.05–2.17) *** | 1.84(1.78–1.89) *** | 1.84(1.78–1.89) *** | 1.02 | 5.20(4.95–5.46) *** | 4.70(4.47–4.94) *** | 4.70(4.47–4.94) *** |
| PCI-related contrast medium exposure | 2.29 | 1.75(1.54–2.00) *** | 1.54(1.35–1.76) *** | 1.54(1.36–1.76) *** | 1.60 | 4.42(3.56–5.48) *** | 3.96(3.19–4.91) *** | 3.96(3.19–4.91) *** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, T.-M.; Chuang, Y.-W.; Huang, S.-T.; Huang, J.-A.; Chen, C.-H.; Chung, M.-C.; Wu, C.-Y.; Chang, P.-Y.; Hsu, C.-C.; Wu, M.-J. Risk of Dementia after Exposure to Contrast Media: A Nationwide, Population-Based Cohort Study. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2015. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10082015
Yu T-M, Chuang Y-W, Huang S-T, Huang J-A, Chen C-H, Chung M-C, Wu C-Y, Chang P-Y, Hsu C-C, Wu M-J. Risk of Dementia after Exposure to Contrast Media: A Nationwide, Population-Based Cohort Study. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(8):2015. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10082015
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Tung-Min, Ya-Wen Chuang, Shih-Ting Huang, Jin-An Huang, Cheng-Hsu Chen, Mu-Chi Chung, Chun-Yi Wu, Pi-Yi Chang, Chih-Cheng Hsu, and Ming-Ju Wu. 2022. "Risk of Dementia after Exposure to Contrast Media: A Nationwide, Population-Based Cohort Study" Biomedicines 10, no. 8: 2015. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10082015
APA StyleYu, T.-M., Chuang, Y.-W., Huang, S.-T., Huang, J.-A., Chen, C.-H., Chung, M.-C., Wu, C.-Y., Chang, P.-Y., Hsu, C.-C., & Wu, M.-J. (2022). Risk of Dementia after Exposure to Contrast Media: A Nationwide, Population-Based Cohort Study. Biomedicines, 10(8), 2015. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10082015






