SERPINA3: Stimulator or Inhibitor of Pathological Changes
Abstract
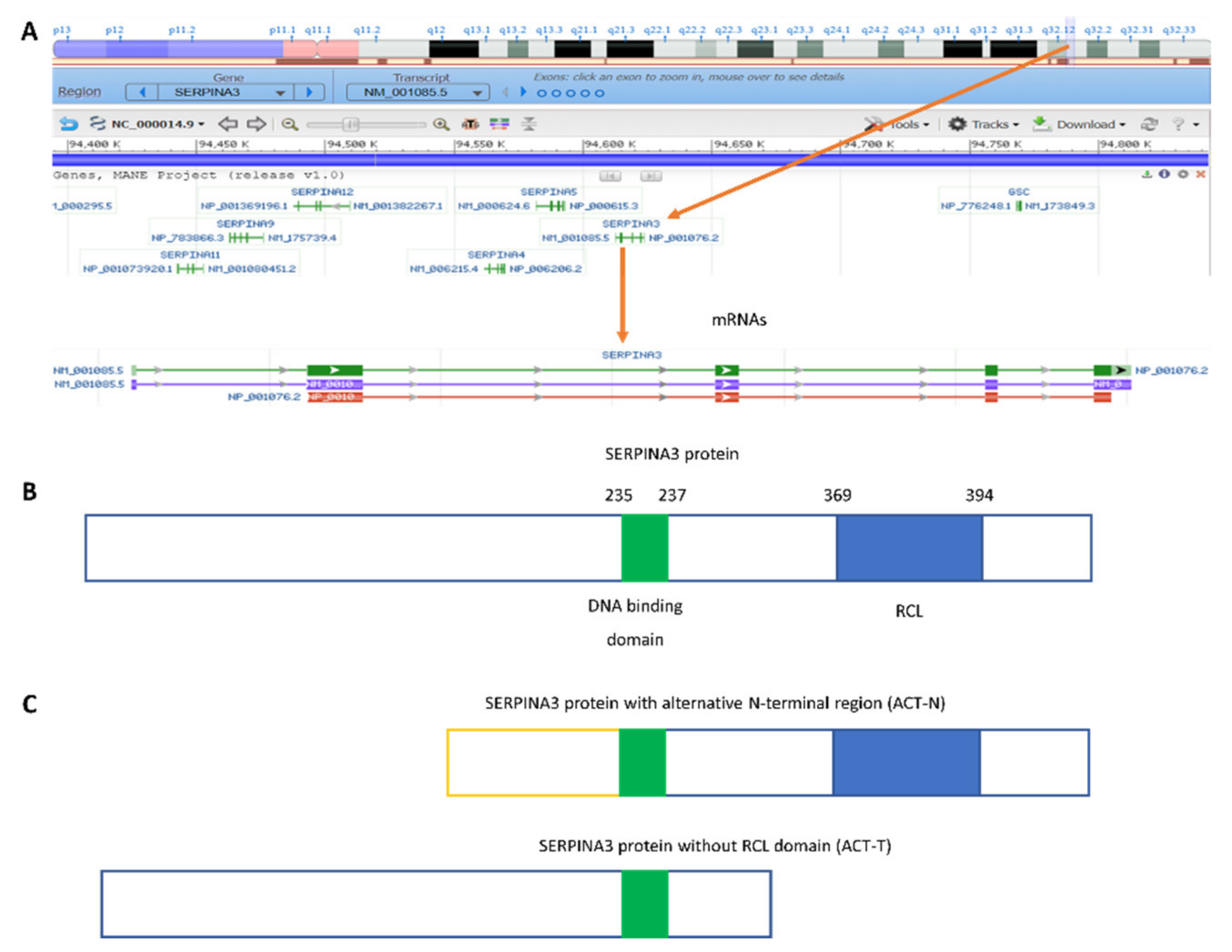
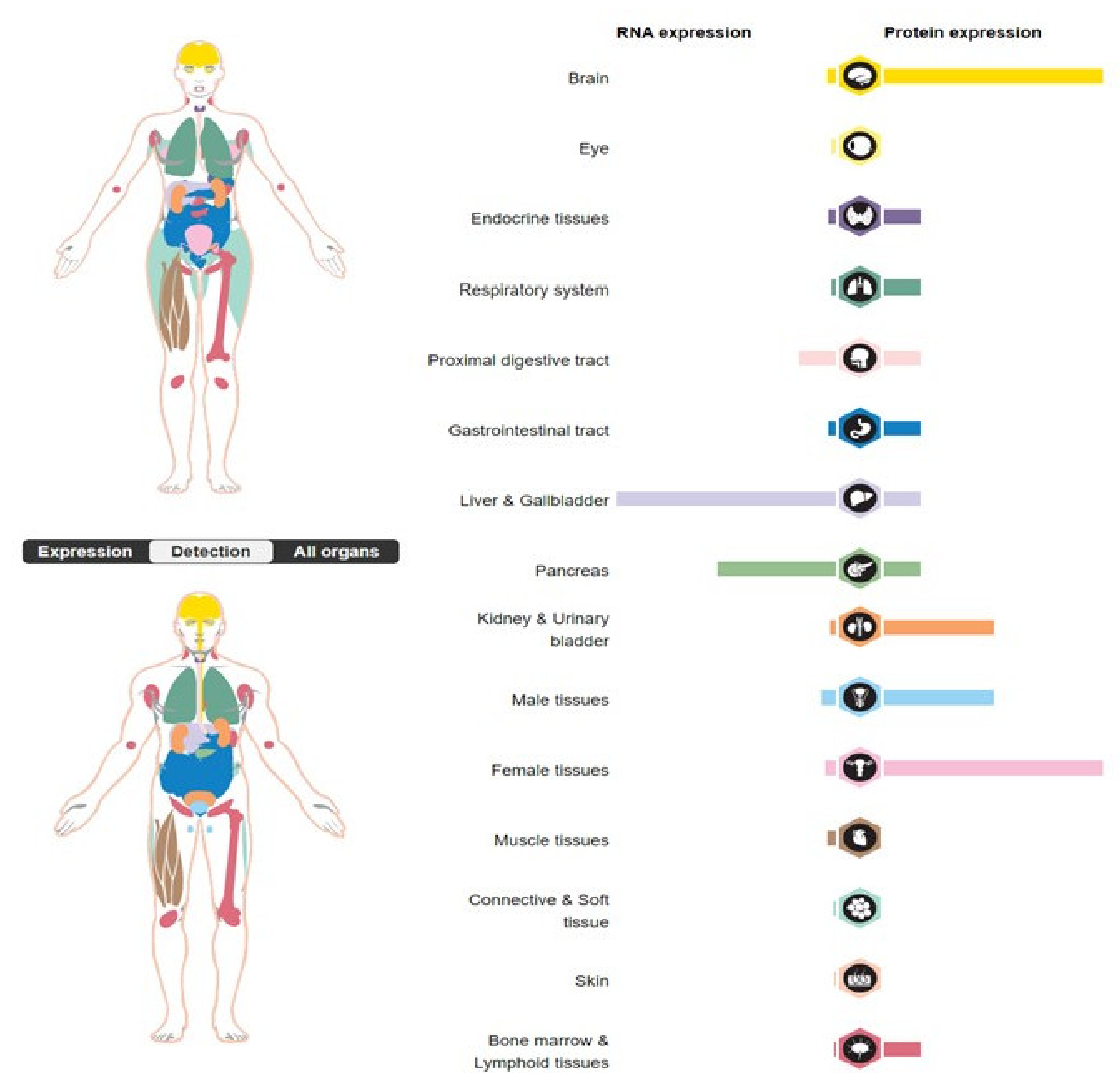
:1. Introduction
2. SERPINA3 as a Nuclear Protein
3. SERPINA3 in Cancers
4. The Role of Non-Coding RNA in the Regulation of SERPINA3 Gene Expression and Function
5. The Role of SERPINA3 in Inflammation
6. SERPINA3 in Antiviral Response
7. SERPINA3 in Heart Failure
8. SERPINA3 in Neurological Diseases
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rabin, M.; Watson, M.; Kidd, V.; Woo, S.L.C.; Breg, W.R.; Ruddle, F.H. Regional Location of C~l-Antichymotrypsin and al-Antitrypsin Genes on Human Chromosome 14. Somat. Cell Mol. Genet. 1986, 12, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, C. SERPINA3 (Aka Alpha-1-Antichymotrypsin). Front. Biosci. 2007, 12, 2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Qian, W.-J.; Gritsenko, M.A.; Camp, D.G.; Monroe, M.E.; Moore, R.J.; Smith, R.D. Human Plasma N-Glycoproteome Analysis by Immunoaffinity Subtraction, Hydrazide Chemistry, and Mass Spectrometry. J. Proteome Res. 2005, 4, 2070–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, R.; Jiang, X.; Sun, D.; Han, G.; Wang, F.; Ye, M.; Wang, L.; Zou, H. Glycoproteomics Analysis of Human Liver Tissue by Combination of Multiple Enzyme Digestion and Hydrazide Chemistry. J. Proteome Res. 2009, 8, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, S.-R.; Steineckert, B.; Kohn, A.; Palkovits, M.; Hook, V.Y.H. Molecular Studies Define the Primary Structure of A1-Antichymotrypsin (ACT) Protease Inhibitor in Alzheimer’s Disease Brains: Comparison of act in hippocampus and liver*. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 1821–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korkmaz, B.; Horwitz, M.S.; Jenne, D.E.; Gauthier, F. Neutrophil Elastase, Proteinase 3, and Cathepsin G as Therapeutic Targets in Human Diseases. Pharmacol. Rev. 2010, 62, 726–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fatima, S.; Gupta, S.; Khan, A.B.; Rehman, S.U.; Jairajpuri, M.A. Identification and Validation of Two Alternatively Spliced Novel Isoforms of Human α-1-Antichymotrypsin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2022, 628, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travis, J.; Bowen, J.; Baugh, R. Human α-1-Antichymotrypsin: Interaction with Chymotrypsin-like Proteinases. Biochemistry 1978, 17, 5651–5656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, C.E.; Kondo, Y.; Walker, A.K.; Rothmond, D.A.; Matsumoto, M.; Shannon Weickert, C. Regional, Cellular and Species Difference of Two Key Neuroinflammatory Genes Implicated in Schizophrenia. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 88, 826–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, W.A.; Seńko, A.; Korczowska, I.; Łącka, K. Assessment of Selected Serum Inflammatory Markers of Acute Phase Response and Their Correlations with Adrenal Androgens and Meta bolic Syndrome in a Population of Men over the Age of 40. Pol. Arch. Med. Wewn. 2009, 119, 704–711. [Google Scholar]
- Santamaria, M.; Pardo-Saganta, A.; Alvarez–Asiain, L.; Di Scala, M.; Qian, C.; Prieto, J.; Avila, M.A. Nuclear A1-Antichymotrypsin Promotes Chromatin Condensation and Inhibits Proliferation of Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 818–828.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Navarro, A.; Mejía-Vilet, J.M.; Pérez-Villalva, R.; Carrillo-Pérez, D.L.; Marquina-Castillo, B.; Gamba, G.; Bobadilla, N.A. SerpinA3 in the Early Recognition of Acute Kidney Injury to Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Transition in the Rat and Its Potentiality in the Recognition of Patients with CKD. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Y.-X.; Wright, H.T.; Janciauskiene, S. A1-Antichymotrypsin/Alzheimer’s Peptide Aβ1–42 Complex Perturbs Lipid Metabolism and Activates Transcription Factors PPARγ and NFκB in Human Neuroblastoma (Kelly) Cells. J. Neurosci. Res. 2002, 67, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanni, S.; Moda, F.; Zattoni, M.; Bistaffa, E.; De Cecco, E.; Rossi, M.; Giaccone, G.; Tagliavini, F.; Haïk, S.; Deslys, J.P.; et al. Differential Overexpression of SERPINA3 in Human Prion Diseases. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalsheker, N.A. A1-Antichymotrypsin. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1996, 28, 961–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsyth, S.; Horvath, A.; Coughlin, P. A Review and Comparison of the Murine A1-Antitrypsin and A1-Antichymotrypsin Multigene Clusters with the Human Clade A Serpins. Genomics 2003, 81, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duranton, J.; Boudier, C.; Belorgey, D.; Mellet, P.; Bieth, J.G. DNA Strongly Impairs the Inhibition of Cathepsin G by A1-Antichymotrypsin and A1-Proteinase Inhibitor. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 3787–3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naidoo, N.; Cooperman, B.S.; Wang, Z.; Liu, X.; Rubin, H. Identification of Lysines within A1-Antichymotrypsin Important for DNA Binding. AN UNUSUAL COMBINATION OF DNA-BINDING ELEMENTS*. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 14548–14555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hurlimann, J.; van Melle, G. Prognostic Value of Serum Proteins Synthesized by Breast Carcinoma Cells. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1991, 95, 835–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karashima, S.; Kataoka, H.; Itoh, H.; Maruyama, R.; Koono, M. Prognostic Significance of Alpha-1-Antitrypsin in Early Stage of Colorectal Carcinomas. Int. J. Cancer 1990, 45, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lein, M.; Stephan, C.; Jung, K.; Schnorr, D.; Loening, S.A. Molekulare Formen des prostataspezifischen Antigens und des humanen Kallikreins 2 als mögliche Indikatoren in der Prostatakarzinomdiagnostik. Urologe A 2000, 39, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Dong, X.; Cai, J.; Yin, S.; Sun, Y.; Yang, D.; Jiang, C. SERPINA3 Induced by Astroglia/Microglia Co-culture Facilitates Glioblastoma Stem-like Cell Invasion. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ko, E.; Kim, J.-S.; Bae, J.W.; Kim, J.; Park, S.-G.; Jung, G. SERPINA3 Is a Key Modulator of HNRNP-K Transcriptional Activity against Oxidative Stress in HCC. Redox Biol. 2019, 24, 101217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, E.; Seo, H.-W.; Jung, E.S.; Ju, S.; Kim, B.; Cho, H.; Kim, Y.J.; Park, Y.M.; Kim, J.-S.; Jung, G. PI3Kδ Is a Therapeutic Target in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatology 2018, 68, 2285–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koivuluoma, S.; Tervasmäki, A.; Kauppila, S.; Winqvist, R.; Kumpula, T.; Kuismin, O.; Moilanen, J.; Pylkäs, K. Exome Sequencing Identifies a Recurrent Variant in SERPINA3 Associating with Hereditary Susceptibility to Breast Cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2021, 143, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tian, J.; Qu, C.; Peng, Y.; Lei, J.; Li, K.; Zong, B.; Sun, L.; Liu, S. Overexpression of SERPINA3 Promotes Tumor Invasion and Migration, Epithelial-Mesenchymal-Transition in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Breast Cancer 2021, 28, 859–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara-Velazquez, M.; Zarco, N.; Carrano, A.; Phillipps, J.; Norton, E.S.; Schiapparelli, P.; Al-kharboosh, R.; Rincon-Torroella, J.; Jeanneret, S.; Corona, T.; et al. Alpha 1-Antichymotrypsin Contributes to Stem Cell Characteristics and Enhances Tumorigenicity of Glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol. 2021, 23, 599–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Chen, W.; Tian, Y.; Li, J.; Xu, X.; Chen, C.; Li, F. Serpin Peptidase Inhibitor, Clade A Member 3 (SERPINA3), Is Overexpressed in Glioma and Associated with Poor Prognosis in Glioma Patients. OTT 2017, 10, 2173–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nimbalkar, V.P.; Kruthika, B.S.; Sravya, P.; Rao, S.; Sugur, H.S.; Verma, B.K.; Chickabasaviah, Y.T.; Arivazhagan, A.; Kondaiah, P.; Santosh, V. Differential Gene Expression in Peritumoral Brain Zone of Glioblastoma: Role of SERPINA3 in Promoting Invasion, Stemness and Radioresistance of Glioma Cells and Association with Poor Patient Prognosis and Recurrence. J. Neurooncol. 2021, 152, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, M.S.; Yuan, L. Serpina3n: Potential Drug and Challenges, Mini Review. J. Drug Target. 2020, 28, 368–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Wang, S.-Q.; Zhang, G.-T.; He, J.; Liu, Z.-D.; Wang, M.-R.; Cai, H.-Q.; Wan, J.-H. Highly Expressed of SERPINA3 Indicated Poor Prognosis and Involved in Immune Suppression in Glioma. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2021, 9, 1618–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, W.; Zhu, S.; Chen, Y. Increased SERPINA3 Level Is Associated with Ulcerative Colitis. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewandowska, A.; Rudzki, G.; Lewandowski, T.; Stryjkowska-Góra, A.; Rudzki, S. Risk Factors for the Diagnosis of Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Control 2022, 29, 107327482110566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.-L.; Pei, X.-F.; Qiao, X.; Yu, J.; Ye, H.; Xi, C.-L.; Wang, P.-Y.; Gong, Z.-L. SERPINA3 Silencing Inhibits the Migration, Invasion, and Liver Metastasis of Colon Cancer Cells. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2018, 63, 2309–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltier, J.; Roperch, J.-P.; Audebert, S.; Borg, J.-P.; Camoin, L. Quantitative Proteomic Analysis Exploring Progression of Colorectal Cancer: Modulation of the Serpin Family. J. Proteom. 2016, 148, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijers, W.C.; Maglione, M.; Bakker, S.J.L.; Oberhuber, R.; Kieneker, L.M.; de Jong, S.; Haubner, B.J.; Nagengast, W.B.; Lyon, A.R.; van der Vegt, B.; et al. Heart Failure Stimulates Tumor Growth by Circulating Factors. Circulation 2018, 138, 678–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Fan, Y.-X.; Yang, Y.; Liu, D.-L.; Wu, K.; Wen, F.-B.; Zhang, C.-Y.; Zhao, S. Identification of Potential Plasma Biomarkers for Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma by a Proteomic Method. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 2, 1535–1544. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Zeng, H.; Zhao, Y.; Gong, Y.; Ma, X. Proteomic Analysis of Cerebrospinal Fluid from Patients with Extranodal NK-/T-Cell Lymphoma of Nasal-Type With Ethmoidal Sinus Metastasis. Front. Oncol. 2020, 9, 1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Wang, J.; Ye, X.; Su, Y.; Yu, G.; Yang, Q.; Liu, W.; Yu, W.; Cai, J.; Chen, X.; et al. Identification of GlcNAcylated Alpha-1-Antichymotrypsin as an Early Biomarker in Human Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer by Quantitative Proteomic Analysis with Two Lectins. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 114, 532–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, J.; Cheng, Y.; Tang, L.; Martinka, M.; Kalia, S. Up-Regulation of SERPINA3 Correlates with High Mortality of Melanoma Patients and Increased Migration and Invasion of Cancer Cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 18712–18725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kulesza, D.W.; Ramji, K.; Maleszewska, M.; Mieczkowski, J.; Dabrowski, M.; Chouaib, S.; Kaminska, B. Search for Novel STAT3-Dependent Genes Reveals SERPINA3 as a New STAT3 Target That Regulates Invasion of Human Melanoma Cells. Lab. Investig. 2019, 99, 1607–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulesza, D.W.; Przanowski, P.; Kaminska, B. Knockdown of STAT3 Targets a Subpopulation of Invasive Melanoma Stem-like Cells. Cell Biol. Int. 2019, 43, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.-D.; Yang, X.-M.; Lu, H.; Ren, Y.; Ma, M.-Z.; Zhu, L.-Y.; Wang, J.-H.; Song, W.-W.; Zhang, W.-M.; Zhang, R.; et al. SERPINA3 Promotes Endometrial Cancer Cells Growth by Regulating G2/M Cell Cycle Checkpoint and Apoptosis. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 1348–1358. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.-L.; Chen, F.-S.; Mao, H. Clinical Significance and Role of Up-Regulation of SERPINA3 Expression in Endometrial Cancer. WJCC 2019, 7, 1996–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soman, A.; Asha Nair, S. Unfolding the Cascade of SERPINA3: Inflammation to Cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Rev. Cancer 2022, 1877, 188760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobb, M. 60 Years Ago, Francis Crick Changed the Logic of Biology. PLoS Biol. 2017, 15, e2003243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beermann, J.; Piccoli, M.-T.; Viereck, J.; Thum, T. Non-Coding RNAs in Development and Disease: Background, Mechanisms, and Therapeutic Approaches. Physiol. Rev. 2016, 96, 1297–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meng, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, P.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, M. Circular RNA: An Emerging Key Player in RNA World. Brief. Bioinform. 2016, 18, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.; Sun, C.; Hu, Q.; Guo, Y.; Xia, G.; Mi, Y.; Zhu, L. Differential Expression Profiles of CircRNAs in Human Prostate Cancer Based on Chip and Bioinformatic Analysis. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2020, 13, 1045–1052. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, Z.; Li, S.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, C.; Bai, Z. CircSERPINA3 Regulates SERPINA3-Mediated Apoptosis, Autophagy and Aerobic Glycolysis of Prostate Cancer Cells by Competitively Binding to MiR-653-5p and Recruiting BUD13. J. Transl. Med. 2021, 19, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, P.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y. Cell Proliferation and Invasion Is Promoted by CircSERPINA3 in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma by Regulating MiR-944/MDM2 Axis. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 3910–3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Tian, Y.; Cao, Y.; Ma, Q.; Zhao, S. MiR-137 Promotes Cell Growth and Inhibits Extracellular Matrix Protein Expression in H2O2-Induced Human Trabecular Meshwork Cells by Targeting Src. Neurosci. Lett. 2021, 755, 135902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čelešnik, H.; Büdefeld, T.; Čizmarević, B.; Švagan, M.; Potočnik, U. MIR137/MIR2682 Locus Is Associated with Perineural Invasiveness in Head and Neck Cancer. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2021, 50, 874–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lok, S.I.; van Mil, A.; Bovenschen, N.; van der Weide, P.; van Kuik, J.; van Wichen, D.; Peeters, T.; Siera, E.; Winkens, B.; Sluijter, J.P.G.; et al. Post-Transcriptional Regulation of α-1-Antichymotrypsin by MicroRNA-137 in Chronic Heart Failure and Mechanical Support. Circ. Heart Fail. 2013, 6, 853–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, F.; Zhang, L.; Wang, E.; Zhang, C.; Li, X. LncRNA GAS5 Regulates Ischemic Stroke as a Competing Endogenous RNA for MiR-137 to Regulate the Notch1 Signaling Pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 496, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Hou, L.; Liu, Y.; Gong, J. LncRNA GAS5 Exacerbates Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury through Regulating Serpina3 by Targeting MiR-137. Int. J. Cardiol. 2020, 306, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, W.; Tuxiu, X.; Xiaobing, L.; Guijun, J.; Lulu, K.; Jie, J.; Lu, Y.; Liying, Z.; Xiaoxing, X.; Jingjun, L. LncRNA GAS5/MiR-137 Is a Hypoxia-Responsive Axis Involved in Cardiac Arrest and Cardiopulmonary Cerebral Resuscitation. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 790750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-H.; Chen, A.-L.; Yu, R.-Q.; Jia, B.-B.; Ye, D.-N.; Wang, M.; Mei, Y.-Z.; Fang, G.-D.; Jiang, S.-Y.; Zhou, Q.; et al. MiR-296-5p Inhibits the Secretion of Pulmonary Surfactants in Pulmonary Epithelial Cells via the Downregulation of Wnt7b/β-Catenin Signaling. Biomed. Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 4051504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Ma, Q.; Wang, B.; Qian, Q.; Xi, Y. Circ-E2F3 Promotes Cervical Cancer Progression by Inhibiting MicroRNA-296-5p and Increasing STAT3 Nuclear Translocation. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2022, 1507, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granger, D.N.; Senchenkova, E. Inflammation and the Microcirculation; Integrated Systems Physiology—From Cell to Function; Morgan & Claypool Life Sciences: San Rafael, CA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Sobieska, M.; Steiner, I.; Pucher, B.; Grzegorowski, M.; Samborski, W. Glycosylation profile of selected acute phase proteins in children with chronic tonsillitis and allergic symptoms. Ann. Acad. Med. Stetin. 2006, 52, 39–43. [Google Scholar]
- Anada, R.P.; Wong, K.T.; Jayapalan, J.J.; Hashim, O.H.; Ganesan, D. Panel of Serum Protein Biomarkers to Grade the Severity of Traumatic Brain Injury. Electrophoresis 2018, 39, 2308–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobieska, M.; Mikstacki, A.; Wiktorowicz, K. Zmiany Stężeń Cytokin i Wybranych Białek Ostrej Fazy Pod Wpływem Urazów Wielonarządowych. Now. Lek 1998, 67, 515–523. [Google Scholar]
- Sobieska, M.; Steiner, I.; Olejnik, J.; Szydłowski, J.; Antyborzec, J.; Grzegorowski, M.; Wiktorowicz, K. Increased Concentration of A1-Antichymotrypsin as a Marker of Necrotic Processes during Chronic Tonsillitis. Nowa Pediatr. 1999, 3, 237–240. [Google Scholar]
- Steiner, I.; Sobieska, M.; Grzegorowski, M.; Wiktorowicz, K. Monitoring of the Inflammation in Children before and after Tonsillectomy. Otolaringol. Polska 2000, 54, 51–56. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zahid, K.R.; Raza, U.; Gong, Y. Alpha-1-Antichymotrypsin as a Novel Biomarker for Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Therapy Prediction in Human Diseases. Cancer Cell Int. 2022, 22, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kissel, T.; Toes, R.E.M.; Huizinga, T.W.J.; Wuhrer, M. Glycobiology of Rheumatic Diseases. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2022, 19, 28–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almahayni, K.; Spiekermann, M.; Fiore, A.; Yu, G.; Pedram, K.; Möckl, L. Small Molecule Inhibitors of Mammalian Glycosylation. Matrix Biol. Plus 2022, 16, 100108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgener, A.; Rahman, S.; Ahmad, R.; Lajoie, J.; Ramdahin, S.; Mesa, C.; Brunet, S.; Wachihi, C.; Kimani, J.; Fowke, K.; et al. Comprehensive Proteomic Study Identifies Serpin and Cystatin Antiproteases as Novel Correlates of HIV-1 Resistance in the Cervicovaginal Mucosa of Female Sex Workers. J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 5139–5149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woollard, S.M.; Bhargavan, B.; Yu, F.; Kanmogne, G.D. Differential Effects of Tat Proteins Derived from HIV-1 Subtypes B and Recombinant CRF02_AG on Human Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells: Implications for Blood–Brain Barrier Dysfunction. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2014, 34, 1047–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johri, M.K.; Sharma, N.; Singh, S.K. HIV Tat Protein: Is Tat-C Much Trickier than Tat-B? J. Med. Virol. 2015, 87, 1334–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chasman, D.; Walters, K.B.; Lopes, T.J.S.; Eisfeld, A.J.; Kawaoka, Y.; Roy, S. Integrating Transcriptomic and Proteomic Data Using Predictive Regulatory Network Models of Host Response to Pathogens. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2016, 12, e1005013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferrarini, M.G.; Lal, A.; Rebollo, R.; Gruber, A.J.; Guarracino, A.; Gonzalez, I.M.; Floyd, T.; de Oliveira, D.S.; Shanklin, J.; Beausoleil, E.; et al. Genome-Wide Bioinformatic Analyses Predict Key Host and Viral Factors in SARS-CoV-2 Pathogenesis. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suvarna, K.; Biswas, D.; Pai, M.G.J.; Acharjee, A.; Bankar, R.; Palanivel, V.; Salkar, A.; Verma, A.; Mukherjee, A.; Choudhury, M.; et al. Proteomics and Machine Learning Approaches Reveal a Set of Prognostic Markers for COVID-19 Severity With Drug Repurposing Potential. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 652799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuñez, E.; Orera, I.; Carmona-Rodríguez, L.; Paño, J.R.; Vázquez, J.; Corrales, F.J. Mapping the Serum Proteome of COVID-19 Patients; Guidance for Severity Assessment. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akgun, E.; Tuzuner, M.B.; Sahin, B.; Kilercik, M.; Kulah, C.; Cakiroglu, H.N.; Serteser, M.; Unsal, I.; Baykal, A.T. Proteins Associated with Neutrophil Degranulation Are Upregulated in Nasopharyngeal Swabs from SARS-CoV-2 Patients. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0240012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, S.; Hosseinkhan, N.; Shafiei Jandaghi, N.Z.; Sadeghi, K.; Foroushani, A.R.; Hassani, S.A.; Yavarian, J.; Azad, T.M. Impact of Human Rhinoviruses on Gene Expression in Pediatric Patients with Severe Acute Respiratory Infection. Virus Res. 2021, 300, 198408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jentho, E.; Weis, S. DAMPs and Innate Immune Training. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 699563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seong, S.-Y.; Matzinger, P. Hydrophobicity: An Ancient Damage-Associated Molecular Pattern That Initiates Innate Immune Responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, C. Integrated Gene Expression Profiling Analysis Reveals SERPINA3, FCN3, FREM1, MNS1 as Candidate Biomarkers in Heart Failure and Their Correlation with Immune Infiltration. J. Thorac. Dis. 2022, 14, 1106–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delrue, L.; Vanderheyden, M.; Beles, M.; Paolisso, P.; Di Gioia, G.; Dierckx, R.; Verstreken, S.; Goethals, M.; Heggermont, W.; Bartunek, J. Circulating SERPINA3 Improves Prognostic Stratification in Patients with a de Novo or Worsened Heart Failure. ESC Heart Fail. 2021, 8, 4780–4790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zheng, M.; Guo, Z.; Li, K.; Liu, Y.; Chen, M.; Yang, X. Circulating Serpina3 Levels Predict the Major Adverse Cardiac Events in Patients with Myocardial Infarction. Int. J. Cardiol. 2020, 300, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Jia, J.; Jia, X.-F.; Qin, W.; Wang, S. Combination of Plasma Biomarkers and Clinical Data for the Detection of Sporadic Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2012, 516, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeKosky, S.T.; Ikonomovic, M.D.; Wang, X.; Farlow, M.; Wisniewski, S.; Lopez, O.L.; Becker, J.T.; Saxton, J.; Klunk, W.E.; Sweet, R.; et al. Plasma and Cerebrospinal Fluid A1-Antichymotrypsin Levels in Alzheimer’s Disease: Correlation with Cognitive Impairment. Ann. Neurol. 2003, 53, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, H.M.; Minthon, L.; Londos, E.; Blennow, K.; Miranda, E.; Perez, J.; Crowther, D.C.; Lomas, D.A.; Janciauskiene, S.M. Plasma and CSF Serpins in Alzheimer Disease and Dementia with Lewy Bodies. Neurology 2007, 69, 1569–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mucke, L.; Yu, G.Q.; McConlogue, L.; Rockenstein, E.M.; Abraham, C.R.; Masliah, E. Astroglial Expression of Human Alpha(1)-Antichymotrypsin Enhances Alzheimer-like Pathology in Amyloid Protein Precursor Transgenic Mice. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 157, 2003–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, C.R.; Selkoe, D.J.; Potter, H. Immunochemical Identification of the Serine Protease Inhibitor A1-Antichymotrypsin in the Brain Amyloid Deposits of Alzheimer’s Disease. Cell 1988, 52, 487–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozemuller, J.M.; Stam, F.C.; Eikelenboom, P. Acute Phase Proteins Are Present in Amorphous Plaques in the Cerebral but Not in the Cerebellar Cortex of Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurosci. Lett. 1990, 119, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozemuller, J.M.; Abbink, J.J.; Kamp, A.M.; Stam, E.C.; Hack, C.E.; Eikelenboom, P. Distribution Pattern and Functional State of L-Antichymotrypsin in Plaques and Vascular Amyloid in Alzheimer’s Disease. Acta Neuropathol. 1991, 82, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Ren, Y.; Yamazaki, Y.; Qiao, W.; Li, F.; Felton, L.M.; Mahmoudiandehkordi, S.; Kueider-Paisley, A.; Sonoustoun, B.; Arnold, M.; et al. Alzheimer’s Risk Factors Age, APOE Genotype, and Sex Drive Distinct Molecular Pathways. Neuron 2020, 106, 727–742.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Pan, J.; Tang, K.; Lei, Q.; He, L.; Cai, X.; Li, Z. Alpha 1-Antichymotrypsin May Be a Biomarker for the Progression of Amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment. Acta Neurol. Belg. 2021, 121, 451–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamboh, M.I.; Minster, R.L.; Kenney, M.; Ozturk, A.; Desai, P.P.; Kammerer, C.M.; DeKosky, S.T. Alpha-1-Antichymotrypsin (ACT or SERPINA3) Polymorphism May Affect Age-at-Onset and Disease Duration of Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2006, 27, 1435–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fissolo, N.; Matute-Blanch, C.; Osman, M.; Costa, C.; Pinteac, R.; Miró, B.; Sanchez, A.; Brito, V.; Dujmovic, I.; Voortman, M.; et al. CSF SERPINA3 Levels Are Elevated in Patients with Progressive MS. Neurol Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 8, e941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, C.E.; Lawther, A.J.; Webster, M.J.; Asai, M.; Kondo, Y.; Matsumoto, M.; Walker, A.K.; Weickert, C.S. Nuclear Factor Kappa B Activation Appears Weaker in Schizophrenia Patients with High Brain Cytokines than in Non-Schizophrenic Controls with High Brain Cytokines. J. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 17, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zsila, F. Inhibition of Heat- and Chemical-Induced Aggregation of Various Proteins Reveals Chaperone-like Activity of the Acute-Phase Component and Serine Protease Inhibitor Human A1-Antitrypsin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 393, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colini Baldeschi, A.; Vanni, S.; Zattoni, M.; Legname, G. Novel Regulators of PrP C Expression as Potential Therapeutic Targets in Prion Diseases. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2020, 24, 759–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colini Baldeschi, A.; Zattoni, M.; Vanni, S.; Nikolic, L.; Ferracin, C.; La Sala, G.; Summa, M.; Bertorelli, R.; Bertozzi, S.M.; Giachin, G.; et al. Innovative Non-PrP-Targeted Drug Strategy Designed to Enhance Prion Clearance. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 8998–9010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukacs, C.M.; Rubin, H.; Christianson, D.W. Engineering an Anion-Binding Cavity in Antichymotrypsin Modulates the “Spring-Loaded” Serpin–Protease Interaction. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 3297–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanfilippo, C.; Longo, A.; Lazzara, F.; Cambria, D.; Distefano, G.; Palumbo, M.; Cantarella, A.; Malaguarnera, L.; Di Rosa, M. CHI3L1 and CHI3L2 Overexpression in Motor Cortex and Spinal Cord of SALS Patients. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 85, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Mezer, M.; Rogaliński, J.; Przewoźny, S.; Chojnicki, M.; Niepolski, L.; Sobieska, M.; Przystańska, A. SERPINA3: Stimulator or Inhibitor of Pathological Changes. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 156. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11010156
de Mezer M, Rogaliński J, Przewoźny S, Chojnicki M, Niepolski L, Sobieska M, Przystańska A. SERPINA3: Stimulator or Inhibitor of Pathological Changes. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(1):156. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11010156
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Mezer, Mateusz, Jan Rogaliński, Stanisław Przewoźny, Michał Chojnicki, Leszek Niepolski, Magdalena Sobieska, and Agnieszka Przystańska. 2023. "SERPINA3: Stimulator or Inhibitor of Pathological Changes" Biomedicines 11, no. 1: 156. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11010156
APA Stylede Mezer, M., Rogaliński, J., Przewoźny, S., Chojnicki, M., Niepolski, L., Sobieska, M., & Przystańska, A. (2023). SERPINA3: Stimulator or Inhibitor of Pathological Changes. Biomedicines, 11(1), 156. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11010156





