Cannabidiol Modulates M-Type K+ and Hyperpolarization-Activated Cation Currents
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals, Drugs, and Solutions Used for This Work
2.2. Preparation of Pituitary GH3 Cells
2.3. Electrophysiological Recordings Using Patch-Clamp Technique
2.4. Analyses of Whole-Cell Recordings
2.5. Methods for Curve-Fitting and Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Cannabidiol (CBD) on the M-Type K+ Current (IK(M)) Identified in Pituitary GH3 Cells
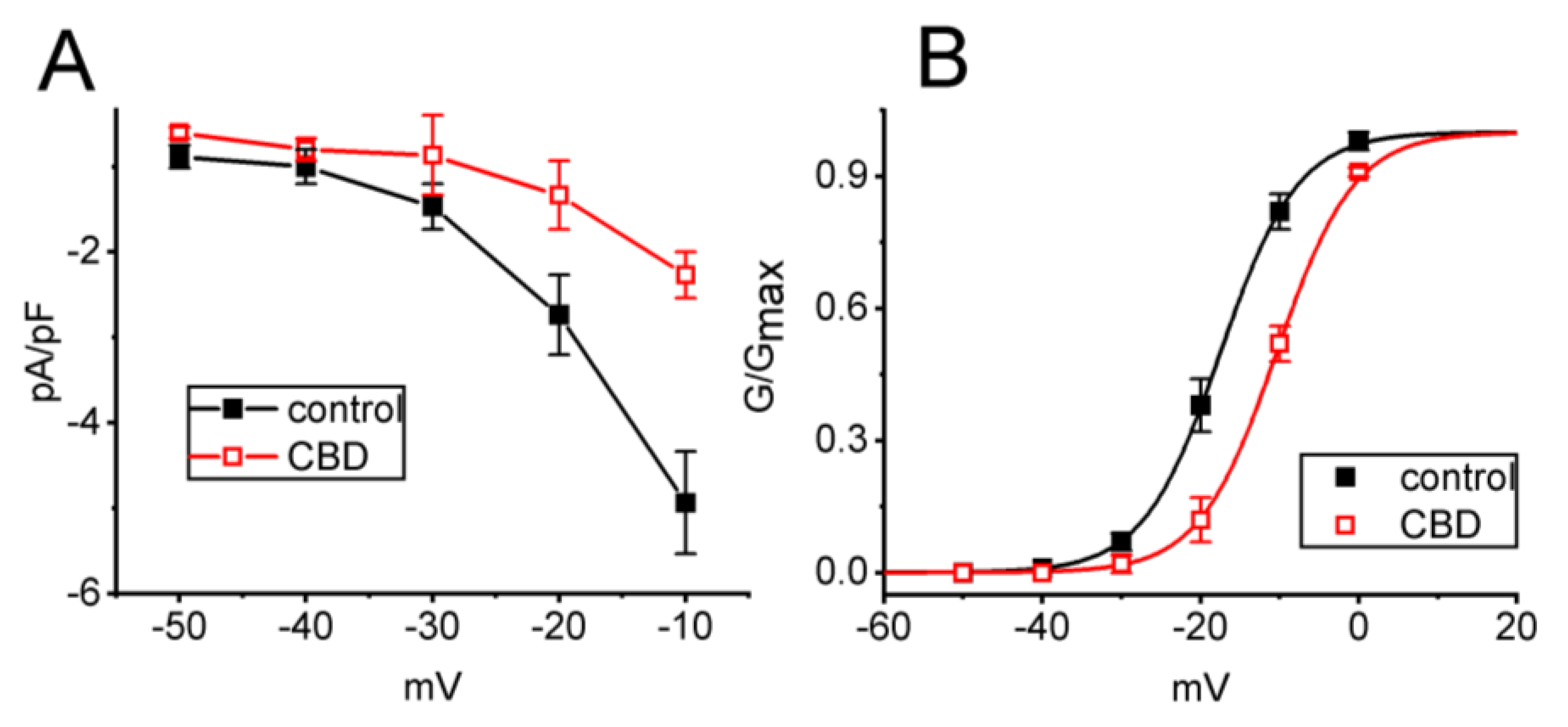
3.2. Effect of CBD on the Current Density Versus Voltage Relationship and the Quasi-Steady-State Activation Curve of IK(M) in GH3 Cells
3.3. Comparisons among Effects of CBD, CBD plus Naloxone, Linopirdine (Lino), Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone (TRH), and Liraglutinide (Lira) on the Density of IK(M) in GH3 Cells
3.4. Modification by CBD of IK(M) Elicited by Pulse-Train (PT) Stimulation
3.5. Mild Inhibitory Effect of CBD on the erg-Mediated K+ Current (IK(erg)) in GH3 Cells
3.6. Failure of CBD Effect on Voltage-Gated Na+ Current (INa) in GH3 Cells
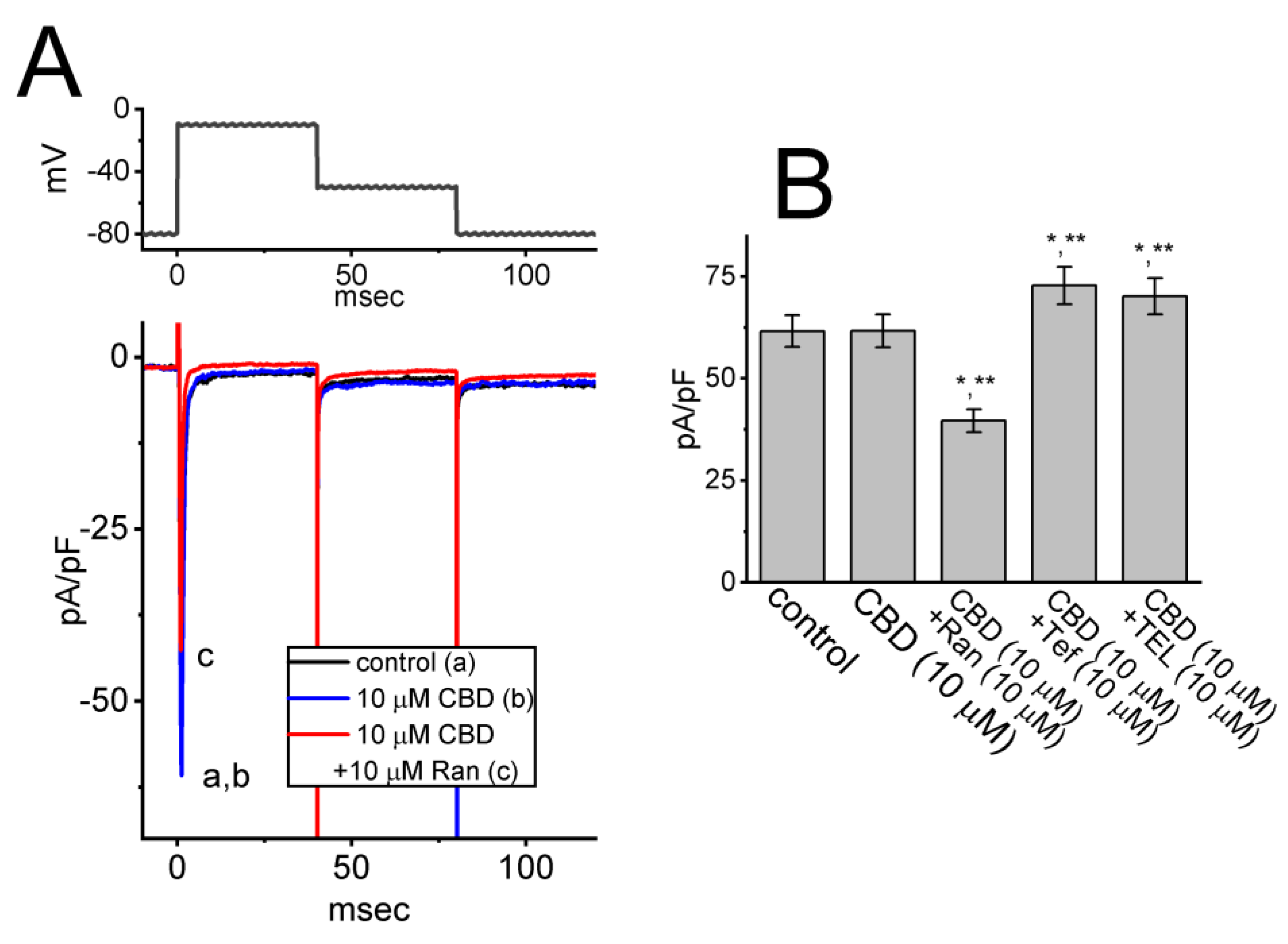
3.7. Effect of CBD on Hyperpolarization-Activated Cation Current (Ih) Measured in GH3 Cells
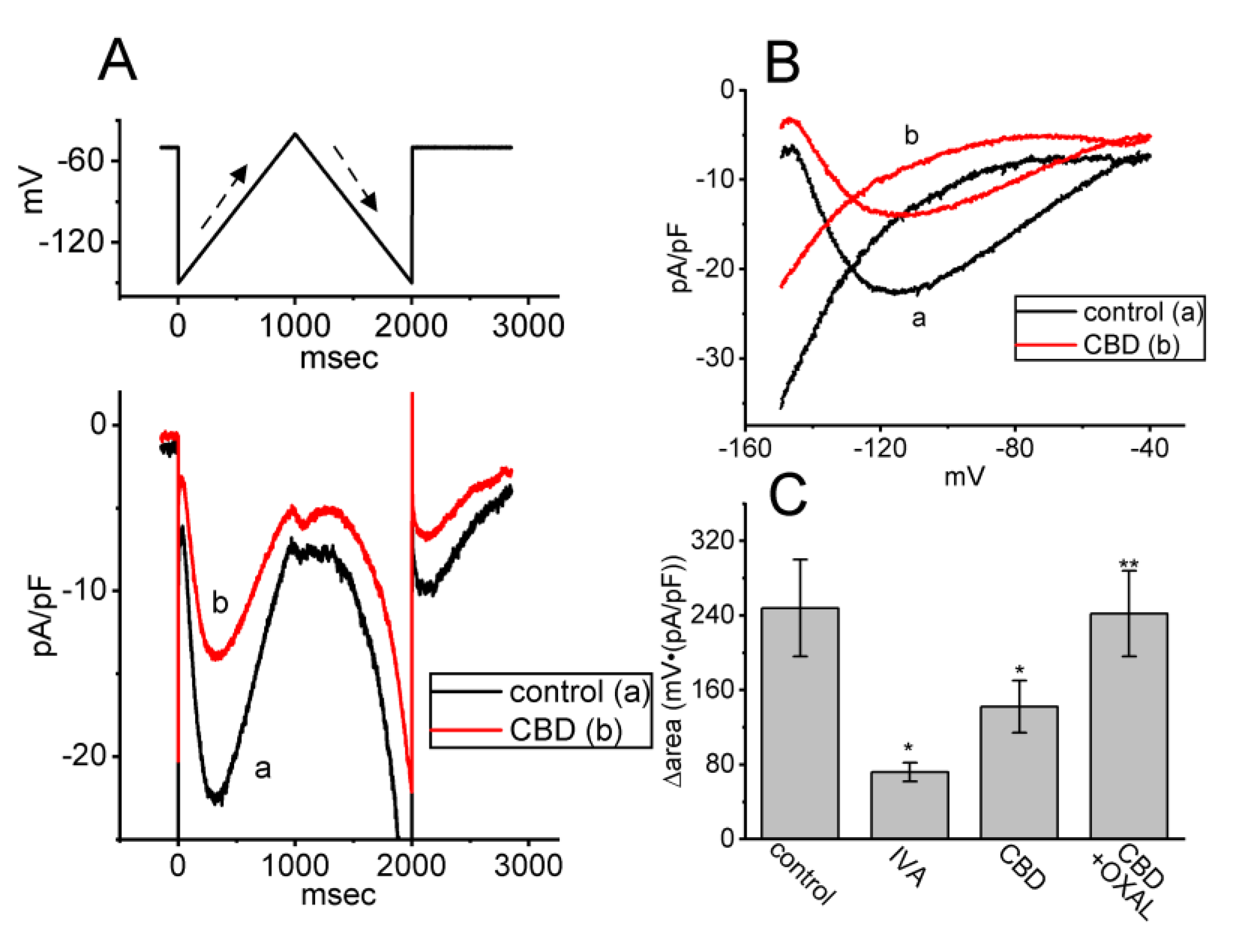
3.8. Effect of CBD on the Hysteretic Behavior (i.e., Voltage-Dependent Hysteresis (Hys(V))) of Ih Elicited by Isosceles-Triangular Ramp Voltage (Vramp) in GH3 Cells
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Howlett, A.C.; Abood, M.E. CB(1) and CB(2) Receptor Pharmacology. Adv. Pharmacol. 2017, 80, 169–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraguas-Sánchez, A.I.; Torres-Suárez, A.I. Medical Use of Cannabinoids. Drugs 2018, 78, 1665–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schurman, L.D.; Lu, D.; Kendall, D.A.; Howlett, A.C.; Lichtman, A.H. Molecular Mechanism and Cannabinoid Pharmacology. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2020, 258, 323–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Britch, S.C.; Babalonis, S.; Walsh, S.L. Cannabidiol: Pharmacology and therapeutic targets. Psychopharmacology 2021, 238, 9–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghovanloo, M.R.; Ruben, P.C. Cannabidiol and Sodium Channel Pharmacology: General Overview, Mechanism, and Clinical Implications. Neuroscientist 2022, 28, 318–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viudez-Martínez, A.; García-Gutiérrez, M.S.; Manzanares, J. Cannabidiol regulates the expression of hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis-related genes in response to acute restraint stress. J. Psychopharmacol. 2018, 32, 1379–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopresti, A.L.; Smith, S.J.; Drummond, P.D. Modulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis by plants and phytonutrients: A systematic review of human trials. Nutr. Neurosci. 2022, 25, 1704–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.W.; Lin, P.C.; Chen, J.L.; Lee, M.J. Cannabidiol Selectively Binds to the Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel Na(v)1.4 in Its Slow-Inactivated State and Inhibits Sodium Current. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, X.; Drummond-Main, C.; Greening, D.; Yao, J.; Chen, S.W.R.; Appendino, J.P.; Au, P.Y.B.; Turner, R.W. Cannabidiol counters the effects of a dominant-negative pathogenic Kv7.2 variant. iScience 2022, 25, 105092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miceli, F.; Soldovieri, M.V.; Martire, M.; Taglialatela, M. Molecular pharmacology and therapeutic potential of neuronal Kv7-modulating drugs. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2008, 8, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankaranarayanan, S.; Simasko, S.M. Characterization of an M-like current modulated by thyrotropin-releasing hormone in normal rat lactotrophs. J. Neurosci. 1996, 16, 1668–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selyanko, A.A.; Hadley, J.K.; Wood, I.C.; Abogadie, F.C.; Delmas, P.; Buckley, N.J.; London, B.; Brown, D.A. Two types of K(+) channel subunit, Erg1 and KCNQ2/3, contribute to the M-like current in a mammalian neuronal cell. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 7742–7756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gribkoff, V.K. The therapeutic potential of neuronal KCNQ channel modulators. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2003, 7, 737–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baculis, B.C.; Zhang, J.; Chung, H.J. The Role of K(v)7 Channels in Neural Plasticity and Behavior. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 568667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nappi, P.; Miceli, F.; Soldovieri, M.V.; Ambrosino, P.; Barrese, V.; Taglialatela, M. Epileptic channelopathies caused by neuronal Kv7 (KCNQ) channel dysfunction. Pflügers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2020, 472, 881–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Darwish, Y.; Fu, X.; Trussell, L.O.; Huang, H. KCNQ Channels Enable Reliable Presynaptic Spiking and Synaptic Transmission at High Frequency. J. Neurosci. 2022, 42, 3305–3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.B.; Heckman, L.; Niday, Z.; Jo, S.; Fujita, A.; Shim, J.; Pandey, R.; Al Jandal, H.; Jayakar, S.; Barrett, L.B.; et al. Cannabidiol activates neuronal Kv7 channels. eLife 2022, 11, e73246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irisawa, H.; Brown, H.F.; Giles, W. Cardiac pacemaking in the sinoatrial node. Physiol. Rev. 1993, 73, 197–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.C.; Wang, Y.J.; Wu, P.Y.; Wu, S.N. Tramadol-induced block of hyperpolarization-activated cation current in rat pituitary lactotrophs. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2009, 379, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, H.T.; Liu, Y.C.; Liu, P.Y.; Wu, S.N. Concerted suppression of I(h) and activation of I(K(M)) by ivabradine, an HCN-channel inhibitor, in pituitary cells and hippocampal neurons. Brain Res. Bull. 2019, 149, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, C.W.; Chang, K.P.; Cho, H.Y.; Chuang, T.H.; Yu, M.C.; Wu, C.L.; Wu, S.N. Characterization of Inhibitory Capability on Hyperpolarization-Activated Cation Current Caused by Lutein (β,ε-Carotene-3,3’-Diol), a Dietary Xanthophyll Carotenoid. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, C.H.; Singh, R.K.; Bankston, J.R.; Proenza, C. Regulation of HCN Channels by Protein Interactions. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 928507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mäki-Marttunen, T.; Mäki-Marttunen, V. Excitatory and inhibitory effects of HCN channel modulation on excitability of layer V pyramidal cells. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2022, 18, e1010506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surges, R.; Kukley, M.; Brewster, A.; Rüschenschmidt, C.; Schramm, J.; Baram, T.Z.; Beck, H.; Dietrich, D. Hyperpolarization-activated cation current Ih of dentate gyrus granule cells is upregulated in human and rat temporal lobe epilepsy. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 420, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yongning, Z.; Xianguang, L.; Hengling, C.; Su, C.; Fang, L.; Chenhong, L. The hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated channel currents contribute to oxaliplatin-induced hyperexcitability of DRG neurons. Somatosens. Mot. Res. 2021, 38, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohashi, N.; Uta, D.; Ohashi, M.; Baba, H. Analgesic effect of ivabradine against inflammatory pain mediated by hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated cation channels expressed on primary afferent terminals in the spinal dorsal horn. Pain 2022, 163, 1356–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, M.; Obana, M.; Akaike, N. Inhibition of M-type K+ current by linopirdine, a neurotransmitter-release enhancer, in NG108-15 neuronal cells and rat cerebral neurons in culture. Brain Res. 1998, 794, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dods, R.L.; Donnelly, D. The peptide agonist-binding site of the glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor based on site-directed mutagenesis and knowledge-based modelling. Biosci. Rep. 2015, 36, e00285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drucker, D.J. GLP-1 physiology informs the pharmacotherapy of obesity. Mol. Metab. 2022, 57, 101351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casis, O.; Olesen, S.P.; Sanguinetti, M.C. Mechanism of action of a novel human ether-a-go-go-related gene channel activator. Mol. Pharmacol. 2006, 69, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.S.; Lo, Y.C.; Peng, H.; Hsu, T.I.; Wu, S.N. Effects of ranolazine, a novel anti-anginal drug, on ion currents and membrane potential in pituitary tumor GH(3) cells and NG108-15 neuronal cells. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2009, 110, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- So, E.C.; Wu, S.N.; Lo, Y.C.; Su, K. Differential regulation of tefluthrin and telmisartan on the gating charges of I(Na) activation and inactivation as well as on resurgent and persistent I(Na) in a pituitary cell line (GH(3)). Toxicol. Lett. 2018, 285, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Männikkö, R.; Pandey, S.; Larsson, H.P.; Elinder, F. Hysteresis in the voltage dependence of HCN channels: Conversion between two modes affects pacemaker properties. J. Gen. Physiol. 2005, 125, 305–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.F.; Chandler, N.; Dobrzynski, H.; Richardson, E.S.; Tenbroek, E.M.; Wilhelm, J.J.; Sharma, V.; Varghese, A.; Boyett, M.R.; Iaizzo, P.A.; et al. Hysteresis in human HCN4 channels: A crucial feature potentially affecting sinoatrial node pacemaking. Sheng Li Xue Bao 2010, 62, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chang, W.T.; Gao, Z.H.; Li, S.W.; Liu, P.Y.; Lo, Y.C.; Wu, S.N. Characterization in Dual Activation by Oxaliplatin, a Platinum-Based Chemotherapeutic Agent of Hyperpolarization-Activated Cation and Electroporation-Induced Currents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kretschmannova, K.; Gonzalez-Iglesias, A.E.; Tomić, M.; Stojilkovic, S.S. Dependence of hyperpolarisation-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated channel activity on basal cyclic adenosine monophosphate production in spontaneously firing GH3 cells. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2006, 18, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, R.B.; Siegelbaum, S.A. Hyperpolarization-activated cation currents: From molecules to physiological function. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2003, 65, 453–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramentol, R.; Perez, M.E.; Larsson, H.P. Gating mechanism of hyperpolarization-activated HCN pacemaker channels. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 332a. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, S.A.; Stone, N.L.; Yates, A.S.; O’Sullivan, S.E. A Systematic Review on the Pharmacokinetics of Cannabidiol in Humans. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathmann, M.; Flau, K.; Redmer, A.; Tränkle, C.; Schlicker, E. Cannabidiol is an allosteric modulator at mu- and delta-opioid receptors. Naunyn Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2006, 372, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.-C.; So, E.C.; Wu, S.-N. Cannabidiol Modulates M-Type K+ and Hyperpolarization-Activated Cation Currents. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2651. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11102651
Liu Y-C, So EC, Wu S-N. Cannabidiol Modulates M-Type K+ and Hyperpolarization-Activated Cation Currents. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(10):2651. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11102651
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yen-Chin, Edmund Cheung So, and Sheng-Nan Wu. 2023. "Cannabidiol Modulates M-Type K+ and Hyperpolarization-Activated Cation Currents" Biomedicines 11, no. 10: 2651. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11102651
APA StyleLiu, Y.-C., So, E. C., & Wu, S.-N. (2023). Cannabidiol Modulates M-Type K+ and Hyperpolarization-Activated Cation Currents. Biomedicines, 11(10), 2651. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11102651






