Identification of SEC61G as a Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Data Source
2.2. Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) of SEC61G
2.3. Ethical Statement, Human OSCC Tissue Microarray, and OSCC Patient Cohort
2.4. Immunohistochemistry
2.5. Evaluation of Immunohistochemistry
2.6. Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells (PBMCs) Separation
2.7. Tumor Infiltrated Lymphocytes (TILs) Isolation
2.8. Flow Cytometry
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
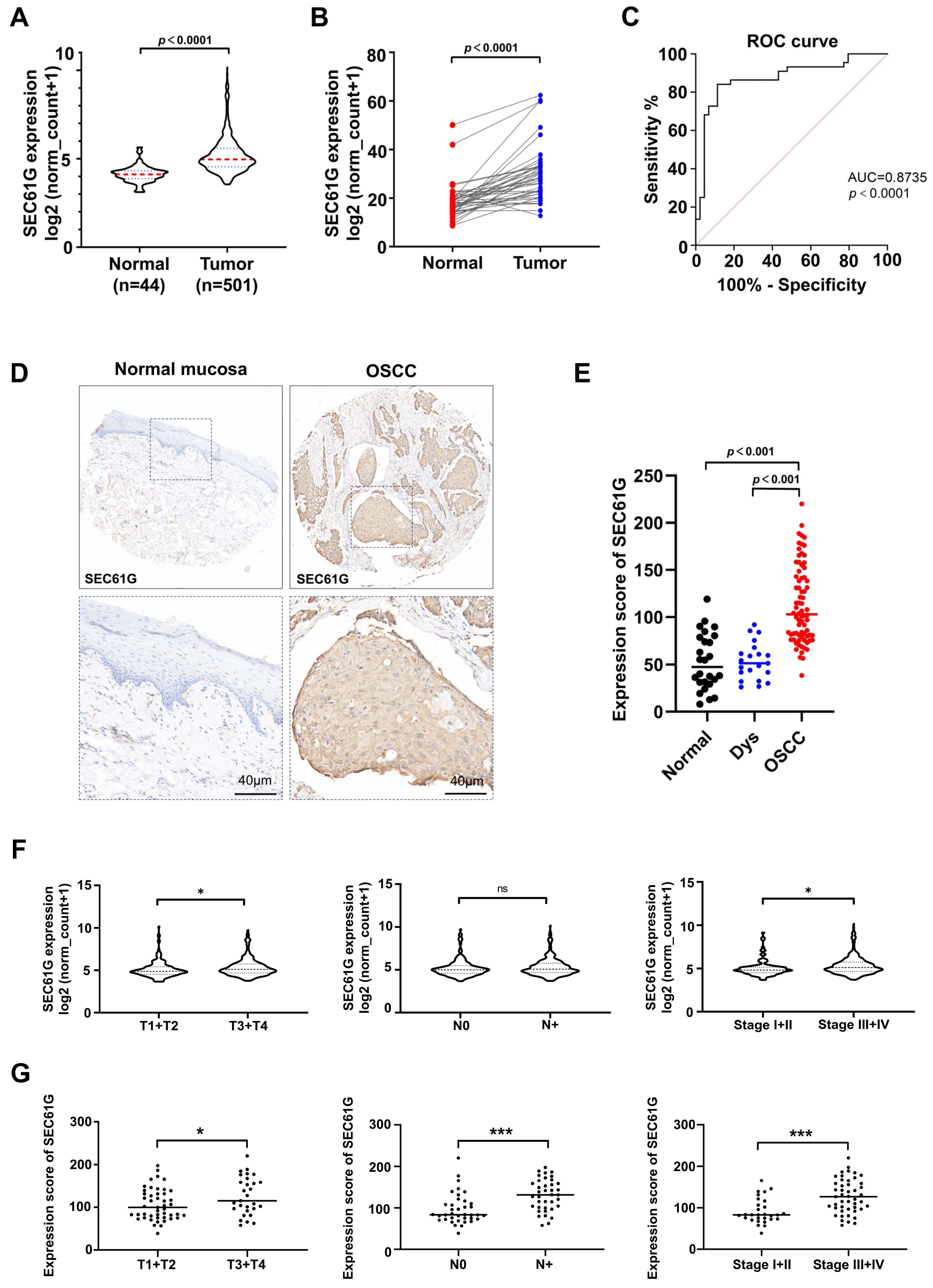
3.1. The Expression Level of SEC61G Is Significantly Increased and Correlated with Clinicopathological Characteristics in Human OSCC Samples
3.2. Prognostic Value of SEC61G in OSCC
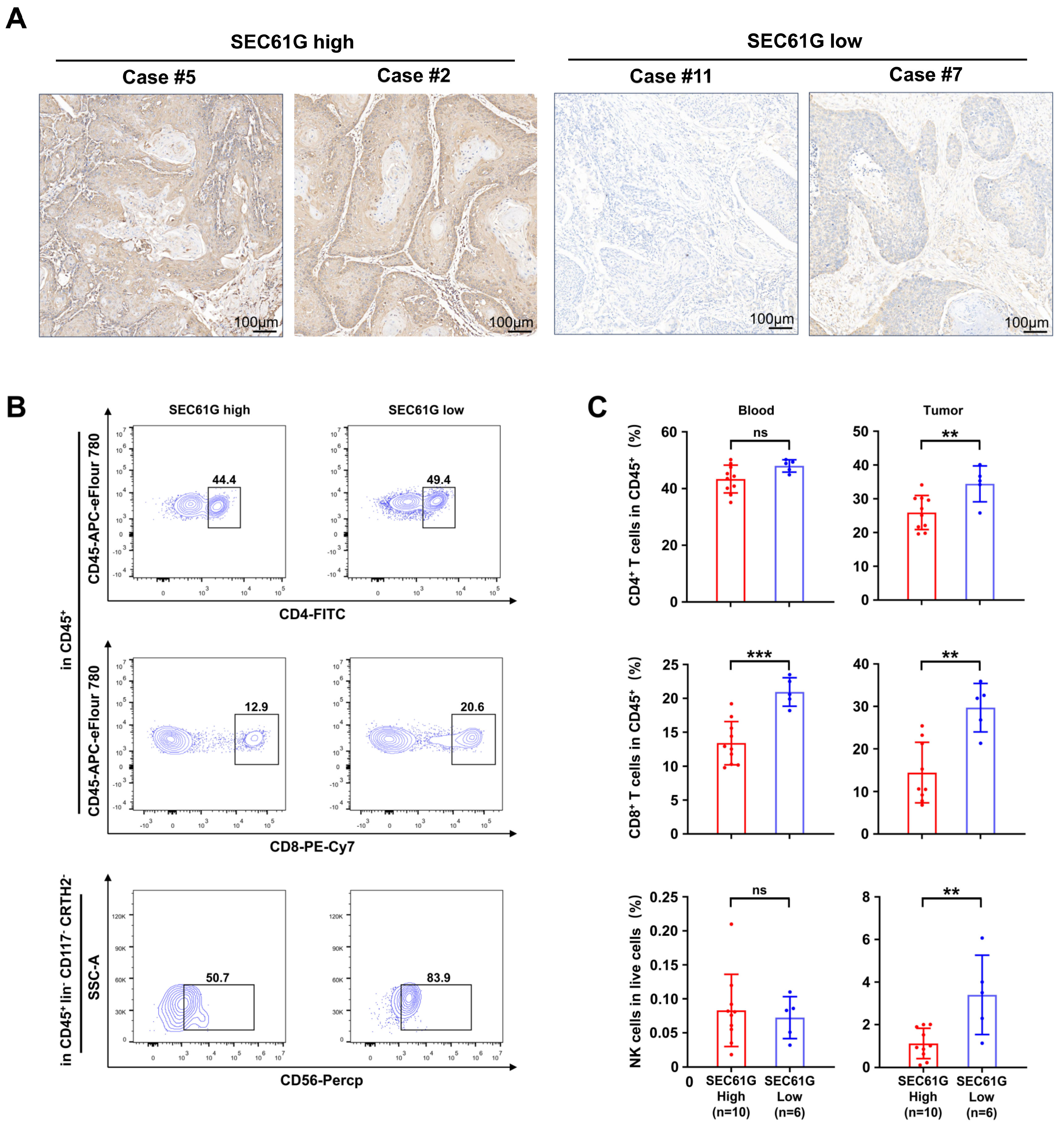
3.3. SEC61G Expression Level Is Negatively Associated with Immunostimulation and Immune Cell Infiltration in OSCC
3.4. SEC61G Shows a Negative Correlation with the Accumulation of Immune Cells in OSCC Patients’ Samples
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Torre, L.A.; Bray, F.; Siegel, R.L.; Ferlay, J.; Lortet-Tieulent, J.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2015, 65, 87–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, L.Q.M. Head and Neck Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, D.E.; Burtness, B.; Leemans, C.R.; Lui, V.W.Y.; Bauman, J.E.; Grandis, J.R. Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanoni, D.K.; Montero, P.H.; Migliacci, J.C.; Shah, J.P.; Wong, R.J.; Ganly, I.; Patel, S.G. Survival outcomes after treatment of cancer of the oral cavity (1985–2015). Oral Oncol. 2019, 90, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenfield, J.J.; High, S. The Sec61 complex is located in both the ER and the ER-Golgi intermediate compartment. J. Cell Sci. 1999, 112 Pt 10, 1477–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponsero, A.J.; Igbaria, A.; Darch, M.A.; Miled, S.; Outten, C.E.; Winther, J.R.; Palais, G.; D’Autreaux, B.; Delaunay-Moisan, A.; Toledano, M.B. Endoplasmic Reticulum Transport of Glutathione by Sec61 Is Regulated by Ero1 and Bip. Mol. Cell 2017, 67, 962–973.e965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalies, K.U.; Romisch, K. Inhibitors of Protein Translocation Across the ER Membrane. Traffic 2015, 16, 1027–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Li, X.; Geng, J.; Cao, Y.; Yu, Y.; Qi, L. Sec61gamma is a vital protein in the endoplasmic reticulum membrane promoting tumor metastasis and invasion in lung adenocarcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2023, 128, 1478–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, L.; Chen, D.; Hirachan, S.; Bhandari, A.; Huang, Q. SEC61G regulates breast cancer cell proliferation and metastasis by affecting the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. J. Cancer 2022, 13, 831–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linxweiler, M.; Schick, B.; Zimmermann, R. Let’s talk about Secs: Sec61, Sec62 and Sec63 in signal transduction, oncology and personalized medicine. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2017, 2, 17002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Liu, J.; Liao, Y.; Jin, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Liu, K.; Huang, H.; Cao, H.; Cheng, Q. Identification of SEC61G as a Novel Prognostic Marker for Predicting Survival and Response to Therapies in Patients with Glioblastoma. Med. Sci. Monit. 2019, 25, 3624–3635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.; Niu, W.; He, Z.; Gao, C.; Peng, C.; Niu, J. SEC61G plays an oncogenic role in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cell Cycle 2020, 19, 3348–3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.; Jiang, X.; Wang, J.; Sang, Z.; Guo, L.; Yin, G.; Wang, Y. SEC61G is upregulated and required for tumor progression in human kidney cancer. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 23, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaderbhai, C.; Tharin, Z.; Ghiringhelli, F. The Role of Molecular Profiling to Predict the Response to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Lung Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwantwi, L.B. Overcoming anti-PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint blockade resistance: The role of macrophage, neutrophils and mast cells in the tumor microenvironment. Clin. Exp. Med. 2023, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, K.; Zeng, Y.; Zhan, H.; Zhan, Z.; Wang, L.; Xie, Y.; Tang, Y.; Li, C.; Chen, Y.; Li, S.; et al. SEC61G assists EGFR-amplified glioblastoma to evade immune elimination. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2303400120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.R.; Liu, J.F.; Jia, R.; Deng, W.W.; Jia, J. Identification of a Favorable Prognostic Subgroup in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Characterization of ITGB4/PD-L1(high) with CD8/PD-1(high). Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, Y.L.; LeBon, L.; Basso, A.M.; Kohlhaas, K.L.; Nikkel, A.L.; Robb, H.M.; Donnelly-Roberts, D.L.; Prakash, J.; Swensen, A.M.; Rubinstein, N.D.; et al. eIF2B activator prevents neurological defects caused by a chronic integrated stress response. eLife 2019, 8, e42940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paschalis, A.; Sheehan, B.; Riisnaes, R.; Rodrigues, D.N.; Gurel, B.; Bertan, C.; Ferreira, A.; Lambros, M.B.K.; Seed, G.; Yuan, W.; et al. Prostate-specific Membrane Antigen Heterogeneity and DNA Repair Defects in Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2019, 76, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Berry, L.D.; Aisner, D.L.; Sheren, J.; Boyle, T.; Bunn, P.A., Jr.; Johnson, B.E.; Kwiatkowski, D.J.; Drilon, A.; Sholl, L.M.; et al. MET IHC Is a Poor Screen for MET Amplification or MET Exon 14 Mutations in Lung Adenocarcinomas: Data from a Tri-Institutional Cohort of the Lung Cancer Mutation Consortium. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 1666–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Zhou, L.; Killela, P.; Rasheed, A.B.; Di, C.; Poe, W.E.; McLendon, R.E.; Bigner, D.D.; Nicchitta, C.; Yan, H. Glioblastoma proto-oncogene SEC61gamma is required for tumor cell survival and response to endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 9105–9111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Liang, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, G. SEC61G identified as a prognostic biomarker of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2022, 279, 2039–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Huang, Q.; Gan, M.; Jiang, L.; Yan, H.; Lin, Z.; Zhu, H.; Wang, R.; Hu, K. High SEC61G expression predicts poor prognosis in patients with Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas. J. Cancer 2021, 12, 3887–3899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Sayans, M.; Suarez-Penaranda, J.M.; Pilar, G.D.; Barros-Angueira, F.; Gandara-Rey, J.M.; Garcia-Garcia, A. What real influence does the proto-oncogene c-myc have in OSCC behavior? Oral Oncol. 2011, 47, 688–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marconi, G.D.; Della Rocca, Y.; Fonticoli, L.; Melfi, F.; Rajan, T.S.; Carradori, S.; Pizzicannella, J.; Trubiani, O.; Diomede, F. C-Myc Expression in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Molecular Mechanisms in Cell Survival and Cancer Progression. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, D.R.; Galluzzi, L.; Kroemer, G. Cell biology. Metabolic control of cell death. Science 2014, 345, 1250256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essers, P.B.M.; van der Heijden, M.; Verhagen, C.V.M.; Ploeg, E.M.; de Roest, R.H.; Leemans, C.R.; Brakenhoff, R.H.; van den Brekel, M.W.M.; Bartelink, H.; Verheij, M.; et al. Drug Sensitivity Prediction Models Reveal a Link between DNA Repair Defects and Poor Prognosis in HNSCC. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 5597–5611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Hong, W.; Wei, X. The molecular mechanisms and therapeutic strategies of EMT in tumor progression and metastasis. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dongre, A.; Weinberg, R.A. New insights into the mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and implications for cancer. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bindea, G.; Mlecnik, B.; Tosolini, M.; Kirilovsky, A.; Waldner, M.; Obenauf, A.C.; Angell, H.; Fredriksen, T.; Lafontaine, L.; Berger, A.; et al. Spatiotemporal dynamics of intratumoral immune cells reveal the immune landscape in human cancer. Immunity 2013, 39, 782–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palucka, A.K.; Coussens, L.M. The Basis of Oncoimmunology. Cell 2016, 164, 1233–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- St Paul, M.; Ohashi, P.S. The Roles of CD8(+) T Cell Subsets in Antitumor Immunity. Trends Cell Biol. 2020, 30, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edner, N.M.; Carlesso, G.; Rush, J.S.; Walker, L.S.K. Targeting co-stimulatory molecules in autoimmune disease. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 19, 860–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Ruiter, E.J.; Ooft, M.L.; Devriese, L.A.; Willems, S.M. The prognostic role of tumor infiltrating T-lymphocytes in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncoimmunology 2017, 6, e1356148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lequerica-Fernandez, P.; Suarez-Canto, J.; Rodriguez-Santamarta, T.; Rodrigo, J.P.; Suarez-Sanchez, F.J.; Blanco-Lorenzo, V.; Dominguez-Iglesias, F.; Garcia-Pedrero, J.M.; de Vicente, J.C. Prognostic Relevance of CD4(+), CD8(+) and FOXP3(+) TILs in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Correlations with PD-L1 and Cancer Stem Cell Markers. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, S.; Hiratsuka, H.; Koike, K.; Tsuchihashi, K.; Sonoda, T.; Ogi, K.; Miyakawa, A.; Kobayashi, J.; Kaneko, T.; Igarashi, T.; et al. Tumor-infiltrating CD8(+) T-cell density is an independent prognostic marker for oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristics | Cases | Percentages (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | <65 years | 330 | 62.62% |
| ≥65 years | 196 | 37.19% | |
| Unknown | 1 | 0.19% | |
| Gender | Male | 385 | 73.06% |
| Female | 142 | 26.94% | |
| Histological grade | G1 | 63 | 11.95% |
| G2 | 311 | 59.01% | |
| G3 | 124 | 23.53% | |
| G4 | 7 | 1.33% | |
| GX | 18 | 3.42% | |
| Unknown | 4 | 0.76% | |
| Clinical stage | I/II | 101 | 19.17% |
| III/IV | 351 | 66.60% | |
| Unknown | 75 | 14.23% | |
| Tumor size | T0 | 1 | 0.19% |
| T1/T2 | 189 | 35.86% | |
| T3/T4 | 275 | 52.18% | |
| TX | 39 | 7.40% | |
| Unknown | 23 | 4.36% | |
| Lymphoid nodal status | N0 | 179 | 33.97% |
| N1+ | 248 | 47.06% | |
| NX | 75 | 14.23% | |
| Unknown | 25 | 4.74% | |
| Distant metastasis status | M0 | 190 | 36.05% |
| M1 | 1 | 0.19% | |
| MX | 65 | 12.33% | |
| Unknown | 271 | 51.42% | |
| Radiation therapy | Yes | 203 | 38.52% |
| No | 324 | 61.48% | |
| Survival status | Death | 199 | 37.76% |
| Survival | 328 | 62.24% |
| No. | Gender | Age | TNM Stage | Grade | Alive (0) or Dead (1) | Survival Time (Months) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | male | 49 | T2N0M0 | I | 0 | 74 |
| 2 | male | 50 | T2N1M0 | III | 1 | 49 |
| 3 | male | 50 | T3N1M0 | II | 1 | 9 |
| 4 | female | 43 | T2N0M0 | II | 0 | 72 |
| 5 | female | 65 | T3N0M0 | II | 1 | 13 |
| 6 | female | 73 | T3N0M0 | II | 0 | 68 |
| 7 | male | 40 | T3N2M0 | II | 1 | 4 |
| 8 | male | 38 | T2N1M0 | I | 0 | 31 |
| 9 | male | 44 | T1N0M0 | II | 0 | 59 |
| 10 | female | 67 | T2N0M0 | II | 0 | 51 |
| 11 | male | 73 | T2N1M0 | I | 0 | 45 |
| 12 | male | 61 | T1N0M0 | II | 1 | 39 |
| 13 | male | 68 | T2N0M0 | II | 0 | 39 |
| 14 | female | 57 | T1N0M0 | II | 0 | 65 |
| 15 | male | 60 | T3N0M0 | III | 1 | 3 |
| 16 | male | 40 | T2N1M0 | II | 0 | 97 |
| 17 | male | 39 | T2N0M0 | II | 0 | 96 |
| 18 | male | 77 | T1N0M0 | III | 1 | 5 |
| 19 | male | 68 | T2N2M0 | I | 0 | 93 |
| 20 | male | 63 | T3N1M0 | I | 1 | 20 |
| 21 | male | 43 | T2N0M0 | III | 1 | 30 |
| 22 | female | 78 | T4N2M0 | II | 0 | 88 |
| 23 | male | 57 | T3N1M0 | II | 1 | 0 |
| 24 | male | 72 | T4N0M0 | II | 0 | 85 |
| 25 | male | 62 | T4N1M0 | II | 1 | 24 |
| 26 | male | 80 | T4N0M0 | II | 1 | 12 |
| 27 | male | 70 | T4N1M0 | II | 0 | 84 |
| 28 | male | 72 | T2N2M0 | II | 0 | 29 |
| 29 | male | 57 | T3N1M0 | II | 0 | 83 |
| 30 | male | 53 | T3N1M0 | IIII | 1 | 12 |
| 31 | male | 55 | T3N0M0 | II | 1 | 8 |
| 32 | female | 66 | T1N1M0 | III | 1 | 16 |
| 33 | male | 62 | T1N0M0 | II | 0 | 82 |
| 34 | male | 46 | T4N0M0 | II | 0 | 82 |
| 35 | male | 54 | T4N1M0 | I | 1 | 11 |
| 36 | male | 54 | T2N1M0 | I | 0 | 79 |
| 37 | male | 41 | T2N1M0 | III | 0 | 76 |
| 38 | male | 46 | T2N1M0 | II | 1 | 7 |
| 39 | male | 62 | T2N0M0 | III | 1 | 4 |
| 40 | male | 49 | T2N0M0 | II | 0 | 73 |
| 41 | male | 78 | T2N1M0 | I | 0 | 73 |
| 42 | male | 63 | T4N2M0 | II | 1 | 64 |
| 43 | male | 48 | T3N0M0 | II | 0 | 70 |
| 44 | female | 65 | T4N2M0 | I | 0 | 69 |
| 45 | male | 57 | T4N1M0 | III | 1 | 57 |
| 46 | female | 58 | T2N0M0 | II | 0 | 68 |
| 47 | male | 35 | T2N0M0 | II | 0 | 68 |
| 48 | male | 50 | T4N0M0 | III | 0 | 67 |
| 49 | male | 48 | T2N1M0 | II | 0 | 11 |
| 50 | male | 57 | T2N0M0 | II | 0 | 67 |
| 51 | male | 52 | T2N0M0 | III | 1 | 21 |
| 52 | male | 59 | T2N2M0 | II | 1 | 9 |
| 53 | female | 46 | T2N0M0 | II | 1 | 30 |
| 54 | male | 51 | T4N1M0 | I | 0 | 65 |
| 55 | male | 61 | T1N0M0 | II | 1 | 1 |
| 56 | male | 46 | T4N1M0 | II | 0 | 63 |
| 57 | male | 47 | T2N2M0 | II | 1 | 3 |
| 58 | male | 63 | T4N2M0 | II | 1 | 4 |
| 59 | male | 61 | T2N0M0 | III | 1 | 10 |
| 60 | male | 69 | T2N2M0 | II | 1 | 17 |
| No. | Gender | Age | TNM Stage | Grade | Stage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | male | 50 | T3N2bM0 | II | IVA |
| 2 | male | 39 | T3N1M0 | III | III |
| 3 | male | 38 | T1N0M0 | I | I |
| 4 | male | 48 | T2N0M0 | III | II |
| 5 | male | 43 | T3N1M0 | II | III |
| 6 | female | 57 | T2N0M0 | II | II |
| 7 | male | 64 | T1N1M0 | II | III |
| 8 | male | 38 | T3N1M0 | II | III |
| 9 | male | 54 | T3N0M0 | II | III |
| 10 | female | 74 | T3N0M0 | II | III |
| 11 | male | 70 | T2N1M0 | II | III |
| 12 | male | 64 | T3N0M0 | I | III |
| 13 | male | 57 | T2N3bM0 | III | IVB |
| 14 | female | 53 | T2N1M0 | II | III |
| 15 | male | 38 | T3N1M0 | III | III |
| 16 | male | 74 | T2N0M0 | I | II |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.-L.; Chen, L.; Bu, L.-L.; Yu, Z.-L.; Ma, S.-R. Identification of SEC61G as a Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2718. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11102718
Zhang S-L, Chen L, Bu L-L, Yu Z-L, Ma S-R. Identification of SEC61G as a Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(10):2718. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11102718
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Shi-Long, Lei Chen, Lin-Lin Bu, Zi-Li Yu, and Si-Rui Ma. 2023. "Identification of SEC61G as a Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma" Biomedicines 11, no. 10: 2718. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11102718
APA StyleZhang, S.-L., Chen, L., Bu, L.-L., Yu, Z.-L., & Ma, S.-R. (2023). Identification of SEC61G as a Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Biomedicines, 11(10), 2718. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11102718








