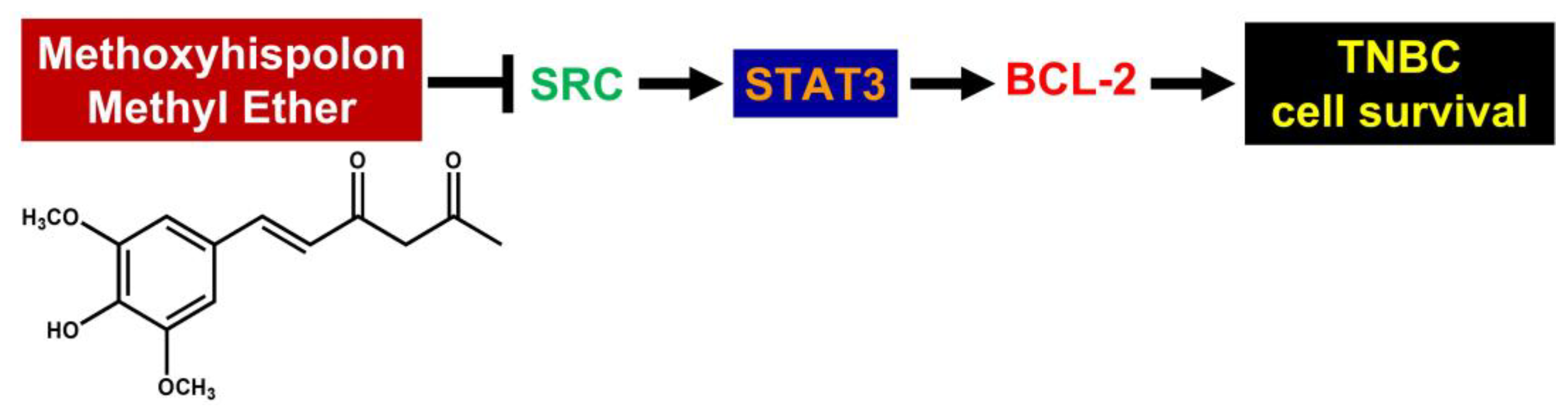
Methoxyhispolon Methyl Ether, a Hispolon Analog, Thwarts the SRC/STAT3/BCL-2 Axis to Provoke Human Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cell Apoptosis In Vitro
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Cell Culture
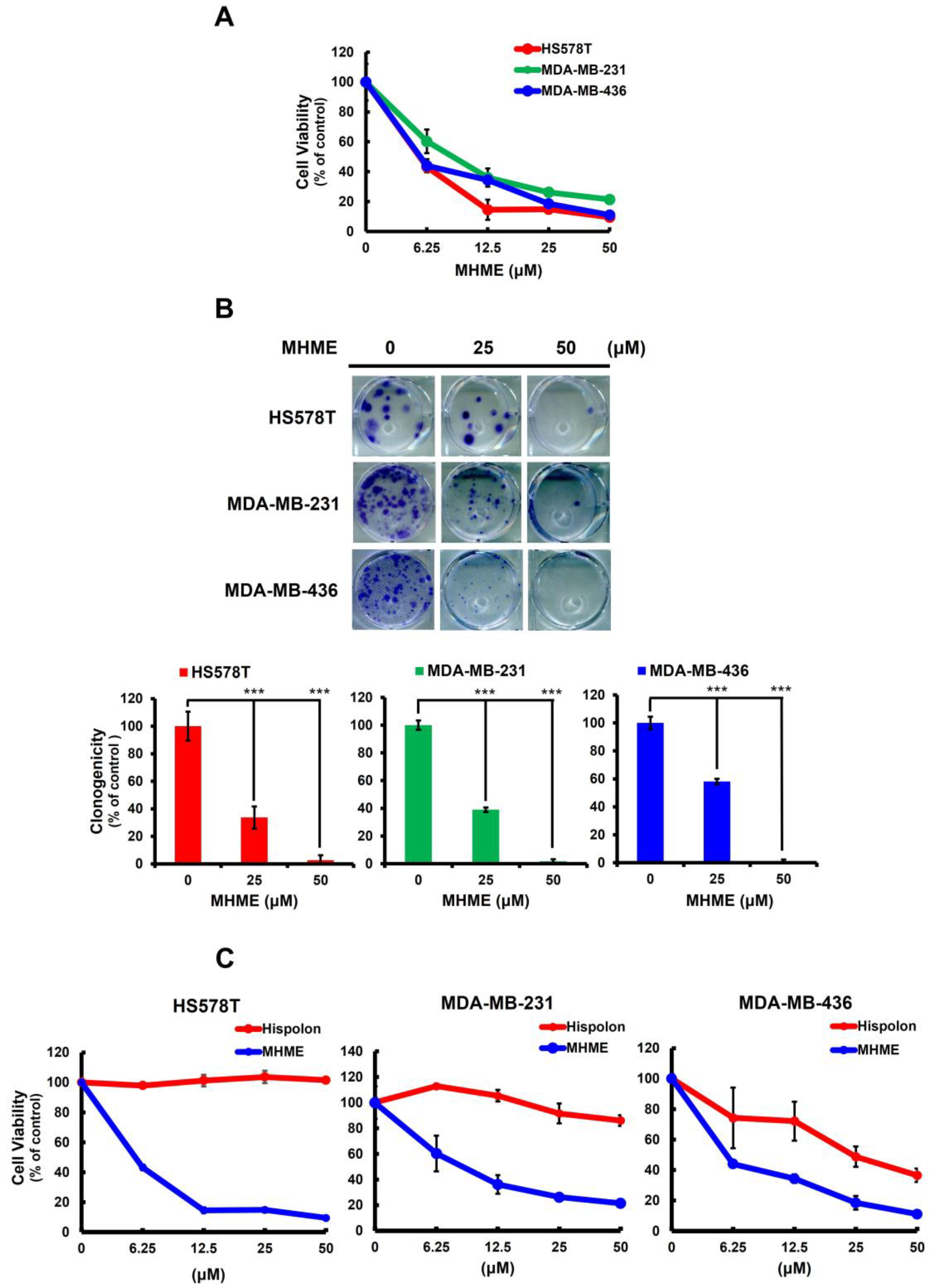
2.3. Cell Viability Assay
2.4. Clonogenicity Assay
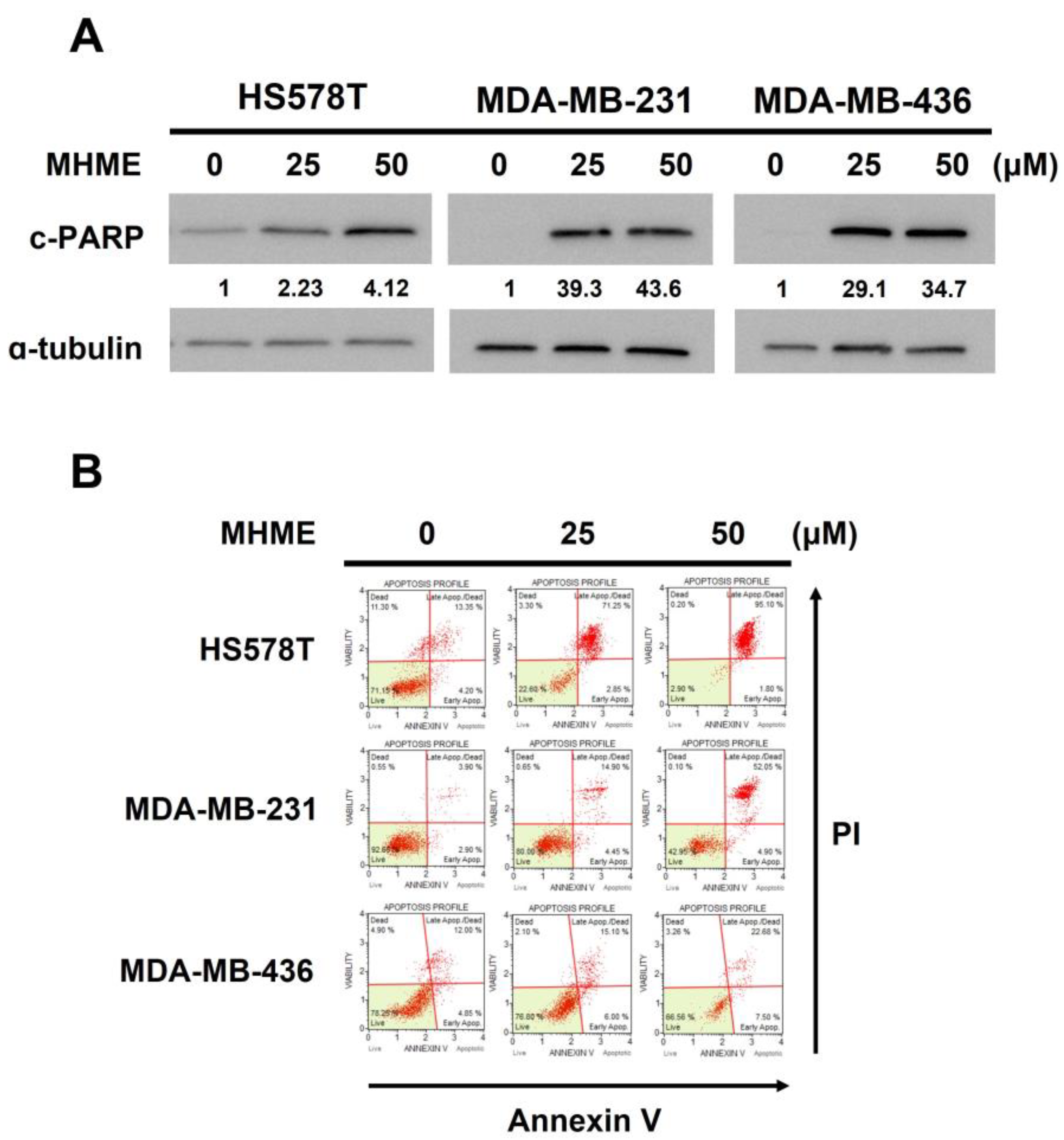
2.5. Apoptosis Assay
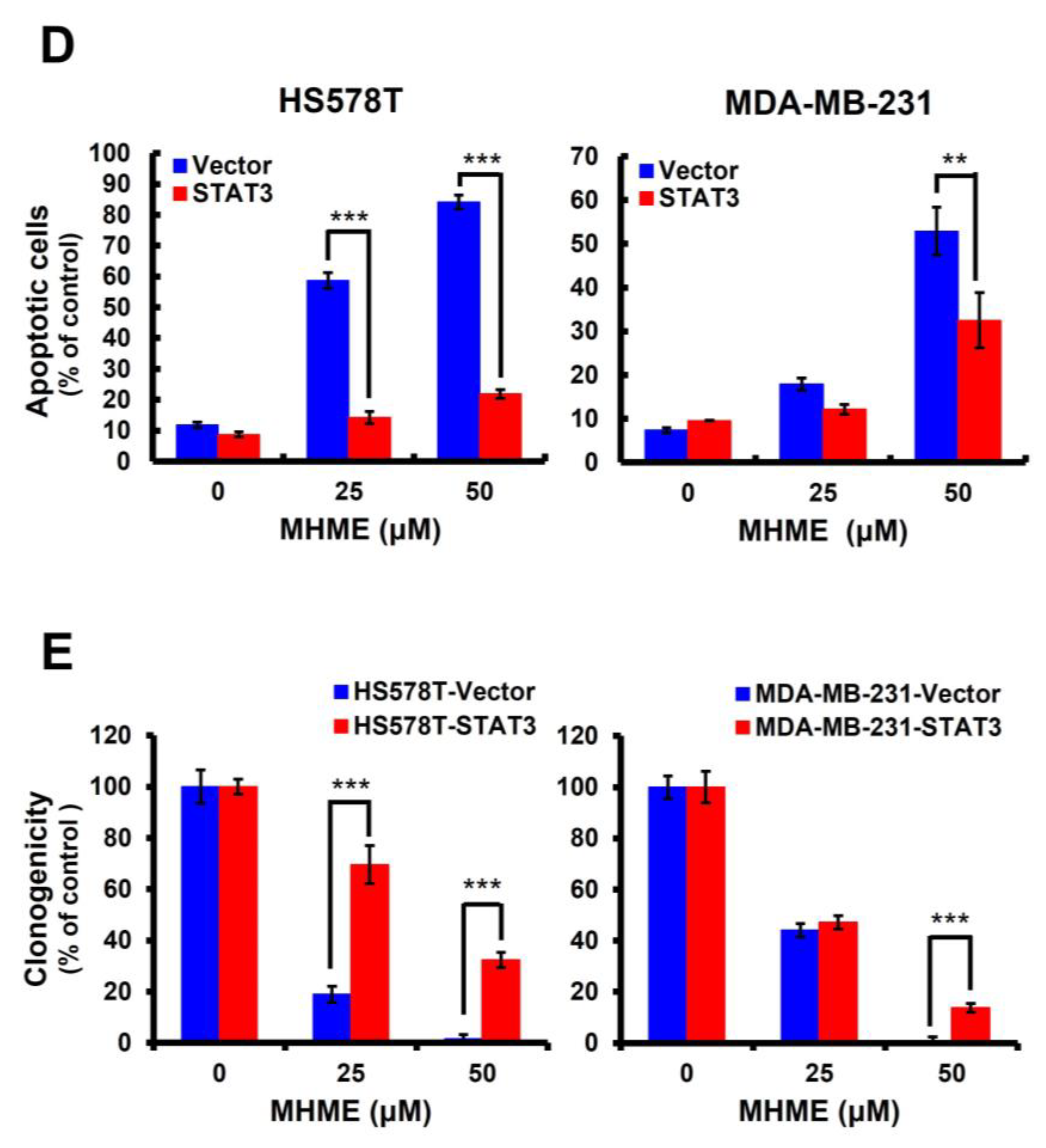
2.6. Establishment of Stable Clones
2.7. Immunoblottinghme
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. MHME Is More Potent Than Hispolon to Exert In Vitro Cytotoxicity in TNBC Cells
3.2. MHME-Elicited TNBC Cytotoxicity Involves the Induction of Apoptosis
3.3. Blockade of STAT3 Activation Is Pivotal for MHME to Elicit TNBC Cytotoxicity
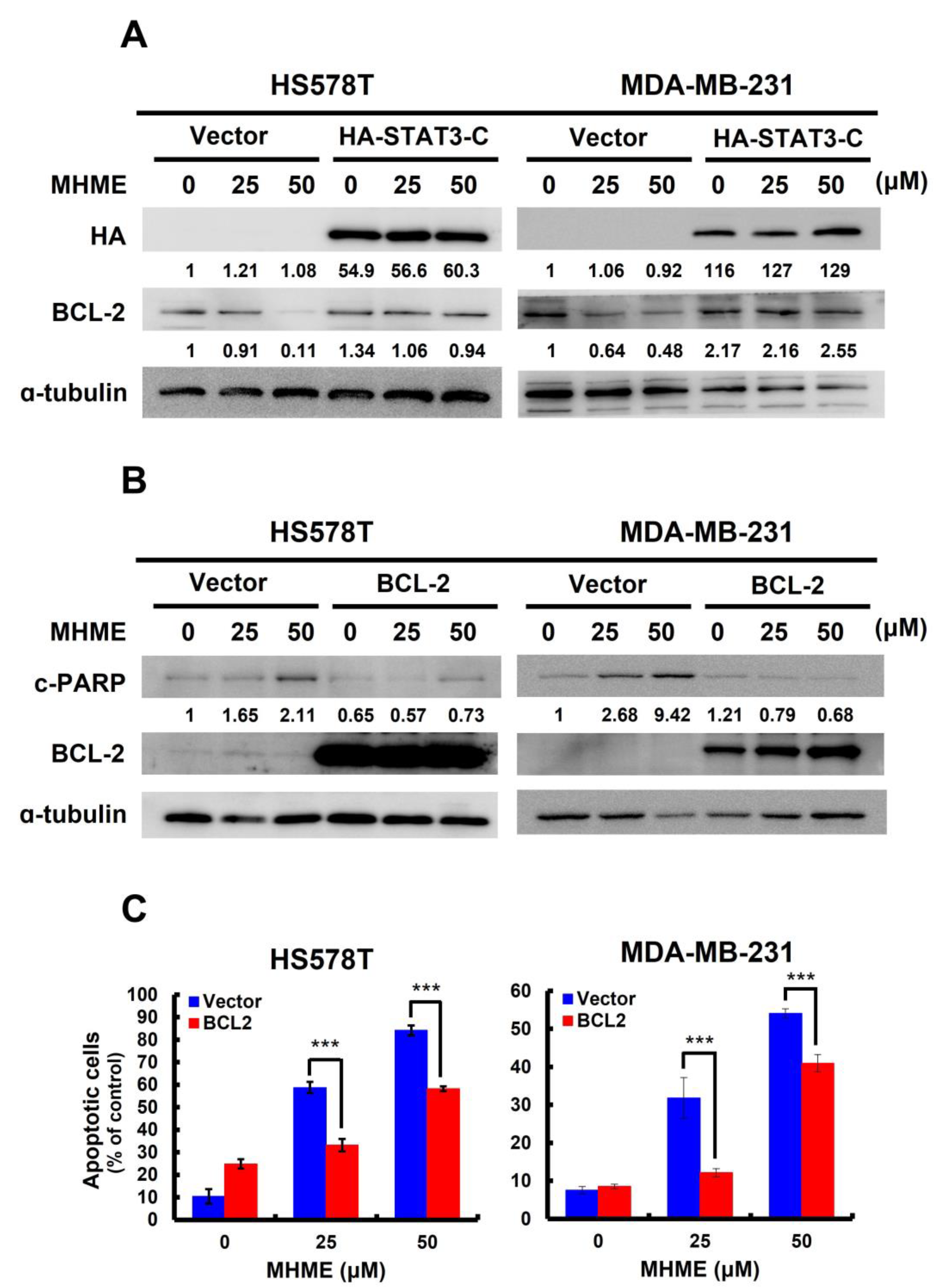
3.4. MHME Blocks STAT3 to Downregulate BCL-2 for Inducing Apoptosis in TNBC Cells
3.5. MHME Inhibits SRC to Repress STAT3 Activation in TNBC Cells
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fahad Ullah, M. Breast cancer: Current perspectives on the disease status. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1152, 51–64. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, J.Y.; Chang, C.J.; Cheng, J.S. Survival, treatment regimens and medical costs of women newly diagnosed with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.H.; Kuo, W.H.; Tsai, M.H.; Chen, P.C.; Hsiao, C.K.; Chuang, E.Y.; Chang, L.Y.; Hsieh, F.J.; Lai, L.C.; Chang, K.J. Identification of prognostic genes for recurrent risk prediction in triple negative breast cancer patients in Taiwan. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Chien, S.Y.; Kuo, S.J.; Chen, L.S.; Chen, S.T.; Lai, H.W.; Chang, T.W.; Chen, D.R. A 10-year follow-up of triple-negative breast cancer patients in Taiwan. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 42, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chang, W.S.; Liu, L.C.; Hsiao, C.L.; Su, C.H.; Wang, H.C.; Ji, H.X.; Tsai, C.W.; Maa, M.C.; Bau, D.T. The contributions of the tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 genotypes to triple negative breast cancer risk. Biomedicine 2016, 6, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiangying, M.; Shikai, W.; Zefei, J.; Bing, S.; Yan, M.; Xin, Z.; Lijuan, D.; Yue, W.; Tao, W.; Shaohua, Z.; et al. Progestin as an alternative treatment option for multi-treated recurrent triple-negative breast cancer. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2013, 143, w13765. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, S. Triple negative breast cancer: A continuing challenge. Indian J. Med. Paediatr. Oncol. 2013, 34, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bardia, A.; Hurvitz, S.A.; Tolaney, S.M.; Loirat, D.; Punie, K.; Oliveira, M.; Brufsky, A.; Sardesai, S.D.; Kalinsky, K.; Zelnak, A.B.; et al. Sacituzumab govitecan in metastatic triple-negative breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1529–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robson, M.E.; Tung, N.; Conte, P.; Im, S.A.; Senkus, E.; Xu, B.; Masuda, N.; Delaloge, S.; Li, W.; Armstrong, A.; et al. OlympiAD final overall survival and tolerability results: Olaparib versus chemotherapy treatment of physician’s choice in patients with a germline BRCA mutation and HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geyer, C.E., Jr.; Garber, J.E.; Gelber, R.D.; Yothers, G.; Taboada, M.; Ross, L.; Rastogi, P.; Cui, K.; Arahmani, A.; Aktan, G.; et al. Overall survival in the OlympiA phase III trial of adjuvant olaparib in patients with germline pathogenic variants in BRCA1/2 and high-risk, early breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, 1250–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehmsen, S.; Ditzel, H.J. Signaling pathways essential for triple-negative breast cancer stem-like cells. Stem Cells 2021, 39, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merikhian, P.; Eisavand, M.R.; Farahmand, L. Triple-negative breast cancer: Understanding Wnt signaling in drug resistance. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, L.; Zhu, J.; Cao, Y.; Gao, X. The signaling pathways and targets of traditional Chinese medicine and natural medicine in triple-negative breast cancer. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 264, 113249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almansour, N.M. Triple-negative breast cancer: A brief review about epidemiology, risk factors, signaling pathways, treatment and role of artificial intelligence. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 836417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Lee, H.; Herrmann, A.; Buettner, R.; Jove, R. Revisiting STAT3 signaling in cancer: New and unexpected biological functions. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 736–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, J.; Chand, A.; Gough, D.; Ernst, M. Therapeutically exploiting STAT3 activity in cancer—Using tissue repair as a road map. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2019, 19, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, L.; Guan, X.; Qin, J.J. Inhibiting STAT3 signaling pathway by natural products for cancer prevention and therapy: In vitro and in vivo activity and mechanisms of action. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 182, 106357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.J.; Yan, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, W.D. STAT3 as a potential therapeutic target in triple negative breast cancer: A systematic review. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarfraz, A.; Rasul, A.; Sarfraz, I.; Shah, M.A.; Hussain, G.; Shafiq, N.; Masood, M.; Adem, Ş.; Sarker, S.D.; Li, X. Hispolon: A natural polyphenol and emerging cancer killer by multiple cellular signaling pathways. Environ. Res. 2020, 190, 110017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.T.; Ali, E.S.; Khan, I.N.; Shaw, S.; Uddin, S.J.; Rouf, R.; Dev, S.; Saravi, S.S.S.; Das, N.; Tripathi, S.; et al. Anticancer perspectives on the fungal-derived polyphenolic hispolon. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2020, 20, 1636–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindran, J.; Subbaraju, G.V.; Ramani, M.V.; Sung, B.; Aggarwal, B.B. Bisdemethylcurcumin and structurally related hispolon analogues of curcumin exhibit enhanced prooxidant, anti-proliferative and anti-inflammatory activities in vitro. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 79, 1658–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaji, N.V.; Ramani, M.V.; Viana, A.G.; Sanglard, L.P.; White, J.; Mulabagal, V.; Lee, C.; Gana, T.J.; Egiebor, N.O.; Subbaraju, G.V.; et al. Design, synthesis and in vitro cell-based evaluation of the anti-cancer activities of hispolon analogs. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 2148–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Paul, M.; Kumar Panda, M.; Thatoi, H. Developing hispolon-based novel anticancer therapeutics against human (NF-κβ) using in silico approach of modelling, docking and protein dynamics. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2019, 37, 3947–3967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, M.; Caruso, F.; Costanzini, I.; Kloer, C.; Sulovari, A.; Monti, E.; Gariboldi, M.; Marras, E.; Balaji, N.V.; Ramani, M.V.; et al. X-ray crystal structures, density functional theory and docking on deacetylase enzyme for antiproliferative activity of hispolon derivatives on HCT116 colon cancer. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 3805–3812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, M.Y.; Yang, W.T.; Ho, Y.J.; Chang, G.M.; Chang, H.H.; Hsu, C.Y.; Chang, C.C.; Chen, Y.H. Hispolon methyl ether, a Hispolon analog, suppresses the SRC/STAT3/Survivin signaling axis to induce cytotoxicity in human urinary bladder transitional carcinoma cell lines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.C.; Hsieh, Y.C.; Li, L.H.; Chang, C.C.; Janoušková, K.; Ramani, M.V.; Subbaraju, G.V.; Cheng, K.T.; Chang, C.C. Dehydroxyhispolon methyl ether, a Hispolon derivative, inhibits WNT/β-catenin signaling to elicit human colorectal carcinoma cell apoptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, Y.C.; Dai, Y.C.; Cheng, K.T.; Yang, W.T.; Ramani, M.V.; Subbaraju, G.V.; Chen, Y.J.; Chang, C.C. Blockade of the SRC/STAT3/BCL-2 signaling axis sustains the cytotoxicity in human colorectal cancer cell lines induced by Dehydroxyhispolon methyl ether. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.P.; Li, S.; Chuang, W.L.; Li, C.H.; Chen, G.J.; Chang, C.C.; Or, C.R.; Lin, P.Y.; Chang, C.C. Blockade of STAT3 Signaling contributes to anticancer effect of 5-Acetyloxy-6,7,8,4′-tetra-methoxyflavone, a Tangeretin derivative, on human glioblastoma multiforme cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromberg, J.F.; Wrzeszczynska, M.H.; Devgan, G.; Zhao, Y.; Pestell, R.G.; Albanese, C.; Darnell, J.E., Jr. Stat3 as an oncogene. Cell 1999, 98, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fincham, V.; Frame, M.; Haefner, B.; Unlu, M.; Wyke, A.; Wyke, J. Functions of the v-Src protein tyrosine kinase. Cell Biol. Int. 1994, 18, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, S.H.; Desnoyers, S.; Ottaviano, Y.; Davidson, N.E.; Poirier, G.G. Specific proteolytic cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase: An early marker of chemotherapy-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res. 1993, 53, 3976–3985. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Ray, R.M.; Johnson, L.R. STAT3-mediated transcription of Bcl-2, Mcl-1 and c-IAP2 prevents apoptosis in polyamine-depleted cells. Biochem. J. 2005, 392, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pangjantuk, A.; Chueaphromsri, P.; Kunhorm, P.; Phonchai, R.; Chumkiew, S.; Chaicharoenau-domrung, N.; Noisa, P. Hispolon, a bioactive compound from Phellinus linteus, induces apoptosis of human breast cancer cells through the modulation of oxidative stress and autophagy. J. Biol. Activ. Prod. Nat. 2023, 13, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsin, M.C.; Hsieh, Y.H.; Wang, P.H.; Ko, J.L.; Hsin, I.L.; Yang, S.F. Hispolon suppresses metastasis via autophagic degradation of cathepsin S in cervical cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masood, M.; Rasul, A.; Sarfraz, I.; Jabeen, F.; Liu, S.; Liu, X.; Wei, W.; Li, J.; Li, X. Hispolon induces apoptosis against prostate DU145 cancer cells via modulation of mitochondrial and STAT3 pathways. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 32 (Suppl. S5), 2237–2243. [Google Scholar]
- Chun, J.; Li, R.J.; Cheng, M.S.; Kim, Y.S. Alantolactone selectively suppresses STAT3 activation and exhibits potent anticancer activity in MDA-MB-231 cells. Cancer Lett. 2015, 357, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Cao, W.; Shen, W.; Zhang, L.; Gu, X.; Guo, Y.; Tsai, H.I.; Liu, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; et al. Arctigenin inhibits STAT3 and exhibits anticancer potential in human triple-negative breast cancer therapy. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Zou, H.; Guo, Y.; Tong, T.; Ye, L.; Zhu, C.; Deng, L.; Wang, B.; Pan, Y.; Li, P. SRC kinase-mediated signaling pathways and targeted therapies in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2022, 24, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, L.; Yu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhao, Y. c-Src inhibitor selectively inhibits triple-negative breast cancer overexpressed Vimentin in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 1648–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohale, I.N.; Yu, J.; Zhuang, Y.; Fan, X.; Reddy, R.J.; Sinnwell, J.; Kalari, K.R.; Boughey, J.C.; Carter, J.M.; Goetz, M.P.; et al. Identification of Src family kinases as potential therapeutic targets for chemotherapy-resistant triple negative breast cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 4220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liao, C.-P.; Hsieh, Y.-C.; Lu, C.-H.; Dai, W.-C.; Yang, W.-T.; Cheng, K.-T.; Ramani, M.V.; Subbaraju, G.V.; Chang, C.-C. Methoxyhispolon Methyl Ether, a Hispolon Analog, Thwarts the SRC/STAT3/BCL-2 Axis to Provoke Human Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cell Apoptosis In Vitro. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2742. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11102742
Liao C-P, Hsieh Y-C, Lu C-H, Dai W-C, Yang W-T, Cheng K-T, Ramani MV, Subbaraju GV, Chang C-C. Methoxyhispolon Methyl Ether, a Hispolon Analog, Thwarts the SRC/STAT3/BCL-2 Axis to Provoke Human Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cell Apoptosis In Vitro. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(10):2742. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11102742
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiao, Chih-Pin, Ya-Chu Hsieh, Chien-Hsing Lu, Wen-Chi Dai, Wei-Ting Yang, Kur-Ta Cheng, Modukuri V. Ramani, Gottumukkala V. Subbaraju, and Chia-Che Chang. 2023. "Methoxyhispolon Methyl Ether, a Hispolon Analog, Thwarts the SRC/STAT3/BCL-2 Axis to Provoke Human Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cell Apoptosis In Vitro" Biomedicines 11, no. 10: 2742. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11102742
APA StyleLiao, C.-P., Hsieh, Y.-C., Lu, C.-H., Dai, W.-C., Yang, W.-T., Cheng, K.-T., Ramani, M. V., Subbaraju, G. V., & Chang, C.-C. (2023). Methoxyhispolon Methyl Ether, a Hispolon Analog, Thwarts the SRC/STAT3/BCL-2 Axis to Provoke Human Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cell Apoptosis In Vitro. Biomedicines, 11(10), 2742. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11102742






