Expression of Claudin-9 (CLDN9) in Breast Cancer, the Clinical Significance in Connection with Its Subcoat Anchorage Proteins ZO-1 and ZO-3 and Impact on Drug Resistance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines
2.2. Mammary Tissue Cohort
2.3. Key Research Materials
2.4. Creation of CLDN9 Knockdown Cell Models
2.5. Analysis of Gene Transcript by PCR and QPCR
2.6. Western Blotting
2.7. Cellular Response to Chemotherapy Drugs
2.8. Immunohistochemical Staining of CLDN9 Protein
2.9. Immunofluorescence (IFC)
2.10. Patients’ Response to Chemotherapies and Evaluation
2.11. Statistical Methods
3. Results
3.1. Transcript Levels of CLDN9 in Breast Cancer Tissues
3.2. CLDN9 Protein Expression in Mammary Tissues
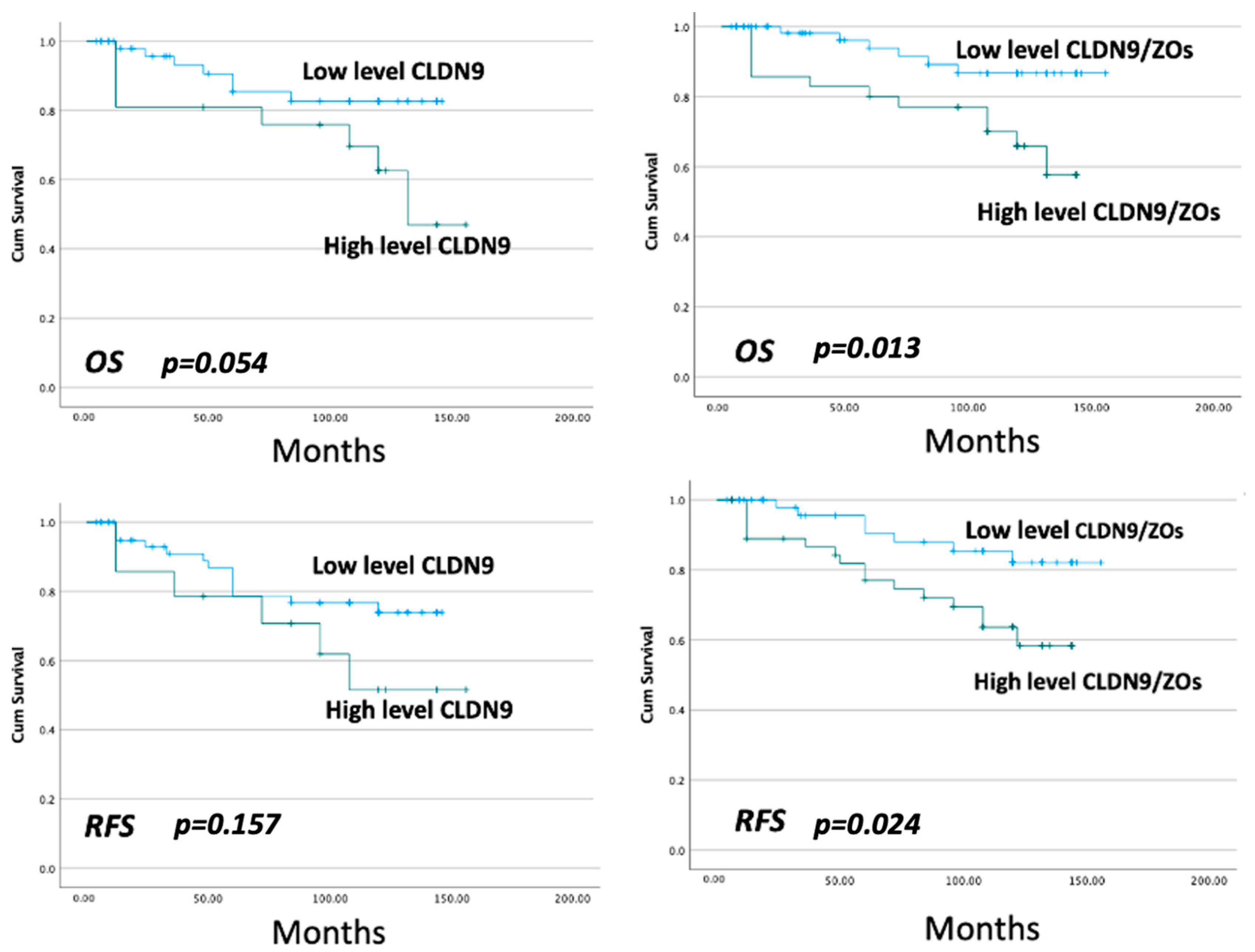
3.3. CLDN9 and Patient Clinical Outcome
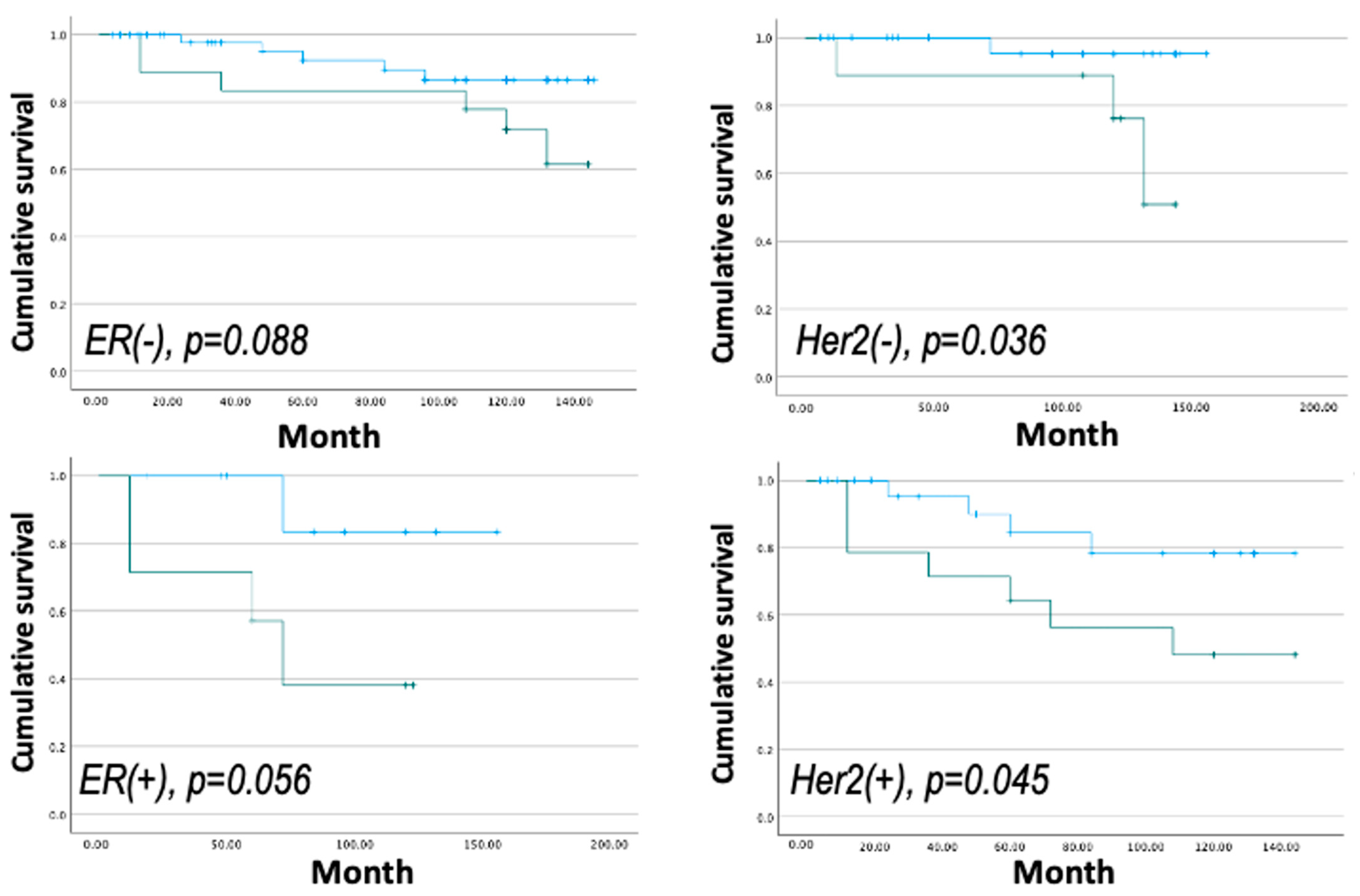
3.4. CLDN9 and Hormone Status Outcome
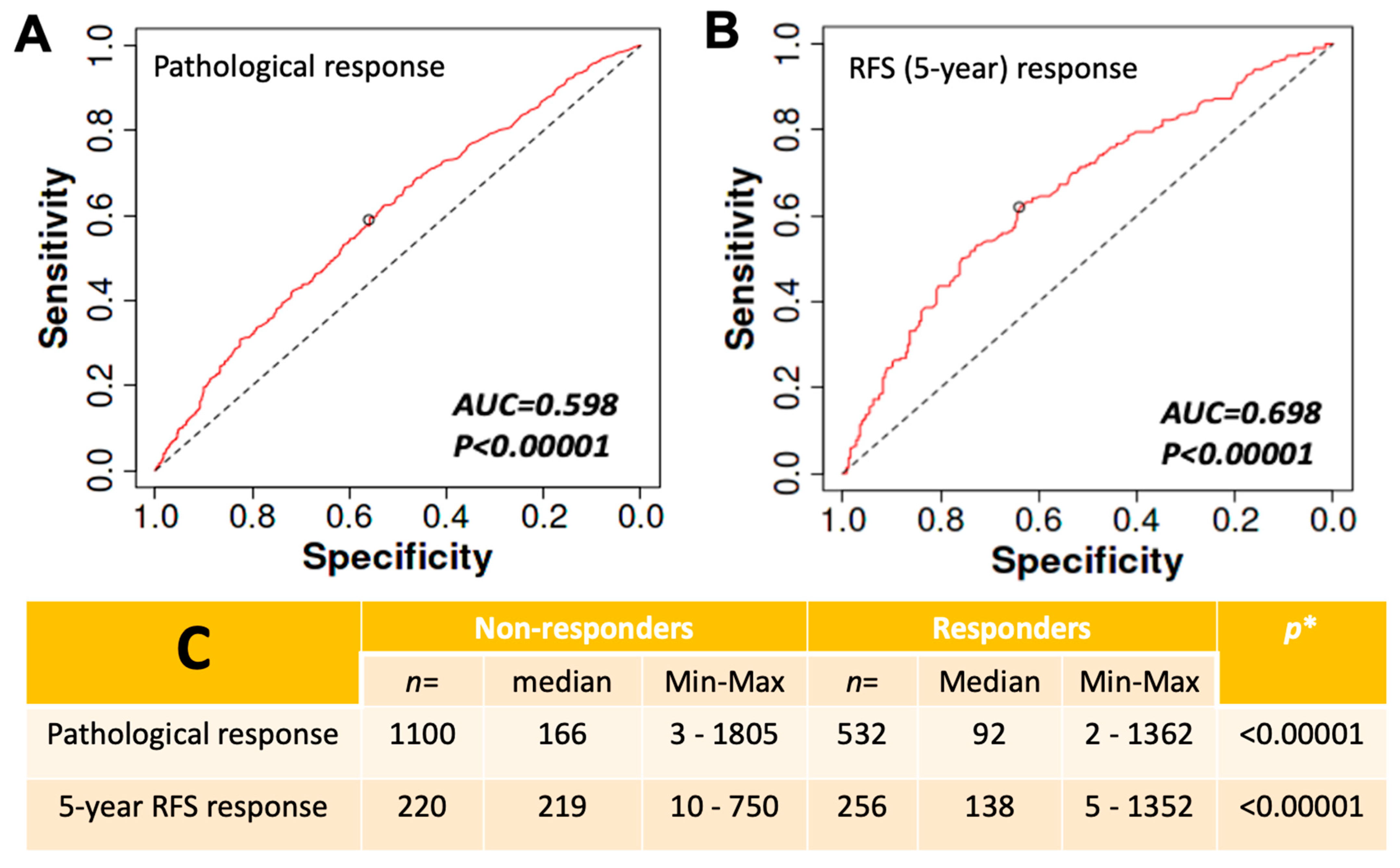
3.5. CLDN9 and Patient Response to Drug Treatment
3.5.1. High Expression of CLDN9 and Patient Resistance to Chemotherapies
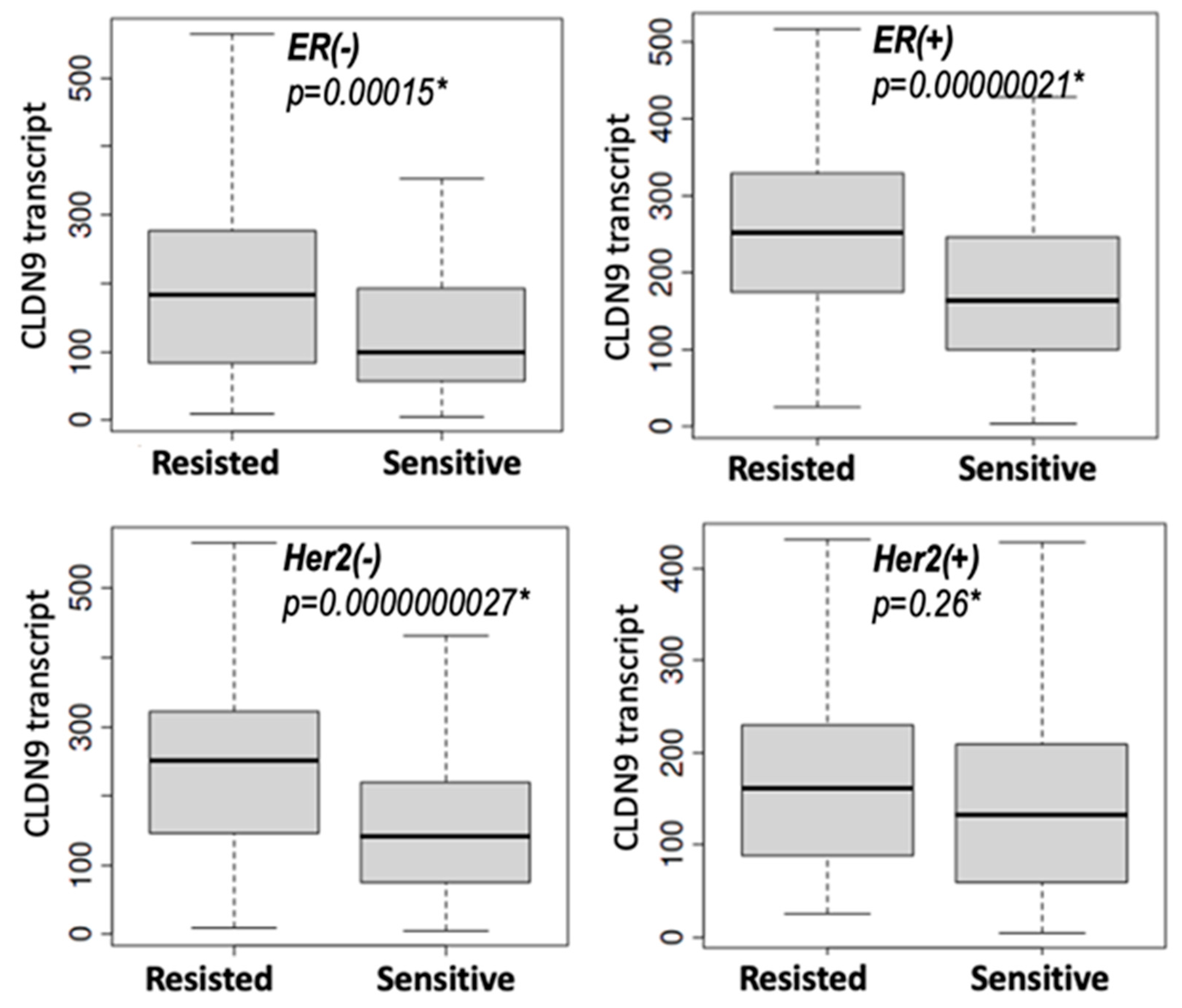
3.5.2. Expression of CLDN9 and Patient Resistance to Chemotherapies in Relation to Hormone Receptor Status and Molecular Subtypes
3.5.3. CLDN9 Is Not Connected to Endocrine or Anti-Her-2 Therapies
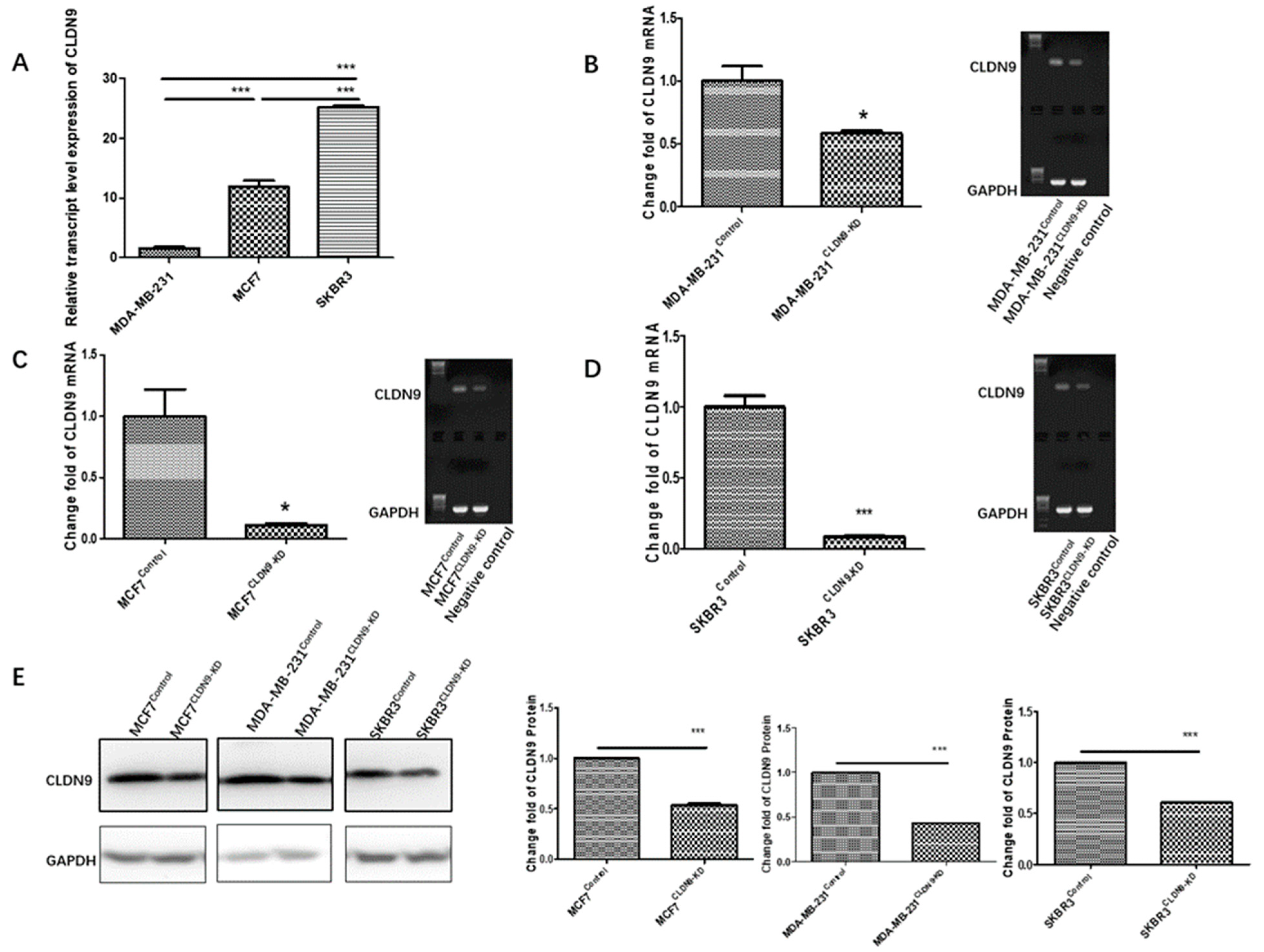
3.6. Creation of CLDN9 Knockdown Breast Cancer Cell Model
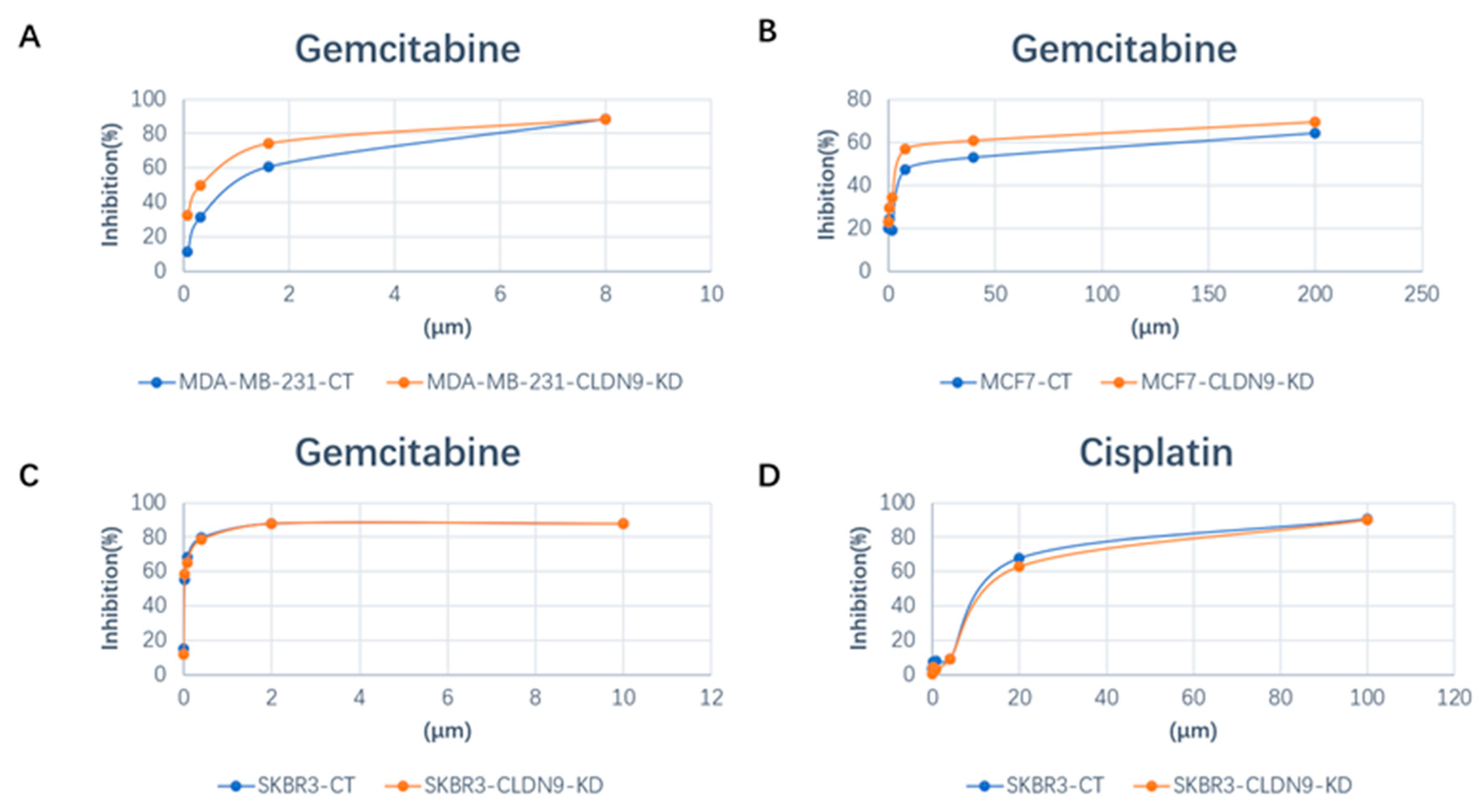
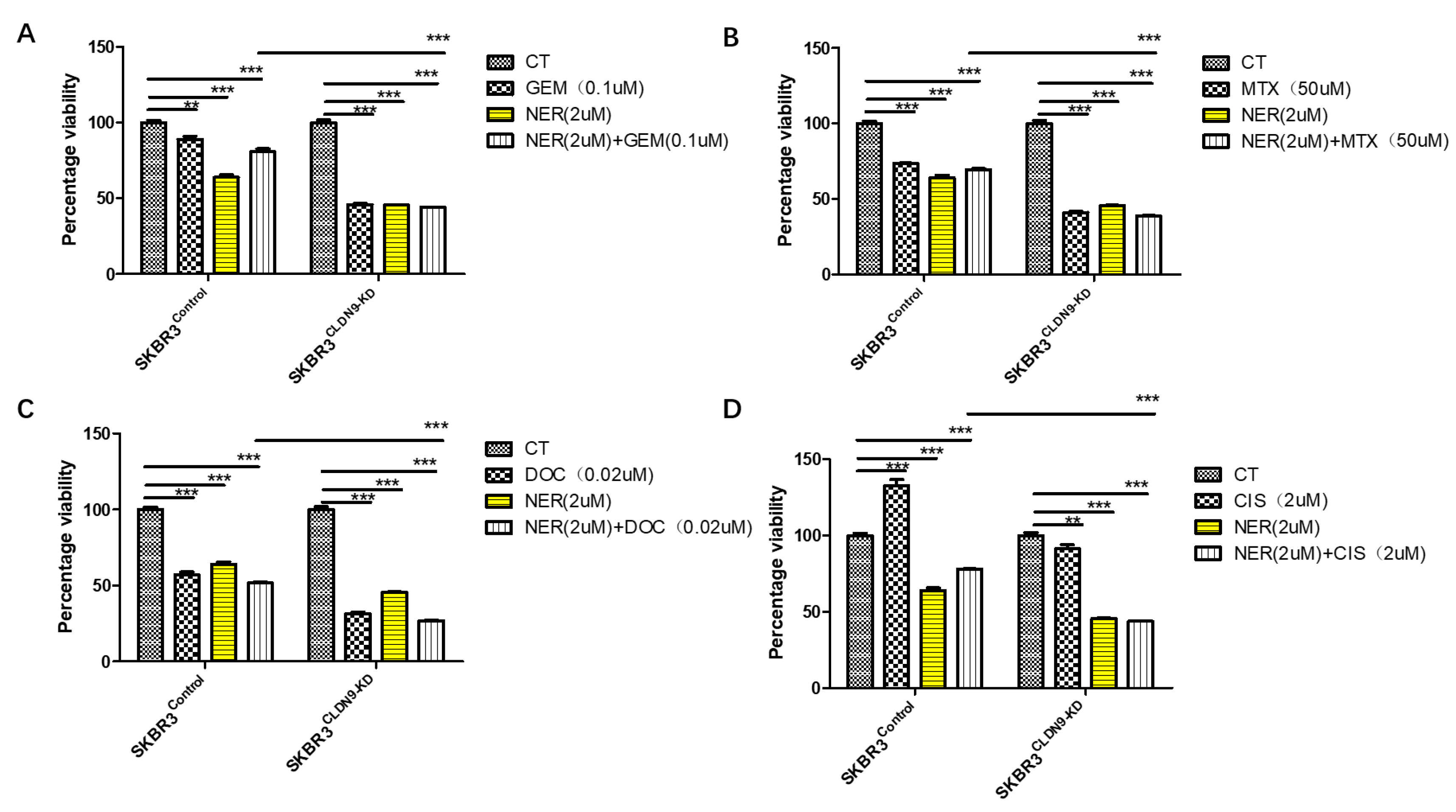
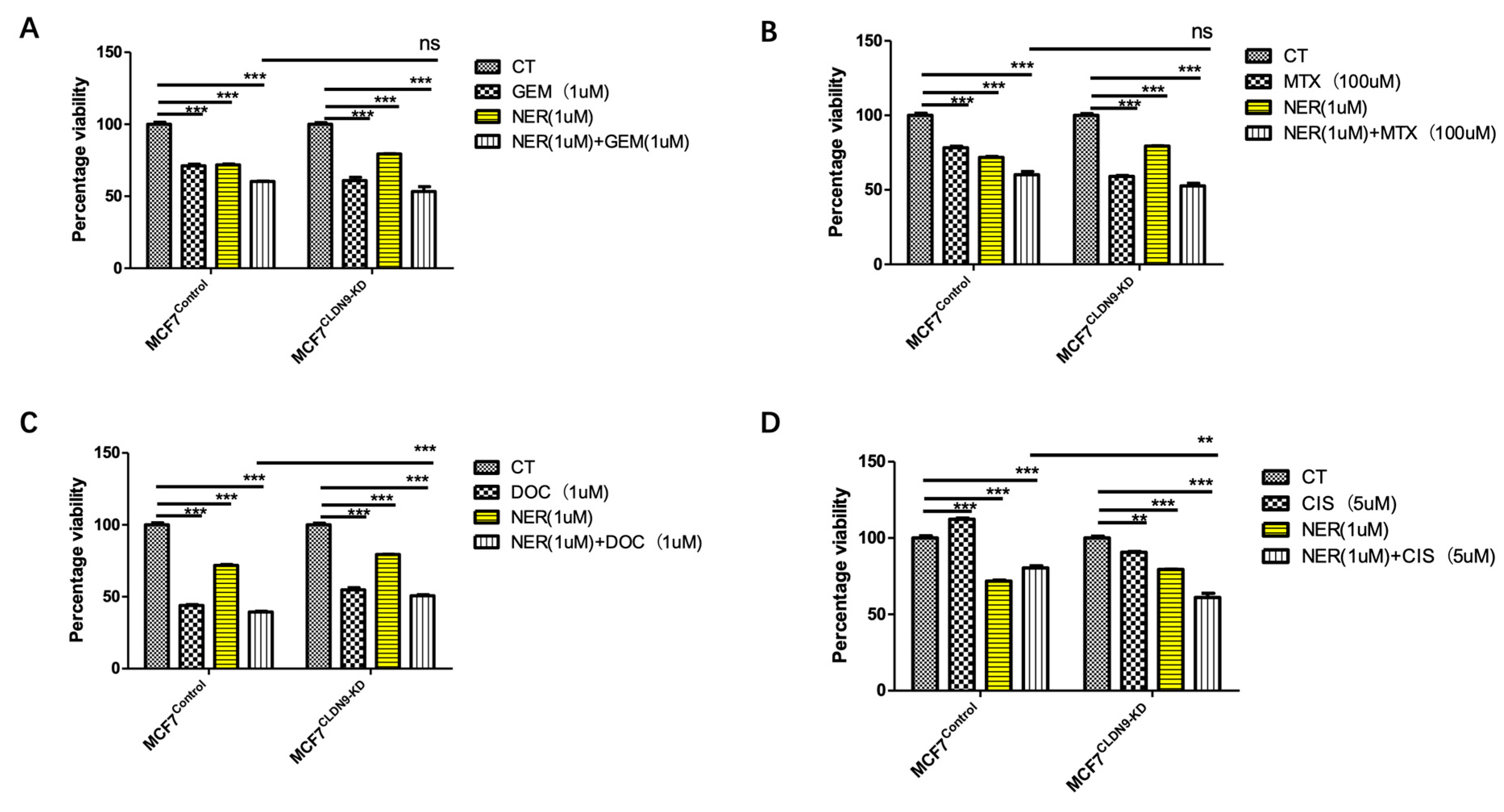
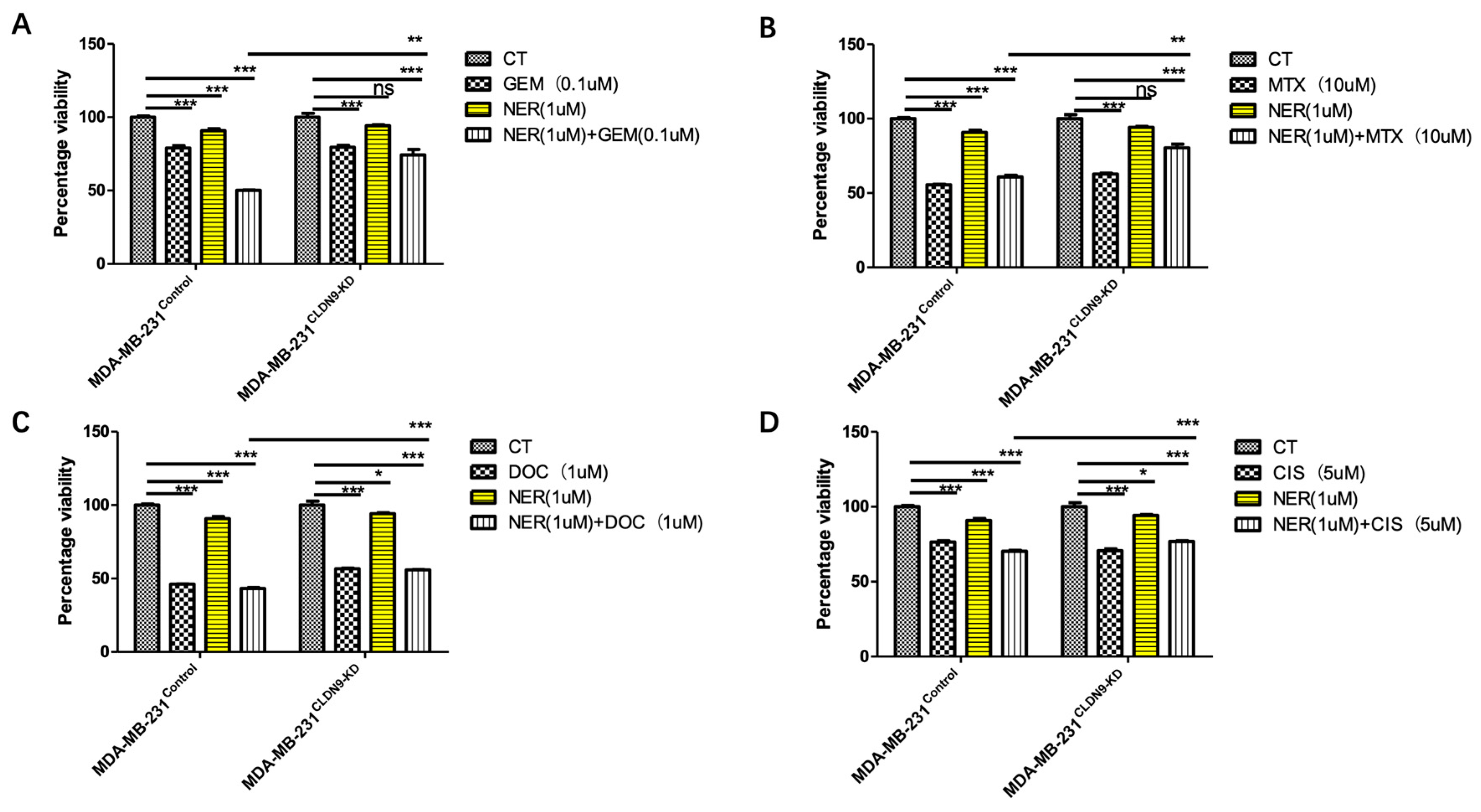
3.7. CLDN9 Expression and Cell’s Response to Chemodrugs
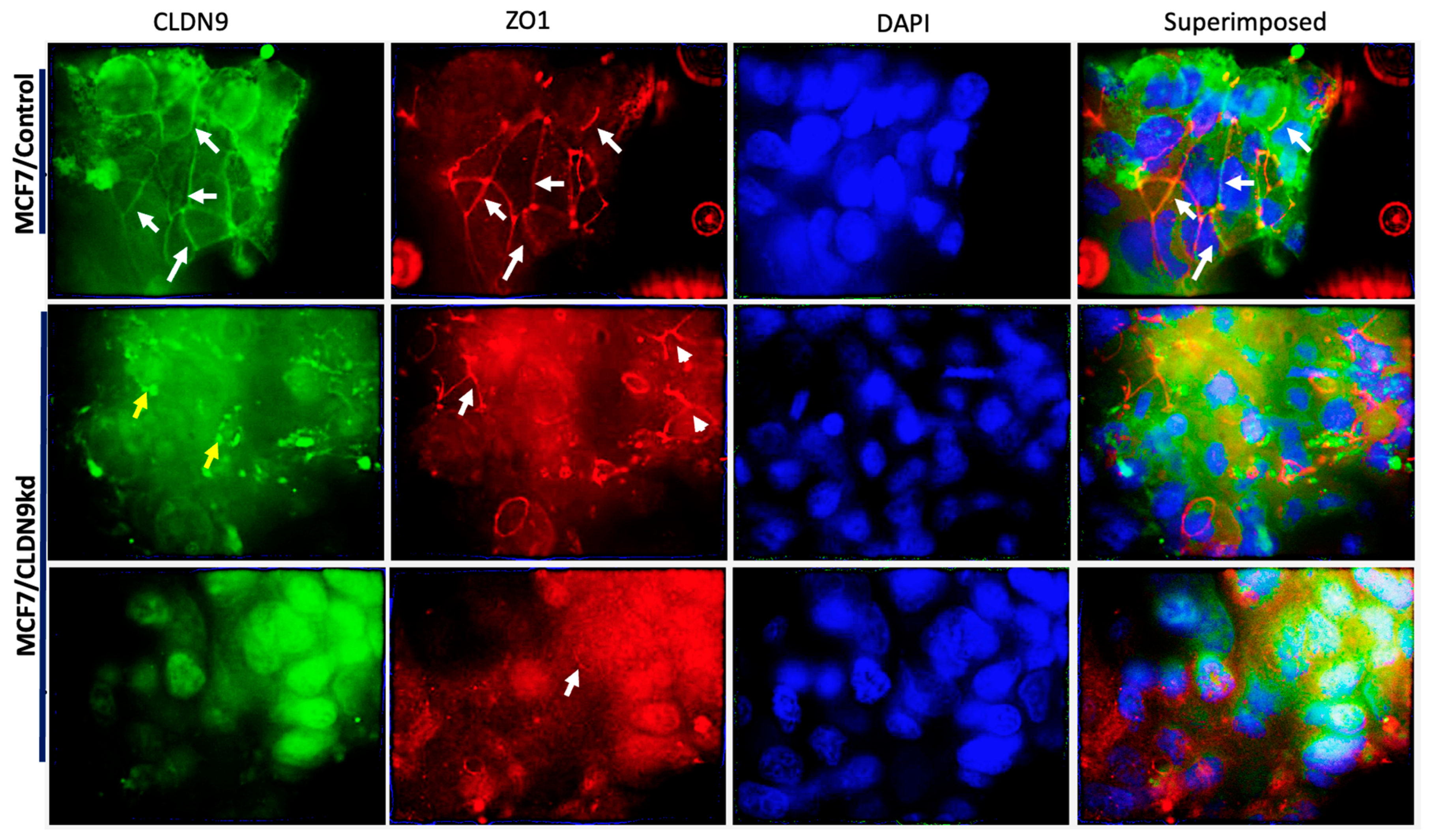
3.8. The Relationship between CLDN9 and ZO-1 and ZO-3, Respectively
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blanchard, A.A.; Skliris, G.P.; Watson, P.H.; Murphy, L.C.; Penner, C.; Tomes, L.; Young, T.L.; Leygue, E.; Myal, Y. Claudins 1, 3, and 4 protein expression in ER negative breast cancer correlates with markers of the basal phenotype. Virchows Arch. 2009, 454, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kominsky, S.L.; Argani, P.; Korz, D.; Evron, E.; Raman, V.; Garrett, E.; Rein, A.; Sauter, G.; Kallioniemi, O.P.; Sukumar, S. Loss of the tight junction protein claudin-7 correlates with histological grade in both ductal carcinoma in situ and invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast. Oncogene 2003, 22, 2021–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.W.; Lee, S.J.; Seo, J.; Song, S.Y.; Ahn, G.; Park, C.S.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, B.G.; Bae, D.S. Increased expressions of claudin-1 and claudin-7 during the progression of cervical neoplasia. Gynecol. Oncol. 2005, 97, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morohashi, S.; Kusumi, T.; Sato, F.; Odagiri, H.; Chiba, H.; Yoshihara, S.; Hakamada, K.; Sasaki, M.; Kijima, H. Decreased expression of claudin-1 correlates with recurrence status in breast cancer. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2007, 20, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.H.; Huh, J.H.; Lee, S.; Kang, H.; Kim, G.I.; An, H.J. Down-regulation of claudin-2 in breast carcinomas is associated with advanced disease. Histopathology 2008, 53, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, T.A.; Harrison, G.M.; Watkins, G.; Jiang, W.G. Claudin-16 reduces the aggressive behavior of human breast cancer cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2008, 105, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, T.A.; Lane, J.; Ozupek, H.; Jiang, W.G. Claudin-20 promotes an aggressive phenotype in human breast cancer cells. Tissue Barriers 2013, 1, e26518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimbung, S.; Kovacs, A.; Bendahl, P.O.; Malmstrom, P.; Ferno, M.; Hatschek, T.; Hedenfalk, I. Claudin-2 is an independent negative prognostic factor in breast cancer and specifically predicts early liver recurrences. Mol. Oncol. 2014, 8, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elazeem, M.A.; Abd-Elazeem, M.A. Claudin 4 expression in triple-negative breast cancer: Correlation with androgen receptors and Ki-67 expression. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2015, 19, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabaries, S.; Dong, Z.; Annis, M.G.; Omeroglu, A.; Pepin, F.; Ouellet, V.; Russo, C.; Hassanain, M.; Metrakos, P.; Diaz, Z.; et al. Claudin-2 is selectively enriched in and promotes the formation of breast cancer liver metastases through engagement of integrin complexes. Oncogene 2011, 30, 1318–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Miao, H.; Jing, B.; Pan, Q.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, D.; Liang, Z.; Wen, Z.; Li, M. Claudin-4 controls the proliferation, apoptosis, migration and in vivo growth of MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 34, 681–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugimoto, H.; Nagahara, M.; Bae, Y.; Nakagawa, T.; Ishikawa, T.; Sato, T.; Uetake, H.; Eishi, Y.; Sugihara, K. Clinicopathologic relevance of claudin 5 expression in breast cancer. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2015, 143, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaaskelainen, A.; Soini, Y.; Jukkola-Vuorinen, A.; Auvinen, P.; Haapasaari, K.M.; Karihtala, P. High-level cytoplasmic claudin 3 expression is an independent predictor of poor survival in triple-negative breast cancer. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulka, J.; Szasz, A.M.; Nemeth, Z.; Madaras, L.; Schaff, Z.; Molnar, I.A.; Tokes, A.M. Expression of tight junction protein claudin-4 in basal-like breast carcinomas. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2009, 15, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanigan, F.; McKiernan, E.; Brennan, D.J.; Hegarty, S.; Millikan, R.C.; McBryan, J.; Jirstrom, K.; Landberg, G.; Martin, F.; Duffy, M.J.; et al. Increased claudin-4 expression is associated with poor prognosis and high tumour grade in breast cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 124, 2088–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauer, T.; Pedersen, M.K.; Ebeltoft, K.; Naess, O. Reduced expression of Claudin-7 in fine needle aspirates from breast carcinomas correlate with grading and metastatic disease. Cytopathology 2005, 16, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szasz, A.M.; Tokes, A.M.; Micsinai, M.; Krenacs, T.; Jakab, C.; Lukacs, L.; Nemeth, Z.; Baranyai, Z.; Dede, K.; Madaras, L.; et al. Prognostic significance of claudin expression changes in breast cancer with regional lymph node metastasis. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2011, 28, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, H.; Sumi, T.; Zhi, X.; Yasui, T.; Honda, K.I.; Ishiko, O. Claudin-4: A Potential Therapeutic Target in Chemotherapy-resistant Ovarian Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2011, 31, 1271–1277. [Google Scholar]
- Hicks, D.A.; Galimanis, C.E.; Webb, P.G.; Spillman, M.A.; Behbakht, K.; Neville, M.C.; Baumgartner, H.K. Claudin-4 activity in ovarian tumor cell apoptosis resistance and migration. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Takasawa, A.; Takasawa, K.; Murakami, T.; Akimoto, T.; Kyuno, D.; Kawata, Y.; Shano, K.; Kirisawa, K.; Ota, M.; et al. Aberrant expression of claudin-6 contributes to malignant potentials and drug resistance of cervical adenocarcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2022, 113, 1519–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.L.; Li, Y.R.; Shen, X.F.; Ruan, Y.; Lu, Y.; Jin, X.S.; Song, P.Y.; Guo, Y.T.; Zhang, X.L.; Qu, H.N.; et al. CLDN6 promotes chemoresistance through GSTP1 in human breast cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 36, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paquet-Fifield, S.; Koh, S.L.; Cheng, L.; Beyit, L.M.; Shembrey, C.; Molck, C.; Behrenbruch, C.; Papin, M.; Gironella, M.; Guelfi, S.; et al. Tight Junction Protein Claudin-2 Promotes Self-Renewal of Human Colorectal Cancer Stem-like Cells. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 2925–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gowrikumar, S.; Primeaux, M.; Pravoverov, K.; Wu, C.; Szeglin, B.C.; Sauve, C.E.G.; Thapa, I.; Bastola, D.; Chen, X.S.; Smith, J.J.; et al. A Claudin-Based Molecular Signature Identifies High-Risk, Chemoresistant Colorectal Cancer Patients. Cells 2021, 10, 2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eguchi, H.; Matsunaga, H.; Onuma, S.; Yoshino, Y.; Matsunaga, T.; Ikari, A. Down-Regulation of Claudin-2 Expression by Cyanidin-3-Glucoside Enhances Sensitivity to Anticancer Drugs in the Spheroid of Human Lung Adenocarcinoma A549 Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eguchi, H.; Matsunaga, T.; Endo, S.; Ichihara, K.; Ikari, A. Kaempferide Enhances Chemosensitivity of Human Lung Adenocarcinoma A549 Cells Mediated by the Decrease in Phosphorylation of Akt and Claudin-2 Expression. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemesle, M.; Geoffroy, M.; Alpy, F.; Tomasetto, C.L.; Kuntz, S.; Grillier-Vuissoz, I. CLDN1 Sensitizes Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells to Chemotherapy. Cancers 2022, 14, 5026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherradi, S.; Garambois, V.; Marines, J.; Andrade, A.F.; Fauvre, A.; Morand, O.; Fargal, M.; Mancouri, F.; Ayrolles-Torro, A.; Vezzo-Vie, N.; et al. Improving the response to oxaliplatin by targeting chemotherapy-induced CLDN1 in resistant metastatic colorectal cancer cells. Cell Biosci 2023, 13, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briehl, M.M.; Miesfeld, R.L. Isolation and Characterization of Transcripts Induced by Androgen Withdrawal and Apoptotic Cell-Death in the Rat Ventral Prostate. Mol. Endocrinol. 1991, 5, 1381–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Peacock, R.E.; Keen, T.J.; Inglehearn, C.F. Analysis of a human gene homologous to rat ventral prostate.1 protein. Genomics 1997, 46, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, Y.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, H.M.; Sanneman, J.D.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Smith, R.J.H.; Marcus, D.C.; Wangemann, P.; Nessler, R.A.; Banfi, B. A Claudin-9-Based Ion Permeability Barrier Is Essential for Hearing. PLoS Genet. 2009, 5, e1000610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramzan, M.; Philippe, C.; Belyantseva, I.A.; Nakano, Y.; Fenollar-Ferrer, C.; Tona, R.; Yousaf, R.; Basheer, R.; Imtiaz, A.; Faridi, R.; et al. Variants of human CLDN9 cause mild to profound hearing loss. Hum. Mutat. 2021, 42, 1321–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, A.H.; Yuan, F.; Li, Y.Q.; Zhu, F.F.; Hou, P.P.; Li, J.Q.; Song, X.J.; Ding, M.X.; Deng, H.K. Claudin-6 and claudin-9 function as additional coreceptors for hepatitis C virus. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 12465–12471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meertens, L.; Bertaux, C.; Cukierman, L.; Cormier, E.; Lavillette, D.; Cosset, F.L.; Dragic, T. The tight junction proteins claudin-1,-6, and-9 are entry cofactors for hepatitis C virus. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 3555–3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vecchio, A.J.; Stroud, R.M. Claudin-9 structures reveal mechanism for toxin-induced gut barrier breakdown. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 17817–17824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rendon-Huerta, E.; Teresa, F.; Teresa, G.M.; Xochitl, G.S.; Georgina, A.F.; Veronica, Z.Z.; Montano, L.F. Distribution and expression pattern of claudins 6, 7, and 9 in diffuse- and intestinal-type gastric adenocarcinomas. J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2010, 41, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zavala-Zendejas, V.E.; Torres-Martinez, A.C.; Salas-Morales, B.; Fortoul, T.I.; Montano, L.F.; Rendon-Huerta, E.P. Claudin-6, 7, or 9 Overexpression in the Human Gastric Adenocarcinoma Cell Line AGS Increases Its Invasiveness, Migration, and Proliferation Rate. Cancer Investig. 2011, 29, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, L.C.; Wu, Y.G.; Feng, J.; Yu, S.Y.; Li, C.Z.; Wu, Y.T.; Li, Z.Y.; Cao, L.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Y.Z. Overexpression of the cell adhesion molecule claudin-9 is associated with invasion in pituitary oncocytomas. Hum. Pathol. 2014, 45, 2423–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashi, A.Y.; Higashi, T.; Furuse, K.; Ozeki, K.; Furuse, M.; Chiba, H. Claudin-9 constitutes tight junctions of folliculo-stellate cells in the anterior pituitary gland. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.Y.; Wang, R.G.; Cao, H.Y.; Zhang, H.P.; Xu, S.Y.; Wang, A.Y.; Liu, B.; Wang, Y.T.; Wang, R.C. Expression of claudin-5,-7,-8 and-9 in cervical carcinoma tissues and adjacent non-neoplastic tissues. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 9479–9486. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.H.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Wang, Y.S.; Ma, X.X. Identification of novel cell glycolysis related gene signature predicting survival in patients with endometrial cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, Y.; Sugimoto, K.; Kobayashi, M.; Kobayashi, Y.; Kojima, M.; Furukawa, S.; Soeda, S.; Watanabe, T.; Higashi, A.Y.; Higashi, T.; et al. Claudin-9 is a novel prognostic biomarker for endometrial cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2022, 61, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, R.K.; Chheda, Z.S.; Das Purkayastha, B.P.; Gomez-Gutierrez, J.G.; Jala, V.R.; Haribabu, B. A spontaneous metastasis model reveals the significance of claudin-9 overexpression in lung cancer metastasis. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2016, 33, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.Y.; Chai, X.; Li, S.J.; Wu, D.; Fan, Z.M. Identification of claudin-2,-6,-11 and-14 as prognostic markers in human breast carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2019, 12, 2195–2204. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Martin, T.A.; Lane, J.; Harrison, G.M.; Jiang, W.G. The Expression of the Nectin Complex in Human Breast Cancer and the Role of Nectin-3 in the Control of Tight Junctions during Metastasis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.G.; Watkins, G.; Douglas-Jones, A.; Holmgren, L.; Mansel, R.E. Angiomotin and angiomotin like proteins, their expression and correlation with angiogenesis and clinical outcome in human breast cancer. BMC Cancer 2006, 6, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Xin, L.; Liu, C.; Liu, Y.; Mansel, R.E.; Ruge, F.; Davies, E.; Jiang, W.G.; Martin, T.A. SIKs suppress tumor function and regulate drug resistance in breast cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2021, 11, 3537–3557. [Google Scholar]
- Fekete, J.T.; Gyorffy, B. ROCplot.org: Validating predictive biomarkers of chemotherapy/hormonal therapy/anti-HER2 therapy using transcriptomic data of 3,104 breast cancer patients. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 145, 3140–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, T.A.; Watkins, G.; Mansel, R.E.; Jiang, W.G. Loss of tight junction plaque molecules in breast cancer tissues is associated with a poor prognosis in patients with breast cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2004, 40, 2717–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, T.A.; Jiang, W.G. Loss of tight junction barrier function and its role in cancer metastasis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1788, 872–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akashi, T.; Noguchi, S.; Takahashi, Y.; Nishimura, T.; Tomi, M. L-type Amino Acid Transporter 1 (SLC7A5)-Mediated Transport of Pregabalin at the Rat Blood-Spinal Cord Barrier and its Sensitivity to Plasma Branched-Chain Amino Acids. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 112, 1137–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meurer, M.; Hocherl, K. Deregulated renal magnesium transport during lipopolysaccharide-induced acute kidney injury in mice. Pflug. Arch.-Eur. J. Physiol. 2019, 471, 619–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldeman, C.; Andersen, M.; Al-Robai, A.; Buchholtz, T.; Svane, N.; Ozgur, B.; Holst, B.; Shusta, E.; Hall, V.J.; Saaby, L.; et al. Human induced pluripotent stem cells (BIONi010-C) generate tight cell monolayers with blood-brain barrier traits and functional expression of large neutral amino acid transporter 1 (SLC7A5). Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 156, 105577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurkiewicz, D.; Michalec, K.; Skowronek, K.; Nalecz, K.A. Tight junction protein ZO-1 controls organic cation/carnitine transporter OCTN2 (SLC22A5) in a protein kinase C-dependent way. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Mol. Cell Res. 2017, 1864, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Category | Subgroup | n | CLDN9 (Median (Q1–Q3) | p Value * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tissue type | Normal | 33 | 15 (4–764) | 0.035 |
| Tumour | 127 | 77 (4–4342) | ||
| Grade | 1 | 24 | 1500 (158–21,800) | |
| 2 | 43 | 41 (3–5418) | 0.025 | |
| 3 | 58 | 31 (4–1442) | 0.0036 | |
| TNM staging | 1 | 70 | 125 (6–6170) | |
| 2 | 40 | 57 (3–1467) | 0.18 | |
| 3 | 7 | 226 (32–32,600) | 0.59 | |
| 4 | 4 | 89 (20–5529) | 0.76 | |
| Clinical outcome | Disease free | 90 | 80 (7–6505) | |
| Died of BrCa | 16 | 729 (11–16,375) | 0.071 | |
| All BrCa Incidence | 28 | 125 (4–1467) | 0.05 | |
| ER status | Negative | 75 | 32 (4–700) | 0.09 |
| Positive | 38 | 924 (4–18,520) | ||
| Her2 | Her2(−) | 57 | 81 (3–5165) | 0.75 |
| Her2(+) | 55 | 75 (7–1970) |
| Spearman’s Correlation with CLDN9 | ||
|---|---|---|
| ZO-1 | Correlation Coefficient | 0.297 ** |
| Significance (2-tailed) | 0.001 | |
| ZO-2 | Correlation Coefficient | −0.084 |
| Significance (2-tailed) | 0.374 | |
| ZO-3 | Correlation Coefficient | 0.252 * |
| Significance (2-tailed) | 0.011 | |
| Intensity | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Negative to Weak (0–1) | Moderate to Strong (2–3) | Membrane | Nucleus | Statistical Significance | ||||
| Positive | Negative | Positive | Negative | Chi Value | p Value | |||
| Normal (n = 3) | 0 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 3 | ||
| Tumor (n = 128) | 74 | 54 | 19 | 109 | 23 | 105 | 19.85 | 0.0013 |
| Grade1 (n = 4) | 2 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 2 | ||
| Grade2 (n = 57) | 29 | 28 | 8 | 49 | 13 | 44 | 1.849 | 0.8696 |
| Grade3 (n = 28) | 16 | 12 | 2 | 26 | 2 | 26 | 7.264 | 0.2018 |
| T1 (n = 4) | 4 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 4 | ||
| T2 (n = 69) | 35 | 34 | 11 | 58 | 11 | 58 | 5.191 | 0.393 |
| T3 (n = 25) | 15 | 10 | 5 | 20 | 7 | 18 | 4.885 | 0.4301 |
| T4 (n = 15) | 9 | 6 | 1 | 14 | 2 | 13 | 3.216 | 0.6667 |
| HER-2- (n = 81) | 52 | 29 | 12 | 69 | 13 | 68 | ||
| HER-2+ (n = 3) | 1 | 2 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 2.272 | 0.8104 |
| HER2++ (n = 9) | 3 | 6 | 2 | 7 | 0 | 9 | 5.273 | 0.3834 |
| HER2+++ (n = 29) | 15 | 14 | 5 | 24 | 7 | 22 | 2.431 | 0.7869 |
| ER- (n = 59) | 33 | 26 | 10 | 49 | 13 | 46 | ||
| ER+ (n = 18) | 10 | 8 | 3 | 15 | 1 | 17 | 2.519 | 0.7736 |
| ER++ (n = 20) | 12 | 8 | 4 | 16 | 1 | 19 | 3.168 | 0.674 |
| ER+++ (n = 25) | 16 | 9 | 2 | 23 | 5 | 20 | 1.662 | 0.8937 |
| Factors | OS | RFS | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Ratio | p Value * | Hazard Ratio | p Value * | |
| CLDN9/ZO signature | 2.033 | 0.004 | 1.239 | 0.010 |
| NPI ** | 3.028 | 0.089 | 2.068 | 0.045 |
| Grade | 1.287 | 0.432 | 1.275 | 0.530 |
| TNM staging | 1.034 | 0.902 | 1.412 | 0.033 |
| ER status | 2.022 | 0.266 | 3.896 | 0.008 |
| Her-2 status | 3.016 | 0.083 | 7.697 | 0.008 |
| 5-Year RFS Response | Non-Responders | Responders | p * | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Median | Min–Max | n | Median | Min–Max | |||
| ER status | ER(−) | 111 | 182 | 10–564 | 115 | 99 | 6–922 | 0.000034 |
| ER(+) | 109 | 252 | 26–750 | 141 | 163 | 6–1315 | 5.9 × 10−9 | |
| Her2 status | Her2 (−) | 173 | 250 | 10–750 | 183 | 141 | 6–1362 | 7.1 × 10−11 |
| Her2 (+) | 47 | 162 | 25–432 | 73 | 133 | 5–622 | 0.12 | |
| ER(+)/Her2(−) | 88 | 262 | 26–750 | 103 | 163 | 12–1352 | 0.000000009 | |
| ER(+)/Her2(+) | 21 | 200 | 75–432 | 38 | 168 | 5–429 | 0.14 | |
| ER(−)/Her2(+) | 26 | 140 | 25–343 | 35 | 122 | 7–622 | 0.13 | |
| TNBC | 84 | 218 | 10–564 | 80 | 96 | 6–439 | 0.000075 | |
| Luminal-A | 20 | 202 | 59–304 | 58 | 126 | 15–501 | 0.0068 | |
| Luminal-B | 90 | 262 | 26–750 | 83 | 199 | 5–1352 | 0.00005 | |
| Gemcitabine (µM) | Docetaxel (µM) | Cisplatin (µM) | Methotrexate (µM) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MDA-MB-231Control | 0.820 | 54.612 | 12.520 | 107.927 |
| MDA-MB-231CLDN9-KD | 0.287 | 31.134 | 4.723 | 2.7834 |
| MCF7Control | 27.261 | 6.575 | 13.462 | 2179.402 |
| MCF7CLDN9-KD | 7.334 | 17.876 | 12.414 | 1510.961 |
| SKBR3Control | 0.028 | 0.100 | 10.162 | 1012.070 |
| SKBR3CLDN9-KD | 0.031 | 0.086 | 12.493 | 706.855 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhuang, X.; Martin, T.A.; Ruge, F.; Zeng, J.; Li, X.; Khan, E.; Dou, Q.; Davies, E.; Jiang, W.G. Expression of Claudin-9 (CLDN9) in Breast Cancer, the Clinical Significance in Connection with Its Subcoat Anchorage Proteins ZO-1 and ZO-3 and Impact on Drug Resistance. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 3136. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11123136
Zhuang X, Martin TA, Ruge F, Zeng J, Li X, Khan E, Dou Q, Davies E, Jiang WG. Expression of Claudin-9 (CLDN9) in Breast Cancer, the Clinical Significance in Connection with Its Subcoat Anchorage Proteins ZO-1 and ZO-3 and Impact on Drug Resistance. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(12):3136. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11123136
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhuang, Xinguo, Tracey A. Martin, Fiona Ruge, Jianyuan (Jimmy) Zeng, Xinyu (Amber) Li, Elyas Khan, Qingping Dou, Eleri Davies, and Wen G. Jiang. 2023. "Expression of Claudin-9 (CLDN9) in Breast Cancer, the Clinical Significance in Connection with Its Subcoat Anchorage Proteins ZO-1 and ZO-3 and Impact on Drug Resistance" Biomedicines 11, no. 12: 3136. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11123136
APA StyleZhuang, X., Martin, T. A., Ruge, F., Zeng, J., Li, X., Khan, E., Dou, Q., Davies, E., & Jiang, W. G. (2023). Expression of Claudin-9 (CLDN9) in Breast Cancer, the Clinical Significance in Connection with Its Subcoat Anchorage Proteins ZO-1 and ZO-3 and Impact on Drug Resistance. Biomedicines, 11(12), 3136. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11123136









