Cortico-Subcortical White Matter Bundle Changes in Cervical Dystonia and Blepharospasm
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants and Clinical Assessment
2.2. MRI Acquisition
2.3. MRI Data Analysis
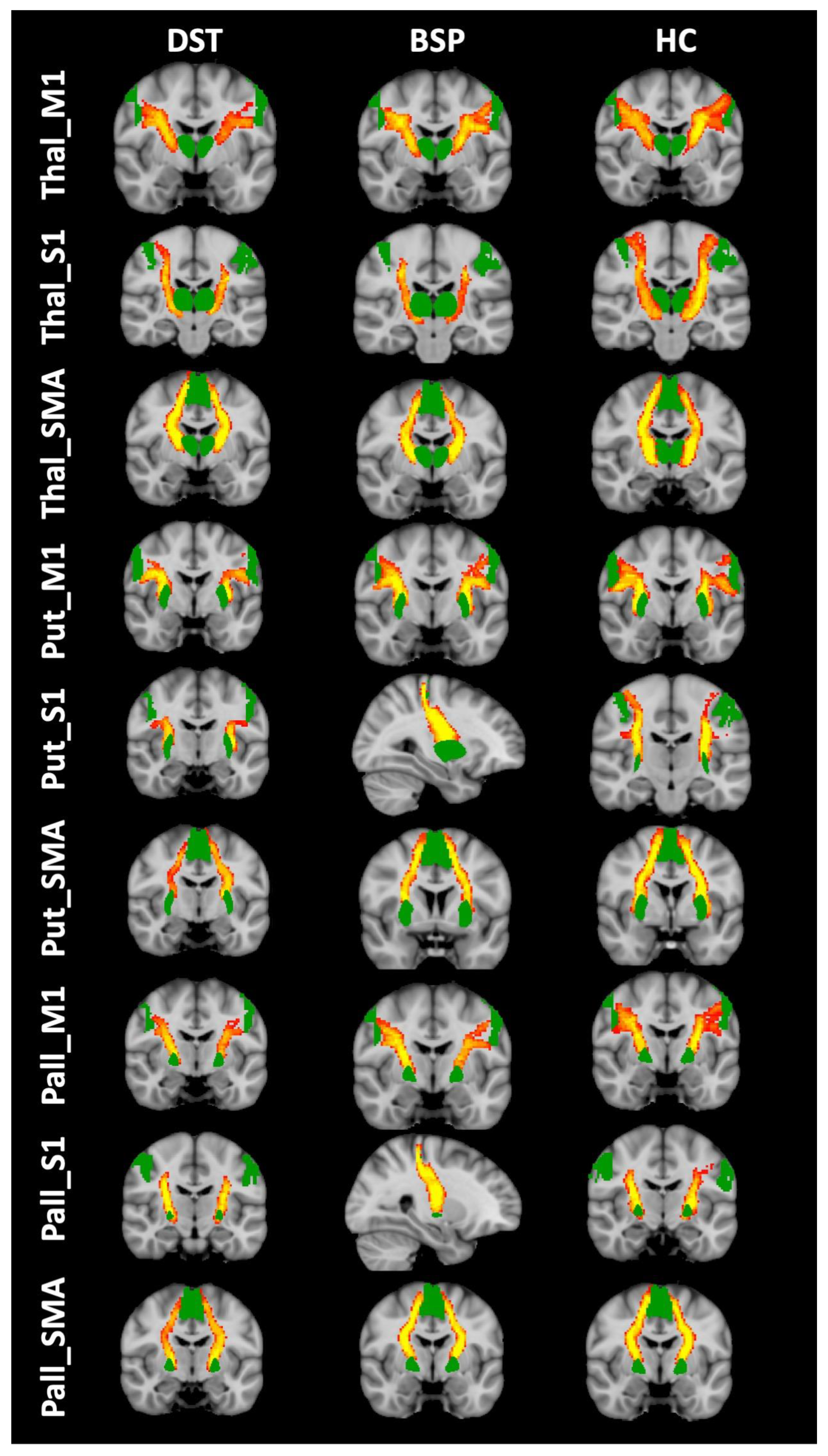
2.3.1. Selection of ROIs
2.3.2. Tractography
2.4. Statistical Analysis
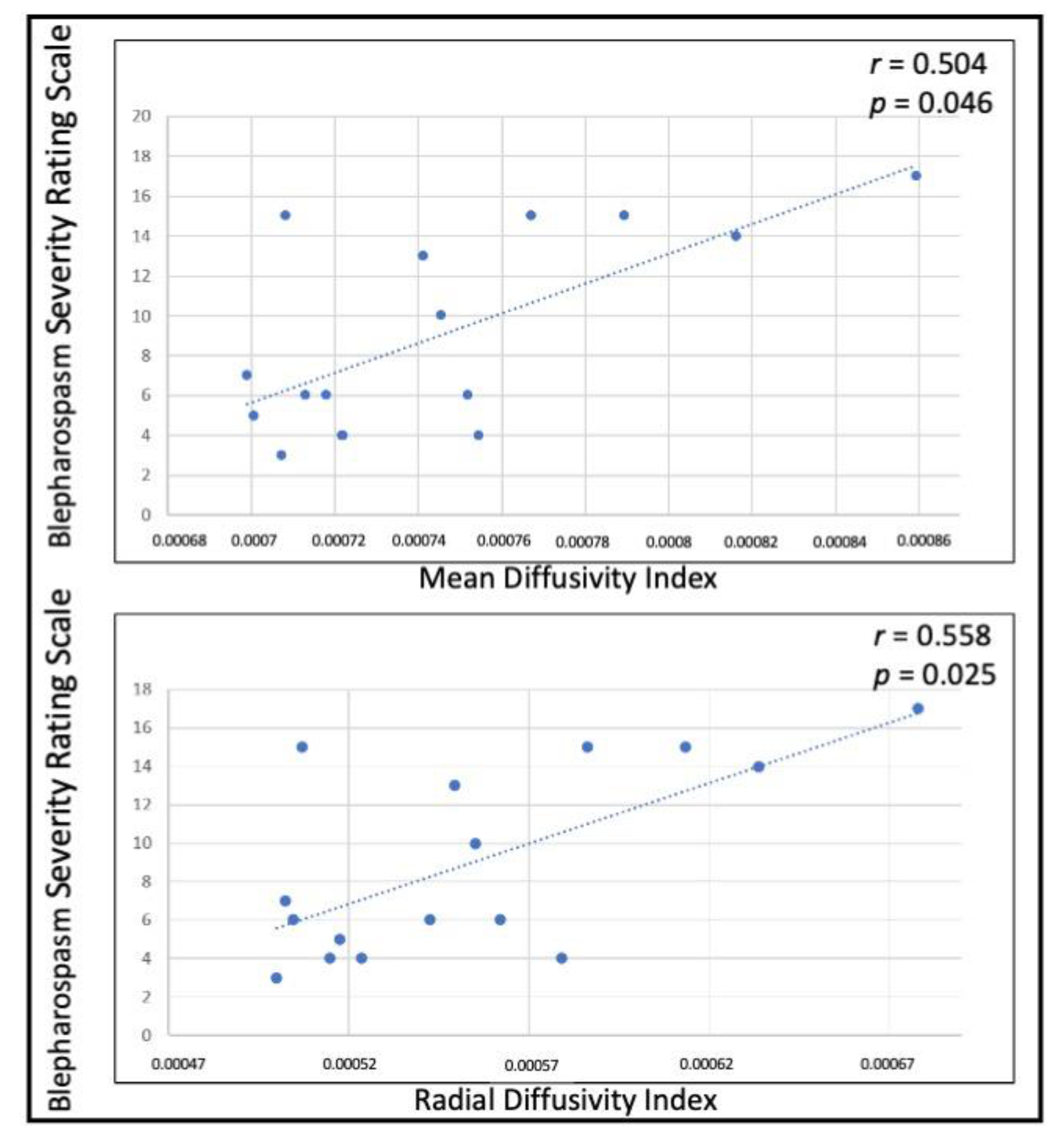
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Conte, A.; Defazio, G.; Hallett, M.; Fabbrini, G.; Berardelli, A. The Role of Sensory Information in the Pathophysiology of Focal Dystonias. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conte, A.; Rocchi, L.; Latorre, A.; Belvisi, D.; Rothwell, J.C.; Berardelli, A. Ten-Year Reflections on the Neurophysiological Abnormalities of Focal Dystonias in Humans. Mov. Disord. 2019, 34, 1616–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quartarone, A.; Hallett, M. Emerging Concepts in the Physiological Basis of Dystonia. Mov. Disord. 2013, 28, 958–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannì, C.; Pasqua, G.; Ferrazzano, G.; Tommasin, S.; De Bartolo, M.I.; Petsas, N.; Belvisi, D.; Conte, A.; Berardelli, A.; Pantano, P. Focal Dystonia: Functional Connectivity Changes in Cerebellar-Basal Ganglia-Cortical Circuit and Preserved Global Functional Architecture. Neurology 2022, 98, e1499–e1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodoehl, S.; Wagner, F.; Prell, T.; Klingner, C.; Witte, O.W.; Günther, A. Cause or Effect: Altered Brain and Network Activity in Cervical Dystonia Is Partially Normalized by Botulinum Toxin Treatment. Neuroimage Clin. 2019, 22, 101792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, S.A.; Morris, A.E.; Campbell, M.C.; Karimi, M.; Adeyemo, B.; Paniello, R.C.; Snyder, A.Z.; Petersen, S.E.; Mink, J.W.; Perlmutter, J.S. Regional, Not Global, Functional Connectivity Contributes to Isolated Focal Dystonia. Neurology 2020, 95, e2246–e2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, P.; Wei, S.; Ou, Y.; Jiang, W.; Li, W.; Lei, Y.; Liu, F.; Guo, W.; Luo, S. Reduced Global-Brain Functional Connectivity and Its Relationship with Symptomatic Severity in Cervical Dystonia. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomić, A.; Agosta, F.; Sarasso, E.; Svetel, M.; Kresojević, N.; Fontana, A.; Canu, E.; Petrović, I.; Kostić, V.S.; Filippi, M. Brain Structural Changes in Focal Dystonia-What About Task Specificity? A Multimodal MRI Study. Mov. Disord. 2021, 36, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacIver, C.L.; Tax, C.M.W.; Jones, D.K.; Peall, K.J. Structural Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Dystonia: A Systematic Review of Methodological Approaches and Findings. Eur. J. Neurol. 2022, 29, 3418–3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, B.D.; Honce, J.M.; Shelton, E.; Sillau, S.H.; Nagae, L.M. Isolated Focal Dystonia Phenotypes Are Associated with Distinct Patterns of Altered Microstructure. Neuroimage Clin. 2018, 19, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Peng, K.; Liu, Y.; Zhong, L.; Dang, C.; Yan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, J.; Zhang, W.; Ou, Z.; et al. Topological Alterations in White Matter Structural Networks in Blepharospasm. Mov. Disord. 2021, 36, 2802–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Luo, C.; Song, W.; Guo, X.; Zhao, B.; Chen, X.; Huang, X.; Gong, Q.; Shang, H.-F. Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Blepharospasm and Blepharospasm-Oromandibular Dystonia. J. Neurol. 2014, 261, 1413–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prell, T.; Peschel, T.; Köhler, B.; Bokemeyer, M.H.; Dengler, R.; Günther, A.; Grosskreutz, J. Structural Brain Abnormalities in Cervical Dystonia. BMC Neurosci. 2013, 14, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantano, P.; Totaro, P.; Fabbrini, G.; Raz, E.; Contessa, G.M.; Tona, F.; Colosimo, C.; Berardelli, A. A Transverse and Longitudinal MR Imaging Voxel-Based Morphometry Study in Patients with Primary Cervical Dystonia. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2011, 32, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontillo, G.; Castagna, A.; Vola, E.A.; Macerollo, A.; Peluso, S.; Russo, C.; Baglio, F.; Manganelli, F.; Brunetti, A.; Cocozza, S.; et al. The Cerebellum in Idiopathic Cervical Dystonia: A Specific Pattern of Structural Abnormalities? Park. Relat. Disord. 2020, 80, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etgen, T.; Mühlau, M.; Gaser, C.; Sander, D. Bilateral Grey-Matter Increase in the Putamen in Primary Blepharospasm. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2006, 77, 1017–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horovitz, S.G.; Ford, A.; Najee-Ullah, M.A.; Ostuni, J.L.; Hallett, M. Anatomical Correlates of Blepharospasm. Transl. Neurodegener. 2012, 1, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martino, D.; Di Giorgio, A.; D’Ambrosio, E.; Popolizio, T.; Macerollo, A.; Livrea, P.; Bertolino, A.; Defazio, G. Cortical Gray Matter Changes in Primary Blepharospasm: A Voxel-Based Morphometry Study. Mov. Disord. 2011, 26, 1907–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Gao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Yan, Z.; Ou, Z.; Zhong, L.; Xie, C.; Zeng, J.; Zhang, W.; et al. Machine Learning for Predicting Individual Severity of Blepharospasm Using Diffusion Tensor Imaging. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 670475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramdhani, R.A.; Kumar, V.; Velickovic, M.; Frucht, S.J.; Tagliati, M.; Simonyan, K. What’s Special about Task in Dystonia? A Voxel-Based Morphometry and Diffusion Weighted Imaging Study. Mov. Disord. 2014, 29, 1141–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blood, A.J.; Kuster, J.K.; Woodman, S.C.; Kirlic, N.; Makhlouf, M.L.; Multhaupt-Buell, T.J.; Makris, N.; Parent, M.; Sudarsky, L.R.; Sjalander, G.; et al. Evidence for Altered Basal Ganglia-Brainstem Connections in Cervical Dystonia. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonilha, L.; de Vries, P.M.; Hurd, M.W.; Rorden, C.; Morgan, P.S.; Besenski, N.; Bergmann, K.J.; Hinson, V.K. Disrupted Thalamic Prefrontal Pathways in Patients with Idiopathic Dystonia. Park. Relat. Disord. 2009, 15, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sondergaard, R.E.; Rockel, C.P.; Cortese, F.; Jasaui, Y.; Pringsheim, T.M.; Sarna, J.R.; Monchi, O.; Sadikot, A.F.; Pike, B.G.; Martino, D. Microstructural Abnormalities of the Dentatorubrothalamic Tract in Cervical Dystonia. Mov. Disord. 2021, 36, 2192–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantel, T.; Altenmüller, E.; Li, Y.; Lee, A.; Meindl, T.; Jochim, A.; Zimmer, C.; Haslinger, B. Structure-Function Abnormalities in Cortical Sensory Projections in Embouchure Dystonia. Neuroimage Clin. 2020, 28, 102410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albanese, A.; Bhatia, K.; Bressman, S.B.; Delong, M.R.; Fahn, S.; Fung, V.S.C.; Hallett, M.; Jankovic, J.; Jinnah, H.A.; Klein, C.; et al. Phenomenology and Classification of Dystonia: A Consensus Update. Mov. Disord. 2013, 28, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comella, C.L.; Fox, S.H.; Bhatia, K.P.; Perlmutter, J.S.; Jinnah, H.A.; Zurowski, M.; McDonald, W.M.; Marsh, L.; Rosen, A.R.; Waliczek, T.; et al. Development of the Comprehensive Cervical Dystonia Rating Scale: Methodology. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2015, 2, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Defazio, G.; Hallett, M.; Jinnah, H.A.; Stebbins, G.T.; Gigante, A.F.; Ferrazzano, G.; Conte, A.; Fabbrini, G.; Berardelli, A. Development and Validation of a Clinical Scale for Rating the Severity of Blepharospasm. Mov. Disord. 2015, 30, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leemans, A.; Jones, D.K. The B-Matrix Must Be Rotated When Correcting for Subject Motion in DTI Data. Magn. Reson. Med. 2009, 61, 1336–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.M. Fast Robust Automated Brain Extraction. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2002, 17, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Li, H.; Zhuo, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, L.; Yang, Z.; Chu, C.; Xie, S.; Laird, A.R.; et al. The Human Brainnetome Atlas: A New Brain Atlas Based on Connectional Architecture. Cereb. Cortex 2016, 26, 3508–3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jbabdi, S.; Woolrich, M.W.; Andersson, J.L.R.; Behrens, T.E.J. A Bayesian Framework for Global Tractography. Neuroimage 2007, 37, 116–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gschwind, M.; Pourtois, G.; Schwartz, S.; Van De Ville, D.; Vuilleumier, P. White-Matter Connectivity between Face-Responsive Regions in the Human Brain. Cereb. Cortex 2012, 22, 1564–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javad, F.; Warren, J.D.; Micallef, C.; Thornton, J.S.; Golay, X.; Yousry, T.; Mancini, L. Auditory Tracts Identified with Combined FMRI and Diffusion Tractography. Neuroimage 2014, 84, 562–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakabek, D.; Power, B.D.; Macfarlane, M.D.; Walterfang, M.; Velakoulis, D.; van Westen, D.; Lätt, J.; Nilsson, M.; Looi, J.C.L.; Santillo, A.F. Regional Structural Hypo- and Hyperconnectivity of Frontal-Striatal and Frontal-Thalamic Pathways in Behavioral Variant Frontotemporal Dementia. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2018, 39, 4083–4093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naito, A.; Kita, H. The Cortico-Pallidal Projection in the Rat: An Anterograde Tracing Study with Biotinylated Dextran Amine. Brain Res. 1994, 653, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephenson-Jones, M.; Kardamakis, A.A.; Robertson, B.; Grillner, S. Independent Circuits in the Basal Ganglia for the Evaluation and Selection of Actions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E3670–E3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacciola, A.; Milardi, D.; Bertino, S.; Basile, G.A.; Calamuneri, A.; Chillemi, G.; Rizzo, G.; Anastasi, G.; Quartarone, A. Structural Connectivity-Based Topography of the Human Globus Pallidus: Implications for Therapeutic Targeting in Movement Disorders. Mov. Disord. 2019, 34, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grewal, S.S.; Holanda, V.M.; Middlebrooks, E.H. Corticopallidal Connectome of the Globus Pallidus Externus in Humans: An Exploratory Study of Structural Connectivity Using Probabilistic Diffusion Tractography. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2018, 39, 2120–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milardi, D.; Gaeta, M.; Marino, S.; Arrigo, A.; Vaccarino, G.; Mormina, E.; Rizzo, G.; Milazzo, C.; Finocchio, G.; Baglieri, A.; et al. Basal Ganglia Network by Constrained Spherical Deconvolution: A Possible Cortico-Pallidal Pathway? Mov. Disord. 2015, 30, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, W.-J.; Jha, A.; Bock, A.; Huebl, J.; Horn, A.; Schneider, G.-H.; Sander, T.H.; Litvak, V.; Kühn, A.A. Cortico-Pallidal Oscillatory Connectivity in Patients with Dystonia. Brain 2015, 138, 1894–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Z.; Kim, S.J.; Phielipp, N.; Ghosh, S.; Udupa, K.; Gunraj, C.A.; Saha, U.; Hodaie, M.; Kalia, S.K.; Lozano, A.M.; et al. Pallidal Deep Brain Stimulation Modulates Cortical Excitability and Plasticity. Ann. Neurol. 2018, 83, 352–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gass, A.; Niendorf, T.; Hirsch, J.G. Acute and Chronic Changes of the Apparent Diffusion Coefficient in Neurological Disorders--Biophysical Mechanisms and Possible Underlying Histopathology. J. Neurol. Sci. 2001, 186 (Suppl. 1), S15–S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotak, C.H. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Measurement of the Apparent Diffusion Coefficient (ADC) of Tissue Water and Its Relationship to Cell Volume Changes in Pathological States. Neurochem. Int. 2004, 45, 569–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfefferbaum, A.; Sullivan, E.V. Disruption of Brain White Matter Microstructure by Excessive Intracellular and Extracellular Fluid in Alcoholism: Evidence from Diffusion Tensor Imaging. Neuropsychopharmacology 2005, 30, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierpaoli, C.; Jezzard, P.; Basser, P.J.; Barnett, A.; Di Chiro, G. Diffusion Tensor MR Imaging of the Human Brain. Radiology 1996, 201, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harsan, L.A.; Poulet, P.; Guignard, B.; Steibel, J.; Parizel, N.; de Sousa, P.L.; Boehm, N.; Grucker, D.; Ghandour, M.S. Brain Dysmyelination and Recovery Assessment by Noninvasive in Vivo Diffusion Tensor Magnetic Resonance Imaging. J. Neurosci. Res 2006, 83, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M.; Hackney, D.B.; Zhang, G.; Wehrli, S.L.; Wright, A.C.; O’Brien, W.T.; Uematsu, H.; Wehrli, F.W.; Selzer, M.E. Magnetic Resonance Microimaging of Intraaxonal Water Diffusion in Live Excised Lamprey Spinal Cord. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 16192–16196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werring, D.J.; Toosy, A.T.; Clark, C.A.; Parker, G.J.; Barker, G.J.; Miller, D.H.; Thompson, A.J. Diffusion Tensor Imaging Can Detect and Quantify Corticospinal Tract Degeneration after Stroke. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2000, 69, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabresi, P.; Picconi, B.; Tozzi, A.; Ghiglieri, V.; Di Filippo, M. Direct and Indirect Pathways of Basal Ganglia: A Critical Reappraisal. Nat. Neurosci. 2014, 17, 1022–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, Y.; Wichmann, T. The Cortico-Pallidal Projection: An Additional Route for Cortical Regulation of the Basal Ganglia Circuitry. Mov. Disord. 2015, 30, 293–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colosimo, C.; Pantano, P.; Calistri, V.; Totaro, P.; Fabbrini, G.; Berardelli, A. Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Primary Cervical Dystonia. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2005, 76, 1591–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabbrini, G.; Pantano, P.; Totaro, P.; Calistri, V.; Colosimo, C.; Carmellini, M.; Defazio, G.; Berardelli, A. Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Patients with Primary Cervical Dystonia and in Patients with Blepharospasm. Eur. J. Neurol. 2008, 15, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonilha, L.; de Vries, P.M.; Vincent, D.J.; Rorden, C.; Morgan, P.S.; Hurd, M.W.; Besenski, N.; Bergmann, K.J.; Hinson, V.K. Structural White Matter Abnormalities in Patients with Idiopathic Dystonia. Mov. Disord. 2007, 22, 1110–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Peng, K.; Ou, Z.; Zhong, L.; Wang, Y.; Xie, C.; Zeng, J.; Zhang, W.; Liu, G. Structural Brain Changes in Blepharospasm: A Cortical Thickness and Diffusion Tensor Imaging Study. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 543802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Group (Subjects) | Cervical Dystonia (n = 17) | Blepharospasm (n = 18) | Healthy Subjects (n = 17) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 55.7 (10.1) | 61.5 (8.8) | 54.4 (13.9) | >0.05 |
| Sex (female/male) | 14/3 | 12/6 | 8/9 | >0.05 |
| Disease duration, years | 13.9 (9.9) | 11.6 (3.8) | - | >0.05 |
| TWSTRS | 16.6 (11.2) | - | - | NA |
| CDIP-58 | 56.4 (19.1) | - | - | NA |
| BSRS | - | 9.1 (4.7) | - | NA |
| BSDI | - | 9.5 (6.6) | - | NA |
| Head tremor (Y/N) | 9/8 | NA | NA | NA |
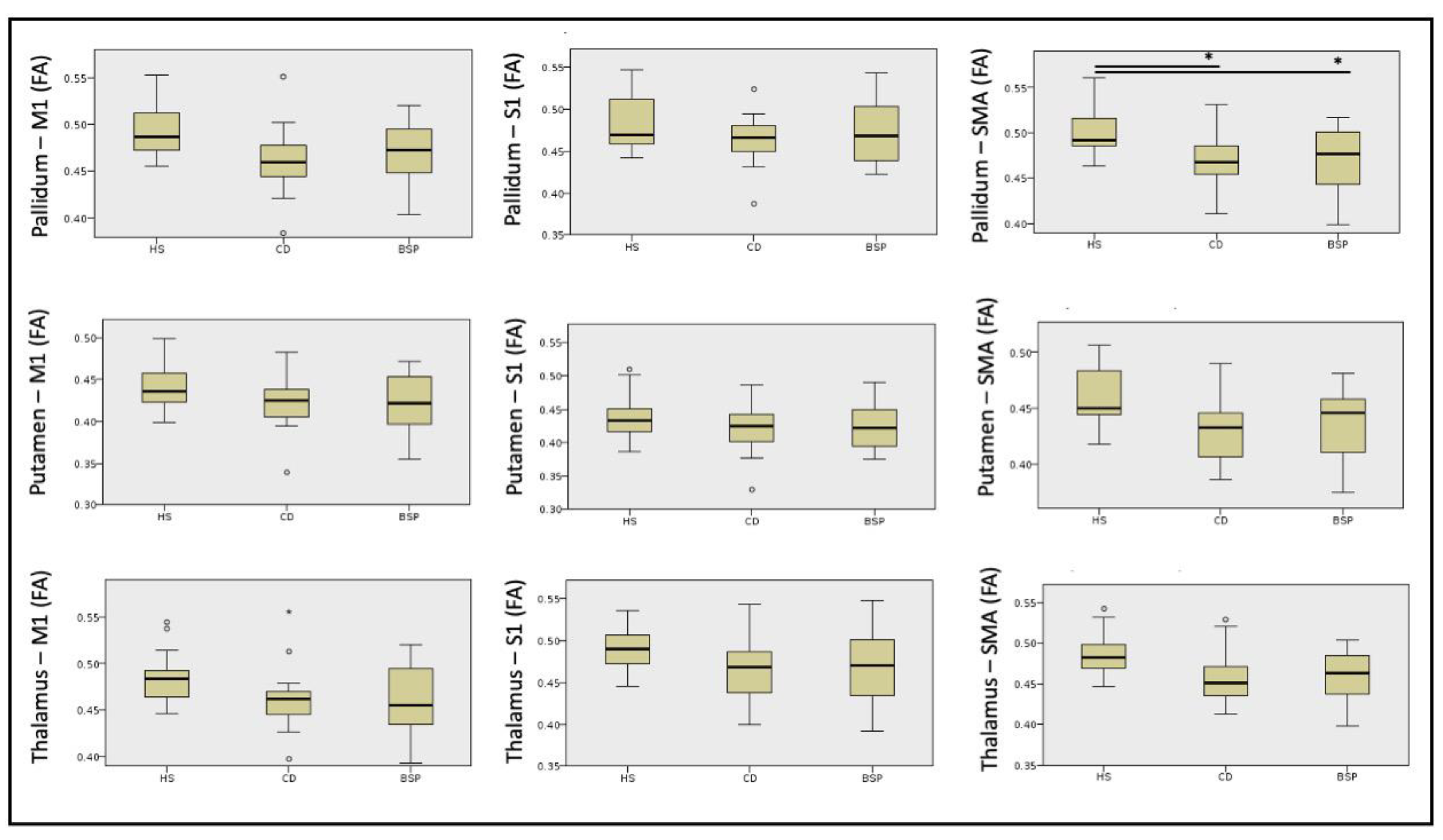
| Healthy Subjects (n = 17) | Cervical Dystonia (n = 17) | Blepharospasm (n = 18) | p | H | Post Hoc | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PALLIDUM—M1 Mean (SD) | 0.494 (0.03) | 0.462 (0.03) | 0.467 (0.03) | >0.05 | 8.75 | - |
| PALLIDUM—S1 Mean (SD) | 0.482 (0.03) | 0.463 (0.03) | 0.472 (0.03) | >0.05 | 2.58 | - |
| PALLIDUM—SMA Mean (SD) | 0.504 (0.03) | 0.468 (0.03) | 0.469 (0.03) | 0.005 | 10.74 | HS-BSP p = 0.026 |
| HS-CD p = 0.008 | ||||||
| BSP-CD ns | ||||||
| PUTAMEN—M1 Mean (SD) | 0.443 (0.03) | 0.421 (0.03) | 0.423 (0.03) | >0.05 | 3.68 | - |
| PUTAMEN—S1 Mean (SD) | 0.441 (0.03) | 0.423 (0.03) | 0.426 (0.04) | >0.05 | 1.65 | - |
| PUTAMEN—SMA Mean (SD) | 0.459 (0.03) | 0.432 (0.03) | 0.435 (0.03) | >0.05 | 5.56 | - |
| THALAMUS—M1 Mean (SD) | 0.485 (0.03) | 0.462 (0.03) | 0.461 (0.04) | >0.05 | 5.74 | - |
| THALAMUS—S1 Mean (SD) | 0.489 (0.03) | 0.468 (0.04) | 0.472 (0.04) | >0.05 | 3.76 | - |
| THALAMUS—SMA Mean (SD) | 0.487 (0.03) | 0.457 (0.03) | 0.459 (0.03) | >0.05 | 9.15 | - |
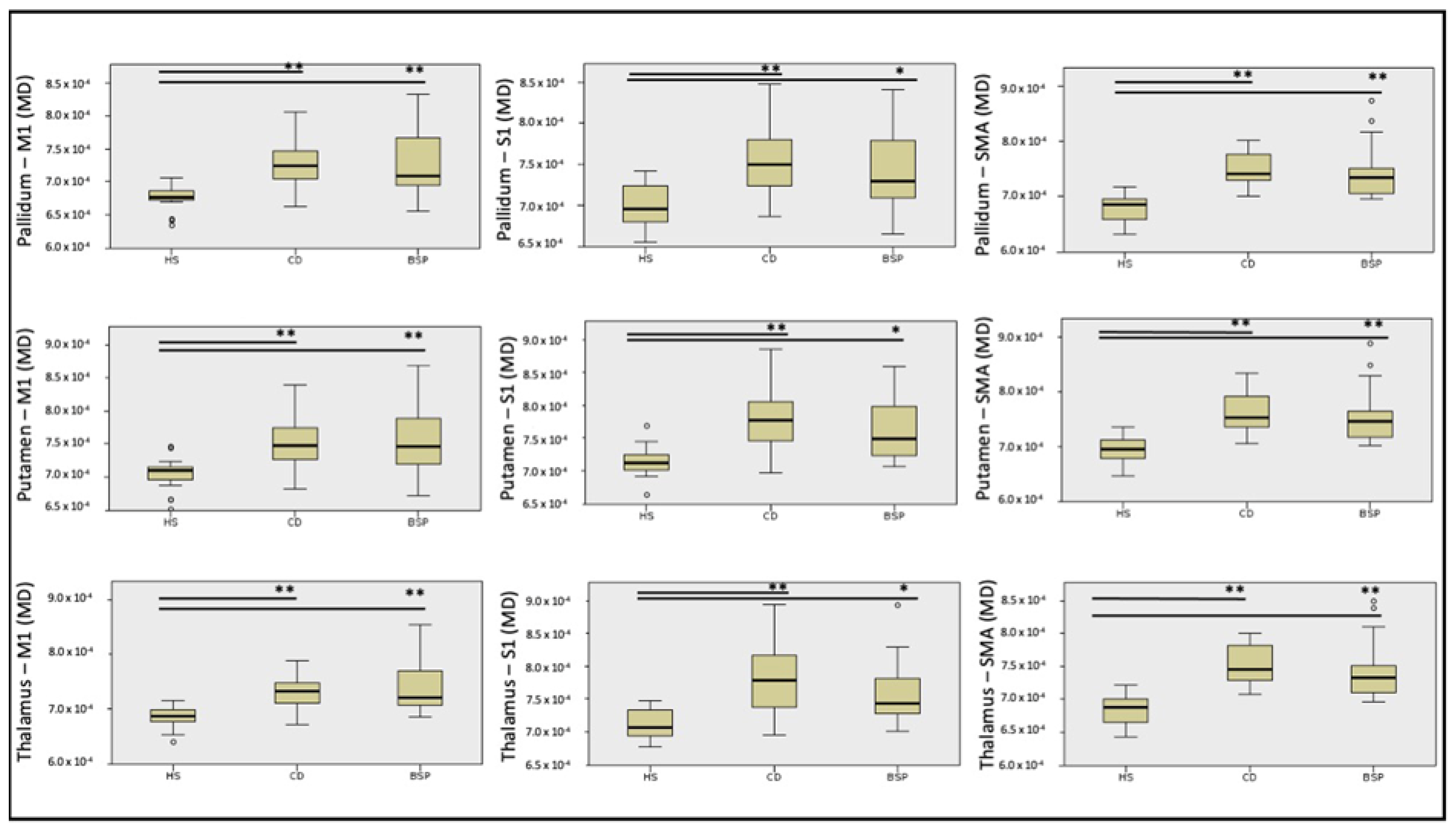
| Mean Diffusivity | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Healthy Subjects (n = 17) | Cervical Dystonia (n = 17) | Blepharospasm (n = 18) | p | H | Post Hoc | |
| PALLIDUM—M1 Mean (SD) | 0.00068 (0.00002) | 0.00073 (0.00004) | 0.00073 (0.00005) | <0.0001 | 22.57 | HS-BSP p < 0.0001 |
| HS-CD p < 0.0001 | ||||||
| BSP-CD ns | ||||||
| PALLIDUM—S1 Mean (SD) | 0.00070 (0.00002) | 0.00076 (0.00004) | 0.00074 (0.0004) | <0.0001 | 16.57 | HS-BSP p = 0.014 |
| HS-CD p < 0.0001 | ||||||
| BSP-CD ns | ||||||
| PALLIDUM—SMA Mean (SD) | 0.00068 (0.00003) | 0.00075 (0.00003) | 0.00075 (0.00005) | <0.0001 | 28,84 | HS-BSP p < 0.0001 |
| HS-CD p < 0.0001 | ||||||
| BSP-CD ns | ||||||
| PUTAMEN—M1 Mean (SD) | 0.00070 (0.00003) | 0.00075 (0.00004) | 0.00076 (0.00005) | <0.0001 | 17.53 | HS-BSP p = 0.001 |
| HS-CD p = 0.001 | ||||||
| BSP-CD ns | ||||||
| PUTAMEN—S1 Mean (SD) | 0.00071 (0.00002) | 0.00078 (0.00005) | 0.00076 (0.00005) | <0.0001 | 18.97 | HS-BSP p = 0.02 |
| HS-CD p < 0.0001 | ||||||
| BSP-CD ns | ||||||
| PUTAMEN—SMA Mean (SD) | 0.00070 (0.00003) | 0.00076 (0.00004) | 0.00076 (0.00005) | <0.0001 | 24.71 | HS-BSP p < 0.0001 |
| HS-CD p < 0.0001 | ||||||
| BSP-CD ns | ||||||
| THALAMUS—M1 Mean (SD) | 0.00069 (0.00002) | 0.00073 (0.00003) | 0.00074 (0.00002) | <0.0001 | 21.33 | HS-BSP p < 0.0001 |
| HS-CD p < 0.0001 | ||||||
| BSP-CD ns | ||||||
| THALAMUS—S1 Mean (SD) | 0.00071 (0.00002) | 0.00078 (0.00005) | 0.00076 (0.00005) | <0.0001 | 18.25 | HS-BSP p = 0.006 |
| HS-CD p < 0.0001 | ||||||
| BSP-CD ns | ||||||
| THALAMUS—SMA Mean (SD) | 0.00069 (0.00002) | 0.00075 (0.00003) | 0.00075 (0.00005) | <0.0001 | 27.91 | HS-BSP p < 0.0001 |
| HS-CD p < 0.0001 | ||||||
| BSP-CD ns | ||||||
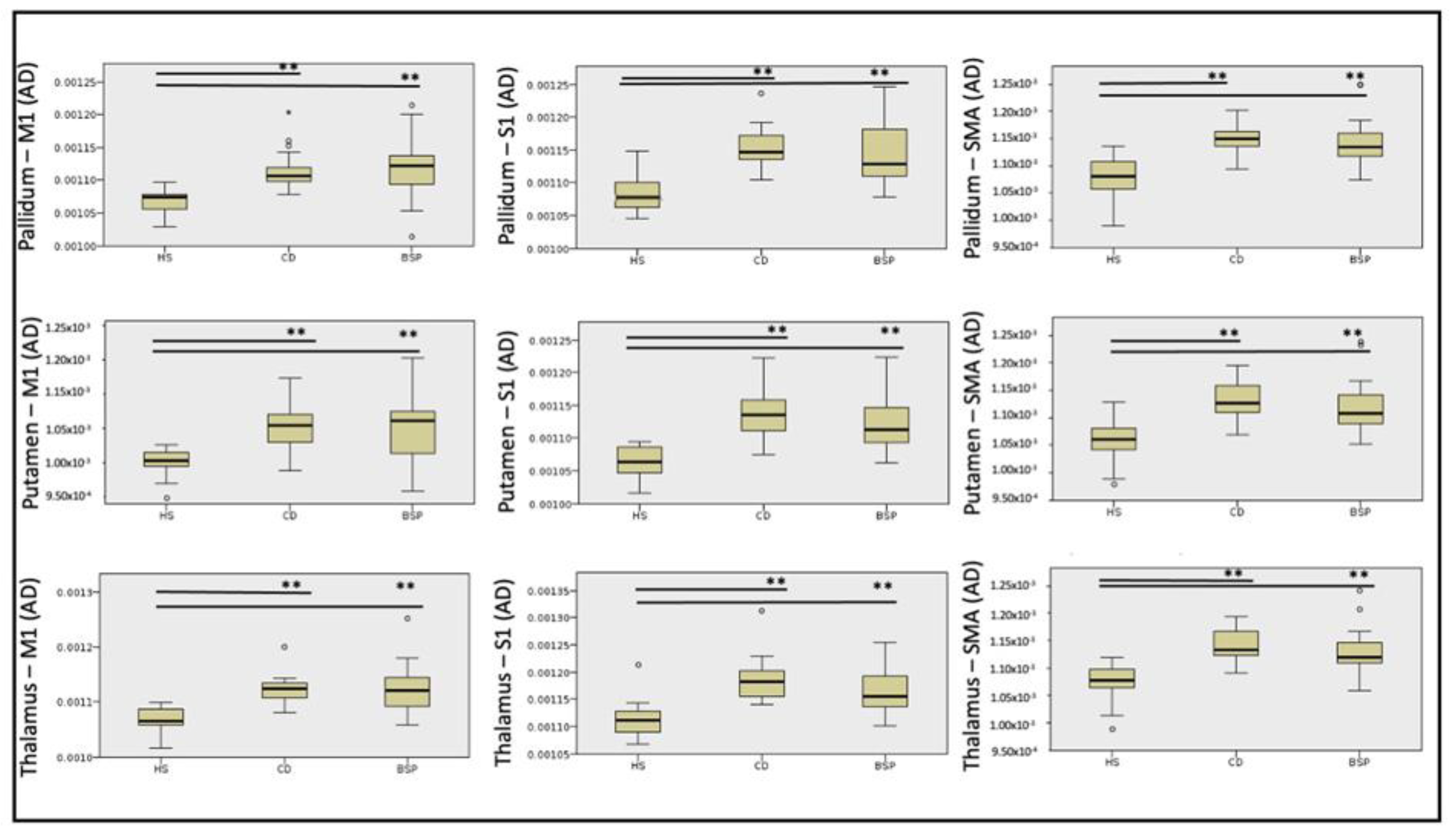
| Axial Diffusivity | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HS (n = 17) | CD (n = 17) | BSP (n = 18) | p | H | Post Hoc | |
| PALLIDUM—M1 Mean (SD) | 0.001065 (0.000021) | 0.001116 (0.000033) | 0.001117 (0.000051) | <0.0001 | 21.12 | HS-BSP p < 0.0001 |
| HS-CD p < 0.0001 | ||||||
| BSP-CD ns | ||||||
| PALLIDUM—S1 Mean (SD) | 0.001088 (0.000031) | 0.001153 (0.000034) | 0.001141 (0.000045) | <0.0001 | 21.14 | HS-BSP p = 0.002 |
| HS-CD p < 0.0001 | ||||||
| BSP-CD ns | ||||||
| PALLIDUM—SMA Mean (SD) | 0.001080 (0.000040) | 0.001153 (0.000028) | 0.001146 (0.000046) | <0.0001 | 23.91 | HS-BSP p = 0.001 |
| HS-CD p < 0.0001 | ||||||
| BSP-CD ns | ||||||
| PUTAMEN—M1 Mean (SD) | 0.001050 (0.000022) | 0.001101 (0.000037) | 0.001107 (0.000056) | <0.0001 | 16.07 | HS-BSP p = 0.002 |
| HS-CD p = 0.001 | ||||||
| BSP-CD ns | ||||||
| PUTAMEN—S1 Mean (SD) | 0.001064 (0.000024) | 0.001137 (0.000040) | 0.001124 (0.000049) | <0.0001 | 25.75 | HS-BSP p < 0.0001 |
| HS-CD p < 0.0001 | ||||||
| BSP-CD ns | ||||||
| PUTAMEN—SMA Mean (SD) | 0.001057 (0.000040) | 0.001132 (0.000032) | 0.001124 (0.000050) | <0.0001 | 23.58 | HS-BSP p = 0.001 |
| HS-CD p < 0.0001 | ||||||
| BSP-CD ns | ||||||
| THALAMUS—M1 Mean (SD) | 0.001068 (0.000024) | 0.001122 (0.000028) | 0.001124 (0.000046) | <0.0001 | 23.93 | HS-BSP p < 0.0001 |
| HS-CD p < 0.0001 | ||||||
| BSP-CD ns | ||||||
| THALAMUS—S1 Mean (SD) | 0.001113 (0.000035) | 0.001186 (0.000042) | 0.001166 (0.000039) | <0.0001 | 24.46 | HS-BSP p = 0.001 |
| HS-CD p < 0.0001 | ||||||
| BSP-CD ns | ||||||
| THALAMUS—SMA Mean (SD) | 0.001071 (0.000035) | 0.001141 (0.000046) | 0.001132 (0.000042) | <0.0001 | 26.74 | HS-BSP p < 0.0001 |
| HS-CD p < 0.0001 | ||||||
| BSP-CD ns | ||||||
| Radial Diffusivity | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HS (n = 17) | CD (n = 17) | BSP (n = 18) | p (Bonferroni) | H | Post Hoc | |
| PALLIDUM—M1 Mean (SD) | 0.000481 (0.000029) | 0.000536 (0.000044) | 0.000533 (0.000050) | <0.0001 | 15.83 | HS-BSP p = 0.005 |
| HS-CD p = 0.001 | ||||||
| BSP-CD ns | ||||||
| PALLIDUM—S1 Mean (SD) | 0.000505 (0.000032) | 0.000559 (0.000050) | 0.000539 (0.000051) | 0.005 | 10.54 | HS-BSP ns |
| HS-CD p = 0.005 | ||||||
| BSP-CD ns | ||||||
| PALLIDUM—SMA Mean (SD) | 0.000478 (0.000028) | 0.000546 (0.000039) | 0.000545 (0.000058) | <0.0001 | 23.73 | HS-BSP p < 0.0001 |
| HS-CD p < 0.0001 | ||||||
| BSP-CD ns | ||||||
| PUTAMEN—M1 Mean (SD) | 0.000531 (0.000034) | 0.000581 (0.000047) | 0.000583 (0.000054) | 0.002 | 11.99 | HS-BSP p = 0.009 |
| HS-CD p = 0.007 | ||||||
| BSP-CD ns | ||||||
| PUTAMEN—S1 Mean (SD) | 0.000539 (0.000033) | 0.000599 (0.000057) | 0.000585 (0.000055) | 0.003 | 11.32 | HS-BSP p = 0.041 |
| HS-CD p = 0.004 | ||||||
| BSP-CD ns | ||||||
| PUTAMEN—SMA Mean (SD) | 0.000515 (0.000027) | 0.000577 (0.000042) | 0.000572 (0.000058) | <0.0001 | 18.34 | HS-BSP p = 0.003 |
| HS-CD p < 0.0001 | ||||||
| BSP-CD ns | ||||||
| THALAMUS—M1 Mean (SD) | 0.000494 (0.000029) | 0.000540 (0.000040) | 0.000548 (0.000056) | 0.001 | 14.0 | HS-BSP p = 0.005 |
| HS-CD p = 0.003 | ||||||
| BSP-CD ns | ||||||
| THALAMUS—S1 Mean (SD) | 0.000509 (0.000031) | 0.000573 (0.000061) | 0.000555 (0.000062) | 0.005 | 10.78 | HS-BSP ns |
| HS-CD p = 0.005 | ||||||
| BSP-CD ns | ||||||
| THALAMUS—SMA Mean (SD) | 0.000494 (0.000026) | 0.000556 (0.000036) | 0.000552 (0.000052) | <0.0001 | 21.75 | HS-BSP p = 0.001 |
| HS-CD p < 0.0001 | ||||||
| BSP-CD ns | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giannì, C.; Piervincenzi, C.; Belvisi, D.; Tommasin, S.; De Bartolo, M.I.; Ferrazzano, G.; Petsas, N.; Leodori, G.; Fantoni, N.; Conte, A.; et al. Cortico-Subcortical White Matter Bundle Changes in Cervical Dystonia and Blepharospasm. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 753. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11030753
Giannì C, Piervincenzi C, Belvisi D, Tommasin S, De Bartolo MI, Ferrazzano G, Petsas N, Leodori G, Fantoni N, Conte A, et al. Cortico-Subcortical White Matter Bundle Changes in Cervical Dystonia and Blepharospasm. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(3):753. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11030753
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiannì, Costanza, Claudia Piervincenzi, Daniele Belvisi, Silvia Tommasin, Maria Ilenia De Bartolo, Gina Ferrazzano, Nikolaos Petsas, Giorgio Leodori, Nicoletta Fantoni, Antonella Conte, and et al. 2023. "Cortico-Subcortical White Matter Bundle Changes in Cervical Dystonia and Blepharospasm" Biomedicines 11, no. 3: 753. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11030753
APA StyleGiannì, C., Piervincenzi, C., Belvisi, D., Tommasin, S., De Bartolo, M. I., Ferrazzano, G., Petsas, N., Leodori, G., Fantoni, N., Conte, A., Berardelli, A., & Pantano, P. (2023). Cortico-Subcortical White Matter Bundle Changes in Cervical Dystonia and Blepharospasm. Biomedicines, 11(3), 753. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11030753






