HIV-HBV Coinfection—Current Challenges for Virologic Monitoring
Abstract
1. Introduction
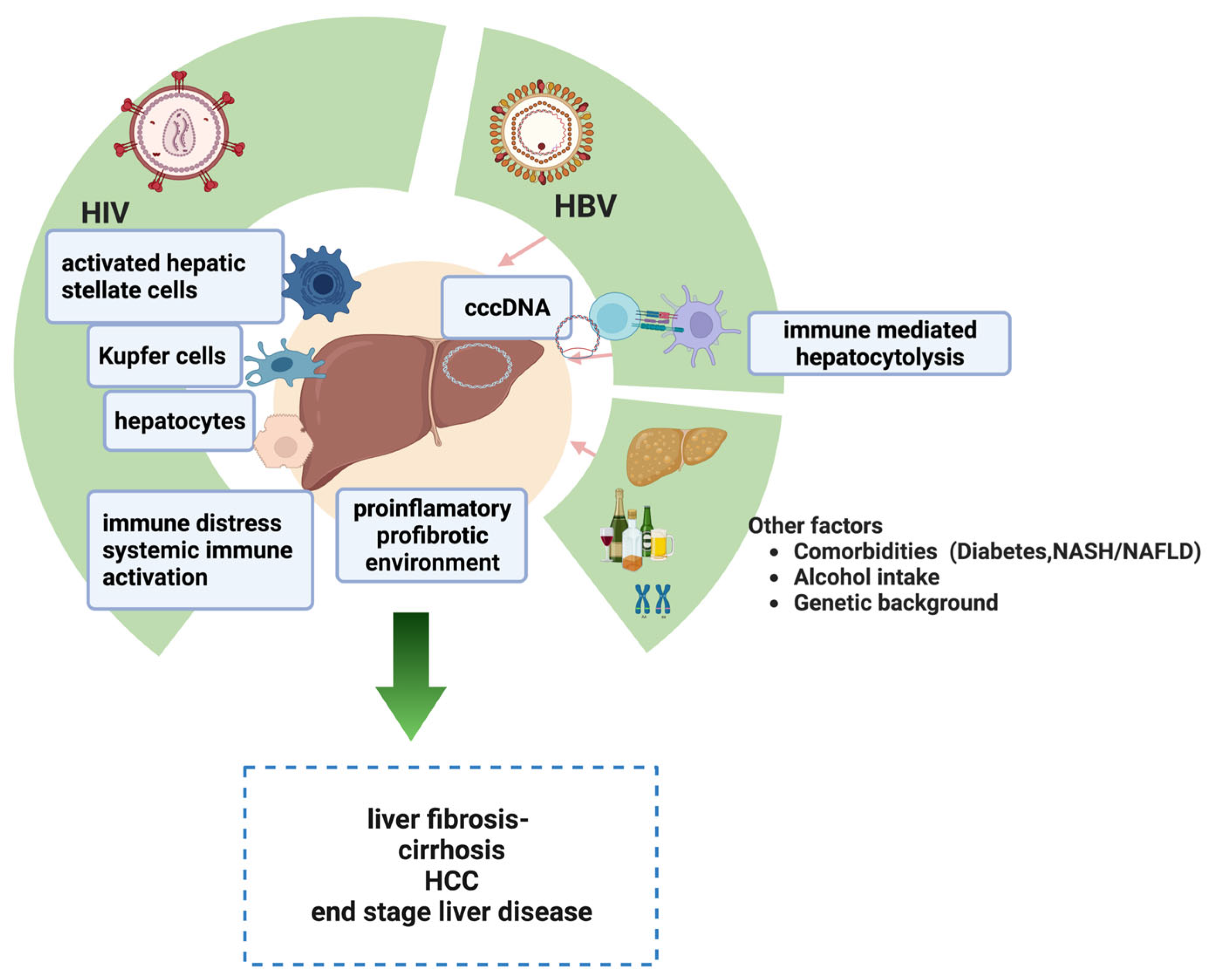
2. Pathogenesis of Liver Injuries in HIV-HBV Coinfected Patients
2.1. HIV-Related Factors
2.2. HBV-Related Factors
2.3. Other Contributing Factors
3. Virological Monitoring of Therapeutic Success in HIV-HBV Coinfection
3.1. Predictors of Treatment Efficacy—Biomarkers of Viral Replication
3.1.1. Covalently Closed Circular DNA (cccDNA)
3.1.2. Serum HBV-RNA
3.1.3. Hepatitis B Core–Related Antigen (HBcrAg)
3.1.4. Quantitative HBsAg
3.2. Predictors of Liver Fibrosis
3.2.1. Fibrosis Indexes Based on Serum Biomarkers
3.2.2. Imaging-Based Techniques for Detection of Liver Fibrosis
3.2.3. MicroRNAs, as Potential Surrogate Biomarkers for Liver Fibrosis
3.3. Tumor Markers and Predictors of Oncogenesis
3.3.1. Classic Tumor Markers
3.3.2. Indexes Based on Biochemical Markers as Predictors of Oncogenesis
3.3.3. Genetic Biomarkers
3.4. Viral and Host miRNAs That Can Act as Oncogenes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): Goal 3. Target 3.3: By 2030, End the Epidemics of AIDS, Tuberculosis, Malaria and Neglected Tropical Diseases and Combat Hepatitis, Water-Borne Diseases and Other Communicable Diseases [Poster]. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/208281 (accessed on 20 March 2023).
- Ganesan, M.; Poluektova, L.Y.; Kharbanda, K.K.; Osna, N.A. Human immunodeficiency virus and hepatotropic viruses comorbidities as the inducers of liver injury progression. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 398–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, P.A.; Zu, J.; Owolabi, K.M. Modeling the mechanics of viral kinetics under immune control during primary infection of HIV-1 with treatment in fractional order. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2020, 545, 123816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farman, M.; Tabassum, M.F.; Naik, P.A.; Akram, S. Numerical treatment of a nonlinear dynamical Hepatitis-B model: An evolutionary approach. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2020, 135, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Approximate Solution of a Nonlinear Fractional-Order HIV Model Using Homotopy Analysis Method. Available online: https://global-sci.org/intro/article_detail/ijnam/20349.html (accessed on 20 April 2023).
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Public Health Guidance on HIV, Hepatitis B and C Testing in the EU/EEA—An Integrated Approach. Stockholm: ECDC. 2018. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/sites/default/files/documents/hiv-hep-testing-guidance_0.pdf (accessed on 2 February 2023). [CrossRef]
- Platt, L.; French, C.E.; McGowan, C.R.; Sabin, K.; Gower, E.; Trickey, A.; McDonald, B.; Ong, J.; Stone, J.; Easterbrook, P.; et al. Prevalence and burden of HBV co-infection among people living with HIV: A global systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Viral Hepat. 2020, 27, 294–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutin, Y.; Nasrullah, M.; Easterbrook, P.; Nguimfack, B.D.; Burrone, E.; Averhoff, F.; Bulterys, M. Access to Treatment for Hepatitis B Virus Infection—Worldwide, 2016. MMWR. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2018, 67, 773–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thio, C.L.; Seaberg, E.C.; Skolasky, R.; Phair, J.; Visscher, B.; Muñoz, A.; Thomas, D.L. HIV-1, hepatitis B virus, and risk of liver-related mortality in the Multicenter Cohort Study (MACS). Lancet 2002, 360, 1921–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, K.E.; Peters, M.G.; Thomas, D. Human immunodeficiency virus and liver disease: A comprehensive update. Hepatol. Commun. 2017, 1, 987–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinchoff, J.; Tran, O.C.; Chen, L.; Bornschlegel, K.; Drobnik, A.; Kersanske, L.; Fuld, J. Impact of hepatitis B on mortality and specific causes of death in adults with and without HIV co-infection in NYC, 2000–2011. Epidemiol. Infect. 2016, 144, 3354–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, G.S.; Thompson, A.J. Viral hepatitis B: Clinical and epidemiological characteristics. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2014, 4, a024935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poynard, T.; Lebray, P.; Ingiliz, P.; Varaut, A.; Varsat, B.; Ngo, Y.; Norha, P.; Munteanu, M.; Drane, F.; Messous, D.; et al. Prevalence of liver fibrosis and risk factors in a general population using non-invasive biomarkers (FibroTest). BMC Gastroenterol. 2010, 10, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roșca, A.; Iacob, D.; Ene, L.; Temereanca, A.; Grancea, C.; Sultana, C.; Achim, C.L.; Ruță, S. Liver function in a cohort of young HIV-HBV co-infected patients on long-term combined antiretroviral therapy. Farmacia 2020, 68, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wandeler, G.; Mulenga, L.; Vinikoor, M.J.; Kovari, H.; Battegay, M.; Calmy, A.; Cavassini, M.; Bernasconi, E.; Schmid, P.; Bolton-Moore, C.; et al. Liver fibrosis in treatment-naïve HIV-infected and HIV/HBV co-infected patients: Zambia and Switzerland compared. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 51, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallet, V.; Vallet-Pichard, A.; Pol, S. The impact of human immunodeficiency virus on viral hepatitis. Liver Int. 2011, 31, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thio, C.L.; Smeaton, L.; Saulynas, M.; Hwang, H.; Saravan, S.; Kulkarni, S.; Hakim, J.; Nyirenda, M.; Iqbal, H.S.; Lalloo, U.G.; et al. Characterization of HIV-HBV coinfection in a multinational HIV-infected cohort. AIDS 2013, 27, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haussig, J.M.; Nielsen, S.; Gassowski, M.; Bremer, V.; Marcus, U.; Wenz, B.; Bannert, N.; Bock, C.T.; Zimmermann, R. A large proportion of people who inject drugs are susceptible to hepatitis B: Results from a bio-behavioural study in eight German cities. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 66, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, M.-H.; Tsai, J.-J.; Hsieh, M.-Y.; Huang, C.-F.; Yeh, M.-L.; Yang, J.-F.; Chang, K.; Lin, W.-R.; Lin, C.-Y.; Chen, T.-C.; et al. Hepatitis C Virus Infection among Injection Drug Users with and without Human Immunodeficiency Virus Co-Infection. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, J.D.D.; Simaleko, M.M.; Diemer, H.S.C.; Grésenguet, G.; Brücker, G.; Belec, L. Risk factors for HIV infection among female sex workers in Bangui, Central African Republic. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EACS European AIDS Clinical Society. EACS Guidelines 11.0. 2021. Available online: https://www.eacsociety.org/media/final2021eacsguidelinesv11.0_oct2021.pdf (accessed on 3 March 2022).
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL 2017 Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of hepatitis B virus infection q. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 370–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, H.; Dunn, D.; Pillay, D.; Bani-Sadr, F.; de Vries-Sluijs, T.; Jain, M.K.; Kuzushita, N.; Mauss, S.; Núñez, M.; Nüesch, R.; et al. Suppression of HBV by Tenofovir in HBV/HIV Coinfected Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, A.; Bottero, J.; Miailhes, P.; Lascoux-Combe, C.; Rougier, H.; Girard, P.-M.; Serfaty, L.; Lacombe, K. Liver fibrosis regression and progression during controlled hepatitis B virus infection among HIV-HBV patients treated with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate in France: A prospective cohort study. J. Int. AIDS Soc. 2017, 20, 21426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozaras, R.; Corti, G.; Ruta, S.; Lacombe, K.; Mondelli, M.U.; Irwing, W.L.; Puoti, M.; Khalighi, A.; Santos, M.L.; Harxhi, A.; et al. Differences in the availability of diagnostics and treatment modalities for chronic hepatitis B across Europe. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015, 21, 1027–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Welzen, B.J.; Smit, C.; Boyd, A.; I Lieveld, F.; Mudrikova, T.; Reiss, P.; E Brouwer, A.; Hoepelman, A.I.M.; E Arends, J. Decreased All-Cause and Liver-Related Mortality Risk in HIV/Hepatitis B Virus Coinfection Coinciding With the Introduction of Tenofovir-Containing Combination Antiretroviral Therapy. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2020, 7, ofaa226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Althoff, K.N.; Jing, Y.; Horberg, M.A.; Buchacz, K.; Gill, M.J.; Justice, A.C.; Rabkin, C.S.; Goedert, J.J.; Sigel, K.; et al. Trends in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Incidence and Risk Among Persons With HIV in the US and Canada, 1996–2015. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, 2037512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nina Kim, H.; Newcomb, C.W.; Carbonari, D.M.; Roy, J.A.; Torgersen, J.; Althoff, K.N.; Kitahata, M.M.; Rajender Reddy, K.; Lim, J.K.; Silverberg, M.J.; et al. Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Hepatitis B Viremia among HIV/Hepatitis B Virus-Coinfected Persons in North America. Hepatology 2021, 74, 1190–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willemse, S.; Smit, C.; Sogni, P.; Sarcletti, M.; Uberti-Foppa, C.; Wittkop, L.; Raben, D.; Monforte, A.D. Low compliance with hepatocellular carcinoma screening guidelines in hepatitis B/C virus co-infected HIV patients with cirrhosis. J. Viral Hepat. 2019, 26, 1224–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corcorran, M.A.; Kim, N. Chronic hepatitis B and HIV coinfection. Top. Antivir. Med. 2023, 31, 14–22. [Google Scholar]
- Parvez, M.K. HBV and HIV co-infection: Impact on liver pathobiology and: Therapeutic approaches. World J. Hepatol. 2015, 7, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- North, T.W.; Higgins, J.; Deere, J.D.; Hayes, T.L.; Villalobos, A.; Adamson, L.; Shacklett, B.L.; Schinazi, R.F.; Luciw, P.A. Viral Sanctuaries during Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy in a Nonhuman Primate Model for AIDS. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 2913–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, F.; Saiman, Y.; Si, C.; Mosoian, A.; Bansal, M.B. X4 Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 gp120 Promotes Human Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation and Collagen I Expression through Interactions with CXCR4. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debes, J.D.; Bohjanen, P.R.; Boonstra, A. Mechanisms of accelerated liver fibrosis progression during HIV infection. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2016, 4, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Gong, R.; Mu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, C.; Sun, Z.; Chen, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, J. Hepatitis B Virus Induces a Novel Inflammation Network Involving Three Inflammatory Factors, IL-29, IL-8, and Cyclooxygenase-2. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 4844–4860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maggi, P.; Altizio, S.; Di Biagio, A.; Nicolini, L.; Volpe, A.; Tancorre, T.; Leone, A.; Bellacosa, C.; Ladisa, N.; Angarano, G. Prevalence and Risk Factors for Significant Liver Fibrosis in Patients with HIV Infection. In Vivo 2015, 29, 771–775. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lombardi, R.; Lever, R.; Smith, C.; Marshall, N.; Rodger, A.; Bhagani, S.; Tsochatzis, E. Liver test abnormalities in patients with HIV mono-infection: Assessment with simple noninvasive fibrosis markers. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2017, 30, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, S.L. Hepatic stellate cells: Protean, multifunctional, and enigmatic cells of the liver. Physiol. Rev. 2008, 88, 125–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuyama, A.C.; Hong, F.; Saiman, Y.; Wang, C.; Ozkok, D.; Mosoian, A.; Chen, P.; Chen, B.K.; Klotman, M.E.; Bansal, M.B. Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)-1 Infects Human Hepatic Stellate Cells and Promotes Collagen I and Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 Expression: Implications for the Pathogenesis of HIV/Hepatitis C Virus–Induced Liver Fibrosis. Hepatology 2010, 52, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitahata, M.M.; Drozd, D.R.; Crane, H.M.; Van Rompaey, S.E.; Althoff, K.N.; Gange, S.J.; Klein, M.B.; Lucas, G.M.; Abraham, A.G.; Lo Re, V.; et al. Ascertainment and verification of end-stage renal disease and end-stage liver disease in the north american AIDS cohort collaboration on research and design. AIDS Res. Treat. 2015, 2015, 923194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gange, S.J.; Kitahata, M.M.; Saag, M.S.; Bangsberg, D.R.; Bosch, R.J.; Brooks, J.T.; Calzavara, L.; Deeks, S.G.; Eron, J.J.; Gebo, K.A.; et al. Cohort Profile: The North American AIDS Cohort Collaboration on Research and Design (NA-ACCORD). Int. J. Epidemiol. 2007, 36, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Bansal, M.B. Role of Kupffer Cells in Driving Hepatic Inflammation and Fibrosis in HIV Infection. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, M.B.; Althoff, K.N.; Jing, Y.; Lau, B.; Kitahata, M.; Lo Re, V.; Kirk, G.D.; Hull, M.; Kim, H.N.; Sebastiani, G.; et al. Risk of End-Stage Liver Disease in HIV-Viral Hepatitis Coinfected Persons in North America from the Early to Modern Antiretroviral Therapy Eras. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 63, 1160–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobran, S.T.; Ancuta, P.; Shoukry, N.H. A Tale of Two Viruses: Immunological Insights into HCV/HIV Coinfection. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 726419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.; Gaseitsiwe, S.; Moyo, S.; Thami, K.P.; Mohammed, T.; Setlhare, D.; Sebunya, T.K.; Powell, E.A.; Makhema, J.; Blackard, J.T.; et al. Slow CD4+ T-Cell Recovery in Human Immunodeficiency Virus/Hepatitis B Virus-Coinfected Patients Initiating Truvada-Based Combination Antiretroviral Therapy in Botswana. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2016, 3, ofw140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouame, G.M.; Boyd, A.; Moh, R.; Badje, A.; Gabillard, D.; Ouattara, E.; Ntakpe, J.B.; Emième, A.; Maylin, S.; Chekaraou, M.A.; et al. Higher Mortality Despite Early Antiretroviral Therapy in Human Immunodeficiency Virus and Hepatitis B Virus (HBV)-Coinfected Patients with High HBV Replication. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 66, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crane, M.; Oliver, B.; Matthews, G.; Avihingsanon, A.; Ubolyam, S.; Markovska, V.; Chang, J.J.; Dore, G.J.; Price, P.; Visvanathan, K.; et al. Immunopathogenesis of Hepatic Flare in HIV/Hepatitis B Virus (HBV)–Coinfected Individuals after the Initiation of HBV-Active Antiretroviral Therapy. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 199, 974–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, M.L.; Liaw, Y.F. Hepatitis B flares in chronic hepatitis B: Pathogenesis, natural course, and management. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, 1407–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ming, D.; Yu, X.; Guo, R.; Deng, Y.; Li, J.; Lin, C.; Su, M.; Lin, Z.; Su, Z. Elevated TGF-β1/IL-31 pathway is associated with the disease severity of Hepatitis B virus-related liver cirrhosis. Viral Immunol. 2015, 28, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakimi, K.; Isogawa, M.; Chung, J.; Sette, A.; Chisari, F.V. Immunogenicity and Tolerogenicity of Hepatitis B Virus Structural and Nonstructural Proteins: Implications for Immunotherapy of Persistent Viral Infections. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 8609–8620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reignat, S.; Webster, G.J.M.; Brown, D.; Ogg, G.S.; King, A.; Seneviratne, S.L.; Dusheiko, G.; Williams, R.; Maini, M.K.; Bertoletti, A. Escaping high viral load exhaustion: CD8 cells with altered tetramer binding in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J. Exp. Med. 2002, 195, 1089–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Fu, J.; Jin, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, C.; Zou, Z.; Zhao, J.-M.; Zhang, B.; Shi, M.; Ding, X.; et al. Circulating and Liver Resident CD4 + CD25 + Regulatory T Cells Actively Influence the Antiviral Immune Response and Disease Progression in Patients with Hepatitis B. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Sun, X.-H.; Zhu, X.-J.; Jin, S.-G.; Zeng, Z.-J.; Zhou, Z.-H.; Yu, Z.; Gao, Y.-Q. HBcAg induces PD-1 upregulation on CD4+T cells through activation of JNK, ERK and PI3K/AKT pathways in chronic hepatitis-B-infected patients. Lab. Investig. 2012, 92, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.S.; Zhou, Y.; Li, C.Z.; Wan, M. Bin Natural course of chronic hepatitis B is characterized by changing patterns of programmed death type-1 of CD8-positive T cells. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 618–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Meng, Z.; Jiang, M.; Pei, R.; Trippler, M.; Broering, R.; Bucchi, A.; Sowa, J.P.; Dittmer, U.; Yang, D.; et al. Hepatitis B virus suppresses toll-like receptor-mediated innate immune responses in murine parenchymal and nonparenchymal liver cells. Hepatology 2009, 49, 1132–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, Z.-T.; Liu, W.; Wu, S.-X.; He, Y.; Lin, Y.-T.; Chen, W.-N.; Lin, X.-J.; Lin, X. Hepatitis B Virus Surface Antigen Enhances the Sensitivity of Hepatocytes to Fas-Mediated Apoptosis via Suppression of AKT Phosphorylation. J. Immunol. 2018, 201, 2303–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-Romieu, A.C.; Garg, S.; Rosenberg, E.S.; Thompson-Paul, A.M.; Skarbinski, J. Is diabetes prevalence higher among HIV-infected individuals compared with the general population? Evidence from MMP and NHANES 2009–2010. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2017, 5, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, T.F.; Rosen, E.; Carr, R.; Brashear, M.; Simon, L.; Theall, K.P.; Ronis, M.J.; Welsh, D.A.; Molina, P.E. Associations of Liver Disease with Alcohol Use among People Living with HIV and the Role of Hepatitis C: The New Orleans Alcohol Use in HIV Study. Alcohol Alcohol. 2020, 55, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, Z.A.; Wong, S.; Rossi, C.; Binka, M.; Wong, J.; Yu, A.; Darvishian, M.; Alvarez, M.; Chapinal, N.; Mckee, G.; et al. Concurrent Hepatitis C and B Virus and Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infections Are Associated with Higher Mortality Risk Illustrating the Impact of Syndemics on Health Outcomes. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2020, 7, ofaa347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soti, S.; Corey, K.E.; Lake, J.E.; Erlandson, K.M. NAFLD and HIV: Do Sex, Race, and Ethnicity Explain HIV-Related Risk? Curr. HIV/AIDS Rep. 2018, 15, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woreta, T.A.; Chalasani, N. Fatty Liver Disease in Human Immunodeficiency Virus–Hepatitis B Virus Coinfection: A Cause for Concern. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 73, e3286–e3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suliman, I.; Abdelgelil, N.; Kassamali, F.; Hassanein, T.I. The Effects of Hepatic Steatosis on the Natural History of HBV Infection. Clin. Liver Dis. 2019, 23, 433–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, G.; Owusu, D.; Smith, C.; Azumah, M.; Abdullahi, A.; Phillips, S.; Sayeed, L.; Austin, H.; Chadwick, D.; Phillips, R.O.; et al. Liver steatosis and fibrosis in people with human immunodeficiency virus in West Africa and the relationship with hepatitis B virus coinfection. Hepatol. Commun. 2022, 6, 3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.-W.; Kramvis, A.; Liang, S.; He, X.; Chen, Q.-Y.; Wang, C.; Yang, Q.-L.; Hu, L.-P.; Jia, H.-H.; Fang, Z.-L. Higher prevalence of cancer related mutations 1762T/1764A and PreS deletions in hepatitis B virus (HBV) isolated from HBV/HIV co-infected compared to HBV-mono-infected Chinese adults. Virus Res. 2017, 227, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audsley, J.; Littlejohn, M.; Yuen, L.; Sasadeusz, J.; Ayres, A.; Desmond, C.; Spelman, T.; Lau, G.; Matthews, G.V.; Avihingsanon, A.; et al. HBV mutations in untreated HIV-HBV co-infection using genomic length sequencing. Virology 2010, 405, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryom, L.; Cotter, A.; De Miguel, R.; Béguelin, C.; Podlekareva, D.; Arribas, J.R.; Marzolini, C.; Mallon, P.G.M.; Rauch, A.; Kirk, O.; et al. 2019 update of the European AIDS Clinical Society Guidelines for treatment of people living with HIV version 10.0. HIV Med. 2020, 21, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokrzycki, M.H.; Harris, C.; May, H.; Laut, J.; Palmisano, J. Lactic acidosis associated with stavudine administration: A report of five cases. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2000, 30, 198–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte-Rojo, A.; Heathcote, E.J. Efficacy and safety of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Therap. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2010, 3, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamroonkul, N.; Bansal, M.B. HIV and the liver. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharan, N.J.; Neuhaus, J.; Rockstroh, J.K.; Peters, L.; Gordin, F.; Arenas-Pinto, A.; Emerson, C.; Marks, K.; Hidalgo, J.; Sarmento-Castro, R.; et al. Benefit of Early versus Deferred Antiretroviral Therapy on Progression of Liver Fibrosis among People with HIV in the START Randomized Trial. Hepatology 2019, 69, 1135–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassal, M. HBV cccDNA: Viral persistence reservoir and key obstacle for a cure of chronic hepatitis B. Gut 2015, 64, 1972–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.L.; Wong, D.; Ip, P.; Kopaniszen, M.; Seto, W.K.; Fung, J.; Huang, F.Y.; Lee, B.; Cullaro, G.; Chong, C.K.; et al. Reduction of covalently closed circular DNA with long-term nucleos(t)ide analogue treatment in chronic hepatitis B. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebossé, F.; Inchauspé, A.; Locatelli, M.; Miaglia, C.; Diederichs, A.; Fresquet, J.; Chapus, F.; Hamed, K.; Testoni, B.; Zoulim, F. Quantification and epigenetic evaluation of the residual pool of hepatitis B covalently closed circular DNA in long-term nucleoside analogue-treated patients. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Bai, R.; Zhao, Z.; Tao, L.; Ma, M.; Ji, Z.; Jian, M.; Ding, Z.; Dai, X.; Bao, F.; et al. Application of droplet digital PCR to detect the pathogens of infectious diseases. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38, BSR20181170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jiang, M.; Xue, J.; Yan, H.; Liang, X. Serum HBV RNA quantification: Useful for monitoring natural history of chronic hepatitis B infection. BMC Gastroenterol. 2019, 19, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, R.T.; King, W.C.; Ghany, M.G.; Lisker-Melman, M.; Hinerman, A.S.; Khalili, M.; Sulkowski, M.; Jain, M.K.; Choi, E.Y.K.; Nalesnik, M.A.; et al. A Prospective Cohort Study of Novel Markers of Hepatitis B Virus Replication in Human Immunodeficiency Virus Coinfection. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 21, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkins, C.; Kang, M.; Bhattacharya, D.; Cloherty, G.; Kuhns, M.; Matining, R.; Thio, C.; Samaneka, W.; Chinula, L.; Mulinda, N.; et al. Hepatitis B surface antigen and hepatitis B RNA changes in HIV/hepatitis B virus co-infected participants receiving hepatitis B virus-active antiretroviral therapy. AIDS 2022, 36, 975–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, T.; Tanaka, Y. Novel biomarkers for the management of chronic hepatitis B. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2020, 26, 261–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Li, X.; Lu, L.; Liu, X.; Song, X.; Li, Y.; Han, Y.; Zhu, T.; Cao, W.; Li, T. HBV pgRNA profiles in Chinese HIV/HBV coinfected patients under pre- and posttreatment: A multicentre observational cohort study. J. Viral Hepat. 2022, 29, 616–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, T.; Tanaka, Y. The role of hepatitis B core-related antigen. Genes 2019, 10, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locarnini, S.; Zoulim, F. Molecular genetics of HBV infection. Antivir. Ther. 2010, 15, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, T.; Ohno, N.; Terada, N.; Rokuhara, A.; Matsumoto, A.; Yagi, S.; Tanaka, E.; Kiyosawa, K.; Ohno, S.; Maki, N. Hepatitis B Virus DNA-negative Dane Particles Lack Core Protein but Contain a 22-kDa Precore Protein without C-terminal Arginine-rich Domain*. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 21713–21719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, T.C.; Liu, C.J.; Yang, W.T.; Chen, C.L.; Yang, H.C.; Su, T.H.; Wang, C.C.; Kuo, S.F.T.; Liu, C.H.; Chen, P.J.; et al. Hepatitis B surface antigen level complements viral load in predicting viral reactivation in spontaneous HBeAg seroconverters. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 29, 1242–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinot-Peignoux, M.; Asselah, T.; Marcellin, P. HBsAg quantification to optimize treatment monitoring in chronic hepatitis B patients. Liver Int. 2015, 35, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Li, W.; Lu, C.; Huang, Y.; Chen, L. Serum hepatitis B surface antigen levels predict insignificant fibrosis and non-cirrhosis in hepatitis B e antigen positive patients with normal or mildly elevated alanine transaminase levels. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 86463–86470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonneveld, M.J.; Hansen, B.E.; Brouwer, W.P.; Chan, H.L.Y.; Piratvisuth, T.; Jia, J.D.; Zeuzem, S.; Chien, R.N.; De Knegt, R.J.; Wat, C.; et al. Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Levels Can Be Used to Rule Out Cirrhosis in Hepatitis B e Antigen-Positive Chronic Hepatitis B: Results From the SONIC-B Study. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 225, 1967–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limothai, U.; Chuaypen, N.; Poovorawan, K.; Chotiyaputta, W.; Tanwandee, T.; Poovorawan, Y.; Tangkijvanich, P. Reverse transcriptase droplet digital PCR vs reverse transcriptase quantitative real-time PCR for serum HBV RNA quantification. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 3365–3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vachon, A.; Osiowy, C. Novel Biomarkers of Hepatitis B Virus and Their Use in Chronic Hepatitis B Patient Management. Viruses 2021, 13, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dezanet, L.N.C.; Maylin, S.; Gabassi, A.; Rougier, H.; Miailhes, P.; Lascoux-Combe, C.; Chas, J.; Girard, P.M.; Delaugerre, C.; Lacombe, K.; et al. Kinetics of hepatitis B core-related antigen and anti-hepatitis B core antibody and their association with serological response in human immunodeficiency virus-hepatitis B coinfection. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 221, 1826–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevaliez, S.; Hézode, C.; Bahrami, S.; Grare, M.; Pawlotsky, J.M. Long-term hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) kinetics during nucleoside/nucleotide analogue therapy: Finite treatment duration unlikely. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Lu, S.N.; Hung, C.H.; Wang, J.H.; Hu, T.H.; Changchien, C.S.; Lee, C.M. The role of hepatitis B surface antigen quantification in predicting HBsAg loss and HBV relapse after discontinuation of lamivudine treatment. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaroszewicz, J.; Reiberger, T.; Meyer-Olson, D.; Mauss, S.; Vogel, M.; Ingiliz, P.; Payer, B.A.; Stoll, M.; Manns, M.P.; Schmidt, R.E.; et al. Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Concentrations in Patients with HIV/HBV Co-Infection. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrault, N.A.; Bzowej, N.H.; Chang, K.M.; Hwang, J.P.; Jonas, M.M.; Murad, M.H. AASLD guidelines for treatment of chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2016, 63, 261–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for the Prevention, Care and Treatment of Persons with Chronic Hepatitis B Infection; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, W.; Sun, Q.; Fan, J.; Lin, S.; Ye, B. AST to Platelet Ratio Index Predicts Mortality in Hospitalized Patients With Hepatitis B-Related Decompensated Cirrhosis. Medicine 2016, 95, e2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Gui, X.; Ke, H.; Yu, X.; Yan, Y.; Xiong, Y. Accuracy of FIB-4 and APRI scores compared to transient elastography for liver fibrosis in patients with HIV and HBV co-infection. Int. J. STD AIDS 2023, 34, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottero, J.; Lacombe, K.; Guéchot, J.; Serfaty, L.; Miailhes, P.; Bonnard, P.; Wendum, D.; Molina, J.M.; Lascoux-Combe, C.; Girard, P.M. Performance of 11 biomarkers for liver fibrosis assessment in HIV/HBV co-infected patients. J. Hepatol. 2009, 50, 1074–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stockdale, A.J.; Phillips, R.O.; Beloukas, A.; Appiah, L.T.; Chadwick, D.; Bhagani, S.; Bonnett, L.; Sarfo, F.S.; Dusheiko, G.; Geretti, A.M. Liver Fibrosis by Transient Elastography and Virologic Outcomes after Introduction of Tenofovir in Lamivudine-Experienced Adults with HIV and Hepatitis B Virus Coinfection in Ghana. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 61, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraioli, G.; Filice, C.; Castera, L.; Choi, B.I.; Sporea, I.; Wilson, S.R.; Cosgrove, D.; Dietrich, C.F.; Amy, D.; Bamber, J.C.; et al. WFUMB Guidelines and Recommendations for Clinical Use of Ultrasound Elastography: Part 3: Liver. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2015, 41, 1161–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van de Putte, D.F.; Blom, R.; van Soest, H.; Mundt, M.; Verveer, C.; Arends, J.; de Knegt, R.E.; Mauser-Bunschoten, E.; van Erpecum, K. Impact of Fibroscan on management of chronic viral hepatitis in clinical practice. Ann. Hepatol. 2011, 10, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.E.; Chen, Y.P. Clinical application of vibration controlled transient elastography in patients with chronic hepatitis B. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2017, 5, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waidmann, O.; Bihrer, V.; Pleli, T.; Farnik, H.; Berger, A.; Zeuzem, S.; Kronenberger, B.; Piiper, A. Serum microRNA-122 levels in different groups of patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J. Viral Hepat. 2012, 19, e58–e65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, D.D.; Suzuki, K.; Law, M.; Trebicka, J.; Neuhaus Nordwall, J.; Johnson, M.; Vjecha, M.J.; Kelleher, A.D.; Emery, S. Circulating MIR-122 and MIR-200a as biomarkers for fatal liver disease in ART-treated, HIV-1-infected individuals. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantri, C.K.; Pandhare Dash, J.; Mantri, J.V.; Dash, C.C.V. Cocaine Enhances HIV-1 Replication in CD4+ T Cells by Down-Regulating MiR-125b. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loureiro, D.; Tout, I.; Narguet, S.; Benazzouz, S.M.; Mansouri, A.; Asselah, T. miRNAs as Potential Biomarkers for Viral Hepatitis B and C. Viruses 2020, 12, 1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefpouran, S.; Mostafaei, S.; Manesh, P.V.; Iranifar, E.; Bokharaei-Salim, F.; Nahand, J.S.; Mirzaei, H.; Taran, M.; Babaei, F.; Sayad, B.; et al. The assessment of selected MiRNAs profile in HIV, HBV, HCV, HIV/HCV, HIV/HBV Co-infection and elite controllers for determination of biomarker. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 147, 104355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyoda, H.; Kumada, T.; Tada, T.; Sone, Y.; Kaneoka, Y.; Maeda, A. Tumor Markers for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Simple and Significant Predictors of Outcome in Patients with HCC. Liver Cancer 2015, 4, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuaypen, N.; Chittmittraprap, S.; Pinjaroen, N.; Sirichindakul, B.; Poovorawan, Y.; Tanaka, Y.; Tangkijvanich, P. Serum Wisteria floribunda agglutinin-positive Mac-2 binding protein level as a diagnostic marker of hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol. Res. 2018, 48, 872–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.U.; Heo, J.Y.; Kim, B.K.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, D.Y.; Han, K.H.; Ahn, S.H.; Kim, H.S. Wisteria floribunda agglutinin-positive human Mac-2 binding protein predicts the risk of HBV-related liver cancer development. Liver Int. 2017, 37, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.D.; Addissie, B.D.; Mara, K.C.; Harmsen, W.S.; Dai, J.; Zhang, N.; Wongjarupong, N.; Ali, H.M.; Ali, H.A.; Hassan, F.A.; et al. GALAD Score for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Detection in Comparison to Liver Ultrasound and Proposal of GALADUS Score. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2019, 28, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Zhou, Y.; Sui, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xie, H.; Gao, H.; Fan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, M.; et al. HBV-encoded miR-2 functions as an oncogene by downregulating TRIM35 but upregulating RAN in liver cancer cells. EBioMedicine 2019, 48, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavalit, T.; Nimsamer, P.; Sirivassanametha, K.; Anuntakarun, S.; Saengchoowong, S.; Tangkijvanich, P.; Payungporn, S. Hepatitis B Virus-Encoded MicroRNA (HBV-miR-3) Regulates Host Gene PPM1A Related to Hepatocellular Carcinoma. MicroRNA 2019, 9, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.; Li, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, J.; Sheng, Y.; Wang, S.; Huang, A.; Tang, H. Up-regulated MicroRNA-181a induces carcinogenesis in Hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting E2F5. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, R.; Papatheodoridis, G.; Sun, J.; Innes, H.; Toyoda, H.; Xie, Q.; Mo, S.; Sypsa, V.; Guha, I.N.; Kumada, T.; et al. aMAP risk score predicts hepatocellular carcinoma development in patients with chronic hepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 1368–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Macedo Costa, A.P.; da Silva, M.A.C.N.; Castro, R.S.; de Oliveira Sampaio, A.L.; Júnior, A.M.A.; da Silva, M.C.; Ferreira, A.d.S.P. PAGE-B and REACH-B Predicts the Risk of Developing Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients from Northeast, Brazil. Viruses 2022, 14, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galle, P.R.; Forner, A.; Llovet, J.M.; Mazzaferro, V.; Piscaglia, F.; Raoul, J.L.; Schirmacher, P.; Vilgrain, V. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 182–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, W.; Lin, Z.; Xin, Y.; Jiang, X.; Dong, Q.; Xuan, S. Diagnostic accuracy of the aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index for the prediction of hepatitis B-related fibrosis: A leading meta-analysis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2012, 12, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.K.; Kim, D.Y.; Park, J.Y.; Ahn, S.H.; Chon, C.Y.; Kim, J.K.; Paik, Y.H.; Lee, K.S.; Park, Y.N.; Han, K.H. Validation of FIB-4 and comparison with other simple noninvasive indices for predicting liver fibrosis and cirrhosis in hepatitis B virus-infected patients. Liver Int. 2010, 30, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berzigotti, A.; Tsochatzis, E.; Boursier, J.; Castera, L.; Cazzagon, N.; Friedrich-Rust, M.; Petta, S.; Thiele, M. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines on non-invasive tests for evaluation of liver disease severity and prognosis—2021 update. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, 659–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterling, R.K.; Lissen, E.; Clumeck, N.; Sola, R.; Correa, M.C.; Montaner, J.; Sulkowski, M.S.; Torriani, F.J.; Dieterich, D.T.; Thomas, D.L.; et al. Development of a simple noninvasive index to predict significant fibrosis in patients with HIV/HCV coinfection. Hepatology 2006, 43, 1317–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Zou, J.; Li, Q.; Chen, L. Diagnostic value of FIB-4 for liver fibrosis in patients with hepatitis B: A meta-analysis of diagnostic test. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 22944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wai, C.T.; Greenson, J.K.; Fontana, R.J.; Kalbfleisch, J.D.; Marrero, J.A.; Conjeevaram, H.S.; Lok, A.S.F. A simple noninvasive index can predict both significant fibrosis and cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 2003, 38, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.H.; Xin, Y.N.; Dong, Q.J.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, X.J.; Zhan, S.H.; Sun, Y.; Xuan, S.Y. Performance of the aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index for the staging of hepatitis C-related fibrosis: An updated meta-analysis. Hepatology 2011, 53, 726–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Jiang, Y.; Gong, G. Evaluation of seven noninvasive models in staging liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 25, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ucar, F.; Sezer, S.; Ginis, Z.; Ozturk, G.; Albayrak, A.; Basar, O.; Ekiz, F.; Coban, S.; Yuksel, O.; Armutcu, F.; et al. APRI, the FIB-4 score, and Forn’s index have noninvasive diagnostic value for liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 25, 1076–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iacob, D.G.; Luminos, M.; Benea, O.E.; Tudor, A.M.; Olariu, C.M.; Iacob, S.A.; Ruta, S. Liver fibrosis progression in a cohort of young HIV and HIV/HBV co-infected patients: A longitudinal study using non-invasive APRI and Fib-4 scores. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Gui, X.; Ke, H.; Xiong, Y.; Gao, S. Combination antiretroviral therapy is associated with reduction in liver fibrosis scores in patients with HIV and HBV co-infection. AIDS Res. Ther. 2021, 18, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calès, P.; Oberti, F.; Michalak, S.; Hubert-Fouchard, I.; Rousselet, M.C.; Konaté, A.; Gallois, Y.; Ternisien, C.; Chevallier, A.; Lunel, F. A novel panel of blood markers to assess the degree of liver fibrosis. Hepatology 2005, 42, 1373–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; An, Y.; Liao, Y.; Wu, X.; Tao, C.; Wang, L.; Cai, B. Circulating IL-1β, IL-17, and IP-10 as Potential Predictors of Hepatitis B Virus Infection Prognosis. J. Immunol. Res. 2022, 2022, 5202898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultana, C.; Erscoiu, S.M.; Grancea, C.; Ceausu, E.; Ruta, S. Predictors of Chronic Hepatitis C Evolution in HIV Co-Infected Patients From Romania. Hepat. Mon. 2013, 13, e8611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Yin, X.; Shang, H.; Jiang, Y. IP-10 is highly involved in HIV infection. Cytokine 2019, 115, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterling, R.K.; Wahed, A.S.; King, W.C.; Kleiner, D.E.; Khalili, M.; Sulkowski, M.; Chung, R.T.; Jain, M.K.; Lisker-Melman, M.; Wong, D.K.; et al. Spectrum of Liver Disease in Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Patients Co-infected with Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV): Results of the HBV-HIV Cohort Study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 114, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maida, I.; Soriano, V.; Castellares, C.; Ramos, B.; Sotgiu, G.; Martin-Carbonero, L.; Barreiro, P.; Rivas, P.; González-Lahoz, J.; Núñez, M. Liver fibrosis in HIV-infected patients with chronic hepatitis B extensively exposed to antiretroviral therapy with anti-HBV activity. HIV Clin. Trials 2006, 7, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audsley, J.; Robson, C.; Aitchison, S.; Matthews, G.V.; Iser, D.; Sasadeusz, J.; Lewin, S.R. Liver fibrosis regression measured by transient elastography in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-hepatitis B virus (HBV)-coinfected individuals on long-term HBV-active combination antiretroviral therapy. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2016, 3, ofw035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miailhes, P.; Pradat, P.; Chevallier, M.; Lacombe, K.; Bailly, F.; Cotte, L.; Trabaud, M.A.; Boibieux, A.; Bottero, J.; Trepo, C.; et al. Proficiency of transient elastography compared to liver biopsy for the assessment of fibrosis in HIV/HBV-coinfected patients. J. Viral Hepat. 2011, 18, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Chen, L.; Zhou, Y. Diagnostic accuracy of liver stiffness measurement in chronic hepatitis B patients with normal or mildly elevated alanine transaminase levels. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, X.; An, M.; Wu, T.; Jiang, D.; Peng, M.; Wang, W.; Wang, J.; Zhang, C.; Li, Z.; Liu, F.; et al. Transient Elastography for Significant Liver Fibrosis and Cirrhosis in Chronic Hepatitis B: A Meta-Analysis. Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 2018, 3406789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, G.V.; Seaberg, E.C.; Avihingsanon, A.; Bowden, S.; Dore, G.J.; Lewin, S.R.; Sasadeusz, J.; Revill, P.A.; Littlejohn, M.; Hoy, J.F.; et al. Patterns and causes of suboptimal response to tenofovir-based therapy in individuals coinfected with HIV and hepatitis B virus. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 56, e87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, L.; Xie, H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, B.; Luo, C.; Wang, S.; Tang, M.; Fu, Z.; Ruan, H.; et al. The relationship between serum hepatitis B virus DNA level and liver histology in patients with chronic HBV infection. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iacob, D.G.; Rosca, A.; Ruta, S.M. Circulating microRNAs as non-invasive biomarkers for hepatitis B virus liver fibrosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 1113–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhou, P.; Deng, W.; Wang, J.; Mao, R.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Yu, J.; Yang, F.; Huang, Y.; et al. Serum microRNA-125b correlates with hepatitis B viral replication and liver necroinflammation. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 384.e1–384.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosca, A.; Anton, G.; Botezatu, A.; Temereanca, A.; Ene, L.; Achim, C.; Ruta, S. miR-29a associates with viro-immunological markers of HIV infection in treatment experienced patients. J. Med. Virol. 2016, 88, 2132–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrero, J.A.; Kulik, L.M.; Sirlin, C.B.; Zhu, A.X.; Finn, R.S.; Abecassis, M.M.; Roberts, L.R.; Heimbach, J.K. Diagnosis, Staging, and Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: 2018 Practice Guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2018, 68, 723–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichl, P.; Mikulits, W. Accuracy of novel diagnostic biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma: An update for clinicians (Review). Oncol. Rep. 2016, 36, 613–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyoda, H.; Kumada, T.; Tada, T. Highly sensitive Lens culinaris agglutinin-reactive α-fetoprotein: A new tool for the management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncology 2011, 81, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Q.; Anugwom, C.; Desalegn, H.; Debes, J.D. Hepatocellular carcinoma in Hepatitis B and Human Immunodeficiency Virus coinfection in Africa: A focus on surveillance. Hepatoma Res. 2022, 8, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cevik, D.; Yildiz, G.; Ozturk, M. Common telomerase reverse transcriptase promoter mutations in hepatocellular carcinomas from different geographical locations. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kisiel, J.B.; Dukek, B.A.; Kanipakam, R.V.S.R.; Ghoz, H.M.; Yab, T.C.; Berger, C.K.; Taylor, W.R.; Foote, P.H.; Giama, N.H.; Onyirioha, K.; et al. Hepatocellular Carcinoma Detection by Plasma Methylated DNA: Discovery, Phase I Pilot, and Phase II Clinical Validation. Hepatology 2019, 69, 1180–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalasani, N.P.; Ramasubramanian, T.S.; Bhattacharya, A.; Olson, M.C.; Roberts, L.R.; Kisiel, J.B.; Reddy, K.R.; Lidgard, G.P.; Johnson, S.C.; Bruinsma, J.J. A Novel Blood-Based Panel of Methylated DNA and Protein Markers for Detection of Early-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 19, 2597–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Qin, Y.; Liang, Q.; Xia, W.; Zhang, T.; Wang, W.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, T.; Wu, H.; Tian, Y. Increased HBV Coinfection and Decreased IFN-γ-Producing HBV-Specific CD8+ T Cell Numbers During HIV Disease Progression. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 861804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, C.M.; de Peder, L.D.; Silva, E.S.; Previdelli, I.; Pereira, O.C.N.; Teixeira, J.J.V.; Bertolini, D.A. Impact of HBV and HCV coinfection on CD4 cells among HIV-infected patients: A longitudinal retrospective study. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2018, 12, 1009–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Biomarker | Diagnostic Test | Significance in Chronic HBV Mono-Infection | Significance in HIV-HBV Coinfection |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Predictors of treatment efficacy | |||
| cccDNA | q Rt PCR ddPCR RCA in liver biopsies | Viral reservoir, declining levels associated with therapeutic success [71] | Reduced transcription under prolonged ART [73] |
| Serum HBV-RNA | qRT-PCR RT-ddPCR [74] | Good correlation with cccDNA [75] indicates patients with cirrhosis who may safely discontinue HBV therapy. | Correlated with detectable HBeAg [76,77,78,79] and quantitative HBsAg [66,78,79] potential use to guide ART changes |
| HBcrAg | Chemiluminescence/EIA | Predict the evolution of liver disease and the risk of carcinogenesis [80,81] | Monitors the evolution and the clearance of HBeAg [82] |
| qHBsAg | EIA Chemiluminescence | Decreased in patients receiving treatment with nucleoside analogs and peginterferon therapy [83,84,85,86,87,88,89] | Decreased with an increasing number of CD4+ T cells [90,91,92] |
| 2. Predictors of liver fibrosis | |||
| Fibrosis indexes based on serum markers | |||
| Fib-4 score | Index that combines age, AST, ALT, and PLT count levels | Diagnosis and follow-up of liver fibrosis (≥F2); can indicate the need to start HBV treatment; potential use as predictors of mortality [93,94,95] | Indicated for the screening of liver fibrosis in cases with elevated transaminases [94] |
| APRI | AST to Platelet Ratio | APRI threshold of 0.7 is sensitive and specific for the detection of significant fibrosis | An APRI < 0.5 are reported accordant with Fibroscan results to exclude fibrosis in 96.8% [96] |
| Fibrotest® | GGT, bilirubin, haptoglobin, α2-macroglobulin, apolipoprotein A1 | Diagnosis, staging, and follow-up of liver fibrosis [94] | Good accuracy for the diagnosis of liver fibrosis [97] |
| Imaging-based techniques for the detection of liver fibrosis | |||
| Transient elastography (TE) | FibroScan/Echosens, (Paris, France) | Good accuracy for the diagnosis staging and follow-up of liver fibrosis, including cases with normal/discrete ALT elevations [97,98,99] | Indicated in the diagnosis, staging, and follow-up of liver fibrosis in HIV-HBV coinfected patients [99,100]. |
| VCTE | Vibration-controlled transient elastography | Predicts liver fibrosis accurately in patients with chronic hepatitis, irrespective of the etiology [101] | Noninvasive tool to assess liver fibrosis [32,52] |
| MicroRNAs as potential surrogate biomarkers for liver fibrosis | |||
| miR-122 | RT-PCR, 2−ΔΔCT method [102] | Upregulated. Associated with the necroinflammatory activity, stage of fibrosis, HBsAg, and HBV DNA [103] | Biomarker of severe liver disease evolution in HIV infection [104]; more data needed for HIV-HBV coinfection |
| miR-125 | RT-PCR; 2−ΔΔCT method | Downregulated, correlates with HBV viral load and necroinflammatory activity | In HIV infection negatively correlate with HIV-RNA [105]; more data is needed for HIV-HBV coinfection |
| miR-29 | RT-PCR; 2−ΔΔCT method | Downregulated in HBV infection [106] | Over-expressed in HIV infection, control of viral replication (mechanism unknown) [107] |
| 3. Tumor markers | |||
| Classic tumor markers | |||
| AFP/PIVKA-II/AFP-L3 | EIA IHC | Usually increase as HCC develops, irrespective of the etiology | No data [108] |
| M2BPGi | Lectin-antibody sandwich immunoassay | Marker for liver fibrosis stage | No data [109,110] |
| GALAD score | Statistical model that includes gender, age, AFP, L3-AFP, and Des-carboxy-prothrombin (DCP) | Predicts early HCC The association with ultrasound and elastography increases the performance | No data [111] |
| miRNAs as oncogenes | |||
| HBV-miR-2 | Deep sequencing technology | HBV-encoded miRNA; promotes tumoral cell growth by suppressing apoptosis | No data [112] |
| HBV-miR-3 | Deep sequencing technology | HBV-encoded miRNA; promotes tumoral cell growth by silencing PPM1A (Protein phosphatase 1A) | No data [113] |
| MiR-181 | RT-PCR; 2−ΔΔCT method | Cellular miRNA; promotes cell growth, tumorigenesis, and decreasing of apoptosis; it is an epigenetic target for the HBX gene of HBV [114] | Similar activity in HIV-HBV coinfected patients correlated with carcinogenesis [107] |
| Indexes based on biochemical markers as predictors of oncogenesis | |||
| aMAP | Index that comprises age, gender, albumin, bilirubin, and PLT count levels | A cutoff value of 50 is predictive of the risk of carcinogenesis [115] | Not yet tested |
| PAGE-B index | Index that comprises platelets, age, sex, and HBV infection | Carcinogenesis prediction in treated HBV-infected patients [116] Recommended by EASL guidelines to delay the HCC surveillance [117] | Not yet tested |
| Author | Study Group | Assessment Method | Median ART Duration (Years) | Median CD4 T Cell Count | Undetectable HIV-RNA/Undetectable HBV DNA (%) | Prevalence of Liver Fibrosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Iacob, D., 2022 [127] | 212 HIV infected, 101 HIV-HBV coinfected | APRI and Fib-4 scores | 13 | 369 | 68%/46% | 10.8% at baseline, 11.3% at 5 years follow up |
| Sterling, R.K., 2018 [133] | 114 HIV-HBV patients | Liver Histology, APRI and Fib-4 scores | 14 | 568 | 77.9%/57.9% | 37% significant fibrosis (Ishak ≥ 2) 24% advanced fibrosis (Ishak ≥ 3) |
| Maida, I., 2006 [134] | 37 HIV-HBV patients | Transient elastography | 3.3 | 490 | 89%/70% | 57% no or mild fibrosis 13% significant fibrosis (F3) 11% advanced fibrosis (F4) |
| Audsley, J., 2016 [135] | 70 HIV-HBV patients, of which 20 co-infected with HCV | Transient elastography | 10 | 381 | 74.6%/74.6% | 35.7% significant fibrosis (≥F3) |
| Boyd, A., 2017 [24] | 148 HIV-HBV patients, of which 12 co-infected with HDV 19 co-infected with HCV | Fibrometer score and liver biopsy | 5.7 | 420 | 53.4%/17.8% | 31% F3–F4 fibrosis |
| Miailhes, P., 2011 [136] | 59 patients (46 patients on cART) | Transient elastography, liver biopsy, and Fibrotest | Not specified | 397 | 85%/78% | 33.8% F3–F4 fibrosis |
| Stockdale, A.J., 2015 [98] | 106 HIV-HBV patients on ART and 15 ART-naive | Transient elastography | 3.75 | 571 | 67%/49.1% | 2.7% F3–F4 fibrosis |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruta, S.; Grecu, L.; Iacob, D.; Cernescu, C.; Sultana, C. HIV-HBV Coinfection—Current Challenges for Virologic Monitoring. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1306. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11051306
Ruta S, Grecu L, Iacob D, Cernescu C, Sultana C. HIV-HBV Coinfection—Current Challenges for Virologic Monitoring. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(5):1306. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11051306
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuta, Simona, Laura Grecu, Diana Iacob, Costin Cernescu, and Camelia Sultana. 2023. "HIV-HBV Coinfection—Current Challenges for Virologic Monitoring" Biomedicines 11, no. 5: 1306. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11051306
APA StyleRuta, S., Grecu, L., Iacob, D., Cernescu, C., & Sultana, C. (2023). HIV-HBV Coinfection—Current Challenges for Virologic Monitoring. Biomedicines, 11(5), 1306. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11051306





