Biomarkers for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: From Origin to Clinical Diagnosis
Abstract
1. Hepatocellular Carcinoma
1.1. Epidemiology of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
1.2. Epidemiology of HCC in Egypt
2. Diagnosis of HCC
2.1. Imaging Methods
2.1.1. Ultrasonography (US)
2.1.2. Multiphasic Enhanced Computed Tomography (CT)
2.1.3. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
2.2. Liver Tissue Biopsy
2.3. Liquid Biopsy
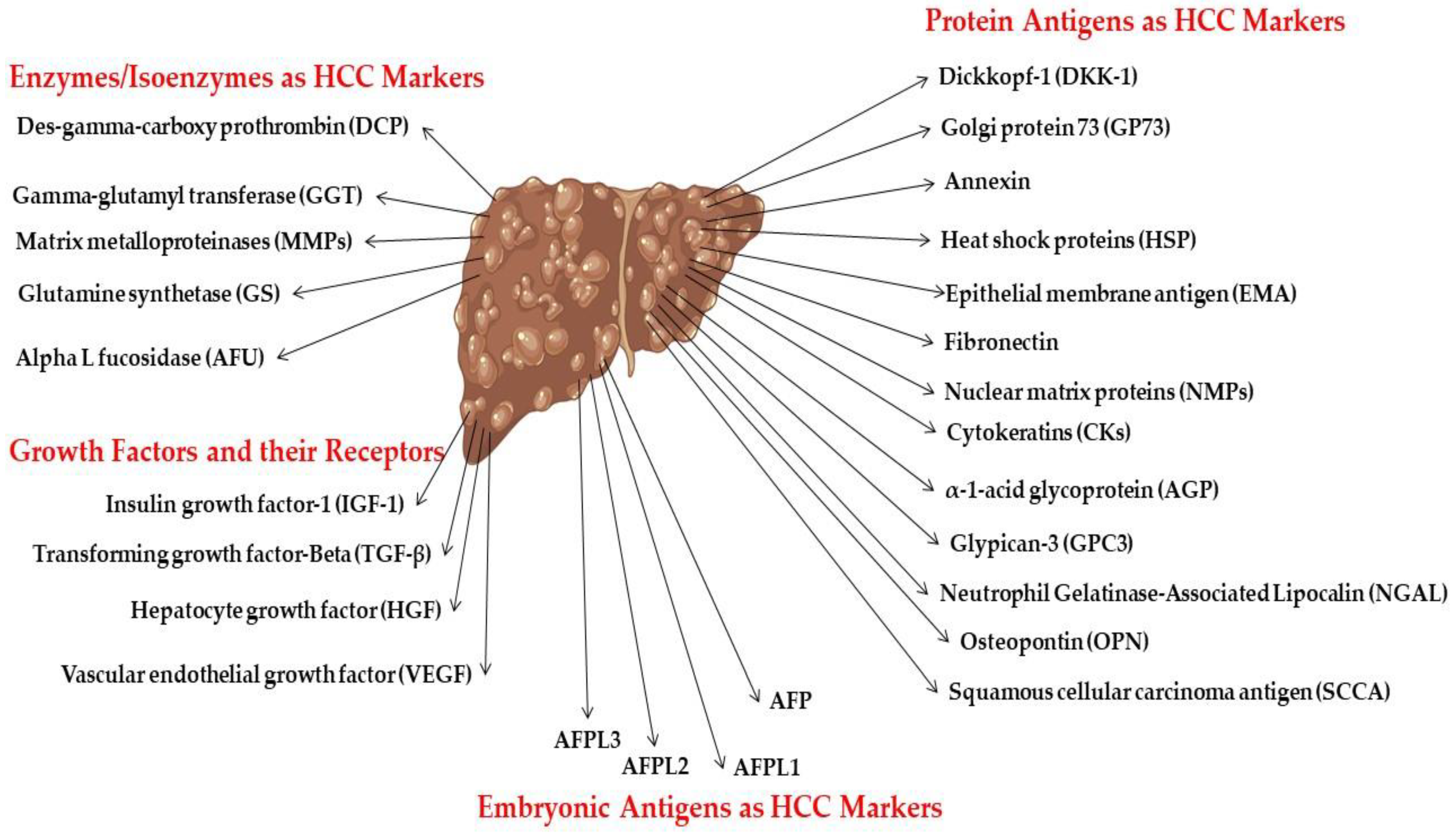
2.4. Biomarkers
2.4.1. Embryonic Antigen
2.4.2. Protein Antigens
- A.
- Dickkopf-1 (DKK-1)
- B.
- Golgi protein 73 (GP73)
- C.
- Annexin
- D.
- Heat shock proteins (HSP)
- E.
- Epithelial membrane antigen (EMA)
- F.
- Fibronectin
- G.
- Nuclear matrix proteins (NMPs)
- H.
- Cytokeratins (CKs)
- I.
- α-1-acid glycoprotein (AGP)
- J.
- Glypican-3 (GPC3)
- K.
- Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin (NGAL)
- L.
- Osteopontin (OPN)
- M.
- Squamous cellular carcinoma antigen (SCCA)
2.4.3. Enzymes and Isoenzymes as HCC Biomarkers
- A.
- Des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin (DCP)
- B.
- Gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT)
- C.
- Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs)
- D.
- Glutamine synthetase (GS)
- E.
- Alpha L fucosidase (AFU)
- F.
- Paraoxonase 1 (PON1)
2.4.4. Growth Factors and Their Receptors
- A.
- Transforming growth factor beta (TGFβ)
- B.
- Insulin growth factor-1 (IGF-1)
- C.
- Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)
- D.
- Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF)
2.4.5. Cytokines
2.4.6. Metabolites
2.4.7. Molecular Markers
Circulating RNAs
- A.
- AFP mRNA
- B.
- Gamma-glutamyl transferase mRNA (GGT mRNA)
- C.
- Toll like receptor (TLR) mRNAs
MicroRNA (miRNA)
Long Noncoding RNA (lncRNA)
Circulating Tumor Cells (CTCs)
3. Future Perspectives
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Single Marker | Abb. | Characteristics | AUC | Sn | Sp | Author |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alpha-fetoprotein | AFP | Oncofetal glycoprotein | 0.8 | 59 | 89 | [92] |
| 0.66 | 30 | 100 | [27] | |||
| 0.76 | 36 | 100 | [93] | |||
| Lens culinaris agglutinin-reactivee AFP | AFP-L3 | Glycosylated isoform of AFP | 0.67 | 51 | 83 | [94] |
| Dickkopf-1 | DKK1 | Glycoprotein | 0.82 | 68 | 89 | [95] |
| 0.65 | 50 | 81 | [96] | |||
| Golgi protein 73 | GP73 | Transmembrane glycoprotein | 0.94 | 92 | 84 | [97] |
| 0.94 | 75 | 97 | [98] | |||
| Annexin A2 | ANXA2 | Phospholipid-binding protein | 0.8 | 83 | 68 | [32] |
| Epithelial membrane antigen | EMA | A mucins transmembrane glycoprotein | 0.81 | 70 | 78 | [35] |
| Fibronectin | FN | Glycoprotein | 0.7 | 67 | 82 | [35] |
| Cytokeratin-1 | CK1 | Cytoplasmic protein | 0.83 | 75 | 82 | [39] |
| Nuclear matrix protein-52 | NMP-52 | Nuclear protein | 0.72 | 62 | 70 | [99] |
| Midkine | MDK | A heparin-binding growth factor | 0.81 | 76 | 71 | [73] |
| 0.7 | 71 | 62 | [100] | |||
| 0.83 | 82 | 84 | [101] | |||
| Insulin-like growth factor 2 | IGF2 | Growth factor | 0.86 | 80 | 73 | [102] |
| Interleukin-6 | IL-6 | Cytokine | 0.78 | 72 | 70 | [102] |
| Thioredoxin | TRX | Antioxidant protein | 0.79 | 74 | 71 | [73] |
| 0.84 | 75 | 80 | [103] | |||
| 1-methyladenosine | M1A | Modified nucleoside metabolites | 0.75 | 74 | 75 | [73] |
| α-1-acid glycoprotein | AGP | Glycoprotein | 0.74 | 74 | 75 | [40] |
| 0.83 | [104] | |||||
| 0.91 | 77 | [105] | ||||
| 0.94 | 71 | [106] | ||||
| C-reactive protein | CRP | Acute-phase protein | 0.71 | 66 | 75 | [40] |
| 0.76 | 72 | 70 | [107] | |||
| Glypican-3 | GPC3 | Glycoprotein antigens | 0.76 | 55 | 84 | [92] |
| 0.79 | 60 | 52 | [93] | |||
| 0.87 | 68 | 92 | [108] | |||
| Osteopontin | OPN | Glycophosphoprotein | 0.8 | 82 | 65 | [109] |
| 0.99 | 100 | 98 | [110] | |||
| 0.63 | 46 | 80 | [96] | |||
| 0.88 | 71 | 80 | [111] | |||
| Squamous cellular carcinoma antigen | SCCA | Glycoprotein antigens | 0.81 | 89 | 50 | [112] |
| Des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin or protein induced by vitamin K absence or antagonist II | PIVKA-II (DCP) | Enzymes and isoenzymes | 0.71 | 51 | 91 | [96] |
| 0.71 | 71 | 70 | [94] | |||
| MicroRNA-21 | miR-21 | Genetic and molecular marker | 0.63 | 65 | 63 | [113] |
| MicroRNA-29 | miR-29 | 0.68 | 62 | 65 | ||
| MicroRNA-200 | miR-200 | 0.72 | 65 | 63 | ||
| MicroRNA-355 | miR-355 | 0.6 | 60 | 55 | ||
| MicroRNA-148a | miR-148a | 0.92 | 89 | 89 | [114] | |
| MicroRNA-122 | miR-122 | 0.93 | 95 | 81 | [115] | |
| MicroRNA-224 | miR-224 | 0.77 | 85 | 79 | ||
| MicroRNA-301 | miR-301 | 0.84 | 78 | 98 | [116] |
| Combined Marker | AUC | Sn | Sp | Author |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AFP + DKK-1 | 0.76 | 78 | 73 | [96] |
| AFP + GPC3 | 0.85 | 77 | 83 | [92] |
| AFP + PIVKA-II | 0.76 | 64 | 88 | [96] |
| PIVKA-II + DKK-1 | 0.73 | 74 | 73 | [96] |
| AFP + TRX | 0.88 | 82 | 87 | [103] |
| AFP + OPN | 0.74 | 75 | 72 | [96] |
| 0.81 | 86 | 60 | [109] | |
| 0.9 | 82 | 77 | [111] | |
| Annexin + AFP | 0.85 | 76 | 81 | [32] |
| AFP + PIVKA-II + OPN | 0.73 | 76 | 71 | [96] |
| AFP + PIVKA-II + DKK-1 | 0.75 | 79 | 70 | [96] |
| AFP + AGP | 0.94 | 89 | 90 | [105] |
| C-Myc + P53 | 0.9 | 100 | 87 | [117] |
| miR-200 + AFP | 0.7 | 70 | 75 | [113] |
| miR-200 + miR-29 | 0.74 | 70 | 65 | |
| miR-200 + miR-29 + AFP | 0.84 | 80 | 65 | |
| miR-200 + miR-29 + AFP + miR-21 | 0.88 | 80 | 80 | |
| miR-200- miR-29-AFP + miR-21 + miR-355 | 0.92 | 90 | 80 | |
| AFP + miR-122 | 0.96 | 98 | 87 | [115] |
| AFP + miR-224 | 0.83 | 94 | 79 | |
| AFP + miR-301 | 0.93 | 90 | 95 | [116] |
| miRNA-122-5p + miRNA-486-5p + miRNA-142-3p | 0.94 | 80 | 95 | [118] |
| Marker/Model | AUC | Sn | Sp | Author | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK1 score | [1.392 + CK1(μg/mL) × 0.005 + logAFP × 0.141 − albumin (g/L) × 0.032] | 0.87 | 87 | 77 | [39] |
| FEBA-Test | [0.001 × fibronectin(mg/L) + 0.13 × EMA (μg/mL) + 0.036 × total bilirubin (mg/dL) + 0.83 × logAFP (U/L) − 0.063] | 0.92 | 89 | 85 | [35] |
| GPC-HCC | [0.517 + 0.018 × GPC3 (ng/mL) + 0.108 × logAFP (U/L) + 0.025 × total bilirubin (mg/dL) − 0.233 × albumin (g/dL)] | 0.91 | 93 | 91 | [93] |
| HCC-ART | [2.17 + [log(AFP − 1) × 10 × 0.117] + AAR × 0.025 + age × 0.012 + ALP (U/L) × 0.001] − [albumin (g/L) × 0.015] | 0.97 | 96 | 99 | [119] |
| Simplified HCC-ART | [Age(years) × logAFP (U/L) × AAR × ALP (U/L)]/[Alb (g/L)] | 0.92 | 91 | 95 | [120] |
| HCC-DETECT | [0.004 × CK-1 (μg/mL) + 0.007 × NMP-52 (μg/mL) + 0.248 × LogAFP (U/L) + 0.951] | 0.9 | 80 | 92 | [99] |
| 3AC | [3.057 + AGP (ng/mL) × 0.199 − albumin (g/L) × 0.052 + LogAFP × 0.136 + CRP (mg/L) × 0.008] | 0.95 | 85 | 90 | [40] |
| ATM2 | [0.533 + 0.146 × logAFP + 0.062 × MDK (ng/mL) + 0.004 × TRX (ng/mL) + 0.009 × M1A (ng/mL)] | 0.94 | 90 | 88 | [73] |
| AFP- IGF2- IL6- platelet count | 1.17 + AFP (U/L) × 0.002 + IGF2 (pg/mL) × 0.001 + IL6 (pg/mL) × 0.008 − platelet count (×109/L) × 0.001 | 0.95 | 90 | 82 | [102] |
| HCC-Mark | [AFP(U/L) × hs-CRP (mg/L)/(Albumin (g/L) × PLT (×109/L))] × 100 | 0.9 | 84 | 80 | [107] |
References
- Elshimi, E.; Sakr, M.A.M.; Morad, W.S.; Mohammad, L. Optimizing the Diagnostic Role of Alpha-Fetoprotein and Abdominal Ultrasound by Adding Overexpressed Blood mRNA Matrix Metalloproteinase-12 for Diagnosis of HCV-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gastrointest. Tumors 2019, 5, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcon, P.D.S.; Tovo, C.V.; Kliemann, D.A.; Fisch, P.; de Mattos, A.A. Incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic liver disease due to hepatitis B or C and coinfected with the human immunodeficiency virus: A retrospective cohort study. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Tang, Q.; Feng, X.; Tang, W. Biomarkers: Evaluation of clinical utility in surveillance and early diagnosis for hepatocellular carcinoma. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. Suppl. 2016, 245, S70–S76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGlynn, K.A.; London, W.T. The global epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma: Present and future. Clin. Liver Dis. 2011, 15, 223–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.X.; Seto, W.K.; Lai, C.L.; Yuen, M.F. Epidemiology of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in the Asia-Pacific Region. Gut Liver 2016, 10, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Feng, Y.; Lin, H.; Ma, R.; Cai, X. Role of estrogen in hepatocellular carcinoma: Is inflammation the key? J. Transl. Med. 2014, 12, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Zucman-Rossi, J.; Pikarsky, E.; Sangro, B.; Schwartz, M.; Sherman, M.; Gores, G. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2016, 2, 16018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartke, J.; Johnson, M.; Ghabril, M. The diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin. Diagn. Pathol. 2017, 34, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashed, W.M.; Kandeil, M.A.M.; Mahmoud, M.O.; Ezzat, S. Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) in Egypt: A comprehensive overview. J. Egypt. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2020, 32, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elsalam, S.; Elwan, N.; Soliman, H.; Ziada, D.; Elkhalawany, W.; Salama, M.; Hawash, N.; Arafa, M.; Badawi, R.; Shehata, W.M.; et al. Epidemiology of liver cancer in Nile delta over a decade: A single-center study. South Asian J. Cancer 2018, 7, 24–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgharably, A.; Gomaa, A.I.; Crossey, M.M.; Norsworthy, P.J.; Waked, I.; Taylor-Robinson, S.D. Hepatitis C in Egypt—Past, present, and future. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2017, 10, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzat, R.; Eltabbakh, M.; El Kassas, M. Unique situation of hepatocellular carcinoma in Egypt: A review of epidemiology and control measures. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2021, 13, 1919–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaafar, R.; Allam, J.; Ali, A.; Habib, J.; Faraj, W.J.C.O. Epidemiology of Liver Diseases Across the Levant and Egypt: A Review. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 6, 1822. [Google Scholar]
- Granito, A.; Muratori, L.; Lalanne, C.; Quarneti, C.; Ferri, S.; Guidi, M.; Lenzi, M.; Muratori, P. Hepatocellular carcinoma in viral and autoimmune liver diseases: Role of CD4+ CD25+ Foxp3+ regulatory T cells in the immune microenvironment. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 2994–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrero, J.A.; Kulik, L.M.; Sirlin, C.B.; Zhu, A.X.; Finn, R.S.; Abecassis, M.M.; Roberts, L.R.; Heimbach, J.K. Diagnosis, Staging, and Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: 2018 Practice Guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatol. Baltim. Md. 2018, 68, 723–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H. Current role of ultrasound in the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Med. Ultrason. 2020, 47, 239–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chartampilas, E.; Rafailidis, V.; Georgopoulou, V.; Kalarakis, G.; Hatzidakis, A.; Prassopoulos, P. Current Imaging Diagnosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2022, 14, 3997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osho, A.; Rich, N.E.; Singal, A.G. Role of imaging in management of hepatocellular carcinoma: Surveillance, diagnosis, and treatment response. Hepatoma Res. 2020, 6, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Tommaso, L.; Spadaccini, M.; Donadon, M.; Personeni, N.; Elamin, A.; Aghemo, A.; Lleo, A. Role of liver biopsy in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 6041–6052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granito, A.; Galassi, M.; Piscaglia, F.; Romanini, L.; Lucidi, V.; Renzulli, M.; Borghi, A.; Grazioli, L.; Golfieri, R.; Bolondi, L. Impact of gadoxetic acid (Gd-EOB-DTPA)-enhanced magnetic resonance on the non-invasive diagnosis of small hepatocellular carcinoma: A prospective study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 37, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gisder, D.M.; Tannapfel, A.; Tischoff, I.J.H.R. Histopathology of hepatocellular carcinoma-when and what. Hepatoma Res. 2022, 8, 10.20517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labgaa, I.; Villanueva, A.; Dormond, O.; Demartines, N.; Melloul, E. The Role of Liquid Biopsy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Prognostication. Cancers 2021, 13, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrín, G.; Aguilar-Melero, P.; Rodríguez-Perálvarez, M.; Montero-Álvarez, J.L.; de la Mata, M. Biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma: Diagnostic and therapeutic utility. Hepatic Med. Evid. Res. 2015, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behne, T.; Copur, M.S. Biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Hepatol. 2012, 2012, 859076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Wei, C. Advances in the early diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Genes Dis. 2020, 7, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suda, T.; Yamashita, T.; Sunagozaka, H.; Okada, H.; Nio, K.; Sakai, Y.; Yamashita, T.; Mizukoshi, E.; Honda, M.; Kaneko, S. Dickkopf-1 Promotes Angiogenesis and is a Biomarker for Hepatic Stem Cell-like Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchiya, N.; Sawada, Y.; Endo, I.; Saito, K.; Uemura, Y.; Nakatsura, T. Biomarkers for the early diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 10573–10583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.U.; Shariff, M.I.; Crossey, M.M.; Gomez-Romero, M.; Holmes, E.; Cox, I.J.; Fye, H.K.; Njie, R.; Taylor-Robinson, S.D. Hepatocellular carcinoma: Review of disease and tumor biomarkers. World J. Hepatol. 2016, 8, 471–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlSalloom, A.A. An update of biochemical markers of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Health Sci. 2016, 10, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, M.; Awad, S.; Barakat, S.; Saleh, A.; Rozaik, S. Serum Golgi protein 73 as a sensitive biomarker for early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma among Egyptian patients with hepatitis C virus-related cirrhosis. Med. J. Armed India 2021, 77, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElZefzafy, W.M.; Hussien, M.; Mohmmed, Z.A.Z.; Abd Elbaky, N.M. The diagnostic value of golgi protien-73 and DICKKOPF-1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Immunoass. Immunochem. 2021, 42, 174–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Gao, G.; Cai, J.; Wang, Y.; Qu, X.; He, L.; Liu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, K.; Ma, S.; et al. Annexin A2 is a discriminative serological candidate in early hepatocellular carcinoma. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seclì, L.; Fusella, F.; Avalle, L.; Brancaccio, M. The dark-side of the outside: How extracellular heat shock proteins promote cancer. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2021, 78, 4069–4083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoter, A.; Rizk, S.; Naim, H.Y. Heat Shock Protein 60 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Insights and Perspectives. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attallah, A.M.; El-Far, M.; Malak, C.A.A.; Omran, M.M.; Farid, K.; Yahya, R.S.; Saad, E.A.; Albannan, M.S.; Attallah, A.A.; El Basuni, M.A.; et al. A simple diagnostic index comprising epithelial membrane antigen and fibronectin for hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann. Hepatol. 2015, 14, 869–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Park, J.; Kim, Y.; Sohn, A.; Yeo, I.; Jong Yu, S.; Yoon, J.H.; Park, T.; Kim, Y. Serum fibronectin distinguishes the early stages of hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, G.S.; Lee, H.; Jung, Y.; Yu, E.; Moon, H.B.; Song, K.; Lee, I. Nuclear matrix of calreticulin in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 1117–1120. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, D.W.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Sun, X.D.; Chen, Y.G.; Qiu, W.; Ji, M.; Lv, G.Y. Prognostic value of cytokeratin 19 in hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Clin. Chim. Acta Int. J. Clin. Chem. 2015, 448, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attallah, A.M.; El-Far, M.; Abdel Malak, C.A.; Zahran, F.; Farid, K.; Omran, M.M.; Zagloul, H.; El-Deen, M.S. Evaluation of cytokeratin-1 in the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Chim. Acta Int. J. Clin. Chem. 2011, 412, 2310–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omran, M.M.; Emran, T.M.; Farid, K.; Eltaweel, F.M.; Omar, M.A.; Bazeed, F.B. An Easy and Useful Noninvasive Score Based on α-1-acid Glycoprotein and C-Reactive Protein for Diagnosis of Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Associated with Hepatitis C Virus Infection. J. Immunoass. Immunochem. 2016, 37, 273–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Zhu, J.; Wang, M.; Singal, A.G.; Odewole, M.; Kagan, S.; Renteria, V.; Liu, S.; Parikh, N.D.; Lubman, D.M. Evaluation of AGP Fucosylation as a Marker for Hepatocellular Carcinoma of Three Different Etiologies. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, H.; Ding, H. GPC-3 in hepatocellular carcinoma: Current perspectives. J. Hepatocell. Carcinoma 2016, 3, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, F.; Shang, W.; Yu, X.; Tian, J. Glypican-3: A promising biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma diagnosis and treatment. Med. Res. Rev. 2018, 38, 741–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauvois, B.; Susin, S.A. Revisiting Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin (NGAL) in Cancer: Saint or Sinner? Cancers 2018, 10, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dertli, R.; Biyik, M.; Yolacan, R.; Karakarcayildiz, A.; Keskin, M.; Kayar, Y.; Asil, M. May Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin (NGAL) Level Predict Mortality in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)? J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2020, 51, 932–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candido, S.; Abrams, S.L.; Steelman, L.S.; Lertpiriyapong, K.; Fitzgerald, T.L.; Martelli, A.M.; Cocco, L.; Montalto, G.; Cervello, M.; Polesel, J.; et al. Roles of NGAL and MMP-9 in the tumor microenvironment and sensitivity to targeted therapy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1863, 438–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelsameea, E.; Nada, A.; Omar, N.; Saleh, S.M.; Naguib, M.; El-Ezawy, H.E.M.; Bakry, L.; Elsabaawy, M. Urine Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin a Possible Diagnostic Marker for Egyptian Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. APJCP 2020, 21, 2259–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.; Wong, J.P.C.; Kwok, H.F. Osteopontin -- a promising biomarker for cancer therapy. J. Cancer 2017, 8, 2173–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Li, L.; Miao, C.; Hasnat, M.; Sun, L.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, L. Osteopontin promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression through inducing JAK2/STAT3/NOX1-mediated ROS production. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montagnana, M.; Danese, E.; Lippi, G. Squamous cell carcinoma antigen in hepatocellular carcinoma: Ready for the prime time? Clin. Chim. Acta Int. J. Clin. Chem. 2015, 445, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyemi, O.M.; Otegbayo, J.A.; Ola, S.O.; Akere, A.; Soyemi, T. Comparative diagnostic efficacy of serum squamous cell carcinoma antigen in hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Res. Notes 2012, 5, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Taniguchi, T.; Sannomiya, K.; Takenaka, H.; Tomonari, T.; Okamoto, K.; Kitamura, S.; Okahisa, T.; Tamaki, K.; Mikasa, H.; et al. Novel des-γ-carboxy prothrombin in serum for the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 28, 1348–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lok, A.S.; Sterling, R.K.; Everhart, J.E.; Wright, E.C.; Hoefs, J.C.; Di Bisceglie, A.M.; Morgan, T.R.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, W.M.; Bonkovsky, H.L.; et al. Des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin and alpha-fetoprotein as biomarkers for the early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, B.I.; Akkiz, H.; Bag, H.G.; Karaoğullarından, U.; Yalçın, K.; Ekin, N.; Özakyol, A.; Altıntaş, E.; Balaban, H.Y.; Şimşek, H.; et al. Serum levels of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase in relation to HCC human biology and prognosis. J. Transl. Sci. 2021, 7, 1000446. [Google Scholar]
- Geervliet, E.; Bansal, R. Matrix Metalloproteinases as Potential Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets in Liver Diseases. Cells 2020, 9, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheau, C.; Badarau, I.A.; Costache, R.; Caruntu, C.; Mihai, G.L.; Didilescu, A.C.; Constantin, C.; Neagu, M. The Role of Matrix Metalloproteinases in the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Anal. Cell. Pathol. 2019, 2019, 9423907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, J.; Lang, Z.W.; Wang, H.G.; Wang, T.L.; Wang, B.E.; Liu, S.Q. Glutamine synthetase as an early marker for hepatocellular carcinoma based on proteomic analysis of resected small hepatocellular carcinomas. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. Int. HBPD INT 2010, 9, 296–305. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, Z.; Xue, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, L.; Zhu, J.; Xuan, S.; Tian, J.; Pang, Z. The Applicability of ADA, AFU, and LAC in the Early Diagnosis and Disease Risk Assessment of Hepatitis B-Associated Liver Cirrhosis and Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 740029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ying, X.; Zhao, Q.; Ma, J.; Zhang, D.; He, C.; Han, S. Identification of Protein Expression Changes in Hepatocellular Carcinoma through iTRAQ. Dis. Mrk. 2020, 2020, 2632716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Höpfner, M.; Schuppan, D.; Scherübl, H. Growth factor receptors and related signalling pathways as targets for novel treatment strategies of hepatocellular cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Gingold, J.A.; Su, X. Immunomodulatory TGF-β Signaling in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Trends Mol. Med. 2019, 25, 1010–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamek, A.; Kasprzak, A. Insulin-Like Growth Factor (IGF) System in Liver Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmashad, N.; Ibrahim, W.S.; Mayah, W.W.; Farouk, M.; Ali, L.A.; Taha, A.; Elmashad, W. Predictive value of serum insulin-like growth factor-1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. APJCP 2015, 16, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaseb, A.O.; Hanbali, A.; Cotant, M.; Hassan, M.M.; Wollner, I.; Philip, P.A. Vascular endothelial growth factor in the management of hepatocellular carcinoma: A review of literature. Cancer 2009, 115, 4895–4906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenleber, S.J.; Kurtz, D.M.; Talwalkar, J.A.; Roberts, L.R.; Gores, G.J. Prognostic role of vascular endothelial growth factor in hepatocellular carcinoma: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Cancer 2009, 100, 1385–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daveau, M.; Scotte, M.; François, A.; Coulouarn, C.; Ros, G.; Tallet, Y.; Hiron, M.; Hellot, M.F.; Salier, J.P. Hepatocyte growth factor, transforming growth factor alpha, and their receptors as combined markers of prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Carcinog. 2003, 36, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliaz, R.; Akyuz, U.; Tekin, D.; Serilmez, M.; Evirgen, S.; Cavus, B.; Soydinc, H.; Duranyildiz, D.; Karaca, C.; Demir, K.; et al. Role of several cytokines and adhesion molecules in the diagnosis and prediction of survival of hepatocellular carcinoma. Arab J. Gastroenterol. Off. Publ. Pan-Arab Assoc. Gastroenterol. 2016, 17, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koca, Y.S.; Bulbul, M.; Barut, I. The Diagnostic Roles of Cytokines in Hepatobiliary Cancers. BioMed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 2979307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öcal, O.; Schütte, K.; Kupčinskas, J.; Morkunas, E.; Jurkeviciute, G.; de Toni, E.N.; Ben Khaled, N.; Berg, T.; Malfertheiner, P.; Klümpen, H.J.; et al. Baseline Interleukin-6 and -8 predict response and survival in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated with sorafenib monotherapy: An exploratory post hoc analysis of the SORAMIC trial. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 148, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakiba, E.; Sadeghi, M.; Shakiba, M. A systematic review and meta-analysis of evaluation of serum interleukin 8 levels in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2019, 5, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H. N(1)-methyladenosine modification in cancer biology: Current status and future perspectives. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 6578–6585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, C.; Wang, W.; He, C. m1A methylation modification patterns and metabolic characteristics in hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022, 22, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omran, M.M.; Farid, K.; Omar, M.A.; Emran, T.M.; El-Taweel, F.M.; Tabll, A.A. A combination of α-fetoprotein, midkine, thioredoxin and a metabolite for predicting hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann. Hepatol. 2020, 19, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Nakeep, S. Molecular and genetic markers in hepatocellular carcinoma: In silico analysis to clinical validation (current limitations and future promises). World J. Gastrointest. Pathophysiol. 2022, 13, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, S.; Tomokuni, A.; Takahashi, H.; Akita, H.; Sugimura, K.; Miyoshi, N.; Moon, J.H.; Yasui, M.; Omori, T.; Ohue, M.; et al. The Clinical Significance of Alpha-Fetoprotein mRNAs in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gastrointest. Tumors 2017, 3, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.-X.; Huang, Y.-H.; Liu, L.-L.; Zhang, C.Z.; Yang, X.; Yang, Y.-Z.; Shao, C.-K.; Li, J.-M.; Xie, D.; Zhang, X.; et al. α-Fetoprotein mRNA in situ hybridisation is a highly specific marker of hepatocellular carcinoma: A multi-centre study. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 124, 1988–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutsumi, M.; Sakamuro, D.; Takada, A.; Zang, S.C.; Furukawa, T.; Taniguchi, N. Detection of a unique gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase messenger RNA species closely related to the development of hepatocellular carcinoma in humans: A new candidate for early diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol. Baltim. Md. 1996, 23, 1093–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Li, J.; Guo, Y.; Dong, W.; Zheng, X. Expression Status and Prognostic Significance of Gamma-Glutamyl Transpeptidase Family Genes in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 731144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.; Omran, D.; El-Feky, S.; Darwish, H.; Kassas, A.; Farouk, A.; Ezzat, O.; Abdo, S.; Zahran, F.; El-Demery, A.; et al. Toll-like receptor 7 mRNA is reduced in hepatitis C-based liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma, out-performs alpha-fetoprotein levels, and with age and serum aspartate aminotransferase is a new diagnostic index. Br. J. Biomed. Science 2021, 78, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Liu, B.; Yu, J.; Zhang, D.; Shi, J.; Liang, P. Development of a Toll-Like Receptor-Based Gene Signature That Can Predict Prognosis, Tumor Microenvironment, and Chemotherapy Response for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 729789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, R.K.; Yu, F.S.; Kumar, A. Targeting toll-like receptor signaling as a novel approach to prevent ocular infectious diseases. Indian J. Med. Res. 2013, 138, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Annese, T.; Tamma, R.; De Giorgis, M.; Ribatti, D. microRNAs Biogenesis, Functions and Role in Tumor Angiogenesis. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 581007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidhu, K.; Kapoor, N.R.; Pandey, V.; Kumar, V. The “Macro” World of microRNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2015, 5, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sen, S. MicroRNA functional network in pancreatic cancer: From biology to biomarkers of disease. J. Biosci. 2011, 36, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomimaru, Y.; Eguchi, H.; Nagano, H.; Wada, H.; Kobayashi, S.; Marubashi, S.; Tanemura, M.; Tomokuni, A.; Takemasa, I.; Umeshita, K.; et al. Circulating microRNA-21 as a novel biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, A.M.; Yao, T.J.; Wang, W.; Wong, K.F.; Lee, N.P.; Fan, S.T.; Poon, R.T.; Gao, C.; Luk, J.M. Circulating miR-15b and miR-130b in serum as potential markers for detecting hepatocellular carcinoma: A retrospective cohort study. BMJ Open 2012, 2, e000825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Yu, L.; Gao, X.; Hu, J.; Wang, J.; Dai, Z.; Wang, J.-F.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, S.; Huang, X.; et al. Plasma microRNA panel to diagnose hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 4781–4788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Wu, L.; Lei, X.; Shi, K.; Shi, L.; Shi, Y. Long non-coding RNA-based signature for predicting prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 673–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Ling, S.; Zheng, S.; Xu, X. Liquid biopsy in hepatocellular carcinoma: Circulating tumor cells and circulating tumor DNA. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.C.; Teng, P.C.; Chen, P.J.; Posadas, E.; Tseng, H.R.; Lu, S.C.; Yang, J.D. Detection of Circulating Tumor Cells and Their Implications as a Biomarker for Diagnosis, Prognostication, and Therapeutic Monitoring in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatol. Baltim. Md. 2021, 73, 422–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Rong, Y.; Yi, K.; Huang, L.; Chen, M.; Wang, F. Circulating tumor cells in hepatocellular carcinoma: Single-cell based analysis, preclinical models, and clinical applications. Theranostics 2020, 10, 12060–12071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, X.; Liu, J.; Gao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Du, Z. Diagnosis accuracy of serum glypican-3 in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Arch. Med. Res. 2014, 45, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attallah, A.M.; El-Far, M.; Omran, M.M.; Abdelrazek, M.A.; Attallah, A.A.; Saeed, A.M.; Farid, K. GPC-HCC model: A combination of glybican-3 with other routine parameters improves the diagnostic efficacy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumour Biol. J. Int. Soc. Oncodev. Biol. Med. 2016, 37, 12571–12577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Jang, J.Y.; Jeong, S.W.; Cho, Y.K.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, S.G.; Cha, S.-W.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, B.S.; et al. Usefulness of AFP, AFP-L3, and PIVKA-II, and their combinations in diagnosing hepatocellular carcinoma. Medicine 2017, 96, e5811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouad, Y.M.; Mohamed, H.I.; Kamal, E.M.; Rasek, M.A. Clinical significance and diagnostic value of serum dickkopf-1 in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 51, 1133–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, E.S.; Jeong, S.H.; Kim, J.W.; Choi, Y.S.; Leissner, P.; Brechot, C. Diagnostic Performance of Alpha-Fetoprotein, Protein Induced by Vitamin K Absence, Osteopontin, Dickkopf-1 and Its Combinations for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, J.S.; Ye, W.; Jiang, Y.K.; Ma, J.; Zhu, M.Q.; Ma, J.M.; Zhou, H.; Yu, L.Q.; Yang, Y.F.; Wang, S.C. The Value of GPC3 and GP73 in Clinical Diagnosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clin. Lab. 2017, 63, 1903–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Yang, H.; Xu, H.; Lu, X.; Sang, X.; Du, S.; Zhao, H.; Chen, W.; Xu, Y.; Chi, T.; et al. Golgi protein 73 (GOLPH2) is a valuable serum marker for hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut 2010, 59, 1687–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attallah, A.M.; El-Far, M.; Malak, C.A.A.; Omran, M.M.; Shiha, G.E.; Farid, K.; Barakat, L.A.; Albannan, M.S.; Attallah, A.A.; Abdelrazek, M.A.; et al. HCC-DETECT: A combination of nuclear, cytoplasmic, and oncofetal proteins as biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumour Biol. J. Int. Soc. Oncodev. Biol. Med. 2015, 36, 7667–7674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vongsuvanh, R.; van der Poorten, D.; Iseli, T.; Strasser, S.I.; McCaughan, G.W.; George, J. Midkine Increases Diagnostic Yield in AFP Negative and NASH-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashaly, A.H.; Anwar, R.; Ebrahim, M.A.; Eissa, L.A.; El Shishtawy, M.M. Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of Talin-1 and Midkine as Tumor Markers in Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Egyptian Patients. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. APJCP 2018, 19, 1503–1508. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Omran, M.M.; Mosaad, S.; Emran, T.M.; Eltaweel, F.M.; Farid, K. A novel model based on interleukin 6 and insulin-like growth factor II for detection of hepatocellular carcinoma associated with hepatitis C virus. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2021, 19, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Cheng, Z.J.; Liu, Y.; Yan, Z.L.; Wang, K.; Wu, D.; Wan, X.Y.; Xia, Y.; Lau, W.Y.; Wu, M.C.; et al. Serum thioredoxin is a diagnostic marker for hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 9551–9563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Sun, L.; Guo, K.; Shu, H.; Yao, J.; Qin, X.; Liu, Y. Serum protein biomarkers screening in HCC patients with liver cirrhosis by ICAT-LC-MS/MS. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 136, 1151–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachtiar, I.; Santoso, J.M.; Atmanegara, B.; Gani, R.A.; Hasan, I.; Lesmana, L.A.; Sulaiman, A.; Gu, J.; Tai, S. Combination of alpha-1-acid glycoprotein and alpha-fetoprotein as an improved diagnostic tool for hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Chim. Acta Int. J. Clin. Chem. 2009, 399, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachtiar, I.; Kheng, V.; A Wibowo, G.; A Gani, R.; Hasan, I.; Sanityoso, A.; Budhihusodo, U.; Lelosutan, S.A.; Martamala, R.; A Achwan, W.; et al. Alpha-1-acid glycoprotein as potential biomarker for alpha-fetoprotein-low hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Res. Notes 2010, 3, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, M.; Farid, K.; Emran, T.; El-Taweel, F.; Tabll, A.; Omran, M. HCC-Mark: A simple non-invasive model based on routine parameters for predicting hepatitis C virus related hepatocellular carcinoma. Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 2021, 78, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, T.; Jin, B.; Li, W.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Song, Y.; Li, N. Diagnosis accuracy of serum glypican-3 level in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Int. J. Biol. Mrk. 2018, 33, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, S.; Plymoth, A.; Ge, S.; Feng, Z.; Rosen, H.R.; Sangrajrang, S.; Hainaut, P.; Marrero, J.A.; Beretta, L. Identification of osteopontin as a novel marker for early hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2012, 55, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouad, S.A.; Mohamed, N.A.; Fawzy, M.W.; Moustafa, D.A. Plasma Osteopontin Level in Chronic Liver Disease and Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepat. Mon. 2015, 15, e30753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, X.; Dai, M.; Huang, S.; Chen, J.; Dai, S. Diagnostic accuracy of osteopontin plus alpha-fetoprotein in the hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2017, 41, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biasiolo, A.; Trotta, E.; Fasolato, S.; Ruvoletto, M.; Martini, A.; Gallotta, A.; Fassina, G.; Angeli, P.; Gatta, A.; Pontisso, P. Squamous cell carcinoma antigen-IgM is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis: A prospective study. Dig. Liver Dis. Off. J. Ital. Soc. Gastroenterol. Ital. Assoc. Study Liver 2016, 48, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fouda, M.S.; Omran, M.M.; Tarek, G.; Hady, A.A.W.A. Development of a novel panel based on micro-RNAs (21, 29a, 200 and 335) and alpha-fetoprotein as diagnostic biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma associated with hepatitis C infection. Arab J. Gastroenterol. Off. Publ. Pan-Arab Assoc. Gastroenterol. 2021, 22, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Li, J.; Qian, Y.; Liu, W.; Liang, J.; Huang, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhao, C. Identification of plasma miR-148a as a noninvasive biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2019, 43, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shehab-Eldeen, S.; Nada, A.; Abou-Elela, D.; El-Naidany, S.; Arafat, E.; Omar, T. Diagnostic Performance of microRNA-122 and microRNA-224 in Hepatitis C Virus-Induced Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC). Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. APJCP 2019, 20, 2515–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Hamouly, M.S.; Azzam, A.A.; Ghanem, S.E.; El-Bassal, F.I.; Shebl, N.; Shehata, A.M.F. Circulating microRNA-301 as a promising diagnostic biomarker of hepatitis C virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2019, 46, 5759–5765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attallah, A.M.; El-Far, M.; Abdelrazek, M.A.; Omran, M.M.; Attallah, A.A.; Elkhouly, A.A.; Elkenawy, H.M.; Farid, K. Combined use of nuclear phosphoprotein c-Myc and cellular phosphoprotein p53 for hepatocellular carcinoma detection in high-risk chronic hepatitis C patients. Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 2017, 74, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, A.; Marquart, L.; Calvopina, D.A.; Genz, B.; Ramm, G.A.; Skoien, R. Serum MicroRNAs as Biomarkers in Hepatitis C: Preliminary Evidence of a MicroRNA Panel for the Diagnosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attallah, A.M.; Omran, M.M.; Attallah, A.A.; Abdallah, S.O.; Farid, K.; Darwish, H.; El-Dosoky, I.; Shaker, Y.M. HCC-ART score, a simple, highly sensitive and specific test for early diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: A large-scale, multicentre study. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 109, 1657–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attallah, A.M.; Omran, M.M.; Attallah, A.A.; Abdelrazek, M.A.; Farid, K.; El-Dosoky, I. Simplified HCC-ART score for highly sensitive detection of small-sized and early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma in the widely used Okuda, CLIP, and BCLC staging systems. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 22, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Omar, M.A.; Omran, M.M.; Farid, K.; Tabll, A.A.; Shahein, Y.E.; Emran, T.M.; Petrovic, A.; Lucic, N.R.; Smolic, R.; Kovac, T.; et al. Biomarkers for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: From Origin to Clinical Diagnosis. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1852. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11071852
Omar MA, Omran MM, Farid K, Tabll AA, Shahein YE, Emran TM, Petrovic A, Lucic NR, Smolic R, Kovac T, et al. Biomarkers for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: From Origin to Clinical Diagnosis. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(7):1852. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11071852
Chicago/Turabian StyleOmar, Mona A., Mohamed M. Omran, Khaled Farid, Ashraf A. Tabll, Yasser E. Shahein, Tarek M. Emran, Ana Petrovic, Nikola R. Lucic, Robert Smolic, Tanja Kovac, and et al. 2023. "Biomarkers for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: From Origin to Clinical Diagnosis" Biomedicines 11, no. 7: 1852. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11071852
APA StyleOmar, M. A., Omran, M. M., Farid, K., Tabll, A. A., Shahein, Y. E., Emran, T. M., Petrovic, A., Lucic, N. R., Smolic, R., Kovac, T., & Smolic, M. (2023). Biomarkers for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: From Origin to Clinical Diagnosis. Biomedicines, 11(7), 1852. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11071852







