Bioinformatic Analysis and Machine Learning Methods in Neonatal Sepsis: Identification of Biomarkers and Immune Infiltration
Abstract
1. Introduction
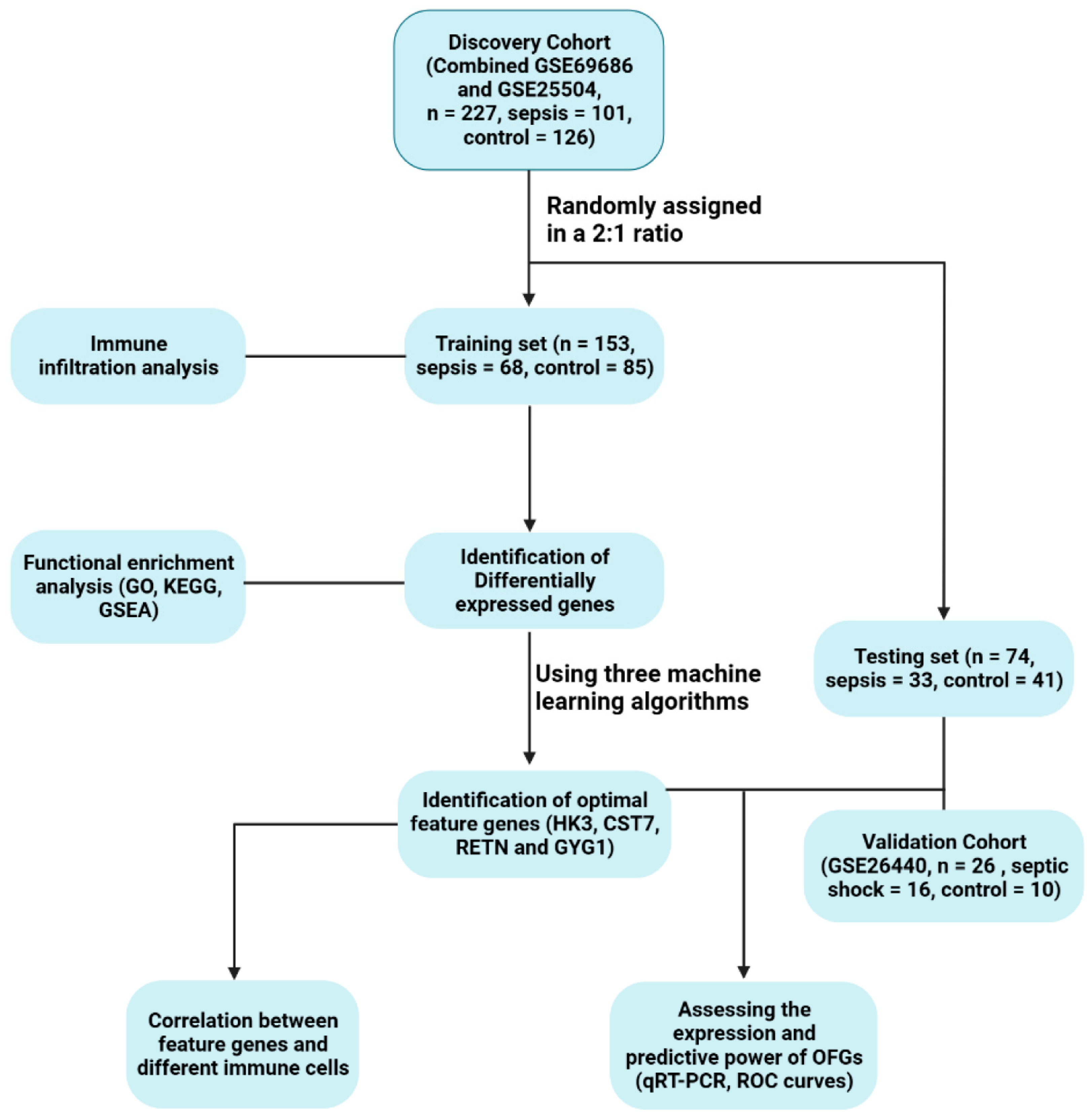
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collecting and Preprocessing Data
2.2. Identification of Differentially Expressed Genes
2.3. Evaluation of Functional Enrichment
2.4. Filtering of Optimal Feature Genes
2.5. Validation of the OFGs’ Diagnostic Quality
2.6. Assessment of Immune Cell Infiltration
2.7. Culture and Stimulation of Cells
2.8. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
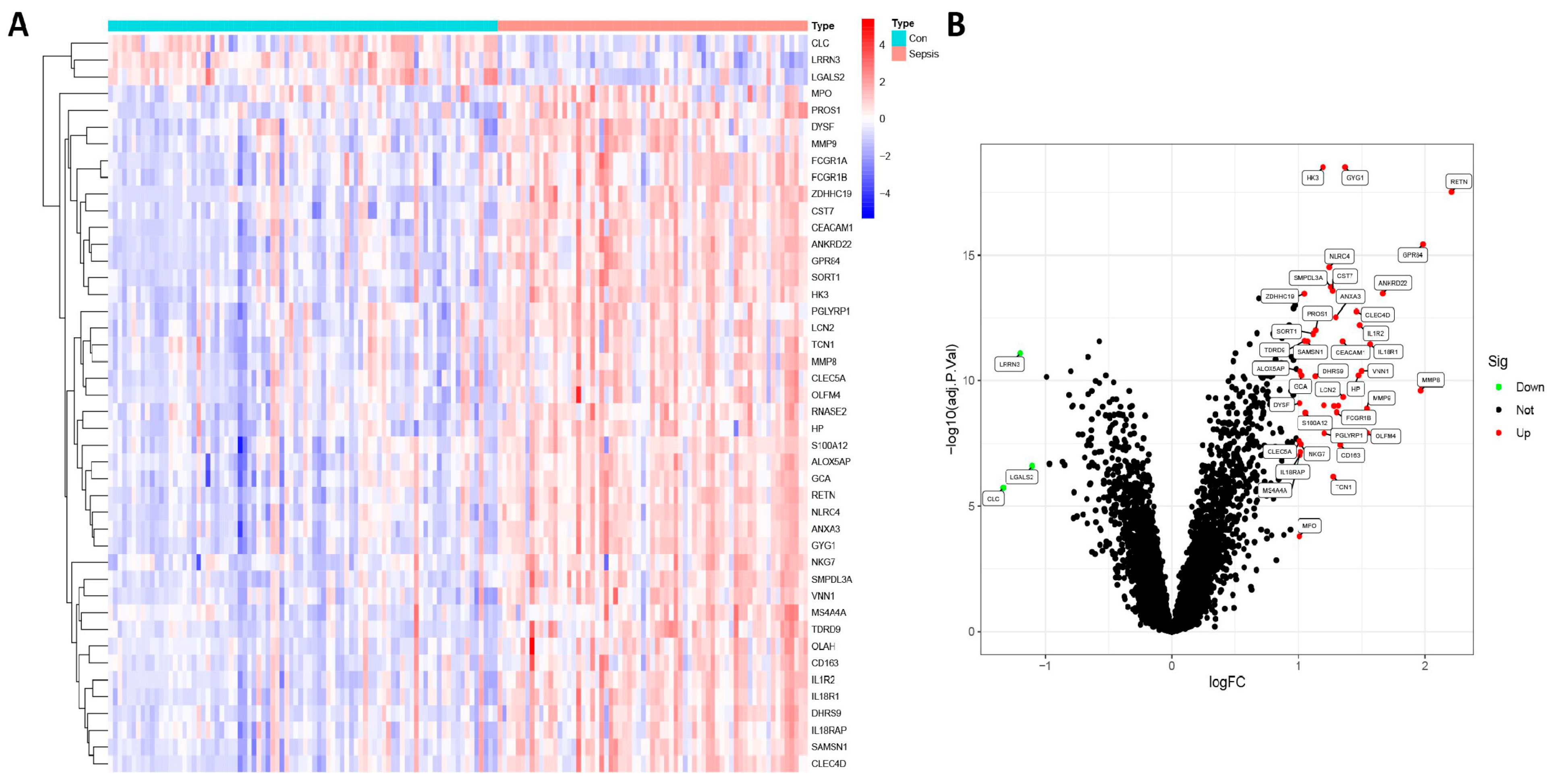
3.1. Identification of DEGs
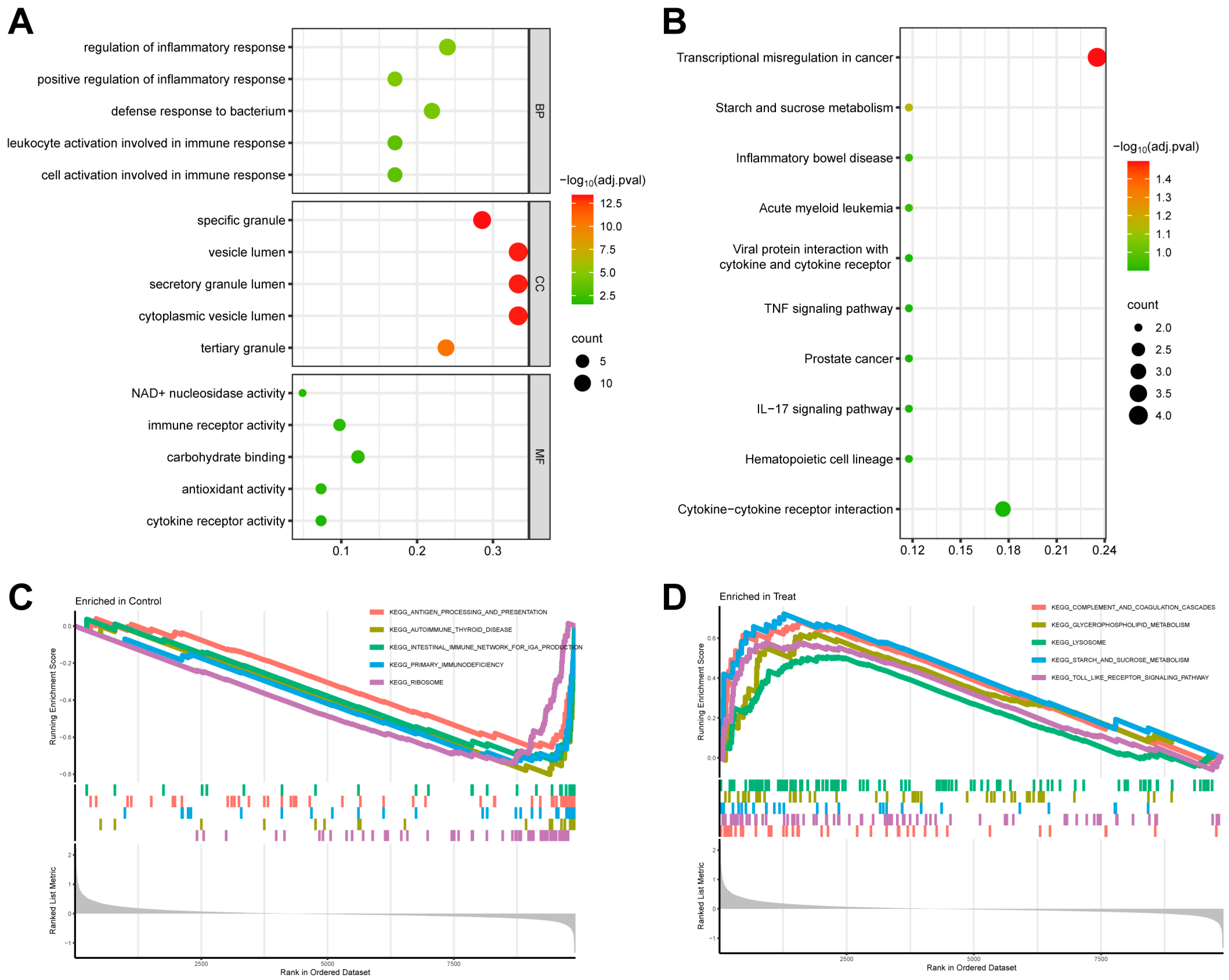
3.2. Evaluation of Functional Enrichment
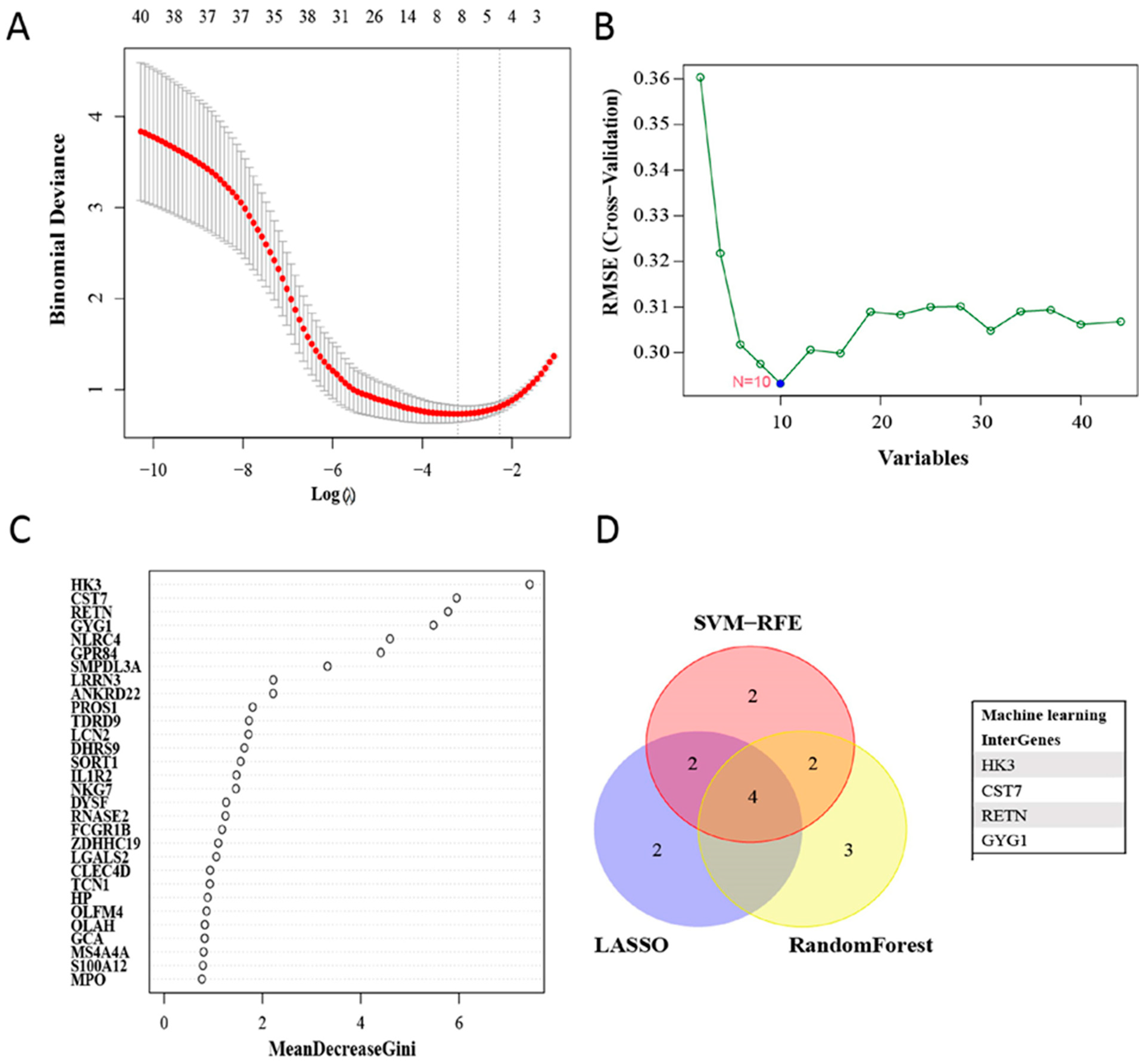
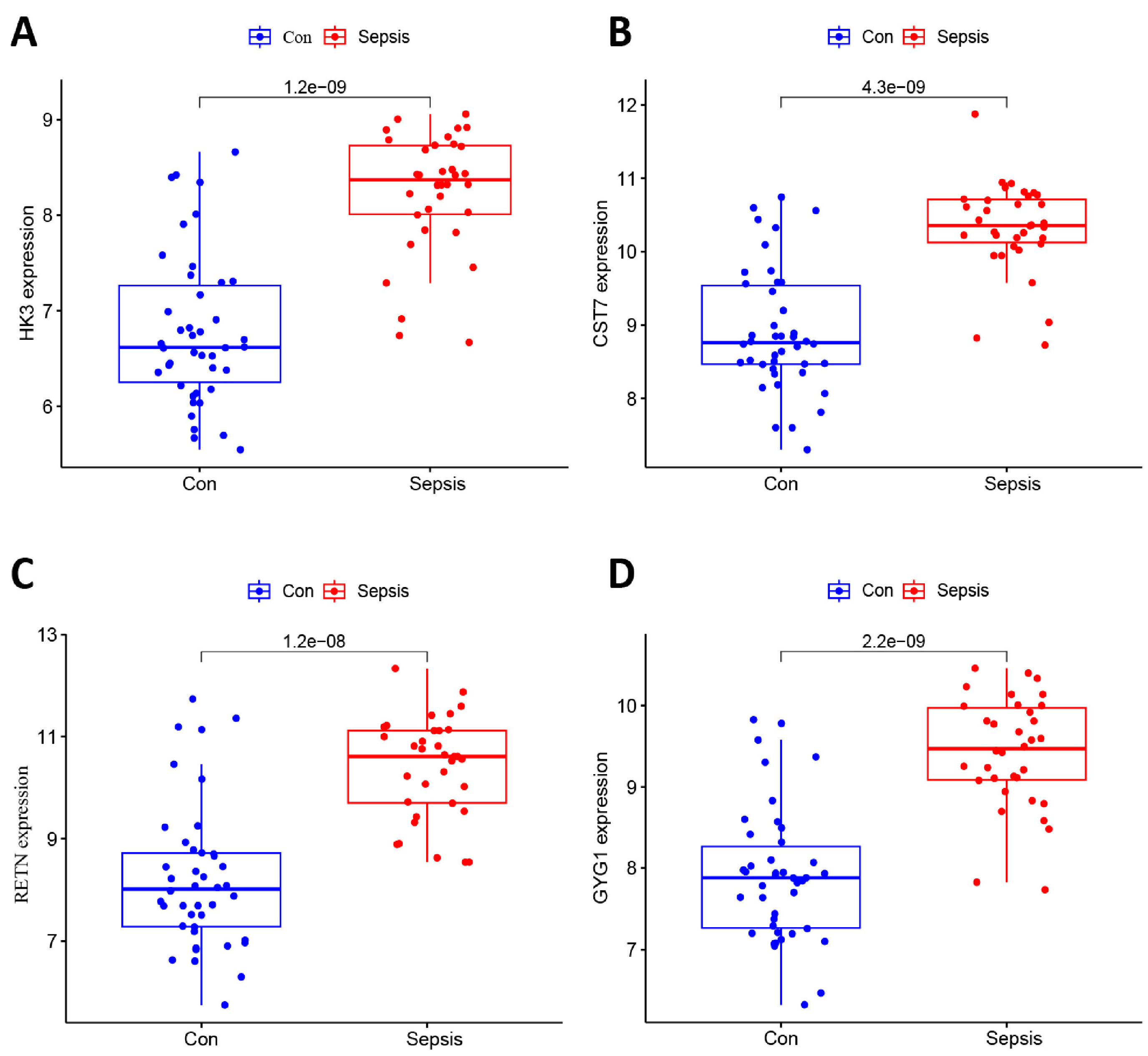
3.3. Filtering and Validation of the OFGs
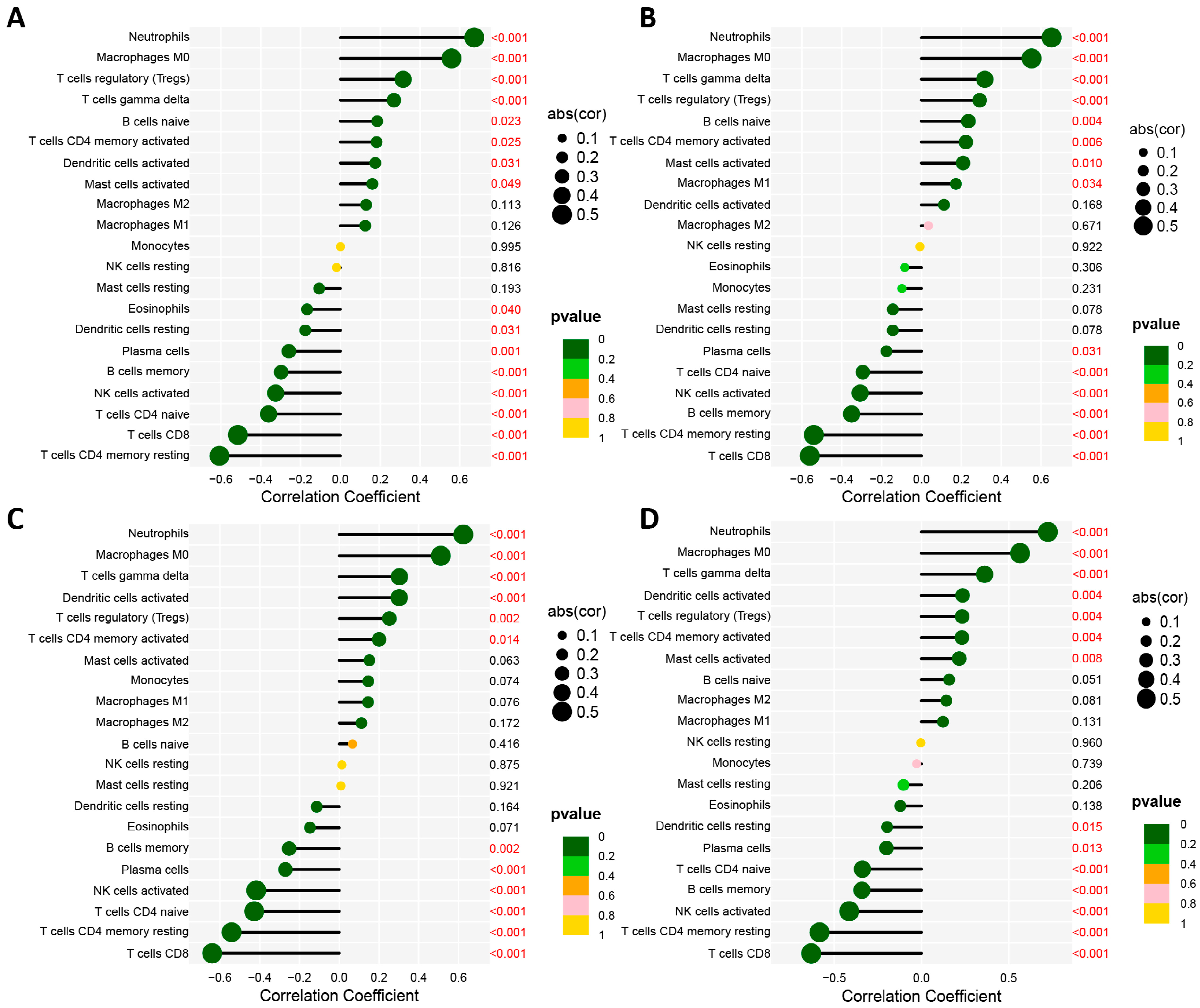
3.4. Assessment of Immune Cell Infiltration
3.5. Association of Biomarkers with Infiltrating Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Weiss, S.L.; Peters, M.J.; Alhazzani, W.; Agus, M.S.D.; Flori, H.R.; Inwald, D.P.; Nadel, S.; Schlapbach, L.J.; Tasker, R.C.; Argent, A.C.; et al. Surviving sepsis campaign international guidelines for the management of septic shock and sepsis-associated organ dysfunction in children. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46 (Suppl. S1), 10–67. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yismaw, A.E.; Abebil, T.Y.; Biweta, M.A.; Araya, B.M. Proportion of neonatal sepsis and determinant factors among neonates admitted in University of Gondar comprehensive specialized hospital neonatal Intensive care unit Northwest Ethiopia 2017. BMC Res. Notes 2019, 12, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weitkamp, J.H. The Role of Biomarkers in Suspected Neonatal Sepsis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, e391–e393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shane, A.L.; Sanchez, P.J.; Stoll, B.J. Neonatal sepsis. Lancet 2017, 390, 1770–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.; McElvania, E. Diagnostic Challenges and Laboratory Considerations for Pediatric Sepsis. J. Appl. Lab. Med. 2019, 3, 587–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altunhan, H.; Annagur, A.; Ors, R.; Mehmetoglu, I. Procalcitonin measurement at 24 hours of age may be helpful in the prompt diagnosis of early-onset neonatal sepsis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 15, e854–e858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Farahbakhsh, N.; Shastri, S.; Sharma, P. Biomarkers for diagnosis of neonatal sepsis: A literature review. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2018, 31, 1646–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilfillan, M.; Bhandari, V. Biomarkers for the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis and necrotizing enterocolitis: Clinical practice guidelines. Early Hum. Dev. 2017, 105, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iroh Tam, P.Y.; Bendel, C.M. Diagnostics for neonatal sepsis: Current approaches and future directions. Pediatr. Res. 2017, 82, 574–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, N.; Tiwari, S.; Jain, U. Potential biomarkers for effective screening of neonatal sepsis infections: An overview. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 107, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sweeney, T.E.; Wynn, J.L.; Cernada, M.; Serna, E.; Wong, H.R.; Baker, H.V.; Vento, M.; Khatri, P. Validation of the Sepsis MetaScore for Diagnosis of Neonatal Sepsis. J. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. Soc. 2018, 7, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.R., 3rd; Lopansri, B.K.; Burke, J.P.; Levy, M.; Opal, S.; Rothman, R.E.; D’Alessio, F.R.; Sidhaye, V.K.; Aggarwal, N.R.; Balk, R.; et al. Validation of a Host Response Assay, SeptiCyte LAB, for Discriminating Sepsis from Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome in the ICU. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 198, 903–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, M.; El-Manzalawy, Y. Machine learning based refined differential gene expression analysis of pediatric sepsis. BMC Med. Genom. 2020, 13, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Zhou, T. Identification of key biomarkers in neonatal sepsis by integrated bioinformatics analysis and clinical validation. Heliyon 2022, 8, e11634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delano, M.J.; Ward, P.A. The immune system’s role in sepsis progression, resolution, and long-term outcome. Immunol. Rev. 2016, 274, 330–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhao, B.; Yang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, H.; Wang, G. Diagnostic and Predictive Values of Ferroptosis-Related Genes in Child Sepsis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 881914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Tan, J.; Chen, X.; Zhao, L. Identifying Potential Effective Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers in Sepsis by Bioinformatics Analysis and Validation. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2022, 15, 6055–6071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, T.; Wilhite, S.E.; Ledoux, P.; Evangelista, C.; Kim, I.F.; Tomashevsky, M.; Marshall, K.A.; Phillippy, K.H.; Sherman, P.M.; Holko, M.; et al. NCBI GEO: Archive for functional genomics data sets–update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D991–D995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leek, J.T.; Johnson, W.E.; Parker, H.S.; Jaffe, A.E.; Storey, J.D. The sva package for removing batch effects and other unwanted variation in high-throughput experiments. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 882–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, H.R.; Amos, C.I. Gene set selection via LASSO penalized regression (SLPR). Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, e114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, X.; Zou, B.; Zou, F.; Hu, J. Permutation-based identification of important biomarkers for complex diseases via machine learning models. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kursa, M.B. Robustness of Random Forest-based gene selection methods. BMC Bioinform. 2014, 15, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robin, X.; Turck, N.; Hainard, A.; Tiberti, N.; Lisacek, F.; Sanchez, J.C.; Muller, M. pROC: An open-source package for R and S+ to analyze and compare ROC curves. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, A.M.; Liu, C.L.; Green, M.R.; Gentles, A.J.; Feng, W.; Xu, Y.; Hoang, C.D.; Diehn, M.; Alizadeh, A.A. Robust enumeration of cell subsets from tissue expression profiles. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mussap, M.; Cibecchini, F.; Noto, A.; Fanos, V. In search of biomarkers for diagnosing and managing neonatal sepsis: The role of angiopoietins. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2013, 26 (Suppl. S2), 24–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrasanta, C.; Pugni, L.; Ronchi, A.; Bottino, I.; Ghirardi, B.; Sanchez-Schmitz, G.; Borriello, F.; Mosca, F.; Levy, O. Vascular Endothelium in Neonatal Sepsis: Basic Mechanisms and Translational Opportunities. Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bzdok, D.; Krzywinski, M.; Altman, N. Machine learning: Supervised methods. Nat. Methods 2018, 15, 5–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, L.; Singbartl, K.; Chroneos, Z.C.; Ruiz-Velasco, V.; Lang, C.H.; Bonavia, A. Resistin directly inhibits bacterial killing in neutrophils. Intensive Care Med. Exp. 2019, 7, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattab, A.A.; El-Mekkawy, M.S.; Helwa, M.A.; Omar, E.S. Utility of serum resistin in the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis and prediction of disease severity in term and late preterm infants. J. Perinat. Med. 2018, 46, 919–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyer, A.J.; Garand, M.; Chaussabel, D.; Feng, C.G. Transcriptomic Profiling Identifies Neutrophil-Specific Upregulation of Cystatin F as a Marker of Acute Inflammation in Humans. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 634119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kos, J.; Nanut, M.P.; Prunk, M.; Sabotic, J.; Dautovic, E.; Jewett, A. Cystatin F as a regulator of immune cell cytotoxicity. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2018, 67, 1931–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cekmez, F.; Canpolat, F.E.; Cetinkaya, M.; Aydinoz, S.; Aydemir, G.; Karademir, F.; Ipcioglu, O.M.; Sarici, S.U. Diagnostic value of resistin and visfatin, in comparison with C-reactive protein, procalcitonin and interleukin-6 in neonatal sepsis. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2011, 22, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gokmen, Z.; Ozkiraz, S.; Kulaksizoglu, S.; Kilicdag, H.; Ozel, D.; Ecevit, A.; Tarcan, A. Resistin—A novel feature in the diagnosis of sepsis in premature neonates. Am. J. Perinatol. 2013, 30, 513–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aliefendioglu, D.; Gursoy, T.; Caglayan, O.; Aktas, A.; Ovali, F. Can resistin be a new indicator of neonatal sepsis? Pediatr. Neonatol. 2014, 55, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visuttijai, K.; Hedberg-Oldfors, C.; Thomsen, C.; Glamuzina, E.; Kornblum, C.; Tasca, G.; Hernandez-Lain, A.; Sandstedt, J.; Dellgren, G.; Roach, P.; et al. Glycogenin is Dispensable for Glycogen Synthesis in Human Muscle, and Glycogenin Deficiency Causes Polyglucosan Storage. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomsen, C.; Malfatti, E.; Jovanovic, A.; Roberts, M.; Kalev, O.; Lindberg, C.; Oldfors, A. Proteomic characterisation of polyglucosan bodies in skeletal muscle in RBCK1 deficiency. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2022, 48, e12761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazeldine, J.; Hampson, P.; Lord, J.M. The impact of trauma on neutrophil function. Injury 2014, 45, 1824–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, R.; Barlow, C.; Lekstrom-Himes, J.; Castilla, L.H.; Liu, P.P.; Eckhaus, M.; Decker, T.; Wynshaw-Boris, A.; Xanthopoulos, K.G. Impaired granulopoiesis, myelodysplasia, and early lethality in CCAAT/enhancer binding protein epsilon-deficient mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 13187–13192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Luo, L.; Wang, Y.; Rahman, M.; Lepsenyi, M.; Syk, I.; Jeppsson, B.; Thorlacius, H. Simvastatin protects against T cell immune dysfunction in abdominal sepsis. Shock 2012, 38, 524–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, Z.; Palani, K.; Zhang, S.; Lepsenyi, M.; Hwaiz, R.; Rahman, M.; Syk, I.; Jeppsson, B.; Thorlacius, H. Rho kinase regulates induction of T-cell immune dysfunction in abdominal sepsis. Infect. Immun. 2013, 81, 2499–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgeson, G.D.; Szony, B.J.; Streitman, K.; Kovacs, A.; Kovacs, L.; Laszlo, A. Natural killer cell cytotoxicity is deficient in newborns with sepsis and recurrent infections. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2001, 160, 478–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhmaltdinova, L.L.; Zhumadilova, Z.A.; Kolesnichenko, S.I.; Lavrinenko, A.V.; Kadyrova, I.A.; Avdienko, O.V.; Panibratec, L.G.; Vinogradskaya, E.V. The Presence of PDL-1 on CD8+ Lymphocytes Is Linked to Survival in Neonatal Sepsis. Children 2022, 9, 1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Primers | Sequence (5′→3′) | |
|---|---|---|
| HK3 | Forward | 5′-GGACAGGAGCACCCTCATTTC-3′ |
| Reverse | 5′-CCTCCGAATGGCATCTCTCAG-3′ | |
| CST7 | Forward | 5′-GTGTGAAGCCAGGATTTCCTAA-3′ |
| Reverse | 5′-TGTCGTTCGTGCAGTTGTTGA-3′ | |
| RETN | Forward | 5′-CTGTTGGTGTCTAGCAAGACC-3′ |
| Reverse | 5′-CCAATGCTGCTTATTGCCCTAAA-3′ | |
| GYG1 | Forward | 5′-TGACACTAACCACAAACGATGC-3′ |
| Reverse | 5′-TAGATGAGCAGAATCGCCACT-3′ | |
| CLC | Forward | 5′-TCTACTGTGACAATCAAAGGGC-3′ |
| Reverse | 5′-CACGACGACCAAAGCACAC-3′ | |
| LRRN3 | Forward | 5′-AAGCCTCTTATCAATCTTCGCAG-3′ |
| Reverse | 5′-CCAGTCCAACCAAGGCGTTA-3′ | |
| MMP8 | Forward | 5′-GGAAGGCAGGAGAGGTTGTC-3′ |
| Reverse | 5′-GTTGAAAGGCATGGGCAAGG-3′ | |
| MPO | Forward | 5′-TTGACAACCTGCACGATGAC-3′ |
| Reverse | 5′-TGTGCTCCCGAAGTAAGAG-3′ | |
| GAPDH | Forward | 5′-GCCTCAAAATCCTCTCGTTGTG-3′ |
| Reverse | 5′-GGAAGATGGTGATGGGATTTC-3′ | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, Z.; Luo, Y.; Wei, L.; Gu, R.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, S. Bioinformatic Analysis and Machine Learning Methods in Neonatal Sepsis: Identification of Biomarkers and Immune Infiltration. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1853. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11071853
Jiang Z, Luo Y, Wei L, Gu R, Zhang X, Zhou Y, Zhang S. Bioinformatic Analysis and Machine Learning Methods in Neonatal Sepsis: Identification of Biomarkers and Immune Infiltration. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(7):1853. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11071853
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Zhou, Yujia Luo, Li Wei, Rui Gu, Xuandong Zhang, Yuanyuan Zhou, and Songying Zhang. 2023. "Bioinformatic Analysis and Machine Learning Methods in Neonatal Sepsis: Identification of Biomarkers and Immune Infiltration" Biomedicines 11, no. 7: 1853. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11071853
APA StyleJiang, Z., Luo, Y., Wei, L., Gu, R., Zhang, X., Zhou, Y., & Zhang, S. (2023). Bioinformatic Analysis and Machine Learning Methods in Neonatal Sepsis: Identification of Biomarkers and Immune Infiltration. Biomedicines, 11(7), 1853. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11071853




