Anti-Cytosolic 5′-Nucleotidase 1A in the Diagnosis of Patients with Suspected Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies: An Italian Real-Life, Single-Centre Retrospective Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
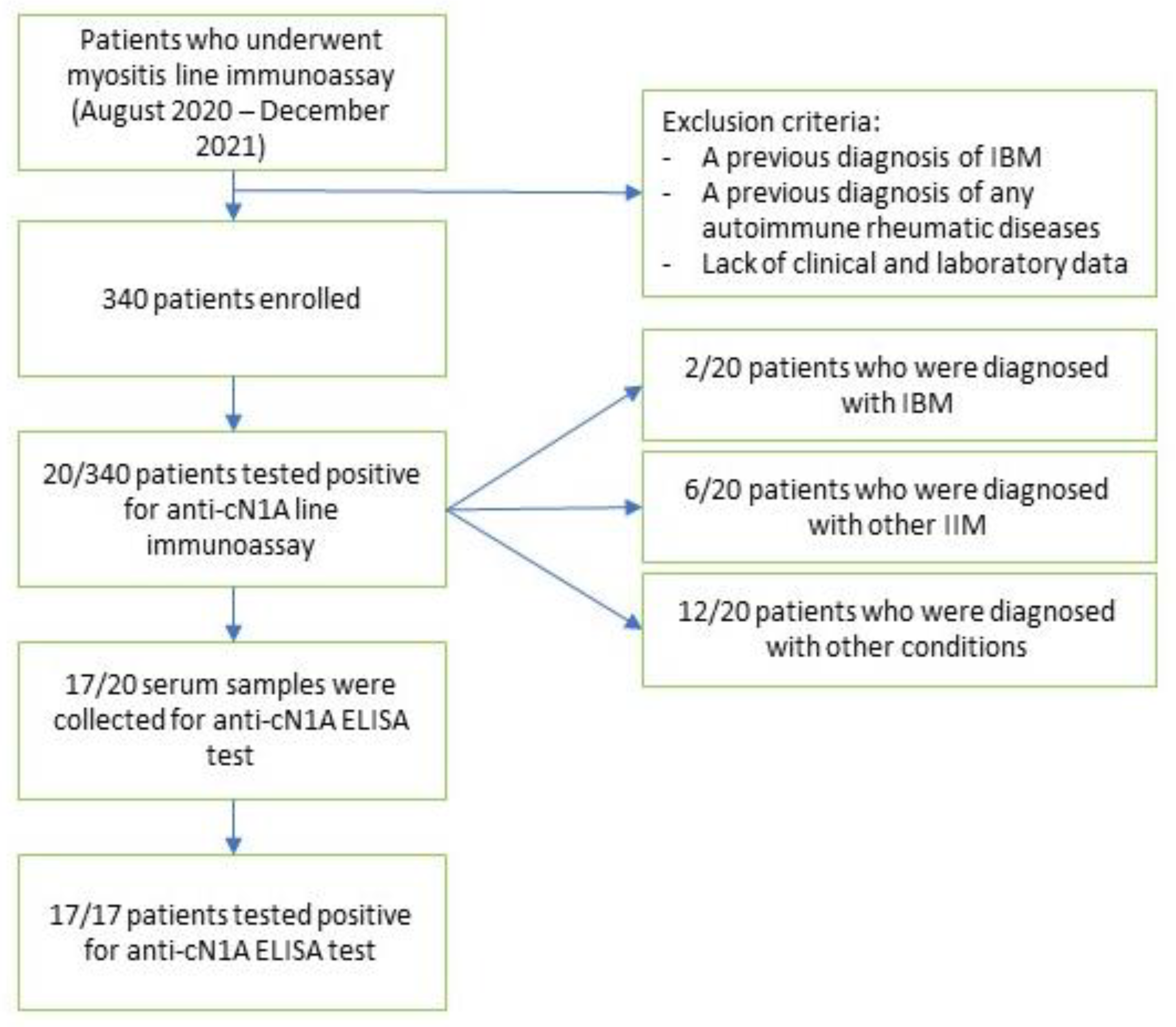
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Diagnostic Criteria
2.3. Clinical Details
2.4. cN1A Assay
2.5. Muscle Biopsy
2.6. Ethics
3. Results
Clinical Profile of the Cohort
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Key Messages
- -
- An excellent concordance was achieved between line immunoassay and ELISA test for anti-cN1A antibodies
- -
- anti-cN1A appears far from being considered a specific biomarker for inclusion body myositis (IBM)
- -
- patients carrying anti-cN1A positivity warrant a cautious assessment, inclusive of muscle biopsy
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Pinto, M.V.; Laughlin, R.S.; Klein, C.J.; Mandrekar, J.; Naddaf, E. Inclusion body myositis: Correlation of clinical outcomes with histopathology, electromyography and laboratory findings. Rheumatology 2022, 61, 2504–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenberg, S.A. Inclusion body myositis: Clinical features and pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2019, 15, 257–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moll, S.A.; Platenburg, M.G.J.P.; Platteel, A.C.M.; Vorselaars, A.D.M.; Janssen Bonàs, M.; Roodenburg-Benschop, C.; Meek, B.; van Moorsel, C.H.M.; Grutters, J.C. Prevalence of Novel Myositis Autoantibodies in a Large Cohort of Patients with Interstitial Lung Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucchini, M.; Maggi, L.; Pegoraro, E.; Filosto, M.; Rodolico, C.; Antonini, G.; Garibaldi, M.; Valentino, M.L.; Siciliano, G.; Tasca, G.; et al. Anti-cN1A Antibodies Are Associated with More Severe Dysphagia in Sporadic Inclusion Body Myositis. Cells 2021, 10, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavroudis, I.; Knights, M.; Petridis, F.; Chatzikonstantinou, S.; Karantali, E.; Kazis, D. Diagnostic Accuracy of Anti-CN1A on the Diagnosis of Inclusion Body Myositis. A Hierarchical Bivariate and Bayesian Meta-analysis. J. Clin. Neuromuscul. Dis. 2021, 23, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rietveld, A.; van den Hoogen, L.L.; Bizzaro, N.; Blokland, S.L.M.; Dähnrich, C.; Gottenberg, J.-E.; Houen, G.; Johannsen, N.; Mandl, T.; Meyer, A.; et al. Autoantibodies to Cytosolic 5′-Nucleotidase 1A in Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, P.; Liewluck, T.; Ernste, F.C.; Mandrekar, J.; Milone, M. Anti-cN1A antibodies do not correlate with specific clinical, electromyographic, or pathological findings in sporadic inclusion body myositis. Muscle Nerve 2021, 63, 490–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, S.; Dimachkie, M.M.; Hanna, M.G.; Machado, P.M. Diagnostic and prognostic value of anti-cN1A antibodies in inclusion body myositis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2022, 40, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pestronk, A.; Li, F.; Bieser, K.; Choksi, R.; Whitton, A.; Kornberg, A.J.; Goldstein, J.M.; Yee, W.C. Anti-MAG antibodies: Major effects of antigen purity and antibody cross-reactivity on ELISA results and clinical correlation. Neurology 1994, 44, 1131–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, N.A.; Cash, T.M.; Alam, U.; Enam, S.; Tierney, P.; Araujo, N.; Mozaffar, F.H.; Pestronk, A.; Mozaffar, T. Seropositivity for NT5c1A antibody in sporadic inclusion body myositis predicts more severe motor, bulbar and respiratory involvement. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2016, 87, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramp, S.L.; Karayev, D.; Shen, G.; Metzger, A.L.; Morris, R.I.; Karayev, E.; Lam, Y.; Kazdan, R.M.; Pruijn, G.J.M.; Saschenbrecker, S.; et al. Development and evaluation of a standardized ELISA for the determination of autoantibodies against cN-1A (Mup44, NT5C1A) in sporadic inclusion body myositis. Auto-Immun. Highlights 2016, 7, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. Ann. Intern. Med. 2007, 147, 573–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, M.R.; ENMC IBM Working Group. 188th ENMC International Workshop: Inclusion Body Myositis, 2–4 December 2011, Naarden, The Netherlands. Neuromuscul. Disord. NMD 2013, 23, 1044–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohan, A.; Peter, J.B. Polymyositis and dermatomyositis (first of two parts). N. Engl. J. Med. 1975, 292, 344–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lega, J.-C.; Reynaud, Q.; Belot, A.; Fabien, N.; Durieu, I.; Cottin, V. Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies and the lung. Eur. Respir. Rev. Off. J. Eur. Respir. Soc. 2015, 24, 216–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aringer, M.; Costenbader, K.; Daikh, D.; Brinks, R.; Mosca, M.; Ramsey-Goldman, R.; Smolen, J.S.; Wofsy, D.; Boumpas, D.T.; Kamen, D.L.; et al. 2019 European League Against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology Classification Criteria for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 1400–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Hoogen, F.; Khanna, D.; Fransen, J.; Johnson, S.R.; Baron, M.; Tyndall, A.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; Naden, R.P.; Medsger, T.A.; Carreira, P.E.; et al. 2013 classification criteria for systemic sclerosis: An American college of rheumatology/European league against rheumatism collaborative initiative. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, 1747–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiboski, C.H.; Shiboski, S.C.; Seror, R.; Criswell, L.A.; Labetoulle, M.; Lietman, T.M.; Rasmussen, A.; Scofield, H.; Vitali, C.; Bowman, S.J.; et al. 2016 American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism Classification Criteria for Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome: A Consensus and Data-Driven Methodology Involving Three International Patient Cohorts. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017, 69, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autoimmune Inflammatory Myopathies 16 Ag (IgG) EUROLINE. Available online: http://shop.tinyteria.com/index.php?route=product/product&product_id=1317 (accessed on 1 August 2022).
- Larman, H.B.; Salajegheh, M.; Nazareno, R.; Lam, T.; Sauld, J.; Steen, H.; Kong, S.W.; Pinkus, J.L.; Amato, A.A.; Elledge, S.J.; et al. Cytosolic 5′-nucleotidase 1A autoimmunity in sporadic inclusion body myositis. Ann. Neurol. 2013, 73, 408–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damoiseaux, J.; Vulsteke, J.-B.; Tseng, C.-W.; Platteel, A.C.M.; Piette, Y.; Shovman, O.; Bonroy, C.; Hamann, D.; De Langhe, E.; Musset, L.; et al. Autoantibodies in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies: Clinical associations and laboratory evaluation by mono- and multispecific immunoassays. Autoimmun. Rev. 2019, 18, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conticini, E.; Sota, J.; Falsetti, P.; Bellisai, F.; Bacarelli, M.R.; Al-Khayyat, S.G.; Cantarini, L.; Frediani, B. Anti-dense fine speckled 70 antibodies in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2020, 38 (Suppl. S126), 326. [Google Scholar]
- Herbert, M.K.; Stammen-Vogelzangs, J.; Verbeek, M.M.; Rietveld, A.; Lundberg, I.E.; Chinoy, H.; Lamb, J.A.; Cooper, R.G.; Roberts, M.; Badrising, U.A.; et al. Disease specificity of autoantibodies to cytosolic 5′-nucleotidase 1A in sporadic inclusion body myositis versus known autoimmune diseases. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 696–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
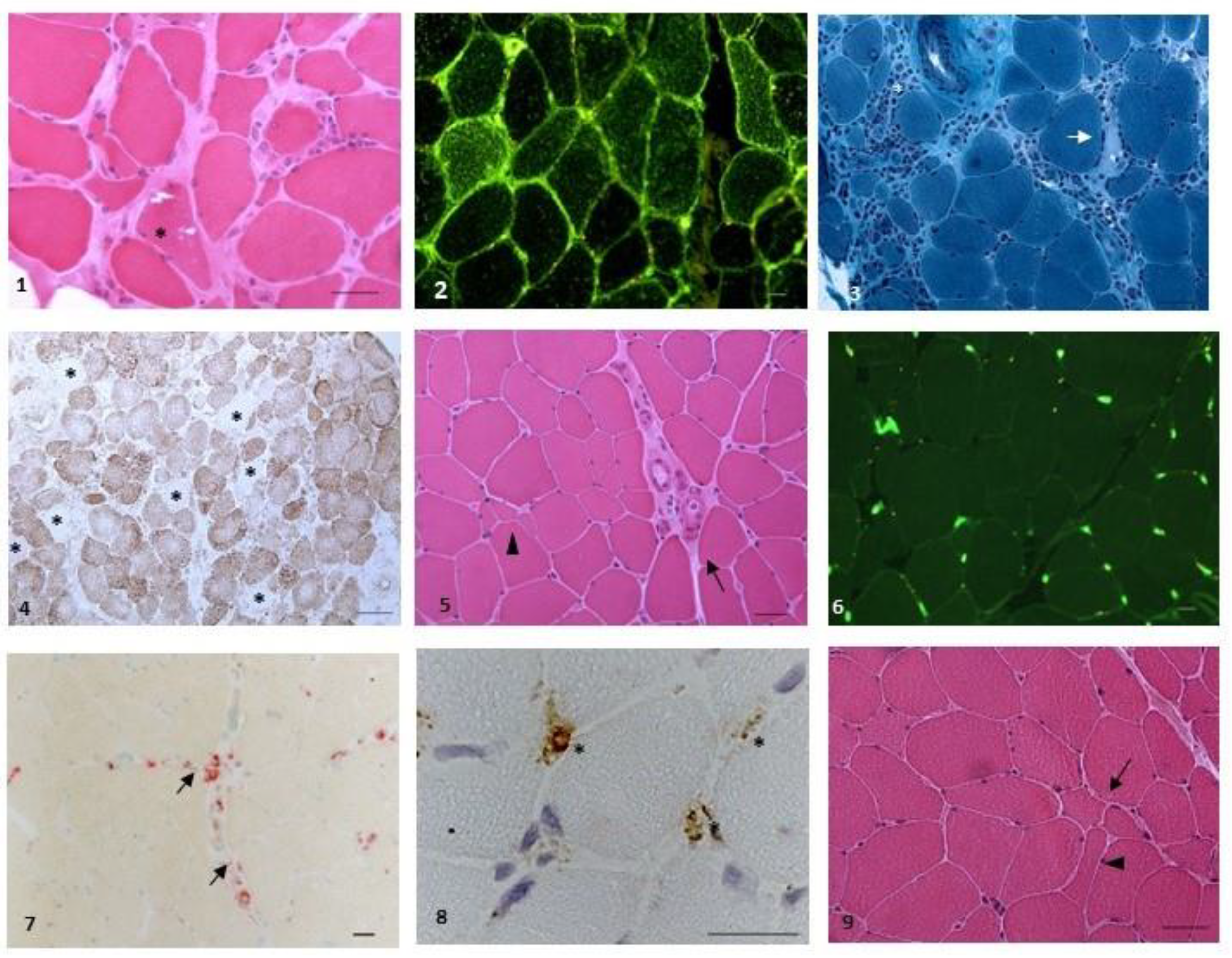
| n | Age | Gender | Definite Diagnosis | Other Autoantibodies | ANA Titre | ANA Pattern | ELISA Anti-cN1A Ratio (v.n. < 1.0) | Biopsy Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 68 | F | Scleromyositis | anti-CENP, AMA-M2, M2-3E | 1:160 | AC-3 | 3.86 | Myopathic changes, no inflammation |
| 2 | 30 | M | SpA | - | - | - | 1.9 | - |
| 3 | 79 | F | Seronegative arthritis, myopathic changes | - | 1:320 | AC-1 | 5.3 | Mild myopathic changes, no inflammation |
| 4 | 69 | F | IBM | - | - | - | 5.21 | Rimmed vacuoles, inflammation, mitochondrial changes |
| 5 | 23 | M | SpA | - | - | - | 1.49 | - |
| 6 | 64 | F | UCTD | anti-RNA-POL III | 1:160 | AC-8 | 2.9 | |
| 7 | 66 | F | PM | anti-Tg, anti-TPO | 1:640 | AC-4 | 2.55 | Myopathic changes. Endomysial inflammation, necrosis and regeneration |
| 8 | 53 | F | Seronegative arthritis, panuveitis | anti-Tg, anti-TPO | 1:160 | AC-18 | 1.01 | - |
| 9 | 84 | M | DM | - | - | - | 5.79 | Microvasculopathy, myopathic changes |
| 10 | 49 | F | Seronegative arthritis | - | - | - | 3.61 | |
| 11 | 80 | F | DM | - | 1:160 | AC-1 | 4.17 | Mild myopathic changes, microvasculopathy |
| 12 | 62 | F | Myasthenia gravis | anti-SM | 1:320 | AC-1 | Not performed | |
| 13 | 67 | F | DM | - | - | - | 4.28 | Mild perivascular inflammation |
| 14 | 40 | F | SpA | - | 1:320 | AC-15 | 1.77 | |
| 15 | 50 | F | PM | - | 1:160 | AC-4 | 1.6 | Mild aspecific myopathic changes |
| 16 | 85 | F | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | - | - | - | 2.86 | |
| 17 | 55 | F | Hypersensitivity pneumonia | - | - | - | 2.71 | |
| 18 | 41 | F | No definite diagnosis- | - | - | - | 4.18 | |
| 19 | 86 | M | IBM | - | - | - | Not performed | Rimmed vacuoles, inflammation, mitochondrial changes |
| 20 | 51 | F | UCTD | - | 1:320 | AC-1 | Not performed | Myopathy, no inflammation |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Porcelli, B.; d’Alessandro, M.; Gupta, L.; Grazzini, S.; Volpi, N.; Bacarelli, M.R.; Ginanneschi, F.; Biasi, G.; Bellisai, F.; Fabbroni, M.; et al. Anti-Cytosolic 5′-Nucleotidase 1A in the Diagnosis of Patients with Suspected Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies: An Italian Real-Life, Single-Centre Retrospective Study. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1963. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11071963
Porcelli B, d’Alessandro M, Gupta L, Grazzini S, Volpi N, Bacarelli MR, Ginanneschi F, Biasi G, Bellisai F, Fabbroni M, et al. Anti-Cytosolic 5′-Nucleotidase 1A in the Diagnosis of Patients with Suspected Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies: An Italian Real-Life, Single-Centre Retrospective Study. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(7):1963. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11071963
Chicago/Turabian StylePorcelli, Brunetta, Miriana d’Alessandro, Latika Gupta, Silvia Grazzini, Nila Volpi, Maria Romana Bacarelli, Federica Ginanneschi, Giovanni Biasi, Francesca Bellisai, Marta Fabbroni, and et al. 2023. "Anti-Cytosolic 5′-Nucleotidase 1A in the Diagnosis of Patients with Suspected Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies: An Italian Real-Life, Single-Centre Retrospective Study" Biomedicines 11, no. 7: 1963. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11071963
APA StylePorcelli, B., d’Alessandro, M., Gupta, L., Grazzini, S., Volpi, N., Bacarelli, M. R., Ginanneschi, F., Biasi, G., Bellisai, F., Fabbroni, M., Bennett, D., Fabiani, C., Cantarini, L., Bargagli, E., Frediani, B., & Conticini, E. (2023). Anti-Cytosolic 5′-Nucleotidase 1A in the Diagnosis of Patients with Suspected Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies: An Italian Real-Life, Single-Centre Retrospective Study. Biomedicines, 11(7), 1963. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11071963








