DNA Methylation Signatures of Response to Conventional Synthetic and Biologic Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs) in Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Genetic and Transcriptomic Biomarkers of RA Treatment Response
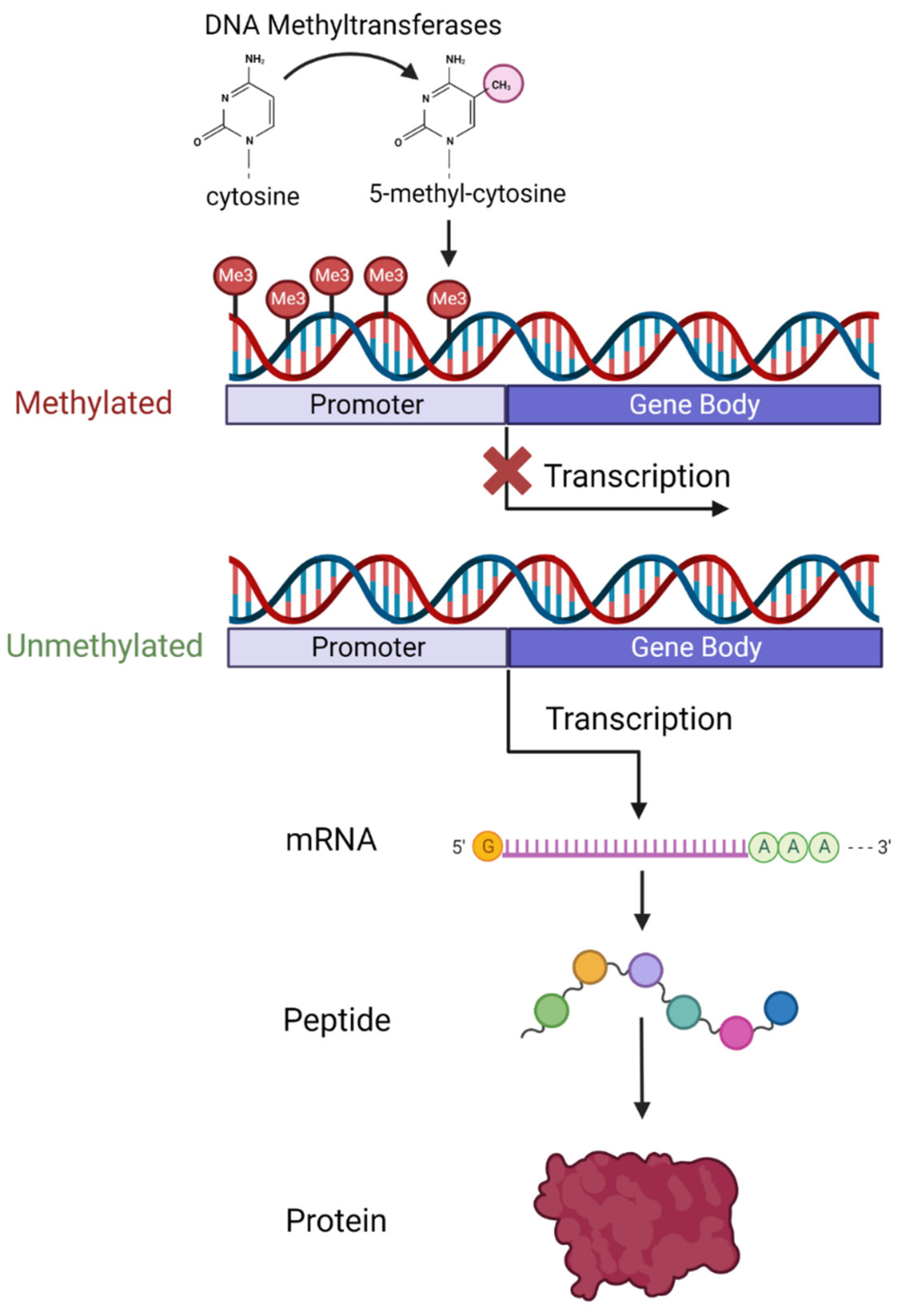
3. An Overview of DNA Methylation
4. DNA Methylation in RA
5. DNA Methylation Biomarkers in Other Autoimmune Diseases
6. DNA Methylation as a Biomarker
7. DNA Methylation and Response to csDMARDs
8. DNA Methylation and Response to Biological and Targeted Synthetic (Jak-Inhibitors-JAKI) DMARDs
9. Discussion
10. Future Perspectives
11. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- MacGregor, A.J.; Snieder, H.; Rigby, A.S.; Koskenvuo, M.; Kaprio, J.; Aho, K.; Silman, A.J. Characterizing the quantitative genetic contribution to rheumatoid arthritis using data from twins. Arthritis Rheum. 2000, 43, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silman, A.J.; MacGregor, A.; Thomson, W.; Holligan, S.; Carthy, D.; Farhan, A.; Ollier, W.E.R. Twin concordance rates for rheumatoid arthritis: Results from a nationwide study. Br. J. Rheumatol. 1993, 32, 903–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, J.; Gallazzi, F.; Bono, E.; Karr, R.W.; Guenot, J.; Valsasnini, P.; Nagy, Z.A.; Sinigaglia, F. Peptide binding specificity of HLA-DR4 molecules: Correlation with rheumatoid arthritis association. J. Exp. Med. 1995, 181, 1847–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messemaker, T.C.; Huizinga, T.W.; Kurreeman, F. Immunogenetics of rheumatoid arthritis: Understanding functional implications. J. Autoimmun. 2015, 64, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Woude, D.; Houwing-Duistermaat, J.J.; Toes, R.E.; Huizinga, T.W.; Thomson, W.; Worthington, J.; van der Helm-van Mil, A.H.; de Vries, R.R. Quantitative heritability of anti–citrullinated protein antibody–positive and anti–citrullinated protein antibody–negative rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. Off. J. Am. Coll. Rheumatol. 2009, 60, 916–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deane, K.D.; Demoruelle, M.K.; Kelmenson, L.B.; Kuhn, K.A.; Norris, J.M.; Holers, V.M. Genetic and environmental risk factors for rheumatoid arthritis. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2017, 31, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Wang, Y.; Xu, D.; Nossent, J.; Pavlos, N.J.; Xu, J. Rheumatoid arthritis: Pathological mechanisms and modern pharmacologic therapies. Bone Res. 2018, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panagopoulos, P.K.; Lambrou, G.I. Bone erosions in rheumatoid arthritis: Recent developments in pathogenesis and therapeutic implications. J. Musculoskelet. Neuronal Interact. 2018, 18, 304–319. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sokka, T.; Kautiainen, H.; Pincus, T.; Verstappen, S.M.; Aggarwal, A.; Alten, R.; Andersone, D.; Badsha, H.; Baecklund, E.; Belmonte, M.; et al. Work disability remains a major problem in rheumatoid arthritis in the 2000s: Data from 32 countries in the QUEST-RA Study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2010, 12, R42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallert, E.; Husberg, M.; Bernfort, L. The incidence of permanent work disability in patients with rheumatoid arthritis in Sweden 1990-2010: Before and after introduction of biologic agents. Rheumatology 2011, 51, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolen, J.S.; Landewé, R.B.M.; Bergstra, S.A.; Kerschbaumer, A.; Sepriano, A.; Aletaha, D.; Caporali, R.; Edwards, C.J.; Hyrich, K.L.; Pope, J.E.; et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2022 update. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 82, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, P.M.; Pratt, A.G.; Isaacs, J.D. Mechanism of action of methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis, and the search for biomarkers. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 731–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessels, J.A.M.; Huizinga, T.W.J.; Guchelaar, H.-J. Recent insights in the pharmacological actions of methotrexate in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2008, 47, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergeant, J.C.; RAMS Co-Investigators; Hyrich, K.L.; Anderson, J.; Kopec-Harding, K.; Hope, H.; Symmons, D.P.M.; Barton, A.; Verstappen, S.M.M. Prediction of primary non-response to methotrexate therapy using demographic, clinical and psychosocial variables: Results from the UK Rheumatoid Arthritis Medication Study (RAMS). Arthritis Res. Ther. 2018, 20, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rendas-Baum, R.; Wallenstein, G.V.; Koncz, T.; Kosinski, M.; Yang, M.; Bradley, J.; Zwillich, S.H. Evaluating the efficacy of sequential biologic therapies for rheumatoid arthritis patients with an inadequate response to tumor necrosis factor-α inhibitors. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2011, 13, R25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mysler, E.; Caubet, M.; Lizarraga, A. Current and Emerging DMARDs for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Open Access Rheumatol. 2021, 13, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teitsma, X.M.; Jacobs, J.W.G.; Welsing, P.M.J.; de Jong, P.H.P.; Hazes, J.M.W.; Weel, A.E.A.M.; Pethö-Schramm, A.; Borm, M.E.A.; van Laar, J.M.; Lafeber, F.P.J.G.; et al. Inadequate response to treat-to-target methotrexate therapy in patients with new-onset rheumatoid arthritis: Development and validation of clinical predictors. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 1261–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burmester, G.R.; Ferraccioli, G.; Flipo, R.-M.; Monteagudo-Sáez, I.; Unnebrink, K.; Kary, S.; Kupper, H. Clinical remission and/or minimal disease activity in patients receiving adalimumab treatment in a multinational, open-label, twelve-week study. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 59, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyrich, K.L.; Watson, K.D.; Silman, A.J.; Symmons, D.P.M.; Register, T.B.B. Predictors of response to anti-TNF-alpha therapy among patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Results from the British Society for Rheumatology Biologics Register. Rheumatology 2006, 45, 1558–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijbrandts, C.A.; Tak, P.P. Prediction of Response to Targeted Treatment in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2017, 92, 1129–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancarella, L.; Bobbio-Pallavicini, F.; Ceccarelli, F.; Falappone, P.C.; Ferrante, A.; Malesci, D.; Massara, A.; Nacci, F.; Secchi, M.E.; Manganelli, S.; et al. Good clinical response, remission, and predictors of remission in rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with tumor necrosis factor-alpha blockers: The GISEA study. J. Rheumatol. 2007, 34, 1670–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potter, C.; Hyrich, K.L.; Tracey, A.; Lunt, M.; Plant, D.; Symmons, D.P.M.; Thomson, W.; Worthington, J.; Emery, P.; Morgan, A.W.; et al. Association of rheumatoid factor and anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide positivity, but not carriage of shared epitope or PTPN22 susceptibility variants, with anti-tumour necrosis factor response in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2009, 68, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijbrandts, C.A.; Dijkgraaf, M.G.W.; Kraan, M.C.; Vinkenoog, M.; Smeets, T.J.; Dinant, H.; Vos, K.; Lems, W.F.; Wolbink, G.J.; Sijpkens, D.; et al. The clinical response to infliximab in rheumatoid arthritis is in part dependent on pretreatment tumour necrosis factor alpha expression in the synovium. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2008, 67, 1139–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plant, D.; Wilson, A.G.; Barton, A. Genetic and epigenetic predictors of responsiveness to treatment in RA. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2014, 10, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senapati, S.; Singh, S.; Das, M.; Kumar, A.; Gupta, R.; Kumar, U.; Jain, S.; Juyal, R.C.; Thelma, B. Genome-wide analysis of methotrexate pharmacogenomics in rheumatoid arthritis shows multiple novel risk variants and leads for TYMS regulation. Pharmacogenetics Genom. 2014, 24, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.C.; Matura, O.B.O.T.; Bongartz, T.; Massey, J.; Mifsud, B.; Spiliopoulou, A.; Scott, I.C.; Wang, J.; Morgan, M.; Plant, D.; et al. Genome-wide association study of response to methotrexate in early rheumatoid arthritis patients. Pharmacogenomics J. 2018, 18, 528–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Padilla, A.J.; Gamez-Nava, J.I.; Saldaña-Cruz, A.M.; Murillo-Vazquez, J.D.; Vazquez-Villegas, M.L.; Zavaleta-Muñiz, S.A.; Martín-Márquez, B.T.; Ponce-Guarneros, J.M.; Jimenez, N.A.R.; Flores-Chavez, A.; et al. The -174G/C Interleukin-6 Gene Promoter Polymorphism as a Genetic Marker of Differences in Therapeutic Response to Methotrexate and Leflunomide in Rheumatoid Arthritis. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 4193538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humby, F.; Lewis, M.; Ramamoorthi, N.; Hackney, J.A.; Barnes, M.R.; Bombardieri, M.; Setiadi, A.F.; Kelly, S.; Bene, F.; DiCicco, M.; et al. Synovial cellular and molecular signatures stratify clinical response to csDMARD therapy and predict radiographic progression in early rheumatoid arthritis patients. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 761–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, M.J.; Barnes, M.R.; Blighe, K.; Goldmann, K.; Rana, S.; Hackney, J.A.; Ramamoorthi, N.; John, C.R.; Watson, D.S.; Kummerfeld, S.K.; et al. Faculty Opinions recommendation of Molecular portraits of early rheumatoid arthritis identify clinical and treatment response phenotypes. Cell Rep. 2019, 28, 2455–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lliso-Ribera, G.; Humby, F.; Lewis, M.; Nerviani, A.; Mauro, D.; Rivellese, F.; Kelly, S.; Hands, R.; Bene, F.; Ramamoorthi, N.; et al. Synovial tissue signatures enhance clinical classification and prognostic/treatment response algorithms in early inflammatory arthritis and predict requirement for subsequent biological therapy: Results from the pathobiology of early arthritis cohort (PEAC). Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 1642–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Saevarsdottir, S.; Thomson, B.; Padyukov, L.; van der Helm-Van Mil, A.H.; Nititham, J.; Hughes, L.B.; De Vries, N.; Raychaudhuri, S.; Alfredsson, L.; et al. Rheumatoid arthritis risk allele PTPRC is also associated with response to anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha therapy. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 1849–1861. [Google Scholar]
- Plant, D.; Prajapati, R.; Hyrich, K.L.; Morgan, A.W.; Wilson, A.G.; Isaacs, J.D.; Barton, A. Biologics in Rheumatoid Arthritis Genetics and Genomics Study Syndicate. Replication of association of the PTPRC gene with response to anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy in a large UK cohort. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 665–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zervou, M.I.; Myrthianou, E.; Flouri, I.; Plant, D.; Chlouverakis, G.; Castro-Giner, F.; Rapsomaniki, P.; Barton, A.; Boumpas, D.T.; Sidiropoulos, P.; et al. Lack of Association of Variants Previously Associated with Anti-TNF Medication Response in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients: Results from a Homogeneous Greek Population. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maxwell, J.R.; Potter, C.; Hyrich, K.L.; Barton, A.; Worthington, J.; Isaacs, J.D.; Morgan, A.W.; Wilson, A.G. Association of the tumour necrosis factor-308 variant with differential response to anti-TNF agents in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2008, 17, 3532–3538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuchacovich, M.; Soto, L.; Edwardes, M.; Gutierrez, M.; Llanos, C.; Pacheco, D.; Sabugo, F.; Alamo, M.; Fuentealba, C.; Villanueva, L.; et al. Tumour necrosis factor (TNF)α −308 G/G promoter polymorphism and TNFα levels correlate with a better response to adalimumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2006, 35, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dávila-Fajardo, C.L.; Márquez, A.; Pascual-Salcedo, D.; Ramos, M.J.M.; García-Portales, R.; Magro, C.; Alegre-Sancho, J.J.; Balsa, A.; Cabeza-Barrera, J.; Raya, E.; et al. Confirmation of −174G/C interleukin-6 gene promoter polymorphism as a genetic marker predicting antitumor necrosis factor treatment outcome. Pharmacogenetics Genom. 2014, 24, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jančić, I.; Arsenović-Ranin, N.; Šefik-Bukilica, M.; Živojinović, S.; Damjanov, N.; Spasovski, V.; Srzentić, S.; Stanković, B.; Pavlović, S. -174G/C interleukin-6 gene promoter polymorphism predicts therapeutic response to etanercept in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol. Int. 2012, 33, 1481–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canet, L.M.; Sánchez-Maldonado, J.M.; Cáliz, R.; Rodríguez-Ramos, A.; Lupiañez, C.B.; Canhão, H.; Martínez-Bueno, M.; Escudero, A.; Segura-Catena, J.; Sorensen, S.B.; et al. Polymorphisms at phase I-metabolizing enzyme and hormone receptor loci influence the response to anti-TNF therapy in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Pharmacogenomics J. 2019, 19, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirkov, M.U.; Cui, J.; Vermeulen, S.H.; Stahl, E.A.; Toonen, E.J.M.; Makkinje, R.R.; Lee, A.T.; Huizinga, T.W.J.; Allaart, R.; Barton, A.; et al. Genome-wide association analysis of anti-TNF drug response in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, 1375–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Stahl, E.A.; Saevarsdottir, S.; Miceli, C.; Diogo, R.; Trynka, G.; Raj, T.; Mirkov, M.U.; Canhão, H.; Ikari, K.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study and Gene Expression Analysis Identifies CD84 as a Predictor of Response to Etanercept Therapy in Rheumatoid Arthritis. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plant, D.; Bowes, J.; Potter, C.; Hyrich, K.L.; Morgan, A.W.; Wilson, A.G.; Isaacs, J.D.; Barton, A.; Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium; British Society for Rheumatology Biologics Register. Genome-wide association study of genetic predictors of anti–tumor necrosis factor treatment efficacy in rheumatoid arthritis identifies associations with polymorphisms at seven loci. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreiro-Iglesias, A.; Montes, A.; Perez-Pampin, E.; Cañete, J.D.; Raya, E.; Magro-Checa, C.; Vasilopoulos, Y.; Caliz, R.; Ferrer, M.A.; Joven, B.; et al. Evaluation of 12 GWAS-drawn SNPs as biomarkers of rheumatoid arthritis response to TNF inhibitors. A potential SNP association with response to etanercept. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0213073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humby, F.; Durez, P.; Buch, M.H.; Lewis, M.J.; Rizvi, H.; Rivellese, F.; Nerviani, A.; Giorli, G.; Mahto, A.; Montecucco, C.; et al. Rituximab versus tocilizumab in anti-TNF inadequate responder patients with rheumatoid arthritis (R4RA): 16-week outcomes of a stratified, biopsy-driven, multicentre, open-label, phase 4 randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2021, 397, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivellese, F.; Surace, A.E.A.; Goldmann, K.; Sciacca, E.; Çubuk, C.; Giorli, G.; John, C.R.; Nerviani, A.; Fossati-Jimack, L.; Thorborn, G.; et al. Rituximab versus tocilizumab in rheumatoid arthritis: Synovial biopsy-based biomarker analysis of the phase 4 R4RA randomized trial. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1256–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lequerré, T.; Gauthier-Jauneau, A.-C.; Bansard, C.; Derambure, C.; Hiron, M.; Vittecoq, O.; Daveau, M.; Mejjad, O.; Daragon, A.; Tron, F.; et al. Gene profiling in white blood cells predicts infliximab responsiveness in rheumatoid arthritis. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 8, R105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Julià, A.; Erra, A.; Palacio, C.; Tomas, C.; Sans, X.; Barceló, P.; Marsal, S. An Eight-Gene Blood Expression Profile Predicts the Response to Infliximab in Rheumatoid Arthritis. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuhlmüller, B.; Häupl, T.; Hernández, M.M.; Grützkau, A.; Kuban, R.-J.; Tandon, N.; Voss, J.W.; Salfeld, J.; Kinne, R.W.; Burmester, G.R. CD11c as a Transcriptional Biomarker to Predict Response to Anti-TNF Monotherapy with Adalimumab in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 87, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toonen, E.J.M.; Gilissen, C.; Franke, B.; Kievit, W.; Eijsbouts, A.M.; Broeder, A.A.D.; van Reijmersdal, S.V.; Veltman, J.A.; Scheffer, H.; Radstake, T.R.D.J.; et al. Validation Study of Existing Gene Expression Signatures for Anti-TNF Treatment in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valli, A.; Kuuliala, K.; Virtanen, A.; Kuuliala, A.; Palmroth, M.; Peltomaa, R.; Vidqvist, K.-L.; Leirisalo-Repo, M.; Silvennoinen, O.; Isomäki, P. Tofacitinib treatment modulates the levels of several inflammation-related plasma proteins in rheumatoid arthritis and baseline levels of soluble biomarkers associate with the treatment response. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2022, 210, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciechomska, M.; Roszkowski, L.; Burakowski, T.; Massalska, M.; Felis-Giemza, A.; Roura, A.-J. Circulating miRNA-19b as a biomarker of disease progression and treatment response to baricitinib in rheumatoid arthritis patients through miRNA profiling of monocytes. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 980247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lu, Q.; Chang, C. Epigenetics in Health and Disease. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1253, 3–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deaton, A.M.; Bird, A. CpG islands and the regulation of transcription. Genes Dev. 2011, 25, 1010–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vavouri, T.; Lehner, B. Human genes with CpG island promoters have a distinct transcription-associated chromatin organization. Genome Biol. 2012, 13, R110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, A. DNA methylation patterns and epigenetic memory. Genes Dev. 2002, 16, 6–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorincz, M.C.; Dickerson, D.R.; Schmitt, M.; Groudine, M. Faculty Opinions recommendation of Intragenic DNA methylation alters chromatin structure and elongation efficiency in mammalian cells. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2004, 11, 1068–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Xiong, F.; Wu, G.; Liu, W.; Chen, J.; Wang, B.; Chen, Y. Gene body methylation in cancer: Molecular mechanisms and clinical applications. Clin. Epigenetics 2022, 14, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopalakrishnan, S.; Van Emburgh, B.O.; Robertson, K.D. DNA methylation in development and human disease. Mutat. Res. 2008, 647, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messerschmidt, D.M.; Knowles, B.B.; Solter, D. DNA methylation dynamics during epigenetic reprogramming in the germline and preimplantation embryos. Genes Dev. 2014, 28, 812–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govender, P.; Ghai, M.; Okpeku, M. Sex-specific DNA methylation: Impact on human health and development. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2022, 297, 1451–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, L.D.; Le, T.; Fan, G. DNA Methylation and Its Basic Function. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013, 38, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerkel, K.; Spadola, A.; Yuan, E.; Kosek, J.; Jiang, L.; Hod, E.; Li, K.; Murty, V.V.; Schupf, N.; Vilain, E.; et al. Genomic surveys by methylation-sensitive SNP analysis identify sequence-dependent allele-specific DNA methylation. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 904–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, L.L.; Emberly, E.; Fraser, H.B.; Neumann, S.M.; Chen, E.; Miller, G.E.; Kobor, M.S. Factors underlying variable DNA methylation in a human community cohort. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109 (Suppl. S2), 17253–17260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Aryee, M.J.; Padyukov, L.; Fallin, M.D.; Hesselberg, E.; Runarsson, A.; Reinius, L.; Acevedo, N.; Taub, M.; Ronninger, M.; et al. Epigenome-wide association data implicate DNA methylation as an intermediary of genetic risk in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Ubreva, J.; de la Calle-Fabregat, C.; Li, T.; Ciudad, L.; Ballestar, M.L.; Català-Moll, F.; Morante-Palacios, O.; Garcia-Gomez, A.; Celis, R.; Humby, F.; et al. Inflammatory cytokines shape a changing DNA methylome in monocytes mirroring disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 1505–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liebold, I.; Grützkau, A.; Göckeritz, A.; Gerl, V.; Lindquist, R.; Feist, E.; Zänker, M.; Häupl, T.; Poddubnyy, D.; Zernicke, J.; et al. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells are hypomethylated in active rheumatoid arthritis and methylation correlates with disease activity. Rheumatology 2020, 60, 1984–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Wu, L.-F.; Mo, X.-B.; Lu, X.; Tang, H.; Zhu, X.-W.; Xia, W.; Guo, Y.-F.; Wang, M.-J.; Zeng, K.-Q.; et al. Rheumatoid arthritis–associated DNA methylation sites in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glossop, J.R.; Emes, R.D.; Nixon, N.B.; Packham, J.C.; Fryer, A.A.; Mattey, D.L.; Farrell, W.E. Genome-wide profiling in treatment-naive early rheumatoid arthritis reveals DNA methylome changes in T and B lymphocytes. Epigenomics 2016, 8, 209–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glossop, J.R.; Emes, R.D.; Nixon, N.B.; Haworth, K.E.; Packham, J.C.; Dawes, P.T.; Fryer, A.A.; Mattey, D.L.; Farrell, W.E. Genome-wide DNA methylation profiling in rheumatoid arthritis identifies disease-associated methylation changes that are distinct to individual T- and B-lymphocyte populations. Epigenetics 2014, 9, 1228–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Q.; Li, T.; Chen, P.; Wu, Y.; Wang, T.; Mo, L.; Ou, J.; Nandakumar, K.S. Comparative Analysis on Abnormal Methylome of Differentially Expressed Genes and Disease Pathways in the Immune Cells of RA and SLE. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 668007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guderud, K.; Sunde, L.H.; Flåm, S.T.; Mæhlen, M.T.; Mjaavatten, M.D.; Lillegraven, S.; Aga, A.B.; Evenrød, I.M.; Norli, E.S.; Andreassen, B.K.; et al. Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients, Both Newly Diagnosed and Methotrexate Treated, Show More DNA Methylation Differences in CD4(+) Memory Than in CD4(+) Naïve T Cells. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Chang, H.D.; Ivascu, C.; Qian, Y.; Rezai, S.; Okhrimenko, A.; Cosmi, L.; Maggi, L.; Eckhardt, F.; Wu, P.; et al. Loss of methylation at the IFNG promoter and CNS-1 is associated with the development of functional IFN-γ memory in human CD4(+) T lymphocytes. Eur. J. Immunol. 2013, 43, 793–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitaksalee, R.; Burska, A.N.; Ajaib, S.; Rogers, J.; Parmar, R.; Mydlova, K.; Xie, X.; Droop, A.; Nijjar, J.S.; Chambers, P.; et al. Differential CpG DNA methylation in peripheral naïve CD4+ T-cells in early rheumatoid arthritis patients. Clin. Epigenetics 2020, 12, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cribbs, A.P.; Kennedy, A.; Penn, H.; Amjadi, P.; Green, P.; Read, J.E.; Brennan, F.; Gregory, B.; Williams, R.O. Methotrexate Restores Regulatory T Cell Function through Demethylation of the FoxP3 Upstream Enhancer in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 1182–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cribbs, A.P.; Kennedy, A.; Penn, H.; Read, J.E.; Amjadi, P.; Green, P.; Syed, K.; Manka, S.W.; Brennan, F.M.; Gregory, B.; et al. Treg Cell Function in Rheumatoid Arthritis Is Compromised by CTLA-4 Promoter Methylation Resulting in a Failure to Activate the Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase Pathway. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 66, 2344–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, H.; Ba, X.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Qin, K.; Huang, Y.; Shen, P.; Tu, S. Decipher manifestations and Treg/Th17 imbalance in multi-staging rheumatoid arthritis and correlation with TSDR/RORC methylation. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 127, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, K.; Whitaker, J.W.; Boyle, D.L.; Wang, W.; Firestein, G.S. DNA methylome signature in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ham, S.; Bae, J.-B.; Lee, S.; Kim, B.-J.; Han, B.-G.; Kwok, S.-K.; Roh, T.-Y. Epigenetic analysis in rheumatoid arthritis synoviocytes. Exp. Mol. Med. 2019, 51, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, R.; Hammaker, D.; Boyle, D.L.; Morgan, R.; Walsh, A.M.; Fan, S.; Firestein, G.S.; Wang, W. Joint-specific DNA methylation and transcriptome signatures in rheumatoid arthritis identify distinct pathogenic processes. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhead, B.; Holingue, C.; Cole, M.; Shao, X.; Quach, H.L.; Quach, D.; Shah, K.; Sinclair, E.; Graf, J.; Link, T.; et al. Rheumatoid Arthritis Naive T Cells Share Hypermethylation Sites with Synoviocytes. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017, 69, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, K.; Boyle, D.L.; Firestein, G.S. Regulation of DNA Methylation in Rheumatoid Arthritis Synoviocytes. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.-F.; Wu, S.; Yan, Q.; Wu, Y.-Y.; Chen, H.; Yin, S.-Q.; Chen, X.; Wang, H.; Li, J. PTEN Methylation Promotes Inflammation and Activation of Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 700373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, R.; Bs, D.L.B.; Wang, W.; Firestein, G.S. Distinct DNA Methylation Patterns of Rheumatoid Arthritis Peripheral Blood and Synovial Tissue T Cells. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2021, 3, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephenson, W.; Donlin, L.T.; Butler, A.; Rozo, C.; Bracken, B.; Rashidfarrokhi, A.; Goodman, S.M.; Ivashkiv, L.B.; Bykerk, V.P.; Orange, D.E.; et al. Single-cell RNA-seq of rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissue using low-cost microfluidic instrumentation. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joustra, V.; Hageman, I.L.; Satsangi, J.; Adams, A.; Ventham, N.T.; de Jonge, W.J.; Henneman, P.; D’haens, G.R.; Yim, A.Y.F.L. Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Peripheral Blood DNA Methylation Studies in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2022, 17, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Liu, H.; Liu, H.; Chen, Y.; Liu, T.; Shen, X.; Liu, L. Genome-wide DNA methylation profiling in differentiating Crohn’s disease from intestinal tuberculosis. Genes Genom. 2022, 44, 603–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanata, C.M.; Nititham, J.; Taylor, K.E.; Solomon, O.; Chung, S.A.; Blazer, A.; Trupin, L.; Katz, P.; Dall’Era, M.; Yazdany, J.; et al. Dynamics of Methylation of CpG Sites Associated with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Subtypes in a Longitudinal Cohort. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022, 74, 1676–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreté-Bonastre, A.G.; Cortés-Hernández, J.; Ballestar, E. What can we learn from DNA methylation studies in lupus? Clin. Immunol. 2022, 234, 108920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Gole, J.; Gore, A.; He, Q.; Lu, M.; Min, J.; Yuan, Z.; Yang, X.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, T.; et al. Non-invasive early detection of cancer four years before conventional diagnosis using a blood test. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, D.; Győrffy, B. DNA methylation-based diagnostic, prognostic, and predictive biomarkers in colorectal cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Rev. Cancer 2022, 1877, 188722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervena, K.; Siskova, A.; Buchler, T.; Vodicka, P.; Vymetalkova, V. Methylation-Based Therapies for Colorectal Cancer. Cells 2020, 9, 1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, B.; Clifton, S.; Locke, W.; Luu, P.-L.; Du, Q.; Lam, D.; Armstrong, N.J.; Kumar, B.; Deng, N.; Harvey, K.; et al. Identification of DNA methylation biomarkers with potential to predict response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer. Clin. Epigenetics 2021, 13, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigin, V.O.; Kalinkin, A.I.; Kuznetsova, E.B.; Simonova, O.A.; Chesnokova, G.G.; Litviakov, N.V.; Slonimskaya, E.M.; Tsyganov, M.M.; Ibragimova, M.K.; Volodin, I.V.; et al. DNA methylation markers panel can improve prediction of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in luminal B breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houseman, E.A.; Accomando, W.P.; Koestler, D.C.; Christensen, B.C.; Marsit, C.J.; Nelson, H.H.; Wiencke, J.K.; Kelsey, K.T. DNA methylation arrays as surrogate measures of cell mixture distribution. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Andres, M.C.; Perez-Pampin, E.; Calaza, M.; Santaclara, F.J.; Ortea, I.; Gomez-Reino, J.J.; Gonzalez, A. Assessment of global DNA methylation in peripheral blood cell subpopulations of early rheumatoid arthritis before and after methotrexate. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Gestel, A.M.; Haagsma, C.J.; van Riel, P.L. Validation of rheumatoid arthritis improvement criteria that include simplified joint counts. Arthritis Rheum. 1998, 41, 1845–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosselt, H.R.; van Zelst, B.D.; de Rotte, M.C.F.J.; Hazes, J.M.W.; de Jonge, R.; Heil, S.G. Higher baseline global leukocyte DNA methylation is associated with MTX non-response in early RA patients. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2019, 21, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glossop, J.R.; Nixon, N.B.; Emes, R.D.; Sim, J.; Packham, J.C.; Mattey, D.L.; Farrell, W.E.; Fryer, A.A. DNA methylation at diagnosis is associated with response to disease-modifying drugs in early rheumatoid arthritis. Epigenomics 2017, 9, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, N.; Wilson, A.G.; Barton, A. DNA methylation as a marker of response in rheumatoid arthritis. Pharmacogenomics 2017, 18, 1323–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosselt, H.R.; Vallerga, C.L.; Mandaviya, P.R.; Lubberts, E.; Hazes, J.M.W.; de Jonge, R.; Heil, S.G. Epigenome wide association study of response to methotrexate in early rheumatoid arthritis patients. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0247709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guderud, K.; Sunde, L.H.; Flåm, S.T.; Mæhlen, M.T.; Mjaavatten, M.D.; Norli, E.S.; Evenrød, I.M.; Andreassen, B.K.; Franzenburg, S.; Franke, A.; et al. Methotrexate Treatment of Newly Diagnosed RA Patients Is Associated with DNA Methylation Differences at Genes Relevant for Disease Pathogenesis and Pharmacological Action. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 713611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plant, D.; Webster, A.; Nair, N.; Oliver, J.; Smith, S.L.; Eyre, S.; Hyrich, K.L.; Wilson, A.G.; Morgan, A.W.; Isaacs, J.D.; et al. Differential Methylation as a Biomarker of Response to Etanercept in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 1353–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Julià, A.; Gómez, A.; López-Lasanta, M.; Blanco, F.; Erra, A.; Fernández-Nebro, A.; Mas, A.J.; Pérez-García, C.; Vivar, M.L.G.; Sánchez-Fernández, S.; et al. Longitudinal analysis of blood DNA methylation identifies mechanisms of response to tumor necrosis factor inhibitor therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. Ebiomedicine 2022, 80, 104053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, W.; Concepcion, A.N.; Vianen, M.; Marijnissen, A.C.A.; Lafeber, F.P.G.J.; Radstake, T.R.D.J.; Pandit, A. Multiomics and Machine Learning Accurately Predict Clinical Response to Adalimumab and Etanercept Therapy in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021, 73, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, O.; MacIsaac, J.; Quach, H.; Tindula, G.; Kobor, M.; Huen, K.; Meaney, M.J.; Eskenazi, B.; Barcellos, L.F.; Holland, N. Comparison of DNA methylation measured by Illumina 450K and EPIC BeadChips in blood of newborns and 14-year-old children. Epigenetics 2018, 13, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansell, G.; Gorrie-Stone, T.J.; Bao, Y.; Kumari, M.; Schalkwyk, L.S.; Mill, J.; Hannon, E. Guidance for DNA methylation studies: Statistical insights from the Illumina EPIC array. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannens, M.M.A.M.; Lombardi, M.P.; Alders, M.; Henneman, P.; Bliek, J. Further Introduction of DNA Methylation (DNAm) Arrays in Regular Diagnostics. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 831452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziller, M.J.; Gu, H.; Müller, F.; Donaghey, J.; Tsai, L.T.-Y.; Kohlbacher, O.; De Jager, P.L.; Rosen, E.D.; Bennett, D.A.; Bernstein, B.E.; et al. Charting a dynamic DNA methylation landscape of the human genome. Nature 2013, 500, 477–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logue, M.W.; Smith, A.K.; Wolf, E.J.; Maniates, H.; Stone, A.; Schichman, S.A.; McGlinchey, R.E.; Milberg, W.; Miller, M.W. The correlation of methylation levels measured using Illumina 450K and EPIC BeadChips in blood samples. Epigenomics 2017, 9, 1363–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Li, D.; Teng, D.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhong, Z.; Yang, G.-J. Epigenetic Regulation in the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 859400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhoundova, D.; Rubin, M.A. Clinical application of advanced multi-omics tumor profiling: Shaping precision oncology of the future. Cancer Cell 2022, 40, 920–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Kannan, B.; Lim, B.Y.; Li, Z.; Lim, A.H.; Loh, J.W.; Ko, T.K.; Ng, C.C.-Y.; Chan, J.Y. The Multi-Dimensional Biomarker Landscape in Cancer Immunotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Study | Medication | Patients | Sample Type | Sample Timeline | Outcome | Methylation Assay |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| De Andres et al., 2015 [94] | MTX | 19 RA (csDMARD naïve) 17 healthy controls | T, B, NK, monocytes, polymorphonuclear leukocytes | Baseline and 1 month | DAS28 at 6 months | Global methylation using mass spectrometry |
| Liebold et al., 2020 [65] | MTX, sarilumab, baricitinib or tofacitinib | 45 RA patients 17 healthy controls | PBMCs | Baseline and 3 months | EULAR criteria [95] at 6 months | Global methylation using immunofluorescence staining |
| Gosselt et al., 2019 [96] | MTX, MTX + SSZ + HCQ + corticosteroids | 181 | Leukocytes | Baseline and 3 months | EULAR criteria at 3 months | Global methylation using mass spectrometry |
| Glossop et al., 2017 [97] | MTX, SSZ and HCQ | 46 RA (csDMARD naïve) | T-cells | Baseline | EULAR criteria at 6 months | Illumina HumanMethylation450 BeadChip Array |
| Nair et al., 2017 [98] | MTX | 72 RA (36 GR, 36 NR) | Whole blood | Baseline and 4 weeks | EULAR criteria at 6 months | Illumina HumanMethylation450 BeadChip Array |
| Gosselt et al., 2021 [99] | MTX, MTX + corticosteroidsMTX+SSZ/HCQ | 68 RA (csDMARD naive) | PBMCs | Baseline and at 3 months | DAS28 at 3 months | Illumina Human Methylation EPIC array |
| Guderud et al., 2021 [70] | MTX | 11 RA (csDMARD naïve) 18 RA (MTX treated) 7 healthy controls | CD4+ T-cells | Baseline | N/A | Representation bisulfite sequencing |
| Study | Medication | Patients | Sample Type | Sample Timeline | Outcome | Methylation Assay |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plant et al., 2017 [101] | ETN | 72 (36 GR/36 NR) | Whole blood | Baseline | EULAR criteria at 3 months | Illumina HumanMethylation450 BeadChip Array |
| Julia et al., 2022 [102] | TNFi (ADA, CTZ, ETN, GOL, IFX) | 62 RA (discovery cohort) 60 RA (validation cohort) | Whole blood | Baseline and 3 months | EULAR criteria at 3 months | Illumina Human Methylation EPIC array |
| Tao et al., 2021 [103] | ADA, ETN monotherapy | 80 RA | PBMCs, monocytes, CD4+ T-cells | Baseline | EULAR criteria at 6 months | Illumina Human Methylation EPIC array |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.S.; Lewis, M.J.; Pitzalis, C. DNA Methylation Signatures of Response to Conventional Synthetic and Biologic Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs) in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1987. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11071987
Wang SS, Lewis MJ, Pitzalis C. DNA Methylation Signatures of Response to Conventional Synthetic and Biologic Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs) in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(7):1987. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11071987
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Susan Siyu, Myles J. Lewis, and Costantino Pitzalis. 2023. "DNA Methylation Signatures of Response to Conventional Synthetic and Biologic Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs) in Rheumatoid Arthritis" Biomedicines 11, no. 7: 1987. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11071987
APA StyleWang, S. S., Lewis, M. J., & Pitzalis, C. (2023). DNA Methylation Signatures of Response to Conventional Synthetic and Biologic Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs) in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Biomedicines, 11(7), 1987. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11071987






