Association between Psoriasis and Renal Functions: An Integration Study of Observational Study and Mendelian Randomization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
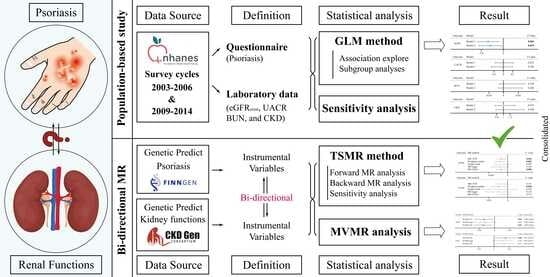
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Epidemiological Observational Study
2.2.1. Data Source
2.2.2. Measurements and Definitions
2.2.3. Covariates
2.3. Mendelian Randomization Analysis
2.3.1. Summary-Level GWAS Data
2.3.2. Selection of Instrument Variables
2.4. Statistical Analyses
2.4.1. Cross-Sectional Study
2.4.2. TSMR and MVMR Analyses
3. Result
3.1. Population-Based Study
3.2. MR Framework Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boehncke, W.H.; Schön, M.P. Psoriasis. Lancet 2015, 386, 983–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damiani, G.; Bragazzi, N.L.; Karimkhani Aksut, C.; Wu, D.; Alicandro, G.; McGonagle, D.; Guo, C.; Dellavalle, R.; Grada, A.; Wong, P. The global, regional, and national burden of psoriasis: Results and insights from the global burden of disease 2019 study. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 743180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritchlin, C.T.; Colbert, R.A.; Gladman, D.D. Psoriatic arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 957–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freuer, D.; Linseisen, J.; Meisinger, C. Association Between Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Both Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis: A Bidirectional 2-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. JAMA Dermatol. 2022, 158, 1262–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, I.M.; Ellervik, C.; Yazdanyar, S.; Jemec, G.B. Meta-analysis of psoriasis, cardiovascular disease, and associated risk factors. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2013, 69, 1014–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottlieb, A.B.; Chao, C.; Dann, F. Psoriasis comorbidities. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2008, 19, 5–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, P.S. IL-17 in renal immunity and autoimmunity. J. Immunol. 2018, 201, 3153–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Prakash, A.; Kubba, S.; Ganguli, A.; Singh, A.K.; Sikdar, S.; Dinda, A.K.; Grover, C.; Agarwal, S.K. Psoriatic nephropathy—Does an entity exist? Ren. Fail. 2005, 27, 123–127. [Google Scholar]
- Bae, E.H.; Kim, B.; Song, S.H.; Oh, T.R.; Suh, S.H.; Choi, H.S.; Kim, C.S.; Ma, S.K.; Han, K.D.; Kim, S.W. Proteinuria and Psoriasis Risk: A Nationwide Population-Based Study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, C.-C.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.-F.; Wang, S.-H.; Chen, F.-L.; Tung, T.-H. Risk of incident chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease in patients with psoriasis: A nationwide population-based cohort study. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2015, 78, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, F.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, C.; Sang, H. Psoriasis-like Inflammation Induced Renal Dysfunction through the TLR/NF-κB Signal Pathway. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 3535264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visconti, L.; Leonardi, G.; Buemi, M.; Santoro, D.; Cernaro, V.; Ricciardi, C.A.; Lacquaniti, A.; Coppolino, G. Kidney disease and psoriasis: Novel evidences beyond old concepts. Clin. Rheumatol. 2016, 35, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.-F.; Chen, T.-H.; Tsai, S.-H.; Chen, P.-E.; Chi, C.-C.; Tung, T.-H. Risk of chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease in patients with psoriasis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Dermatol. Sin. 2021, 39, 19. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, J.; Wang, S.; Haynes, K.; Denburg, M.R.; Shin, D.B.; Gelfand, J.M. Risk of moderate to advanced kidney disease in patients with psoriasis: Population based cohort study. BMJ 2013, 347, f5961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.; Han, J.H.; Bang, C.H.; Yoo, S.A.; Han, K.D.; Kim, H.N.; Park, Y.M.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, J.H. Risk of End-Stage Renal Disease in Psoriatic Patients: Real-World Data from a Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedland, R.; Kridin, K.; Cohen, A.D.; Landau, D.; Ben-Amitai, D. Psoriasis and Renal Disorders: A Large-Scale Population-Based Study in Children and Adults. Dermatology 2022, 238, 904–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, S.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, J.; Wang, X.; Lin, T. Psoriasis and risk of chronic kidney diseases: A population-based cross-sectional study and Mendelian randomization analysis. Nephrology 2023, 28, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, E.; Glymour, M.M.; Holmes, M.V.; Kang, H.; Morrison, J.; Munafò, M.R.; Palmer, T.; Schooling, C.M.; Wallace, C.; Zhao, Q.; et al. Mendelian randomization. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 2022, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, J.; Knoblauch, N.; Marcus, J.H.; Stephens, M.; He, X. Mendelian randomization accounting for correlated and uncorrelated pleiotropic effects using genome-wide summary statistics. Nat. Genet. 2020, 52, 740–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zipf, G.; Chiappa, M.; Porter, K.S.; Ostchega, Y.; Lewis, B.G.; Dostal, J. National health and nutrition examination survey: Plan and operations, 1999–2010. Vital Health Stat. 2013, 1, 1–37. [Google Scholar]
- Levey, A.S.; Stevens, L.A.; Schmid, C.H.; Zhang, Y.; Castro, A.F., III; Feldman, H.I.; Kusek, J.W.; Eggers, P.; Van Lente, F.; Greene, T. A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 150, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.; Fu, Y.; Huang, F.; Wen, L.; Weng, X.; Yao, H.; Liang, H.; Kuang, M.; Jing, C. Association between blood metal exposures and hyperuricemia in the US general adult: A subgroup analysis from NHANES. Chemosphere 2023, 318, 137873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levey, A.S.; Eckardt, K.-U.; Tsukamoto, Y.; Levin, A.; Coresh, J.; Rossert, J.; Zeeuw, D.D.; Hostetter, T.H.; Lameire, N.; Eknoyan, G. Definition and classification of chronic kidney disease: A position statement from Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO). Kidney Int. 2005, 67, 2089–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 16. Diabetes Care in the Hospital: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care 2022, 45, S244–S253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurki, M.I.; Karjalainen, J.; Palta, P.; Sipilä, T.P.; Kristiansson, K.; Donner, K.M.; Reeve, M.P.; Laivuori, H.; Aavikko, M.; Kaunisto, M.A.; et al. FinnGen provides genetic insights from a well-phenotyped isolated population. Nature 2023, 613, 508–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuttke, M.; Li, Y.; Li, M.; Sieber, K.B.; Feitosa, M.F.; Gorski, M.; Tin, A.; Wang, L.; Chu, A.Y.; Hoppmann, A.; et al. A catalog of genetic loci associated with renal function from analyses of a million individuals. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 957–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teumer, A.; Li, Y.; Ghasemi, S.; Prins, B.P.; Wuttke, M.; Hermle, T.; Giri, A.; Sieber, K.B.; Qiu, C.; Kirsten, H.; et al. Genome-wide association meta-analyses and fine-mapping elucidate pathways influencing albuminuria. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z. Multiple imputation with multivariate imputation by chained equation (MICE) package. Ann. Transl. Med. 2016, 4, 30. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, B.; Yang, X.R.; Xu, Y.; Sun, Y.F.; Sun, C.; Guo, W.; Zhang, X.; Wang, W.M.; Qiu, S.J.; Zhou, J.; et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index predicts prognosis of patients after curative resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 6212–6222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, S.; Labrecque, J.A. Mendelian randomization with a binary exposure variable: Interpretation and presentation of causal estimates. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2018, 33, 947–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, S.; Bowden, J.; Fall, T.; Ingelsson, E.; Thompson, S.G. Sensitivity analyses for robust causal inference from Mendelian randomization analyses with multiple genetic variants. Epidemiology 2017, 28, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, K.; Stringer, S.; Frei, O.; Umićević Mirkov, M.; de Leeuw, C.; Polderman, T.J.C.; van der Sluis, S.; Andreassen, O.A.; Neale, B.M.; Posthuma, D. A global overview of pleiotropy and genetic architecture in complex traits. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 1339–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klimentidis, Y.C.; Raichlen, D.A.; Bea, J.; Garcia, D.O.; Wineinger, N.E.; Mandarino, L.J.; Alexander, G.E.; Chen, Z.; Going, S.B. Genome-wide association study of habitual physical activity in over 377,000 UK Biobank participants identifies multiple variants including CADM2 and APOE. Int. J. Obes. 2018, 42, 1161–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurki, M.I.; Karjalainen, J.; Palta, P.; Sipilä, T.P.; Kristiansson, K.; Donner, K.; Reeve, M.P.; Laivuori, H.; Aavikko, M.; Kaunisto, M.A.; et al. FinnGen: Unique genetic insights from combining isolated population and national health register data. medRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Xue, H.; Pan, W. Robust multivariable Mendelian randomization based on constrained maximum likelihood. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2023, 110, 592–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, A.; Giovannini, L.; Mandel, V.D.; Odorici, G.; Lasagni, C.; Bigi, L.; Pellacani, G.; Cappelli, G. Chronic kidney disease in psoriasis: A cohort study. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2020, 18, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davey Smith, G.; Holmes, M.V.; Davies, N.M.; Ebrahim, S. Mendel’s laws, Mendelian randomization and causal inference in observational data: Substantive and nomenclatural issues. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2020, 35, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramseyer, V.D.; Garvin, J.L. Tumor necrosis factor-α: Regulation of renal function and blood pressure. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2013, 304, F1231–F1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.; Francis, J.; Majid, D.S. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces renal vasoconstriction as well as natriuresis in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2008, 295, F1836–F1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazor, R.; Itzhaki, O.; Sela, S.; Yagil, Y.; Cohen-Mazor, M.; Yagil, C.; Kristal, B. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha: A possible priming agent for the polymorphonuclear leukocyte-reduced nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase in hypertension. Hypertension 2010, 55, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Rebholz, C.M.; Wong, E.; Chen, Y.; Matsushita, K.; Coresh, J.; Grams, M.E. Association Between Hypertension and Renal function Decline: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2019, 74, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, R.; Yasuda, Y.; Tsushita, K.; Wakai, K.; Hamajima, N.; Matsuo, S. Glomerular hyperfiltration in prediabetes and prehypertension. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 27, 1821–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaglino, P.; Bergallo, M.; Ponti, R.; Barberio, E.; Cicchelli, S.; Buffa, E.; Comessatti, A.; Costa, C.; Terlizzi, M.E.; Astegiano, S. Th1, Th2, Th17 and regulatory T cell pattern in psoriatic patients: Modulation of cytokines and gene targets induced by etanercept treatment and correlation with clinical response. Dermatology 2011, 223, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brembilla, N.C.; Senra, L.; Boehncke, W.-H. The IL-17 family of cytokines in psoriasis: IL-17A and beyond. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, S.B.; Cicek, N.; Coskun, M.; Yegin, O.; Alpsoy, E. Serum and tissue levels of IL-17 in different clinical subtypes of psoriasis. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2012, 304, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summers, S.A.; Steinmetz, O.M.; Li, M.; Kausman, J.Y.; Semple, T.; Edgtton, K.L.; Borza, D.B.; Braley, H.; Holdsworth, S.R.; Kitching, A.R. Th1 and Th17 cells induce proliferative glomerulonephritis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 2518–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, J.-E.; Paust, H.-J.; Steinmetz, O.M.; Panzer, U. The Th17 immune response in renal inflammation. Kidney Int. 2010, 77, 1070–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Kyttaris, V.C.; Tsokos, G.C. The role of IL-23/IL-17 axis in lupus nephritis. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 3160–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haridasan, S.; Rathi, M.; Sharma, A.; Nada, R.; Kumar, S.; Ramachandran, R.; Kohli, H.S. Outcome of biopsy-proven lupus nephritis with low glomerular filtration rate at presentation. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 23, 1201–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroni, G.; Calatroni, M.; Ponticelli, C. Severe lupus nephritis in the present days. Front. Nephrol. 2022, 2, 984613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veronesi, G.; Guglielmo, A.; Gardini, A.; Sacchelli, L.; Loi, C.; Patrizi, A.; Bardazzi, F. Biological therapy in patients with psoriasis: What we know about the effects on renal function. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 35, e15202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Overall | Psoriasis | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | |||
| N | 20,944 | 20,395 (97.4) | 549 (2.6) | |
| Age, n (%) | 0.223 | |||
| 20~60 | 16,739 (79.9) | 16,312 (80.0) | 427 (77.8) | |
| ≥60 | 4205 (20.1) | 4083 (20.0) | 122 (22.2) | |
| Gender, n (%) | 0.731 | |||
| Male | 10,738 (51.3) | 10,461 (51.3) | 277 (50.5) | |
| Female | 10,206 (48.7) | 9934 (48.7) | 272 (49.5) | |
| BMI | <0.001 | |||
| Mean (SD) | 28.92 (6.91) | 28.89 (6.91) | 30.00 (6.99) | |
| Race/Ethnicity, n (%) | <0.001 | |||
| White | 8735 (41.7) | 8410 (41.2) | 325 (59.2) | |
| Black | 4761 (22.7) | 4687 (23.0) | 74 (13.5) | |
| Mexican American | 3425 (16.4) | 3379 (16.6) | 46 (8.4) | |
| Other Race | 4023 (19.2) | 3919 (19.2) | 104 (18.9) | |
| Ratio of family income to poverty, n (%) | 0.435 | |||
| <1.0 | 4344 (22.5) | 4237 (22.5) | 107 (21.0) | |
| ≥1.0 | 14,961 (77.5) | 14,558 (77.5) | 403 (79.0) | |
| Education level, n (%) | 0.052 | |||
| Less Than 9th Grade | 2066 (9.9) | 2029 (10.0) | 37 (6.7) | |
| 9–11th/12th grade with no diploma | 3129 (15.0) | 3054 (15.0) | 75 (13.7) | |
| High School Grad/GED or Equivalent | 4810 (23.0) | 4686 (23.0) | 124 (22.6) | |
| Some College or AA degree | 6281 (30.0) | 6107 (30.0) | 174 (31.7) | |
| College Graduate or above | 4633 (22.1) | 4494 (22.1) | 139 (25.3) | |
| Marital status, n (%) | 0.068 | |||
| Married/Living with partner | 12,289 (58.7) | 11,958 (58.7) | 331 (60.3) | |
| Widowed/Divorced/Separated | 4153 (19.8) | 4032 (19.8) | 121 (22.0) | |
| Never married | 4490 (21.5) | 4393 (21.6) | 97 (17.7) | |
| Smoking status, n (%) | 0.641 | |||
| NO | 14,087 (72.9) | 13,722 (72.9) | 365 (71.9) | |
| Yes | 5248 (27.1) | 5105 (27.1) | 143 (28.1) | |
| Alcohol use per day | 0.221 | |||
| median [IQR] | 0.10 [0.01, 0.57] | 0.10 [0.01, 0.57] | 0.07 [0.01, 0.57] | |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 0.001 | |||
| NO | 10,268 (53.6) | 10,038 (53.8) | 230 (46.2) | |
| Yes | 8875 (46.4) | 8607 (46.2) | 268 (53.8) | |
| Diabetes, n (%) | 0.035 | |||
| No | 17,845 (85.2) | 17,395 (85.3) | 450 (82.0) | |
| Yes | 3097 (14.8) | 2998 (14.7) | 99 (18.0) | |
| eGFR | 0.001 | |||
| mean (SD) | 96.94 (21.25) | 97.02 (21.24) | 93.96 (21.52) | |
| UACR | 0.147 | |||
| median [IQR] | 6.49 [4.19, 12.13] | 6.48 [4.19, 12.07] | 6.81 [4.28, 13.94] | |
| BUN | 0.016 | |||
| mean (SD) | 12.68 (5.47) | 12.67 (5.45) | 13.26 (6.18) | |
| CKD, n (%) | 0.351 | |||
| No | 17,438 (86.1) | 16,991 (86.2) | 447 (84.7) | |
| Yes | 2806 (13.9) | 2725 (13.8) | 81 (15.3) | |
| Exposure | MR Methods | IVs | Estimate | SE | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| eGFR | |||||
| MR-PRESSO (Raw) | 31 | −0.0016 | 0.0006 | 0.023 | |
| MR-PRESSO (Removed outliers) | 25 | −0.0012 | 0.0006 | 0.035 | |
| UACR | |||||
| MR PRESSO (Raw) | 31 | −0.0049 | 0.0032 | 0.132 | |
| MR-PRESSO (Removed outliers) | 26 | −0.002 | 0.0031 | 0.520 | |
| BUN | |||||
| MR-PRESSO (Raw) | 31 | 0.0011 | 0.0012 | 0.370 | |
| MR-PRESSO (Removed outliers) | - | - | - | - | |
| CKD | |||||
| MR-PRESSO (Raw) | 31 | 0.0137 | 0.0132 | 0.307 | |
| MR-PRESSO (Removed outliers) | - | - | - | - | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, Y.; Huang, Z.; Li, H.; Yao, H.; Fu, Y.; Wu, X.; Lin, C.; Lai, Z.; Yang, G.; Jing, C. Association between Psoriasis and Renal Functions: An Integration Study of Observational Study and Mendelian Randomization. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12010249
Tan Y, Huang Z, Li H, Yao H, Fu Y, Wu X, Lin C, Lai Z, Yang G, Jing C. Association between Psoriasis and Renal Functions: An Integration Study of Observational Study and Mendelian Randomization. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(1):249. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12010249
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Yuxuan, Zhizhuo Huang, Haiying Li, Huojie Yao, Yingyin Fu, Xiaomei Wu, Chuhang Lin, Zhengtian Lai, Guang Yang, and Chunxia Jing. 2024. "Association between Psoriasis and Renal Functions: An Integration Study of Observational Study and Mendelian Randomization" Biomedicines 12, no. 1: 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12010249
APA StyleTan, Y., Huang, Z., Li, H., Yao, H., Fu, Y., Wu, X., Lin, C., Lai, Z., Yang, G., & Jing, C. (2024). Association between Psoriasis and Renal Functions: An Integration Study of Observational Study and Mendelian Randomization. Biomedicines, 12(1), 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12010249