Exploration of Novel Biomarkers for Neurodegenerative Diseases Using Proteomic Analysis and Ligand-Binding Assays
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Selection
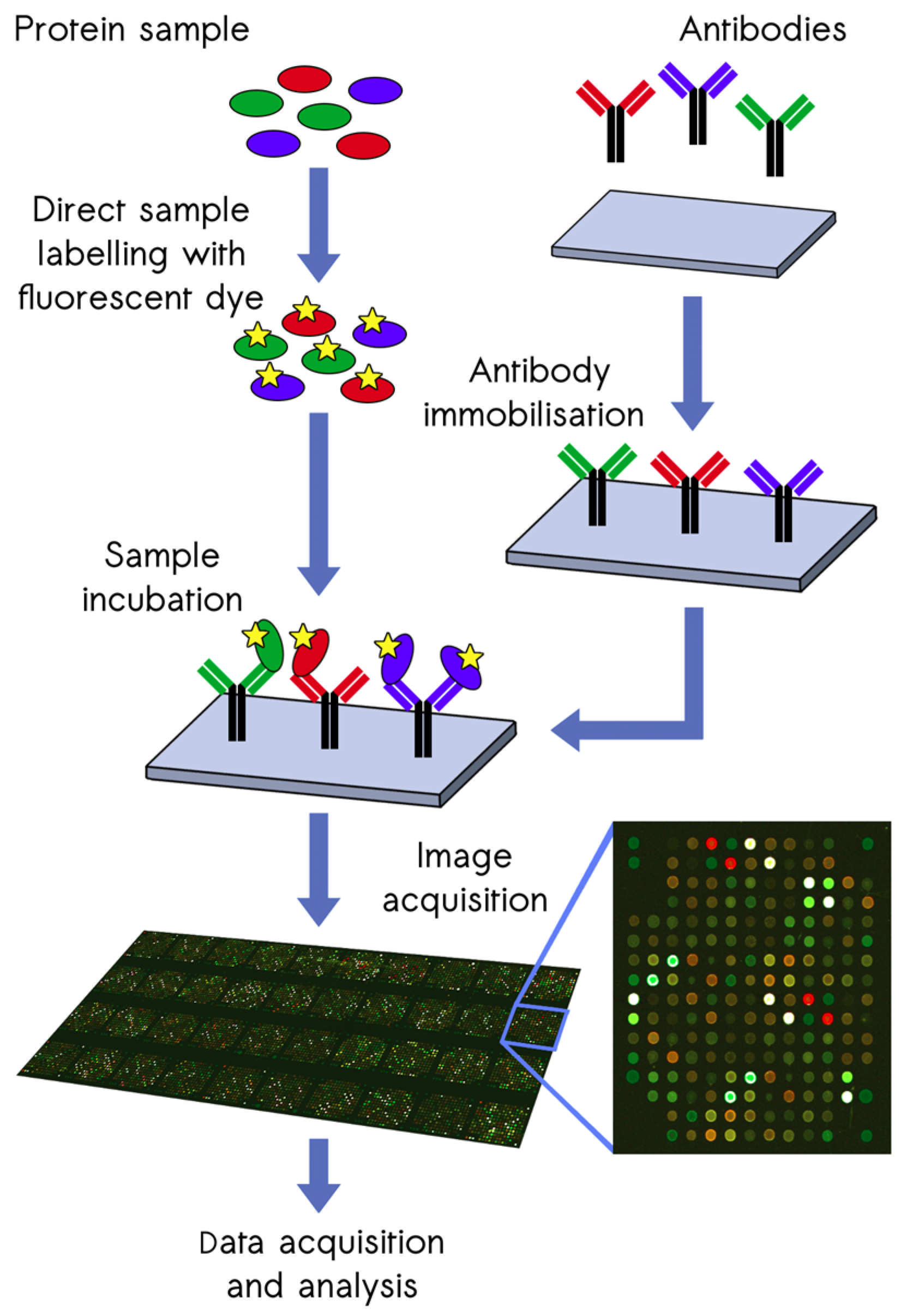
2.2. Proteomic Screening with the ScioDiscover Platform
2.3. Statistical Analysis of Proteomic Screening Data
2.4. Automated Fluorescence Immunoassays
2.5. Standards, Quality Controls, and Dilution Linearity
2.6. Statistical Analysis of Fluorescence Immunoassay Data
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Study Participants
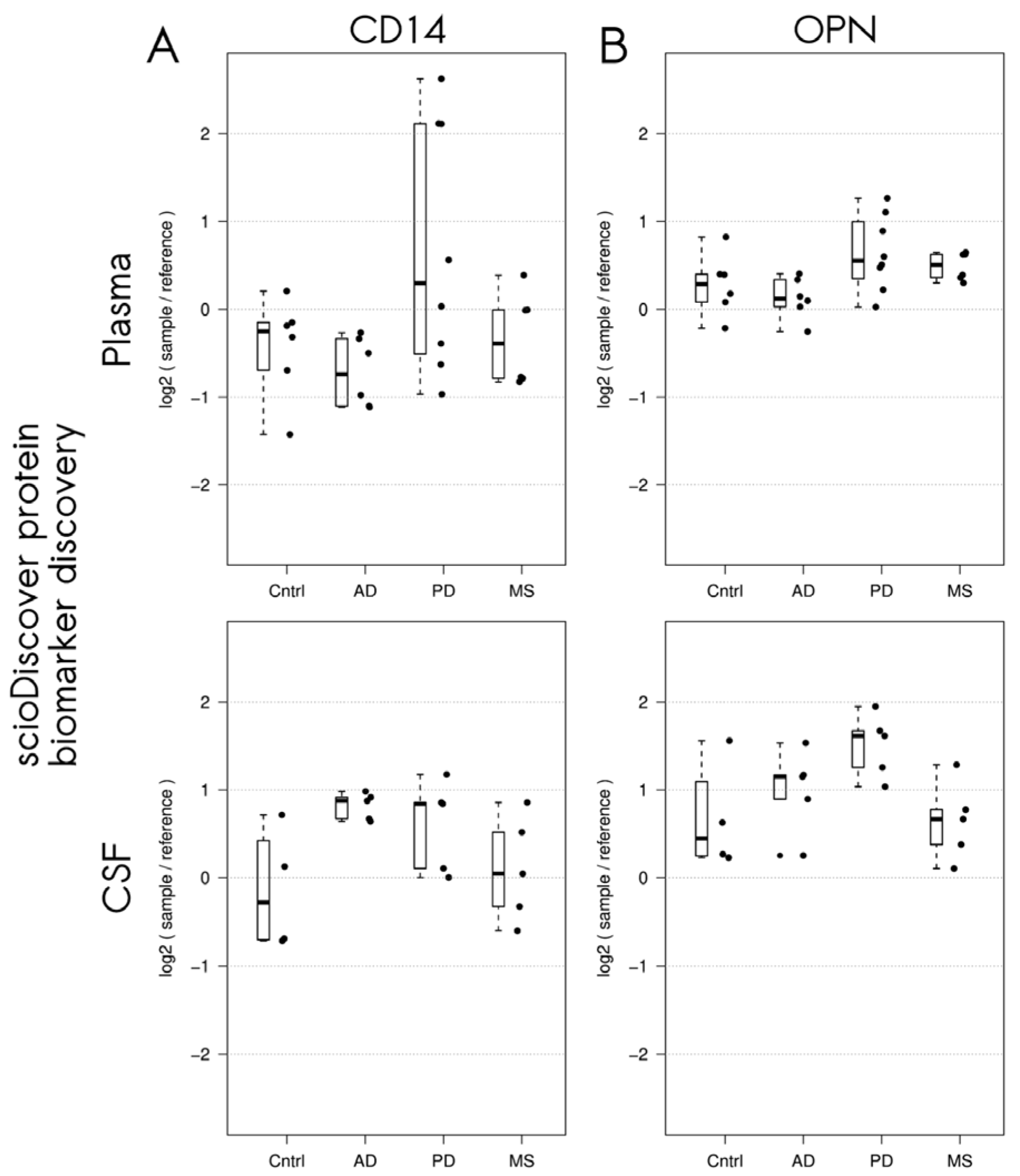
3.2. Differentially Expressed Proteins in Patients with Neurodegenerative Disorders Detected Using the Sciodiscover Proteomic Screening Platform
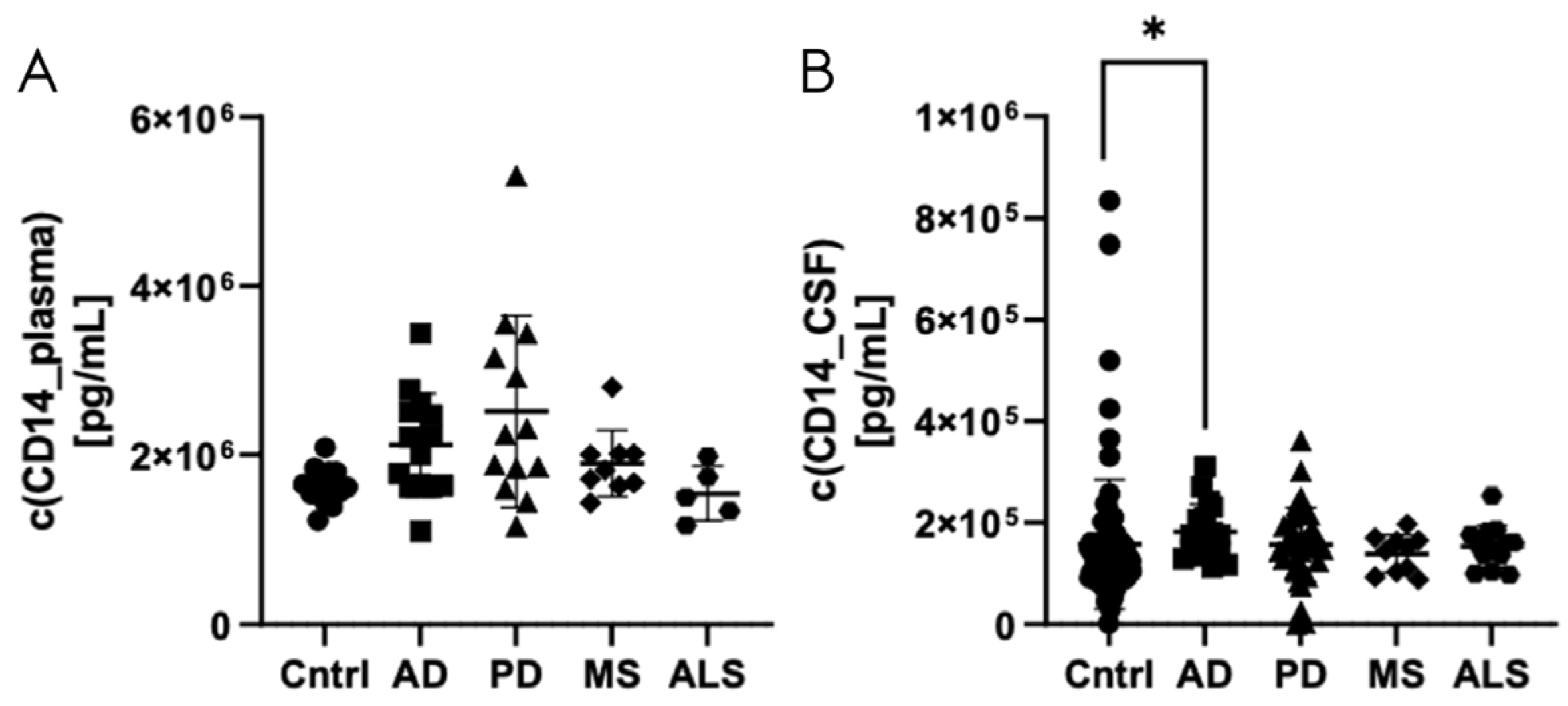
3.3. Validation of Elevated CD14 Levels in CSF of Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease Using Automated Fluorescence Immunoassay
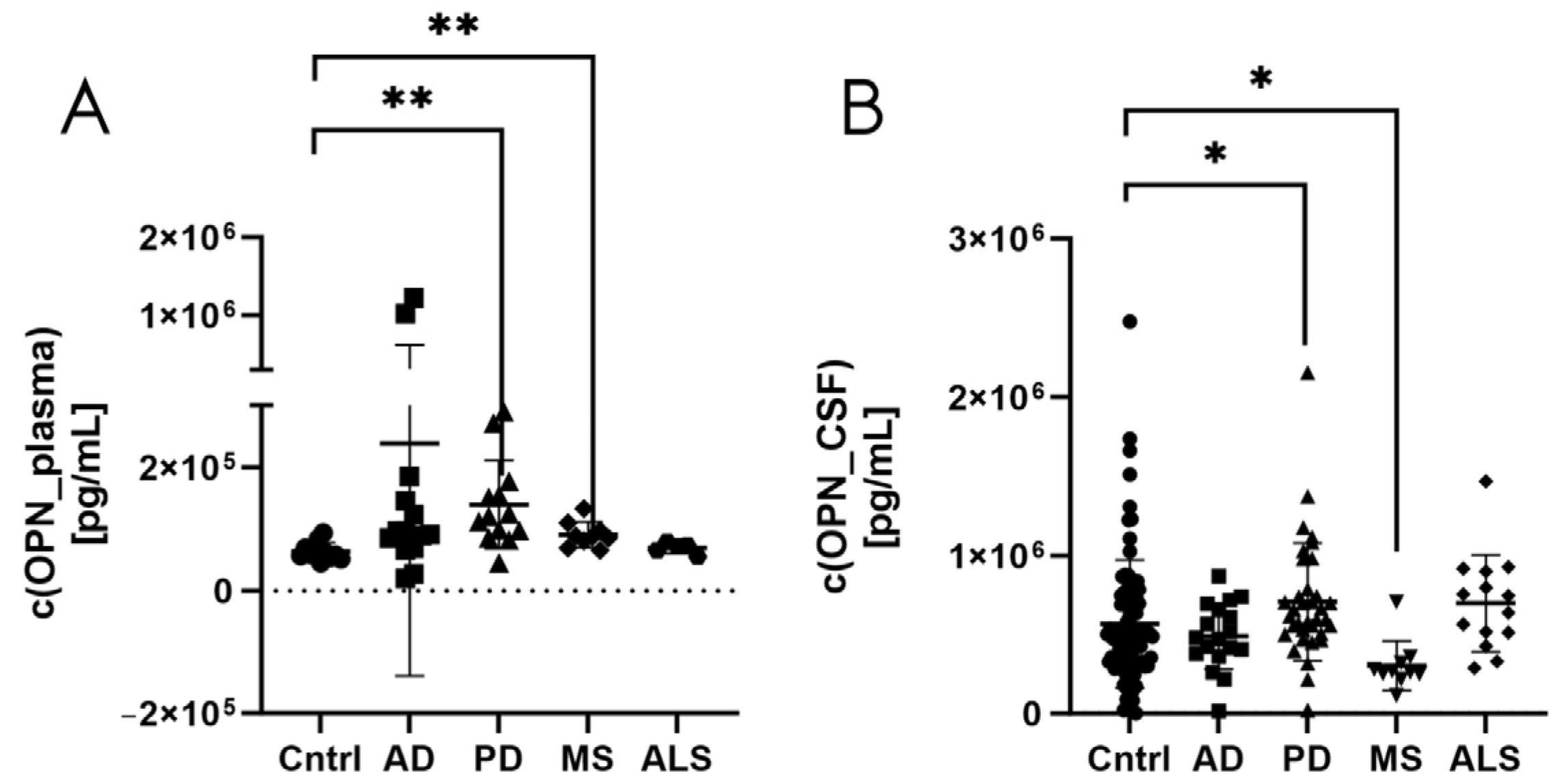
3.4. Validation of Elevated Osteopontin Levels in CSF of Patients with Parkinson’s Disease Using Automated Fluorescence Immunoassay
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Erkkinen, M.G.; Kim, M.O.; Geschwind, M.D. Clinical neurology and epidemiology of the major neurodegenerative diseases. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2018, 10, a033118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deuschl, G.; Beghi, E.; Fazekas, F.; Varga, T.; Christoforidi, K.A.; Sipido, E.; Bassetti, C.L.; Vos, T.; Feigin, V.L. The burden of neurological diseases in Europe: An analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet Public Health 2020, 5, e551–e567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tondo, G.; De Marchi, F. From biomarkers to precision medicine in neurodegenerative diseases: Where are we? J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dugger, B.N.; Dickson, D.W. Pathology of neurodegenerative diseases. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2017, 9, a028035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, A. Multiple sclerosis is primarily a neurodegenerative disease. J. Neural Transm. 2013, 120, 1463–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourdenx, M.; Koulakiotis, N.S.; Sanoudou, D.; Bezard, E.; Dehay, B.; Tsarbopoulos, A. Protein aggregation and neurodegeneration in prototypical neurodegenerative diseases: Examples of amyloidopathies, tauopathies and synucleinopathies. Prog. Neurobiol. 2017, 155, 171–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, G.G. Molecular pathological classification of neurodegenerative diseases: Turning towards precision medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golde, T.E. The therapeutic importance of understanding mechanisms of neuronal cell death in neurodegenerative disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2009, 4, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parnetti, L.; Gaetani, L.; Eusebi, P.; Paciotti, S.; Hansson, O.; El-Agnaf, O.; Mollenhauer, B.; Blennow, K.; Calabresi, P. CSF and blood biomarkers for Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 573–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, O. Biomarkers for neurodegenerative diseases. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 954–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trejo-Lopez, J.A.; Yachnis, A.T.; Prokop, S. Neuropathology of Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurotherapeutics 2022, 19, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koníčková, D.; Menšíková, K.; Tučková, L.; Hényková, E.; Strnad, M.; Friedecký, D.; Stejskal, D.; Matěj, R.; Kaňovský, P. Biomarkers of neurodegenerative diseases: Biology, taxonomy, clinical relevance, and current research status. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcolea, D.; Beeri, M.S.; Rojas, J.C.; Gardner, R.C.; Lleó, A. Blood biomarkers in neurodegenerative diseases: Implications for the clinical neurologist. Neurology 2023, 101, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, E.H.; Tennagels, S.; Gold, R.; Gerwert, K.; Beyer, L.; Tönges, L. Update on CSF biomarkers in Parkinson’s disease. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sill, M.; Schröder, C.; Shen, Y.; Marzoq, A.; Komel, R.; Hoheisel, J.D.; Nienhüser, H.; Schmidt, T.; Kastelic, D. Protein profiling gastric cancer and neighboring control tissues using high-content antibody microarrays. Microarrays 2016, 5, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrebaeck, C.A.; Wingren, C. Antibody array generation and use. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1131, 563–571. [Google Scholar]
- Pušić, M.; Klančič, T.; Knific, T.; Vogler, A.; Schmidt, R.; Schröder, C.; Lanišnik Rižner, T. Antibody arrays identified cycle-dependent plasma biomarker candidates of peritoneal endometriosis. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janša, V.; Klančič, T.; Pušić, M.; Klein, M.; Bokal, E.V.; Frangež, H.B.; Rižner, T.L. Proteomic analysis of peritoneal fluid identified COMP and TGFBI as new candidate biomarkers for endometriosis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 20870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hufnagel, K.; Fathi, A.; Stroh, N.; Klein, M.; Skwirblies, F.; Girgis, R.; Dahlke, C.; Hoheisel, J.D.; Lowy, C.; Schmidt, R.; et al. Discovery and systematic assessment of early biomarkers that predict progression to severe COVID-19 disease. Commun. Med. 2023, 3, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldo, P.; Marusov, G.; Svancara, D.; David, J.; Mor, G. Simple Plex(™): A novel multi-analyte, automated microfluidic immunoassay platform for the detection of human and mouse cytokines and chemokines. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2016, 75, 678–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, S.L.; Lukk, T.; Nair, S.K.; Tapping, R.I. The crystal structure of human soluble CD14 reveals a bent solenoid with a hydrophobic amino-terminal pocket. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 1304–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Lei, Z.; Lei, P. CD14: Biology and role in the pathogenesis of disease. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2019, 48, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed-Geaghan, E.G.; Savage, J.C.; Hise, A.G.; Landreth, G.E. CD14 and toll-like receptors 2 and 4 are required for fibrillar A{beta}-stimulated microglial activation. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 11982–11992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fassbender, K.; Walter, S.; Kühl, S.; Landmann, R.; Ishii, K.; Bertsch, T.; Stalder, A.K.; Muehlhauser, F.; Liu, Y.; Ulmer, A.J.; et al. The LPS receptor (CD14) links innate immunity with Alzheimer’s disease. FASEB J. 2004, 18, 203–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Walter, S.; Stagi, M.; Cherny, D.; Letiembre, M.; Schulz-Schaeffer, W.; Heine, H.; Penke, B.; Neumann, H.; Fassbender, K. LPS receptor (CD14): A receptor for phagocytosis of Alzheimer’s amyloid peptide. Brain 2005, 128, 1778–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letiembre, M.; Liu, Y.; Walter, S.; Hao, W.; Pfander, T.; Wrede, A.; Schulz-Schaeffer, W.; Fassbender, K. Screening of innate immune receptors in neurodegenerative diseases: A similar pattern. Neurobiol. Aging 2009, 30, 759–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busse, S.; Hoffmann, J.; Michler, E.; Hartig, R.; Frodl, T.; Busse, M. Dementia-associated changes of immune cell composition within the cerebrospinal fluid. Brain Behav. Immun.-Health 2021, 14, 100218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharygin, D.; Koniaris, L.G.; Wells, C.; Zimmers, T.A.; Hamidi, T. Role of CD14 in human disease. Immunology 2023, 169, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, G.N.; Jeon, H.; Lee, S.; Lee, H.W.; Cho, J.Y.; Suk, K. Role of soluble CD14 in cerebrospinal fluid as a regulator of glial functions. J. Neurosci. Res. 2009, 87, 2578–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pase, M.P.; Himali, J.J.; Beiser, A.S.; DeCarli, C.; McGrath, E.R.; Satizabal, C.L.; Aparicio, H.J.; Adams, H.H.H.; Reiner, A.P.; Longstreth, W.T., Jr.; et al. Association of CD14 with incident dementia and markers of brain aging and injury. Neurology 2020, 94, e254–e266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Icer, M.A.; Gezmen-Karadag, M. The multiple functions and mechanisms of osteopontin. Clin. Biochem. 2018, 59, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosmus, D.-D.; Lange, C.; Ludwig, F.; Ajami, B.; Wieghofer, P. The role of osteopontin in microglia biology: Current concepts and future perspectives. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappellano, G.; Vecchio, D.; Magistrelli, L.; Clemente, N.; Raineri, D.; Mazzucca, C.B.; Virgilio, E.; Dianzani, U.; Chiocchetti, A.; Comi, C. The Yin-Yang of osteopontin in nervous system diseases: Damage versus repair. Neural Regen. Res. 2021, 16, 1131–1137. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maetzler, W.; Berg, D.; Schalamberidze, N.; Melms, A.; Schott, K.; Mueller, J.C.; Liaw, L.; Gasser, T.; Nitsch, C. Osteopontin is elevated in Parkinson’s disease and its absence leads to reduced neurodegeneration in the MPTP model. Neurobiol. Dis. 2007, 25, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Zhou, M.; Dai, W.; Guo, W.; Qiu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Mo, M.; Ding, L.; Ye, P.; Wu, Y.; et al. Bone-derived factors as potential biomarkers for Parkinson’s disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 634213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agah, E.; Zardoui, A.; Saghazadeh, A.; Ahmadi, M.; Tafakhori, A.; Rezaei, N. Osteopontin (OPN) as a CSF and blood biomarker for multiple sclerosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storkebaum, E.; Carmeliet, P. VEGF: A critical player in neurodegeneration. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 113, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.Z.; Li, F.Y.; Xu, J.; Li, B.Q.; Li, Y.; Jia, J.P. Vascular endothelial growth factor is an effective biomarker for vascular dementia, not for Alzheimer’s disease: A meta-analysis. Alzheimers Dement 2024, 16, e12612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kenzelmann, A.; Boch, C.; Schmidt, R.; Richter, M.; Schulz, M. Exploration of Novel Biomarkers for Neurodegenerative Diseases Using Proteomic Analysis and Ligand-Binding Assays. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2794. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122794
Kenzelmann A, Boch C, Schmidt R, Richter M, Schulz M. Exploration of Novel Biomarkers for Neurodegenerative Diseases Using Proteomic Analysis and Ligand-Binding Assays. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(12):2794. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122794
Chicago/Turabian StyleKenzelmann, Annalena, Christina Boch, Ronny Schmidt, Mario Richter, and Michael Schulz. 2024. "Exploration of Novel Biomarkers for Neurodegenerative Diseases Using Proteomic Analysis and Ligand-Binding Assays" Biomedicines 12, no. 12: 2794. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122794
APA StyleKenzelmann, A., Boch, C., Schmidt, R., Richter, M., & Schulz, M. (2024). Exploration of Novel Biomarkers for Neurodegenerative Diseases Using Proteomic Analysis and Ligand-Binding Assays. Biomedicines, 12(12), 2794. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122794




