Treated and Untreated Primary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis: Walkthrough Immunological Changes of Monocytes and T Regulatory Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Data Collection Procedures: Peripheral Blood (PB) Collection, Flow Cytometry, and Clinical Assessment (Neurological)
2.3. Flow Cytometry
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
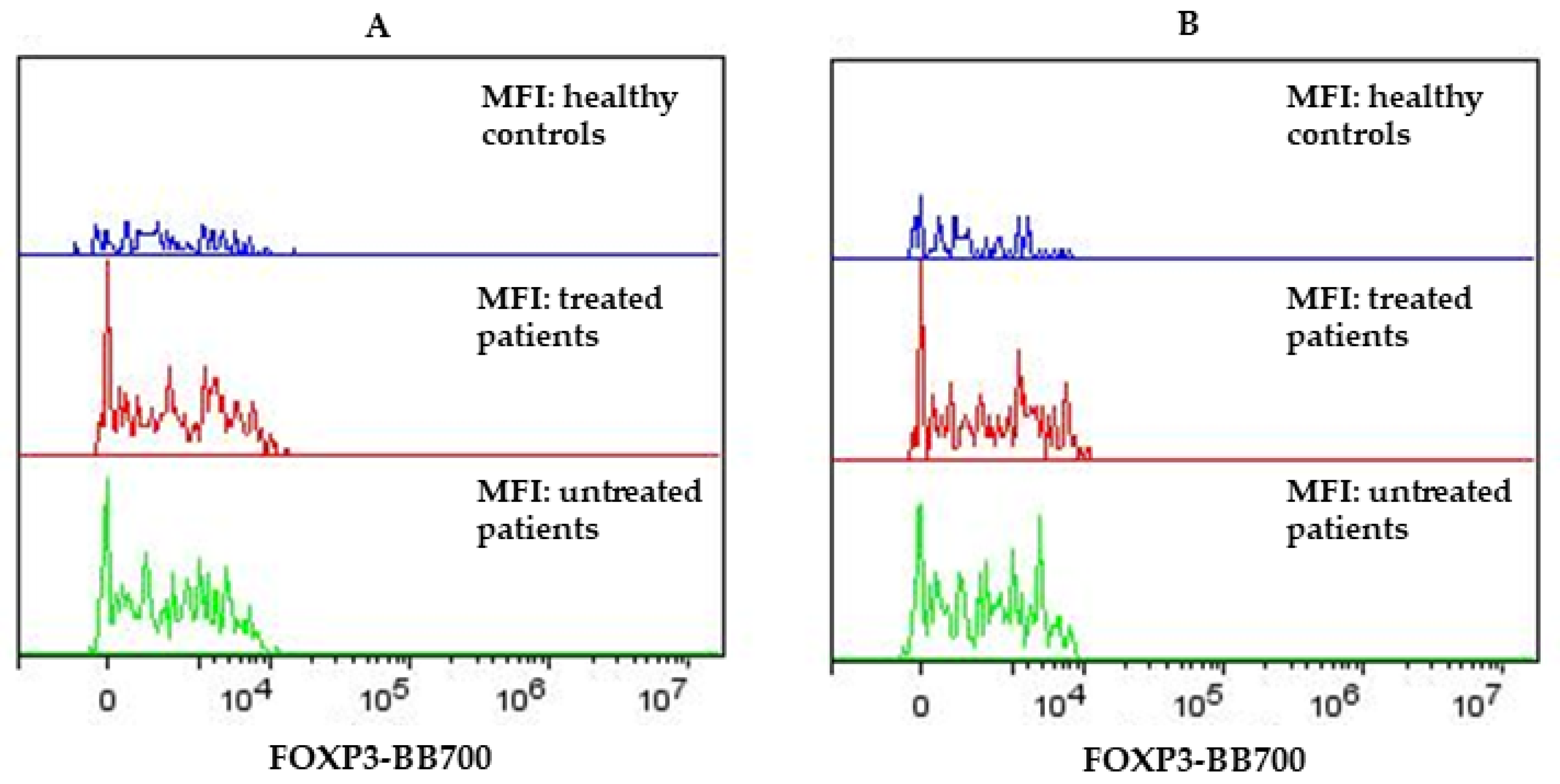
3.1. Flow Cytometry Results on Lymphocytes of PPMS and HC Subjects
3.2. Flow Cytometry Results for Monocytes of PPMS and HC Subjects
4. Discussion
4.1. Discussion Related to Lymphocytes Results in PPMS and HC Subjects
4.2. Discussion Related to Monocyte Results in PPMS and HC Subjects
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Axisa, P.P.; Hafler, D.A. Multiple sclerosis: Genetics, biomarkers, treatments. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2016, 29, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafler, D.A. Multiple sclerosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 113, 788–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klineova, S.; Lublin, F.D. Clinical Course of Multiple Sclerosis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2018, 8, a028928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGinley, M.P.; Goldschmidt, C.H.; Rae-Grant, A.D. Diagnosis and Treatment of Multiple Sclerosis: A Review. JAMA 2021, 325, 765–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassmann, H.; Brück, W.; Lucchinetti, C. Heterogeneity of multiple sclerosis pathogenesis: Implications for diagnosis and therapy. Trends Mol. Med. 2001, 7, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitteri, M.; Romualdi, C.; Magliozzi, R.; Monaco, S.; Calabrese, M. Cognitive impairment predicts disability progression and cortical thinning in MS: An 8-year study. Mult. Scler. 2017, 23, 848–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goverman, J. Autoimmune T cell responses in the central nervous system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 393–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dendrou, C.A.; Fugger, L.; Friese, M.A. Immunopathology of multiple sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Langelaar, J.; Rijvers, L.; Smolders, J.; van Luijn, M.M. B and T Cells Driving Multiple Sclerosis: Identity, Mechanisms and Potential Triggers. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monti, P.; Heninger, A.K.; Bonifacio, E. Differentiation, expansion, and homeostasis of autoreactive T cells in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2009, 9, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima, W.; Ohtani, H.; Nakayama, T.; Sugawara, Y.; Sato, E.; Nagura, H.; Yoshie, O.; Sasano, T. Infiltrating CD8+ T cells in oral lichen planus predominantly express CCR5 and CXCR3 and carry respective chemokine ligands RANTES/CCL5 and IP-10/CXCL10 in their cytolytic granules: A potential self-recruiting mechanism. Am. J. Pathol. 2003, 163, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Amezquita, R.A.; Kleinstein, S.H.; Stathopoulos, P.; Nowak, R.J.; O’Connor, K.C. Autoreactive T Cells from Patients with Myasthenia Gravis Are Characterized by Elevated IL-17, IFN-γ, and GM-CSF and Diminished IL-10 Production. J. Immunol. 2016, 196, 2075–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diani, M.; Altomare, G.; Reali, E. T cell responses in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2015, 14, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreurs, O.; Karatsaidis, A.; Schenck, K. Phenotypically non-suppressive cells predominate among FOXP3-positive cells in oral lichen planus. J. Oral. Pathol. Med. 2016, 45, 766–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xufré, C.; Costa, M.; Roura-Mir, C.; Codina-Busqueta, E.; Usero, L.; Pizarro, E.; Obiols, G.; Jaraquemada, D.; Martí, M. Low frequency of GITR+ T cells in ex vivo and in vitro expanded Treg cells from type 1 diabetic patients. Int. Immunol. 2013, 25, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richetta, A.G.; Mattozzi, C.; Salvi, M.; Giancristoforo, S.; D’epiro, S.; Milana, B.; Carboni, V.; Zampetti, M.; Calvieri, S.; Morrone, S. CD4+CD25+ T-regulatory cells in psoriasis. Correlation between their numbers and biologics-induced clinical improvement. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2011, 21, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Q.Y.; Zhang, S.X.; Yang, L.; Luo, J.; Li, X.F.; Zhang, J.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.Q.; Shi, L. Peripheral Treg Levels and Transforming Growth Factor-β (TGFβ) in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis: A Systematic Review Meta-Analysis. Adv. Ther. 2023, 40, 102–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiruppathi, M.; Rowin, J.; Li Jiang, Q.; Sheng, J.R.; Prabhakar, B.S.; Meriggioli, M.N. Functional defect in regulatory T cells in myasthenia gravis. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2012, 1274, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohler, S.; Keil, T.O.P.; Hoffmann, S.; Swierzy, M.; Ismail, M.; Rückert, J.C.; Alexander, T.; Meisel, A. CD4+ FOXP3+ T regulatory cell subsets in myasthenia gravis patients. Clin. Immunol. 2017, 179, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, L.J.; Wang, H.B.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.Z. Abnormality of circulating CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T cell in patients with Guillain-Barré syndrome. J. Neuroimmunol. 2007, 192, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tapia-Maltos, M.A.; Treviño-Frenk, I.; García-González, H.B.; Rosetti, M.; Barriga-Maldonado, V.; Morales-Ramírez, F.; López-Hernández, D.C.; Rosetti, F.; Crispín, J.C. Identification of regulatory T cell molecules associated with severity of multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. 2021, 27, 1695–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalla Libera, D.; Di Mitri, D.; Bergami, A.; Centonze, D.; Gasperini, C.; Grasso, M.G.; Galgani, S.; Martinelli, V.; Comi, G.; Avolio, C.; et al. T regulatory cells are markers of disease activity in multiple sclerosis patients. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjerg, L.; Brosbøl-Ravnborg, A.; Tørring, C.; Dige, A.; Bundgaard, B.; Petersen, T.; Höllsberg, P. Altered frequency of T regulatory cells is associated with disability status in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis patients. J. Neuroimmunol. 2012, 249, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viglietta, V.; Baecher-Allan, C.; Weiner, H.L.; Hafler, D.A. Loss of functional suppression by CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells in patients with multiple sclerosis. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 199, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venken, K.; Hellings, N.; Thewissen, M.; Somers, V.; Hensen, K.; Rummens, J.L.; Medaer, R.; Hupperts, R.; Stinissen, P. Compromised CD4+ CD25(high) regulatory T-cell function in patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis is correlated with a reduced frequency of FOXP3-positive cells and reduced FOXP3 expression at the single-cell level. Immunology 2008, 123, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, J.; Hug, A.; Viehöver, A.; Fritzsching, B.; Falk, C.S.; Filser, A.; Vetter, T.; Milkova, L.; Korporal, M.; Fritz, B.; et al. Reduced suppressive effect of CD4+CD25high regulatory T cells on the T cell immune response against myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein in patients with multiple sclerosis. Eur. J. Immunol. 2005, 35, 3343–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Li, H.; Yang, X.; Hu, H.; Liu, P.; Liu, H. Crosstalk between dendritic cells and regulatory T cells: Protective effect and therapeutic potential in multiple sclerosis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 970508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colamatteo, A.; Carbone, F.; Bruzzaniti, S.; Galgani, M.; Fusco, C.; Maniscalco, G.T.; Di Rella, F.; de Candia, P.; De Rosa, V. Molecular Mechanisms Controlling FOXp3 Expression in Health and Autoimmunity: From Epigenetic to Post-translational Regulation. Front. Immunol. 2020, 10, 3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eggenhuizen, P.J.; Ng, B.H.; Ooi, J.D. Treg Enhancing Therapies to Treat Autoimmune Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Li, Y.Y.; Zheng, S.G.; Tsun, A.; Li, B. FOXP3(+) Treg Cells and Gender Bias in Autoimmune Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danikowski, K.M.; Jayaraman, S.; Prabhakar, B.S. Regulatory T cells in multiple sclerosis and myasthenia gravis. J. Neuroinflamm. 2017, 14, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tekguc, M.; Wing, J.B.; Osaki, M.; Long, J.; Sakaguchi, S. Treg-expressed CTLA-4 depletes CD80/CD86 by trogocytosis, releasing free PD-L1 on antigen-presenting cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2023739118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calahorra, L.; Camacho-Toledano, C.; Serrano-Regal, M.P.; Ortega, M.C.; Clemente, D. Regulatory Cells in Multiple Sclerosis: From Blood to Brain. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carstensen, M.; Christensen, T.; Stilund, M.; Møller, H.J.; Petersen, E.L.; Petersen, T. Activated monocytes and markers of inflammation in newly diagnosed multiple sclerosis. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2020, 98, 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waschbisch, A.; Schröder, S.; Schraudner, D.; Sammet, L.; Weksler, B.; Melms, A.; Pfeifenbring, S.; Stadelmann, C.; Schwab, S.; Linker, R.A. Pivotal Role for CD16+ Monocytes in Immune Surveillance of the Central Nervous System. J. Immunol. 2016, 196, 1558–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjelstrup, M.C.; Stilund, M.; Petersen, T.; Møller, H.J.; Petersen, E.L.; Christensen, T. Subsets of activated monocytes and markers of inflammation in incipient and progressed multiple sclerosis. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2018, 96, 160–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dargahi, N.; Katsara, M.; Tselios, T.; Androutsou, M.E.; de Courten, M.; Matsoukas, J.; Apostolopoulos, V. Multiple Sclerosis: Immunopathology and Treatment Update. Brain Sci. 2017, 7, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, S.L.; Cree, B.A.C. Treatment of Multiple Sclerosis: A Review. Am. J. Med. 2020, 133, 1380–1390.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, K. Regulatory T cells in multiple sclerosis. Clin. Exp. Neuroimmunol. 2020, 11, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, L.M.; Rudensky, A.Y. Maintenance of the FOXp3-dependent developmental program in mature regulatory T cells requires continued expression of FOXp3. Nat. Immunol. 2007, 8, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Skowronek, I. IPEX Syndrome: Genetics and Treatment Options. Genes 2021, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leon, J.; Chowdhary, K.; Zhang, W.; Ramirez, R.N.; André, I.; Hur, S.; Mathis, D.; Benoist, C. Mutations from patients with IPEX ported to mice reveal different patterns of FOXP3 and Treg dysfunction. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 113018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.F.; Zhang, S.X.; Ma, X.W.; Xue, Y.L.; Gao, C.; Li, X.Y.; Xu, A.D. The proportion of peripheral regulatory T cells in patients with Multiple Sclerosis: A meta-analysis. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2019, 28, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Oria, M.C.; Márquez-Coello, M.; Girón-Ortega, J.A.; Argente, J.; Moya, M.; Girón-González, J.A. Monocyte and Lymphocyte Activation and Regulation in Multiple Sclerosis Patients. Therapy Effects. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. Off. J. Soc. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2019, 14, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouchaki, E.; Salehi, M.; Reza Sharif, M.; Nikoueinejad, H.; Akbari, H. Numerical status of CD4+CD25+FOXP3+ and CD8+CD28− regulatory T cells in multiple sclerosis. Iran. J. Basic. Med. Sci. 2014, 17, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howlett-Prieto, Q.; Feng, X.; Kramer, J.F.; Kramer, K.J.; Houston, T.W.; Reder, A.T. Anti-CD20 therapy corrects a CD8 regulatory T cell deficit in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. 2021, 27, 2170–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, J.A.; Otsuka, A.; Kabashima, K. Anti-PD-1 and Anti-CTLA-4 Therapies in Cancer: Mechanisms of Action, Efficacy, and Limitations. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, D.V.; Gibson, H.M.; Aufiero, B.M.; Wilson, A.J.; Hafner, M.S.; Mi, Q.S.; Wong, H.K. Differential CTLA-4 expression in human CD4+ versus CD8+ T cells is associated with increased NFAT1 and inhibition of CD4+ proliferation. Genes Immun. 2014, 15, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.S.; Cox, M.A.; Zajac, A.J. T-cell exhaustion: Characteristics, causes and conversion. Immunology 2010, 129, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sellebjerg, F.; Krakauer, M.; Khademi, M.; Olsson, T.; Sørensen, P.S. FOXP3, CBLB and ITCH gene expression and cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4 expression on CD4+ CD25high T cells in multiple sclerosis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2012, 170, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina, S.; Sainz de la Maza, S.; Villarrubia, N.; Álvarez-Lafuente, R.; Costa-Frossard, L.; Arroyo, R.; Monreal, E.; Tejeda-Velarde, A.; Rodríguez-Martín, E.; Roldán, E.; et al. Teriflunomide induces a tolerogenic bias in blood immune cells of MS patients. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2019, 6, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabe, H.; Lundell, A.C.; Andersson, K.; Adlerberth, I.; Wold, A.E.; Rudin, A. Higher proportions of circulating FOXP3+ and CTLA-4+ regulatory T cells are associated with lower fractions of memory CD4+ T cells in infants. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2011, 90, 1133–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadzadeh, A.; Rad, I.A.; Ahmadi-Salmasi, B. CTLA-4, PD-1 and TIM-3 expression predominantly downregulated in MS patients. J. Neuroimmunol. 2018, 323, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, K.; Zhong, X.; Dai, Y.; Wu, A.; Li, Y.; Hu, X. Plasma sCD28, sCTLA-4 levels in neuromyelitis optica and multiple sclerosis during relapse. J. Neuroimmunol. 2012, 243, 52–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derakhshani, A.; Asadzadeh, Z.; Safarpour, H.; Leone, P.; Shadbad, M.A.; Heydari, A.; Baradaran, B.; Racanelli, V. Regulation of CTLA-4 and PD-L1 Expression in Relapsing-Remitting Multiple Sclerosis Patients after Treatment with Fingolimod, IFNβ-1α, Glatiramer Acetate, and Dimethyl Fumarate Drugs. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mena, E.; Rohowsky-Kochan, C. Expression of costimulatory molecules on peripheral blood mononuclear cells in multiple sclerosis. Acta Neurol. Scand. 1999, 100, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavon, I.; Heli, C.; Brill, L.; Charbit, H.; Vaknin-Dembinsky, A. Blood Levels of Co-inhibitory-Receptors: A Biomarker of Disease Prognosis in Multiple Sclerosis. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, E.M.; Bar-Or, A.; Waliszewska, A.I.; Cai, G.; Anderson, D.E.; Krieger, J.I.; Hafler, D.A. CTLA-4 dysregulation in the activation of myelin basic protein reactive T cells may distinguish patients with multiple sclerosis from healthy controls. J. Autoimmun. 2003, 20, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosmaczewska, A.; Bilinska, M.; Ciszak, L.; Noga, L.; Pawlak, E.; Szteblich, A.; Podemski, R.; Frydecka, I. Different patterns of activation markers expression and CD4+ T-cell responses to ex vivo stimulation in patients with clinically quiescent multiple sclerosis (MS). J. Neuroimmunol. 2007, 189, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-Or, A. The immunology of multiple sclerosis. Semin. Neurol. 2008, 28, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinbach, K.; Piedavent, M.; Bauer, S.; Neumann, J.T.; Friese, M.A. Neutrophils amplify autoimmune central nervous system infiltrates by maturing local APCs. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 4531–4539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajami, B.; Bennett, J.L.; Krieger, C.; McNagny, K.M.; Rossi, F.M.V. Infiltrating monocytes trigger EAE progression, but do not contribute to the resident microglia pool. Nat. Neurosci. 2011, 14, 1142–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsdoerffer, M.; Schreiner, B.; Kieseier, B.C.; Neuhaus, O.; Dichgans, J.; Hartung, H.P.; Weller, M.; Wiendl, H. Monocyte-derived HLA-G acts as a strong inhibitor of autologous CD4 T cell activation and is upregulated by interferon-β in vitro and in vivo: Rationale for the therapy of multiple sclerosis. J. Neuroimunol. 2005, 159, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler-Heitbrock, L. The CD14þ CD16þ blood monocytes: Their role in infection and inflammation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2007, 81, 584592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuluundorj, D.; Harding, S.A.; Abernethy, D.; La Flamme, A.C. Expansion and preferential activation of the CD14+CD16+ monocyte subset during multiple sclerosis. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2014, 92, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haschka, D.; Tymoszuk, P.; Bsteh, G.; Petzer, V.; Berek, K.; Theurl, I.; Berger, T.; Weiss, G. Expansion of Neutrophils and Classical and Nonclassical Monocytes as a Hallmark in Relapsing-Remitting Multiple Sclerosis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 29, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, R.; Kanti Barman, P.; Kumar Thatoi, P.; Tripathy, R.; Kumar Das, B.; Ravindran, B. Non-Classical monocytes display inflammatory features: Validation in Sepsis and Systemic Lupus Erythematous. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paré, A.; Mailhot, B.; Lévesque, S.A.; Juzwik, C.; Ignatius Arokia Doss, P.M.; Lécuyer, M.A.; Prat, A.; Rangachari, M.; Fournier, A.; Lacroix, S. IL-1β enables CNS access to CCR2hi monocytes and the generation of pathogenic cells through GM-CSF released by CNS endothelial cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 1194–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chitnis, T.; Khoury, S.J. Role of costimulatory pathways in the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 112, 837–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breij, E.C.; Brink, B.P.; Veerhuis, R.; Van den Berg, C.; Vloet, R.; Yan, R.; Dijkstra, C.D.; Van der Valk, P.; Bö, L. Homogeneity of active demyelinating lesions in established multiple sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 2008, 63, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Essen, M.R.; Ammitzbøll, C.; Hansen, R.H.; Petersen, E.R.S.; McWilliam, O.; Marquart, H.V.; Damm, P.; Sellebjerg, F. Proinflammatory CD20+ T cells in the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis. Brain 2019, 142, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatino, J.J., Jr.; Wilson, M.R.; Calabresi, P.A.; Hauser, S.L.; Schneck, J.P.; Zamvil, S.S. Anti-CD20 therapy depletes activated myelin-specific CD8+ T cells in multiple sclerosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 25800–25807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-Or, A.; Fawaz, L.; Fan, B.; Darlington, P.J.; Rieger, A.; Ghorayeb, C.; Calabresi, P.A.; Waubant, E.; Hauser, S.L.; Zhang, J.; et al. Abnormal B-cell cytokine responses a trigger of T-cell-mediated disease in MS? Ann. Neurol. 2010, 67, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.L.; Yeap, W.H.; Tai, J.J.; Ong, S.M.; Dang, T.M.; Wong, S.C. The three human monocyte subsets: Implications for health and disease. Immunol. Res. 2012, 53, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.L.; Tai, J.J.; Wong, W.C.; Han, H.; Sem, X.; Yeap, W.H.; Kourilsky, P.; Wong, S.C. Gene expression profiling reveals the defining features of the classical, intermediate, and nonclassical human monocyte subsets. Blood 2011, 118, e16–e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawada, A.M.; Rogacev, K.S.; Rotter, B.; Winter, P.; Marell, R.R.; Fliser, D.; Heine, G.H. SuperSAGE evidence for CD14++CD16+ monocytes as a third monocyte subset. Blood 2011, 118, e50–e61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randolph, G.J.; Sanchez-Schmitz, G.; Liebman, R.M.; Schäkel, K. The CD16+ (FcγRIII+) subset of human monocytes preferentially becomes migratory dendritic cells in a model tissue setting. J. Exp. Med. 2002, 196, 517–527, Erratum in: J. Exp. Med. 2002, 196, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinoda, K.; Li, R.; Rezk, A.; Mexhitaj, I.; Patterson, K.R.; Kakara, M.; Zuroff, L.; Bennett, J.L.; von Büdingen, H.C.; Carruthers, R.; et al. Differential effects of anti-CD20 therapy on CD4 and CD8 T cells and implication of CD20-expressing CD8 T cells in MS disease activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2207291120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Parameter | All PPMS (N = 28) | Treated PPMS (N = 15) | Untreated PPMS (N = 13) | HCs (N = 10) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | ||||
| Age (years) | 54.57 ± 8.71 | 53 ± 7.47 | 56.3 ± 9.97 | 37 ± 13.90 |
| EDSS | 4.94 ± 1.54 | 4.8 ± 1.53 | 5.11 ± 1.6 | / |
| Disease duration (years) | 10.74 ± 7.58 | 6.86 ± 5.39 | 15.58 ± 7.26 | / |
| Female/Male (N) | 21/7 | 13/2 | 8/5 | 6/4 |
| % of CD4+ CD25+high | MFI of CD4+ CD25+high | % of CD4+ CD25+high FOXP3+ | MFI of CD4+ CD25+high FOXP3+ | % of CD4+ CD25+ | MFI of CD4+CD25+ | % of CD4+ CD25+ FOXP3+ | MFI of CD4+ CD25+ FOXP3+ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treated PPMS (N = 15) | M | 3.02 | 3720.74 | 10.57 | 1798.26 | 5.502 | 36,098.34 | 21.89 | 1866.49 |
| SD | 0.66 | 399.85 | 3.06 | 433.07 | 1.28 | 3422.33 | 5.41 | 474.53 | |
| HCs (N = 10) | M | 2.56 | 3550.99 | 8.63 | 1417.0.3 | 4.54 | 34,907.46 | 15.48 | 1415.77 |
| SD | 0.65 | 154.51 | 1.28 | 233.17 | 0.91 | 2195.62 | 2.63 | 209.94 | |
| Untreated PPMS (N = 13) | M | 3.7 | 3679.51 | 11.06 | 1687.15 | 6.26 | 35,148.44 | 21.03 | 1744.54 |
| SD | 1.08 | 215.02 | 2.68 | 258.27 | 1.76 | 3060.79 | 3.91 | 232.4 | |
| All PPMS (N = 28) | M | 3.33 | 3701.6 | 10.76 | 1746.68 | 5.85 | 35,657.31 | 21.49 | 1809.87 |
| SD | 0.93 | 322.32 | 2.89 | 360.6711 | 1.54 | 3235.67 | 4.71 | 380.26 | |
| All PPMS vs. HCs | t | 2.4 | 1.14 | 2.22 | 2.69 | 2.47 | 0.67 | 3.8 | 3 |
| df | 37 | 37 | 37 | 37 | 37 | 37 | 37 | 37 | |
| p | 0.02 * | 0.16 | 0.03 * | 0.01 * | 0.01 * | 0.05 | 0.0005 *** | 0.003 ** | |
| Treated PPMS vs. HCs | t | 1.7 | 1.27 | 1.88 | 2.55 | 1.99 | 0.97 | 3.46 | 2.81 |
| df | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | |
| p | 0.1 | 0.21 | 0.07 | 0.01 * | 0.058 | 0.34 | 0.002 ** | 0.009 ** | |
| Untreated PPMS vs. HCs | t | 2.9 | 1.56 | 2.62 | 2.63 | 2.76 | 0.21 | 3.84 | 3.5 |
| df | 22 | 22 | 22 | 22 | 22 | 22 | 22 | 22 | |
| p | 0.008 ** | 0.12 | 0.01* | 0.01 * | 0.01 * | 0.83 | 0.0009 *** | 0.002 ** | |
| Treated PPMS vs. Untreated PPMS | t | 2 | 0.33 | 0.43 | 0.8 | 1.32 | 0.76 | 0.47 | 0.84 |
| df | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | |
| p | 0.053 | 0.74 | 0.66 | 0.42 | 0.19 | 0.44 | 0.63 | 0.4 |
| % of CD4+CD25−CTLA-4+ | MFI of CTLA-4+ in CD4+CD25− | % of CD4+ CTLA-4+ | MFI of CD4+ CTLA-4+ | % of CD4+CD25+ FOXP3+ CTLA-4+ | MFI of CD4+CD25+ FOXP3+ CTLA-4+ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treated PPMS (N = 15) | M | 39.96 | 1327.11 | 15.29 | 2742.4 | 34.01 | 2378.26 |
| SD | 9.59 | 196.92 | 4.34 | 144.93 | 7.84 | 294.41 | |
| HCs (N = 10) | M | 36.61 | 1179.32 | 12.65 | 2711.42 | 25.57 | 2291.86 |
| SD | 7.01 | 60.62 | 3.51 | 194.87 | 3.89 | 294.41 | |
| Untreated PPMS (N = 13) | M | 42.16 | 1278.63 | 14.86 | 2652.08 | 30.41 | 2372.1 |
| SD | 5.67 | 151.23 | 3.72 | 124.01 | 4.99 | 259 | |
| All PPMS (N = 28) | M | 40.98 | 1308.14 | 15.09 | 2700.47 | 32.34 | 2375.4 |
| SD | 7.95 | 178.37 | 4.00 | 140.82 | 6.08 | 273.44 | |
| All PPMS vs. HCs | t | 1.53 | 2.1 | 1.7 | 0.19 | 2.96 | 0.85 |
| df | 37 | 31 | 37 | 37 | 37 | 36 | |
| p | 0.13 | 0.04 * | 0.09 | 0.85 | 0.005 ** | 0.4 | |
| Treated PPMS vs. HCs | t | 0.94 | 2.17 | 1.59 | 0.45 | 3.14 | 0.78 |
| df | 24 | 22 | 24 | 22 | 24 | 23 | |
| p | 0.35 | 0.04 * | 0.12 | 0.93 | 0.004 ** | 0.44 | |
| Untreated PPMS vs. HCs | t | 2.09 | 1.82 | 1.44 | 0.89 | 2.53 | 0.79 |
| df | 22 | 17 | 22 | 22 | 22 | 21 | |
| p | 0.04 * | 0.08 | 0.16 | 0.38 | 0.01 * | 0.43 | |
| Treated PPMS vs. Untreated PPMS | t | 0.72 | 0.62 | 0.27 | 1.75 | 1.42 | 0.05 |
| df | 27 | 22 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | |
| p | 0.47 | 0.53 | 0.78 | 0.09 | 0.16 | 0.95 |
| % of CD40+ CD14++CD16− | MFI of CD40 in CD14++CD16− | % of CD192+ CD14++CD16− | MFI of CD192+ in CD14++CD16− | % of CD14++ CD16+ | % of CD40+ in CD14++CD16+ | MFI of CD40+ in CD14++CD16+ | % of CD40+ in CD14+CD16++ | % of CD192+ in CD14+CD16++ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treated PPMS (N = 15) | M | 60.48 | 4200.943 | 83.92 | 101,066.2 | 7.37 | 79.59 | 9922.6 | 61.09 | 62.82 |
| SD | 23.26 | 1398.083 | 9.665 | 8739.41 | 4.59 | 16.34 | 3149.26 | 11.67 | 15.3 | |
| HC (N = 10) | M | 49.82 | 3442.95 | 97.77 | 81,837.85 | 3.53 | 83.274 | 8774.08 | 65.4 | 70.3 |
| SD | 19.96 | 796.503 | 1.53 | 8242.14 | 2.37 | 6.36 | 2163.78 | 20.32 | 20.95 | |
| Untreated PPMS (N = 13) | M | 52.142 | 3596.253 | 84.1 | 95,454.87 | 6.11 | 83.02 | 10,381.84 | 75.69 | 76.19 |
| SD | 19.20 | 751.187 | 13.04 | 10,285.6 | 4.6 | 18.16 | 4155.25 | 13.61 | 13.13 | |
| All PPMS (N = 28) | M | 56.61 | 3920.19 | 84.003 | 98,461 | 6.79 | 81.18 | 10,135.82 | 67.58 | 68.76 |
| SD | 21.5 | 1165.84 | 11.13 | 9733.66 | 6.75 | 16.97 | 3586.68 | 14.36 | 15.65 | |
| All PPMS vs. HCs | t | 0.87 | 1.19 | 3.9 | 4.8 | 2.11 | 0.37 | 1.12 | 0.36 | 0.24 |
| df | 37 | 37 | 37 | 37 | 37 | 37 | 37 | 36 | 36 | |
| p | 0.38 | 0.24 | 0.0004 ** | 0.00002 *** | 0.041 * | 0.7 | 0.26 | 0.7 | 0.81 | |
| Treated PPMS vs. HCs | t | 1.19 | 1.5 | 4.46 | 5.5 | 2.42 | 0.67 | 1 | 0.67 | 1.03 |
| df | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | |
| p | 0.24 | 0.13 | 0.0001 *** | 0.00001 *** | 0.02 * | 0.5 | 0.32 | 0.5 | 0.31 | |
| Untreated PPMS vs. HCs | t | 0.28 | 0.47 | 3.28 | 3.4 | −1.56 | 0.04 | 1.1 | 1.41 | 0.8 |
| df | 22 | 22 | 22 | 22 | 22 | 22 | 22 | 21 | 21 | |
| p | 0.77 | 0.64 | 0.003* | 0.002** | 0.13 | 0.96 | 0.27 | 0.17 | 0.43 | |
| Treated PPMS vs. Untreated PPMS | t | 1.02 | 1.3 | 0.04 | 1.5 | 0.71 | 0.52 | 0.33 | 3 | 2.39 |
| df | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 36 | 26 | |
| p | 0.31 | 0.17 | 0.96 | 0.13 | 0.48 | 0.6 | 0.74 | 0.006 *** | 0.02 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ipavec, N.; Rogić Vidaković, M.; Markotić, A.; Pavelin, S.; Buljubašić Šoda, M.; Šoda, J.; Dolić, K.; Režić Mužinić, N. Treated and Untreated Primary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis: Walkthrough Immunological Changes of Monocytes and T Regulatory Cells. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 464. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12020464
Ipavec N, Rogić Vidaković M, Markotić A, Pavelin S, Buljubašić Šoda M, Šoda J, Dolić K, Režić Mužinić N. Treated and Untreated Primary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis: Walkthrough Immunological Changes of Monocytes and T Regulatory Cells. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(2):464. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12020464
Chicago/Turabian StyleIpavec, Nina, Maja Rogić Vidaković, Anita Markotić, Sanda Pavelin, Maja Buljubašić Šoda, Joško Šoda, Krešimir Dolić, and Nikolina Režić Mužinić. 2024. "Treated and Untreated Primary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis: Walkthrough Immunological Changes of Monocytes and T Regulatory Cells" Biomedicines 12, no. 2: 464. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12020464
APA StyleIpavec, N., Rogić Vidaković, M., Markotić, A., Pavelin, S., Buljubašić Šoda, M., Šoda, J., Dolić, K., & Režić Mužinić, N. (2024). Treated and Untreated Primary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis: Walkthrough Immunological Changes of Monocytes and T Regulatory Cells. Biomedicines, 12(2), 464. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12020464









