Roles of Macrophages and Endothelial Cells and Their Crosstalk in Acute Lung Injury
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Macrophages in Acute Lung Injury
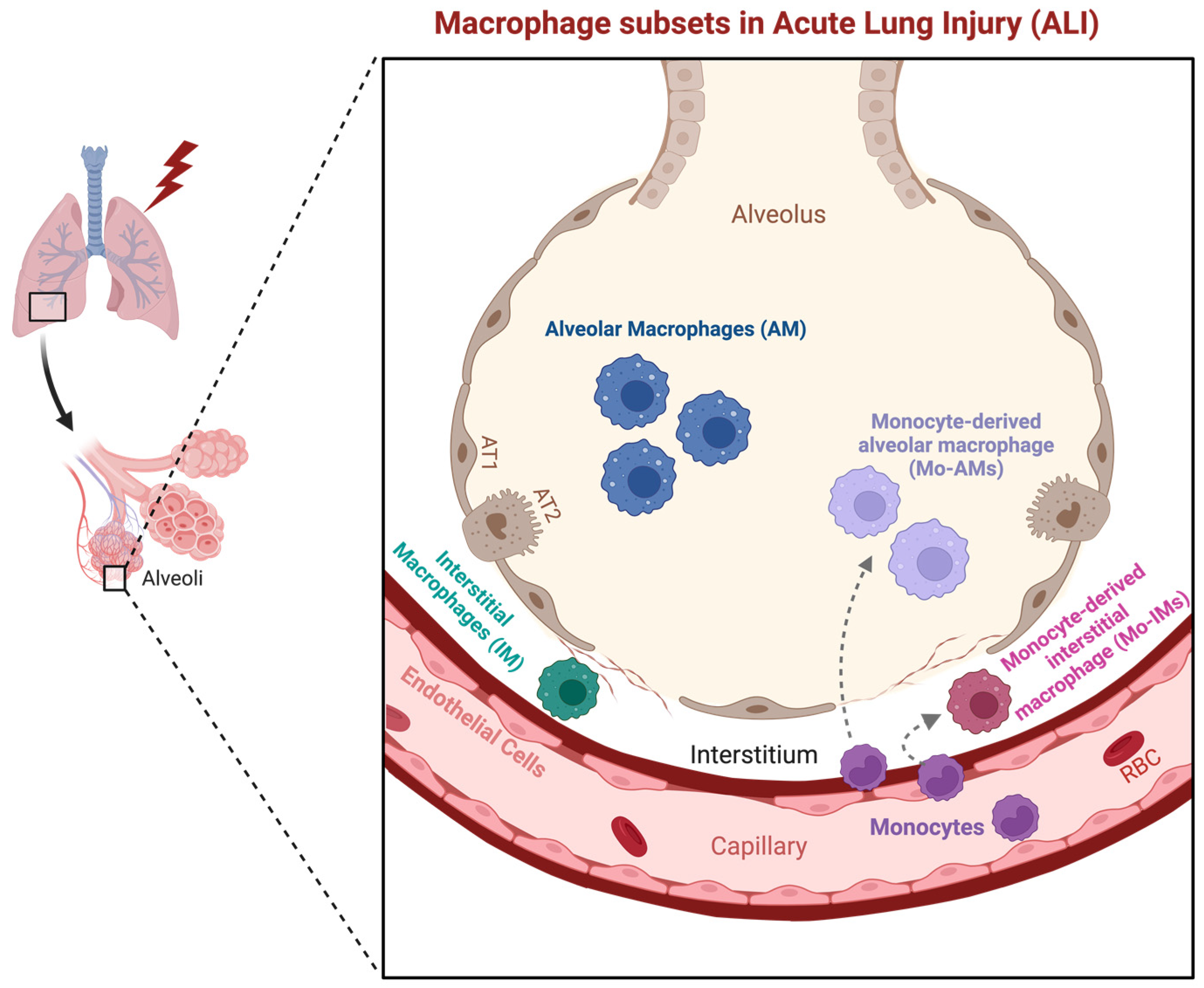
2.1. Macrophage Subsets in the Lung
2.2. Macrophage Polarization in Acute Lung Injury
2.3. Macrophage-Derived Soluble Factors in Acute Lung Injury
2.4. Macrophage Inflammasomes and Pyroptosis in Acute Lung Injury
3. Endothelial Cells in Acute Lung Injury
3.1. Endothelial Cells (ECs) and Pulmonary Vasculature in Acute Lung Injury
3.2. Activation and Dysfunction of ECs in ALI/ARDS
3.3. Endothelial Regeneration and Vascular Repair in ALI/ARDS
3.4. Lung Endothelial Heterogeneity—Emerging EC Subpopulation and Their Potential Roles in ALI
4. Macrophage–Endothelial Cell Crosstalk in Acute Lung Injury
4.1. Macrophage Regulation of Endothelial Function in ALI
4.2. Endothelial Regulation of Macrophage Function in ALI
5. Future Perspectives
5.1. Perivascular Macrophages (PVMs)
5.2. Immunomodulatory Endothelial Cells (IMECs)
5.3. Future Perspectives and Therapeutic Opportunities
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Matthay, M.A.; Zemans, R.L.; Zimmerman, G.A.; Arabi, Y.M.; Beitler, J.R.; Mercat, A.; Herridge, M.; Randolph, A.G.; Calfee, C.S. Acute respiratory distress syndrome. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2019, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Shi, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Huang, L.; Zhang, C.; Liu, S.; Zhao, P.; Liu, H.; Zhu, L.; et al. Pathological findings of COVID-19 associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 420–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakowitz, M.; Bruns, B.; McCunn, M. Acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome in the injured patient. Scand. J. Trauma Resusc. Emerg. Med. 2012, 20, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragaller, M.; Richter, T. Acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome. J. Emerg. Trauma Shock. 2010, 3, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, B.T.; Chambers, R.C.; Liu, K.D. Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 562–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McVey, M.J.; Steinberg, B.E.; Goldenberg, N.M. Inflammasome activation in acute lung injury. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2021, 320, L165–L178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; Weiner, A.I.; Neupauer, K.M.; Costa, M.F.d.M.; Palashikar, G.; Adams-Tzivelekidis, S.; Mangalmurti, N.S.; Vaughan, A.E. Regeneration of the pulmonary vascular endothelium after viral pneumonia requires COUP-TF2. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabc4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’agnillo, F.; Walters, K.-A.; Xiao, Y.; Sheng, Z.-M.; Scherler, K.; Park, J.; Gygli, S.; Rosas, L.A.; Sadtler, K.; Kalish, H.; et al. Lung epithelial and endothelial damage, loss of tissue repair, inhibition of fibrinolysis, and cellular senescence in fatal COVID-19. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabj7790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruhl, L.; Pink, I.; Kühne, J.F.; Beushausen, K.; Keil, J.; Christoph, S.; Sauer, A.; Boblitz, L.; Schmidt, J.; David, S.; et al. Endothelial dysfunction contributes to severe COVID-19 in combination with dysregulated lymphocyte responses and cytokine networks. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borek, I.; Birnhuber, A.; Voelkel, N.F.; Marsh, L.M.; Kwapiszewska, G. The vascular perspective on acute and chronic lung disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 133, e170502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Huang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Machireddy, N.; Machireddy, N.; Evans, C.E.; Evans, C.E.; Trewartha, S.D.; Trewartha, S.D.; et al. Endothelial FoxM1 reactivates aging-impaired endothelial regeneration for vascular repair and resolution of inflammatory lung injury. Sci. Transl. Med. 2023, 15, eabm5755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, C.E.; Iruela-Arispe, M.L.; Zhao, Y.-Y. Mechanisms of Endothelial Regeneration and Vascular Repair and Their Application to Regenerative Medicine. Am. J. Pathol. 2021, 191, 52–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marichal, T. Endothelial cells instruct macrophages on how to Rspond to lung injury. Nat. Immunol. 2020, 21, 1317–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huertas, A.; Guignabert, C.; Barberà, J.A.; Bärtsch, P.; Bhattacharya, J.; Bhattacharya, S.; Bonsignore, M.R.; Dewachter, L.; Dinh-Xuan, A.T.; Dorfmüller, P.; et al. Pulmonary vascular endothelium: The orchestra conductor in respiratory diseases: Highlights from basic research to therapy. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 51, 1700745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millar, F.R.; Summers, C.; Griffiths, M.J.; Toshner, M.R.; Proudfoot, A.G. The pulmonary endothelium in acute respiratory distress syndrome: Insights and therapeutic opportunities. Thorax 2016, 71, 462–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniatis, N.A.; Kotanidou, A.; Catravas, J.D.; Orfanos, S.E. Endothelial pathomechanisms in acute lung injury. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2008, 49, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aegerter, H.; Lambrecht, B.N.; Jakubzick, C.V. Biology of lung macrophages in health and disease. Immunity 2022, 55, 1564–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, F.; Xiao, K.; Tang, L.; Xie, L. Diversity of Macrophages in Lung Homeostasis and Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 753940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herold, S.; Mayer, K.; Lohmeyer, J. Acute Lung Injury: How Macrophages Orchestrate Resolution of Inflammation and Tissue Repair. Front. Immunol. 2011, 2, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, P.J.; Wynn, T.A. Protective and pathogenic functions of macrophage subsets. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 723–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, A.J.; Mathie, S.A.; Gregory, L.G.; Lloyd, C.M. Pulmonary macrophages: Key players in the innate defence of the airways. Thorax 2015, 70, 1189–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Xiu, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, G. The Role of Macrophages in the Pathogenesis of ALI/ARDS. Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 1264913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Tang, J.; Shuai, W.; Meng, J.; Feng, J.; Han, Z. Macrophage polarization and its role in the pathogenesis of acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome. Inflamm. Res. 2020, 69, 883–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leach, H.G.; Chrobak, I.; Han, R.; Trojanowska, M. Endothelial Cells Recruit Macrophages and Contribute to a Fibrotic Milieu in Bleomycin Lung Injury. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2013, 49, 1093–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baer, C.; Squadrito, M.L.; Iruela-Arispe, M.L.; De Palma, M. Reciprocal interactions between endothelial cells and macrophages in angiogenic vascular niches. Exp. Cell Res. 2013, 319, 1626–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sefik, E.; Qu, R.; Junqueira, C.; Kaffe, E.; Mirza, H.; Zhao, J.; Brewer, J.R.; Han, A.; Steach, H.R.; Israelow, B.; et al. Inflammasome activation in infected macrophages drives COVID-19 pathology. Nature 2022, 606, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Ji, W.; Yang, H.; Chen, S.; Zhang, W.; Duan, G. Endothelial activation and dysfunction in COVID-19: From basic mechanisms to potential therapeutic approaches. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzales, J.N.; Lucas, R.; Verin, A.D. The Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Mechanisms and Perspective Therapeutic Approaches. Austin J. Vasc. Med. 2015, 2, 1009. [Google Scholar]
- Dang, W.; Tao, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhao, H.; Zou, L.; Li, Y. The role of lung macrophages in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Inflamm. Res. 2022, 71, 1417–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.Y.S.; Krasnow, M.A. Developmental origin of lung macrophage diversity. Development 2016, 143, 1318–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, L.K.; Rims, C.R.; Gill, S.E.; McGuire, J.K.; Manicone, A.M. Pulmonary macrophage subpopulations in the induction and resolution of acute lung injury. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2012, 47, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evren, E.; Ringqvist, E.; Willinger, T. Origin and ontogeny of lung macrophages: From mice to humans. Immunology 2020, 160, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, S.; Alexander, M.; Misharin, A.V.; Budinger, G.S. The role of macrophages in the resolution of inflammation. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 2619–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Li, H.; Bao, M.; Zhuo, R.; Jiang, G.; Wang, W. Alveolar macrophage-derived exosomes modulate severity and outcome of acute lung injury. Aging 2020, 12, 6120–6128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Fernandez, L.G.; Doctor, A.; Sharma, A.K.; Zarbock, A.; Tribble, C.G.; Kron, I.L.; Laubach, V.E.; Charles, E.J.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Alveolar macrophage activation is a key initiation signal for acute lung ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2006, 291, L1018–L1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbings, S.L.; Thomas, S.M.; Atif, S.M.; McCubbrey, A.L.; Desch, A.N.; Danhorn, T.; Leach, S.M.; Bratton, D.L.; Henson, P.M.; Janssen, W.J.; et al. Three Unique Interstitial Macrophages in the Murine Lung at Steady State. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2017, 57, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liegeois, M.; Legrand, C.; Desmet, C.J.; Marichal, T.; Bureau, F. The interstitial macrophage: A long-neglected piece in the puzzle of lung immunity. Cell. Immunol. 2018, 330, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schyns, J.; Bureau, F.; Marichal, T. Lung Interstitial Macrophages: Past, Present, and Future. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 5160794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McQuattie-Pimentel, A.C.; Budinger, G.R.S.; Ballinger, M.N. Monocyte-derived Alveolar Macrophages: The Dark Side of Lung Repair? Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2018, 58, 5–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aegerter, H.; Kulikauskaite, J.; Crotta, S.; Patel, H.; Kelly, G.; Hessel, E.M.; Mack, M.; Beinke, S.; Wack, A. Influenza-induced monocyte-derived alveolar macrophages confer prolonged antibacterial protection. Nat. Immunol. 2020, 21, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öz, H.H.; Cheng, E.-C.; Di Pietro, C.; Tebaldi, T.; Biancon, G.; Zeiss, C.; Zhang, P.-X.; Huang, P.H.; Esquibies, S.S.; Britto, C.J.; et al. Recruited monocytes/macrophages drive pulmonary neutrophilic inflammation and irreversible lung tissue remodeling in cystic fibrosis. Cell Rep. 2022, 41, 111797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graney, P.L.; Ben-Shaul, S.; Landau, S.; Bajpai, A.; Singh, B.; Eager, J.; Cohen, A.; Levenberg, S.; Spiller, K.L. Macrophages of diverse phenotypes drive vascularization of engineered tissues. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaay6391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bain, C.C.; MacDonald, A.S. The impact of the lung environment on macrophage development, activation and function: Diversity in the face of adversity. Mucosal Immunol. 2022, 15, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Tanjore, H.; Liu, Y.; Hunt, R.P.; Gutor, S.S.; Serezani, A.P.M.; Blackwell, T.S. Identification and Characterization of Alveolar and Recruited Lung Macrophages during Acute Lung Inflammation. J. Immunol. 2023, 210, 1827–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, P.K.; Anderson, K.C.; McManus, S.A.; Tu, T.-H.; King, E.M.; Mould, K.J.; Redente, E.F.; Henson, P.M.; Janssen, W.J.; McCubbrey, A.L. Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals unique monocyte-derived interstitial macrophage subsets during lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung inflammation. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2023, 324, L536–L549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ural, B.B.; Yeung, S.T.; Damani-Yokota, P.; Devlin, J.C.; de Vries, M.; Vera-Licona, P.; Samji, T.; Sawai, C.M.; Jang, G.; Perez, O.A.; et al. Identification of a nerve-associated, lung-resident interstitial macrophage subset with distinct localization and immunoregulatory properties. Sci. Immunol. 2020, 5, eaax8756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schyns, J.; Bai, Q.; Ruscitti, C.; Radermecker, C.; De Schepper, S.; Chakarov, S.; Farnir, F.; Pirottin, D.; Ginhoux, F.; Boeckxstaens, G.; et al. Non-classical tissue monocytes and two functionally distinct populations of interstitial macrophages populate the mouse lung. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard, B.; Panariti, A.; Martin, J.G. Alveolar Macrophages in the Resolution of Inflammation, Tissue Repair, and Tolerance to Infection. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brieland, J.K.; Kunkel, R.G.; Fantone, J.C. Pulmonary alveolar macrophage function during acute inflammatory lung injury. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1987, 135, 1300–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakarov, S.; Lim, H.Y.; Tan, L.; Lim, S.Y.; See, P.; Lum, J.; Zhang, X.-M.; Foo, S.; Nakamizo, S.; Duan, K.; et al. Two distinct interstitial macrophage populations coexist across tissues in specific subtissular niches. Science 2019, 363, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Magana, L.; Hong, Z.; Huang, L.S.; Chakraborty, S.; Tsukasaki, Y.; Huang, C.; Wang, L.; Di, A.; Ganesh, B.; et al. The angiocrine Rspondin3 instructs interstitial macrophage transition via metabolic–epigenetic reprogramming and resolves inflammatory injury. Nat. Immunol. 2020, 21, 1430–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedoret, D.; Wallemacq, H.; Marichal, T.; Desmet, C.; Quesada Calvo, F.; Henry, E.; Closset, R.; Dewals, B.G.; Thielen, C.; Gustin, P.; et al. Lung interstitial macrophages alter dendritic cell functions to prevent airway allergy in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 3723–3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misharin, A.V.; Morales-Nebreda, L.; Reyfman, P.A.; Cuda, C.M.; Walter, J.M.; McQuattie-Pimentel, A.C.; Chen, C.-I.; Anekalla, K.R.; Joshi, N.; Williams, K.J.N.; et al. Monocyte-derived alveolar macrophages drive lung fibrosis and persist in the lung over the life span. J. Exp. Med. 2017, 214, 2387–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, T.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, W.; Lin, H. Regulatory T cell and macrophage crosstalk in acute lung injury: Future perspectives. Cell Death Discov. 2023, 9, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, P.J. Macrophage Polarization. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2017, 79, 541–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arafa, E.I.; Shenoy, A.T.; Barker, K.A.; Etesami, N.S.; Martin, I.M.; De Ana, C.L.; Na, E.; Odom, C.V.; Goltry, W.N.; Korkmaz, F.T.; et al. Recruitment and training of alveolar macrophages after pneumococcal pneumonia. JCI Insight 2022, 7, e150239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McQuattie-Pimentel, A.C.; Ren, Z.; Joshi, N.; Watanabe, S.; Stoeger, T.; Chi, M.; Lu, Z.; Sichizya, L.; Aillon, R.P.; Chen, C.-I.; et al. The lung microenvironment shapes a dysfunctional response of alveolar macrophages in aging. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e140299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corry, J.D.; Kettenburg, G.; Upadhyay, A.A.; Wallace, M.; Marti, M.M.; Wonderlich, E.R.; Bissel, S.J.; Goss, K.; Sturgeon, T.J.; Watkins, S.C.; et al. Infiltration of inflammatory macrophages and neutrophils and widespread pyroptosis in lung drive influenza lethality in nonhuman primates. PLoS Pathog. 2022, 18, e1010395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, S.M.; Karki, R.; Kanneganti, T. Molecular mechanisms and functions of pyroptosis, inflammatory caspases and inflammasomes in infectious diseases. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 277, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Z. The role of macrophages polarization in sepsis-induced acute lung injury. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1209438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Song, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, L.; Yu, J.; Zhu, D.; Zhong, M. M2 macrophages promote pulmonary endothelial cells regeneration in sepsis-induced acute lung injury. Ann. Transl. Med. 2019, 7, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, N.R.; King, L.S.; D’Alessio, F.R. Diverse macrophage populations mediate acute lung inflammation and resolution. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2014, 306, L709–L725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duque, G.A.; Descoteaux, A. Macrophage cytokines: Involvement in immunity and infectious diseases. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Jin, Y.; Lee, M.; Kim, Y.; Lee, H. Macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1 promotes angiogenesis by eliciting the GFRAL-mediated endothelial cell signaling. J. Cell. Physiol. 2021, 236, 4008–4023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerhardt, T.; Ley, K. Monocyte trafficking across the vessel wall. Cardiovasc. Res. 2015, 107, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puttur, F.; Gregory, L.G.; Lloyd, C.M. Airway macrophages as the guardians of tissue repair in the lung. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2019, 97, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gieseck, R.L.; Wilson, M.S.; Wynn, T.A. Type 2 immunity in tissue repair and fibrosis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidzadeh, K.; Christensen, S.M.; Dalby, E.; Chandrasekaran, P.; Mosser, D.M. Macrophages and the Recovery from Acute and Chronic Inflammation. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2017, 79, 567–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Borthwick, L.; Barron, L.; Hart, K.M.; Vannella, K.M.; Thompson, R.W.; Oland, S.; Cheever, A.; Sciurba, J.; Ramalingam, T.R.; Fisher, A.J.; et al. Macrophages are critical to the maintenance of IL-13-dependent lung inflammation and fibrosis. Mucosal. Immunol. 2016, 9, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosser, D.M.; Hamidzadeh, K.; Goncalves, R. Macrophages and the maintenance of homeostasis. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ntokou, A.; Dave, J.M.; Kauffman, A.C.; Sauler, M.; Ryu, C.; Hwa, J.; Herzog, E.L.; Singh, I.; Saltzman, W.M.; Greif, D.M. Macrophage-derived PDGF-B induces muscularization in murine and human pulmonary hypertension. JCI Insight 2021, 6, e139067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Fan, G.; Tao, N.; Sun, T. Role of Pyroptosis in Respiratory Diseases and its Therapeutic Potential. J. Inflamm. Res. 2022, 15, 2033–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Zhang, X.; Liu, N.; Tang, L.; Peng, C.; Chen, X. Pyroptosis: Mechanisms and diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; He, R.; Zhang, L.; Hao, B.; Jiang, W.; Wang, W.; Geng, Q. Inflammatory Caspases Drive Pyroptosis in Acute Lung Injury. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 631256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Callaway, J.B.; Ting, J.P.-Y. Inflammasomes: Mechanism of action, role in disease, and therapeutics. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yan, Z.; Schwartz, D.E.; Yu, J.; Malik, A.B.; Hu, G. Activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in alveolar macrophages contributes to mechanical stretch-induced lung inflammation and injury. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 3590–3599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergsbaken, T.; Fink, S.L.; Cookson, B.T. Pyroptosis: Host cell death and inflammation. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovarova, M.; Hesker, P.R.; Jania, L.; Nguyen, M.; Snouwaert, J.N.; Xiang, Z.; Lommatzsch, S.E.; Huang, M.T.; Ting, J.P.-Y.; Koller, B.H. NLRP1-dependent pyroptosis leads to acute lung injury and morbidity in mice. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 2006–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godoy, R.S.; Cober, N.D.; Cook, D.P.; McCourt, E.; Deng, Y.; Wang, L.; Schlosser, K.; Rowe, K.; Stewart, D.J. Single-cell transcriptomic atlas of lung microvascular regeneration after targeted endothelial cell ablation. eLife 2023, 12, e80900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schupp, J.C.; Adams, T.S.; Cosme, C.; Raredon, M.S.B.; Yuan, Y.; Omote, N.; Poli, S.; Chioccioli, M.; Rose, K.-A.; Manning, E.P.; et al. Integrated Single-Cell Atlas of Endothelial Cells of the Human Lung. Circulation 2021, 144, 286–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillich, A.; Zhang, F.; Farmer, C.G.; Travaglini, K.J.; Tan, S.Y.; Gu, M.; Zhou, B.; Feinstein, J.A.; Krasnow, M.A.; Metzger, R.J. Capillary cell-type specialization in the alveolus. Nature 2020, 586, 785–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Gao, S.; White, Z.; Dai, Y.; Malik, A.B.; Rehman, J. Single-cell transcriptomic profiling of lung endothelial cells identifies dynamic inflammatory and regenerative subpopulations. JCI Insight 2022, 7, e158079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, L.; Marsboom, G.; Jambusaria, A.; Xiong, S.; Toth, P.T.; Benevolenskaya, E.V.; Rehman, J.; Malik, A.B. Sox17 is required for endothelial regeneration following inflammation-induced vascular injury. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minamino, T.; Komuro, I. Regeneration of the endothelium as a novel therapeutic strategy for acute lung injury. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 2316–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.-X.; Wang, H.-B.; Li, J.; Jin, J.-B.; Hu, J.-B.; Yang, C.-L. Targeting pulmonary vascular endothelial cells for the treatment of respiratory diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 983816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aird, W.C. The role of the endothelium in severe sepsis and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. Blood 2003, 101, 3765–3777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silliman, C.C.; Kelher, M. The role of endothelial activation in the pathogenesis of transfusion-related acute lung injury. Transfusion 2005, 45, 109S–116S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jambusaria, A.; Hong, Z.; Zhang, L.; Srivastava, S.; Jana, A.; Toth, P.T.; Dai, Y.; Malik, A.B.; Rehman, J.; The University of Illinois College of Medicine; et al. Endothelial heterogeneity across distinct vascular beds during homeostasis and inflammation. eLife 2020, 9, e51413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Saredy, J.; Yang, W.Y.; Sun, Y.; Lu, Y.; Saaoud, F.; Drummer, C., IV; Johnson, C.; Xu, K.; Jiang, X.; et al. Vascular Endothelial Cells and Innate Immunity. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020, 40, e138–e152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsing, S.K.H.; van der Laan, E.Z.; van Stalborch, A.D.; van Buul, J.D.; Kapur, R.; Vlaar, A.P. A pulmonary endothelial amplification loop aggravatesex-vivo transfusion-relatedacute lung injury via increased toll-like receptor 4 andintra-cellularadhesion molecule-1 expression. Transfusion 2022, 62, 1961–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsikis, S.T.; Hirsch, T.I.; Fligor, S.C.; Quigley, M.; Puder, M. Targeting the lung endothelial niche to promote angiogenesis and regeneration: A review of applications. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 1093369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.S.; Hong, Z.; Wu, W.; Xiong, S.; Zhong, M.; Gao, X.; Rehman, J.; Malik, A.B. mtDNA Activates cGAS Signaling and Suppresses the YAP-Mediated Endothelial Cell Proliferation Program to Promote Inflammatory Injury. Immunity 2020, 52, 475–486.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.-Y.; Gao, X.-P.; Zhao, Y.D.; Mirza, M.K.; Frey, R.S.; Kalinichenko, V.V.; Wang, I.-C.; Costa, R.H.; Malik, A.B. Endothelial cell–restricted disruption of FoxM1 impairs endothelial repair following LPS-induced vascular injury. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 2333–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, D.X.; Yin, J.; Hu, G.; Evans, C.E.; Zhao, Y.-Y. Endothelial Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1alpha Is Required for Vascular Repair and Resolution of Inflammatory Lung Injury through Forkhead Box Protein M1. Am. J. Pathol. 2019, 189, 1664–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mammoto, T.; Muyleart, M.; Mammoto, A. Endothelial YAP1 in Regenerative Lung Growth through the Angiopoietin–Tie2 Pathway. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2019, 60, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhter, Z.; Joshi, J.C.; Ragunathrao, V.A.B.; Maienschein-Cline, M.; Proia, R.L.; Malik, A.B.; Mehta, D. Programming to S1PR1 + Endothelial Cells Promotes Restoration of Vascular Integrity. Circ. Res. 2021, 129, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, S.; Hong, Z.; Huang, L.S.; Tsukasaki, Y.; Nepal, S.; Di, A.; Zhong, M.; Wu, W.; Ye, Z.; Gao, X.; et al. IL-1beta suppression of VE-cadherin transcription underlies sepsis-induced inflammatory lung injury. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 133, e169500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Gentile, M.E.; Xue, L.; Cosgriff, C.V.; Weiner, A.I.; Adams-Tzivelekidis, S.; Wong, J.; Li, X.; Kass-Gergi, S.; Holcomb, N.P.; et al. Vascular Endothelial-derived SPARCL1 Exacerbates Viral Pneumonia through Pro-Inflammatory Macrophage Activation. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhya, S.; Rehman, J.; Malik, A.B.; Chen, S. Mechanisms of Lung Injury Induced by SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Physiology 2022, 37, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Li, Y.; Li, M.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xia, B.; et al. Endothelial Shp2 deficiency controls alternative activation of macrophage preventing radiation-induced lung injury through notch signaling. iScience 2022, 25, 103867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amersfoort, J.; Eelen, G.; Carmeliet, P. Immunomodulation by endothelial cells—Partnering up with the immune system? Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2022, 22, 576–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Dai, Z.; Cai, L.; Sun, K.; Cho, J.; Albertine, K.H.; Malik, A.B.; Schraufnagel, D.E.; Zhao, Y.-Y. Endothelial p110gammaPI3K Mediates Endothelial Regeneration and Vascular Repair after Inflammatory Vascular Injury. Circulation 2016, 133, 1093–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niethamer, T.K.; Stabler, C.T.; Leach, J.P.; A Zepp, J.; Morley, M.P.; Babu, A.; Zhou, S.; Morrisey, E.E. Defining the role of pulmonary endothelial cell heterogeneity in the response to acute lung injury. eLife 2020, 9, e53072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niethamer, T.K.; Levin, L.I.; Morley, M.P.; Babu, A.; Zhou, S.; Morrisey, E.E. Atf3 defines a population of pulmonary endothelial cells essential for lung regeneration. eLife 2023, 12, e83835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Xue, L.; I Weiner, A.; Gong, N.; Adams-Tzivelekidis, S.; Wong, J.; E Gentile, M.; Nottingham, A.N.; Basil, M.C.; Lin, S.M.; et al. TGF-betaR2 signaling coordinates pulmonary vascular repair after viral injury in mice and human tissue. Sci. Transl. Med. 2024, 16, eadg6229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travaglini, K.J.; Nabhan, A.N.; Penland, L.; Sinha, R.; Gillich, A.; Sit, R.V.; Chang, S.; Conley, S.D.; Mori, Y.; Seita, J.; et al. A molecular cell atlas of the human lung from single-cell RNA sequencing. Nature 2020, 587, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emoto, T.; Lu, J.; Sivasubramaniyam, T.; Maan, H.; Khan, A.B.; Abow, A.A.; Schroer, S.A.; Hyduk, S.J.; Althagafi, M.G.; McKee, T.D.; et al. Colony stimulating factor-1 producing endothelial cells and mesenchymal stromal cells maintain monocytes within a perivascular bone marrow niche. Immunity 2022, 55, 862–878.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, M.; Tiruppathi, C.; Nepal, S.; Zhao, Y.-Y.; Grzych, D.; Soni, D.; Prockop, D.J.; Malik, A.B. TNFα-stimulated gene-6 (TSG6) activates macrophage phenotype transition to prevent inflammatory lung injury. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E8151–E8158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, H.; Kimura, H.; Karasawa, T.; Hisata, S.; Sadatomo, A.; Inoue, Y.; Yamada, N.; Aizawa, E.; Hishida, E.; Kamata, R.; et al. NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Lung Vascular Endothelial Cells Contributes to Intestinal Ischemia/Reperfusion-Induced Acute Lung Injury. J. Immunol. 2020, 205, 1393–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo-Gonzalez, R.; Zanini, F.; Che, X.; Liu, M.; Jones, R.C.; A Swift, M.; Quake, S.R.; Cornfield, D.N.; Alvira, C.M. Diverse homeostatic and immunomodulatory roles of immune cells in the developing mouse lung at single cell resolution. eLife 2020, 9, e56890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauler, M.; Zhang, Y.; Min, J.; Leng, L.; Shan, P.; Roberts, S.; Jorgensen, W.L.; Bucala, R.; Lee, P.J. Endothelial CD74 mediates macrophage migration inhibitory factor protection in hyperoxic lung injury. FASEB J. 2015, 29, 1940–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Wang, Z.; Lin, H.; Lei, T.; Zhou, Z.; Huang, W.; Wu, X.; Zuo, L.; Wu, J.; Liu, Y.; et al. TRIM47 is a novel endothelial activation factor that aggravates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice via K63-linked ubiquitination of TRAF2. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Zhou, J.; Liu, Y.; Xia, R.; Li, Q.; Yan, L.; Chen, Q.; Chen, X.; Jiang, Y.; Chao, G.; et al. Epithelium- and endothelium-derived exosomes regulate the alveolar macrophages by targeting RGS1 mediated calcium signaling-dependent immune response. Cell Death Differ. 2021, 28, 2238–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapenna, A.; De Palma, M.; Lewis, C.E. Perivascular macrophages in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 689–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.Y.; Lim, S.Y.; Tan, C.K.; Thiam, C.H.; Goh, C.C.; Carbajo, D.; Chew, S.H.S.; See, P.; Chakarov, S.; Wang, X.N.; et al. Hyaluronan Receptor LYVE-1-Expressing Macrophages Maintain Arterial Tone through Hyaluronan-Mediated Regulation of Smooth Muscle Cell Collagen. Immunity 2018, 49, 1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vågesjö, E.; Parv, K.; Ahl, D.; Seignez, C.; Hidalgo, C.H.; Giraud, A.; Leite, C.; Korsgren, O.; Wallén, H.; Juusola, G.; et al. Perivascular Macrophages Regulate Blood Flow following Tissue Damage. Circ. Res. 2021, 128, 1694–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendes, N.F.; Velloso, L.A. Perivascular macrophages in high-fat diet-induced hypothalamic inflammation. J. Neuroinflamm. 2022, 19, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anstee, J.E.; Feehan, K.T.; Opzoomer, J.W.; Dean, I.; Muller, H.P.; Bahri, M.; Cheung, T.S.; Liakath-Ali, K.; Liu, Z.; Choy, D.; et al. LYVE-1(+) macrophages form a collaborative CCR5-dependent perivascular niche that influences chemotherapy responses in murine breast cancer. Dev. Cell 2023, 58, 1548–1561.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.; Zheng, L.; Chen, W.; Zhai, X.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Yu, W.; Lai, Z.; Zhu, Z.; et al. Trends in perivascular macrophages research from 1997 to 2021: A bibliometric analysis. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2023, 29, 816–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siret, C.; van Lessen, M.; Bavais, J.; Jeong, H.W.; Samawar, S.K.R.; Kapupara, K.; Wang, S.; Simic, M.; de Fabritus, L.; Tchoghandjian, A.; et al. Deciphering the heterogeneity of the Lyve1(+) perivascular macrophages in the mouse brain. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, H.M.; Kitoko, J.Z.; Queiroz, C.P.; Kroehling, L.; Matheis, F.; Yang, K.L.; Reis, B.S.; Ren-Fielding, C.; Littman, D.R.; Bozza, M.T.; et al. c-MAF–dependent perivascular macrophages regulate diet-induced metabolic syndrome. Sci. Immunol. 2021, 6, eabg7506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-S.; Kolesnikov, M.; Peled-Hajaj, S.; Scheyltjens, I.; Xia, Y.; Trzebanski, S.; Haimon, Z.; Shemer, A.; Lubart, A.; Van Hove, H.; et al. A Binary Cre Transgenic Approach Dissects Microglia and CNS Border-Associated Macrophages. Immunity 2021, 54, 176–190.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchikawa, H.; Uekawa, K.; Hasegawa, Y. Perivascular macrophages in cerebrovascular diseases. Exp. Neurol. 2024, 374, 114680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, H.; Hunt, M.A.; Kurtović, Z.; Sandor, K.; Kägy, P.B.; Fereydouni, N.; Julien, A.; Göritz, C.; Vazquez-Liebanas, E.; Mäe, M.A.; et al. CD163+ macrophages monitor enhanced permeability at the blood–dorsal root ganglion barrier. J. Exp. Med. 2023, 221, e20230675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Mack, J.J.; Güç, E.; Warren, C.M.; Squadrito, M.L.; Kilarski, W.W.; Baer, C.; Freshman, R.D.; McDonald, A.I.; Ziyad, S.; et al. Perivascular Macrophages Limit Permeability. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2016, 36, 2203–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Guo, Y.; Zhai, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhu, Z.; Xuan, W.; Li, P. Perivascular macrophages in theCNS: From health to neurovascular diseases. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2022, 28, 1908–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goddery, E.N.; Fain, C.E.; Lipovsky, C.G.; Ayasoufi, K.; Yokanovich, L.T.; Malo, C.S.; Khadka, R.H.; Tritz, Z.P.; Jin, F.; Hansen, M.J.; et al. Microglia and Perivascular Macrophages Act as Antigen Presenting Cells to Promote CD8 T Cell Infiltration of the Brain. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 726421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Xu, J.; Warren, C.M.; Duan, D.; Li, X.; Wu, L.; Iruela-Arispe, M.L. Endothelial cells provide an instructive niche for the differentiation and functional polarization of M2-like macrophages. Blood 2012, 120, 3152–3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Osorio-Valencia, S.; Zhou, B. Roles of Macrophages and Endothelial Cells and Their Crosstalk in Acute Lung Injury. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12030632
Osorio-Valencia S, Zhou B. Roles of Macrophages and Endothelial Cells and Their Crosstalk in Acute Lung Injury. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(3):632. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12030632
Chicago/Turabian StyleOsorio-Valencia, Sara, and Bisheng Zhou. 2024. "Roles of Macrophages and Endothelial Cells and Their Crosstalk in Acute Lung Injury" Biomedicines 12, no. 3: 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12030632
APA StyleOsorio-Valencia, S., & Zhou, B. (2024). Roles of Macrophages and Endothelial Cells and Their Crosstalk in Acute Lung Injury. Biomedicines, 12(3), 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12030632





