Exploratory Tau PET/CT with [11C]PBB3 in Patients with Suspected Alzheimer’s Disease and Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration: A Pilot Study on Correlation with PET Imaging and Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Methodology
2.2. Patient Cohort
2.3. Preparation of [11C]PBB3 and PET Imaging
2.4. Visual Interpretation
2.5. Image Processing
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
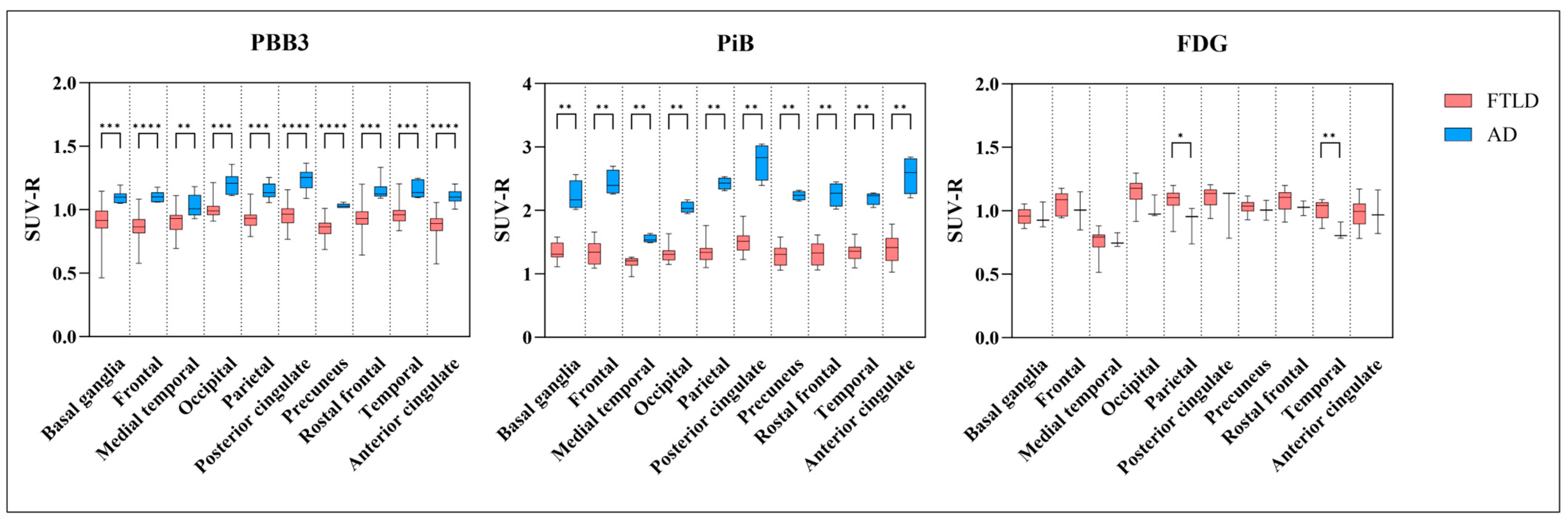
3.1. Visual and Semi-Quantitative Assessment of [11C]PBB3 Binding
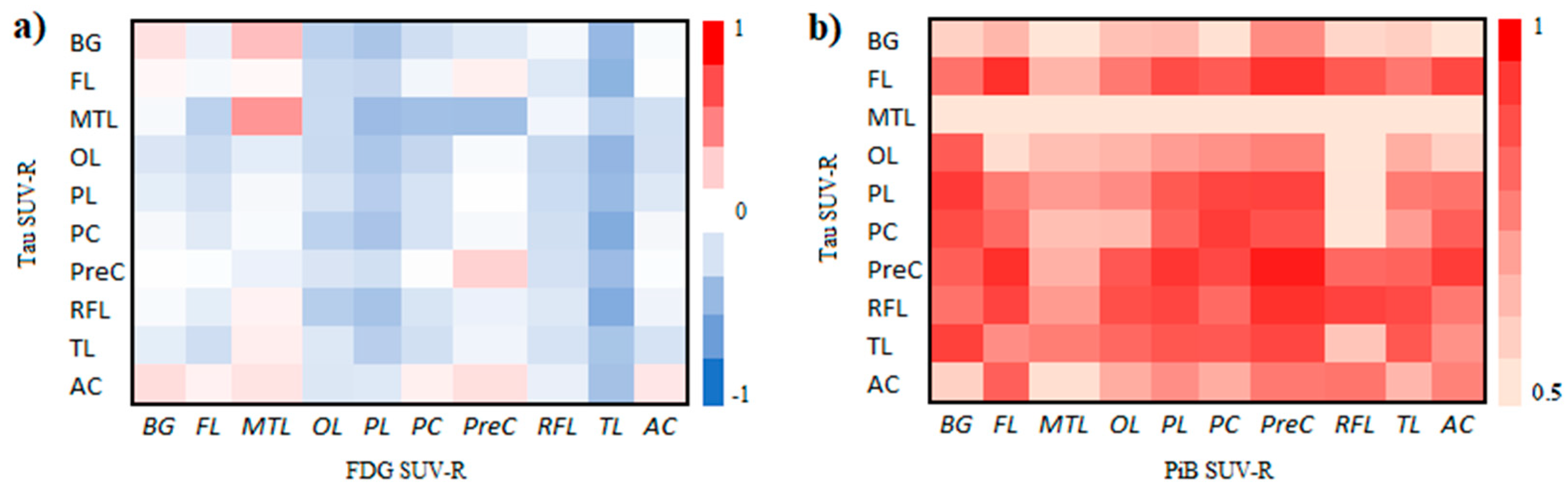
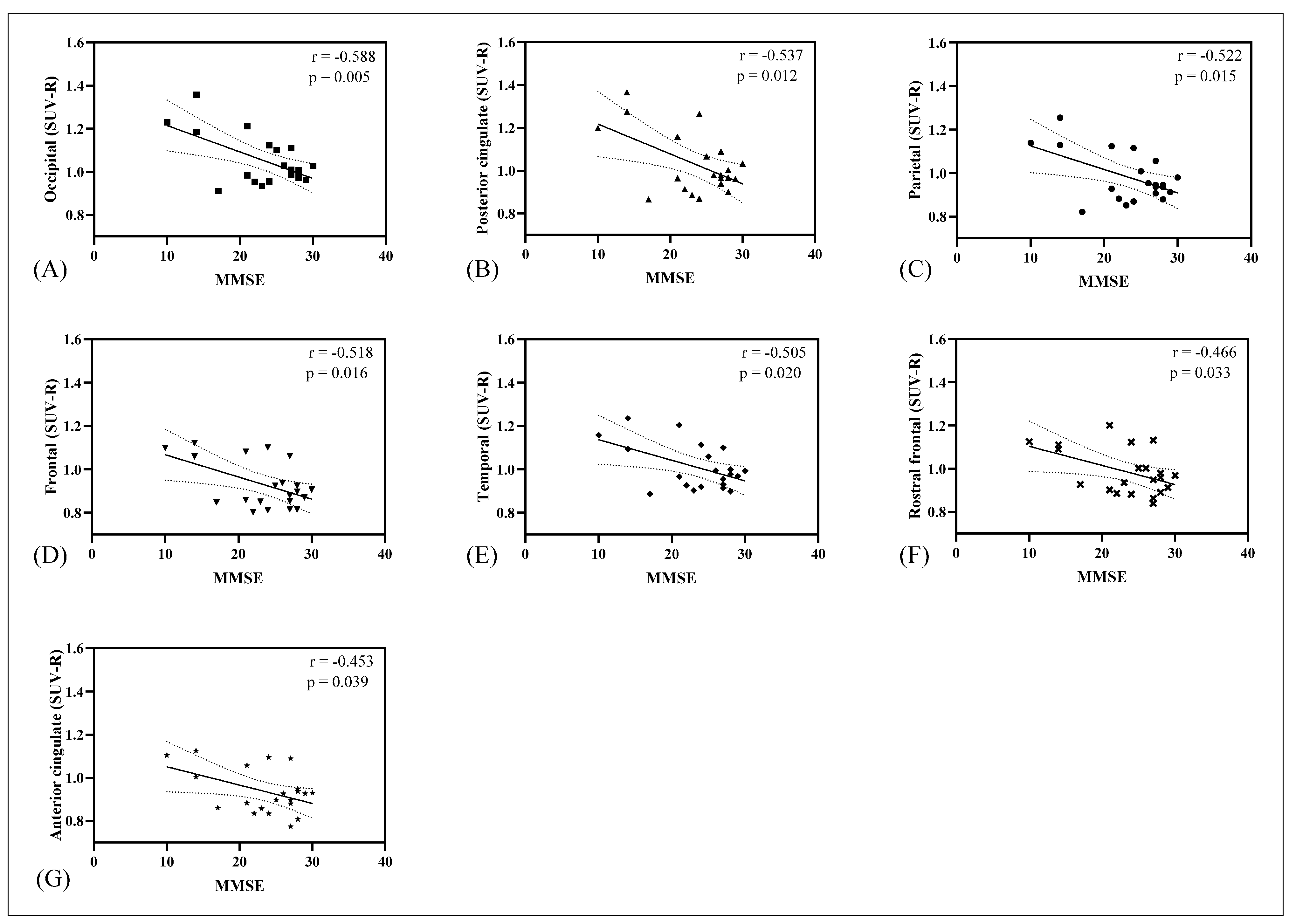
3.2. Correlation of Tau, Amyloid, Metabolism, CSF Biomarkers, and Cognitive Impairment Test
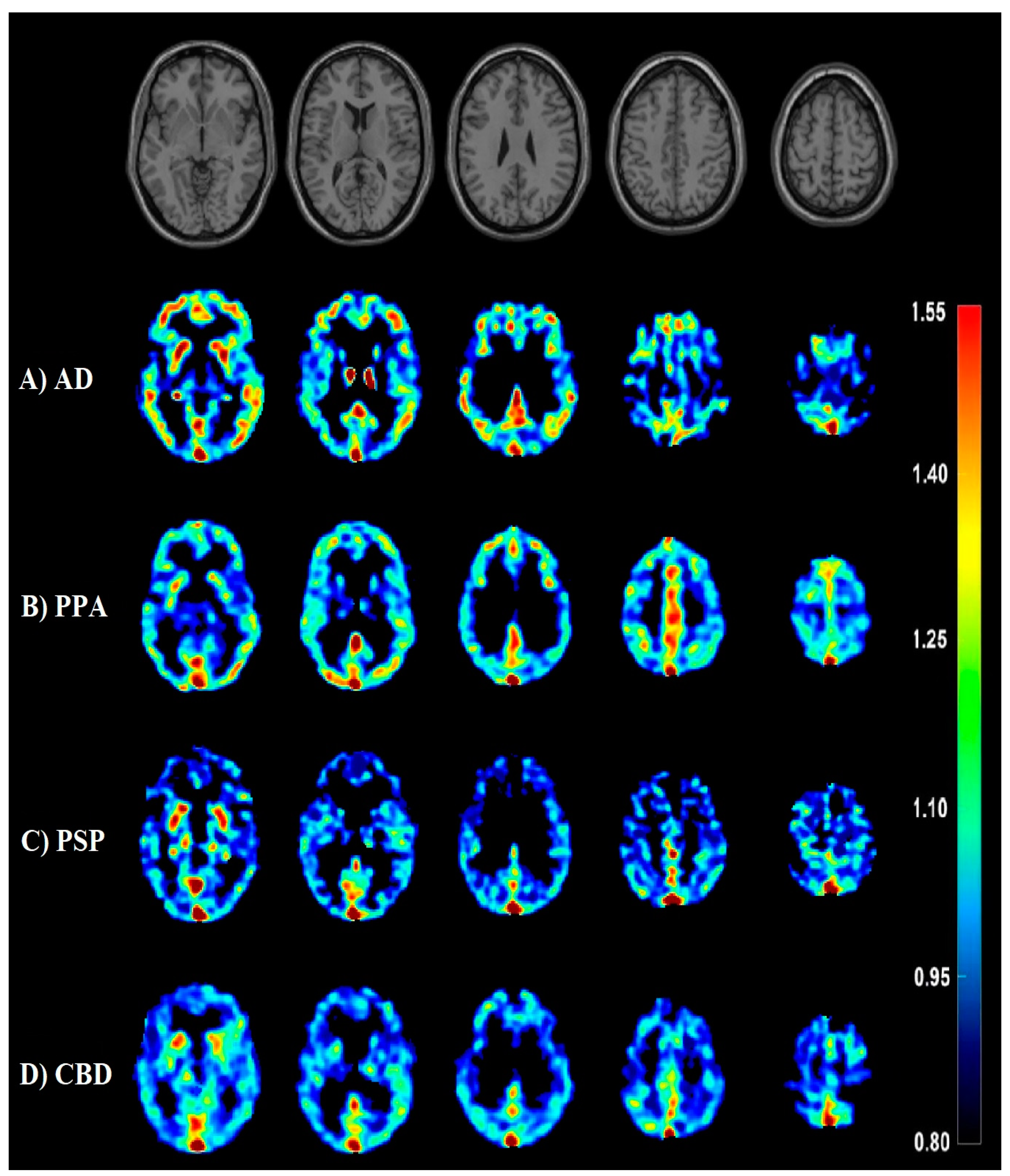
3.3. AD Dementia versus FTLD Disorders
3.4. Summary of Findings
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, P.; Quan, W.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Cai, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, H.; et al. Early-stage differentiation between Alzheimer’s disease and frontotemporal lobe degeneration: Clinical, neuropsychology, and neuroimaging features. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 981451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahami Monfared, A.A.; Byrnes, M.J.; White, L.A.; Zhang, Q. The Humanistic and Economic Burden of Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurol. Ther. 2022, 11, 525–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vu, M.; Mangal, R.; Stead, T.; Lopez-Ortiz, C.; Ganti, L. Impact of Alzheimer’s Disease on Caregivers in the United States. Health Psychol. Res. 2022, 10, 37454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, R.A.; Lantos, P.L.; Cairns, N.J. Overlap between neurodegenerative disorders. Neuropathology 2005, 25, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzheimer’s Association. 2020 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2020, 16, 391–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, W. Economic burden of Alzheimer disease and managed care considerations. Am. J. Manag. Care 2020, 26, S177–S183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evering, T.H.; Marston, J.L.; Gan, L.; Nixon, D.F. Transposable elements and Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis. Trends Neurosci. 2023, 46, 170–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cipriani, G.; Danti, S.; Picchi, L.; Nuti, A.; Fiorino, M.D. Daily functioning and dementia. Dement. Neuropsychol. 2020, 14, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liss, J.L.; Seleri Assuncao, S.; Cummings, J.; Atri, A.; Geldmacher, D.S.; Candela, S.F.; Devanand, D.P.; Fillit, H.M.; Susman, J.; Mintzer, J.; et al. Practical recommendations for timely, accurate diagnosis of symptomatic Alzheimer’s disease (MCI and dementia) in primary care: A review and synthesis. J. Intern. Med. 2021, 290, 310–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peet, B.T.; Spina, S.; Mundada, N.; La Joie, R. Neuroimaging in Frontotemporal Dementia: Heterogeneity and Relationships with Underlying Neuropathology. Neurotherapeutics 2021, 18, 728–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riku, Y.; Yoshida, M.; Iwasaki, Y.; Sobue, G.; Katsuno, M.; Ishigaki, S. TDP-43 Proteinopathy and Tauopathy: Do They Have Pathomechanistic Links? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossman, M.; Seeley, W.W.; Boxer, A.L.; Hillis, A.E.; Knopman, D.S.; Ljubenov, P.A.; Miller, B.; Piguet, O.; Rademakers, R.; Whitwell, J.L.; et al. Frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2023, 9, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, R.; Nitsch, R.M. Recent Developments in Positron Emission Tomography Tracers for Proteinopathies Imaging in Dementia. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 751897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, W.; Xie, F.; Zuo, C.; Guan, Y.; Huang, Y.H. PET Neuroimaging of Alzheimer’s Disease: Radiotracers and Their Utility in Clinical Research. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 624330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobeh, N.S.; Bruce, K.D. Emerging Alzheimer’s disease therapeutics: Promising insights from lipid metabolism and microglia-focused interventions. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2023, 15, 1259012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maito, M.A.; Santamaria-Garcia, H.; Moguilner, S.; Possin, K.L.; Godoy, M.E.; Avila-Funes, J.A.; Behrens, M.I.; Brusco, I.L.; Bruno, M.A.; Cardona, J.F.; et al. Classification of Alzheimer’s disease and frontotemporal dementia using routine clinical and cognitive measures across multicentric underrepresented samples: A cross sectional observational study. Lancet Reg. Health Am. 2023, 17, 100387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musa, G.; Slachevsky, A.; Munoz-Neira, C.; Mendez-Orellana, C.; Villagra, R.; Gonzalez-Billault, C.; Ibanez, A.; Hornberger, M.; Lillo, P. Alzheimer’s Disease or Behavioral Variant Frontotemporal Dementia? Review of Key Points toward an Accurate Clinical and Neuropsychological Diagnosis. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2020, 73, 833–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weintraub, S. Neuropsychological Assessment in Dementia Diagnosis. Continuum 2022, 28, 781–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piguet, O.; Kumfor, F. Frontotemporal dementias: Main syndromes and underlying brain changes. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2020, 33, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staffaroni, A.M.; Elahi, F.M.; McDermott, D.; Marton, K.; Karageorgiou, E.; Sacco, S.; Paoletti, M.; Caverzasi, E.; Hess, C.P.; Rosen, H.J.; et al. Neuroimaging in Dementia. Semin. Neurol. 2017, 37, 510–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouliaras, L.; O’Brien, J.T. The use of neuroimaging techniques in the early and differential diagnosis of dementia. Mol. Psychiatry 2023, 28, 4084–4097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strom, A.; Iaccarino, L.; Edwards, L.; Lesman-Segev, O.H.; Soleimani-Meigooni, D.N.; Pham, J.; Baker, S.L.; Landau, S.M.; Jagust, W.J.; Miller, B.L.; et al. Cortical hypometabolism reflects local atrophy and tau pathology in symptomatic Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 2022, 145, 713–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minoshima, S.; Cross, D.; Thientunyakit, T.; Foster, N.L.; Drzezga, A. 18F-FDG PET Imaging in Neurodegenerative Dementing Disorders: Insights into Subtype Classification, Emerging Disease Categories, and Mixed Dementia with Copathologies. J. Nucl. Med. 2022, 63, 2S–12S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ossenkoppele, R.; Smith, R.; Mattsson-Carlgren, N.; Groot, C.; Leuzy, A.; Strandberg, O.; Palmqvist, S.; Olsson, T.; Jogi, J.; Stormrud, E.; et al. Accuracy of Tau Positron Emission Tomography as a Prognostic Marker in Preclinical and Prodromal Alzheimer Disease: A Head-to-Head Comparison against Amyloid Positron Emission Tomography and Magnetic Resonance Imaging. JAMA Neurol. 2021, 78, 961–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefzadeh-Nowshahr, E.; Winter, G.; Bohn, P.; Kneer, K.; von Arnim, C.A.F.; Otto, M.; Solbach, C.; Anderl-Straub, S.; Polivka, D.; Fissler, P.; et al. Quantitative analysis of regional distribution of tau pathology with 11C-PBB3-PET in a clinical setting. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0266906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuzy, A.; Chiotis, K.; Lemoine, L.; Gillberg, P.G.; Almkvist, O.; Rodriguez-Vieitez, E.; Nordberg, A. Tau PET imaging in neurodegenerative tauopathies-still a challenge. Mol. Psychiatry 2019, 24, 1112–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Flores, R.; Wisse, L.E.M.; Das, S.R.; Xie, L.; McMillan, C.T.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Robinson, J.L.; Grossman, M.; Lee, E.; Irwin, D.J.; et al. Contribution of mixed pathology to medial temporal lobe atrophy in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2020, 16, 843–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samudra, N.; Lane-Donovan, C.; VandeVrede, L.; Boxer, A.L. Tau pathology in neurodegenerative disease: Disease mechanisms and therapeutic avenues. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 133, e168553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassinelli Petersen, G.; Roytman, M.; Chiang, G.C.; Li, Y.; Gordon, M.L.; Franceschi, A.M. Overview of tau PET molecular imaging. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2022, 35, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livingston, G.; Huntley, J.; Sommerlad, A.; Ames, D.; Ballard, C.; Banerjee, S.; Brayne, C.; Burns, A.; Cohen-Mansfield, J.; Cooper, C.; et al. Dementia prevention, intervention, and care: 2020 report of the Lancet Commission. Lancet 2020, 396, 413–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Jeong, M.; Stiles, W.R.; Choi, H.S. Neuroimaging Modalities in Alzheimer’s Disease: Diagnosis and Clinical Features. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arafah, A.; Khatoon, S.; Rasool, I.; Khan, A.; Rather, M.A.; Abujabal, K.A.; Faqih, Y.A.H.; Rashid, H.; Rashid, S.M.; Bilal Ahmad, S.; et al. The Future of Precision Medicine in the Cure of Alzheimer’s Disease. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jin, C.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, R.; Tian, M.; Lee, H.J.; Zhang, H. PET molecular imaging for pathophysiological visualization in Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2023, 50, 765–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.; Ly, M.; Raji, C.A. Brain PET Imaging: Frontotemporal Dementia. PET Clin. 2023, 18, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, G. A how-to guide for a precision medicine approach to the diagnosis and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2023, 15, 1213968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, J.; Kinney, J. Biomarkers for Alzheimer’s Disease: Context of Use, Qualification, and Roadmap for Clinical Implementation. Medicina 2022, 58, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagarde, J.; Olivieri, P.; Tonietto, M.; Rodrigo, S.; Gervais, P.; Caille, F.; Moussion, M.; Bottlaender, M.; Sarazin, M. Could tau-PET imaging contribute to a better understanding of the different patterns of clinical progression in Alzheimer’s disease? A 2-year longitudinal study. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2023, 15, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laton, J.; Van Schependom, J.; Goossens, J.; Wiels, W.; Sieben, A.; De Deyn, P.P.; Goeman, J.; Streffer, J.; van der Zee, J.; Martin, J.J.; et al. Improved Alzheimer’s Disease versus Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration Differential Diagnosis Combining EEG and Neurochemical Biomarkers: A Pilot Study. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2022, 90, 1739–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, M.; Sahara, N.; Kumata, K.; Ji, B.; Ni, R.; Koga, S.; Dickson, D.W.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Lee, V.M.; Yoshida, M.; et al. Distinct binding of PET ligands PBB3 and AV-1451 to tau fibril strains in neurodegenerative tauopathies. Brain 2017, 140, 764–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, H.; Kawamura, K.; Igarashi, N.; Takei, M.; Fujishiro, T.; Aihara, Y.; Shiomi, S.; Muto, M.; Ito, T.; Furutsuka, K.; et al. Radiosynthesis, photoisomerization, biodistribution, and metabolite analysis of 11C-PBB3 as a clinically useful PET probe for imaging of tau pathology. J. Nucl. Med. 2014, 55, 1532–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guedj, E.; Varrone, A.; Boellaard, R.; Albert, N.L.; Barthel, H.; van Berckel, B.; Brendel, M.; Cecchin, D.; Ekmekcioglu, O.; Garibotto, V.; et al. EANM procedure guidelines for brain PET imaging using [18F]FDG, version 3. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2022, 49, 632–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousefzadeh-Nowshahr, E.; Winter, G.; Bohn, P.; Kneer, K.; von Arnim, C.A.F.; Otto, M.; Solbach, C.; Anderl-Straub, S.; Polivka, D.; Fissler, P.; et al. Comparison of MRI-based and PET-based image pre-processing for quantification of 11C-PBB3 uptake in human brain. Z. Fur Med. Phys. 2021, 31, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Della Rosa, P.A.; Cerami, C.; Gallivanone, F.; Prestia, A.; Caroli, A.; Castiglioni, I.; Gilardi, M.C.; Frisoni, G.; Friston, K.; Ashburner, J.; et al. A standardized [18F]-FDG-PET template for spatial normalization in statistical parametric mapping of dementia. Neuroinformatics 2014, 12, 575–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perani, D.; Della Rosa, P.A.; Cerami, C.; Gallivanone, F.; Fallanca, F.; Vanoli, E.G.; Panzacchi, A.; Nobili, F.; Pappata, S.; Marcone, A.; et al. Validation of an optimized SPM procedure for FDG-PET in dementia diagnosis in a clinical setting. Neuroimage Clin. 2014, 6, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimada, H.; Kitamura, S.; Shinotoh, H.; Endo, H.; Niwa, F.; Hirano, S.; Kimura, Y.; Zhang, M.R.; Kuwabara, S.; Suhara, T.; et al. Association between Abeta and tau accumulations and their influence on clinical features in aging and Alzheimer’s disease spectrum brains: A [11C]PBB3-PET study. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2017, 6, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chudzik, A.; Sledzianowski, A.; Przybyszewski, A.W. Machine Learning and Digital Biomarkers Can Detect Early Stages of Neurodegenerative Diseases. Sensors 2024, 24, 1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Q.Q.; Lin, R.R.; Wu, Z.Y. Early Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease: Moving Toward a Blood-Based Biomarkers Era. Clin. Interv. Aging 2023, 18, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, J.; Langerman, H. Alzheimer’s Disease—Why We Need Early Diagnosis. Degener. Neurol. Neuromuscul. Dis. 2019, 9, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiotis, K.; Stenkrona, P.; Almkvist, O.; Stepanov, V.; Ferreira, D.; Arakawa, R.; Takano, A.; Westman, E.; Varrone, A.; Okamura, N.; et al. Dual tracer tau PET imaging reveals different molecular targets for 11C-THK5351 and 11C-PBB3 in the Alzheimer brain. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2018, 45, 1605–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toader, C.; Dobrin, N.; Brehar, F.M.; Popa, C.; Covache-Busuioc, R.A.; Glavan, L.A.; Costin, H.P.; Bratu, B.G.; Corlatescu, A.D.; Popa, A.A.; et al. From Recognition to Remedy: The Significance of Biomarkers in Neurodegenerative Disease Pathology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikonomovic, M.D.; Klunk, W.E.; Abrahamson, E.E.; Mathis, C.A.; Price, J.C.; Tsopelas, N.D.; Lopresti, B.J.; Ziolko, S.; Bi, W.; Paljug, W.R.; et al. Post-mortem correlates of in vivo PiB-PET amyloid imaging in a typical case of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 2008, 131, 1630–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, H.; Kawamura, K.; Takei, M.; Igarashi, N.; Fujishiro, T.; Shiomi, S.; Watanabe, R.; Muto, M.; Furutsuka, K.; Ito, T.; et al. Identification of a major radiometabolite of [11C]PBB3. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2015, 42, 905–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chien, D.T.; Szardenings, A.K.; Bahri, S.; Walsh, J.C.; Mu, F.; Xia, C.; Shankle, W.R.; Lerner, A.J.; Su, M.Y.; Elizarov, A.; et al. Early clinical PET imaging results with the novel PHF-tau radioligand [F18]-T808. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2014, 38, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.; Choi, J.Y.; Hwang, M.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, H.M.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, J.H.; Ryu, Y.H.; Lee, M.S.; Lyoo, C.H. In vivo cortical spreading pattern of tau and amyloid in the Alzheimer disease spectrum. Ann. Neurol. 2016, 80, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, K.A.; Schultz, A.; Betensky, R.A.; Becker, J.A.; Sepulcre, J.; Rentz, D.; Mormino, E.; Chhatwal, J.; Amariglio, R.; Papp, K.; et al. Tau positron emission tomographic imaging in aging and early Alzheimer disease. Ann. Neurol. 2016, 79, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, A.; Scholl, M.; Vogels, T. Tau Seeding Mouse Models with Patient Brain-Derived Aggregates. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanner, J.A.; Rabinovici, G.D. Relationship between Tau and Cognition in the Evolution of Alzheimer’s Disease: New Insights from Tau PET. J. Nucl. Med. 2021, 62, 612–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Wei, W.; Zhao, M.; Ma, L.; Jiang, X.; Pei, H.; Cao, Y.; Li, H. Interaction between Abeta and Tau in the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 2181–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeve, B.F. Behavioral Variant Frontotemporal Dementia. Continuum 2022, 28, 702–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chornenkyy, Y.; Fardo, D.W.; Nelson, P.T. Tau and TDP-43 proteinopathies: Kindred pathologic cascades and genetic pleiotropy. Lab. Investig. 2019, 99, 993–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mankhong, S.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.; Kwak, H.B.; Park, D.H.; Joa, K.L.; Kang, J.H. Development of Alzheimer’s Disease Biomarkers: From CSF- to Blood-Based Biomarkers. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, H.; Pang, Y.; Fu, X.; Ren, Z.; Jia, L. Plasma biomarkers predict Alzheimer’s disease before clinical onset in Chinese cohorts. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- d’Abramo, C.; D’Adamio, L.; Giliberto, L. Significance of Blood and Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers for Alzheimer’s Disease: Sensitivity, Specificity and Potential for Clinical Use. J. Pers. Med. 2020, 10, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ossenkoppele, R.; Reimand, J.; Smith, R.; Leuzy, A.; Strandberg, O.; Palmqvist, S.; Stomrud, E.; Zetterberg, H.; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging, I.; Scheltens, P.; et al. Tau PET correlates with different Alzheimer’s disease-related features compared to CSF and plasma p-tau biomarkers. EMBO Mol. Med. 2021, 13, e14398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattsson-Carlgren, N.; Andersson, E.; Janelidze, S.; Ossenkoppele, R.; Insel, P.; Strandberg, O.; Zetterberg, H.; Rosen, H.J.; Rabinovici, G.; Chai, X.; et al. Abeta deposition is associated with increases in soluble and phosphorylated tau that precede a positive Tau PET in Alzheimer’s disease. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaz2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholl, M.; Maass, A.; Mattsson, N.; Ashton, N.J.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H.; Jagust, W. Biomarkers for tau pathology. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 97, 18–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricci, M.; Cimini, A.; Camedda, R.; Chiaravalloti, A.; Schillaci, O. Tau Biomarkers in Dementia: Positron Emission Tomography Radiopharmaceuticals in Tauopathy Assessment and Future Perspective. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummings, J.L.; Gonzalez, M.I.; Pritchard, M.C.; May, P.C.; Toledo-Sherman, L.M.; Harris, G.A. The therapeutic landscape of tauopathies: Challenges and prospects. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2023, 15, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shusharina, N.; Yukhnenko, D.; Botman, S.; Sapunov, V.; Savinov, V.; Kamyshov, G.; Sayapin, D.; Voznyuk, I. Modern Methods of Diagnostics and Treatment of Neurodegenerative Diseases and Depression. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Choi, J.Y.; Hwang, M.S.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, H.M.; Lyoo, C.H.; Ryu, Y.H.; Lee, M.S. Tau PET in Alzheimer disease and mild cognitive impairment. Neurology 2016, 87, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugan, N.A.; Nordberg, A.; Agren, H. Cryptic Sites in Tau Fibrils Explain the Preferential Binding of the AV-1451 PET Tracer toward Alzheimer’s Tauopathy. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2021, 12, 2437–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stancu, I.C.; Ferraiolo, M.; Terwel, D.; Dewachter, I. Tau Interacting Proteins: Gaining Insight into the Roles of Tau in Health and Disease. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1184, 145–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chetelat, G.; Arbizu, J.; Barthel, H.; Garibotto, V.; Law, I.; Morbelli, S.; van de Giessen, E.; Agosta, F.; Barkhof, F.; Brooks, D.J.; et al. Amyloid-PET and 18F-FDG-PET in the diagnostic investigation of Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias. Lancet Neurol. 2020, 19, 951–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nestor, P.J.; Altomare, D.; Festari, C.; Drzezga, A.; Rivolta, J.; Walker, Z.; Bouwman, F.; Orini, S.; Law, I.; Agosta, F.; et al. Clinical utility of FDG-PET for the differential diagnosis among the main forms of dementia. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2018, 45, 1509–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Eimeren, T.; Bischof, G.N.; Drzezga, A. Is Tau Imaging More than Just Upside-Down 18F-FDG Imaging? J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 58, 1357–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groot, C.; Villeneuve, S.; Smith, R.; Hansson, O.; Ossenkoppele, R. Tau PET Imaging in Neurodegenerative Disorders. J. Nucl. Med. 2022, 63, 20S–26S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyer, L.; Brendel, M. Imaging of Tau Pathology in Neurodegenerative Diseases: An Update. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2021, 51, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marquie, M.; Verwer, E.E.; Meltzer, A.C.; Kim, S.J.W.; Aguero, C.; Gonzalez, J.; Makaretz, S.J.; Siao Tick Chong, M.; Ramanan, P.; Amaral, A.C.; et al. Lessons learned about [F-18]-AV-1451 off-target binding from an autopsy-confirmed Parkinson’s case. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2017, 5, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bevan-Jones, R.W.; Cope, T.E.; Jones, S.P.; Passamonti, L.; Hong, Y.T.; Fryer, T.; Arnold, R.; Coles, J.P.; Aigbirhio, F.A.; Patterson, K.; et al. [18F]AV-1451 binding is increased in frontotemporal dementia due to C9orf72 expansion. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2018, 5, 1292–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dani, M.; Brooks, D.J.; Edison, P. Tau imaging in neurodegenerative diseases. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2016, 43, 1139–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholl, M.; Lockhart, S.N.; Schonhaut, D.R.; O’Neil, J.P.; Janabi, M.; Ossenkoppele, R.; Baker, S.L.; Vogel, J.W.; Faria, J.; Schwimmer, H.D.; et al. PET Imaging of Tau Deposition in the Aging Human Brain. Neuron 2016, 89, 971–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ossenkoppele, R.; Schonhaut, D.R.; Scholl, M.; Lockhart, S.N.; Ayakta, N.; Baker, S.L.; O’Neil, J.P.; Janabi, M.; Lazaris, A.; Cantwell, A.; et al. Tau PET patterns mirror clinical and neuroanatomical variability in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 2016, 139, 1551–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y.K.; Lyoo, C.H.; Park, S.; Oh, S.J.; Cho, H.; Oh, M.; Ryu, Y.H.; Choi, J.Y.; Rabinovici, G.D.; Kim, H.J.; et al. Head to head comparison of [18F] AV-1451 and [18F] THK5351 for tau imaging in Alzheimer’s disease and frontotemporal dementia. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2018, 45, 432–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowe, C.C.; Ellis, K.A.; Rimajova, M.; Bourgeat, P.; Pike, K.E.; Jones, G.; Fripp, J.; Tochon-Danguy, H.; Morandeau, L.; O’Keefe, G.; et al. Amyloid imaging results from the Australian Imaging, Biomarkers and Lifestyle (AIBL) study of aging. Neurobiol. Aging 2010, 31, 1275–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.; Beyer, L.; Kaiser, L.; Barthel, H.; van Eimeren, T.; Marek, K.; Nitschmann, A.; Scheifele, M.; Palleis, C.; Respondek, G.; et al. Binding characteristics of [18F]PI-2620 distinguish the clinically predicted tau isoform in different tauopathies by PET. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2021, 41, 2957–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tagai, K.; Ono, M.; Kubota, M.; Kitamura, S.; Takahata, K.; Seki, C.; Takado, Y.; Shinotoh, H.; Sano, Y.; Yamamoto, Y.; et al. High-Contrast In Vivo Imaging of Tau Pathologies in Alzheimer’s and Non-Alzheimer’s Disease Tauopathies. Neuron 2021, 109, 42–58.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volter, F.; Beyer, L.; Eckenweber, F.; Scheifele, M.; Bui, N.; Patt, M.; Barthel, H.; Katzdobler, S.; Palleis, C.; Franzmeier, N.; et al. Assessment of perfusion deficit with early phases of [18F]PI-2620 tau-PET versus [18F]flutemetamol-amyloid-PET recordings. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2023, 50, 1384–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boxer, A.L.; Gold, M.; Huey, E.; Hu, W.T.; Rosen, H.; Kramer, J.; Gao, F.B.; Burton, E.A.; Chow, T.; Kao, A.; et al. The advantages of frontotemporal degeneration drug development (part 2 of frontotemporal degeneration: The next therapeutic frontier). Alzheimer’s Dement. 2013, 9, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayblyum, D.V.; Sanchez, J.S.; Thibault, E.G.; Jacobs, H.I.L.; Farrell, M.E.; Rubinstein, Z.B.; Buckley, R.F.; Sperling, R.A.; Rentz, D.M.; Papp, K.V.; et al. Surface-based amyloid and tau correlates of digital clock drawing performance. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2020, 16, e046461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
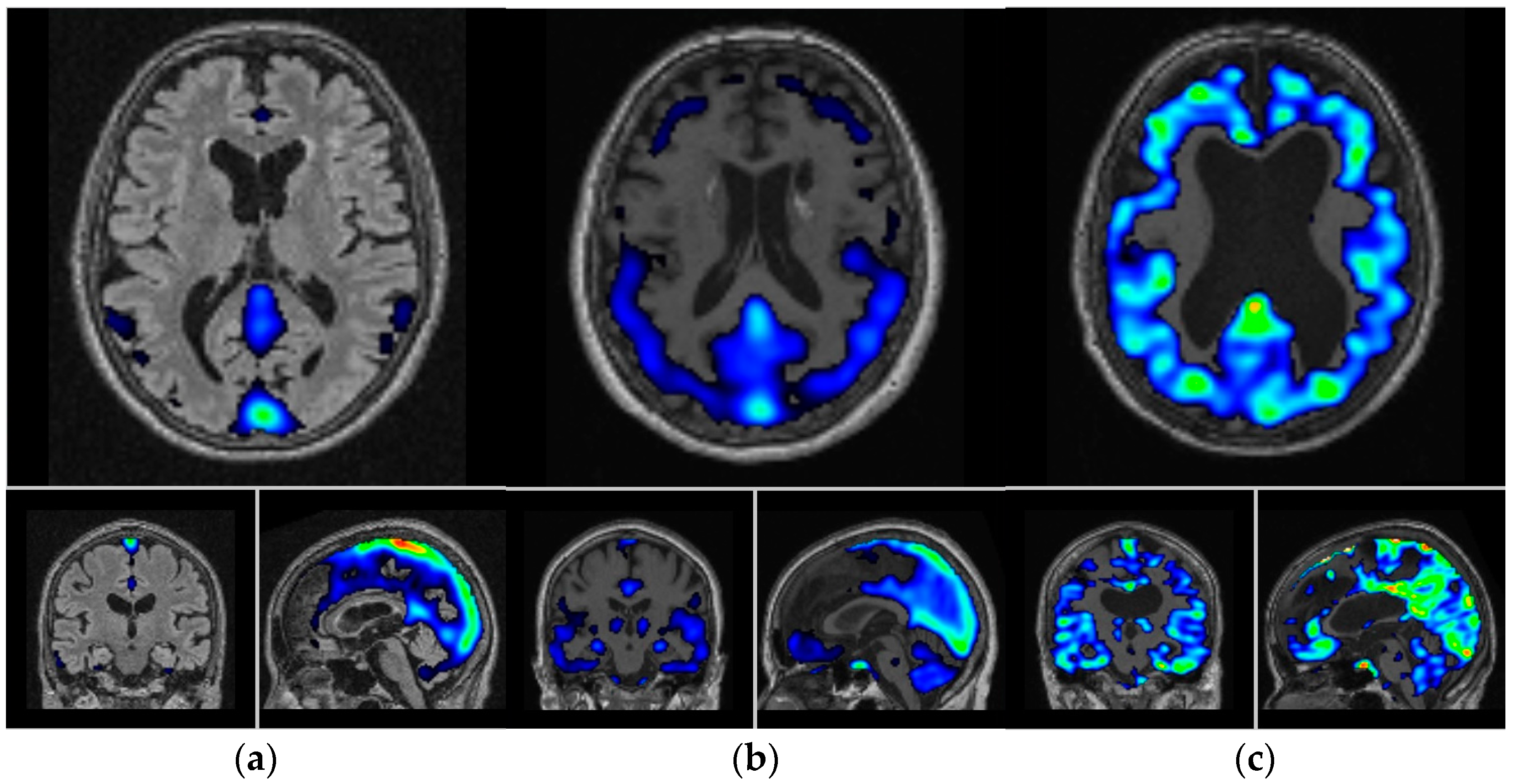

| Overview of the Subjects | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subjects | Tau Imaging | Pib Imaging | FDG Imaging | CSF Aß | CSF Tau | MMSE | |
| FTLD | Subjects 1 | negativ | - | positiv | X | X | X |
| FTLD | Subjects 2 | negativ | negativ | positiv | - | - | X |
| FTLD | Subjects 3 | negativ | negativ | - | X | X | X |
| FTLD | Subjects 4 | negativ | negativ | positiv | - | - | - |
| AD | Subjects 5 | negativ | negativ | positiv | X | X | X |
| FTLD | Subjects 6 | negativ | negativ | - | - | - | X |
| FTLD | Subjects 7 | negativ | - | - | X | X | X |
| FTLD | Subjects 8 | negativ | - | negativ | - | - | X |
| FTLD | Subjects 9 | negativ | - | positiv | - | - | X |
| FTLD | Subjects 10 | negativ | - | positiv | X | X | X |
| AD | Subjects 11 | negativ | - | - | - | X | X |
| FTLD | Subjects 12 | positiv | - | - | - | X | X |
| FTLD | Subjects 13 | positiv | - | - | - | - | - |
| FTLD | Subjects 14 | positiv | - | - | X | X | X |
| FTLD | Subjects 15 | positiv | - | positiv | X | X | X |
| FTLD | Subjects 16 | positiv | negativ | positiv | X | X | X |
| FTLD | Subjects 17 | positiv | positiv | negativ | X | X | X |
| AD | Subjects 18 | positiv | positiv | positiv | X | X | X |
| FTLD | Subjects 19 | positiv | - | - | - | - | - |
| AD | Subjects 20 | positiv | positiv | positiv | - | - | X |
| FTLD | Subjects 21 | positiv | negativ | negativ | X | X | X |
| AD | Subjects 22 | positiv | positiv | positiv | X | X | X |
| FTLD | Subjects 23 | negativ | negativ | positiv | - | - | - |
| AD | Subjects 24 | negativ | negativ | positiv | - | - | X |
| AD | FTLD | |
|---|---|---|
| n | 6 | 18 |
| Age (y) | 64 ± 8 | 64 ± 11 |
| Sex (F/M) | 4/2 | 11/7 |
| MMSE (median, range) | 14 (10–27) | 27 (17–30) |
| No. with [18F]FDG-PET | 3 (50%) | 12 (67%) |
| Global [11C]PiB-PET SUV-R | 2.34 ± 0.09 (n = 4) | 1.35 ± 0.16 (n = 9) |
| CSF-Aβ (ng/L) | 587 ± 105 (n = 2) | 917 ± 488 (n = 11) |
| CSF-tau (ng/L) | 386 ± 297 (n = 2) | 385 ± 180 (n = 12) |
| Number of Subjects | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SUV-R | Frontal | Medial Temporal | Occipital | Parietal | Posterior Cingulate | Precuneus | Rostral Frontal | Temporal | Anterior Cingulate | Average | Basal Ganglia |
| ≤0.9 (AD/FTLD) | 12(0/12) | 6(0/6) | 0 | 6(0/6) | 5(0/5) | 14(0/14) | 6(0/6) | 3(0/3) | 11(0/11) | 6(0.6) | 8(0/8) |
| 0.9 < X < 1.2 (AD/FTLD) | 12(6/6) | 18(6/12) | 20(3/17) | 17(5/12) | 15(2/13) | 10(6/4) | 16(5/11) | 18(4/14) | 12(5/7) | 17(5.12) | 16(6/10) |
| ≥1.2 (AD/FTLD) | 0 | 0 | 4(3/1) | 1(1/0) | 4(4/0) | 0 | 2(1/1) | 3(2/1) | 1(1/0) | 1(1.0) | 0 |
| Mean ± SD | 0.93 ± 0.14 | 0.94 ± 0.11 | 1.06 ± 0.12 | 0.98 ± 0.12 | 1.03 ± 0.15 | 0.90 ± 0.10 | 0.99 ± 0.14 | 1.02 ± 0.12 | 0.94 ± 0.14 | 0.98 ± 0.12 | 0.96 ± 0.15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Strobel, J.; Yousefzadeh-Nowshahr, E.; Deininger, K.; Bohn, K.P.; von Arnim, C.A.F.; Otto, M.; Solbach, C.; Anderl-Straub, S.; Polivka, D.; Fissler, P.; et al. Exploratory Tau PET/CT with [11C]PBB3 in Patients with Suspected Alzheimer’s Disease and Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration: A Pilot Study on Correlation with PET Imaging and Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1460. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12071460
Strobel J, Yousefzadeh-Nowshahr E, Deininger K, Bohn KP, von Arnim CAF, Otto M, Solbach C, Anderl-Straub S, Polivka D, Fissler P, et al. Exploratory Tau PET/CT with [11C]PBB3 in Patients with Suspected Alzheimer’s Disease and Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration: A Pilot Study on Correlation with PET Imaging and Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(7):1460. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12071460
Chicago/Turabian StyleStrobel, Joachim, Elham Yousefzadeh-Nowshahr, Katharina Deininger, Karl Peter Bohn, Christine A. F. von Arnim, Markus Otto, Christoph Solbach, Sarah Anderl-Straub, Dörte Polivka, Patrick Fissler, and et al. 2024. "Exploratory Tau PET/CT with [11C]PBB3 in Patients with Suspected Alzheimer’s Disease and Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration: A Pilot Study on Correlation with PET Imaging and Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers" Biomedicines 12, no. 7: 1460. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12071460
APA StyleStrobel, J., Yousefzadeh-Nowshahr, E., Deininger, K., Bohn, K. P., von Arnim, C. A. F., Otto, M., Solbach, C., Anderl-Straub, S., Polivka, D., Fissler, P., Glatting, G., Riepe, M. W., Higuchi, M., Beer, A. J., Ludolph, A., & Winter, G. (2024). Exploratory Tau PET/CT with [11C]PBB3 in Patients with Suspected Alzheimer’s Disease and Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration: A Pilot Study on Correlation with PET Imaging and Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers. Biomedicines, 12(7), 1460. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12071460







