Anti-Cancer Activities of Nano Amorphous Calcium Phosphates toward Premalignant and Oral Cancer Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of ACP Powder
Powder Characterization
2.2. Biological Assays
2.2.1. Cell Cultures
2.2.2. Nanoparticle Uptake
2.2.3. Cell Adhesion Assay
2.2.4. MTT Assay
2.2.5. Apoptosis Assay (Annexin V)
2.2.6. Cell Cycle Determination
2.2.7. RNA Isolation and Reverse Transcription
2.2.8. qPCR
2.2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. ACP Powder Characterization
3.2. Cell Adhesion Ability after nACP Treatment
3.3. Cytotoxic Effect of ACP Nanoparticles
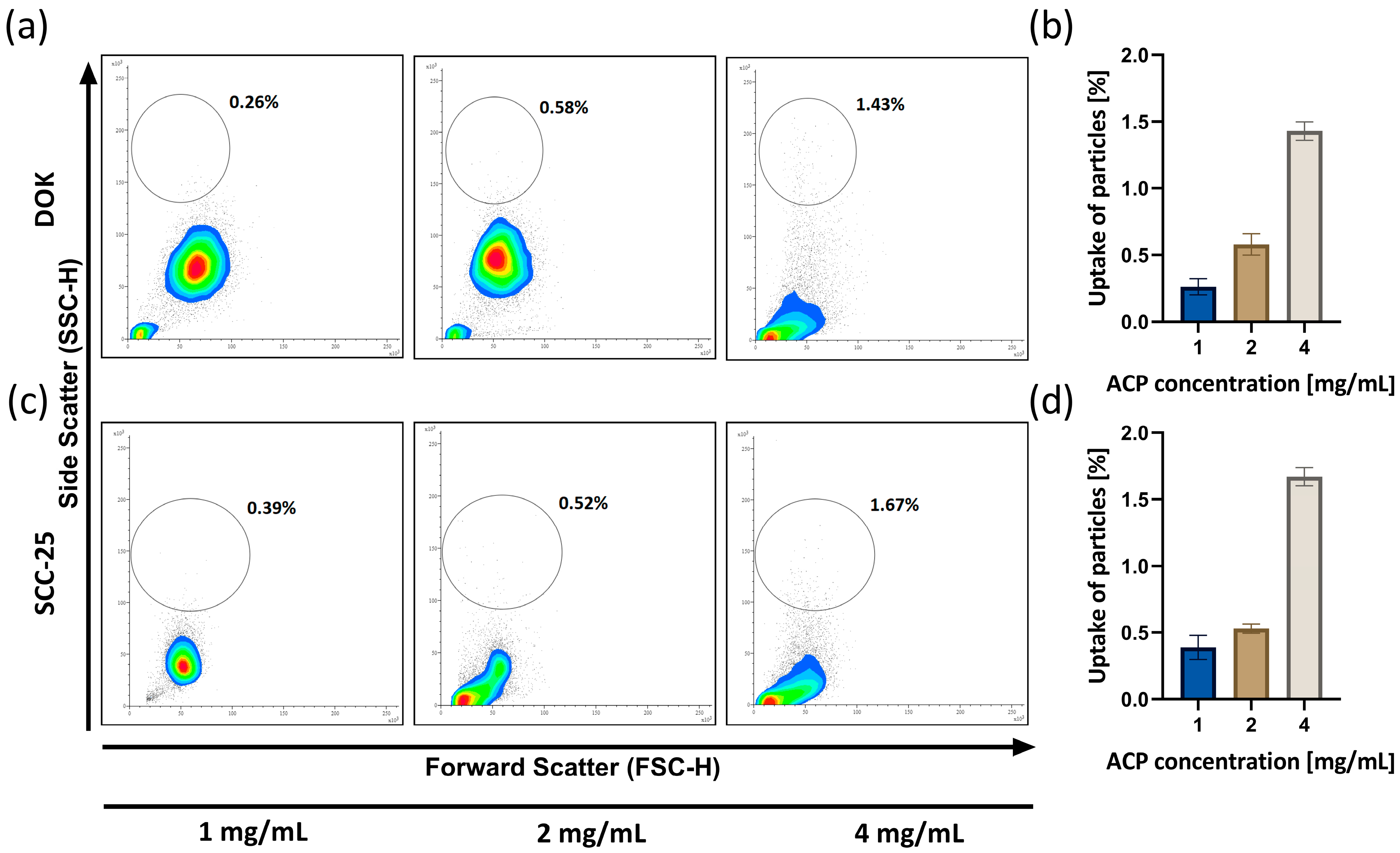
3.4. ACP Nanoparticle Uptake Analysis
3.5. ACP Nanoparticle Effect on Apoptosis
3.6. The Effect of nACP on the Cell Cycle
3.7. Gene Expression Analysis of Apoptotic, Proliferative, and Oncogenic Markers after the nACP Treatment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheng, Z.; Li, M.; Dey, R.; Chen, Y. Nanomaterials for Cancer Therapy: Current Progress and Perspectives. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimi, E.; Furuta, H.; Matsuo, K.; Tominaga, K.; Takahashi, T.; Nakanishi, O. The Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Bone Invasion by Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Oral Dis. 2011, 17, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.-J.; Zhang, X.-Q.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, G. Nanotechnology: A Promising Method for Oral Cancer Detection and Diagnosis. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xu, M.; Li, B.; Huang, Z.; Qin, S.; Nice, E.C.; Tang, J.; Huang, C. Oral Squamous Cell Carcinomas: State of the Field and Emerging Directions. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2023, 15, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markopoulos, A.K. Current Aspects on Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Open Dent. J. 2012, 6, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feller, L.; Lemmer, J. Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Epidemiology, Clinical Presentation and Treatment. J. Cancer Ther. 2012, 3, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, W.; Heo, Y.-J.; Han, D.K. New Opportunities for Nanoparticles in Cancer Immunotherapy. Biomater. Res. 2018, 22, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, C.; Lin, J.; Fu, L.-H.; Huang, P. Calcium-Based Biomaterials for Diagnosis, Treatment, and Theranostics. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 357–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Combes, C.; Rey, C. Amorphous Calcium Phosphates: Synthesis, Properties and Uses in Biomaterials. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 3362–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, K.; Misawa, S.; Kobayashi, Y.; Ishigaki, T.; Ishikawa, Y.; Yin, S.; Kakihana, M.; Goto, T.; Sekino, T. Atomic Arrangement Analysis and Crystal Growth Mechanism of HAp Nanocrystal Synthesized from Amorphous Calcium Phosphate. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2024, 107, 2809–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uskoković, V.; Marković, S.; Veselinović, L.; Škapin, S.; Ignjatović, N.; Uskoković, D.P. Insights into the Kinetics of Thermally Induced Crystallization of Amorphous Calcium Phosphate. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 29221–29235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorozhkin, S.V. Nanosized and Nanocrystalline Calcium Orthophosphates. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 715–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijerathne, H.M.C.S.; Yan, D.; Zeng, B.; Xie, Y.; Hu, H.; Wickramaratne, M.N.; Han, Y. Effect of Nano-Hydroxyapatite on Protein Adsorption and Cell Adhesion of Poly(Lactic Acid)/Nano-Hydroxyapatite Composite Microspheres. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, C.Y.; Fang, W.; Setyawati, M.I.; Chia, S.L.; Tan, K.S.; Hong, C.H.L.; Leong, D.T. Nano-Hydroxyapatite and Nano-Titanium Dioxide Exhibit Different Subcellular Distribution and Apoptotic Profile in Human Oral Epithelium. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 6248–6256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ignjatović, N.L.; Sakač, M.; Kuzminac, I.; Kojić, V.; Marković, S.; Vasiljević-Radović, D.; Wu, V.M.; Uskoković, V.; Uskoković, D.P. Chitosan Oligosaccharide Lactate Coated Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles as a Vehicle for the Delivery of Steroid Drugs and the Targeting of Breast Cancer Cells. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 6957–6968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, P.; Wang, Z.; Xie, Q.; Sun, H.; Huang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Bi, X.; Zhang, D.; Chen, J.; Wang, J.; et al. Electrospun Silk Fibroin/Poly(Lactide-Co-ε-Caprolactone) Nanofibrous Scaffolds for Bone Regeneration. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 1483–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Tong, S.; Zhang, R.; Zhu, T.; Wang, X. In Vitro Evaluation of a Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 Nanometer Hydroxyapatite Collagen Scaffold for Bone Regeneration. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 5830–5836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karisik, M.J.; Lazarevic, M.; Mitic, D.; Nikolic, N.; Markovic, M.M.; Jelovac, D.; Milasin, J. Osteogenic and Adipogenic Differentiation Potential of Oral Cancer Stem Cells May Offer New Treatment Modalities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, T.; Kutsuna, T.; Kurohara, K.; Shimizu, K.; Tomeoku, A.; Arai, N. Evaluation of a New Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticle as a Drug Delivery System to Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 6715–6720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Du, H.; Li, Z.; Bai, X.; Wu, Y.; Li, H.; Zhou, M.; Cao, Y.; Chen, X. Nano-Drug Delivery Systems in Oral Cancer Therapy: Recent Developments and Prospective. Pharmaceutics 2023, 16, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taneja, N.; Alam, A.; Patnaik, R.S.; Taneja, T.; Gupta, S. Understanding Nanotechnology in the Treatment of Oral Cancer: A Comprehensive Review. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carr. Syst. 2021, 38, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaffarin, A.S.M.; Ng, S.-F.; Ng, M.H.; Hassan, H.; Alias, E. Nano-Hydroxyapatite as a Delivery System for Promoting Bone Regeneration In Vivo: A Systematic Review. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natan, Y.; Blum, Y.D.; Arav, A.; Poliansky, Y.; Neuman, S.; Cohen, O.E.; Ben, Y. Amorphous Calcium Carbonate Shows Anti-Cancer Properties That Are Attributed to Its Buffering Capacity. Cancers 2023, 15, 3785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kargozar, S.; Mollazadeh, S.; Kermani, F.; Webster, T.J.; Nazarnezhad, S.; Hamzehlou, S.; Baino, F. Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles for Improved Cancer Theranostics. J. Funct. Biomater. 2022, 13, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, B.; Wang, G.; Xu, X.; Tang, R. Calcium Phosphate Nanoparticles Primarily Induce Cell Necrosis through Lysosomal Rupture: The Origination of Material Cytotoxicity. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 3480–3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Li, S.; Cao, X.; Yuan, L.; Wang, Y.; Yin, Y.; Qiu, T.; Dai, H.; Wang, X. Different Inhibitory Effect and Mechanism of Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles on Normal Cells and Cancer Cells In Vitro and In Vivo. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 7134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remya, N.S.; Syama, S.; Gayathri, V.; Varma, H.K.; Mohanan, P.V. An in Vitro Study on the Interaction of Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles and Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Assessing the Toxicological Behaviour. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 117, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Mccrate, J.M.; Lee, J.C.-M.; Li, H. The Role of Surface Charge on the Uptake and Biocompatibility of Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles with Osteoblast Cells. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 105708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovrlija, I.; Menshikh, K.; Abreu, H.; Cochis, A.; Rimondini, L.; Marsan, O.; Rey, C.; Combes, C.; Locs, J.; Loca, D. Challenging Applicability of ISO 10993-5 for Calcium Phosphate Biomaterials Evaluation: Towards More Accurate in Vitro Cytotoxicity Assessment. Biomater. Adv. 2024, 160, 213866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastan, M.B.; Bartek, J. Cell-Cycle Checkpoints and Cancer. Nature 2004, 432, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, G.H.; Stoeber, K. The Cell Cycle and Cancer. J. Pathol. 2012, 226, 352–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonavida, B. (Ed.) Sensitization of Cancer Cells for Chemo/Immuno/Radio-Therapy; Cancer Drug Discovery and Development; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2008; ISBN 978-1-934115-29-9. [Google Scholar]
- He, S.; Chakraborty, R.; Ranganathan, S. Proliferation and Apoptosis Pathways and Factors in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulbins, E.; Jekle, A.; Ferlinz, K.; Grassmé, H.; Lang, F. Physiology of Apoptosis. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2000, 279, F605–F615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, J.M.; Cory, S. The Bcl-2 Apoptotic Switch in Cancer Development and Therapy. Oncogene 2007, 26, 1324–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, C.; Wu, Y.; Lu, X.; Qian, J. Differential Cytotoxicity and Particle Action of Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles in Human Cancer Cells. Nanomedicine 2014, 9, 397–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-H.; Yoo, E.-S.; Han, S.-H.; Jung, G.-H.; Han, E.-J.; Jung, S.-H.; Seok Kim, B.; Cho, S.-D.; Nam, J.-S.; Choi, C.; et al. Oleanolic Acid Induces Apoptosis and Autophagy via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway in AGS Human Gastric Cancer Cells. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 87, 104854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alao, J.P. The Regulation of Cyclin D1 Degradation: Roles in Cancer Development and the Potential for Therapeutic Invention. Mol. Cancer 2007, 6, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Gene | Forward Primer (5′−3′) | Reverse Primer (5′−3′) |
|---|---|---|
| CASP3 | TGTTTGTGTGCTTCTGAGCC | CACGCCATGTCATCATCAAC |
| Cyclin D | CGGAGGAGAACAAACAGATC | GGGTGTGCAAGCCAGGTCCA |
| BAX | ATGTTTTCTGACGGCAACTTC | AGTCCAATGTCCAGCCCAT |
| BCL2 | ATGTGTGTGGAGAGCGTCAACC | TGAGCAGAGTCTTCAGAGACAGCC |
| β-Catenin | GCTACTCAAGCTGATTTGATGGA | GGTAGTGGCACCAGAATGGATT |
| GAPDH | ATGGGGAAGGTGAAGGTCG | GGGGTCATTGATGGCAACAATA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Herendija, E.; Jakšić Karišik, M.; Milašin, J.; Lazarević, M.; Ignjatović, N. Anti-Cancer Activities of Nano Amorphous Calcium Phosphates toward Premalignant and Oral Cancer Cells. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1499. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12071499
Herendija E, Jakšić Karišik M, Milašin J, Lazarević M, Ignjatović N. Anti-Cancer Activities of Nano Amorphous Calcium Phosphates toward Premalignant and Oral Cancer Cells. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(7):1499. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12071499
Chicago/Turabian StyleHerendija, Evelina, Milica Jakšić Karišik, Jelena Milašin, Miloš Lazarević, and Nenad Ignjatović. 2024. "Anti-Cancer Activities of Nano Amorphous Calcium Phosphates toward Premalignant and Oral Cancer Cells" Biomedicines 12, no. 7: 1499. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12071499
APA StyleHerendija, E., Jakšić Karišik, M., Milašin, J., Lazarević, M., & Ignjatović, N. (2024). Anti-Cancer Activities of Nano Amorphous Calcium Phosphates toward Premalignant and Oral Cancer Cells. Biomedicines, 12(7), 1499. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12071499











