Parecoxib and 5-Fluorouracil Synergistically Inhibit EMT and Subsequent Metastasis in Colorectal Cancer by Targeting PI3K/Akt/NF-κB Signaling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Line, Reagents, and Chemicals
2.2. Cell Culture and Drug Treatment
2.3. Cell Viability Assay
2.4. Transwell Migration and Transwell Invasion Assay
2.5. Isobologram Analysis
2.6. Gap Closure Assay
2.7. Western Blot Analysis
2.8. Antibodies
2.9. Gelatin Zymography Analysis
2.10. Effect of p-Akt Overexpression
2.11. Intracellular ROS Analysis
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
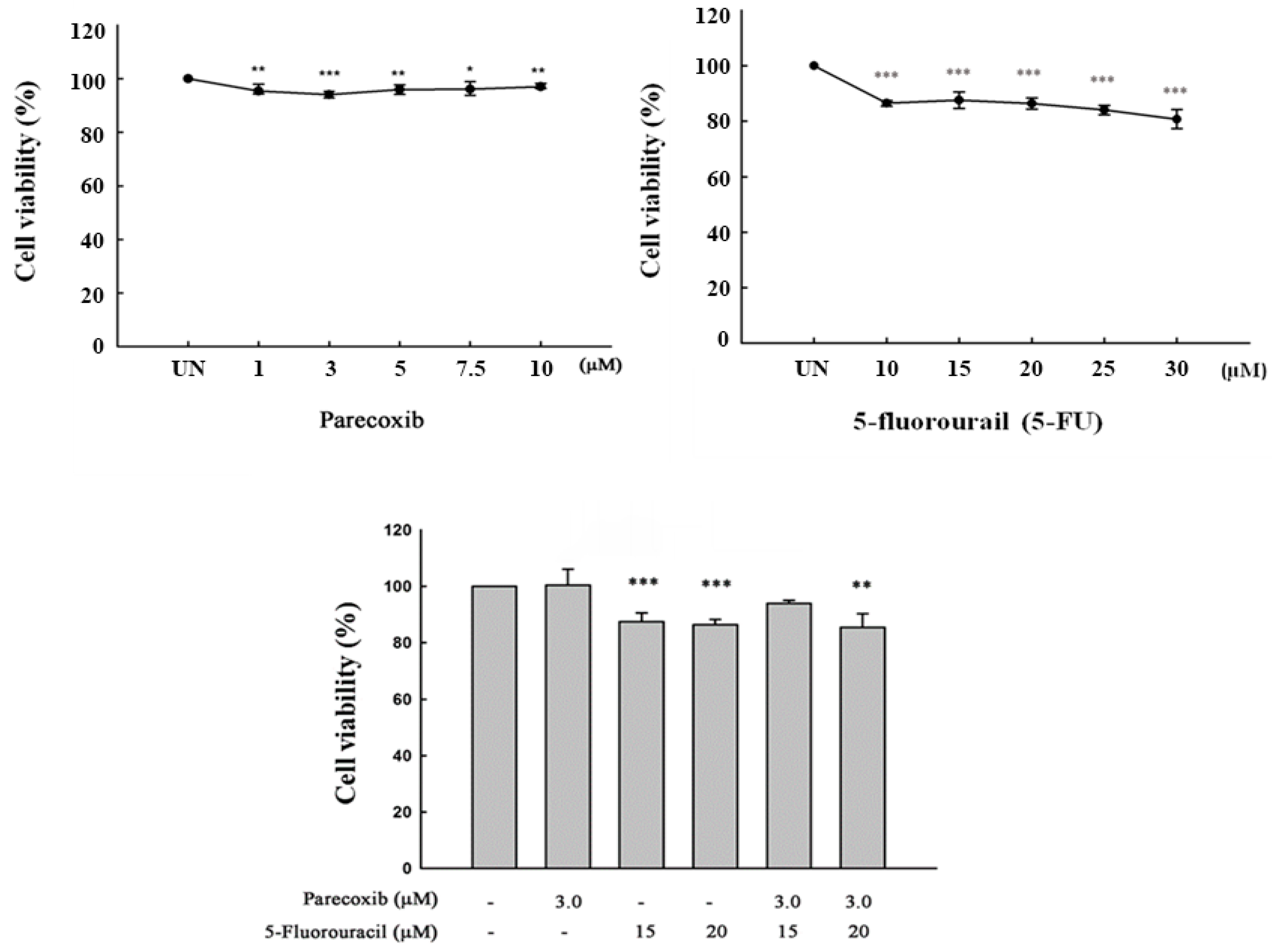
3.1. Cell Viability on Parecoxib and 5-FU Treatment
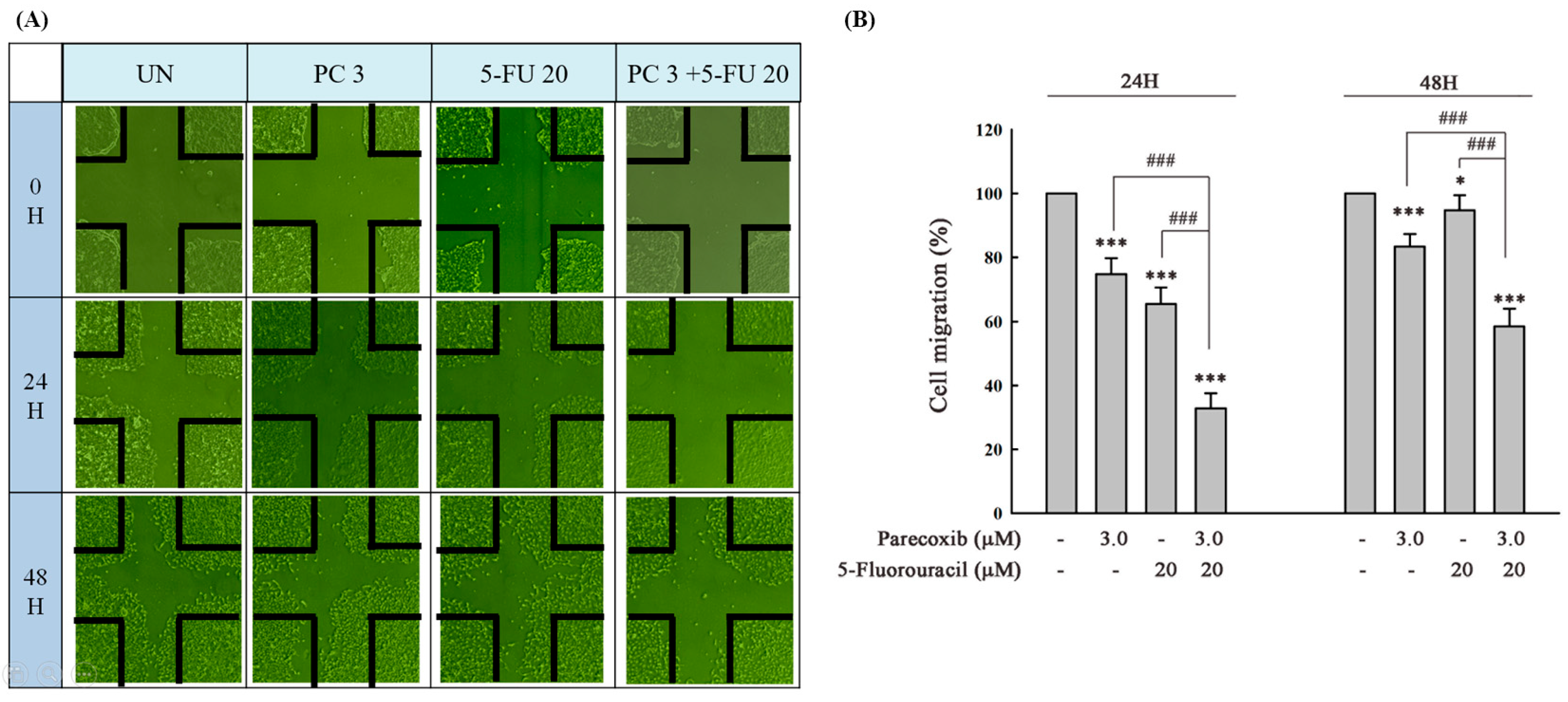
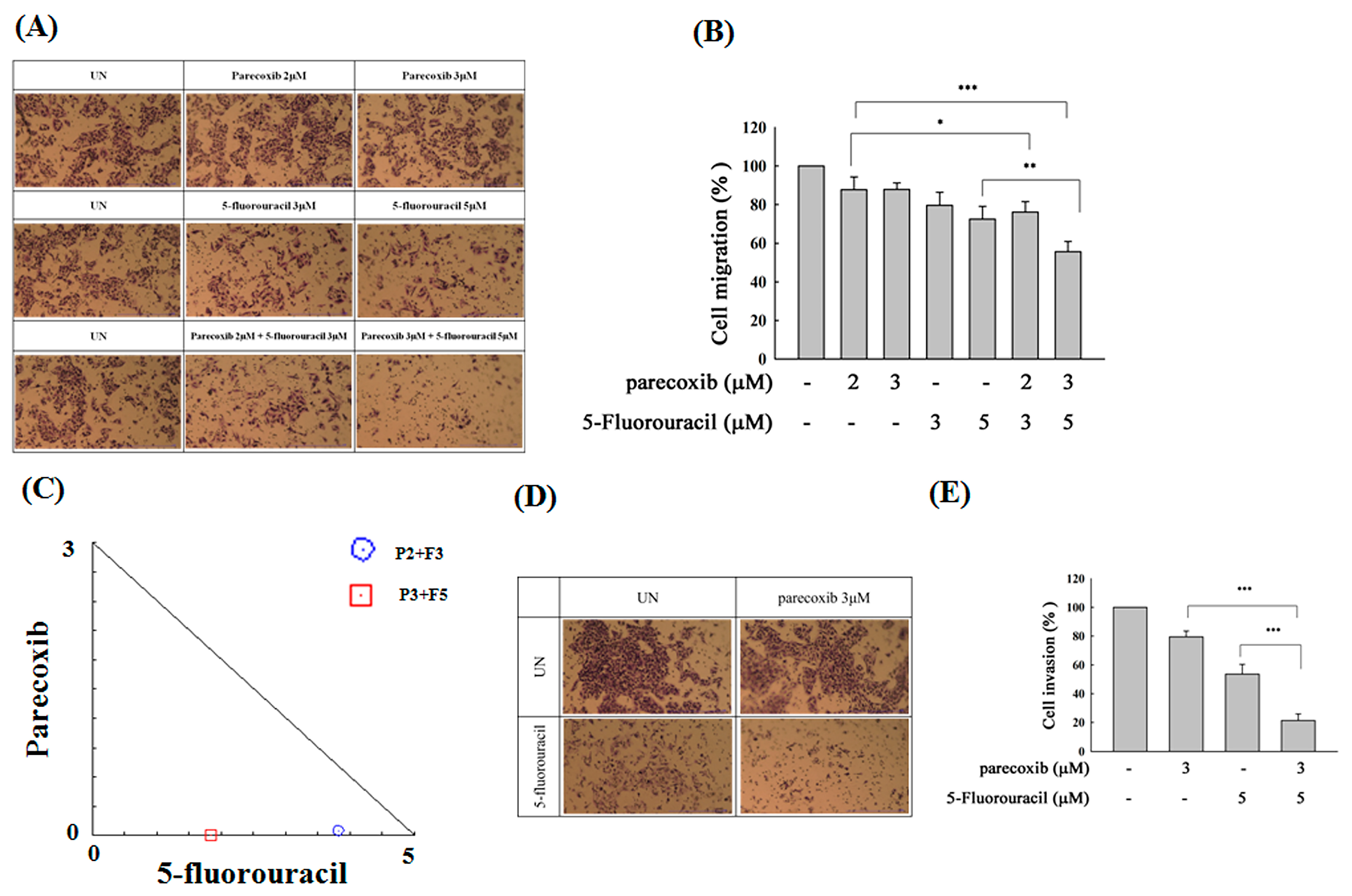
3.2. Synergism of Parecoxib and 5-FU Combination in Antimetastasis in DLD-1 Cells
3.3. Parecoxib Enhances Gap Closure Inhibition of 5-FU Treatment in DLD-1 Cells
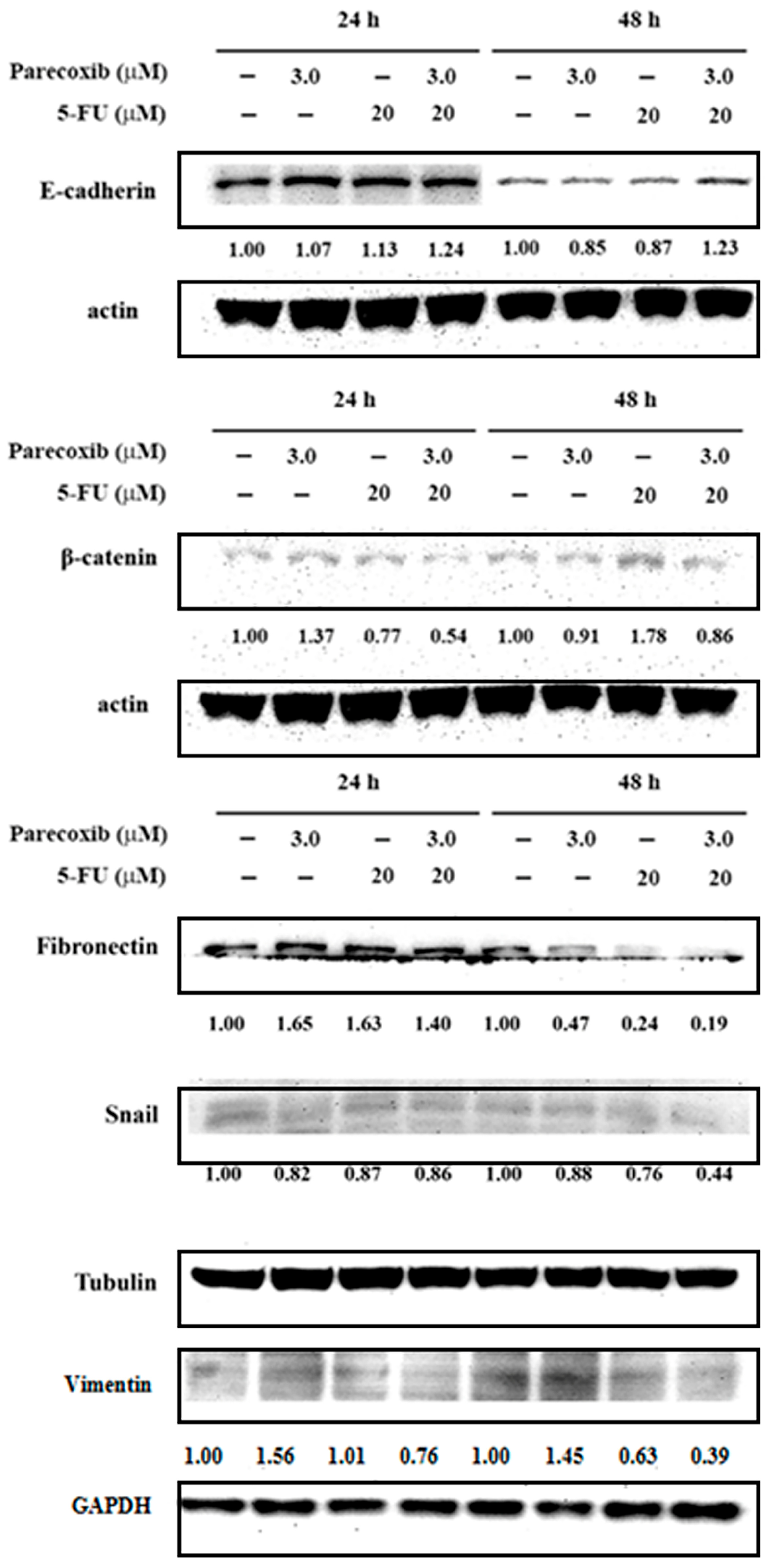
3.4. EMT Suppression on Parecoxib and 5-FU Combination
3.5. Inhibition of MMP-9 Activity on Parecoxib and 5-FU Combination
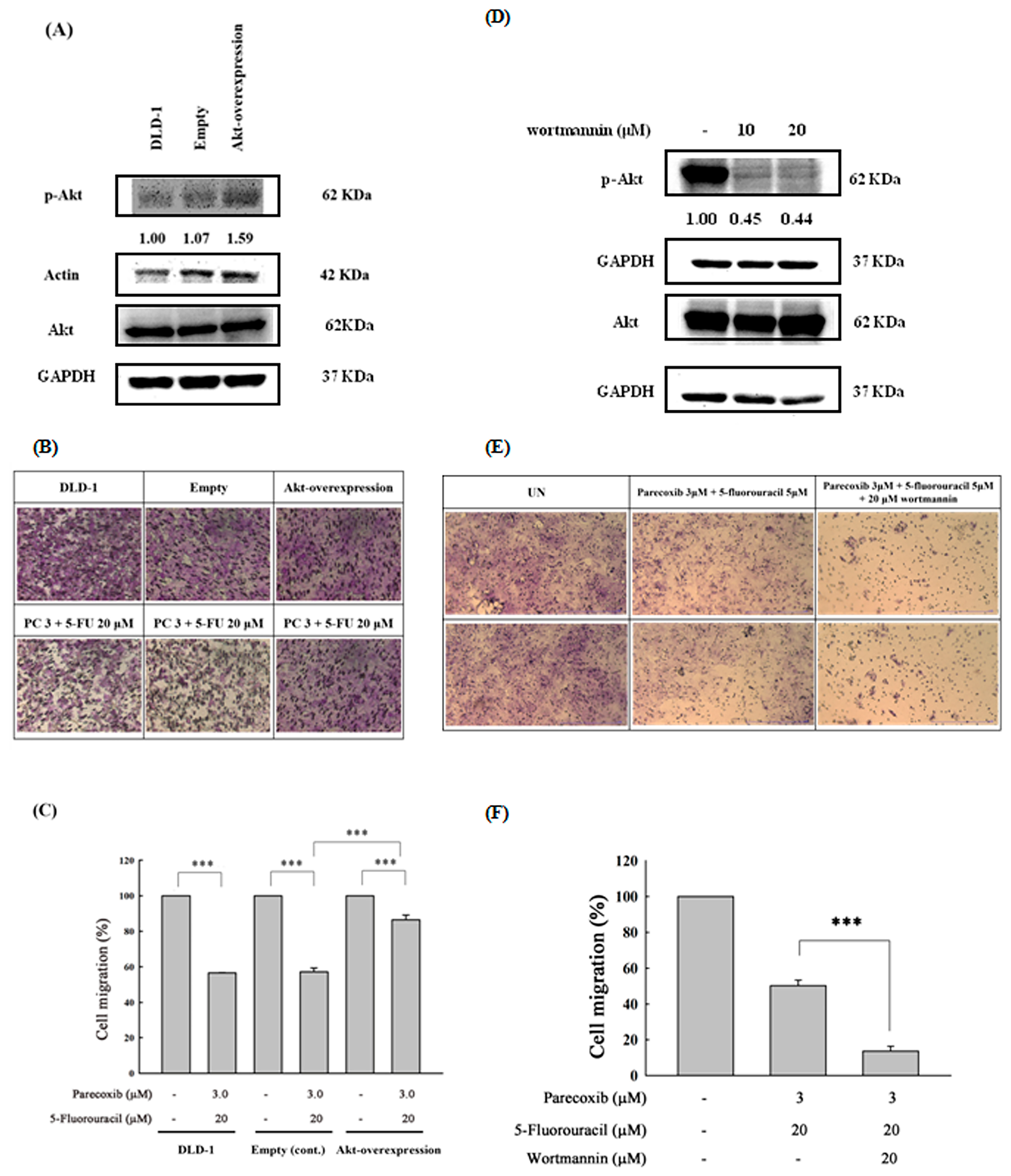
3.6. Inhibition of PI3K/Akt/NF-κB Pathway on Parecoxib and 5-FU Combination
3.7. Akt Phosphorylation as the Critical Mediator by Which Parecoxib Can Potentiate the Anti-Migration Ability of 5-FU
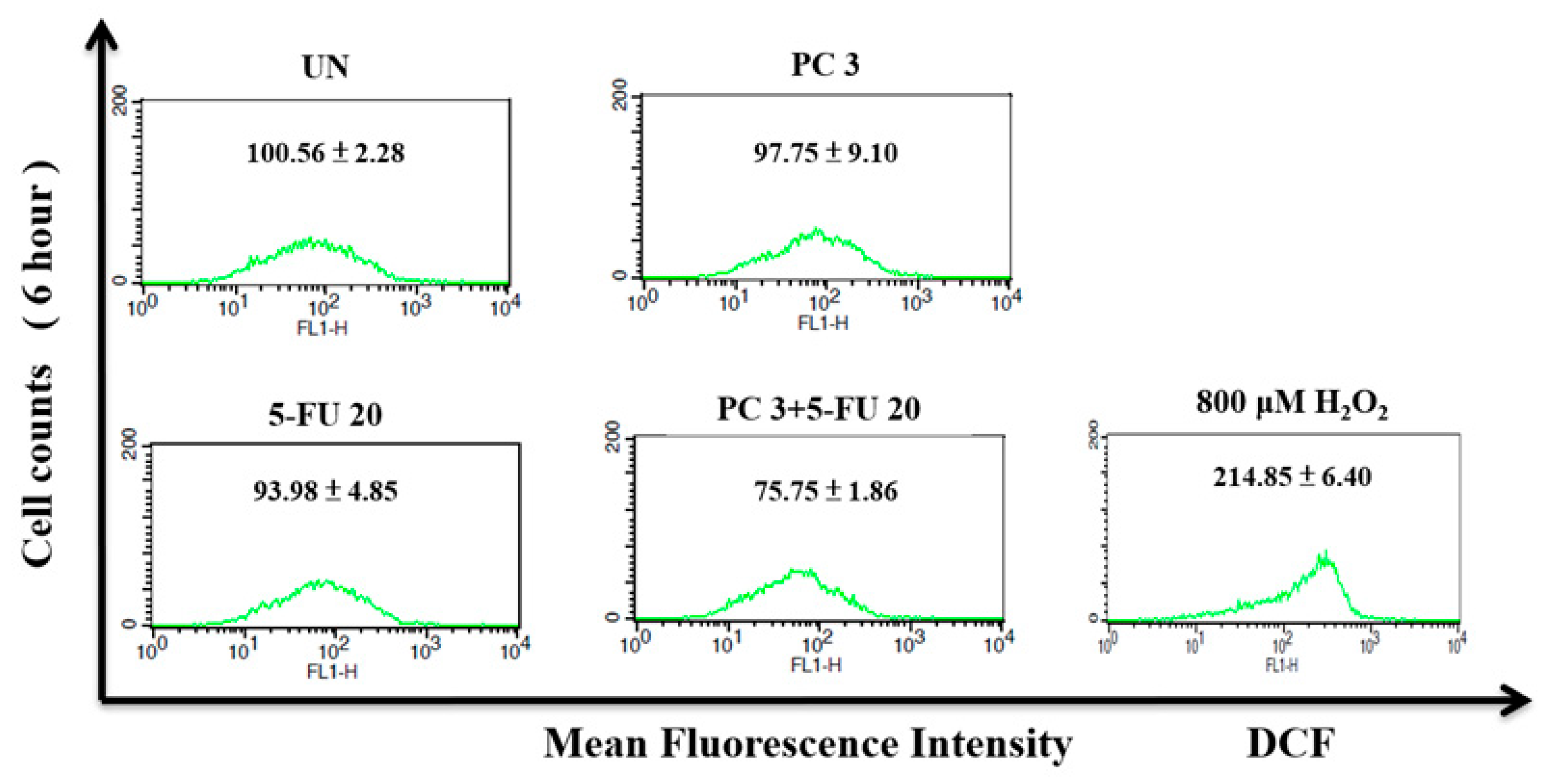
3.8. Parecoxib/5-FU Combination Inhibits Intracellular ROS
3.9. Synergism of Parecoxib and 5-FU Combination in Antimetastatic Effect in SW480 Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vogel, J.D.; Felder, S.I.; Bhama, A.R.; Hawkins, A.T.; Langenfeld, S.J.; Shaffer, V.O.; Thorsen, A.J.; Weiser, M.R.; Chang, G.J.; Lightner, A.L. The American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons clinical practice guidelines for the management of colon cancer. Dis. Colon Rectum 2022, 65, 148–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinji, S.; Yamada, T.; Matsuda, A.; Sonoda, H.; Ohta, R.; Iwai, T.; Takeda, K.; Yonaga, K.; Masuda, Y.; Yoshida, H. Recent advances in the treatment of colorectal cancer: A review. J. Nippon Med. Sch. 2022, 89, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Guillén, L.; Arroyo, A. Immunonutrition in patients with colon cancer. Immunotherapy 2020, 12, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, H.; Yao, Q. Traditional Chinese medicines as effective reversals of epithelial-mesenchymal transition induced-metastasis of colorectal cancer: Molecular targets and mechanisms. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 842295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, N.; Guo, H.; Yin, X.; Zheng, Y. Correlation Analysis of Gene and Radiomic Features in Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastases. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2022, 2022, 8559011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engstrand, J.; Nilsson, H.; Strömberg, C.; Jonas, E.; Freedman, J. Colorectal cancer liver metastases–a population-based study on incidence, management and survival. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rong, D.; Sun, G.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, L.; Chen, X.; Wu, F.; Gu, Y.; Dai, Y.; Zhong, W.; Hao, X. MGP promotes CD8+ T cell exhaustion by activating the NF-κB pathway leading to liver metastasis of colorectal cancer. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 18, 2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagashima, F.; Hamaguchi, T.; Furuse, J. Activity of the JCOG geriatric study committee and chemotherapy of colorectal cancer in older patients. Gan Kagaku Ryoho/Cancer Chemother. 2015, 42, 16–20. [Google Scholar]
- Vodenkova, S.; Buchler, T.; Cervena, K.; Veskrnova, V.; Vodicka, P.; Vymetalkova, V. 5-fluorouracil and other fluoropyrimidines in colorectal cancer: Past, present and future. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 206, 107447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.-H.; Ro, E.J.; Yoon, J.-S.; Mizutani, T.; Kang, D.-W.; Park, J.-C.; Il Kim, T.; Clevers, H.; Choi, K.-Y. 5-FU promotes stemness of colorectal cancer via p53-mediated WNT/β-catenin pathway activation. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glynne-Jones, R.; Wyrwicz, L.; Tiret, E.; Brown, G.; Rödel, C.d.; Cervantes, A.; Arnold, D. Rectal cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, iv22–iv40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rejhová, A.; Opattová, A.; Čumová, A.; Slíva, D.; Vodička, P. Natural compounds and combination therapy in colorectal cancer treatment. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 144, 582–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammond, W.A.; Swaika, A.; Mody, K. Pharmacologic resistance in colorectal cancer: A review. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2016, 8, 57–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, S.; Liang, S.; Cheng, Z.; Zhang, X.; Luo, L.; Li, L.; Zhang, W.; Li, S.; Xu, Q.; Zhong, M. ROS/PI3K/Akt and Wnt/β-catenin signalings activate HIF-1α-induced metabolic reprogramming to impart 5-fluorouracil resistance in colorectal cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 41, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Wang, Q.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Liu, D. Enhanced antitumor effect via combination of triptolide with 5-fluorouracil in pancreatic cancer. Transl. Cancer Res. 2018, 7, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chintala, L.; Vaka, S.; Baranda, J.; Williamson, S.K. Capecitabine versus 5-fluorouracil in colorectal cancer: Where are we now? Oncol. Rev. 2011, 5, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klautke, G.; Küchenmeister, U.; Foitzik, T.; Ludwig, K.; Semrau, S.; Prall, F.; Klar, E.; Fietkau, R. Intensified irinotecan-based neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in rectal cancer: Four consecutive designed studies to minimize acute toxicity and to optimize efficacy measured by pathologic complete response. Radiother. Oncol. 2007, 85, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassidy, J.; Misset, J.-L. Oxaliplatin-related side effects: Characteristics and management. Semin. Oncol. 2002, 29, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stiller, C.O.; Hjemdahl, P. Lessons from 20 years with COX-2 inhibitors: Importance of dose–response considerations and fair play in comparative trials. J. Intern. Med. 2022, 292, 557–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheehan, K.M.; O’Connell, F.; O’Grady, A.; Conroy, R.M.; Leader, M.B.; Byrne, M.F.; Murray, F.E.; Kay, E.W. The relationship between cyclooxygenase-2 expression and characteristics of malignant transformation in human colorectal adenomas. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2004, 16, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, R.; Wallace, M.; Lynch, P.; Hawk, E.; Gordon, G.; Saunders, B.; Wakabayashi, N.; Shen, Y.; Zimmerman, S.; Godio, L. A randomised, double blind, placebo controlled study of celecoxib, a selective cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitor, on duodenal polyposis in familial adenomatous polyposis. Gut 2002, 50, 857–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Y.; Yin, G.; Wang, X.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, G.; Feng, Z.; Sun, Q. Application of ICH Guidelines for the Assessment and Control of Elemental Impurities in Parecoxib Sodium by Graphite-Digestion and ICP-MS. Int. J. Anal. Chem. 2022, 2022, 9299416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, W.; Li, W.-H.; Jiang, Y.-X.; Liu, S.; Ai, Y.-Q.; Liu, R.; Chang, L.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X.-L.; Bai, H. Parecoxib: An enhancer of radiation therapy for colorectal cancer. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2015, 16, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, C.H.; Chang, W.L.; Lu, F.J.; Liu, Y.W.; Peng, J.Y.; Chen, C.H. Parecoxib expresses anti-metastasis effect through inhibition of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in human colon cancer DLD-1 cell line. Environ. Toxicol. 2022, 37, 2718–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, J.G.; Piskounova, E.; Morrison, S.J. Cancer, oxidative stress, and metastasis. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 2016, 81, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, F.; Xu, Q.; Jing, X.; Chi, X.; Zhang, Z.; Meng, X.; Liu, X.; Yan, J.; Liu, X.; Shao, S. GPX2 promotes EMT and metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer by activating PI3K/AKT/mTOR/Snail signaling axis. FASEB BioAdv. 2023, 5, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Ge, X.; Wang, F.; Zhou, F.; Deng, X.; Miao, L. Aprepitant inhibits the development and metastasis of gallbladder cancer via ROS and MAPK activation. BMC Cancer 2023, 23, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, V.; Tuli, H.S.; Varol, A.; Thakral, F.; Yerer, M.B.; Sak, K.; Varol, M.; Jain, A.; Khan, M.A.; Sethi, G. Role of reactive oxygen species in cancer progression: Molecular mechanisms and recent advancements. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastushenko, I.; Blanpain, C. EMT transition states during tumor progression and metastasis. Trends Cell Biol. 2019, 29, 212–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.; Wang, W.W.; Zhang, M.Z.; Ma, Z.X.; Qiu, X.R.; Shen, M.; Yin, X.X. ROS induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the TGF-β1/PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in diabetic nephropathy. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 17, 835–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Feng, J.; Li, Y.; Guan, D.; Chen, H.; Zhai, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, C.; Li, C. The vicious cycle between ferritinophagy and ROS production triggered EMT inhibition of gastric cancer cells was through p53/AKT/mTor pathway. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2020, 328, 109196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Xu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ma, L.; Zhang, Y. Aspirin suppresses chemoresistance and enhances antitumor activity of 5-Fu in 5-Fu-resistant colorectal cancer by abolishing 5-Fu-induced NF-κB activation. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vértessy, B.G.; Tóth, J. Keeping uracil out of DNA: Physiological role, structure and catalytic mechanism of dUTPases. Acc. Chem. Res. 2009, 42, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, P.; Chen, J.; Yan, L.; Yang, L.; Zhang, L.; Dai, J.; Hao, Z.; Bai, T.; Xi, Y.; Li, Y. RasGRF2 promotes migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells by modulating expression of MMP9 through Src/Akt/NF-κB pathway. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2019, 20, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Li, L.; Du, J.; Pan, C.; Zhang, C.; Chen, Y. Placenta-specific protein 1 enhances liver metastatic potential and is associated with the PI3K/AKT/NF-κB signaling pathway in colorectal cancer. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2021, 30, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Yang, L.; Dai, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Jia, X.; Liu, C. 5-FU inhibits migration and invasion of CRC cells through PI3K/AKT pathway regulated by MARCH1. Cell Biol. Int. 2021, 45, 368–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maharati, A.; Moghbeli, M. PI3K/AKT signaling pathway as a critical regulator of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colorectal tumor cells. Cell Commun. Signal. 2023, 21, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarawneh, N.; Hamadneh, L.; Abu-Irmaileh, B.; Shraideh, Z.; Bustanji, Y.; Abdalla, S. Berberine inhibited growth and migration of human colon cancer cell lines by increasing phosphatase and tensin and inhibiting aquaporins 1, 3 and 5 expressions. Molecules 2023, 28, 3823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hseu, Y.-C.; Chao, Y.-H.; Lin, K.-Y.; Way, T.-D.; Lin, H.-Y.; Thiyagarajan, V.; Yang, H.-L. Antrodia camphorata inhibits metastasis and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via the modulation of claudin-1 and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways in human colon cancer cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 208, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Liang, Y.; Sun, R.; Yang, W.; Liang, Z.; Gu, J.; Zhao, F.; Tang, D. Astragalus mongholicus Bunge and Curcuma aromatica Salisb. inhibits liver metastasis of colon cancer by regulating EMT via the CXCL8/CXCR2 axis and PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Chin. Med. 2022, 17, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, Q.; Dai, G.; Jiang, Z.; Bao, H. Down regulation of the expression of ELMO3 by COX2 inhibitor suppresses tumor growth and metastasis in non-small-cell lung cancer. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Güllü, N.; Smith, J.; Herrmann, P.; Stein, U. MACC1-dependent antitumor effect of curcumin in colorectal cancer. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, W.; Cai, H.; Du, B.; Zhang, L.; Ma, W.; Hu, Y.; Feng, S.; Miao, G. MACC1 facilitates chemoresistance and cancer stem cell-like properties of colon cancer cells through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 8747–8754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treese, C.; Werchan, J.; von Winterfeld, M.; Berg, E.; Hummel, M.; Timm, L.; Rau, B.; Daberkow, O.; Walther, W.; Daum, S. Inhibition of MACC1-induced metastasis in esophageal and gastric adenocarcinomas. Cancers 2022, 14, 1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kortüm, B.; Radhakrishnan, H.; Zincke, F.; Sachse, C.; Burock, S.; Keilholz, U.; Dahlmann, M.; Walther, W.; Dittmar, G.; Kobelt, D. Combinatorial treatment with statins and niclosamide prevents CRC dissemination by unhinging the MACC1-β-catenin-S100A4 axis of metastasis. Oncogene 2022, 41, 4446–4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.; Chen, H.; Liang, J.; Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Luo, C.; Tang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Liu, X.; Yuan, Q. Dual role of reactive oxygen species and their application in cancer therapy. J. Cancer 2021, 12, 5543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, H.; Takada, K. Reactive oxygen species in cancer: Current findings and future directions. Cancer Sci. 2021, 112, 3945–3952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piskounova, E.; Agathocleous, M.; Murphy, M.M.; Hu, Z.; Huddlestun, S.E.; Zhao, Z.; Leitch, A.M.; Johnson, T.M.; DeBerardinis, R.J.; Morrison, S.J. Oxidative stress inhibits distant metastasis by human melanoma cells. Nature 2015, 527, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, R.; Mukherjee, S.; Biswas, J.; Roy, M. Phenethyl isothiocyanate, by virtue of its antioxidant activity, inhibits invasiveness and metastatic potential of breast cancer cells: HIF-1α as a putative target. Free Radic. Res. 2016, 50, 84–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, J.; Xu, H.; Fan, P.-z.; Xie, J.; He, J.; Yu, J.; Gu, X.; Zhang, C.-j. Kaempferol blocks neutrophil extracellular traps formation and reduces tumour metastasis by inhibiting ROS-PAD4 pathway. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 7590–7599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.-T.; Lee, I.; Lu, F.-J.; Chung, C.-Y.; Lee, M.-H.; Cheng, Y.-C.; Chen, K.-T.; Chen, C.-H. Propyl gallate exerts an antimigration effect on temozolomide-treated malignant glioma cells through inhibition of ROS and the NF-κB pathway. J. Immunol. Res. 2017, 2017, 9489383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capeloa, T.; Van de Velde, J.A.; d’Hose, D.; Lipari, S.G.; Derouane, F.; Hamelin, L.; Bedin, M.; Vazeille, T.; Duhoux, F.P.; Murphy, M.P. Inhibition of Mitochondrial Redox Signaling with MitoQ Prevents Metastasis of Human Pancreatic Cancer in Mice. Cancers 2022, 14, 4918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, D.K.; Chang, S.N.; Vadlamudi, Y.; Park, J.G.; Kang, S.C. Synergistic therapy with tangeretin and 5-fluorouracil accelerates the ROS/JNK mediated apoptotic pathway in human colorectal cancer cell. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 143, 111529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vessieres, E.; Guihot, A.-L.; Toutain, B.; Maquigneau, M.; Fassot, C.; Loufrani, L.; Henrion, D. COX-2-derived prostanoids and oxidative stress additionally reduce endothelium-mediated relaxation in old type 2 diabetic rats. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.-H.; Choi, S.-Y.; Choi, H.-J.; Ryu, H.-M.; Kim, Y.-J.; Jung, H.-Y.; Cho, J.-H.; Kim, C.-D.; Park, S.-H.; Kwon, T.-H. The emerging role of xanthine oxidase inhibition for suppression of breast cancer cell migration and metastasis associated with hypercholesterolemia. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 7301–7314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, H.; Zhang, M.; Xu, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y. Gypensapogenin H suppresses tumor growth and cell migration in triple-negative breast cancer by regulating PI3K/AKT/NF-κB/MMP-9 signaling pathway. Bioorg. Chem. 2022, 126, 105913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Cheng, T.; Zhao, Y.; Qu, Y. HMGA1 exacerbates tumor progression by activating miR-222 through PI3K/Akt/MMP-9 signaling pathway in uveal melanoma. Cell. Signal. 2019, 63, 109386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolignano, D.; Donato, V.; Lacquaniti, A.; Fazio, M.R.; Bono, C.; Coppolino, G.; Buemi, M. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) in human neoplasias: A new protein enters the scene. Cancer Lett. 2010, 288, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, A.; Jing, J.; Lee, J.; Schedin, P.; Gilbert, S.M.; Peden, A.A.; Junutula, J.R.; Prekeris, R. Rab40b regulates trafficking of MMP2 and MMP9 during invadopodia formation and invasion of breast cancer cells. J. Cell Sci. 2013, 126, 4647–4658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.-Y.; Lee, C.-H.; Chiou, H.-L.; Lin, C.-L.; Chen, P.-N.; Lin, M.-T.; Hsieh, Y.-H.; Chou, M.-C. Praeruptorin-B inhibits 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-induced cell invasion by targeting AKT/NF-κB via matrix metalloproteinase-2/-9 expression in human cervical cancer cells. Cell. Physiol. Biochem 2019, 52, 1255–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Hong, W.; Wei, X. The molecular mechanisms and therapeutic strategies of EMT in tumor progression and metastasis. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Tong, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y. Sunitinib Reduced the Migration of Ectopic Endometrial Cells via p-VEGFR-PI3K-AKT-YBX1-Snail Signaling Pathway. Anal. Cell. Pathol. 2022, 2022, 6042518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, W.-L.; Peng, J.-Y.; Hong, C.-L.; Li, P.-C.; Lu, F.-J.; Chen, C.-H. Parecoxib and 5-Fluorouracil Synergistically Inhibit EMT and Subsequent Metastasis in Colorectal Cancer by Targeting PI3K/Akt/NF-κB Signaling. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1526. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12071526
Chang W-L, Peng J-Y, Hong C-L, Li P-C, Lu F-J, Chen C-H. Parecoxib and 5-Fluorouracil Synergistically Inhibit EMT and Subsequent Metastasis in Colorectal Cancer by Targeting PI3K/Akt/NF-κB Signaling. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(7):1526. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12071526
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Wan-Ling, Jyun-Yu Peng, Chain-Lang Hong, Pei-Ching Li, Fung-Jou Lu, and Ching-Hsein Chen. 2024. "Parecoxib and 5-Fluorouracil Synergistically Inhibit EMT and Subsequent Metastasis in Colorectal Cancer by Targeting PI3K/Akt/NF-κB Signaling" Biomedicines 12, no. 7: 1526. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12071526
APA StyleChang, W.-L., Peng, J.-Y., Hong, C.-L., Li, P.-C., Lu, F.-J., & Chen, C.-H. (2024). Parecoxib and 5-Fluorouracil Synergistically Inhibit EMT and Subsequent Metastasis in Colorectal Cancer by Targeting PI3K/Akt/NF-κB Signaling. Biomedicines, 12(7), 1526. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12071526





