Cannabielsoin (CBE), a CBD Oxidation Product, Is a Biased CB1 Agonist
Abstract
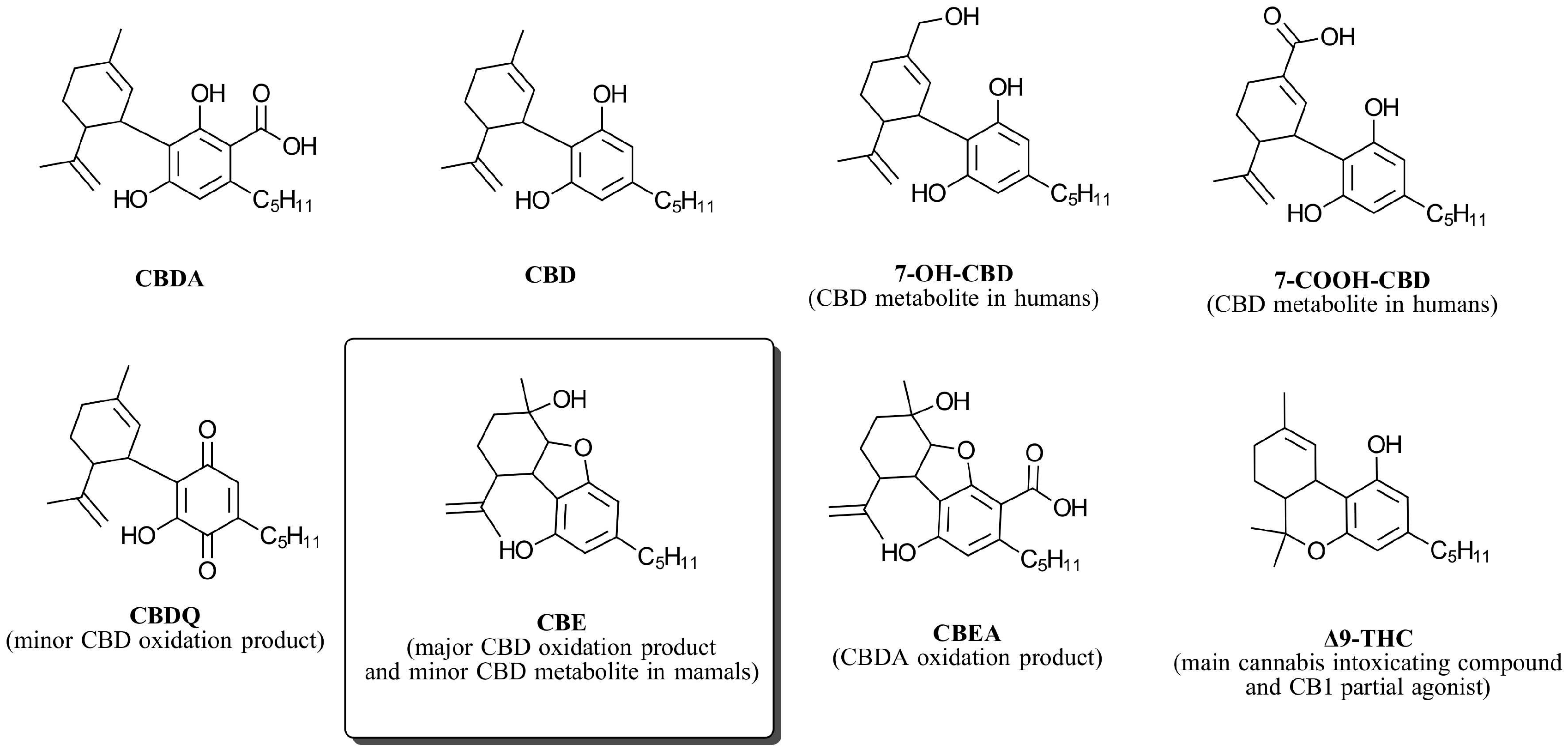
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. PathHunter® Arrestin Assay
2.2. cAMP Hunter Assay
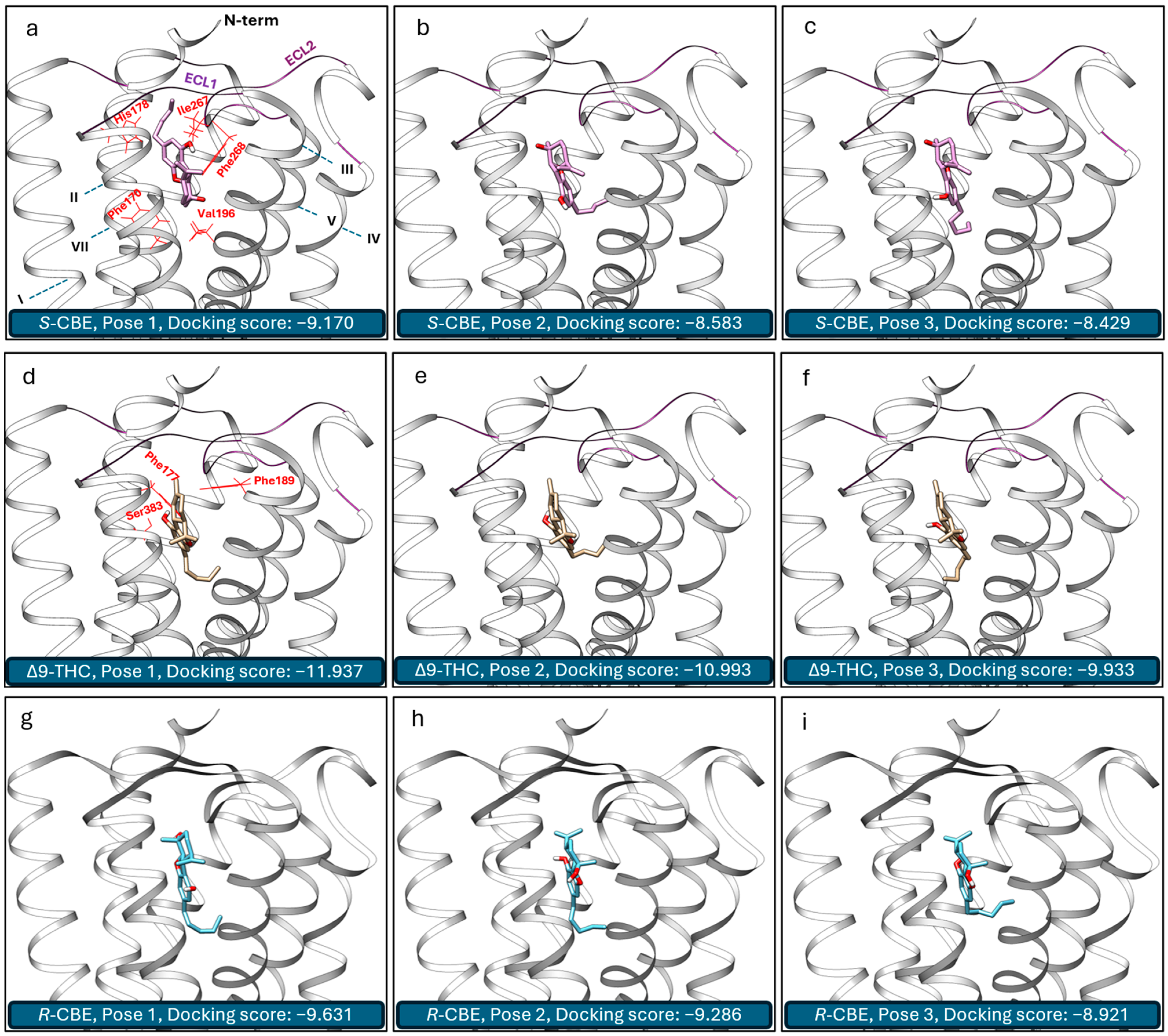
2.3. Molecular Docking Calculations
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. β-Arrestin Recruitment Assay
cAMP Assay
3.2. In Vitro Study Limitation
3.3. In Silico Study
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marzullo, P.; Foschi, F.; Coppini, D.A.; Fanchini, F.; Magnani, L.; Rusconi, S.; Luzzani, M.; Passarella, D. Cannabidiol as the Substrate in Acid-Catalyzed Intramolecular Cyclization. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 2894–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampson, A.J.; Grimaldi, M.; Axelrod, J.; Wink, D. Cannabidiol and (−)Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol Are Neuroprotective Antioxidants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 8268–8273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caprioglio, D.; Mattoteia, D.; Pollastro, F.; Negri, R.; Lopatriello, A.; Chianese, G.; Minassi, A.; Collado, J.A.; Munoz, E.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O.; et al. The Oxidation of Phytocannabinoids to Cannabinoquinoids. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 1711–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, B.J.; Hanna, S.; Schwarzenberg, A.; Kiani, P.; Bizzotto, D.; Kennepohl, P.; Davies, A.; Roggen, M.; Sammis, G.M. CBD Hydroxyquinone Photo-Isomerises to a Highly Reactive Intermediate. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 6967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulo, B.; Phan, K.; Githaiga, J.; Raes, K.; De Meester, S. Natural Quinone Dyes: A Review on Structure, Extraction Techniques, Analysis and Application Potential. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 2021, 12, 6339–6374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capucciati, A.; Casali, E.; Bini, A.; Doria, F.; Merli, D.; Porta, A. Easy and Accessible Synthesis of Cannabinoids from CBD. J. Nat. Prod. 2024, 87, 869–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küppers, F.J.E.M.; Lousberg, R.C.; Bercht, C.A.L.; Salemink, C.A.; Terlouw, J.K.; Heerma, W.; Laven, A. Cannabis—VIII: Pyrolysis of Cannabidiol. Structure Elucidation of the Main Pyrolytic Product. Tetrahedron 1973, 29, 2797–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radwan, M.M.; Chandra, S.; Gul, S.; ElSohly, M.A. Cannabinoids, Phenolics, Terpenes and Alkaloids of Cannabis. Molecules 2021, 26, 2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Go, M.K.; Zhu, T.; Lim, K.J.H.; Hartono, Y.D.; Xue, B.; Fan, H.; Yew, W.S. Cannabinoid Biosynthesis Using Noncanonical Cannabinoid Synthases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, I.; Gohda, H.; Narimatsu, S.; Yoshimura, H. Identification of Cannabielsoin, a New Metabolite of Cannabidiol Formed by Guinea-Pig Hepatic Microsomal Enzymes, and Its Pharmacological Activity in Mice. J. Pharmacobio-Dyn. 1988, 11, 833–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ujváry, I.; Hanuš, L. Human Metabolites of Cannabidiol: A Review on Their Formation, Biological Activity, and Relevance in Therapy. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2016, 1, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nalli, Y.; Dar, M.S.; Bano, N.; Rasool, J.U.; Sarkar, A.R.; Banday, J.; Bhat, A.Q.; Rafia, B.; Vishwakarma, R.A.; Dar, M.J.; et al. Analyzing the Role of Cannabinoids as Modulators of Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway for Their Use in the Management of Neuropathic Pain. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 29, 1043–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komiya, Y.; Habas, R. Wnt Signal Transduction Pathways. Organogenesis 2008, 4, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monroe, A.Z.; Gordon, W.H.; Wood, J.S.; Martin, G.E.; Morgan, J.B.; Williamson, R.T. Structural Revision of a Wnt/β-Catenin Modulator and Confirmation of Cannabielsoin Constitution and Configuration. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 5658–5661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehi, A.; Puchalski, K.; Shokoohinia, Y.; Zolfaghari, B.; Asgary, S. Differentiating Cannabis Products: Drugs, Food, and Supplements. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 906038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- User Manual: PathHunter® β-Arrestin Assay for GPCR Cell Lines. Available online: https://www.discoverx.com/content/uploads/2023/07/70-247-PathHunter-Beta-Arrestin-Assay-for-GPCR-Cell-Lines_REV5-1.pdf (accessed on 23 March 2023).
- User Manual: cAMP Hunter™ Gαs and Gαi Cell Line. Available online: https://www.discoverx.com/content/uploads/2023/07/70-233-cAMP-Hunter-Gs-and-Gi-Cell-Lines_REV10-1.pdf (accessed on 23 March 2023).
- Hua, T.; Vemuri, K.; Nikas, S.P.; Laprairie, R.B.; Wu, Y.; Qu, L.; Pu, M.; Korde, A.; Jiang, S.; Ho, J.-H.; et al. Crystal Structures of Agonist-Bound Human Cannabinoid Receptor CB1. Nature 2017, 547, 468–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapovalov, M.V.; Dunbrack, R.L. A Smoothed Backbone-Dependent Rotamer Library for Proteins Derived from Adaptive Kernel Density Estimates and Regressions. Structure 2011, 19, 844–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banáš, P.; Hollas, D.; Zgarbová, M.; Jurečka, P.; Orozco, M.; Cheatham, T.E.I.; Šponer, J.; Otyepka, M. Performance of Molecular Mechanics Force Fields for RNA Simulations: Stability of UUCG and GNRA Hairpins. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2010, 6, 3836–3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberhardt, J.; Santos-Martins, D.; Tillack, A.F.; Forli, S. AutoDock Vina 1.2.0: New Docking Methods, Expanded Force Field, and Python Bindings. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2021, 61, 3891–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertwee, R.G. The Diverse CB1 and CB2 Receptor Pharmacology of Three Plant Cannabinoids: Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol, Cannabidiol and Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabivarin. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 153, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertwee, R.G.; Ross, R.A.; Craib, S.J.; Thomas, A. (−)-Cannabidiol Antagonizes Cannabinoid Receptor Agonists and Noradrenaline in the Mouse Vas Deferens. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 456, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laprairie, R.B.; Bagher, A.M.; Kelly, M.E.; Denovan-Wright, E. Cannabidiol Is a Negative Allosteric Modulator of the Cannabinoid CB1 Receptor. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 4790–4805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Zoubi, R.; Morales, P.; Reggio, P.H. Structural Insights into CB1 Receptor Biased Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Finlay, D.B.; Glass, M.; Duffull, S.B. Evaluation of the Profiles of CB1 Cannabinoid Receptor Signalling Bias Using Joint Kinetic Modelling. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 3449–3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leo, L.M.; Abood, M.E. CB1 Cannabinoid Receptor Signaling and Biased Signaling. Molecules 2021, 26, 5413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryalls, B.; Patel, M.; Sparkes, E.; Banister, S.D.; Finlay, D.B.; Glass, M. Investigating Selectivity and Bias for G Protein Subtypes and β-Arrestins by Synthetic Cannabinoid Receptor Agonists at the Cannabinoid CB1 Receptor. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2024, 222, 116052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackie, K. Cannabinoid Receptors as Therapeutic Targets. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2006, 46, 101–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Kang, D.S.; Benovic, J.L. β-Arrestins and G Protein-Coupled Receptor Trafficking. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2014, 219, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haghdoost, M.; López de los Santos, Y.; Brunstetter, M.; Ferretti, M.L.; Roberts, M.; Bonn-Miller, M.O. Using In Silico Molecular Docking to Explain Differences in Receptor Binding Behavior of HHC and THCV Isomers: Revealing New Binding Modes. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassone-Corsi, P. The Cyclic AMP Pathway. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2012, 4, a011148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gérard, C.M.; Mollereau, C.; Vassart, G.; Parmentier, M. Molecular Cloning of a Human Cannabinoid Receptor Which Is Also Expressed in Testis. Biochem. J. 1991, 279, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silmore, L.H.; Willmer, A.R.; Capparelli, E.V.; Rosania, G.R. Food Effects on the Formulation, Dosing, and Administration of Cannabidiol (CBD) in Humans: A Systematic Review of Clinical Studies. Pharmacotherapy 2021, 41, 405–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linciano, P.; Citti, C.; Luongo, L.; Belardo, C.; Maione, S.; Vandelli, M.A.; Forni, F.; Gigli, G.; Laganà, A.; Montone, C.M.; et al. Isolation of a High-Affinity Cannabinoid for the Human CB1 Receptor from a Medicinal Cannabis sativa Variety: Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabutol, the Butyl Homologue of Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishna Kumar, K.; Robertson, M.J.; Thadhani, E.; Wang, H.; Suomivuori, C.-M.; Powers, A.S.; Ji, L.; Nikas, S.P.; Dror, R.O.; Inoue, A.; et al. Structural Basis for Activation of CB1 by an Endocannabinoid Analog. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Haghdoost, M.; Young, S.; Roberts, M.; Krebs, C.; Bonn-Miller, M.O. Cannabielsoin (CBE), a CBD Oxidation Product, Is a Biased CB1 Agonist. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1551. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12071551
Haghdoost M, Young S, Roberts M, Krebs C, Bonn-Miller MO. Cannabielsoin (CBE), a CBD Oxidation Product, Is a Biased CB1 Agonist. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(7):1551. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12071551
Chicago/Turabian StyleHaghdoost, Mehdi, Scott Young, Matthew Roberts, Caitlyn Krebs, and Marcel O. Bonn-Miller. 2024. "Cannabielsoin (CBE), a CBD Oxidation Product, Is a Biased CB1 Agonist" Biomedicines 12, no. 7: 1551. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12071551
APA StyleHaghdoost, M., Young, S., Roberts, M., Krebs, C., & Bonn-Miller, M. O. (2024). Cannabielsoin (CBE), a CBD Oxidation Product, Is a Biased CB1 Agonist. Biomedicines, 12(7), 1551. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12071551



