Detection of Viruses with Oncogenic and Oncomodulatory Potential in Head and Neck Tumors—External Auricle
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
2.2. DNA Extraction Procedures
2.3. Molecular Methods for Detection of the Viruses Included in the Study
Sequencing
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. HPV
3.2. Viruses from the Herpesvirus Family
3.3. BKPyV
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BKPyV | BK polyomavirus |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic acid |
| EBV | Epstein–Barr virus |
| HCMV | Human cytomegalovirus |
| HPV | Human papillomaviruses |
| HNCs | Head and neck cancers |
| HSVs | Herpes Simplex Viruses |
| HSV1 | Herpes Simplex Virus 1 |
| HSV2 | Herpes Simplex Virus 2 |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| SCC | Squamous Cell Carcinoma |
References
- Fitzmaurice, C.; Allen, C.; Barber, R.M.; Barregard, L.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Brenner, H.; Dicker, D.J.; Chimed-Orchir, O.; Dandona, R.; Dandona, L.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Cancer Incidence, Mortality, Years of Life Lost, Years Lived With Disability, and Disability-Adjusted Life-years for 32 Cancer Groups, 1990 to 2015: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 524–548. [Google Scholar]
- Hillbertz, N.S.; Hirsch, J.M.; Jalouli, J.; Jalouli, M.M.; Sand, L. Viral and molecular aspects of oral cancer. Anticancer Res. 2012, 32, 4201–4212. [Google Scholar]
- IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. A Review of Human Carcinogens. Biological Agents; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2012; p. 255. ISBN 978-92-832-1319-2. [Google Scholar]
- Chien, Y.C.; Chen, J.Y.; Liu, M.Y.; Yang, H.I.; Hsu, M.M.; Chen, C.J.; Yang, C.S. Serologic markers of Epstein-Barr virus infection and nasopharyngeal carcinoma in Taiwanese men. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 1877–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikoo, H.R.; Ardebili, A.; Ravanshad, M.; Rezaei, F.; Teimoori, A.; Khanizadeh, S.; Pouriayevali, M.H.; Ajorloo, M. E6-Specific Detection and Typing of Human Papillomaviruses in Oral Cavity Specimens from Iranian Patients. Iran. Biomed. J. 2017, 21, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, A.A. Human papillomaviruses: Diversity, infection and host interactions. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doorbar, J.; Egawa, N.; Griffin, H.; Kranjec, C.; Murakami, I. Human papillomavirus molecular biology and disease association. Rev. Med. Virol. 2015, 25, 2–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, S.; Broekema, N.; Imperiale, M. BK polyomavirus: Emerging pathogen. Microbes Infect. 2012, 14, 672–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger-Calderon, R.; Webster-Cyriaque, J. Human BK Polyomavirus—The Potential for Head and Neck Malignancy and Disease. Cancers 2015, 7, 1244–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schowalter, R.; Reinhold, W.; Buck, C. Entry tropism of BK and Merkel cell polyomaviruses in cell culture. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raeesi, N.; Gheissari, A.; Akrami, M.; Moghim, S. Urinary BK virus excretion in children newly diagnosed with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2012, 6, 402–407. [Google Scholar]
- Konietzny, R.; Fischer, R.; Ternette, N.; Wright, C.; Turney, B.; Chakera, A. Detection of BK virus in urine from renal transplant subjects my mass spectrometry. Clin. Proteom. 2012, 9, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffers, L.K.; Madden, V.; Webster-Cyriaque, J. BK virus has tropism for human salivary gland cells in vitro: Implications for transmission. Virology 2009, 394, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levican, J.; Acevedo, M.; León, O.; Gaggero, A.; Aguayo, F. Role of BK human polyomavirus in cancer. Infect. Agents Cancer 2018, 13, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.H.; States, V.A.R.; Afghan, A.K.; Satyanarayana, G. Herpes simplex virus-infected squamous cell carcinoma: A case report. BMC Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takasu, A.; Masui, A.; Hamada, M.; Imai, T.; Yura, Y. Immunogenic cell death by oncolytic herpes simplex virus type 1 in squamous cell carcinoma cells. Cancer Gene Ther. 2016, 23, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbari, M.; Elmi, R. Herpes simplex virus and human papillomavirus coinfections in hyperimmunoglobulin E syndrome presenting as a conjunctival mass lesion. Case Rep. Med. 2017, 2017, 1650841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatton, O.L.; Harris-Arnold, A.; Schaffert, S.; Krams, S.M.; Martinez, O.M. The interplay between Epstein-Barr virus and B lymphocytes: Implications for infection, immunity, and disease. Immunol. Res. 2014, 58, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bibas, A.G.; Ward, V.; Gleeson, M.J. Squamous cell carcinoma of the temporal bone. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2008, 122, 1156–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, S.Y.; Yuen, S.T.; Ho, C.M.; Kwong, W.K.; Chung, L.P. Presence of Epstein-Barr virus in lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma of the middle ear. J. Clin. Pathol. 1998, 51, 602–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Rahbar, A.; Orrego, A.; Peredo, I.; Dzabic, M.; Wolmer-Solberg, N.; Strååt, K.; Stragliotto, G.; Söderberg-Nauclér, C. Human cytomegalovirus infection levels in glioblastoma multiforme are of prognostic value for survival. J. Clin. Virol. 2013, 57, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbein, G.; Kumar, A. The oncogenic potential of human cytomegalovirus and breast cancer. Front. Oncol. 2014, 4, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Peredo-Harvey, I.; Rahbar, A.; Söderberg-Nauclér, C. Presence of the Human Cytomegalovirus in Glioblastomas—A Systematic Review. Cancers 2021, 13, 5051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, B.; Wang, X.; Chen, E.; Zhu, H. Human cytomegalovirus infection and colorectal cancer risk: A meta-analysis. Oncotarget. 2016, 7, 76735–76742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Joshi, D.; Quadri, M.; Gangane, N.; Joshi, R.; Gangane, N. Association of Epstein Barr Virus Infection (EBV) with Breast Cancer in Rural Indian Women. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e8180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michaelis, M.; Doer, W.H.; Cinatl, J. The Story of Human Cytomegalovirus and Cancer: Increasing Evidence and Open Questions. Neoplasia 2009, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cinatl, J.; Scholz, M.; Kotchetkov, R.; Vogel, J.; Doerr, W.H. Molecular mechanisms of the modulatory effects of HCMV infection in tumor cell biology. Trends Mol. Med. 2004, 10, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedham, V.; Divi, R.L.; Starks, V.L.; Verma, M. Multiple infections and cancer: Implications in epidemiology. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 13, 177–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimenes, F.; Medina, F.S.; Abreu, A.L.P.D.; Irie, M.M.T.; Esquicёati, I.B.; Malagutti, N.; Vasconcellos, V.R.B.; Discacciati, M.G.; Bonini, M.G.; Maria-Engler, S.S.; et al. Sensitive Simultaneous Detection of Seven Sexually Transmitted Agents in Semen by Multiplex-PCR and of HPV by Single PCR. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://bg05m2op001-1.002-0001.ncipd.org/images/UserFiles/File/Obshtestveni_poruchki/22.04.2015/Prilojenia/PrilAkvahim.xlsx (accessed on 2 December 2015).
- Available online: https://bg05m2op001-1.002-0001.ncipd.org/images/UserFiles/File/Obshtestveni_poruchki/22.04.2015/Obiavlenie.pdf (accessed on 2 December 2015).
- Merelli, E.; Bedin, R.; Sola, P.; Gentilini, M.; Pietrosemoli, P.; Meacci, M.; Portolani, M. Printed in UK-zyxwvutsrqponml. Acta Neurol. Scand. 1997, 96, 416420. [Google Scholar]
- Sirakov, I. Initial Molecular Screening for High-Risk Human Papilloma Viruses in Patients with Periodontitis. Master Thesis, Sofia University, Sofia, Bulgaria, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sotlar, K.; Diemer, D.; Dethleffs, A.; Hack, Y.; Stubner, A.; Vollmer, N.; Menton, S.; Menton, M.; Dietz, K.; Wallwiener, D.; et al. Detection and typing of human papillomavirus by e6 nested multiplex PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 3176–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiki, R.K.; Bugawan, T.L.; Horn, G.T.; Mullis, K.B.; Erlich, H.A. Analysis of enzymatically amplified β-globin and HLA-DQα DNA with allele-specific oligonucleotide probes. Nature 1986, 324, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritari, J.; Hultman, J.; Fingerroos, R.; Tarkkanen, J.; Pullat, J.; Paulin, L.; Kivi, N.; Auvinen, P.; Auvinen, E. Detection of human papillomaviruses by polymerase chain reaction and ligation reaction on universal microarray. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drop, B.; Strycharz-Dudziak, M.; Kliszczewska, E.; Polz-Dacewicz, M. Coinfection with Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV), Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) and Polyoma BK Virus (BKPyV) in Laryngeal, Oropharyngeal and Oral Cavity Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalianis, T.; Hirsch, H.H. Human polyomaviruses in disease and cancer. Virology 2013, 437, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Ren, X.; Cao, S.; Chen, X.; Yuan, B.; Brasil da Costa, F.H.; Rodriguez Rosario, A.E.; Corona, A.; Michikawa, C.; Veeramachaneni, R.; et al. TP53 gain-of-function mutation modulates the immunosuppressive microenvironment in non-HPV-associated oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2023, 11, e006666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dougherty, M.I.; Dougherty, W.; Kain, J.J.; Hughley, B.B.; Shonka, D.C.; Fedder, K.L.; Jameson, M.J. Non-HPV-Related Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma in a Young Patient Cohort. Ear Nose Throat J. 2020, 100 (Suppl. S10), 1101S–1106S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Günther, K.; Foraita, R.; Friemel, J.; Günther, F.; Bullerdiek, J.; Nimzyk, R.; Markowski, D.N.; Behrens, T.; Ahrens, W. The Stem Cell Factor HMGA2 Is Expressed in Non-HPV–Associated Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Predicts Patient Survival of Distinct Subsites. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2017, 26, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pors, J.; Tessier-Cloutier, B.; Thompson, E.; Almadani, N.; Ho, J.; Gilks, B.; Huntsman, D.; Hoang, L. Targeted Molecular Sequencing of Recurrent and Multifocal Non–HPV-associated Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Vulva. Int. J. Gynecol. Pathol. 2021, 40, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornall, A.M.; Roberts, J.M.; Garland, S.M.; Hillman, R.J.; Grulich, A.E.; Tabrizi, S.N. Anal and perianal squamous carcinomas and high-grade intraepithelial lesions exclusively associated with “low-risk” HPV genotypes 6 and 11. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 133, 2253–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundström, K.; Ploner, A.; Arnheim-Dahlström, L.; Eloranta, S.; Palmgren, J.; Adami, H.O.; Ylitalo Helm, N.; Sparén, P.; Dillner, J. Interactions between high-and low-risk HPV types reduce the risk of squamous cervical cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2015, 107, djv185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huebbers, C.U.; Preuss, S.F.; Kolligs, J.; Vent, J.; Stenner, M.; Wieland, U.; Silling, S.; Drebber, U.; Speel, E.J.; Klussmann, J.P. Integration of HPV6 and downregulation of AKR1C3 expression mark malignant transformation in a patient with juvenile-onset laryngeal papillomatosis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, Q.; Russell, M.; Birch, D.E.; Raymond, J.; Bloch, W. Prevention of pre-PCR mis-priming and primer dimerization improves low-copy-number amplifications. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992, 20, 1717–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachse, K. Specificity and performance of PCR detection assays for microbial pathogens. Mol. Biotechnol. 2004, 26, 61–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruano, G.; Brash, D.E.; Kidd, K.K. PCR: The first few cycles. Amplifiations 1991, 7, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Villalba, A.; van Pelt-Verkuil, E.; Gunst, Q.D.; Ruijter, J.M.; van den Hoff, M.J. Amplification of nonspecific products in quantitative polymerase chain reactions (qPCR). Biomol. Detect. Quantif. 2017, 14, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poritz, M.A.; Ririe, K.M. Getting things backwards to prevent primer dimers. J. Mol. Diagn. 2014, 16, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Huang, J.; Lv, J.; An, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Fan, C.; Hu, J. Nanoparticle PCR: Nanogold-assisted PCR with enhanced specificity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 5100–5103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odelberg, S.J.; Weiss, R.B.; Hata, A.; White, R. Template-switching during DNA synthesis by thermus aquaticus DNA polymerase I. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995, 23, 2049–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trautinger, F.; Jantschitsch, C.; Strohal, R.; Pourmojib, M.; Kindas-Mugge, I. Mispriming and PCR amplification of hsp27. Cell Stress Chaperones 1997, 2, 276–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malgoyre, A.; Banzet, S.; Mouret, C.; Bigard, A.X.; Peinnequin, A. Quantification of low-expressed mRNA using 5′ LNA-containing real-time PCR primers. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 354, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, M.; Maitlan, N.; Scully, C. Human herpes simplex-1 and papillomavirus type 16 homologous DNA sequences in normal, potentially malignant and malignant oral mucosa. Eur. J. Cancer Part B Oral Oncol. 1993, 29, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco, R.; Carrillo-Beltrán, D.; Corvalán, A.H.; Aguayo, F. High-Risk Human Papillomavirus and Epstein–Barr Virus Coinfection: A Potential Role in Head and Neck Carcinogenesis. Biology 2021, 10, 1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Primers | Annealing | Source | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target/Genes | Name | Sequence 3′-5′ | Fragment Size bp | Temperature °C | |
| HSV1/US4(gpG) | F HSV1 | CTGTGGTGTTTTTGGCATCA | 123 | 62 | [29] |
| R HSV1 | GGTTGTGGAGGAGACGTTG | ||||
| HSV2/US6 (gpD) | F HSV2 | CATGGGGCGTTTGACCTC | 249 | 62 | |
| R HSV2 | TACACAGTGATCGGGATGCT | ||||
| BKPyV/BKPyVgp3 | BKV-VP1-F1 | AAACTATTGCCCCAGGAGGT | 1289 | 57 | [30,31] |
| BKV-VP1-R4 | CTAAAACACCACCCCCAAAA | ||||
| BKV-VP1-F4 | CTAATCAAAGAACTGCTCCTCAATG | 1261 | 57 | ||
| BKV-VP1-R8 | ACCACCCCCAAAATAACACA | ||||
| EBV/EBNA-1 | EBV1n | ATCGTGGTCAAGGAGGTTCC | 209 | 53 | [32] |
| EBV2n | ACTCAATGGTGTAAGACGAC | 209 | |||
| EBV3 | AAGGAGGGTGGTTTGGAAAG | 297 | 54 | ||
| EBV4 | AGACAATGGACTCCCTTAGC | 297 | |||
| HPV/E6 and E7 | GP-E6-3F | GGGWGKKACTGAAATCGGT | 630–700 | 55 | [33] |
| GP-E6-5B (R) | CTGAGCTGTCARNTAATTGCTCA | ||||
| GP-E6-6B (R) | TCCTCTGAGTYGYCTAATTGCTC | ||||
| 6/11F | TGCAAGAATGCACTGACCAC | 334 | 56 | [34] | |
| 6/11R | TGCATGTTGTCCAGCAGTGT | ||||
| 42F | CCCAAAGTAGTGGTCCCAGTTA | 277 | |||
| 42R | GATCTTTCGTAGTGTCGCAGTG | ||||
| 43F | GCATAATGTCTGCACGTAGCTG | 219 | |||
| 43R | CATGAAACTGTAGACAGGCCAAG | ||||
| 44F | TAAACAGTTATATGTAGTGTACCG | 163 | |||
| 44R | TATCAGCACGTCCAGAATTGAC | ||||
| Human beta globin | GH20 ** | GAAGAGCCAAGGACAGGTAC | 268 | 52.9–60.3 [33] | [35,36] * |
| PC04 | CAACTTCATCCACGTTCACC | ||||
| Patients | ||
|---|---|---|
| Number | % | |
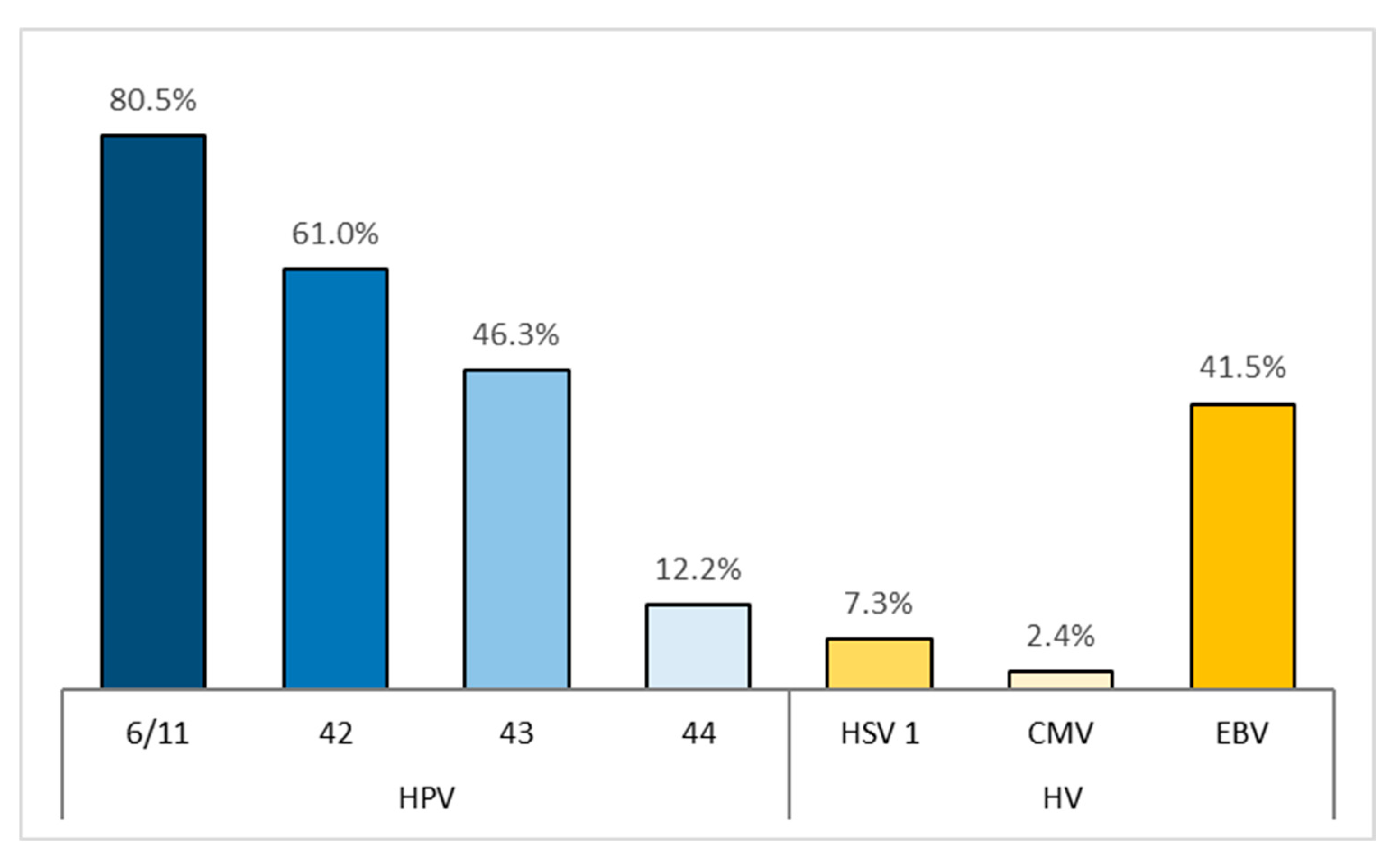
| HPV LR | 36 | 87.8% |
| 6/11 | 33 | 80.5% |
| 42 | 25 | 61.0% |
| 43 | 19 | 46.3% |
| 44 | 5 | 12.2% |
| Number of Genotypes | Patients | |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Samples | % | |
| 4 | 5 | 12.2% |
| 3 | 12 | 29.3% |
| 2 | 7 | 17.1% |
| 1 | 12 | 29.3% |
| 0 | 5 | 12.2% |
| Patients | ||
|---|---|---|
| Number | % | |
| total | 18 | 43.9% |
| HSV 1 | 3 | 7.3% |
| CMV | 1 | 2.4% |
| EBV | 17 | 41.5% |
| Number of Herpes Viruses-HV | Patients | |
|---|---|---|
| Number | % | |
| 3 | 0 | 0% |
| 2 | 3 | 7.3% |
| 1 | 15 | 36.6% |
| 0 | 23 | 56.1% |
| Patients | 95% CI | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Number | % | ||
| HPV LR | 36 | 87.8% | |
| 6/11 | 33 | 80.5% | 66.0, 89.8% |
| 42 | 25 | 61.0% | 45.7, 74.3% |
| 43 | 19 | 46.3% | 32.1, 61.3% |
| 44 | 5 | 12.2% | 5.3, 25.5% |
| HV | 18 | 43.9% | |
| HSV 1 | 3 | 7.3% | 2.5, 19.4% |
| CMV | 1 | 2.4% | 0.4, 12.6% |
| EBV | 17 | 41.5% | 27.8, 56.6% |
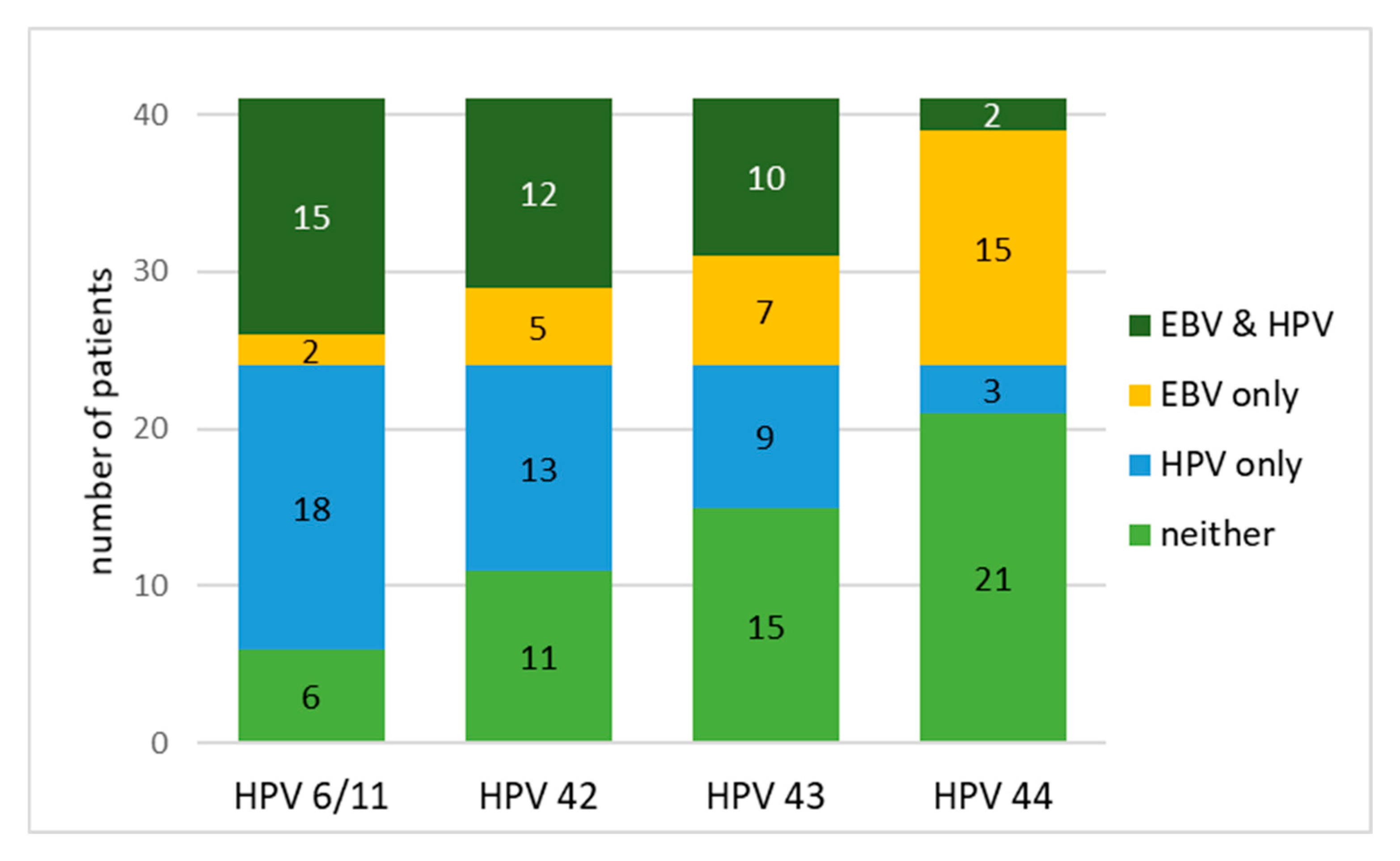
| HPV 6/11 | HPV 42 | HPV 43 | HPV 44 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EBV and HPV | 36.6% | 29.3% | 24.4% | 4.9% |
| EBV only | 4.9% | 12.2% | 17.1% | 36.6% |
| HPV only | 43.9% | 31.7% | 22.0% | 7.3% |
| neither | 14.6% | 26.8% | 36.6% | 51.2% |
| χ2 | 11.3 | 2.72 | 0.06 | 15.4 |
| Adjusted p (Bonferroni) | <0.004 | 0.396 | 1.000 | 0.038 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shishkova, K.; Sirakov, I.; Shishkov, S.; Tasheva-Terzieva, E.; Gergov, S.D.; Tileva, Z.; Dimitrova, R.; Alexiev, I.; Gergova, R. Detection of Viruses with Oncogenic and Oncomodulatory Potential in Head and Neck Tumors—External Auricle. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 2339. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102339
Shishkova K, Sirakov I, Shishkov S, Tasheva-Terzieva E, Gergov SD, Tileva Z, Dimitrova R, Alexiev I, Gergova R. Detection of Viruses with Oncogenic and Oncomodulatory Potential in Head and Neck Tumors—External Auricle. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(10):2339. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102339
Chicago/Turabian StyleShishkova, Kalina, Ivo Sirakov, Stoyan Shishkov, Elena Tasheva-Terzieva, Stefan Dimitrov Gergov, Zornitsa Tileva, Reneta Dimitrova, Ivailo Alexiev, and Raina Gergova. 2025. "Detection of Viruses with Oncogenic and Oncomodulatory Potential in Head and Neck Tumors—External Auricle" Biomedicines 13, no. 10: 2339. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102339
APA StyleShishkova, K., Sirakov, I., Shishkov, S., Tasheva-Terzieva, E., Gergov, S. D., Tileva, Z., Dimitrova, R., Alexiev, I., & Gergova, R. (2025). Detection of Viruses with Oncogenic and Oncomodulatory Potential in Head and Neck Tumors—External Auricle. Biomedicines, 13(10), 2339. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102339









