Causal Relationships Between Environmental Exposures, Iron Metabolism, Hematuria Markers, and Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Investigation Using Mendelian Randomization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
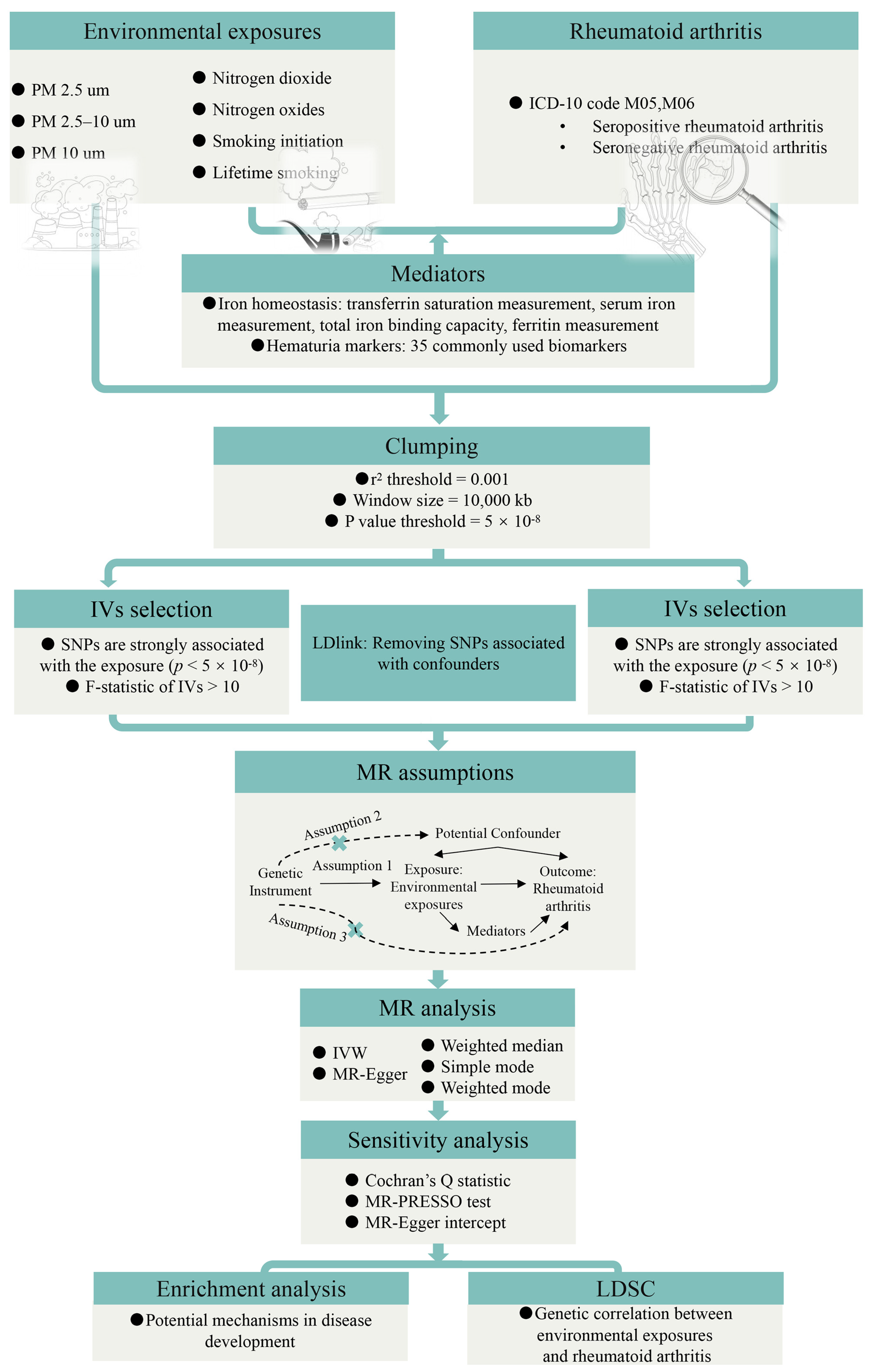
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Genetic Instruments Selection
2.4. MR Analysis
2.5. Enrichment Analysis
2.6. LDSC
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Causal Relationships Between Environmental Exposures and RA
3.1.1. Influence of Environmental Exposures on RA Through Discovery MR
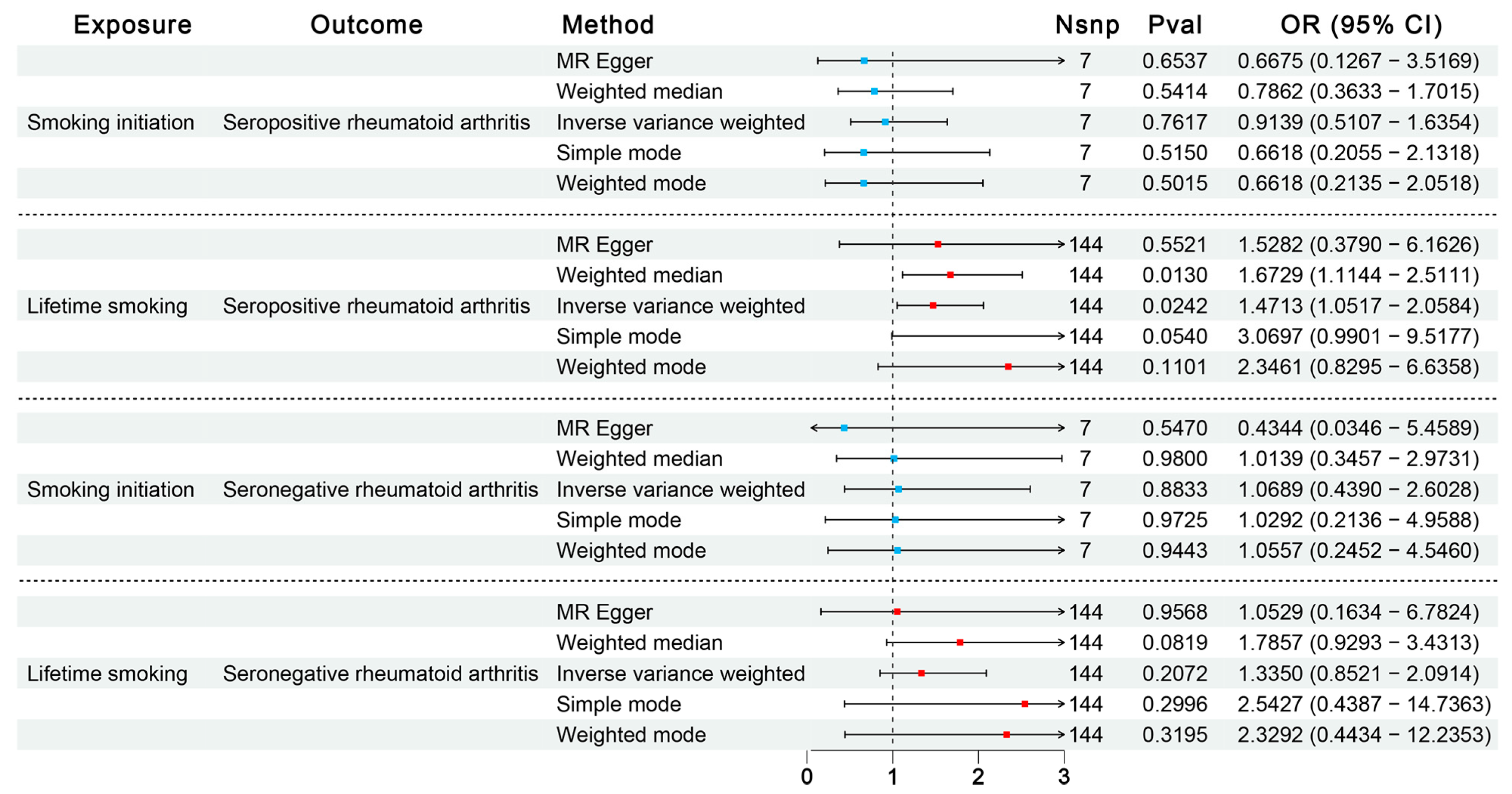
3.1.2. Influence of Smoking on SPRA or SNRA Through Confirmatory MR
3.1.3. Influence of RA on Environmental Exposures
3.2. Two-Step MR Analysis
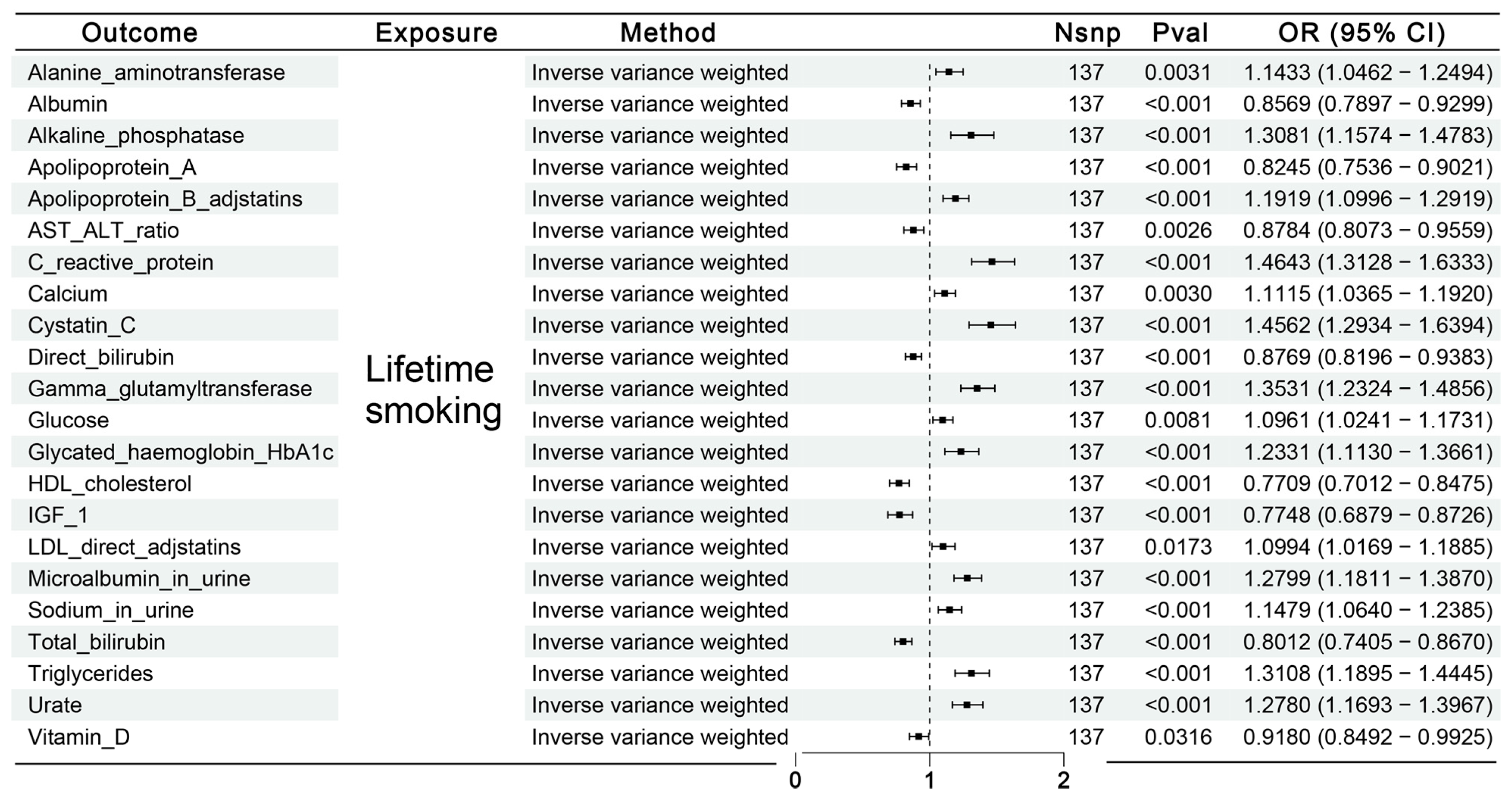
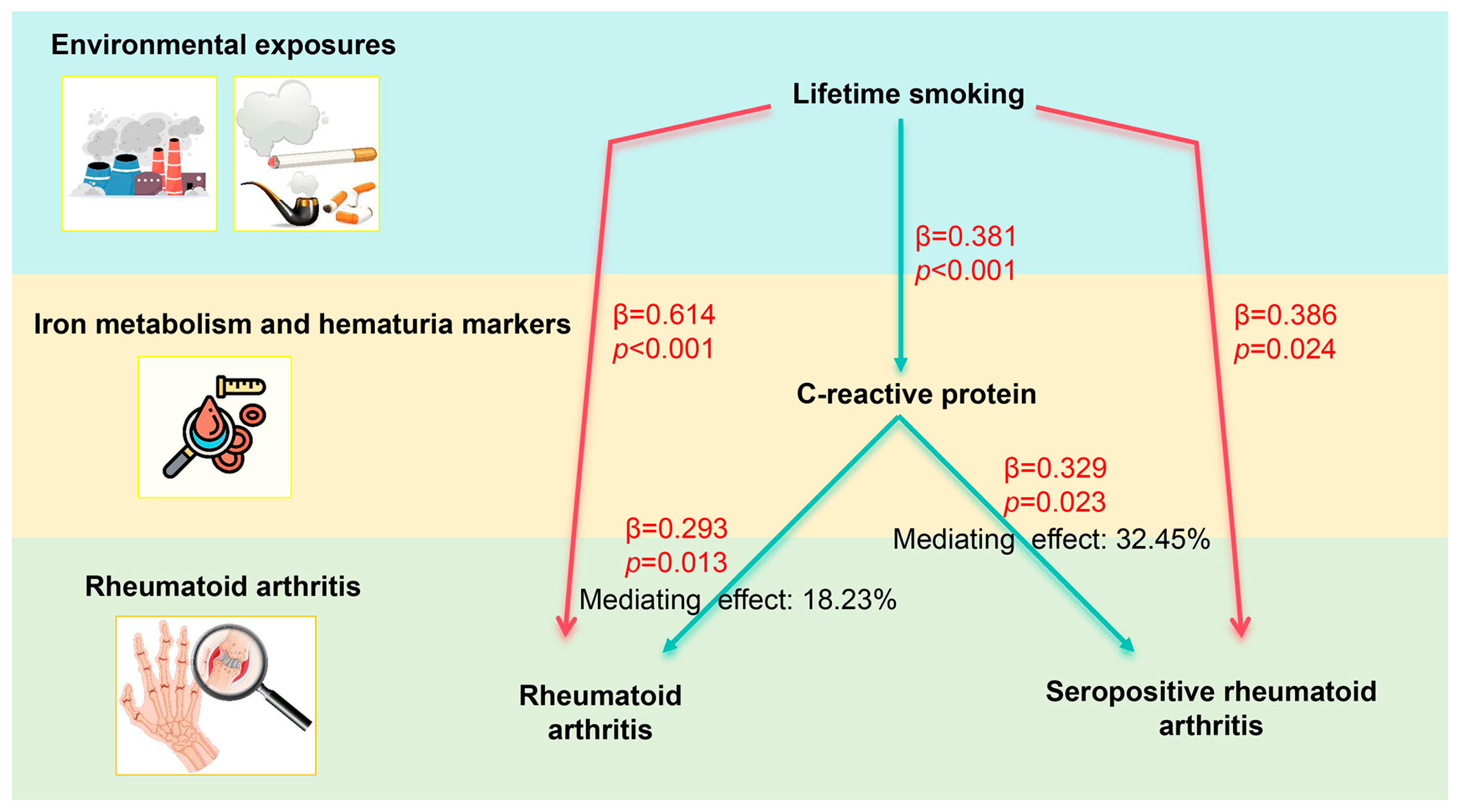
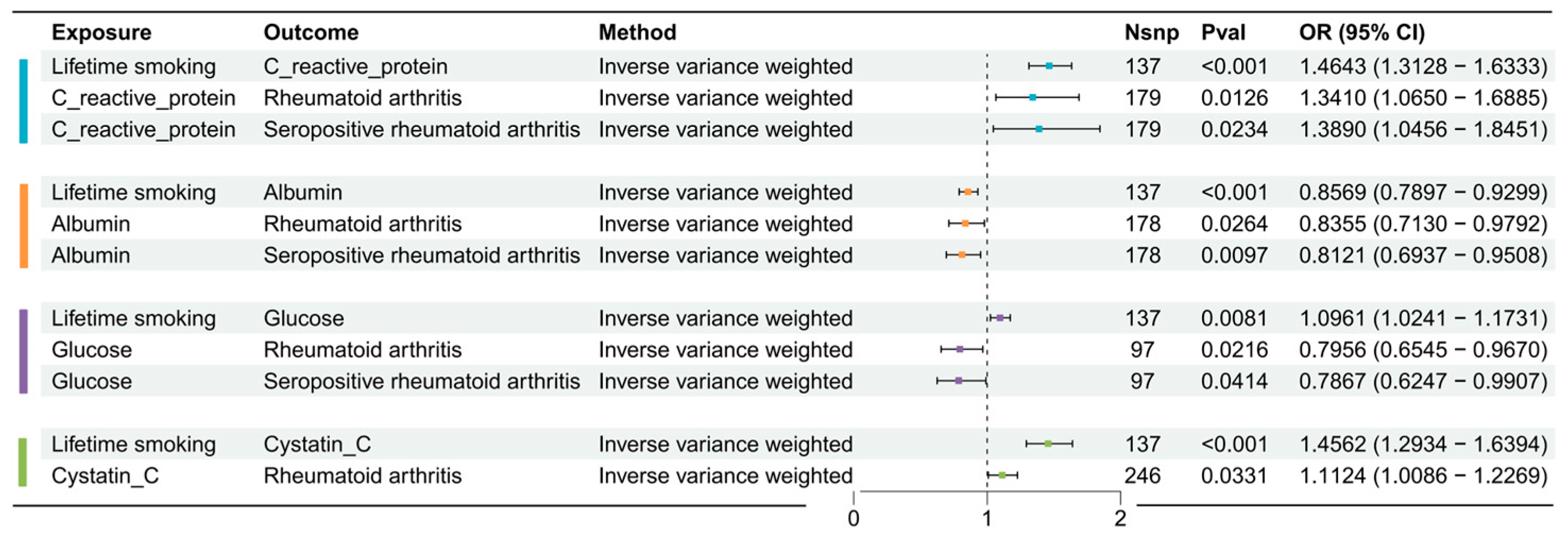
3.2.1. Causal Effects of Lifetime Smoking on Mediator Factors
3.2.2. Causal Effects of Possible Mediator Factors on RA or SPRA
3.2.3. Mediation Proportion
3.3. Results of Enrichment Analysis
3.4. Genetic Correlation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
List of Abbreviations
References
- Di Matteo, A.; Bathon, J.M.; Emery, P. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2023, 402, 2019–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, P.; Pratt, A.G.; Hyrich, K.L. Therapeutic advances in rheumatoid arthritis. BMJ 2024, 384, e070856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finckh, A.; Gilbert, B.; Hodkinson, B.; Bae, S.-C.; Thomas, R.; Deane, K.D.; Alpizar-Rodriguez, D.; Lauper, K. Global epidemiology of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2022, 18, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, G.; Liao, X.; Lin, Z.; Liu, W.; Luo, X.; Zhan, H.; Cai, X. Estimation of the global prevalence, incidence, years lived with disability of rheumatoid arthritis in 2019 and forecasted incidence in 2040: Results from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Clin. Rheumatol. 2023, 42, 2297–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, S.E. The epidemiology of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2001, 27, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safiri, S.; Kolahi, A.A.; Hoy, D.; Smith, E.; Bettampadi, D.; Mansournia, M.A.; Almasi-Hashiani, A.; Ashrafi-Asgarabad, A.; Moradi-Lakeh, M.; Qorbani, M.; et al. Global, regional and national burden of rheumatoid arthritis 1990–2017: A systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease study 2017. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 1463–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, R.J.; Cross, M.; Haile, L.M.; Culbreth, G.T.; Steinmetz, J.D.; Hagins, H.; Kopec, J.A.; Brooks, P.M.; Woolf, A.D.; Liane Ong, K.; et al. Global, regional, and national burden of rheumatoid arthritis, 1990-2020, and projections to 2050: A systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet Rheumatol. 2023, 5, e594–e610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, C.S. Burden of rheumatoid arthritis and forecasted prevalence to 2050. Lancet Rheumatol. 2023, 5, e567–e568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alex, A.M.; Kunkel, G.; Sayles, H.; Arcos, J.D.F.; Mikuls, T.R.; Kerr, G.S. Exposure to ambient air pollution and autoantibody status in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2020, 39, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezuidenhout, J.A.; Pretorius, E. The Central Role of Acute Phase Proteins in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Involvement in Disease Autoimmunity, Inflammatory Responses, and the Heightened Risk of Cardiovascular Disease. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2020, 46, 465–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoovestol, R.A.; Mikuls, T.R. Environmental exposures and rheumatoid arthritis risk. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2011, 13, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, G.G.; Hubbard, J.; Korzenik, J.; Sands, B.E.; Panaccione, R.; Ghosh, S.; Wheeler, A.J.; Villeneuve, P.J. The inflammatory bowel diseases and ambient air pollution: A novel association. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 105, 2412–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, E.C.; Silva, C.A.; Braga, A.L.F.; Sallum, A.M.E.; Campos, L.M.A.; Farhat, S.C.L. Exposure to Air Pollutants and Disease Activity in Juvenile-Onset Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients. Arthritis Care Res. (Hoboken) 2015, 67, 1609–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, J.E.; Laden, F.; Puett, R.C.; Costenbader, K.H.; Karlson, E.W. Exposure to traffic pollution and increased risk of rheumatoid arthritis. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 1065–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Xu, Z.; Dan, Y.-L.; Cheng, J.; Zhao, C.-N.; Mao, Y.-M.; Xiang, K.; Hu, Y.-Q.; He, Y.-S.; Pan, H.-F. Association between traffic-related air pollution and hospital readmissions for rheumatoid arthritis in Hefei, China: A time-series study. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Roos, A.J.; Koehoorn, M.; Tamburic, L.; Davies, H.W.; Brauer, M. Proximity to traffic, ambient air pollution, and community noise in relation to incident rheumatoid arthritis. Environ. Health Perspect. 2014, 122, 1075–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugatti, S.; De Stefano, L.; Gandolfo, S.; Ciccia, F.; Montecucco, C. Autoantibody-negative rheumatoid arthritis: Still a challenge for the rheumatologist. Lancet Rheumatol. 2023, 5, e743–e755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajeganova, S.; Huizinga, T.W. Rheumatoid arthritis: Seronegative and seropositive RA: Alike but different? Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2015, 11, 8–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radu, A.-F.; Bungau, S.G.; Negru, P.A.; Marcu, M.F.; Andronie-Cioara, F.L. In-depth bibliometric analysis and current scientific mapping research in the context of rheumatoid arthritis pharmacotherapy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 154, 113614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radu, A.F.; Bungau, S.G. Nanomedical approaches in the realm of rheumatoid arthritis. Ageing Res. Rev. 2023, 87, 101927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsenault, B.J. From the garden to the clinic: How Mendelian randomization is shaping up atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease prevention strategies. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 4447–4449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulik-Sullivan, B.K.; Loh, P.R.; Finucane, H.K.; Ripke, S.; Yang, J.; Schizophrenia Working Group of the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium; Patterson, N.; Daly, M.J.; Price, A.L.; Neale, B.M. LD Score regression distinguishes confounding from polygenicity in genome-wide association studies. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanski, W.; Chabowski, M.; Jankowska-Polanska, B.; Jankowska, E.A. Iron metabolism in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 25, 4325–4335. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, R.; Shen, J.; Jin, Y.; Chang, C.; Hong, M.; Guo, S.; He, D. Circulating Level of Blood Iron and Copper Associated with Inflammation and Disease Activity of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2023, 201, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Luo, X.; Chen, Y.; Dang, J.; Zeng, D.; Guo, X.; Weng, W.; Zhao, J.; Shi, X.; Chen, J.; et al. Heterogeneous ferroptosis susceptibility of macrophages caused by focal iron overload exacerbates rheumatoid arthritis. Redox Biol. 2024, 69, 103008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, J.E.; Choy, E.H. C-reactive protein and implications in rheumatoid arthritis and associated comorbidities. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2021, 51, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Yang, S.; Han, L.; Ba, X.; Shen, P.; Lin, W.; Li, T.; Zhang, R.; Huang, Y.; Huang, Y.; et al. Dyslipidemia in rheumatoid arthritis: The possible mechanisms. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1254753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudlow, C.; Gallacher, J.; Allen, N.; Beral, V.; Burton, P.; Danesh, J.; Downey, P.; Elliott, P.; Green, J.; Landray, M.; et al. UK biobank: An open access resource for identifying the causes of a wide range of complex diseases of middle and old age. PLoS Med. 2015, 12, e1001779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bycroft, C.; Freeman, C.; Petkova, D.; Band, G.; Elliott, L.T.; Sharp, K.; Motyer, A.; Vukcevic, D.; Delaneau, O.; O’connell, J.; et al. The UK Biobank resource with deep phenotyping and genomic data. Nature 2018, 562, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eeftens, M.; Beelen, R.; De Hoogh, K.; Bellander, T.; Cesaroni, G.; Cirach, M.; Declercq, C.; Dėdelė, A.; Dons, E.; de Nazelle, A.; et al. Development of Land Use Regression models for PM2.5, PM2.5 absorbance, PM10 and PMcoarse in 20 European study areas; results of the ESCAPE project. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 11195–11205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Jiang, Y.; Wedow, R.; Li, Y.; Brazel, D.M.; Chen, F.; Datta, G.; Davila-Velderrain, J.; McGuire, D.; Tian, C.; et al. Association studies of up to 1.2 million individuals yield new insights into the genetic etiology of tobacco and alcohol use. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wootton, R.E.; Richmond, R.C.; Stuijfzand, B.G.; Lawn, R.B.; Sallis, H.M.; Taylor, G.M.J.; Hemani, G.; Jones, H.J.; Zammit, S.; Davey Smith, G.; et al. Evidence for causal effects of lifetime smoking on risk for depression and schizophrenia: A Mendelian randomisation study. Psychol. Med. 2020, 50, 2435–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurki, M.I.; Karjalainen, J.; Palta, P.; Sipilä, T.P.; Kristiansson, K.; Donner, K.; Reeve, M.P.; Laivuori, H.; Aavikko, M.; Kaunisto, M.A.; et al. FinnGen: Unique genetic insights from combining isolated population and national health register data. medRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, S.; Rigas, A.S.; Ferkingstad, E.; Allara, E.; Bjornsdottir, G.; Ramond, A.; Sørensen, E.; Halldorsson, G.H.; Paul, D.S.; Burgdorf, K.S.; et al. A genome-wide meta-analysis yields 46 new loci associating with biomarkers of iron homeostasis. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinnott-Armstrong, N.; Tanigawa, Y.; Amar, D.; Mars, N.; Benner, C.; Aguirre, M.; Venkataraman, G.R.; Wainberg, M.; Ollila, H.M.; Kiiskinen, T.; et al. Genetics of 35 blood and urine biomarkers in the UK Biobank. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.-H.; Brown, D.W.; Machiela, M.J. LDtrait: An Online Tool for Identifying Published Phenotype Associations in Linkage Disequilibrium. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 3443–3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhou, B.; Pache, L.; Chang, M.; Khodabakhshi, A.H.; Tanaseichuk, O.; Benner, C.; Chanda, S.K. Metascape provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of systems-level datasets. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, H.; Fisher, B.A.; Källberg, H.; Plant, D.; Malmström, V.; Rönnelid, J.; Charles, P.; Ding, B.; Alfredsson, L.; Padyukov, L.; et al. Specific interaction between genotype, smoking and autoimmunity to citrullinated alpha-enolase in the etiology of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 1319–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, D.L.; Wolfe, F.; Huizinga, T.W. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2010, 376, 1094–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vittecoq, O.; Richard, L.; Banse, C.; Lequerré, T. The impact of smoking on rheumatoid arthritis outcomes. Jt. Bone Spine 2018, 85, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Stent, S. Smoking’s lasting effect on the immune system. Nature 2024, 626, 724–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Lu, L.; Yang, H.; Wu, X.; Luo, X.; Shen, J.; Xiao, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Du, F.; Chen, Y.; et al. Dysregulation of immunity by cigarette smoking promotes inflammation and cancer: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 339, 122730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radner, H.; Chatzidionysiou, K.; Nikiphorou, E.; Gossec, L.; Hyrich, K.L.; Zabalan, C.; van Eijk-Hustings, Y.; Williamson, P.R.; Balanescu, K.; Burmester, G.R.; et al. 2017 EULAR recommendations for a core data set to support observational research and clinical care in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 476–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Giuseppe, D.; Orsini, N.; Alfredsson, L.; Askling, J.; Wolk, A. Cigarette smoking and smoking cessation in relation to risk of rheumatoid arthritis in women. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2013, 15, R56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Tedeschi, S.K.; Barbhaiya, M.; Leatherwood, C.L.; Speyer, C.B.; Lu, B.; Costenbader, K.H.; Karlson, E.W.; Sparks, J.A. Impact and Timing of Smoking Cessation on Reducing Risk of Rheumatoid Arthritis Among Women in the Nurses’ Health Studies. Arthritis Care Res. (Hoboken) 2019, 71, 914–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedström, A.K.; Rönnelid, J.; Klareskog, L.; Alfredsson, L. Complex Relationships of Smoking, HLA-DRB1 Genes, and Serologic Profiles in Patients With Early Rheumatoid Arthritis: Update From a Swedish Population-Based Case-Control Study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 1504–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saevarsdottir, S.; Wedrén, S.; Seddighzadeh, M.; Bengtsson, C.; Wesley, A.; Lindblad, S.; Askling, J.; Alfredsson, L.; Klareskog, L. Patients with early rheumatoid arthritis who smoke are less likely to respond to treatment with methotrexate and tumor necrosis factor inhibitors: Observations from the Epidemiological Investigation of Rheumatoid Arthritis and the Swedish Rheumatology Register cohorts. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 26–36. [Google Scholar]
- Gianfrancesco, M.A.; Trupin, L.; Shiboski, S.; van der Laan, M.; Graf, J.; Imboden, J.; Yazdany, J.; Schmajuk, G. Smoking Is Associated with Higher Disease Activity in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Longitudinal Study Controlling for Time-varying Covariates. J. Rheumatol. 2019, 46, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Fu, J.; Liu, J.; Wu, X.; Zheng, X.; Wang, S. Association between secondhand smoke exposure and rheumatoid arthritis in US never-smoking adults: A cross-sectional study from NHANES. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 11061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.; Rosen, L.V.; Mulroy, N.M.; Qian, Y.; Shebl, F.M.; Becker, J.E.; Hyle, E.P.; Levy, D.E.; Reddy, K.P. Disparities in tobacco smoking and risk of cardiovascular disease in people with low socioeconomic status or serious psychological distress: A simulation analysis. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2024, 68, 402–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saevarsdottir, S.; Rezaei, H.; Geborek, P.; Petersson, I.; Ernestam, S.; Albertsson, K.; Forslind, K.; van Vollenhoven, R.F. Current smoking status is a strong predictor of radiographic progression in early rheumatoid arthritis: Results from the SWEFOT trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 1509–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christofaro, D.G.D.; Ritti-Dias, R.M.; Tebar, W.R.; Werneck, A.O.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Cucato, G.G.; Santos, R.D. Are C-reactive protein concentrations affected by smoking status and physical activity levels? A longitudinal study. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0293453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, M.E.; Hornick, M.G.; Stefanski, A.; Albanna, H.R.; Gjoni, A.; Hall, G.D.; Hart, P.C.; Rajab, I.M.; Potempa, L.A. A biofunctional review of C-reactive protein (CRP) as a mediator of inflammatory and immune responses: Differentiating pentameric and modified CRP isoform effects. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1264383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, Y.Y.; Yao, Y.M. The Clinical Significance and Potential Role of C-Reactive Protein in Chronic Inflammatory and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizo-Tellez, S.A.; Sekheri, M.; Filep, J.G. C-reactive protein: A target for therapy to reduce inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1237729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciurtin, C.; Helmy, G.A.; Ferreira, A.C.; Manson, J.J.; Jury, E.C.; McDonnell, T. A tale of two functions: C-reactive protein complement-ary structures and their role in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Immunol. 2024, 265, 110281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erre, G.L.; Cacciapaglia, F.; Sakellariou, G.; Manfredi, A.; Bartoloni, E.; Viapiana, O.; Fornaro, M.; Cauli, A.; Mangoni, A.A.; Woodman, R.J.; et al. C-reactive protein and 10-year cardiovascular risk in rheumatoid arthritis. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2022, 104, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suter, T.; Jaworski, A. Cell migration and axon guidance at the border between central and peripheral nervous system. Science 2019, 365, eaaw8231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasterkamp, R.J.; Kolodkin, A.L. SnapShot: Axon Guidance. Cell 2013, 153, 494–494e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Hu, Z.; Wang, S.; Yin, K. Netrin-1: An emerging player in inflammatory diseases. Cytokine Growth Factor. Rev. 2022, 64, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadasz, Z.; Toubi, E. Semaphorin3A: A potential therapeutic tool in immune-mediated diseases. Eur. J. Rheumatol. 2018, 5, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Xu, J.; Sui, J.; Dai, H. Expressions of Peptidoglycan Recognition Protein 1, Neuron Towards Axon Guidance Factor-1 and miR-142-3p and Their Correlations in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2023, 16, 3457–3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.; Ma, X.-X.; Guo, Q.; Xie, L.-F.; Zhong, Y.-C.; Zhang, X.-W. Expression of circulating Semaphorin3A and its association with inflammation and bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 37, 2073–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Wei, P.; Duell, E.J.; Risch, H.A.; Olson, S.H.; Bueno-De-Mesquita, H.B.; Gallinger, S.; Holly, E.A.; Petersen, G.; Bracci, P.M.; et al. Axonal guidance signaling pathway interacting with smoking in modifying the risk of pancreatic cancer: A gene- and pathway-based interaction analysis of GWAS data. Carcinogenesis 2014, 35, 1039–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrivankova, V.W.; Richmond, R.C.; Woolf, B.A.R.; Yarmolinsky, J.; Davies, N.M.; Swanson, S.A.; VanderWeele, T.J.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Timpson, N.J.; Dimou, N.; et al. Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology using Mendelian Randomization (STROBE-MR) Statement. JAMA 2021, 326, 1614–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrivankova, V.W.; Richmond, R.C.; Woolf, B.A.R.; Davies, N.M.; Swanson, S.A.; VanderWeele, T.J.; Timpson, N.J.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Dimou, N.; Langenberg, C.; et al. Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology using Mendelian Randomisation (STROBE-MR): Explanation and Elaboration. BMJ 2021, 375, n2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Trait1 | Trait2 | Genetic Correlation | SE | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lifetime smoking | RA | 0.1581 | 0.0361 | 1.22 × 10−5 |
| Smoking initiation | RA | 0.2106 | 0.0533 | 7.82 × 10−5 |
| PM 2.5 μm | RA | 0.0177 | 0.0681 | 0.7954 |
| PM 2.5–10 μm | RA | −0.0029 | 0.1722 | 0.9865 |
| PM 10 μm | RA | −0.0528 | 0.0691 | 0.4445 |
| Nitrogen oxides | RA | 0.0218 | 0.0667 | 0.7443 |
| Nitrogen dioxide | RA | −0.0980 | 0.0623 | 0.1157 |
| Lifetime smoking | SPRA | 0.1039 | 0.0377 | 0.0058 |
| Smoking initiation | SPRA | 0.1454 | 0.0558 | 0.0092 |
| PM 2.5 μm | SPRA | 0.0746 | 0.0659 | 0.2573 |
| PM 2.5–10 μm | SPRA | 0.1331 | 0.1785 | 0.4559 |
| PM 10 μm | SPRA | 0.0169 | 0.0747 | 0.8213 |
| Nitrogen oxides | SPRA | 0.0695 | 0.0653 | 0.2877 |
| Nitrogen dioxide | SPRA | −0.0066 | 0.0642 | 0.9176 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.; Xie, W.; Wang, C.; Zhu, Y.; Zhong, D. Causal Relationships Between Environmental Exposures, Iron Metabolism, Hematuria Markers, and Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Investigation Using Mendelian Randomization. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13020513
Wang C, Xie W, Wang C, Zhu Y, Zhong D. Causal Relationships Between Environmental Exposures, Iron Metabolism, Hematuria Markers, and Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Investigation Using Mendelian Randomization. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(2):513. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13020513
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Chao, Wenqing Xie, Chenggong Wang, Yong Zhu, and Da Zhong. 2025. "Causal Relationships Between Environmental Exposures, Iron Metabolism, Hematuria Markers, and Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Investigation Using Mendelian Randomization" Biomedicines 13, no. 2: 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13020513
APA StyleWang, C., Xie, W., Wang, C., Zhu, Y., & Zhong, D. (2025). Causal Relationships Between Environmental Exposures, Iron Metabolism, Hematuria Markers, and Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Investigation Using Mendelian Randomization. Biomedicines, 13(2), 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13020513







