The Genetic Mechanisms and Pathology of Atrial Fibrillation: A Narrative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
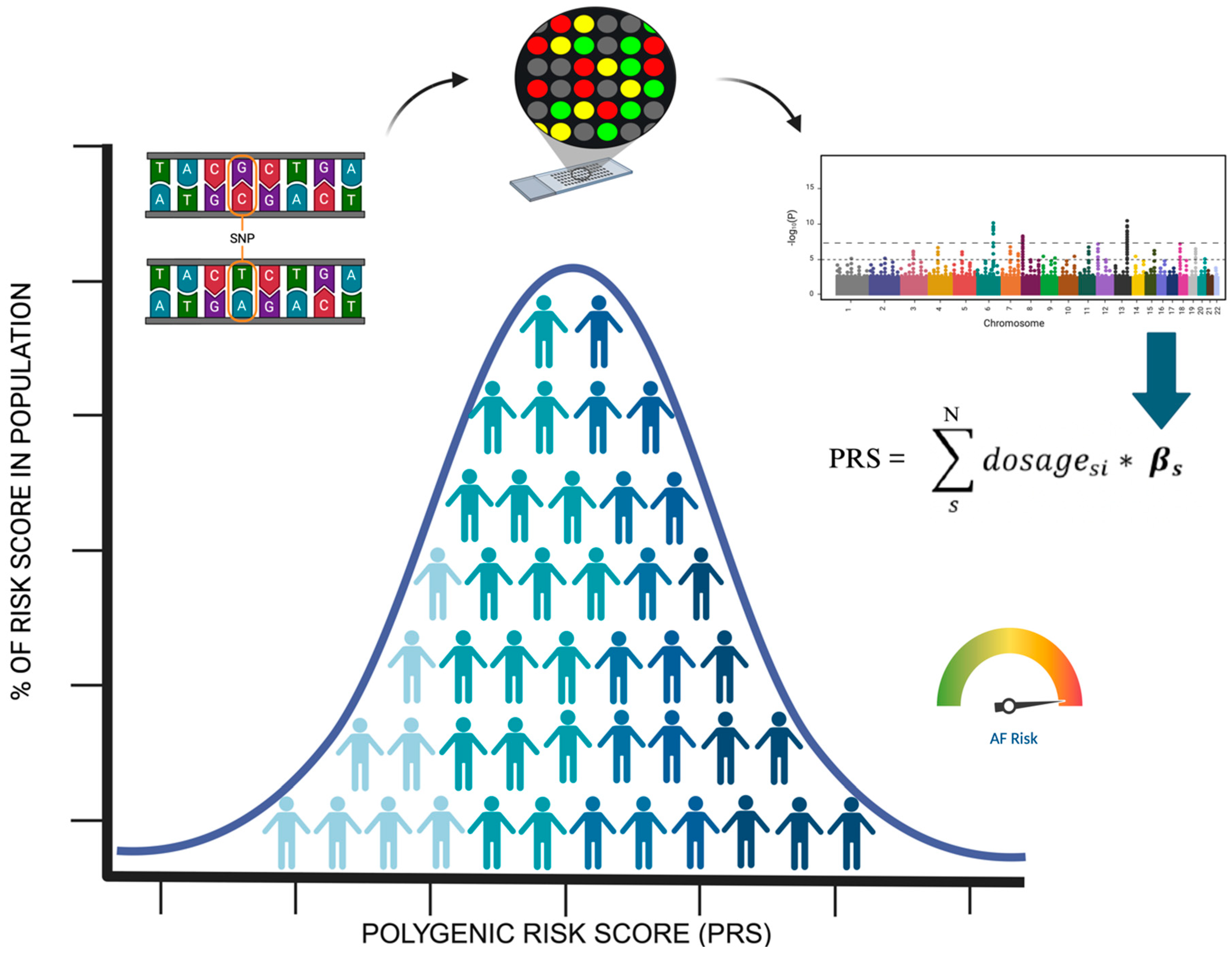
2. Genetic AF Background: Monogenic and Polygenic Contributors to AF Risk, Analysis Techniques, and Polygenic Risk Score
| Gene | Locus | Mode of Inheritance | Functional Effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| KCNQ1 | 11p15.5 | Autosomal dominant | Gain of function |
| KCNE1 | 21q22.1 | Autosomal dominant | Gain of function |
| KCNE2 | 21q22.1 | Autosomal dominant | Gain of function |
| KCNE3 | 11q13.4 | Autosomal dominant | Gain of function |
| KCNE5 | Xq23 | X-linked | Gain of function |
| KCNJ2 | 17Q23.1 | Autosomal dominant | Gain of function |
| KCNJ5 | 11q24.3 | Autosomal dominant | Gain of function |
| KCNJ8 | 12p12.1 | Autosomal dominant | Gain of function |
| KCNH2 | 7q36.1 | Autosomal dominant | Gain of function, Loss of function |
| KCNA5 | 12p13.32 | Autosomal dominant | Gain of function, Loss of function |
| KCND3 | 1p13.2 | Autosomal dominant | Gain of function |
| HCN4 | 15q24.1 | Autosomal dominant | Loss of function |
| MYH6 | 14q11.2 | Autosomal dominant | Loss of function |
| ABCC9 | 12p12.1 | Autosomal dominant | Loss of function |
| RYR2 | 1q43 | Autosomal dominant | Gain of function |
| CACNB2 | 10p12 | Autosomal dominant | Loss of function |
| CACNA2D4 | 12p13.33 | Autosomal dominant | Loss of function |
| CAV1 | 7q31.2 | Autosomal dominant | Loss of function |
| SCN1B | 19q13.11 | Autosomal dominant | Gain of function, Loss of function |
| SCN2B | 11q23.3 | Autosomal dominant | Loss of function |
| SCN3B | 11q24.1 | Autosomal dominant | Loss of function |
| SCN4B | 11q23.3 | Autosomal dominant | Loss of function |
| SCN5A | 3p22.2 | Autosomal dominant | Gain of function, Loss of function |
| SCN10A | 3p22.2 | Autosomal dominant | Gain of function, Loss of function |
| GATA4 | 8p23.1 | Autosomal dominant | Loss of function |
| GATA5 | 20q13.33 | Autosomal dominant | Loss of function |
| GATA6 | 18q11.2 | Autosomal dominant | Loss of function |
| GJA1 | 6q22.31 | Autosomal dominant | Loss of function |
| ZFHX3 | 16q22.2-q22.3 | Autosomal dominant | Loss of function |
| GREM2 | 1q43 | Autosomal dominant | Gain of function |
| JPH2 | 20q13.12 | Autosomal dominant | Loss of function |
| LMNA | 1q22 | Autosomal dominant | N/A |
| NUP155 | 5p13.2 | Autosomal dominant | Loss of function |
| SYNE2 | 14q23.2 | Autosomal dominant | N/A |
| NKX2-5 | 5q34 | Autosomal dominant | Loss of function |
| NKX2-6 | 8p21.2 | Autosomal dominant | Loss of function |
| NPPA | 1p36.22 | Autosomal dominant | Loss of function |
| PITX2c | 4q25 | Autosomal dominant | Loss of function |
3. Pathophysiology of AF: Balance of Triggers, Drivers, and Substrate
4. Perpetuators of AF Maintenance
5. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chugh, S.S.; Havmoeller, R.; Narayanan, K.; Singh, D.; Rienstra, M.; Benjamin, E.J.; Gillum, R.F.; Kim, Y.-H.; McAnulty, J.H., Jr.; Zheng, Z.-J.; et al. Worldwide Epidemiology of Atrial Fibrillation: A Global Burden of Disease 2010 Study. Circulation 2014, 129, 837–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, W.; Swann, P. Lone Auricular Fibrillation. Heart 1954, 16, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pison, L.; Hocini, M.; Potpara, T.S.; Todd, D.; Chen, J.; Blomstrom-Lundqvist, C.; Bongiorni, M.G.; Proclemer, A.; Dagres, N.; Estner, H.; et al. Work-up and management of lone atrial fibrillation: Results of the European Heart Rhythm Association Survey. Europace 2014, 16, 1521–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Fox, C.S.; Parise, H.; D'Agostino, S.R.B.; Lloyd-Jones, D.M.; Vasan, R.S.; Wang, T.J.; Levy, D.; Wolf, P.A.; Benjamin, E.J. Parental Atrial Fibrillation as a Risk Factor for Atrial Fibrillation in Offspring. JAMA 2004, 291, 2851–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darbar, D.; Herron, K.J.; Ballew, J.D.; Jahangir, A.; Gersh, B.J.; Shen, W.-K.; Hammill, S.C.; Packer, D.L.; Olson, T.M. Familial atrial fibrillation is a genetically heterogeneous disorder. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2003, 41, 2185–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnar, D.O.; Thorvaldsson, S.; Manolio, T.A.; Thorgeirsson, G.; Kristjansson, K.; Hakonarson, H.; Stefansson, K. Familial aggregation of atrial fibrillation in Iceland. Eur. Hear. J. 2006, 27, 708–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christophersen, I.E.; Ravn, L.S.; Budtz-Joergensen, E.; Skytthe, A.; Haunsoe, S.; Svendsen, J.H.; Christensen, K. Familial Aggregation of Atrial Fibrillation: A study in Danish twins. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2009, 2, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-H.; Xu, S.-J.; Bendahhou, S.; Wang, X.-L.; Wang, Y.; Xu, W.-Y.; Jin, H.-W.; Sun, H.; Su, X.-Y.; Zhuang, Q.-N.; et al. KCNQ1 Gain-of-Function Mutation in Familial Atrial Fibrillation. Science 2003, 299, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragab, A.A.Y.; Sitorus, G.D.S.; Brundel, B.B.J.J.M.; De Groot, N.M.S. The Genetic Puzzle of Familial Atrial Fibrillation. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Makino, S.; Melman, Y.F.; Shea, M.A.; Goyal, S.B.; Rosenzweig, A.; MacRae, C.A.; Ellinor, P.T. Mutation in the S3 segment of KCNQ1 results in familial lone atrial fibrillation. Hear. Rhythm. 2009, 6, 1146–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olesen, M.S.; Bentzen, B.H.; Nielsen, J.B.; Steffensen, A.B.; David, J.-P.; Jabbari, J.; Jensen, H.K.; Haunsø, S.; Svendsen, J.H.; Schmitt, N. Mutations in the potassium channel subunit KCNE1 are associated with early-onset familial atrial fibrillation. BMC Med. Genet. 2012, 13, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Lin, X.; Yang, Y.; Hong, K.; Wang, L.; Liu, J.; Li, L.; Yan, D.; Liang, D.; et al. Novel KCNA5 loss-of-function mutations responsible for atrial fibrillation. J. Hum. Genet. 2009, 54, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravn, L.S.; Aizawa, Y.; Pollevick, G.D.; Hofman-Bang, J.; Cordeiro, J.M.; Dixen, U.; Jensen, G.; Wu, Y.; Burashnikov, E.; Haunso, S.; et al. Gain of function in IKs secondary to a mutation in KCNE5 associated with atrial fibrillation. Hear. Rhythm. 2008, 5, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattori, T.; Makiyama, T.; Akao, M.; Ehara, E.; Ohno, S.; Iguchi, M.; Nishio, Y.; Sasaki, K.; Itoh, H.; Yokode, M.; et al. A novel gain-of-function KCNJ2 mutation associated with short-QT syndrome impairs inward rectification of Kir2.1 currents. Cardiovasc. Res. 2011, 93, 666–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaney, J.T.; Muhammad, R.; Blair, M.A.; Kor, K.; Fish, F.A.; Roden, D.M.; Darbar, D. A KCNJ8 mutation associated with early repolarization and atrial fibrillation. Europace 2012, 14, 1428–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundby, A.; Ravn, L.S.; Svendsen, J.H.; Haunsø, S.; Olesen, S.-P.; Schmitt, N. KCNE3 Mutation V17M Identified in a Patient with Lone Atrial Fibrillation. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2008, 21, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, N.; Asano, Y.; Fujita, M.; Yamazaki, S.; Inanobe, A.; Matsuura, N.; Kobayashi, H.; Ohno, S.; Ebana, Y.; Tsukamoto, O.; et al. Mutant KCNJ3 and KCNJ5 Potassium Channels as Novel Molecular Targets in Bradyarrhythmias and Atrial Fibrillation. Circulation 2019, 139, 2157–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darbar, D.; Kannankeril, P.J.; Donahue, B.S.; Kucera, G.; Stubblefield, T.; Haines, J.L.; George, A.L.; Roden, D.M. Cardiac Sodium Channel (SCN5A) Variants Associated with Atrial Fibrillation. Circulation 2008, 117, 1927–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, T.M.; Michels, V.V.; Ballew, J.D.; Reyna, S.P.; Karst, M.L.; Herron, K.J.; Horton, S.C.; Rodeheffer, R.J.; Anderson, J.L. Sodium Channel Mutations and Susceptibility to Heart Failure and Atrial Fibrillation. JAMA 2005, 293, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makiyama, T.; Akao, M.; Shizuta, S.; Doi, T.; Nishiyama, K.; Oka, Y.; Ohno, S.; Nishio, Y.; Tsuji, K.; Itoh, H.; et al. A Novel SCN5A Gain-of-Function Mutation M1875T Associated With Familial Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 52, 1326–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Atack, T.C.; Stroud, D.M.; Zhang, W.; Hall, L.; Roden, D.M. Blocking Scn10a Channels in Heart Reduces Late Sodium Current and Is Antiarrhythmic. Circ. Res. 2012, 111, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gollob, M.H.; Jones, D.L.; Krahn, A.D.; Danis, L.; Gong, X.-Q.; Shao, Q.; Liu, X.; Veinot, J.P.; Tang, A.S.; Stewart, A.F.; et al. Somatic Mutations in the Connexin 40 Gene (GJA5) in Atrial Fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 2677–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christophersen, I.E.; Holmegard, H.N.; Jabbari, J.; Haunsø, S.; Tveit, A.; Svendsen, J.H.; Olesen, M.S. Rare Variants in GJA5 Are Associated With Early-Onset Lone Atrial Fibrillation. Can. J. Cardiol. 2012, 29, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.-Q.; Wang, M.-Y.; Zhang, X.-L.; Tan, H.-W.; Shi, H.-F.; Jiang, W.-F.; Wang, X.-H.; Fang, W.-Y.; Liu, X. GATA4 loss-of-function mutations in familial atrial fibrillation. Clin. Chim. Acta 2011, 412, 1825–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.-H.; Huang, C.-X.; Wang, Q.; Li, R.-G.; Xu, Y.-J.; Liu, X.; Fang, W.-Y.; Yang, Y.-Q. A novel GATA5 loss-of-function mutation underlies lone atrial fibrillation. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2012, 31, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, W.-D.; Yang, Z.-L.; Yang, Y.-Q. Novel GATA6 loss-of-function mutation responsible for familial atrial fibrillation. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2012, 30, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yuan, F.; Qiu, X.-B.; Li, R.-G.; Qu, X.-K.; Wang, J.; Xu, Y.-J.; Liu, X.; Fang, W.-Y.; Yang, Y.-Q.; Liao, D.-N. A novel NKX2-5 loss-of-function mutation predisposes to familial dilated cardiomyopathy and arrhythmias. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 35, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Xu, C.; Zhan, C.; Yang, Y.; Shi, L.; Wang, F.; Wang, C.; Xia, Y.; Yang, B.; Wu, G.; et al. Identification of NPPA variants associated with atrial fibrillation in a Chinese GeneID population. Clin. Chim. Acta 2010, 411, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudbjartsson, D.F.; Arnar, D.O.; Helgadottir, A.; Gretarsdottir, S.; Holm, H.; Sigurdsson, A.; Jonasdottir, A.; Baker, A.; Thorleifsson, G.; Kristjansson, K.; et al. Variants conferring risk of atrial fibrillation on chromosome 4q25. Nature 2007, 448, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellinor, P.T.; Lunetta, K.L.; Albert, C.M.; Glazer, N.L.; Ritchie, M.D.; Smith, A.V.; Arking, D.E.; Müller-Nurasyid, M.; Krijthe, B.P.; Lubitz, S.A.; et al. Meta-analysis identifies six new susceptibility loci for atrial fibrillation. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudbjartsson, D.F.; Holm, H.; Gretarsdottir, S.; Thorleifsson, G.; Walters, G.B.; Thorgeirsson, G.; Gulcher, J.; Mathiesen, E.B.; Njølstad, I.; Nyrnes, A.; et al. A sequence variant in ZFHX3 on 16q22 associates with atrial fibrillation and ischemic stroke. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 876–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinner, M.F.; Tucker, N.R.; Lunetta, K.L.; Ozaki, K.; Smith, J.D.; Trompet, S.; Bis, J.C.; Lin, H.; Chung, M.K.; Nielsen, J.B.; et al. Integrating Genetic, Transcriptional, and Functional Analyses to Identify 5 Novel Genes for Atrial Fibrillation. Circulation 2014, 130, 1225–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- E Christophersen, I.; Rienstra, M.; Roselli, C.; Yin, X.; Geelhoed, B.; Barnard, J.; Lin, H.; E Arking, D.; Smith, A.V.; Albert, C.M.; et al. Large-scale analyses of common and rare variants identify 12 new loci associated with atrial fibrillation. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 946–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assum, I.; Krause, J.; Scheinhardt, M.O.; Müller, C.; Hammer, E.; Börschel, C.S.; Völker, U.; Conradi, L.; Geelhoed, B.; Zeller, T.; et al. Tissue-specific multi-omics analysis of atrial fibrillation. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, J.; Gore-Panter, S.; Tchou, G.; Castel, L.; Lovano, B.; Moravec, C.S.; Pettersson, G.B.; Roselli, E.E.; Gillinov, A.M.; McCurry, K.R.; et al. Genetic Control of Left Atrial Gene Expression Yields Insights into the Genetic Susceptibility for Atrial Fibrillation. Circ. Genom. Precis. Med. 2018, 11, e002107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roselli, C.; Chaffin, M.D.; Weng, L.-C.; Aeschbacher, S.; Ahlberg, G.; Albert, C.M.; Almgren, P.; Alonso, A.; Anderson, C.D.; Aragam, K.G.; et al. Multi-ethnic genome-wide association study for atrial fibrillation. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 1225–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, J.B.; Thorolfsdottir, R.B.; Fritsche, L.G.; Zhou, W.; Skov, M.W.; Graham, S.E.; Herron, T.J.; McCarthy, S.; Schmidt, E.M.; Sveinbjornsson, G.; et al. Biobank-driven genomic discovery yields new insight into atrial fibrillation biology. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 1234–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roselli, C.; Rienstra, M.; Ellinor, P.T. Genetics of Atrial Fibrillation in 2020. Circ. Res. 2020, 127, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khera, A.V.; Chaffin, M.; Aragam, K.G.; Haas, M.E.; Roselli, C.; Choi, S.H.; Natarajan, P.; Lander, E.S.; Lubitz, S.A.; Ellinor, P.T.; et al. Genome-wide polygenic scores for common diseases identify individuals with risk equivalent to monogenic mutations. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 1219–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, L.-C.; Preis, S.R.; Hulme, O.L.; Larson, M.G.; Choi, S.H.; Wang, B.; Trinquart, L.; McManus, D.D.; Staerk, L.; Lin, H.; et al. Genetic Predisposition, Clinical Risk Factor Burden, and Lifetime Risk of Atrial Fibrillation. Circulation 2018, 137, 1027–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchhof, P.; Benussi, S.; Kotecha, D.; Ahlsson, A.; Atar, D.; Casadei, B.; Castella, M.; Diener, H.-C.; Heidbuchel, H.; Hendriks, J.; et al. 2016 ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with EACTS. Eur. J. Cardio-Thoracic Surg. 2016, 50, e1–e88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilde, A.A.; Semsarian, C.; Márquez, M.F.; Shamloo, A.S.; Ackerman, M.J.; Ashley, E.A.; Sternick, E.B.; Barajas-Martinez, H.; Behr, E.R.; Bezzina, C.R.; et al. European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA)/Heart Rhythm Society (HRS)/Asia Pacific Heart Rhythm Society (APHRS)/Latin American Heart Rhythm Society (LAHRS) Expert Consensus Statement on the State of Genetic Testing for Cardiac Diseases. Hear. Rhythm. 2022, 19, e1–e60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parvez, B.; Chopra, N.; Rowan, S.; Vaglio, J.C.; Muhammad, R.; Roden, D.M.; Darbar, D. A Common β1-Adrenergic Receptor Polymorphism Predicts Favorable Response to Rate-Control Therapy in Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2012, 59, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parvez, B.; Vaglio, J.; Rowan, S.; Muhammad, R.; Kucera, G.; Stubblefield, T.; Carter, S.; Roden, D.; Darbar, D. Symptomatic Response to Antiarrhythmic Drug Therapy Is Modulated by a Common Single Nucleotide Polymorphism in Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2012, 60, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoemaker, M.B.; Bollmann, A.; Lubitz, S.A.; Ueberham, L.; Saini, H.; Montgomery, J.; Edwards, T.; Yoneda, Z.; Sinner, M.F.; Arya, A.; et al. Common Genetic Variants and Response to Atrial Fibrillation Ablation. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2015, 8, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nia, A.M.; Caglayan, E.; Gassanov, N.; Zimmermann, T.; Aslan, O.; Hellmich, M.; Duru, F.; Erdmann, E.; Rosenkranz, S.; Er, F. Beta1-Adrenoceptor Polymorphism Predicts Flecainide Action in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haïssaguerre, M.; Jaïs, P.; Shah, D.C.; Takahashi, A.; Hocini, M.; Quiniou, G.; Garrigue, S.; Le Mouroux, A.; Le Métayer, P.; Clémenty, J. Spontaneous Initiation of Atrial Fibrillation by Ectopic Beats Originating in the Pulmonary Veins. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briceño, D.F.; Patel, K.; Romero, J.; Alviz, I.; Tarantino, N.; Della Rocca, D.G.; Natale, V.; Zhang, X.-D.; Di Biase, L. Beyond Pulmonary Vein Isolation in Nonparoxysmal Atrial Fibrillation: Posterior Wall, Vein of Marshall, Cor-onary Sinus, Superior Vena Cava, and Left Atrial Appendage. Card. Electrophysiol. Clin. 2020, 12, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, Y.-K.; Nishida, K.; Kato, T.; Nattel, S. Atrial Fibrillation Pathophysiology: Implications for management. Circulation 2011, 124, 2264–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’reilly, M.; Sommerfeld, L.C.; O’shea, C.; Broadway-Stringer, S.; Andaleeb, S.; Reyat, J.S.; Kabir, S.N.; Stastny, D.; Malinova, A.; Delbue, D.; et al. Familial atrial fibrillation mutation M1875T-SCN5A increases early sodium current and dampens the effect of flecainide. Europace 2022, 25, 1152–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgson-Zingman, D.M.; Karst, M.L.; Zingman, L.V.; Heublein, D.M.; Darbar, D.; Herron, K.J.; Ballew, J.D.; de Andrade, M.; Burnett, J.C.J.; Olson, T.M. Atrial Natriuretic Peptide Frameshift Mutation in Familial Atrial Fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Klysik, E.; Sood, S.; Johnson, R.L.; Wehrens, X.H.T.; Martin, J.F. Pitx2 prevents susceptibility to atrial arrhythmias by inhibiting left-sided pacemaker specification. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 9753–9758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavone, M.; Gasperetti, A.; Montemerlo, E.; Pozzi, M.; Sabato, F.; Piazzi, E.; Ruggiero, D.; De Ceglia, S.; Viecca, M.; Calkins, H.; et al. Long-term comparisons of atrial fibrillation ablation outcomes with a cryoballoon or laser-balloon: A propensity-matched analysis based on continuous rhythm monitoring. Hell. J. Cardiol. 2022, 65, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavone, M.; Solimene, F.; Moltrasio, M.; Casella, M.; Bianchi, S.; Iacopino, S.; Rossillo, A.; Schillaci, V.; Fassini, G.; Compagnucci, P.; et al. Pulsed field ablation technology for pulmonary vein and left atrial posterior wall isolation in patients with persistent atrial fibrillation. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2024, 35, 1101–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Jiang, C.-Y.; Betts, T.R.; Chen, J.; Deisenhofer, I.; Mantovan, R.; Macle, L.; Morillo, C.A.; Haverkamp, W.; Weerasooriya, R.; et al. Approaches to Catheter Ablation for Persistent Atrial Fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1812–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianchini, L.; Schiavone, M.; Vettor, G.; Gasperetti, A.; Penza, E.; Ballotta, A.; Pirola, S.; Brambillasca, C.; Zito, E.; De Lio, F.; et al. Hybrid-Convergent Procedure or Pulsed Field Ablation in Long-Standing Persistent Atrial Fibrillation. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2024, 10 Pt 2, 1700–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solimene, F.; Compagnucci, P.; Tondo, C.; La Fazia, V.M.; Schillaci, V.; Mohanty, S.; Cipolletta, L.; Fassini, G.M.; Chiariello, P.; Mottola, G.; et al. Direct Epicardial Validation of Posterior Wall Electroporation in Persistent Atrial Fibrillation. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2024, 10, 1200–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blum, S.; Aeschbacher, S.; Meyre, P.; Zwimpfer, L.; Reichlin, T.; Beer, J.H.; Ammann, P.; Auricchio, A.; Kobza, R.; Erne, P.; et al. Incidence and Predictors of Atrial Fibrillation Progression. J. Am. Hear. Assoc. 2019, 8, e012554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nattel, S.; Heijman, J.; Zhou, L.; Dobrev, D. Molecular Basis of Atrial Fibrillation Pathophysiology and Therapy. Circ. Res. 2020, 127, 51–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Scherlag, B.J.; Lin, J.; Niu, G.; Fung, K.-M.; Zhao, L.; Ghias, M.; Jackman, W.M.; Lazzara, R.; Jiang, H.; et al. Atrial Fibrillation Begets Atrial Fibrillation: Autonomic Mechanism for Atrial Electrical Remod-eling Induced by Short-term Rapid Atrial Pacing. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2008, 1, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nattel, S.; Maguy, A.; Le Bouter, S.; Yeh, Y.-H. Arrhythmogenic Ion-Channel Remodeling in the Heart: Heart Failure, Myocardial Infarction, and Atrial Fibrillation. Physiol. Rev. 2007, 87, 425–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nattel, S.; Burstein, B.; Dobrev, D. Atrial Remodeling and Atrial Fibrillation: Mechanisms and implications. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2008, 1, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nattel, S.; Harada, M. Atrial Remodeling and Atrial Fibrillation: Recent advances and translational perspectives. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 63, 2335–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Rsid | Nearest Gene(s) or eGene * | Rsid | Nearest Gene(s) or eGene * | Rsid | Nearest Gene(s) or eGene * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs187585530 | UBE4B | rs716845 | KCNN2 | rs1822273 | NAV2 |
| rs880315 | CASZI | rs2012809 | FBN2, SLC27A6 | rs949078 | SORL1, MIR100HG |
| rs7529220 | HSPG2, CELA3B | rs34750263 | WNT8A, NME5 | rs76097649 | KCNJ5 |
| rs2885697 | SCMH1 * | rs174048 | ARHGAP26, NR3C1 | rs6490029 | CUX2 |
| rs11590635 | AGBL4 | rs12188351 | SLIT3 | rs10842383 | LINC00477, BCAT1 |
| rs56202902 | FAF1 | rs6882776 | NKX2-5 | rs113819537 | SSPN * |
| rs146518726 | Clorf185 | rs73366713 | ATXN1 | rs12809354 | PKP2 |
| rs12044963 | KCND3 | rs34969716 | KDM1B | rs7978685 | NACA |
| rs4484922 | CASQ2 * | rs1307274 | C6orf1, NUDT3 | rs35349325 | BEST3 |
| rs79187193 | GJA5 | rs3176326 | CDKN1A | rs11180703 | KRR1, PHLDAI |
| rs11264280 | KCNN3, PMVK | rs6907805 | CGA, ZNF292 | rs883079 | TBX5 |
| rs72700114 | METTL11B, LINC01142 | rs210632 | GOPC | rs12810346 | TBX5-AS1, TBX3 |
| rs608930 | GORAB, PRRX1 | rs17079881 | SLC35F1 | rs10773657 | HIPIR |
| rs10753933 | PPFIA4 * | rs13191450 | GJA1, HSF2 | rs12298484 | DNAH10 |
| rs4951261 | NUCKSI | rs12208899 | LINC00326, EYA4 | rs6560886 | FBRSLI |
| rs6546620 | KIF3C | rs117984853 | UST | rs9580438 | LINC00540, BASP1P1 |
| rs6742276 | XPO1 | rs11768850 | SUNI | rs35569628 | CUL4A |
| rs2540949 | CEP68 * | rs55734480 | DGKB | rs28631169 | MYH7 |
| rs10165883 | SNRNP27 | rs6462078 | CREB5 | rs2145587 | AKAP6 |
| rs72926475 | REEP1, KDM3A | rs74910854 | PMS2P2 * | rs73241997 | SNX6, CFL2 |
| rs28387148 | GYPC * | rs11773884 | CDK6 | rs2738413 | SYNE2 |
| rs67969609 | TEX41 | rs62483627 | COG5 | rs74884082 | DPF3 |
| rs12992412 | MBD5 | rs11773845 | CAV1 | rs10873299 | LRRC74, IRF2BPL |
| rs56181519 | WIPF1 * | rs55985730 | OPNISW | rs147301839 | MYZAP |
| rs2288327 | FKBP7 * | rs7789146 | KCNH2 | rs62011291 | USP3 |
| rs3820888 | SPATS2L * | rs35620480 | LINC00208, GATA4 | rs12591736 | TLE3, UACA |
| rs35544454 | ERBB4 | rs7508 | ASAH1 * | rs74022964 | HCN4, REC114 |
| rs6810325 | MKRN2 * | rs7846485 | XPO7 | rs12908004 | LINC00927, ARNT2 |
| rs73032363 | THRB | rs62521286 | FBXO32 | rs12908437 | IGF1R * |
| rs6790396 | SCN10A | rs35006907 | MTSSI, LINC00964 | rs2286466 | RPL3L * |
| rs34080181 | SLC25A26 * | rs7460121 | MIR30B | rs2359171 | ZFHX3 |
| rs17005647 | FRMD4B | rs6993266 | PTK2 | rs7225165 | YWHAE, CRK |
| rs7632427 | EPHA3 | rs4977397 | SLC24A2, MLLT3 | rs8073937 | POLR2A, TNFSF12 |
| rs17490701 | PHLDB2 | rs4385527 | C9orf3 | rs72811294 | MYOCD |
| rs1278493 | PPP2R3A | rs4743034 | ZNF462 | rs11658278 | ZPBP2 |
| rs4855075 | GNB4 | rs10760361 | PSMB7 | rs242557 | MAPT |
| rs60902112 | XXYLT1 | rs2274115 | LHX3 | rs76774446 | GOSR2 |
| rs9872035 | PAK2 | rs2296610 | NEBL | rs7219869 | KCNJ2, CASC17 |
| rs3822259 | WDR1 | rs7919685 | NRBF2 * | rs12604076 | CYTH1 |
| rs1458038 | PRDM8, FGF5 | rs7096385 | SIRTI | rs9953366 | SMAD7 |
| rs3960788 | UBE2D3 * | rs60212594 | SYNPO2L | rs8088085 | MEX3C |
| rs2129977 | PITX2, C4orf32 | rs11001667 | C10orf11 | rs2145274 | CASC20, BMP2 |
| rs55754224 | CAMK2D | rs1044258 | C10orf76 | rs7269123 | C20orf166 |
| rs10213171 | ARHGAP10 | rs11598047 | NEURL | rs2834618 | LOC100506385 |
| rs10520260 | HAND2-AS1 * | rs2047036 | SH3PXD2A | rs465276 | TUBA8 |
| rs6596717 | LOC102467213, EFNA5 | rs10749053 | RBM20 | rs133902 | MYO18B |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zito, E.; Bianchini, L.; Sommariva, E.; Costa, M.; Forleo, G.B.; Tondo, C.; Schiavone, M. The Genetic Mechanisms and Pathology of Atrial Fibrillation: A Narrative Review. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13030654
Zito E, Bianchini L, Sommariva E, Costa M, Forleo GB, Tondo C, Schiavone M. The Genetic Mechanisms and Pathology of Atrial Fibrillation: A Narrative Review. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(3):654. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13030654
Chicago/Turabian StyleZito, Elio, Lorenzo Bianchini, Elena Sommariva, Mariabeatrice Costa, Giovanni B. Forleo, Claudio Tondo, and Marco Schiavone. 2025. "The Genetic Mechanisms and Pathology of Atrial Fibrillation: A Narrative Review" Biomedicines 13, no. 3: 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13030654
APA StyleZito, E., Bianchini, L., Sommariva, E., Costa, M., Forleo, G. B., Tondo, C., & Schiavone, M. (2025). The Genetic Mechanisms and Pathology of Atrial Fibrillation: A Narrative Review. Biomedicines, 13(3), 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13030654








