Atrial Fibrillation Begets Atrial Fibrillation in Small Animals: Characterization of New Rat Model of Spontaneous Atrial Fibrillation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Studied Animals
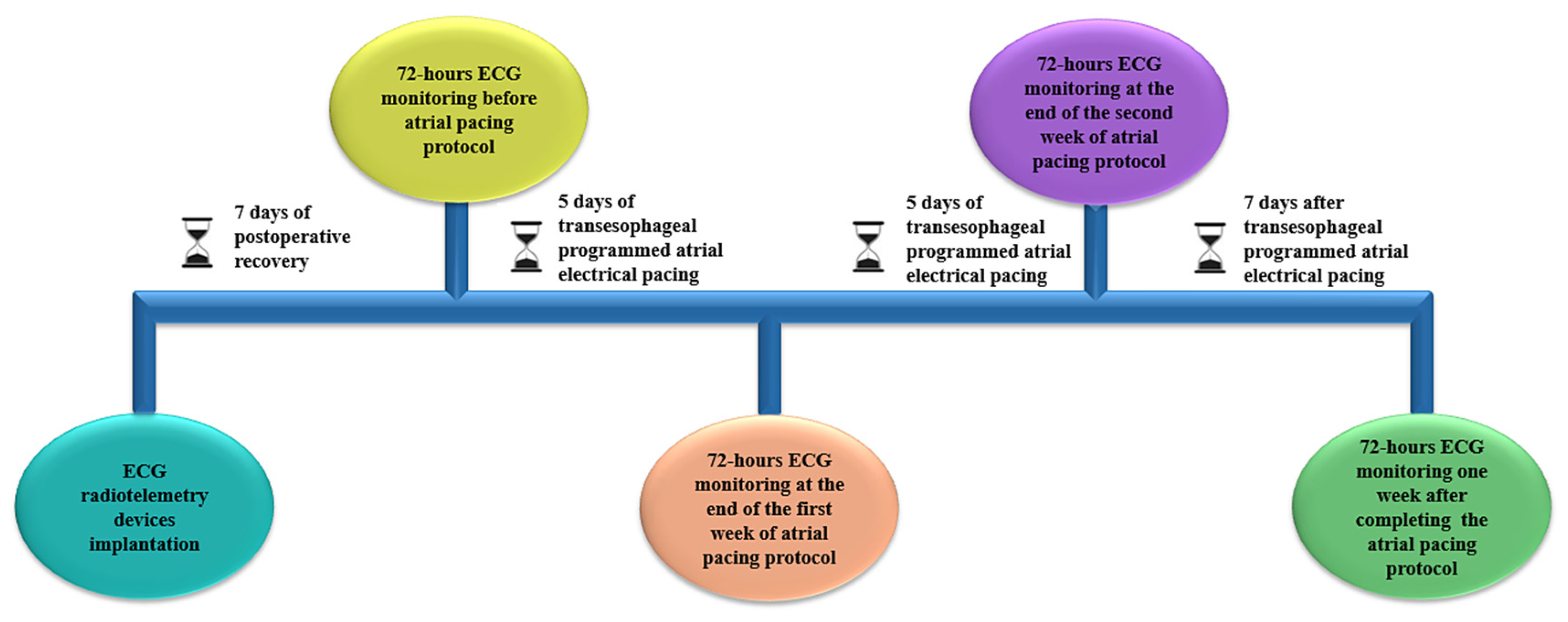
2.2. Transesophageal Programmed Atrial Electrical Pacing and Assessment of Atrial Fibrillation Inducibility
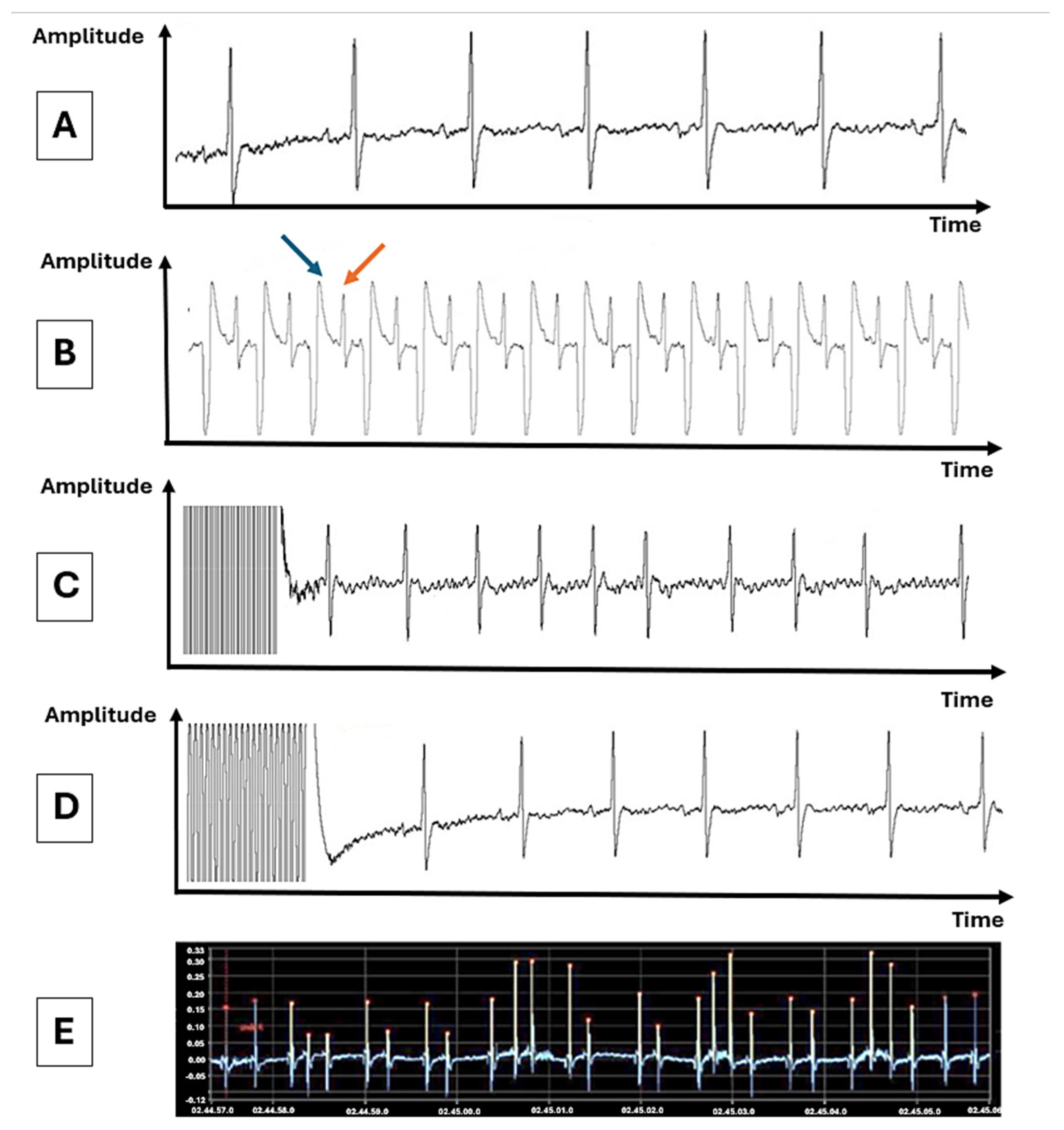
2.3. Implantation of ECG Radiotelemetry Devices and Spontaneous Arrhythmic Burden Assessment
2.4. Heart Rate Variability Analysis
2.5. Left Atrial Expression of Atrial Fibrillation-Related Genes
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Inducibility of Atrial Fibrillation by Transesophageal Atrial Pacing
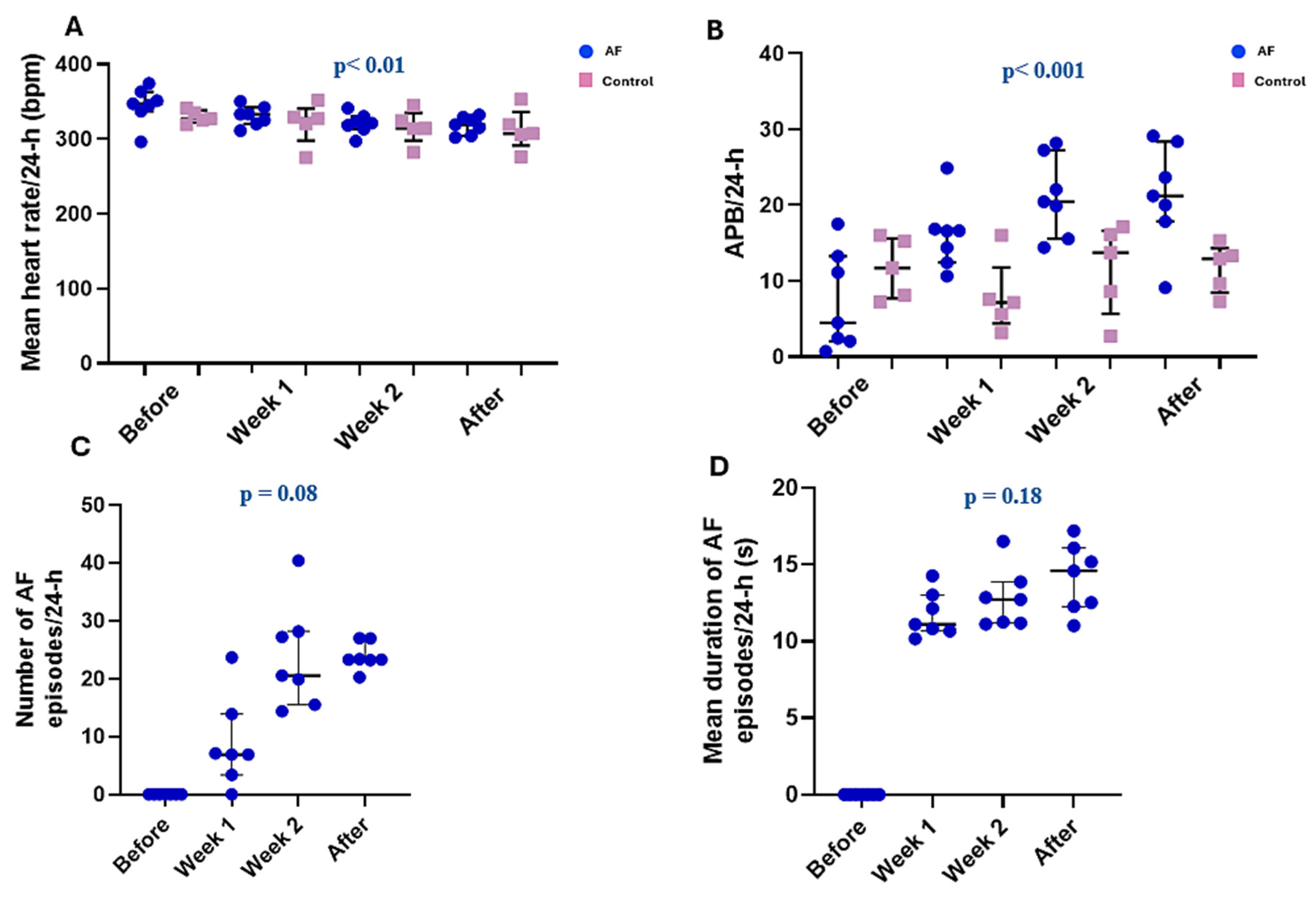
3.2. Spontaneous Arrhythmic Burden in Control and Stimulated Rats
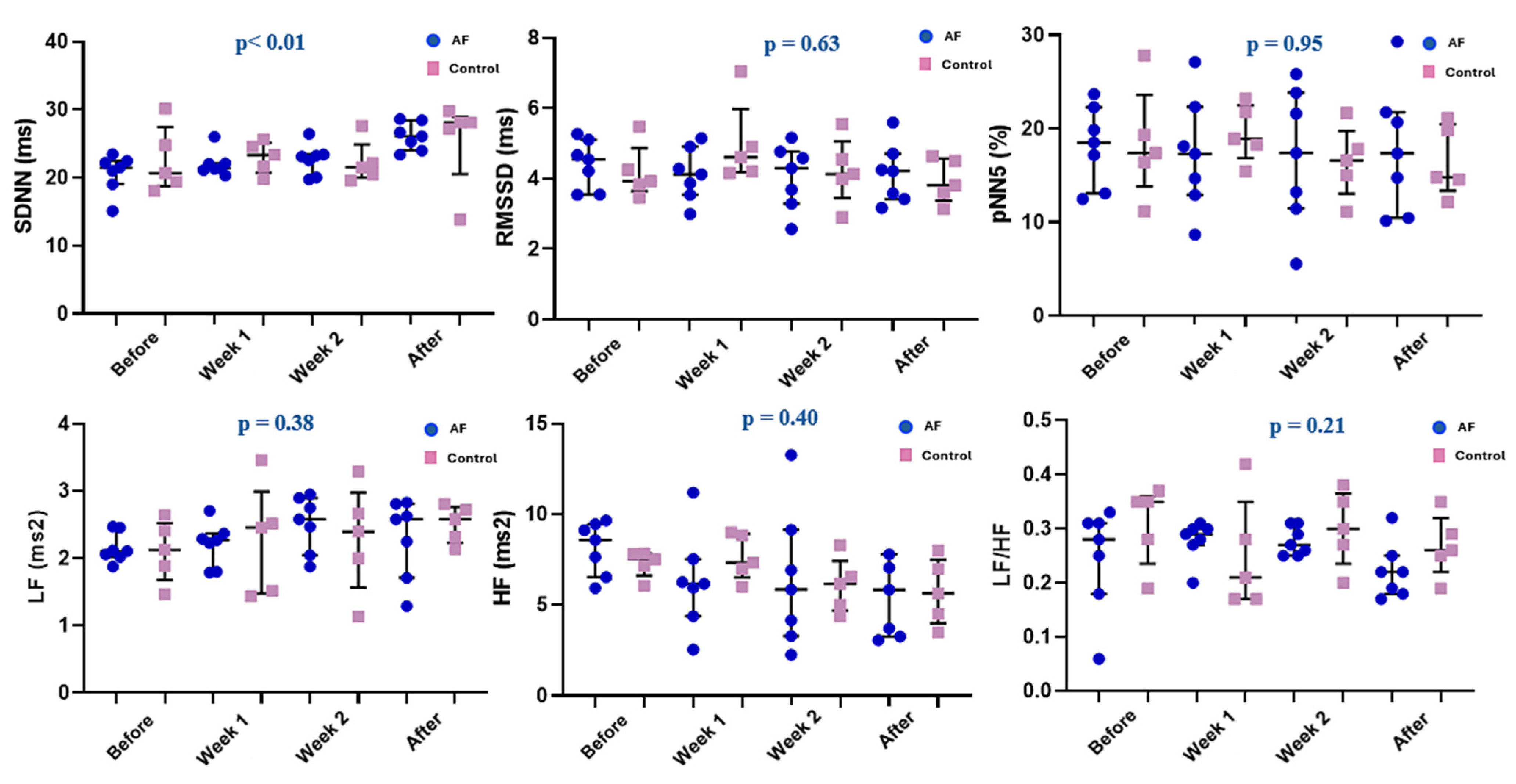
3.3. Time and Frequency Domain Analysis of Heart Rate Variability
3.4. Left Atrial Hcn1, Hcn2, Hcn4, and Pitx2 RNA Expression in the Electrically Stimulated and Non-Stimulated Rats
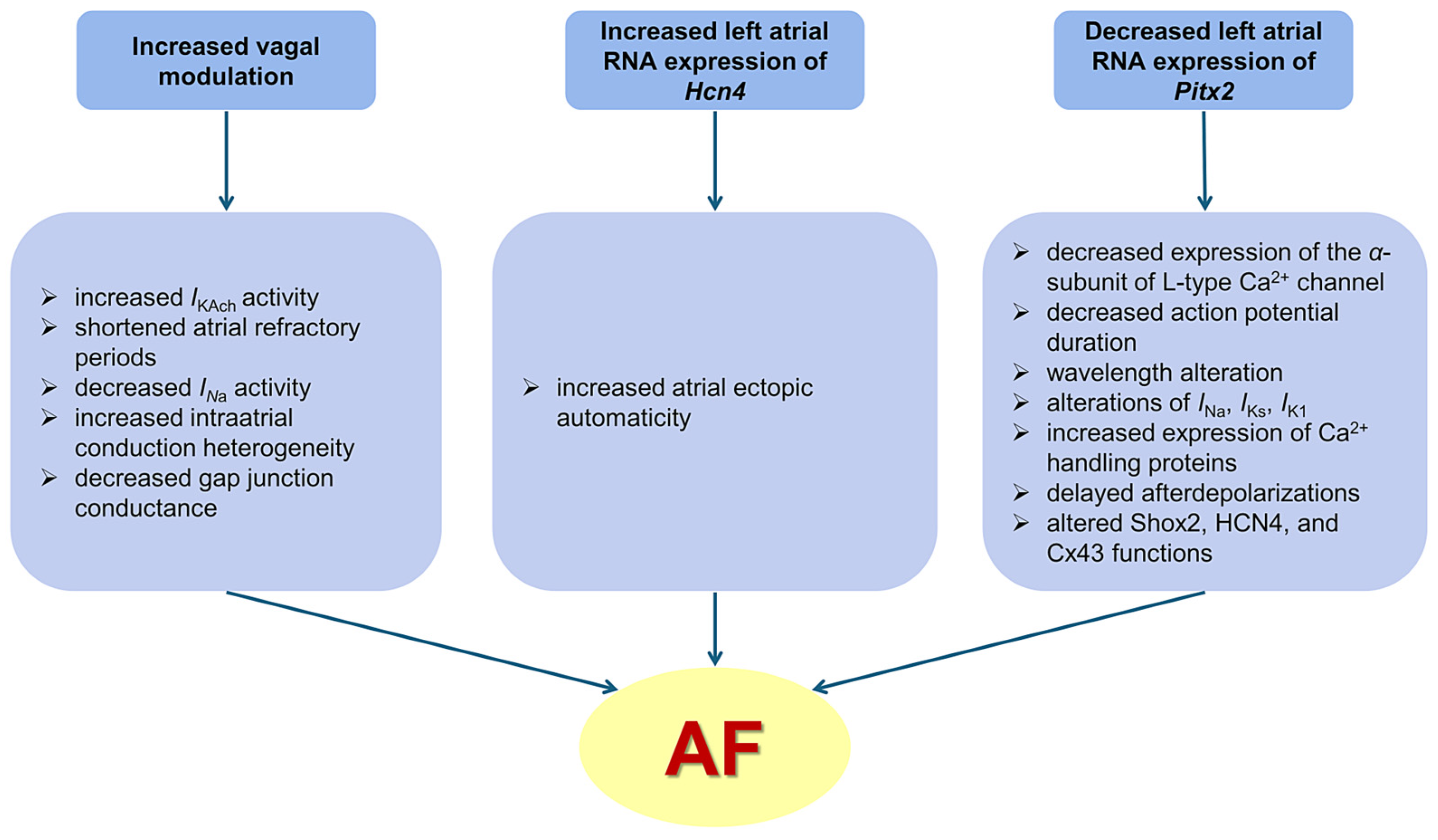
4. Discussion
4.1. Long-Term Atrial Burst Pacing Induces Spontaneous Atrial Fibrillation in Rats
4.2. Long-Term Atrial Burst Pacing Induces a Progressive Increase in Cardiac Vagal Modulation
4.3. Long-Term Atrial Burst Pacing Induces Proarrhythmic Changes in Left Atrial Expression of Atrial Fibrillation-Related Genes
4.4. Translational Perspective
4.5. Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AF | atrial fibrillation |
| ABPs | atrial premature beats |
| Cx43 | connexin 43 |
| HCN | hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated channels |
| IK1 | inwardly rectifying potassium current |
| IKAch | acetylcholine-activated potassium current |
| IKs | slow delayed rectifier potassium current |
| INa | voltage-gated sodium current |
| LF | low-frequency components |
| PITX2 | paired-like homeodomain transcription factor 2 |
| pNN5 | proportion of adjacent RR intervals that differed by >5 ms |
| RMSSD | root mean square of successive RR-interval differences |
| SDNN | standard deviation of normal RR intervals |
References
- Kornej, J.; Börschel, C.S.; Börschel, C.S.; Benjamin, E.J.; Benjamin, E.J.; Schnabel, R.B. Epidemiology of Atrial Fibrillation in the 21st Century: Novel Methods and New Insights. Circ. Res. 2020, 127, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphries, K.H.; Kerr, C.R.; Steinbuch, M.; Dorian, P. Canadian Registry of Atrial Fibrillation investigators. Limitations to antiarrhythmic drug use in patients with atrial fibrillation. CMAJ 2004, 171, 741–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schüttler, D.; Bapat, A.; Kääb, S.; Lee, K.; Tomsits, P.; Clauss, S. Animal Models of Atrial Fibrillation. Circ. Res. 2020, 127, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Q.; LE, X.; Yu, P.; Zhuang, L. Therapeutic advances in atrial fibrillation based on animal models. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2024, 25, 135–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijffels, M.C.; Kirchhof, C.J.; Dorland, R.A.M. Atrial fibrillation begets atrial fibrillation: A study in awake chronically instrumented goats. Circulation 1995, 92, 1954–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haugan, K.; Lam, H.R.; Knudsen, C.B.; Petersen, J.S. Atrial fibrillation in rats induced by rapid transesophageal atrial pacing during brief episodes of asphyxia: A new in vivo model. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2004, 44, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakimoto, H.; Maguire, C.; Kovoor, P.; Hammer, P.; Gehrmann, J.; Triedman, J. Induction of atrial tachycardia and fibrillation in the mouse heart. Cardiovasc. Res. 2001, 50, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halațiu, V.B.; Perian, M.; Balan, A.I.; Scridon, A. Transesophageal atrial burst pacing for atrial fibrillation induction in rats. J. Vis. Exp. 2022, 180, e63567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scridon, A.; Perian, M.; Grigoraş, T.; Halaţiu, V.; Vântu, A.; Balan, A. Spontaneous atrial fibrillation after long-term transesophageal atrial burst pacing in rats. Technical and procedural approach to a new in vivo atrial fibrillation model. Rev. Rom. Med. Lab. 2018, 26, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scridon, A.; Gallet, C.; Arisha, M.; Oréa, V.; Chapuis, B.; Li, N. Unprovoked atrial tachyarrhythmias in aging spontaneously hypertensive rats: The role of the autonomic nervous system. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2012, 303, H386–H392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scridon, A.; Halaţiu, V.; Balan, A.; Cozac, D.; Moldovan, V.; Bănescu, C. Long-term effects of ivabradine on cardiac vagal parasympathetic function in normal rats. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 596956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- We, G. The nature of fibrillary contractions of the heart: Its relation to tissue mass and form. Am. J. Physiol. 1914, 33, 397–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, G.; Prasad, S.; Ripplinger, C.; Cassilly, T.; Schuessler, R.; Boineau, J. Importance of geometry and refractory period in sustaining atrial fibrillation: Testing the critical mass hypothesis. Circulation 2005, 112, I7–I13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; Scherlag, B.; Lin, J.; Niu, G.; Fung, K.; Zhao, L. Atrial fibrillation begets atrial fibrillation: Autonomic mechanism for atrial electrical remodeling induced by short-term rapid atrial pacing. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2008, 1, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.C.; Zhou, S.; Tan, A.Y.; Hayashi, H.; Nihei, M.; Chen, P.S. High-density mapping of pulmonary veins and left atrium during ibutilide administration in a canine model of sustained atrial fibrillation. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2005, 289, H2704–H2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, M.; Pierucci, N.; Trivigno, S.; Cipollone, P.; Piro, A.; Chimenti, C. Probability Score to Predict Spontaneous Conversion to Sinus Rhythm in Patients with Symptomatic Atrial Fibrillation When Less Could Be More? J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosch, R.; Scherer, C.; Rüb, N.; Wöhrl, S.; Steinmeyer, K.; Haase, H. Molecular mechanisms of early electrical remodeling: Transcriptional downregulation of ion channel subunits reduces ICa,L and Ito in rapid atrial pacing in rabbits. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2003, 41, 858–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, L.; Melnyk, P.; Gaspo, R.; Wang, Z.; Nattel, S. Molecular mechanisms underlying ionic remodeling in a dog model of atrial fibrillation. Circ. Res. 1999, 84, 776–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Y.; Cheng, J. Dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system in atrial fibrillation. J. Thorac. Dis. 2015, 7, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scridon, A.; Şerban, R.C.; Chevalier, P. Atrial fibrillation: Neurogenic or myogenic? Arch. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2018, 111, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scridon, A. Autonomic imbalance and atrial ectopic activity-a pathophysiological and clinical view. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 1058427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Sun, B.; Tse, G.; Jiang, J.; Xu, W. Reversibility of both sinus node dysfunction and reduced HCN4 mRNA expression level in an atrial tachycardia pacing model of tachycardia-bradycardia syndrome in rabbit hearts. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2016, 9, 8526–8531. [Google Scholar]
- He, W.; Zhang, J.; Gan, T.; Xu, G.; Tang, B. Expression of hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated channel isoforms in a canine model of atrial fibrillation. Exp. Ther. Med. 2016, 12, 433–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stillitano, F.; Lonardo, G.; Giunti, G.; Del Lungo, M.; Coppini, R.; Spinelli, V. Chronic atrial fibrillation alters the functional properties of If in the human atrium. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2013, 24, 1391–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hong, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Ji, Y.; Li, H. Association between reversal in the expression of hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated (hcn) channel and age-related atrial fibrillation. Med. Sci. Monit. 2014, 20, 2292–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Han, Y.; Liang, X.; Zhang, G.; Lu, Y.; Li, Y. Aging-induced atrial fibrosis in If current change and its effect on atrial fibrillation in dogs. Ann. Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2022, 27, e12951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scridon, A.; Fouilloux-Meugnier, E.; Loizon, E.; Perian, M.; Rome, S.; Julien, C. Age-dependent myocardial transcriptomic changes in the rat. Novel insights into atrial and ventricular arrhythmias pathogenesis. Rev. Rom. Med. Lab. 2014, 22, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syeda, F.; Holmes, A.; Yu, T.; Tull, S.; Kuhlmann, S.; Pavlovic, D. PITX2 Modulates Atrial Membrane Potential and the Antiarrhythmic Effects of Sodium-Channel Blockers. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 68, 1881–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syeda, F.; Kirchhof, P.; Fabritz, L. PITX2-dependent gene regulation in atrial fibrillation and rhythm control. J. Physiol. 2017, 595, 4019–4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puertas, R.D.; Jalabert, A.; Meugnier, E.; Euthine, V.; Chevalier, P.; Rome, S. Analysis of the microRNA signature in left atrium from patients with valvular heart disease reveals their implications in atrial fibrillation. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyat, J.; Chua, W.; Cardoso, V.; Witten, A.; Kastner, P.; Kabir, S.N. Reduced left atrial cardiomyocyte PITX2 and elevated circulating BMP10 predict atrial fibrillation after ablation. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e139179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scridon, A.; Fouilloux-Meugnier, E.; Loizon, E.; Rome, S.; Julien, C.; Barrès, C. Long-standing arterial hypertension is associated with Pitx2 down-regulation in a rat model of spontaneous atrial tachyarrhythmias. Europace 2014, 17, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doñate Puertas, R.; Meugnier, E.; Romestaing, C.; Rey, C.; Morel, E.; Lachuer, J. Atrial fibrillation is associated with hypermethylation in human left atrium, and treatment with decitabine reduces atrial tachyarrhythmias in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Transl. Res. 2017, 184, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Li, L.; Bai, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Moon, A.M.; Kaminski, H.J.; Martin, J.F. Pitx2, an atrial fibrillation predisposition gene, directly regulates ion transport and intercalated disc genes. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2014, 7, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinchilla, A.; Daimi, H.; Lozano-Velasco, E.; Dominguez, J.; Caballero, R.; Delpón, E. PITX2 insufficiency leads to atrial electrical and structural remodeling linked to arrhythmogenesis. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2011, 4, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyat, J.; Sommerfeld, L.; O’Reilly, M.; Cardoso, V.R.; Thiemann, E.; Khan, A. PITX2 deficiency leads to atrial mitochondrial dysfunction. Cardiovasc. Res. 2024, 120, 1907–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirchhof, P.; Kahr, P.; Kaese, S.; Piccini, I.; Vokshi, I.; Scheld, H. PITX2c is expressed in the adult left atrium, and reducing Pitx2c expression promotes atrial fibrillation inducibility and complex changes in gene expression. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2011, 4, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Lu, Y.; Lo, A.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H. PITX2 upregulation increases the risk of chronic atrial fibrillation in a dose-dependent manner by modulating IKs and ICaL—Insights from human atrial modelling. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozano-Velasco, E.; Hernández-Torres, F.; Daimi, H.; Serra, S.A.; Herraiz, A.; Hove-Madsen, L.; Aránega, A.; Franco, D. Pitx2 impairs calcium handling in a dose-dependent manner by modulating Wnt signalling. Cardiovasc. Res. 2014, 109, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Klysik, E.; Sood, S.; Johnson, R.L.; Wehrens, X.H.T.; Martin, J.F. Pitx2 prevents susceptibility to atrial arrhythmias by inhibiting left-sided pacemaker specification. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 9753–9758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolke, C.; Antileo, E.; Lendeckel, U. WNT signaling in atrial fibrillation. Exp. Biol. Med. 2021, 246, 1112–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Xu, Y.; Qiao, Q.; Li, X. A SHOX2 loss-of-function mutation underlying familial atrial fibrillation. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 15, 1564–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| ECG Monitoring Period | AF Group (n = 7) | Control Group (n = 5) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Before stimulation | 344.7 ± 9.3 | 329.4 ± 3.8 | 0.17 |
| Week 1 | 330.6 ± 4.9 | 320.8 ± 12.5 | 0.50 |
| Week 2 | 320.4 ± 5.1 | 315.9 ± 10.1 | 0.70 |
| After stimulation | 318.0 ± 4.4 | 312.2 ± 12.4 | 0.60 |
| Parameter | ECG Monitoring Period | AF Group (n = 7) | Control Group (n = 5) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time domain | ||||
| SDNN (s) | Before stimulation | 20.69 [19.05–22.48] | 21.47 [18.75–27.46] | 0.46 |
| Week 1 | 21.37 [21.10–22.12] | 23.34 [20.71–25.13] | 0.53 | |
| Week 2 | 23.11 [20.06–23.40] | 21.52 [10.03–24.88] | 0.82 | |
| After stimulation | 26.07 [23.97–28.45] | 28.07 [20.52–28.94] | 0.53 | |
| RMSSD (s) | Before stimulation | 4.54 [3.55–5.11] | 3.93 [3.65–4.87] | 0.62 |
| Week 1 | 4.12 [3.54–4.91] | 4.18 [4.61–5.97] | 0.20 | |
| Week 2 | 4.30 [3.29–4.77] | 4.13 [3.44–5.05] | 0.76 | |
| After stimulation | 4.22 [3.42–4.71] | 3.81 [3.37–4.57] | 0.65 | |
| pNN5 (%) | Before stimulation | 18.50 [13.08–22.29] | 17.38 [13.80–23.58] | 0.93 |
| Week 1 | 17.30 [12.90–22.33] | 18.91 [16.86–22.50] | 0.42 | |
| Week 2 | 17.42 [11.47–23.83] | 16.60 [13.08–19.75] | 0.87 | |
| After stimulation | 17.35 [10.46–21.75] | 14.82 [13.37–20.48] | 0.68 | |
| Frequency domain | ||||
| LF (ms2) | Before stimulation | 2.11 [2.02–2.46] | 2.13 [1.68–2.52] | 0.82 |
| Week 1 | 2.27 [1.80–2.37] | 2.46 [1.48–2.99] | 0.86 | |
| Week 2 | 2.58 [2.05–2.90] | 2.40 [1.57–2.98] | 0.61 | |
| After stimulation | 2.58 [1.71–2.81] | 2.58 [2.23–2.76] | 0.42 | |
| HF (ms2) | Before stimulation | 8.58 [6.53–9.46] | 7.52 [6.61–7.83] | 0.22 |
| Week 1 | 6.17 [4.38–7.53] | 7.33 [6.50–8.92] | 0.27 | |
| Week 2 | 5.86 [3.29–9.14] | 6.17 [4.70–7.42] | 0.83 | |
| After stimulation | 5.84 [3.27–7.79] | 5.64 [3.99–7.49] | 0.66 | |
| LF/HF | Before stimulation | 0.28 [0.18–0.31] | 0.35 [0.235–0.36] | 0.23 |
| Week 1 | 0.29 [0.27–0.30] | 0.21 [0.17–0.35] | 0.59 | |
| Week 2 | 0.27 [0.25–0.31] | 0.30 [0.23–0.36] | 0.52 | |
| After stimulation | 0.22 [0.18–0.25] | 0.26 [0.22–0.32] | 0.19 | |
| AF-Related Gene | AF Group (n = 7) | Control Group (n = 5) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hcn1 | 1.42 ± 0.09 | 1.48 ± 0.11 | 0.76 |
| Hcn2 | 1.39 ± 0.03 | 1.33 ± 0.01 | 0.14 |
| Hcn4 | 1.42 ± 0.02 | 1.35 ± 0.01 | 0.03 |
| Pitx2 | 1.22 ± 0.04 | 1.40 ± 0.04 | 0.02 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Balan, A.I.; Halaţiu, V.B.; Cozac, D.A.; Comșulea, E.; Mutu, C.C.; Aspru, I.; Păcurar, D.; Bănescu, C.; Perian, M.; Scridon, A. Atrial Fibrillation Begets Atrial Fibrillation in Small Animals: Characterization of New Rat Model of Spontaneous Atrial Fibrillation. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 704. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13030704
Balan AI, Halaţiu VB, Cozac DA, Comșulea E, Mutu CC, Aspru I, Păcurar D, Bănescu C, Perian M, Scridon A. Atrial Fibrillation Begets Atrial Fibrillation in Small Animals: Characterization of New Rat Model of Spontaneous Atrial Fibrillation. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(3):704. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13030704
Chicago/Turabian StyleBalan, Alkora Ioana, Vasile Bogdan Halaţiu, Dan Alexandru Cozac, Emilian Comșulea, Cosmin Constantin Mutu, Ioana Aspru, Delia Păcurar, Claudia Bănescu, Marcel Perian, and Alina Scridon. 2025. "Atrial Fibrillation Begets Atrial Fibrillation in Small Animals: Characterization of New Rat Model of Spontaneous Atrial Fibrillation" Biomedicines 13, no. 3: 704. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13030704
APA StyleBalan, A. I., Halaţiu, V. B., Cozac, D. A., Comșulea, E., Mutu, C. C., Aspru, I., Păcurar, D., Bănescu, C., Perian, M., & Scridon, A. (2025). Atrial Fibrillation Begets Atrial Fibrillation in Small Animals: Characterization of New Rat Model of Spontaneous Atrial Fibrillation. Biomedicines, 13(3), 704. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13030704








