Inulin Diet Alleviates Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm by Increasing Akkermansia and Improving Intestinal Barrier
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Animals
2.3. Diet Administration
2.4. Elastase-Induced AAA Mouse Model
2.5. Measurement of Aorta Enlargement
2.6. EVG Staining and Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Staining
2.7. Goblet Cell Quantification
2.8. Sample Collection and Single Cell Isolation
2.9. Flow Cytometry Staining and Analysis
2.10. Extraction of Tissue mRNA and Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT–PCR)
2.11. Bacterial Loads by RT–PCR
2.12. IL-1β Measurements
2.13. Measurement of Fasting Serum Lipids
2.14. Intestinal Permeability Assay
2.15. Bacterial Cultivation
2.16. Administration of Akkermansia in Mice
2.17. Endotoxin Detection
2.18. DNA Extraction, 16S rRNA Gene Amplification, and Pyrosequencing
2.19. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Inulin Diet Attenuates Elastase-Induced AAA
3.2. High-Fiber Diets Modulate the Microbiota Composition in the Small Intestine and Colon of AAA Mice
3.3. Inulin Diet Promotes the Enrichment of Akkermansia in Both the Small Intestine and Colon of AAA Mice
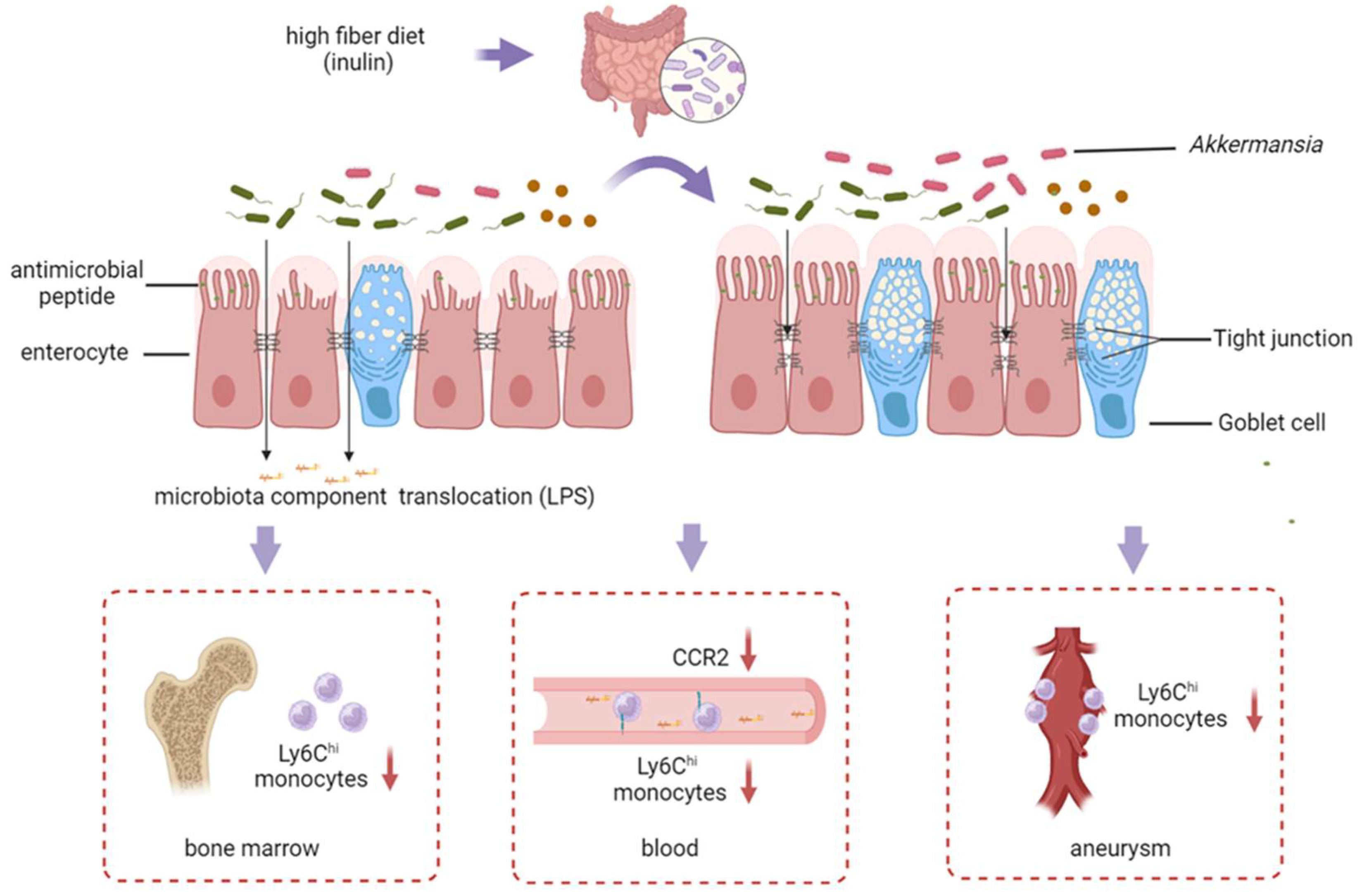
3.4. Inulin’s Impact on Intestinal Barrier of AAA Mice
3.5. The Inulin Diet Decreases Ly6Chi Monocytes in the Bone Marrow, Blood, and Infiltration into the Aneurysm
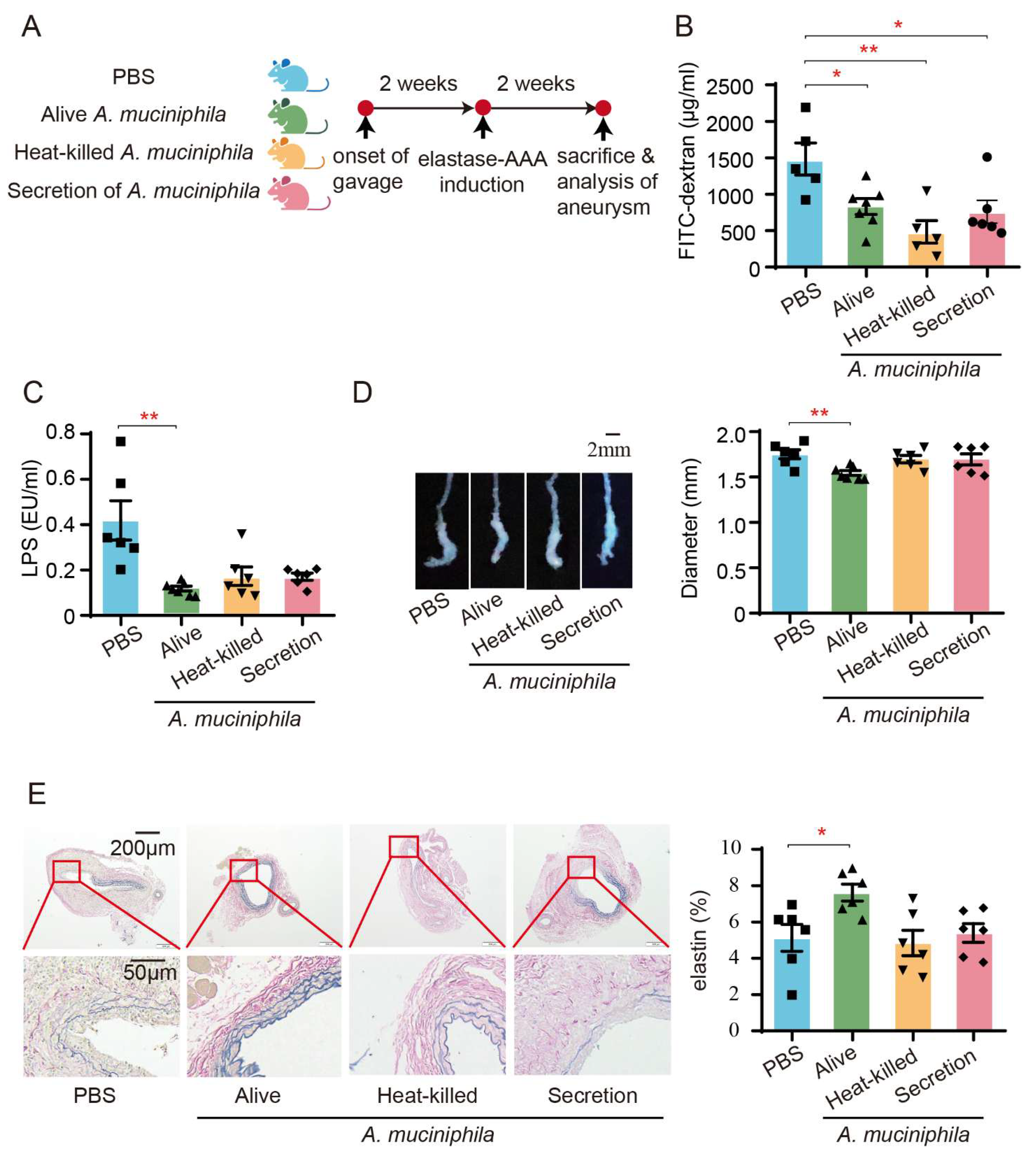
3.6. Administration of Akkermansia Muciniphila Ameliorates AAA in Mice by Enhancing the Intestinal Barrier
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AAA | abdominal aortic aneurysm |
| MMP | matrix metalloproteinase |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharide |
| CCR2 | C-C chemokine receptor 2 |
| IL | interleukin |
| SCFA | short-chain fatty acids |
| SPF | specific pathogen-free |
| SEM | standard error of the mean |
| EVG | Elastica van Gieson |
| IHC | immunohistochemical |
| ASV | amplicon sequence variants |
| PCoA | principal coordinate analyses |
| LDA | linear discriminant analysis |
| LEfSe | LDA effect size |
| PAS-AB | Schiff–Alcian Blue |
| GCs | goblet cells |
| ZO-1 | zonula occludens-1 |
| Muc2 | mucus layer mucin2 |
| Cdh2 | cell adhesion protein cadherin1 |
| Reg3γ | C-type lectin |
| Pla2g2 | phospholipase A2 group-II |
| A. muciniphila | Akkermansia muciniphila |
References
- Reimerink, J.J.; van der Laan, M.J.; Koelemay, M.J.; Balm, R.; Legemate, D.A. Systematic review and meta-analysis of population-based mortality from ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm. Br. J. Surg. 2013, 100, 1405–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Cao, H.; Hu, G.; Wu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Cui, H.; Lu, H.S.; Zheng, L. The mechanism and therapy of aortic aneurysms. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellenthal, F.A.; Buurman, W.A.; Wodzig, W.K.; Schurink, G.W. Biomarkers of AAA progression. Part 1: Extracellular matrix degeneration. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2009, 6, 464–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffort, J.; Lareyre, F.; Clément, M.; Hassen-Khodja, R.; Chinetti, G.; Mallat, Z. Monocytes and macrophages in abdominal aortic aneurysm. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2017, 14, 457–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Jiang, D.; Wang, J.; Wang, R.; Chen, T.; Wang, K.; Durg MS, A.; Wei, X.; Cao, S. Metformin prescription and aortic aneurysm: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Heart 2019, 105, 1351–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salata, K.; Syed, M.; Hussain, M.A.; Eikelboom, R.; de Mestral, C.; Verma, S.; Al-Omran, M. Renin-angiotensin system blockade does not attenuate abdominal aortic aneurysm growth, rupture rate, or perioperative mortality after elective repair. J. Vasc. Surg. 2018, 67, 629–636.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anagnostakos, J.; Lal, B.K. Abdominal aortic aneurysms. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2021, 65, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, A.; Mann, J.; Cummings, J.; Winter, N.; Mete, E.; Te Morenga, L. Carbohydrate quality and human health: A series of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Lancet 2019, 393, 434–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Writing Committee of the Annual Report on Cardiovascular Health and Diseases in China. Interpretation of the Annual Report on Cardiovascular Health and Diseases in China 2021. Cardiol. Discov. 2023, 3, 277–300. [Google Scholar]
- Stackelberg, O.; Björck, M.; Larsson, S.C.; Orsini, N.; Wolk, A. Fruit and vegetable consumption with risk of abdominal aortic aneurysm. Circulation 2013, 128, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.M. Dietary fiber future directions: Integrating new definitions and findings to inform nutrition research and communication. Adv. Nutr. 2013, 4, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Kaoutari, A.; Armougom, F.; Gordon, J.I.; Raoult, D.; Henrissat, B. The abundance and variety of carbohydrate-active enzymes in the human gut microbiota. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Xia, N.; Guo, S.; Zhang, J.; Liao, Y.; Tang, T.; Nie, S.; Zhang, M.; Lv, B.; Lu, Y.; et al. Propionate Alleviates Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm by Modulating Colonic Regulatory T-Cell Expansion and Recirculation. JACC Basic Transl. Sci. 2022, 7, 934–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Chassaing, B.; Singh, V.; Pellizzon, M.; Ricci, M.; Fythe, M.D.; Kumar, M.V.; Gewirtz, A.T. Fiber-Mediated Nourishment of Gut Microbiota Protects against Diet-Induced Obesity by Restoring IL-22-Mediated Colonic Health. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 23, 41–53.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Moltke, J.; Ji, M.; Liang, H.E.; Locksley, R.M. Tuft-cell-derived IL-25 regulates an intestinal ILC2-epithelial response circuit. Nature 2016, 529, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Lin, Y.; Chen, T.; Lv, H.; Diao, F.; Liu, C.; Peng, M.; Ling, X.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; et al. Alternations of gut microbiota composition in neonates conceived by assisted reproductive technology and its relation to infant growth. Gut Microbes 2020, 12, 1794466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Yang, Q.; Rogers, C.J.; Du, M.; Zhu, M.J. AMPK improves gut epithelial differentiation and barrier function via regulating Cdx2 expression. Cell Death Differ. 2017, 24, 819–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bárcena, C.; Valdés-Mas, R.; Mayoral, P.; Garabaya, C.; Durand, S.; Rodríguez, F.; Fernández-García, M.T.; Salazar, N.; Nogacka, A.M.; Garatachea, N.; et al. Healthspan and lifespan extension by fecal microbiota transplantation into progeroid mice. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1234–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lin, S.; Vanhoutte, P.M.; Woo, C.W.; Xu, A. Akkermansia Muciniphila Protects Against Atherosclerosis by Preventing Metabolic Endotoxemia-Induced Inflammation in Apoe−/− Mice. Circulation 2016, 133, 2434–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, M.N.; Dehal, P.S.; Arkin, A.P. FastTree: Computing large minimum evolution trees with profiles instead of a distance matrix. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2009, 26, 1641–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozupone, C.A.; Hamady, M.; Kelley, S.T.; Knight, R. Quantitative and qualitative beta diversity measures lead to different insights into factors that structure microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 1576–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liss, M.A.; White, J.R.; Goros, M.; Gelfond, J.; Leach, R.; Johnson-Pais, T.; Lai, Z.; Rourke, E.; Basler, J.; Ankerst, D.; et al. Metabolic Biosynthesis Pathways Identified from Fecal Microbiome Associated with Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2018, 74, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, Y.; Ivey, K.L.; Wang, D.D.; Wilkinson, J.E.; Franke, A.; Lee, K.H.; Chan, A.; Huttenhower, C.; Hu, F.B.; et al. Interplay between diet and gut microbiome, and circulating concentrations of trimethylamine N-oxide: Findings from a longitudinal cohort of US men. Gut 2022, 71, 724–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Li, F.; Ning, J.; Peng, R.; Shang, J.; Liu, H.; Shang, M.; Bao, X.Q.; Zhang, D. Novel compound FLZ alleviates rotenone-induced PD mouse model by suppressing TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway through microbiota-gut-brain axis. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 2859–2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorsen, J.; Brejnrod, A.; Mortensen, M.; Rasmussen, M.A.; Stokholm, J.; Al-Soud, W.A.; Sørensen, S.; Bisgaard, H.; Waage, J. Large-scale benchmarking reveals false discoveries and count transformation sensitivity in 16S rRNA gene amplicon data analysis methods used in microbiome studies. Microbiome 2016, 4, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, K.E.; Jašarević, E.; Howard, C.D.; Bale, T.L. It’s the fiber, not the fat: Significant effects of dietary challenge on the gut microbiome. Microbiome 2020, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chijiiwa, R.; Hosokawa, M.; Kogawa, M.; Nishikawa, Y.; Ide, K.; Sakanashi, C.; Takahashi, K.; Takeyama, H. Single-cell genomics of uncultured bacteria reveals dietary fiber responders in the mouse gut microbiota. Microbiome 2020, 8, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, B.O.; Birchenough GM, H.; Ståhlman, M.; Arike, L.; Johansson ME, V.; Hansson, G.C.; Bäckhed, F. Bifidobacteria or Fiber Protects against Diet-Induced Microbiota-Mediated Colonic Mucus Deterioration. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 23, 27–40.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everard, A.; Belzer, C.; Geurts, L.; Ouwerkerk, J.P.; Druart, C.; Bindels, L.B.; Guiot, Y.; Derrien, M.; Muccioli, G.G.; Delzenne, N.M.; et al. Cross-talk between Akkermansia muciniphila and intestinal epithelium controls diet-induced obesity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 9066–9071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayama, H.; Okumura, R.; Takeda, K. Interaction Between the Microbiota, Epithelia, and Immune Cells in the Intestine. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 38, 23–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevins, C.L.; Salzman, N.H. Paneth cells, antimicrobial peptides and maintenance of intestinal homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 356–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chopyk, D.M.; Grakoui, A. Contribution of the Intestinal Microbiome and Gut Barrier to Hepatic Disorders. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 849–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacTaggart, J.N.; Xiong, W.; Knispel, R.; Baxter, B.T. Deletion of CCR2 but not CCR5 or CXCR3 inhibits aortic aneurysm formation. Surgery 2007, 142, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wastyk, H.C.; Fragiadakis, G.K.; Perelman, D.; Dahan, D.; Merrill, B.D.; Yu, F.B.; Topf, M.; Gonzalez, C.G.; Van Treuren, W.; Han, S.; et al. Gut-microbiota-targeted diets modulate human immune status. Cell 2021, 184, 4137–4153.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cani, P.D.; Depommier, C.; Derrien, M.; Everard, A.; de Vos, W.M. Akkermansia muciniphila: Paradigm for next-generation beneficial microorganisms. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 19, 625–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.S.; Cho, C.H.; Yun, M.S.; Jang, S.J.; You, H.J.; Kim, J.H.; Han, D.; Cha, K.H.; Moon, S.H.; Lee, K.; et al. Akkermansia muciniphila secretes a glucagon-like peptide-1-inducing protein that improves glucose homeostasis and ameliorates metabolic disease in mice. Nat. Microbiol. 2021, 6, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plovier, H.; Everard, A.; Druart, C.; Depommier, C.; Van Hul, M.; Geurts, L.; Chilloux, J.; Ottman, N.; Duparc, T.; Lichtenstein, L.; et al. A purified membrane protein from Akkermansia muciniphila or the pasteurized bacterium improves metabolism in obese and diabetic mice. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, D.; Whelan, K.; Rossi, M.; Morrison, M.; Holtmann, G.; Kelly, J.T.; Shanahan, E.R.; Staudacher, H.M.; Campbell, K.L. Dietary fiber intervention on gut microbiota composition in healthy adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 107, 965–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolova, V.L.; Smith MR, B.; Hall, L.J.; Cleare, A.J.; Stone, J.M.; Young, A.H. Perturbations in Gut Microbiota Composition in Psychiatric Disorders: A Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Psychiatry 2021, 78, 1343–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, F.Z.; Nelson, E.; Chu, P.Y.; Horlock, D.; Fiedler, A.; Ziemann, M.; Tan, J.K.; Kuruppu, S.; Rajapakse, N.W.; El-Osta, A.; et al. High-Fiber Diet and Acetate Supplementation Change the Gut Microbiota and Prevent the Development of Hypertension and Heart Failure in Hypertensive Mice. Circulation 2017, 135, 964–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabst, O.; Hornef, M.W.; Schaap, F.G.; Cerovic, V.; Clavel, T.; Bruns, T. Gut-liver axis: Barriers and functional circuits. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 20, 447–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cani, P.D.; Van Hul, M. Gut microbiota in overweight and obesity: Crosstalk with adipose tissue. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 21, 164–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agirman, G.; Yu, K.B.; Hsiao, E.Y. Signaling inflammation across the gut-brain axis. Science 2021, 374, 1087–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Cheng, L.; Wang, J.; Hao, M.; Che, H. Antibiotic-Induced Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis Damages the Intestinal Barrier, Increasing Food Allergy in Adult Mice. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokje, V.B.; Hamming, J.F.; Lindeman, J.H. Editor’s Choice—Pharmaceutical Management of Small Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms: A Systematic Review of the Clinical Evidence. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2015, 50, 702–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depommier, C.; Everard, A.; Druart, C.; Plovier, H.; Van Hul, M.; Vieira-Silva, S.; Falony, G.; Raes, J.; Maiter, D.; Delzenne, N.M.; et al. Supplementation with Akkermansia muciniphila in overweight and obese human volunteers: A proof-of-concept exploratory study. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1096–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, E.S.; Byrne, C.S.; Morrison, D.J.; Murphy, K.G.; Preston, T.; Tedford, C.; Garcia-Perez, I.; Fountana, S.; Serrano-Contreras, J.I.; Holmes, E.; et al. Dietary supplementation with inulin-propionate ester or inulin improves insulin sensitivity in adults with overweight and obesity with distinct effects on the gut microbiota, plasma metabolome and systemic inflammatory responses: A randomised cross-over trial. Gut 2019, 68, 1430–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinet, P.; Milewicz, D.M.; Cassis, L.A.; Leeper, N.J.; Lu, H.S.; Smith, J.D. Consideration of Sex Differences in Design and Reporting of Experimental Arterial Pathology Studies-Statement From ATVB Council. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2018, 38, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, S.; Yang, F.; Zhang, J.; Liao, Y.; Xia, N.; Tang, T.; Wang, C.; Wang, Q.K.; Chen, C.; Hu, D.; et al. Inulin Diet Alleviates Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm by Increasing Akkermansia and Improving Intestinal Barrier. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 920. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040920
Guo S, Yang F, Zhang J, Liao Y, Xia N, Tang T, Wang C, Wang QK, Chen C, Hu D, et al. Inulin Diet Alleviates Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm by Increasing Akkermansia and Improving Intestinal Barrier. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(4):920. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040920
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Shuang, Fen Yang, Jiyu Zhang, Yuhan Liao, Ni Xia, Tingting Tang, Chaolong Wang, Qing K. Wang, Chen Chen, Desheng Hu, and et al. 2025. "Inulin Diet Alleviates Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm by Increasing Akkermansia and Improving Intestinal Barrier" Biomedicines 13, no. 4: 920. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040920
APA StyleGuo, S., Yang, F., Zhang, J., Liao, Y., Xia, N., Tang, T., Wang, C., Wang, Q. K., Chen, C., Hu, D., Shan, Z., & Cheng, X. (2025). Inulin Diet Alleviates Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm by Increasing Akkermansia and Improving Intestinal Barrier. Biomedicines, 13(4), 920. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040920






