Chronic Allograft Nephropathy—A Narrative Review of Its Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Evolving Management Strategies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Risk Factors
2.1. Immunologic Factors
2.1.1. Acute Rejection
2.1.2. Subclinical Rejection
2.1.3. Chronic Rejection
2.1.4. HLA Mismatches
2.1.5. Immunosuppressive Regimens
2.2. Non-Immunologic Factors
- Arterionephrosclerosis;
- Prolonged cold ischemia time;
- Non-living donation;
- Increasing donor age;
- Donor–recipient size discrepancy;
- Nephrocalcinosis related to preexisting hyperparathyroidism;
- Calcineurin inhibitor nephrotoxicity;
- Recurrent glomerulonephritis;
- Infections (BK virus, cytomegalovirus, and UTIs).
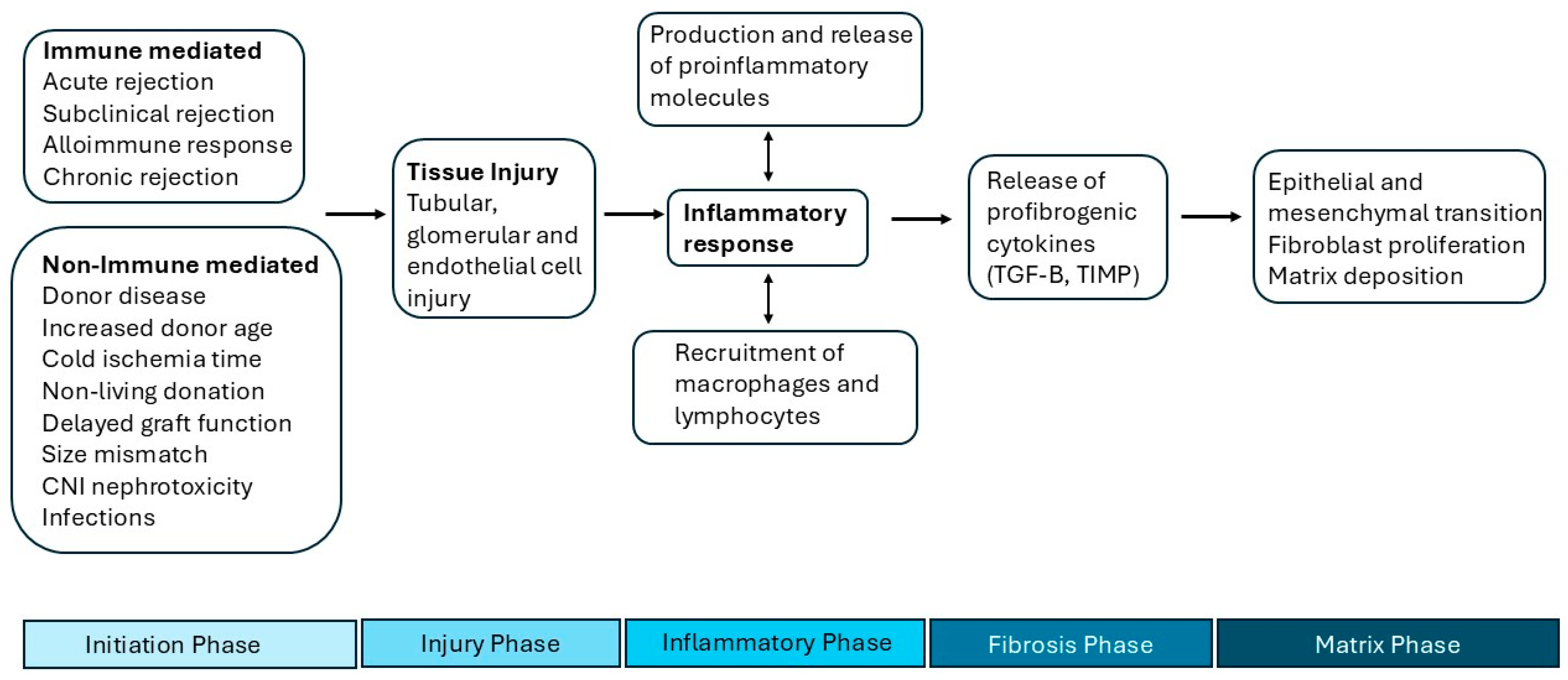
3. Pathogenesis
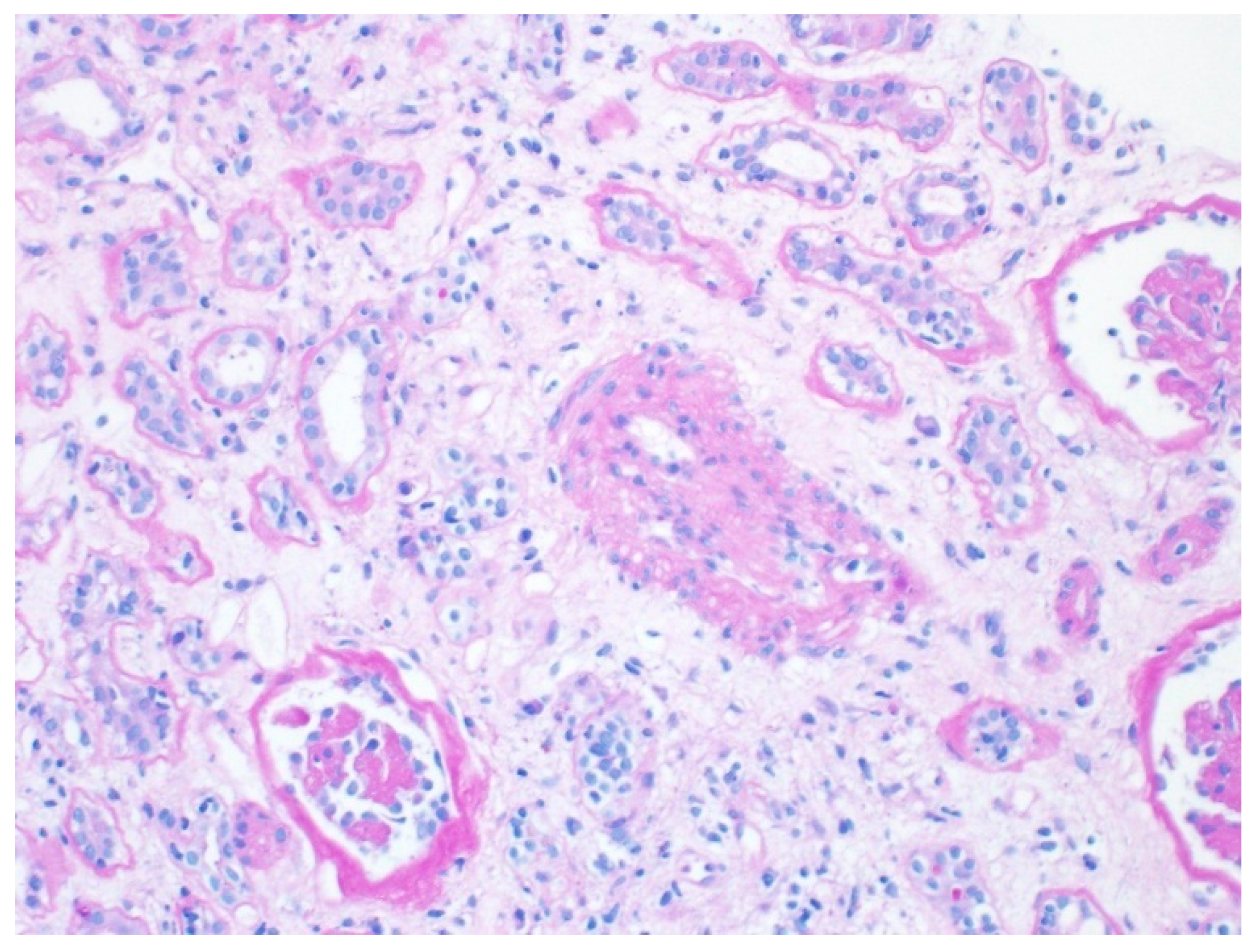
4. Histology
5. Diagnostic Evaluation
- A kidney ultrasound with Dopplers should be performed to assess blood flow and echogenicity of the allograft. A resistive index of 80 or higher has been identified as a strong predictor of long-term allograft failure [25]. While an ultrasound can offer valuable diagnostic information for allografts with chronic dysfunction, it is not a reliable screening test for chronic allograft dysfunction. Acute vascular rejection with endarteritis and chronic allograft nephropathy can both present with elevated resistive index and only a renal biopsy can distinguish them.
- Proteinuria should be assessed by a spot urine protein-to-creatinine ratio. If proteinuria > 1 gm/day is confirmed, a kidney biopsy should be performed.
- The presence of donor-specific antibodies (DSAs) should be assessed. The development of DSAs post-transplant is associated with poor outcomes in kidney transplantation [26,27,28]. Traditionally, DSAs have been associated with antibody-mediated rejection (ABMR) [29]. However, several studies have indicated that the development of DSAs signals a more complex immune response, reflecting the involvement of both humoral and cellular immunity [30,31].
- BK polyoma virus (BKPyV) should be assessed by measuring the BKPyV viral load. The reported incidence of BK nephropathy ranges from 1–10% in the current era of more effective immunosuppression [32,33]. BK nephropathy can result in severe damage to the allograft, potentially causing graft failure [34]. Histologically, it typically presents as a mononuclear cell interstitial infiltration with tubulitis. If left untreated, it can progress to a histologic pattern of tubular atrophy and chronic fibrosis [35].
- Although practices may vary between transplant centers, a kidney biopsy is recommended to confirm the diagnosis, exclude other possible conditions, and provide prognostic insights to aid in patient counseling.
5.1. Protocol Biopsies
5.2. Urinary Biomarkers
5.3. Novel Tissue Diagnostics
5.4. IF by Morphometry
5.5. Blood Biomarkers
5.6. Imaging
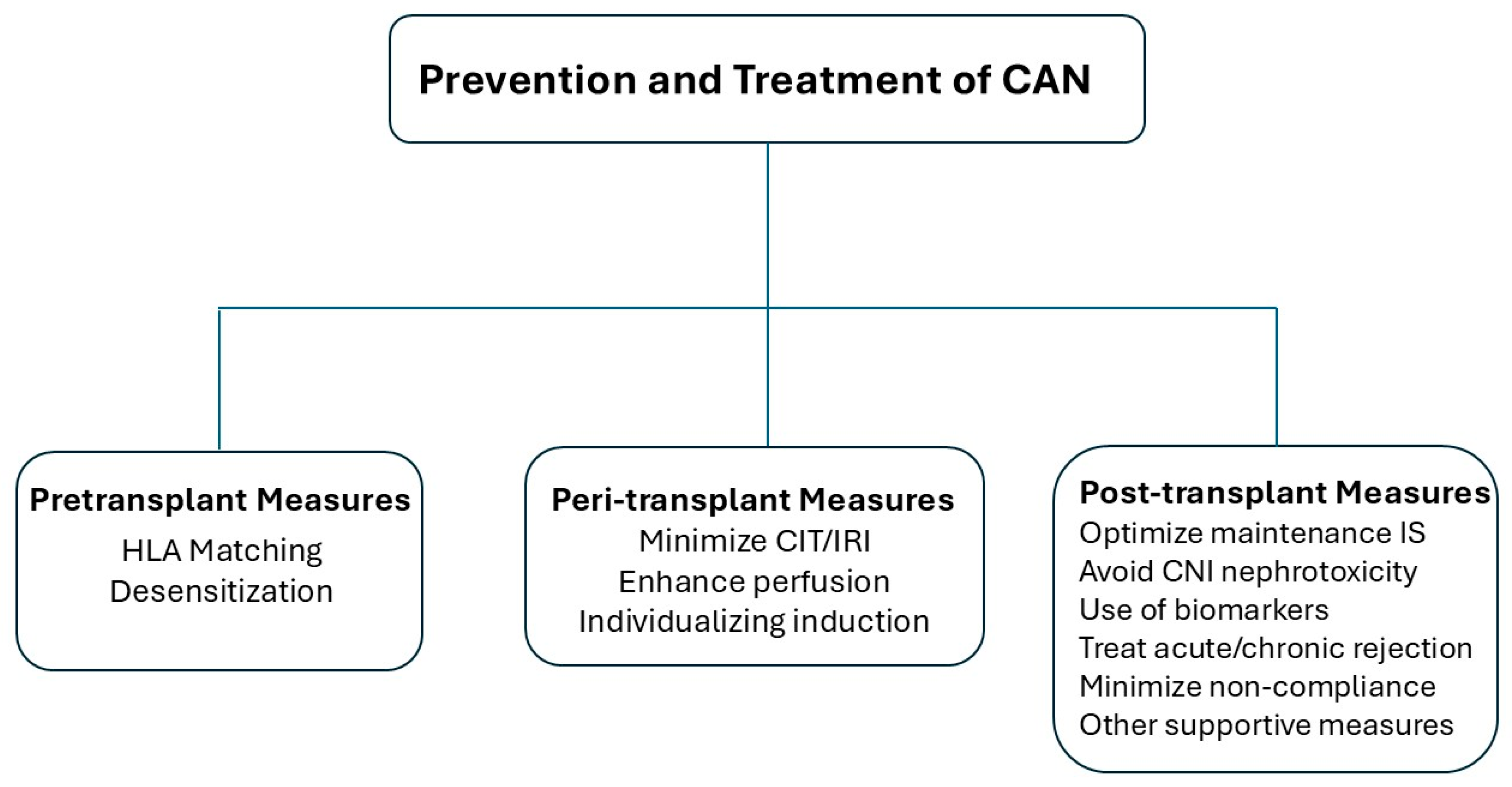
6. Management
6.1. Pre-Transplant Measures
6.1.1. HLA Matching
6.1.2. Desensitization in HLA-Incompatible Kidney Transplantation
6.2. Peri-Transplant Measures
6.2.1. Minimizing Cold Ischemia Time and Ischemia Reperfusion Injury (IRI)
6.2.2. Individualizing Induction Immunosuppression
6.3. Post-Transplant Measures
6.3.1. Optimizing Maintenance Immunosuppression
6.3.2. CNI Avoidance or Minimization Strategies
6.3.3. Treatment of Acute Rejection
6.3.4. Treatment of Chronic Rejection
6.3.5. Other Supportive Measures
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schwarz, A.; Mengel, M.; Gwinner, W.; Radermacher, J.; Hiss, M.; Kreipe, H.; Haller, H. Risk Factors for Chronic Allograft Nephropathy after Renal Transplantation: A Protocol Biopsy Study. Kidney Int. 2005, 67, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nankivell, B.J.; Borrows, R.J.; Fung, C.L.-S.; O’Connell, P.J.; Allen, R.D.M.; Chapman, J.R. The Natural History of Chronic Allograft Nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 2326–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shishido, S. The Impact of Repeated Subclinical Acute Rejection on the Progression of Chronic Allograft Nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2003, 14, 1046–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, W.; Mehta, R.; Jorgensen, D.R.; Sood, P.; Randhawa, P.; Wu, C.M.; Puttarajappa, C.; Shah, N.A.; Tevar, A.D.; Hariharan, S. The Impact of Early Clinical and Subclinical T Cell-Mediated Rejection after Kidney Transplantation. Transplantation 2019, 103, 1457–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gago, M.; Cornell, L.D.; Kremers, W.K.; Stegall, M.D.; Cosio, F.G. Kidney Allograft Inflammation and Fibrosis, Causes and Consequences. Am. J. Transplant. 2012, 12, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opelz, G.; Dohler, B. Effect of Human Leukocyte Antigen Compatibility on Kidney Graft Survival: Comparative Analysis of Two Decades. Transplantation 2007, 84, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambur, A.R. Human Leukocyte Antigen Matching in Organ Transplantation: What We Know and How Can We Make It Better (Revisiting the Past, Improving the Future). Curr. Opin. Organ Transplant. 2018, 23, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, R.; Sood, P.; Hariharan, S. Subclinical Rejection in Renal Transplantation. Transplantation 2016, 100, 1610–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier-Kriesche, H.; Steffen, B.J.; Hochberg, A.M.; Gordon, R.D.; Liebman, M.N.; Morris, J.A.; Kaplan, B. Long-Term Use of Mycophenolate Mofetil Is Associated with a Reduction in the Incidence and Risk of Late Rejection. Am. J. Transplant. 2002, 3, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrian, T.; Siriteanu, L.; Covic, A.S.; Ipate, C.A.; Miron, A.; Morosanu, C.; Caruntu, I.-D.; Covic, A. Non-Traditional Non-Immunological Risk Factors for Kidney Allograft Loss—Opinion. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joosten, S.A.; van Kooten, C.; Sijpkens, Y.W.J.; de Fijter, J.W.; Paul, L.C. The Pathobiology of Chronic Allograft Nephropathy: Immune-Mediated Damage and Accelerated Aging. Kidney Int. 2004, 65, 1556–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kais, H. Chronic Allograft Nephropathy. In After the Kidney Transplant the Patients and Their Allograft; Ortis, J., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Langewisch, E.; Mannon, R.B. Chronic Allograft Injury. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 16, 1723–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, I.B.; Moreso, F.; Sarró, E.; Meseguer, A.; Serón, D. The Interplay between Inflammation and Fibrosis in Kidney Transplantation. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 750602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eddy, A.A. Molecular Basis of Renal Fibrosis. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2000, 15, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, B.D. Mechanisms of Renal Fibrosis. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2018, 80, 309–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nankivell, B.J.; Chapman, J.R. Chronic Allograft Nephropathy: Current Concepts and Future Directions. Transplantation 2006, 81, 643–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halloran, P.F.; Melk, A.; Barth, C. Rethinking Chronic Allograft Nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1999, 10, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racusen, L.C.; Solez, K.; Colvin, R.B.; Bonsib, S.M.; Castro, M.C.; Cavallo, T.; Croker, B.P.; Demetris, A.J.; Drachenberg, C.B.; Fogo, A.B.; et al. The Banff 97 Working Classification of Renal Allograft Pathology. Kidney Int. 1999, 55, 713–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehtonen, S.; Taskinen, E.; Isoniemi, H. Histological Alterations in Implant and One-Year Protocol Biopsy Specimens of Renal Allografts. Transplantation 2001, 72, 1138–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosio, F.G.; Grande, J.P.; Larson, T.S.; Gloor, J.M.; Velosa, J.A.; Textor, S.C.; Griffin, M.D.; Stegall, M.D. Kidney Allograft Fibrosis and Atrophy Early after Living Donor Transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2005, 5, 1130–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, S.; Tomlanovich, S.; Mathew, T.H.; Taskinen, E.; Paavonen, T.; Medina, F.; Ramos, E.L.; Hooftman, L.; Häyry, P. Protocol Core Needle Biopsy and Histologic Chronic Allograft Damage Index (CADI) as Surrogate End Point for Long-Term Graft Survival in Multicenter Studies. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2003, 14, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuypers, D.R.J.; Chapman, J.; O’Connell, P.J.; Allen, R.D.M.; Nankivell, B.J. Predictors of Renal Transplant Histology at Three Months. Transplantation 1999, 67, 1222–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stegall, M.D.; Park, W.D.; Larson, T.S.; Gloor, J.M.; Cornell, L.D.; Sethi, S.; Dean, P.G.; Prieto, M.; Amer, H.; Textor, S.; et al. The Histology of Solitary Renal Allografts at 1 and 5 Years after Transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2010, 11, 698–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radermacher, J.; Mengel, M.; Ellis, S.; Stuht, S.; Hiss, M.; Schwarz, A.; Eisenberger, U.; Burg, M.; Luft, F.C.; Gwinner, W.; et al. The Renal Arterial Resistance Index and Renal Allograft Survival. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viglietti, D.; Loupy, A.; Vernerey, D.; Bentlejewski, C.; Gosset, C.; Aubert, O.; Duong van Huyen, J.-P.; Jouven, X.; Legendre, C.; Glotz, D.; et al. Value of Donor–Specific Anti–HLA Antibody Monitoring and Characterization for Risk Stratification of Kidney Allograft Loss. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 28, 702–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiebe, C.; Gibson, I.W.; Blydt-Hansen, T.D.; Karpinski, M.; Ho, J.; Storsley, L.J.; Goldberg, A.; Birk, P.E.; Rush, D.N.; Nickerson, P.W. Evolution and Clinical Pathologic Correlations of de Novo Donor-Specific HLA Antibody Post Kidney Transplant. Am. J. Transplant. 2012, 12, 1157–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worthington, J.E.; Martin, S.; Al-Husseini, D.M.; Dyer, P.A.; Johnson, R.W.G. Posttransplantation production of donor HLA-specific antibodies as a predictor of renal transplant outcome. Transplantation 2003, 75, 1034–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willicombe, M.; Brookes, P.; Sergeant, R.; Santos-Nunez, E.; Steggar, C.; Galliford, J.; Mclean, A.; Cook, T.H.; Cairns, T.; Roufosse, C.; et al. De Novo DQ Donor-Specific Antibodies Are Associated with a Significant Risk of Antibody-Mediated Rejection and Transplant Glomerulopathy. Transplant. J. 2012, 94, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherukuri, A.; Mehta, R.; Sharma, A.; Molinari, M.; Zeevi, A.; Tevar, A.D.; Rothstein, D.H.; Randhawa, P. Post-Transplant Donor Specific Antibody Is Associated with Poor Kidney Transplant Outcomes Only When Combined with Both T-Cell–Mediated Rejection and Non-Adherence. Kidney Int. 2019, 96, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R. Donor-Specific Antibodies in Kidney Transplant Recipients. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, H.H.; Knowles, W.; Dickenmann, M.; Passweg, J.; Klimkait, T.; Mihatsch, M.J.; Steiger, J. Prospective Study of Polyomavirus Type BK Replication and Nephropathy in Renal-Transplant Recipients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binet, I.; Nickeleit, V.; Hirsch, H.H.; Prince, O.; Dalquen, P.; Gudat, F.; Mihatsch, M.J.; Thiel, G. Polyomavirus Disease Under New Immunosuppressive Drugs. Transplantation 1999, 67, 918–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, H.H.; Randhawa, P.S. BKpolyomavirus in Solid Organ Transplantation—Guidelines from the American Society of Transplantation Infectious Diseases Community of Practice. Clin. Transplant. 2019, 33, e13528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nankivell, B.J.; Renthawa, J.; Sharma, R.N.; Kable, K.; O’Connell, P.J.; Chapman, J.R. BK Virus Nephropathy: Histological Evolution by Sequential Pathology. Am. J. Transplant. 2017, 17, 2065–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, J.R.; O’Connell, P.J.; Nankivell, B.J. Chronic Renal Allograft Dysfunction. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005, 16, 3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, B.; Schold, J.; Meier-Kriesche, H.-U. Poor Predictive Value of Serum Creatinine for Renal Allograft Loss. Am. J. Transplant. 2003, 3, 1560–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nankivell, B.J.; Chapman, J.R. The Significance of Subclinical Rejection and the Value of Protocol Biopsies. Am. J. Transplant. 2006, 6, 2006–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Saeed, M.; Ranganna, K.; Malat, G.; Sustento-Reodica, N.; Kumar, A.; Meyers, W.C. Comparison of Four Different Immunosuppression Protocols without Long-Term Steroid Therapy in Kidney Recipients Monitored by Surveillance Biopsy: Five-Year Outcomes. Transpl. Immunol. 2008, 20, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owoyemi, I.; Tandukar, S.; Jorgensen, D.R.; Wu, C.M.; Sood, P.; Puttarajappa, C.; Sharma, A.; Shah, N.A.; Randhawa, P.; Molinari, M.; et al. Impact of Subclinical and Clinical Kidney Allograft Rejection within 1 Year Posttransplantation among Compatible Transplant with Steroid Withdrawal Protocol. Transplant. Direct 2021, 7, e706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rush, D.; Nickerson, P.; Gough, J.; McKenna, R.; Grimm, P.; Cheang, M.; Trpkov, K.; Solez, K.; Jeffery, J. Beneficial Effects of Treatment of Early Subclinical Rejection. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1998, 9, 2129–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.S.; Lim, S.J.; Jalalonmuhali, M.; Ng, K.S.; Lim, S.K.; Ng, K.P. Clinical Significance of Renal Allograft Protocol Biopsies: A Single Tertiary Center Experience in Malaysia. J. Transplant. 2019, 2019, 9153875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kee, T.Y.-S.; Chapman, J.R.; O’Connell, P.J.; Fung, C.L.-S.; Allen, R.D.M.; Kable, K.; Vitalone, M.J.; Nankivell, B.J. Treatment of Subclinical Rejection Diagnosed by Protocol Biopsy of Kidney Transplants. Transplantation 2006, 82, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loupy, A.; Vernerey, D.; Tinel, C.; Aubert, O.; van Huyen, J.-P.D.; Rabant, M.; Verine, J.; Nochy, D.; Empana, J.-P.; Martinez, F.; et al. Subclinical Rejection Phenotypes at 1 Year Post-Transplant and Outcome of Kidney Allografts. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 1721–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, R.B.; Melgarejo, I.; Viswanathan, V.; Zhang, X.; Pittappilly, M.; Randhawa, P.; Puttarajappa, C.; Sood, P.; Wu, C.; Sharma, A.; et al. Long-Term Immunological Outcomes of Early Subclinical Inflammation on Surveillance Kidney Allograft Biopsies. Kidney Int. 2022, 102, 1371–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anglicheau, D.; Suthanthiran, M. Noninvasive Prediction of Organ Graft Rejection and Outcome Using Gene Expression Patterns. Transplantation 2008, 86, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloom, R.D.; Augustine, J.J. Beyond the Biopsy: Monitoring Immune Status in Kidney Recipients. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 16, 1413–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suthanthiran, M.; Schwartz, J.E.; Ding, R.; Abecassis, M.; Dadhania, D.; Samstein, B.; Knechtle, S.J. Urinary-Cell mRNA Profile and Acute Cellular Rejection in Kidney Allografts. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.; Sharma, A.; Kroeker, K.; Carroll, R.; De Serres, S.; Gibson, I.W.; Hirt-Minkowski, P.; Jevnikar, A.; Joseph Kim, S.; Knoll, G.; et al. Multicentre Randomised Controlled Trial Protocol of Urine CXCL10 Monitoring Strategy in Kidney Transplant Recipients. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e024908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halloran, P.F.; Pereira, A.B.; Chang, J.; Matas, A.; Picton, M.; De Freitas, D.; Bromberg, J.; Serón, D.; Sellarés, J.; Einecke, G.; et al. Microarray Diagnosis of Antibody-Mediated Rejection in Kidney Transplant Biopsies: An International Prospective Study (INTERCOM). Am. J. Transplant. 2013, 13, 2865–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halloran, P.F.; Reeve, J.; Akalin, E.; Aubert, O.; Bohmig, G.A.; Brennan, D.; Bromberg, J.; Einecke, G.; Eskandary, F.; Gosset, C.; et al. Real Time Central Assessment of Kidney Transplant Indication Biopsies by Microarrays: The INTERCOMEX Study. Am. J. Transplant. 2017, 17, 2851–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schachtner, T.; von Moos, S.; Kokkonen, S.M.; Helmchen, B.; Gaspert, A.; Mackova, M.; Halloran, P.F.; Mueller, T.F. The Molecular Diagnosis Might Be Clinically Useful in Discrepant Kidney Allograft Biopsy Findings: An Analysis of Clinical Outcomes. Transplantation 2023, 107, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randhawa, P.S. The Molecular Microscope Diagnostic System (MMDx) in Transplantation: A Pathologist’s Perspective. Am. J. Transplant. 2022, 20, 1965–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connell, P.J.; Zhang, W.; Menon, M.C.; Yi, Z.; Schröppel, B.; Gallon, L.; Luan, Y.; Rosales, I.A.; Ge, Y.; Losic, B.; et al. Biopsy Transcriptome Expression Profiling to Identify Kidney Transplants at Risk of Chronic Injury: A Multicentre, Prospective Study. Lancet 2016, 388, 983–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bestard, O.; Augustine, J.; Wee, A.; Poggio, E.; Mannon, R.B.; Javeed Ansari, M.; Bhati, C.; Maluf, D.; Benken, S.; Leca, N.; et al. Prospective Observational Study to Validate a Next-Generation Sequencing Blood RNA Signature to Predict Early Kidney Transplant Rejection. Am. J. Transplant. 2023, 24, 436–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denic, A.; Bogojevic, M.; Mullan, A.F.; Sabov, M.; Asghar, M.S.; Sethi, S.; Smith, M.; Fervenza, F.C.; Glasscock, R.J.; Hommos, M.S.; et al. Prognostic Implications of a Morphometric Evaluation for Chronic Changes on All Diagnostic Native Kidney Biopsies. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2022, 33, 1927–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricaurte Archila, L.; Denic, A.; Mullan, A.F.; Narasimhan, R.; Bogojevic, M.; Thompson, R.H.; Leibovich, B.C.; Sangaralingham, S.J.; Smith, M.L.; Alexander, M.P.; et al. A Higher Foci Density of Interstitial Fibrosis and Tubular Atrophy Predicts Progressive CKD after a Radical Nephrectomy for Tumor. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 32, 2623–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denic, A.; Rule, A.; Park, W.D.; Smith, B.H.; Mejia, M.V.; Kukla, A.; Grande, J.P.; Stegall, M.D. IFTA Foci Density: An Unrecognized Highly Prognostic Measurement of Fibrosis in Kidney Transplant Biopsies. Kidney360 2024, 5, 1341–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloom, R.; Bromberg, J.; Poggio, E.; Bunnapradist, S.; Langone, A.; Sood, P.; Matas, A.; Mehta, S.; Mannon, R.; Sharfuddin, A.; et al. Cell-Free DNA and Active Rejection in Kidney Allografts. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 2221–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derieppe, M.; Delmas, Y.; Gennisson, J.-L.; Deminière, C.; Placier, S.; Tanter, M.; Combe, C.; Grenier, N. Detection of Intrarenal Microstructural Changes with Supersonic Shear Wave Elastography in Rats. Eur. Radiol. 2011, 22, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.-R.; La, Q.; Ding, X.-M.; Song, Y. Application of Real-Time Sound Touch Elastography for Evaluating Chronic Kidney Disease of Transplanted Kidneys. Transplant. Proc. 2023, 55, 2095–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Distefano, G.; Granata, S.; Morale, W.; Granata, A. Advancements in Elastography for Evaluating Fibrosis in Renal Transplants: Current Perspectives. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, W.H.; Chadban, S.J.; Clayton, P.; Budgeon, C.A.; Murray, K.; Campbell, S.B.; Cohney, S.; Russ, G.R.; McDonald, S.P. Human Leukocyte Antigen Mismatches Associated with Increased Risk of Rejection, Graft Failure, and Death Independent of Initial Immunosuppression in Renal Transplant Recipients. Clin. Transplant. 2012, 26, E428–E437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, R.C.; Opelz, G.; McGarvey, C.J.; Weil, E.J.; Chakkera, H.A. The Risk of Transplant Failure with HLA Mismatch in First Adult Kidney Allografts from Deceased Donors. Transplantation 2016, 100, 1094–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, W.H.; Chapman, J.R.; Coates, P.T.; Lewis, J.R.; Russ, G.; Watson, N.; Holdsworth, R.; Wong, G. HLA-DQ Mismatches and Rejection in Kidney Transplant Recipients. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 11, 875–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeaphorn, N.; Pena, J.R.A.; Thamcharoen, N.; Khankin, E.V.; Pavlakis, M.; Cardarelli, F. HLA-DQ Mismatching and Kidney Transplant Outcomes. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 13, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senev, A.; Coemans, M.; Lerut, E.; Sandt, V.V.; Kerkhofs, J.; Daniëls, L.; Driessche, M.V.; Compernolle, V.; Sprangers, B.; Loon, E.V.; et al. Eplet Mismatch Load and de Novo Occurrence of Donor-Specific Anti-HLA Antibodies, Rejection, and Graft Failure after Kidney Transplantation: An Observational Cohort Study. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 31, 2193–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do Nguyen, H.T.; Wong, G.; Chapman, J.R.; McDonald, S.P.; Coates, P.T.; Watson, N.; Russ, G.R.; D’Orsogna, L.; Lim, W.H. The Association between Broad Antigen HLA Mismatches, Eplet HLA Mismatches and Acute Rejection after Kidney Transplantation. Transplant. Direct 2016, 2, e120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkins, N.G.; Wong, G.; Taverniti, A.; Lim, W.H. Epitope Matching in Kidney Transplantation. Curr. Opin. Organ Transplant. 2019, 24, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, S.; Palanisamy, A.; Tsapepas, D.; Tanriover, B.; Crew, R.J.; Dube, G.; Ratner, L.E.; Cohen, D.J.; Radhakrishnan, J. Donor-Specific Antibodies Adversely Affect Kidney Allograft Outcomes. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 23, 2061–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motter, J.; Massie, A.B.; Segev, D.L. 423.3: Long-Term Outcomes Following HLA-Incompatible Living Donor Kidney Transplantation. Transplantation 2022, 106 (Suppl. S9), S464–S465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnasco, S.M.; Zachary, A.A.; Racusen, L.C.; Arend, L.J.; Carter-Monroe, N.; Alachkar, N.; Nazarian, S.M.; Lonze, B.E.; Montgomery, R.A.; Kraus, E.S. Time Course of Pathologic Changes in Kidney Allografts of Positive Crossmatch HLA-Incompatible Transplant Recipients. Transplantation 2014, 97, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orandi, B.J.; Luo, X.; Massie, A.B.; Garonzik-Wang, J.M.; Lonze, B.E.; Ahmed, R.; Van Arendonk, K.J.; Stegall, M.D.; Jordan, S.C.; Oberholzer, J.; et al. Survival Benefit with Kidney Transplants from HLA-Incompatible Live Donors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 940–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postalcioglu, M.; Kaze, A.D.; Byun, B.C.; Siedlecki, A.; Tullius, S.G.; Milford, E.L.; Paik, J.M.; Abdi, R. Association of Cold Ischemia Time with Acute Renal Transplant Rejection. Transplantation 2018, 102, 1188–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, G.; Teixeira-Pinto, A.; Chapman, J.R.; Craig, J.C.; Pleass, H.; McDonald, S.; Lim, W.H. The Impact of Total Ischemic Time, Donor Age and the Pathway of Donor Death on Graft Outcomes after Deceased Donor Kidney Transplantation. Transplantation 2017, 101, 1152–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debout, A.; Foucher, Y.; Trébern-Launay, K.; Legendre, C.; Kreis, H.; Mourad, G.; Garrigue, V.; Morelon, E.; Buron, F.; Rostaing, L.; et al. Each Additional Hour of Cold Ischemia Time Significantly Increases the Risk of Graft Failure and Mortality Following Renal Transplantation. Kidney Int. 2015, 87, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cashion, W.T.; Zhang, X.; Puttarajappa, C.; Sharma, A.; Mehta, R.; Ganoza, A.; Gunabushanam, V.; Sood, P.; Wu, C.; Cherukuri, A.; et al. Interaction between Cold Ischemia Time and KDPI on Post Renal Transplant Outcomes. Am. J. Transplant. 2024, 24, 781–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Potluri, V.S.; Molinari, M.; Giuntella, O.; Hariharan, S.; Puttarajappa, C.M. Impact of Kidney Allocation System 250 Policy on 1-Year Graft Loss. Am. J. Transplant. 2024; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puttarajappa, C.M.; Hariharan, S.; Zhang, X.; Tevar, A.; Mehta, R.; Gunabushanam, V.; Sood, P.; Hoffman, W.; Mohan, S. Early Effect of the Circular Model of Kidney Allocation in the United States. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2023, 34, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moers, C.; Smits, J.M.; Maathuis, M.-H.J.; Treckmann, J.; van Gelder, F.; Napieralski, B.P.; van Kasterop-Kutz, M.; van der Heide, J.J.H.; Squifflet, J.-P.; van Heurn, E.; et al. Machine Perfusion or Cold Storage in Deceased-Donor Kidney Transplantation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treckmann, J.; Moers, C.; Smits, J.M.; Gallinat, A.; Maathuis, M.-H.J.; van Kasterop-Kutz, M.; Jochmans, I.; Homan van der Heide, J.J.; Squifflet, J.-P.; van Heurn, E.; et al. Machine Perfusion versus Cold Storage for Preservation of Kidneys from Expanded Criteria Donors after Brain Death. Transpl. Int. 2011, 24, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tingle, S.J.; Figueiredo, R.S.; Moir, J.A.G.; Goodfellow, M.; Thompson, E.R.; Ibrahim, I.K.; Bates, L.; Talbot, D.; Wilson, C.H. Hypothermic Machine Perfusion Is Superior to Static Cold Storage in Deceased Donor Kidney Transplantation: A Meta-Analysis. Clin. Transplant. 2020, 34, e13814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delsuc, C.; Faure, A.; Berthiller, J.; Dorez, D.; Matillon, X.; Meas-Yedid, V.; Floccard, B.; Marcotte, G.; Labeye, V.; Rabeyrin, M.; et al. Uncontrolled Donation after Circulatory Death: Comparison of Two Kidney Preservation Protocols on Graft Outcomes. BMC Nephrol. 2018, 19, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearson, R.; Geddes, C.; Mark, P.; Clancy, M.; Asher, J. Transplantation of Kidneys after Normothermic Perfusion: A Single Center Experience. Clin. Transplant. 2021, 35, e14431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demiselle, J.; Augusto, J.-F.; Videcoq, M.; Legeard, E.; Dubé, L.; Templier, F.; Renaudin, K.; Sayegh, J.; Karam, G.; Blancho, G.; et al. Transplantation of Kidneys from Uncontrolled Donation after Circulatory Determination of Death: Comparison with Brain Death Donors with or without Extended Criteria and Impact of Normothermic Regional Perfusion. Transpl. Int. 2016, 29, 432–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoneima, A.S.; Sousa Da Silva, R.X.; Gosteli, M.A.; Barlow, A.D.; Kron, P. Outcomes of Kidney Perfusion Techniques in Transplantation from Deceased Donors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, P.; Vázquez, D.; Rodríguez, G.; Rubio, J.J.; Pérez, M.; Portolés, J.M.; Carballido, J. Kidney Transplants in Controlled Donation Following Circulatory Death, or Maastricht Type III Donors, with Abdominal Normothermic Regional Perfusion, Optimizing Functional Outcomes. Transplant. Direct 2021, 7, e725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla, M.; Coll, E.; Fernández-Pérez, C.; Pont, T.; Ruiz, Á.; Pérez-Redondo, M.; Oliver, E.; Atutxa, L.; Manciño, J.M.; Daga, D.; et al. Improved Short-Term Outcomes of Kidney Transplants in Controlled Donation after the Circulatory Determination of Death with the Use of Normothermic Regional Perfusion. Am. J. Transplant. Off. J. Am. Soc. Transplant. Am. Soc. Transpl. Surg. 2021, 21, 3618–3628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merani, S.; Urban, M.; Westphal, S.G.; Dong, J.; Miles, C.D.; Maskin, A.; Hoffman, A.; Langnas, A.N. Improved Early Post-Transplant Outcomes and Organ Use in Kidney Transplant Using Normothermic Regional Perfusion for Donation after Circulatory Death: National Experience in the US. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2024, 238, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanaway, M.J.; Woodle, E.S.; Mulgaonkar, S.; Peddi, V.R.; Kaufman, D.B.; First, M.R.; Croy, R.; Holman, J. Alemtuzumab Induction in Renal Transplantation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1909–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, R.; Judge, P.; Blackwell, L.; Emberson, J.; Landray, M.J.; Baigent, C.; Friend, P.J. Alemtuzumab-Based Induction Treatment versus Basiliximab-Based Induction Treatment in Kidney Transplantation (the 3C Study): A Randomised Trial. Lancet 2014, 384, 1684–1690. [Google Scholar]
- Ciancio, G.; Burke, G.W.; Gaynor, J.J.; Roth, D.; Kupin, W.; Rosen, A.; Cordovilla, T.; Tueros, L.; Herrada, E.; Miller, J. A Randomized Trial of Thymoglobulin vs. Alemtuzumab (with Lower Dose Maintenance Immunosuppression) vs. Daclizumab in Renal Transplantation at 24 Months of Follow-Up. Clin. Transplant. 2008, 22, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sureshkumar, K.K.; Thai, N.L.; Hussain, S.M.; Ko, T.Y.; Marcus, R.J. Influence of Induction Modality on the Outcome of Deceased Donor Kidney Transplant Recipients Discharged on Steroid-Free Maintenance Immunosuppression. Transplantation 2012, 93, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Heifets, M.; Moritz, M.L.; Saeed, M.; Khan, S.B.; Fyfe, B.; Sustento-Riodeca, N.; Daniel, J.; Kumar, A. Safety and Efficacy of Steroid Withdrawal Two Days after Kidney Transplantation: Analysis of Results at Three Years. Transplantation 2006, 81, 832–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.S.A.; Heifets, M.; Fyfe, B.; Saaed, M.I.; Moritz, M.J.; Parikh, M.H.; Kumar, A. Comparison of Steroid Avoidance in Tacrolimus/Mycophenolate Mofetil and Tacrolimus/Sirolimus Combination in Kidney Transplantation Monitored by Surveillance Biopsy. Transplantation 2005, 80, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomusch, O.; Wiesener, M.S.; Opgenoorth, M.; Pascher, A.; Woitas, R.P.; Witzke, O.; Jaenigen, B.; Rentsch, M.; Wolters, H.; Rath, T.; et al. Rabbit-ATG or Basiliximab Induction for Rapid Steroid Withdrawal after Renal Transplantation (Harmony): An Open-Label, Multicentre, Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet 2016, 388, 3006–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumpf, J.; Thomusch, O.; Opgenoorth, M.; Wiesener, M.; Pascher, A.; Woitas, R.P.; Suwelack, B.; Rentsch, M.; Witzke, O.; Rath, T.; et al. Excellent Efficacy and Beneficial Safety during Observational 5-Year Follow-up of Rapid Steroid Withdrawal after Renal Transplantation (Harmony FU Study). Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2023, 39, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantarovich, D.; Rostaing, L.; Kamar, N.; Ducloux, D.; Saint-Hillier, Y.; Mourad, G.; Garrigue, V.; Wolf, P.; Ellero, B.; Cassuto, E.; et al. Early Corticosteroid Avoidance in Kidney Transplant Recipients Receiving ATG-F Induction: 5-Year Actual Results of a Prospective and Randomized Study. Am. J. Transplant. 2014, 14, 2556–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.; Chen, Y.; Sandal, S.; Lentine, K.L.; Schnitzler, M.; Segev, D.L.; DeMarco, M.A.M. Early Steroid Withdrawal and Kidney Transplant Outcomes in First-Transplant and Retransplant Recipients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2024, 40, 662–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farouk, S.S.; Rein, J.L. The Many Faces of Calcineurin Inhibitor Toxicity—What the FK? Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2020, 27, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diekmann, F.; Budde, K.; Oppenheimer, F.; Fritsche, L.; Neumayer, H.-H.; Campistol, J.M. Predictors of Success in Conversion from Calcineurin Inhibitor to Sirolimus in Chronic Allograft Dysfunction. Am. J. Transplant. 2004, 4, 1869–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diekmann, F.; Campistol, J.M. Conversion from Calcineurin Inhibitors to Sirolimus in Chronic Allograft Nephropathy: Benefits and Risks. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2005, 21, 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawinski, D.; Trofe-Clark, J.; Leas, B.; Uhl, S.; Tuteja, S.; Kaczmarek, J.L.; French, B.; Umscheid, C.A. Calcineurin Inhibitor Minimization, Conversion, Withdrawal, and Avoidance Strategies in Renal Transplantation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Transplant. 2016, 16, 2117–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincenti, F.; Charpentier, B.; Vanrenterghem, Y.; Rostaing, L.; Bresnahan, B.; Darji, P.; Massari, P.; Mondragon-Ramirez, G.A.; Agarwal, M.; Di Russo, G.; et al. A Phase III Study of Belatacept-Based Immunosuppression Regimens versus Cyclosporine in Renal Transplant Recipients (BENEFIT Study). Am. J. Transplant. 2010, 10, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostaing, L.; Vincenti, F.; Grinyó, J.M.; Rice, K.L.; Bresnahan, B.A.; Steinberg, S.M.; Gang, S.; Gaite, L.E.; Moal, M.-C.; Mondragón-Ramirez, G.A.; et al. Long-Term Belatacept Exposure Maintains Efficacy and Safety at 5 Years: Results from the Long-Term Extension of the BENEFIT Study. Am. J. Transplant. 2013, 13, 2875–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincenti, F.; Rostaing, L.; Grinyo, J.; Rice, K.; Steinberg, S.; Gaite, L.; Moal, M.-C.; Mondragon-Ramirez, G.A.; Kothari, J.; Polinsky, M.S.; et al. Belatacept and Long-Term Outcomes in Kidney Transplantation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budde, K.; Prashar, R.; Haller, H.; Rial, M.C.; Kamar, N.; Agarwal, A.; de Fijter, J.W.; Rostaing, L.; Berger, S.P.; Djamali, A.; et al. Conversion from Calcineurin Inhibitor- to Belatacept-Based Maintenance Immunosuppression in Renal Transplant Recipients: A Randomized Phase 3b Trial. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 32, 3252–3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Fijter, J.W. Rejection and Function and Chronic Allograft Dysfunction. Kidney Int. 2010, 78, S38–S41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, F.; Parajuli, S.; Garg, N.; Mohamed, M.; Zhong, W.; Djamali, A.; Mandelbrot, D. How Should Acute T-Cell Mediated Rejection of Kidney Transplants Be Treated: Importance of Follow-up Biopsy. Transplant. Direct 2022, 8, e1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan, S.; Carroll, R. How Should Acute T Cell–Mediated Rejection of Kidney Transplants Be Treated: Importance of Follow-up Biopsy from Kidney Transplantation. Transplant. Direct 2023, 9, e1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landsberg, A.; Raza, S.S.; Seifert, M.E.; Blydt-Hansen, T.D. Follow-up Biopsies Identify High Rates of Persistent Rejection in Pediatric Kidney Transplant Recipients after Treatment of T Cell-Mediated Rejection. Pediatr. Transplant. 2023, 28, e14617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, F.; Parajuli, S.; Jorgenson, M.; Garg, N.; Manchala, V.; Yousif, E.; Mandelbrot, D.; Hidalgo, L.; Mohamed, M.; Zhong, W.; et al. Chronic Active Antibody-Mediated Rejection in Kidney Transplant Recipients: Treatment Response Rates and Value of Early Surveillance Biopsies. Transplant. Direct 2022, 8, e1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redfield, R.R.; Ellis, T.M.; Zhong, W.; Scalea, J.R.; Zens, T.J.; Mandelbrot, D.; Muth, B.L.; Panzer, S.; Samaniego, M.; Kaufman, D.B.; et al. Current Outcomes of Chronic Active Antibody Mediated Rejection—A Large Single Center Retrospective Review Using the Updated BANFF 2013 Criteria. Hum. Immunol. 2016, 77, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schinstock, C.A.; Mannon, R.B.; Budde, K.; Chong, A.S.; Haas, M.; Knechtle, S.; Lefaucheur, C.; Montgomery, R.A.; Nickerson, P.; Tullius, S.G.; et al. Recommended Treatment for Antibody-Mediated Rejection after Kidney Transplantation: The 2019 Expert Consensus from the Transplantion Society Working Group. Transplantation 2020, 104, 911–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, M.; Baliker, M.; Van Gelder, T.; Böhmig, G.A.; Mannon, R.B.; Kumar, D.; Chadban, S.; Nickerson, P.; Lee, L.A.; Djamali, A. Chronic Active Antibody-Mediated Rejection: Opportunity to Determine the Role of Interleukin-6 Blockade. Transplantation 2023, 108, 1109–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stringer, D.; Gardner, L.; Shaw, O.; Clarke, B.; Briggs, D.; Worthington, J.; Buckland, M.; Danzi, G.; Hilton, R.; Picton, M.; et al. Optimized Immunosuppression to Prevent Graft Failure in Renal Transplant Recipients with HLA Antibodies (OuTSMART): A Randomised Controlled Trial. eClinicalMedicine 2023, 56, 101819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CSL Behring. Clazakizumab for the Treatment of Chronic Active Antibody Mediated Rejection in Kidney Transplant Recipients (IMAGINE). ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT03744910. Updated 24 April 2014. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03744910 (accessed on 27 February 2025).
- Mayer, K.A.; Schrezenmeier, E.; Diebold, M.; Halloran, P.F.; Schatzl, M.; Schranz, S.; Haindl, S.; Kasbohm, S.; Kainz, A.; Eskandary, F.; et al. A Randomized Phase 2 Trial of Felzartamab in Antibody-Mediated Rejection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 391, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskandary, F.; Regele, H.; Baumann, L.; Bond, G.; Kozakowski, N.; Wahrmann, M.; Hidalgo, L.G.; Haslacher, H.; Kaltenecker, C.C.; Aretin, M.-B.; et al. A Randomized Trial of Bortezomib in Late Antibody-Mediated Kidney Transplant Rejection. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 29, 591–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreso, F.; Crespo, M.; Ruiz, J.C.; Torres, A.; Gutierrez-Dalmau, A.; Osuna, A.; Perelló, M.; Pascual, J.; Torres, I.B.; Redondo-Pachón, D.; et al. Treatment of Chronic Antibody Mediated Rejection with Intravenous Immunoglobulins and Rituximab: A Multicenter, Prospective, Randomized, Double-Blind Clinical Trial. Am. J. Transplant. 2017, 18, 927–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiu, K.Y.; Stringer, D.; McLaughlin, L.; Shaw, O.; Brookes, P.; Burton, H.; Wilkinson, H.; Douthwaite, H.; Tsui, T.-L.; Mclean, A.; et al. Effect of Optimized Immunosuppression (Including Rituximab) on Anti-Donor Alloresponses in Patients with Chronically Rejecting Renal Allografts. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frederick, T. Fostamatinib in the Treatment of Chronic Active Antibody Mediated Rejection (FOSTAMR). Updated 25 November 2024. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03991780 (accessed on 27 February 2025).
- Doberer, K.; Duerr, M.; Halloran, P.F.; Eskandary, F.; Budde, K.; Regele, H.; Reeve, J.; Borski, A.; Kozakowski, N.; Reindl-Schwaighofer, R.; et al. A Randomized Clinical Trial of Anti–IL-6 Antibody Clazakizumab in Late Antibody-Mediated Kidney Transplant Rejection. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 32, 708–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickerson, P.W.; Böhmig, G.A.; Chadban, S.; Kumar, D.; Mannon, R.B.; van Gelder, T.; Lee, J.C.; Adler, S.; Chong, E.; Djamali, A. Clazakizumab for the Treatment of Chronic Active Antibody-Mediated Rejection (AMR) in Kidney Transplant Recipients: Phase 3 IMAGINE Study Rationale and Design. Trials 2022, 23, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streichart, L.; Felldin, M.; Ekberg, J.; Mjörnstedt, L.; Lindnér, P.; Lennerling, A.; Bröcker, V.; Mölne, J.; Holgersson, J.; Daenen, K.; et al. Tocilizumab in Chronic Active Antibody-Mediated Rejection: Rationale and Protocol of an In-Progress Randomized Controlled Open-Label Multi-Center Trial (INTERCEPT Study). Trials 2024, 25, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eskandary, F.; Jilma, B.; Mühlbacher, J.; Wahrmann, M.; Regele, H.; Kozakowski, N.; Firbas, C.; Panicker, S.; Parry, G.C.; Gilbert, J.C.; et al. Anti-C1s Monoclonal Antibody BIVV009 in Late Antibody-Mediated Kidney Allograft Rejection—Results from a First-In-Patient Phase 1 Trial. Am. J. Transplant. 2018, 18, 916–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, S.; Kirkiles-Smith, N.C.; Deng, Y.H.; Formica, R.N.; Moeckel, G.; Broecker, V.; Bow, L.; Tomlin, R.; Pober, J.S. Eculizumab Therapy for Chronic Antibody-Mediated Injury in Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial. Am. J. Transplant. 2016, 17, 682–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengel, M.; Lubetzky, M. Do We Need to Treat Chronic Active T Cell–Mediated Rejection? Kidney Int. 2021, 100, 275–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helgeson, E.S.; Mannon, R.; Grande, J.; Gaston, R.S.; Cecka, M.J.; Kasiske, B.L.; Rush, D.; Gourishankar, S.; Cosio, F.; Hunsicker, L.; et al. I-IFTA and Chronic Active T Cell–Mediated Rejection: A Tale of 2 (DeKAF) Cohorts. Am. J. Transplant. 2020, 21, 1866–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halloran, P.F.; Matas, A.; Kasiske, B.L.; Madill-Thomsen, K.S.; Mackova, M.; Famulski, K.S. Molecular Phenotype of Kidney Transplant Indication Biopsies with Inflammation in Scarred Areas. Am. J. Transplant. 2018, 19, 1356–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, V.L.; Sandhu, R.; Haas, M.; Huang, E. Chronic Active T Cell–Mediated Rejection Is Variably Responsive to Immunosuppressive Therapy. Kidney Int. 2021, 100, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, H.; Matsukuma, Y.; Nakagawa, K.; Ueki, K.; Tsuchimoto, A.; Nakano, T.; Sato, Y.; Kaku, K.; Okabe, Y.; Nakamura, M. Treatment of Chronic Active T Cell-Mediated Rejection after Kidney Transplantation: A Retrospective Cohort Study of 37 Transplants. Nephrology 2022, 27, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opelz, G.; Dohler, B. Improved Long-Term Outcomes after Renal Transplantation Associated with Blood Pressure Control. Am. J. Transplant. 2005, 5, 2725–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mange, K.C. Blood Pressure and the Survival of Renal Allografts from Living Donors. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2004, 15, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Special Issue: KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for the Care of Kidney Transplant Recipients. Am. J. Transplant. 2009, 9, S1–S155. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knoll, G.A.; Fergusson, D.; Chassé, M.; Hebert, P.; Wells, G.; Tibbles, L.A.; Treleaven, D.; Holland, D.; White, C.; Muirhead, N.; et al. Ramipril versus Placebo in Kidney Transplant Patients with Proteinuria: A Multicentre, Double-Blind, Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2016, 4, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahaim, H.; Jackson, S.; Connaire, J.; Matas, A.; Ney, A.; Najafian, B.; West, A.; Lentsch, N.; Ericksen, J.; Bodner, J.; et al. Angiotensin II Blockade in Kidney Transplant Recipients. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 24, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maigret, L.; Basle, L.; Chatelet, V.; Ecotiere, L.; Perrin, P.; Golbin, L.; Bertrand, D.; Anglicheau, D.; Poulain, C.; Garrouste, C.; et al. SGLT2 Inhibitor in Diabetic and Non-Diabetic Renal Transplant Recipients. Kidney Int. Rep. 2024, 15, 1332397. [Google Scholar]
- Lemke, A.; Brokmeier, H.M.; Leung, S.B.; Mara, K.C.; Mour, G.K.; Wadei, H.M.; Hill, J.M.; Stegall, M.; Kudva, Y.C.; Shah, P.; et al. Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors for Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus after Kidney Transplantation. Clin. Transplant. 2022, 36, e14718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.C.; Brown, A.; Winstead, R.; Yakubu, I.; Demehin, M.; Kumar, D.; Gupta, G. Early Initiation of Sodium-Glucose Linked Transporter Inhibitors (SGLT-2i) and Associated Metabolic and Electrolyte Outcomes in Diabetic Kidney Transplant Recipients. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. 2020, 4, e00185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halden, T.A.S.; Kvitne, K.E.; Midtvedt, K.; Rajakumar, L.; Robertsen, I.; Brox, J.; Bollerslev, J.; Hartmann, A.; Åsberg, A.; Jenssen, T. Efficacy and Safety of Empagliflozin in Renal Transplant Recipients with Posttransplant Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 1067–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S. Efficacy, Mechanisms and Safety of SGLT2 Inhibitors in Kidney Transplant Recipients (INFINITI2019). ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT04965935. Updated 3 February 2025. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04965935 (accessed on 27 February 2025).
- Wolf, M. CardioRenal Effects of SGLT2 Inhibition in Kidney Transplant Recipients (CREST-KT). ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT04906213. Updated 28 February 2024. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04906213 (accessed on 27 February 2025).
| Grade | Histology | Interstitial Fibrosis (ci) | Tubular Atrophy (ct) |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | Mild | ci1: 6–25% of cortical area | ct1: Up to 25% of cortical tubules |
| II | Moderate | ci2: 26–50% of cortical area | ct2: 26–50% of cortical tubules |
| III | Severe | ci3: >50% of cortical area | ct3: >50% of cortical tubules |
| Study Design | Inclusion Criteria | Test Therapeutics | Patients | Follow Up | Major Results | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RCT | DSA+ ABMR, ≥6 mo post-Tx, eGFR ≥ 20 | Bortezomib | 44 | 24 months | No difference | Eskandry et al. [119] |
| RCT | DSA+ ABMR, ≥6 mo post-Tx, eGFR ≥ 20 | Felzartamab | 22 | 52 weeks | Potential therapeutic benefit | Mayer et al. [118] |
| RCT | DSA+ caAMR, eGFR ≥ 20 | IVIG + Rituximab | 25 | 12 months | No difference (prematurely terminated) | Moreso et al. [120] |
| RCT | DSA+ caAMR, eGFR ≥ 20 | Rituximab | 47 | 3 years | No difference (prematurely terminated) | Shiu et al. [121] |
| Single group Assignment (Phase 2) | CAN or TG with c4d, >6 mo post-Tx, eGFR ≥ 20 | Fostamatinib | 10 | 52 weeks | Ongoing | Tam et al. [122] |
| RCT (Phase 2) | DSA+ ABMR, ≥12 mo post-Tx | Clazakizumab | 20 | 52 weeks | Potential therapeutic benefit | Doberer et al. [123] |
| RCT (Phase 3) | DSA+ caAMR, ≥6 mo post-Tx | Clazakizumab | 100 | 52 weeks | No difference (prematurely terminated) | Nickerson et al. [124] |
| RCT | DSA+ caAMR, ≥12 mo post-tx | Tocilizumab | 50 | 24 months | Ongoing | Streichart et al. [125] |
| Single-arm Phase 1 trial | DSA+ ABMR, >6 mo post-tx, eGFR ≥ 20 | Sutimlimab | 10 | 50 days | No effect | Eskandry et al. [126] |
| RCT | DSA+, declining graft function, >6 mo post-tx | Eculizumab | 16 | 52 weeks | Potential therapeutic benefit | Kulkarni et al. [127] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pittappilly, M.; Sharshir, M.; Paramesh, A. Chronic Allograft Nephropathy—A Narrative Review of Its Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Evolving Management Strategies. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 929. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040929
Pittappilly M, Sharshir M, Paramesh A. Chronic Allograft Nephropathy—A Narrative Review of Its Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Evolving Management Strategies. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(4):929. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040929
Chicago/Turabian StylePittappilly, Matthew, Mohammed Sharshir, and Anil Paramesh. 2025. "Chronic Allograft Nephropathy—A Narrative Review of Its Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Evolving Management Strategies" Biomedicines 13, no. 4: 929. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040929
APA StylePittappilly, M., Sharshir, M., & Paramesh, A. (2025). Chronic Allograft Nephropathy—A Narrative Review of Its Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Evolving Management Strategies. Biomedicines, 13(4), 929. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040929







