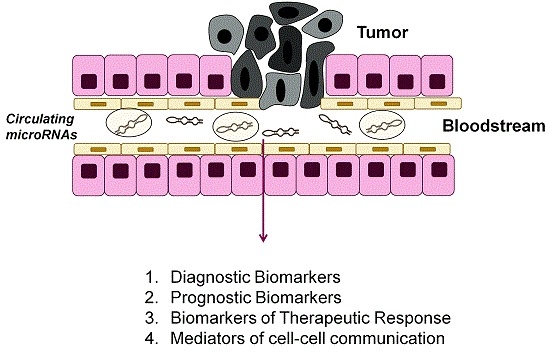
Circulating MicroRNAs as Biomarkers and Mediators of Cell–Cell Communication in Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. MicroRNA Biogenesis and Function
3. MicroRNAs in Cancer
4. MicroRNAs as Biomarkers
4.1. Circulating MicroRNAs as Diagnostic Biomarkers
| Diagnostic miR(s) | Disease Setting | Description | Reference(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| miR-20a, miR-24, miR-25, miR-145, miR-152, miR-199-5p, miR-221, miR-222, miR-223, miR-320 | Lung Cancer | 10 microRNAs were found to have significantly different expression levels in NSCLC serum samples compared with the control serum samples. | [24] |
| miR-10b, miR-155, miR-195, miR34a | Breast Cancer | Increased expression of miR-10b, miR-155, and miR-195 and decreased miR-34a was associated with disease. | [25] |
| miR-221 | Ovarian Cancer, Melanoma, Lymphoma | Increase expression in several different cancers compared to control serum samples. | [27,28,29] |
| miR-141, miR-16, miR-92a, miR-92b, miR-103, miR-107, miR-197, miR-34b, miR-328, miR-485-3p, miR-486-5p, miR-574-3p, miR-636, miR-640, miR-766, and miR-885-5p. | Prostate | Levels of these microRNAs were found to be higher in the serum of patients compared to controls. | [21,26] |
4.2. Circulating MicroRNAs as Prognostic Biomarkers
| Prognostic miR(s) | Disease Setting | Description | Reference(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| miR-21 | Breast Cancer, Ovarian Cancer, Colorectal Cancer, Gastric Cancer, Osteosarcoma, Prostate Cancer | Predicts for late stage and/or metastatic cancer. | [30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39] |
| miR-17–92 | Breast Cancer, Prostate Cancer, Melanoma, Ovarian Cancer | Circulating levels correlate with metastatic disease. | [41,43,44,45] |
| miR-9 | Melanoma | Serum levels predict distant metastatic lesions. | [46] |
| miR-146a | melanoma, Gastric Cancer | Plasma and serum levels predict lymph node metastasis. | [34,37] |
| miR-155 | Breast Cancer, Colorectal Cancer, Lung Cancer, Melanoma, DLBCL | Serum or plasma levels associated with metastasis and decreased relapse-free survival. | [41,44,47,48,49] |
| miR-181 | Melanoma | Plasma levels are associated with increased metastasis. | [44] |
| miR-221/222 | Ovarian Cancer, Melanoma, Prostate Cancer, Lymphoma | Plasma/Serum levels associated with disease progression and metastasis. | [27,28,29,38] |
4.3. MicroRNAs as Biomarkers of Therapeutic Response
| Therapeutic Response miRs | Disease Setting | Description | Reference(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| miR-210 | Breast Cancer | Associated with trastuzamab sensitivity. | [52] |
| miR-155 | Breast Cancer | Circulating levels decrease after surgery or chemotherapy treatment. | [53] |
| miR-17-3p and miR-92 | Colorectal Cancer | Circulating levels decrease after surgical removal of the tumor. | [50] |
| miR-184 | Tongue Cancer | Circulating levels decrease after surgical removal of the tumor. | [51] |
5. Circulating MicroRNAs as Mediators of Cell Communication

6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Torre, L.A.; Bray, F.; Siegel, R.L.; Ferlay, J.; Lortet-Tieulent, J.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2015, 65, 87–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.; Ma, J.; Zou, Z.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2014, 64, 9–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Gramont, A.; Watson, S.; Ellis, L.M.; Rodon, J.; Tabernero, J.; Hamilton, S.R. Pragmatic issues in biomarker evaluation for targeted therapies in cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 12, 197–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golub, T.R.; Slonim, D.K.; Tamayo, P.; Huard, C.; Gaasenbeek, M.; Mesirov, J.P.; Coller, H.; Loh, M.L.; Downing, J.R.; Caligiuri, M.A.; et al. Molecular classification of cancer: Class discovery and class prediction by gene expression monitoring. Science 1999, 286, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perou, C.M.; Sorlie, T.; Eisen, M.B.; van de Rijn, M.; Jeffrey, S.S.; Rees, C.A.; Pollack, J.R.; Ross, D.T.; Johnsen, H.; Akslen, L.A.; et al. Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 2000, 406, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, D.N.; Monti, S.; Parmigiani, G.; Gilks, C.B.; Naoki, K.; Bhattacharjee, A.; Socinski, M.A.; Perou, C.; Meyerson, M. Gene expression profiling reveals reproducible human lung adenocarcinoma subtypes in multiple independent patient cohorts. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 5079–5090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortez, M.A.; Bueso-Ramos, C.; Ferdin, J.; Lopez-Berestein, G.; Sood, A.K.; Calin, G.A. MicroRNAs in body fluids—The mix of hormones and biomarkers. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 8, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarzenbach, H.; Nishida, N.; Calin, G.A.; Pantel, K. Clinical relevance of circulating cell-free microRNAs in cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 11, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aleckovic, M.; Kang, Y. Regulation of cancer metastasis by cell-free miRNAs. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1855, 24–42. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Winter, J.; Jung, S.; Keller, S.; Gregory, R.I.; Diederichs, S. Many roads to maturity: MicroRNA biogenesis pathways and their regulation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 11, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoli, G.; Cava, C.; Castiglioni, I. MicroRNAs: New biomarkers for diagnosis, prognosis, therapy prediction and therapeutic tools for breast cancer. Theranostics 2015, 5, 1122–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, M.A.; Schiemann, W.P. Therapeutic opportunities for targeting microRNAs in cancer. Mol. Cell. Ther. 2014, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Getz, G.; Miska, E.A.; Alvarez-Saavedra, E.; Lamb, J.; Peck, D.; Sweet-Cordero, A.; Ebert, B.L.; Mak, R.H.; Ferrando, A.A.; et al. MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature 2005, 435, 834–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calin, G.A.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Thomson, J.M.; Hemann, M.T.; Hernando-Monge, E.; Mu, D.; Goodson, S.; Powers, S.; Cordon-Cardo, C.; Lowe, S.W.; Hannon, G.J.; et al. A microRNA polycistron as a potential human oncogene. Nature 2005, 435, 828–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, C.; Srinivasan, L.; Calado, D.P.; Patterson, H.C.; Zhang, B.; Wang, J.; Henderson, J.M.; Kutok, J.L.; Rajewsky, K. Lymphoproliferative disease and autoimmunity in mice with increased mir-17–92 expression in lymphocytes. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventura, A.; Young, A.G.; Winslow, M.M.; Lintault, L.; Meissner, A.; Erkeland, S.J.; Newman, J.; Bronson, R.T.; Crowley, D.; Stone, J.R.; et al. Targeted deletion reveals essential and overlapping functions of the mir-17 through 92 family of miRNA clusters. Cell 2008, 132, 875–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seoudi, A.M.; Lashine, Y.A.; Abdelaziz, A.I. MicroRNA-181a—A tale of discrepancies. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2012, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, A.; Tetzlaff, M.T.; Vanbelle, P.; Elder, D.; Feldman, M.; Tobias, J.W.; Sepulveda, A.R.; Xu, X. MicroRNA expression profiling outperforms mRNA expression profiling in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissues. Int J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2009, 2, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, P.S.; Parkin, R.K.; Kroh, E.M.; Fritz, B.R.; Wyman, S.K.; Pogosova-Agadjanyan, E.L.; Peterson, A.; Noteboom, J.; O’Briant, K.C.; Allen, A.; et al. Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 10513–10518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falcone, G.; Felsani, A.; D’Agnano, I. Signaling by exosomal microRNAs in cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanash, S.M.; Baik, C.S.; Kallioniemi, O. Emerging molecular biomarkers—blood-based strategies to detect and monitor cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin Oncol. 2011, 8, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Hu, Z.; Wang, W.; Ba, Y.; Ma, L.; Zhang, C.; Wang, C.; Ren, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, S.; et al. Identification of ten serum microRNAs from a genome-wide serum microRNA expression profile as novel noninvasive biomarkers for nonsmall cell lung cancer diagnosis. Int J. Cancer 2012, 130, 1620–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagrass, H.A.; Sharaf, S.; Pasha, H.F.; Tantawy, E.A.; Mohamed, R.H.; Kassem, R. Circulating microRNAs—A new horizon in molecular diagnosis of breast cancer. Genes Cancer 2015, 6, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lodes, M.J.; Caraballo, M.; Suciu, D.; Munro, S.; Kumar, A.; Anderson, B. Detection of cancer with serum miRNAs on an oligonucleotide microarray. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, F.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, L. Prognostic significance of serum microRNA-221 expression in human epithelial ovarian cancer. J. Int. Med. Res. 2013, 41, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanemaru, H.; Fukushima, S.; Yamashita, J.; Honda, N.; Oyama, R.; Kakimoto, A.; Masuguchi, S.; Ishihara, T.; Inoue, Y.; Jinnin, M.; et al. The circulating microRNA-221 level in patients with malignant melanoma as a new tumor marker. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2011, 61, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.Q.; Huang, G.L.; Guo, C.C.; Pu, X.X.; Lin, T.Y. Diagnostic and prognostic value of circulating mir-221 for extranodal natural killer/t-cell lymphoma. Dis Markers 2010, 29, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asaga, S.; Kuo, C.; Nguyen, T.; Terpenning, M.; Giuliano, A.E.; Hoon, D.S. Direct serum assay for microRNA-21 concentrations in early and advanced breast cancer. Clin. Chem. 2011, 57, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, H.; Sun, X.; Chen, Y.; Cao, Y.; Chen, S.; Wang, H.; Hu, C. Circulating microRNA-92a and microRNA-21 as novel minimally invasive biomarkers for primary breast cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 139, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.Z.; Xi, Q.H.; Ge, W.L.; Zhang, X.Q. Identification of serum microRNA-21 as a biomarker for early detection and prognosis in human epithelial ovarian cancer. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2013, 14, 1057–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Bai, Z.; Song, J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Han, W.; Zhang, J.; Meng, H.; Ma, X.; Wang, T.; et al. Differential expression of serum miR-126, miR-141 and miR-21 as novel biomarkers for early detection of liver metastasis in colorectal cancer. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 2014, 26, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Jeon, T.Y.; Choi, C.I.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, G.H.; Ryu, D.Y.; Lee, B.E.; Kim, H.H. Validation of circulating miRNA biomarkers for predicting lymph node metastasis in gastric cancer. J. Mol. Diagn. 2013, 15, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, G.J.; Gu, R.M.; Zhu, M.; Wen, X.; Li, J.T.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhang, X.M.; Chen, S.Q. Plasma post-operative miR-21 expression in the prognosis of gastric cancers. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2013, 14, 7551–7554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, L.; Liu, P.; Yang, S.; Ye, S.; Xu, W.; Liu, X. A three-plasma miRNA signature serves as novel biomarkers for osteosarcoma. Med. Oncol. 2013, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watahiki, A.; Macfarlane, R.J.; Gleave, M.E.; Crea, F.; Wang, Y.; Helgason, C.D.; Chi, K.N. Plasma miRNAs as biomarkers to identify patients with castration-resistant metastatic prostate cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 7757–7770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaman Agaoglu, F.; Kovancilar, M.; Dizdar, Y.; Darendeliler, E.; Holdenrieder, S.; Dalay, N.; Gezer, U. Investigation of miR-21, miR-141, and miR-221 in blood circulation of patients with prostate cancer. Tumour Biol. 2011, 32, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.L.; Yang, L.F.; Zhu, Y.; Yao, X.D.; Zhang, S.L.; Dai, B.; Zhu, Y.P.; Shen, Y.J.; Shi, G.H.; Ye, D.W. Serum miRNA-21: Elevated levels in patients with metastatic hormone-refractory prostate cancer and potential predictive factor for the efficacy of docetaxel-based chemotherapy. Prostate 2011, 71, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, C.; Rack, B.; Muller, V.; Janni, W.; Pantel, K.; Schwarzenbach, H. Circulating microRNAs as blood-based markers for patients with primary and metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2010, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichelser, C.; Flesch-Janys, D.; Chang-Claude, J.; Pantel, K.; Schwarzenbach, H. Deregulated serum concentrations of circulating cell-free microRNAs miR-17, miR-34a, miR-155, and miR-373 in human breast cancer development and progression. Clin. Chem. 2013, 59, 1489–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenberg, E.; Besser, M.J.; Ben-Ami, E.; Shapira-Frommer, R.; Itzhaki, O.; Zikich, D.; Levy, D.; Kubi, A.; Eyal, E.; Onn, A.; et al. A comparative analysis of total serum miRNA profiles identifies novel signature that is highly indicative of metastatic melanoma: A pilot study. Biomarkers 2013, 18, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryant, R.J.; Pawlowski, T.; Catto, J.W.; Marsden, G.; Vessella, R.L.; Rhees, B.; Kuslich, C.; Visakorpi, T.; Hamdy, F.C. Changes in circulating microRNA levels associated with prostate cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 106, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achberger, S.; Aldrich, W.; Tubbs, R.; Crabb, J.W.; Singh, A.D.; Triozzi, P.L. Circulating immune cell and microRNA in patients with uveal melanoma developing metastatic disease. Mol. Immunol. 2014, 58, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, F.; Tian, J.; Lin, Y.; Jin, Y.; Wang, L.; Cui, M. Serum microRNA-92 expression in patients with ovarian epithelial carcinoma. J. Int. Med. Res. 2013, 41, 1456–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, V.; Place, R.F.; Portnoy, V.; Wang, J.; Qi, Z.; Jia, Z.; Yu, A.; Shuman, M.; Yu, J.; Li, L.C. Upregulation of cyclin b1 by miRNA and its implications in cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 1695–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Hu, T. Predicting distant metastasis and chemoresistance using plasma miRNAs. Med. Oncol. 2014, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, D.; Haddadin, S.; Wang, Y.; Gu, L.Q.; Perry, M.C.; Freter, C.E.; Wang, M.X. Plasma microRNAs as novel biomarkers for early detection of lung cancer. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2011, 4, 575–586. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lawrie, C.H.; Gal, S.; Dunlop, H.M.; Pushkaran, B.; Liggins, A.P.; Pulford, K.; Banham, A.H.; Pezzella, F.; Boultwood, J.; Wainscoat, J.S.; et al. Detection of elevated levels of tumour-associated microRNAs in serum of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 2008, 141, 672–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, E.K.; Chong, W.W.; Jin, H.; Lam, E.K.; Shin, V.Y.; Yu, J.; Poon, T.C.; Ng, S.S.; Sung, J.J. Differential expression of microRNAs in plasma of patients with colorectal cancer: A potential marker for colorectal cancer screening. Gut 2009, 58, 1375–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wong, T.S.; Liu, X.B.; Wong, B.Y.; Ng, R.W.; Yuen, A.P.; Wei, W.I. Mature miR-184 as potential oncogenic microRNA of squamous cell carcinoma of tongue. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 2588–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, E.J.; Santarpia, L.; Kim, J.; Esteva, F.J.; Moretti, E.; Buzdar, A.U.; Di Leo, A.; Le, X.F.; Bast, R.C., Jr.; Park, S.T.; et al. Plasma microRNA 210 levels correlate with sensitivity to trastuzumab and tumor presence in breast cancer patients. Cancer 2012, 118, 2603–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, M.; Lin, G.; Sun, S.; Li, X.; Qi, J.; Li, J. Serum microRNA-155 as a potential biomarker to track disease in breast cancer. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turchinovich, A.; Burwinkel, B. Distinct ago1 and ago2 associated miRNA profiles in human cells and blood plasma. RNA Biol. 2012, 9, 1066–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turchinovich, A.; Weiz, L.; Langheinz, A.; Burwinkel, B. Characterization of extracellular circulating microRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 7223–7233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melo, S.A.; Sugimoto, H.; O’Connell, J.T.; Kato, N.; Villanueva, A.; Vidal, A.; Qiu, L.; Vitkin, E.; Perelman, L.T.; Melo, C.A.; et al. Cancer exosomes perform cell-independent microRNA biogenesis and promote tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell 2014, 26, 707–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paggetti, J.; Haderk, F.; Seiffert, M.; Janji, B.; Distler, U.; Ammerlaan, W.; Kim, Y.J.; Adam, J.; Lichter, P.; Solary, E.; et al. Exosomes released by chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells induce the transition of stromal cells into cancer-associated fibroblasts. Blood 2015, 126, 1106–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Zhao, Z.L.; Zhao, W.T.; Fan, Q.R.; Wang, S.C.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Shi, J.W.; Lin, X.L.; Yang, S.; et al. MiR-9 modulates the expression of interferon-regulated genes and MHC class I molecules in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 431, 610–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabbri, M.; Paone, A.; Calore, F.; Galli, R.; Gaudio, E.; Santhanam, R.; Lovat, F.; Fadda, P.; Mao, C.; Nuovo, G.J.; et al. MicroRNAs bind to toll-like receptors to induce prometastatic inflammatory response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E2110–E2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madhavan, D.; Zucknick, M.; Wallwiener, M.; Cuk, K.; Modugno, C.; Scharpff, M.; Schott, S.; Heil, J.; Turchinovich, A.; Yang, R.; et al. Circulating miRNAs as surrogate markers for circulating tumor cells and prognostic markers in metastatic breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 5972–5982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, M.T.; Hamar, P.; Guo, C.; Basar, E.; Perdigao-Henriques, R.; Balaj, L.; Lieberman, J. MiR-200-containing extracellular vesicles promote breast cancer cell metastasis. J. Clin. Invest. 2014, 124, 5109–5128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Taylor, M.A. Circulating MicroRNAs as Biomarkers and Mediators of Cell–Cell Communication in Cancer. Biomedicines 2015, 3, 270-281. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines3040270
Taylor MA. Circulating MicroRNAs as Biomarkers and Mediators of Cell–Cell Communication in Cancer. Biomedicines. 2015; 3(4):270-281. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines3040270
Chicago/Turabian StyleTaylor, Molly A. 2015. "Circulating MicroRNAs as Biomarkers and Mediators of Cell–Cell Communication in Cancer" Biomedicines 3, no. 4: 270-281. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines3040270
APA StyleTaylor, M. A. (2015). Circulating MicroRNAs as Biomarkers and Mediators of Cell–Cell Communication in Cancer. Biomedicines, 3(4), 270-281. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines3040270