Comparison of Liver Detargeting Strategies for Systemic Therapy with Oncolytic Adenovirus Serotype 5
Abstract
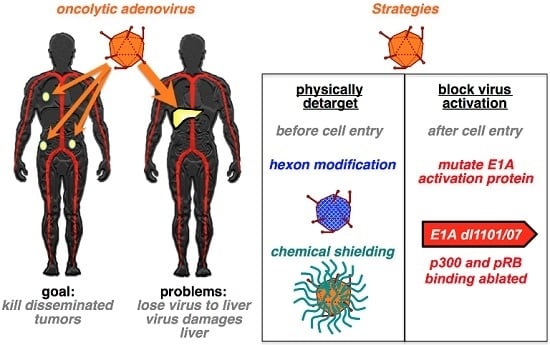
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Cell Lines
2.2. Viruses
2.3. Viral PEGylation
2.4. PEGylation Analysis
2.5. Animal Tumor Models
2.6. IL-6 Assay
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Comparison of Oncolytic Efficacy between Hepatocyte-Detargeted Ad5 and Replicationally Detargeted CRAd5 after Single Intravenous Injection in Immunocompetent Syrian Hamsters
3.2. Liver Damage Caused by Intravenous Ad Injection in Hamsters
3.3. Intratumoral Ad5 Treatment in Ad5 Naive and Ad5-Immunized Hamsters
3.4. Combining Ad5-dl1101/07-ADP CRAd Replication Control with PEG Shielding
3.5. Effects of PEG on Innate Immune Responses against Ad5-dl1101/07 after Intravenous Injection in Mice Bearing Human Tumors
3.6. Oncolytic Efficacy of Unmodifed and PEGylated Ad5-dl1101/07 after Single Intravenous Treatment of Immunocompetent Hamsters
4. Discussion
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Campos, S.K.; Barry, M.A. Current advances and future challenges in adenoviral vector biology and targeting. Curr. Gene Ther. 2007, 7, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cattaneo, R.; Miest, T.; Shashkova, E.V.; Barry, M.A. Reprogrammed viruses as cancer therapeutics: Targeted, armed and shielded. Nat. Rev. 2008, 6, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worgall, S.; Wolff, G.; Falck-Pedersen, E.; Crystal, R.G. Innate immune mechanisms dominate elimination of adenoviral vectors following in vivo administration. Hum. Gene Ther. 1997, 8, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alemany, R.; Suzuki, K.; Curiel, D.T. Blood clearance rates of adenovirus type 5 in mice. J. Gen. Virol. 2000, 81, 2605–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shashkova, E.V.; Doronin, K.; Senac, J.S.; Barry, M.A. Macrophage depletion combined with anticoagulant therapy increases therapeutic window of systemic treatment with oncolytic adenovirus. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 5896–5904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedard, M.B.; Parkkari, M.; Weaver, B.; Riendeau, J.; Dahlquist, M. Assessment of driving performance using a simulator protocol: Validity and reproducibility. Am. J. Occup. Ther. 2010, 64, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khare, R.; Chen, C.Y.; Weaver, E.A.; Barry, M.A. Advances and future challenges in adenoviral vector pharmacology and targeting. Curr. Gene Ther. 2011, 11, 241–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shayakhmetov, D.M.; Gaggar, A.; Ni, S.; Li, Z.Y.; Lieber, A. Adenovirus binding to blood factors results in liver cell infection and hepatotoxicity. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 7478–7491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, A.L.; Waddington, S.N.; Nicol, C.G.; Shayakhmetov, D.M.; Buckley, S.M.; Denby, L.; Kemball-Cook, G.; Ni, S.; Lieber, A.; McVey, J.H.; et al. Multiple vitamin k-dependent coagulation zymogens promote adenovirus-mediated gene delivery to hepatocytes. Blood 2006, 108, 2554–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyuzhniy, O.; Di Paolo, N.C.; Silvestry, M.; Hofherr, S.E.; Barry, M.A.; Stewart, P.L.; Shayakhmetov, D.M. Adenovirus serotype 5 hexon is critical for virus infection of hepatocytes in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 5483–5488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, A.L.; Waddington, S.N.; Buckley, S.M.; Custers, J.; Havenga, M.J.; van Rooijen, N.; Goudsmit, J.; McVey, J.H.; Nicklin, S.A.; Baker, A.H. Effect of neutralizing sera on factor x-mediated adenovirus serotype 5 gene transfer. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shashkova, E.V.; Spencer, J.F.; Wold, W.S.; Doronin, K. Targeting interferon-alpha increases antitumor efficacy and reduces hepatotoxicity of e1a-mutated spread-enhanced oncolytic adenovirus. Mol. Ther. 2007, 15, 598–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shashkova, E.V.; May, S.M.; Doronin, K.; Barry, M.A. Expanded anticancer therapeutic window of hexon-modified oncolytic adenovirus. Mol. Ther. 2009, 17, 2121–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigant, F.; Descamps, D.; Jullienne, B.; Esselin, S.; Connault, E.; Opolon, P.; Tordjmann, T.; Vigne, E.; Perricaudet, M.; Benihoud, K. Substitution of hexon hypervariable region 5 of adenovirus serotype 5 abrogates blood factor binding and limits gene transfer to liver. Mol. Ther. 2008, 16, 1474–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alba, R.; Bradshaw, A.C.; Parker, A.L.; Bhella, D.; Waddington, S.N.; Nicklin, S.A.; van Rooijen, N.; Custers, J.; Goudsmit, J.; Barouch, D.H.; et al. Identification of coagulation factor (f)x binding sites on the adenovirus serotype 5 hexon: Effect of mutagenesis on fx interactions and gene transfer. Blood 2009, 114, 965–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, K.D.; Stallwood, Y.; Green, N.K.; Ulbrich, K.; Mautner, V.; Seymour, L.W. Polymer-coated adenovirus permits efficient retargeting and evades neutralising antibodies. Gene Ther. 2001, 8, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doronin, K.; Shashkova, E.V.; May, S.M.; Hofherr, S.E.; Barry, M.A. Chemical modification with high molecular weight polyethylene glycol reduces transduction of hepatocytes and increases efficacy of intravenously delivered oncolytic adenovirus. Hum. Gene Ther. 2009, 20, 975–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Riordan, C.R.; Lachapelle, A.; Delgado, C.; Parkes, V.; Wadsworth, S.C.; Smith, A.E.; Francis, G.E. Pegylation of adenovirus with retention of infectivity and protection from neutralizing antibody in vitro and in vivo. Hum. Gene Ther. 1999, 10, 1349–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croyle, M.A.; Chirmule, N.; Zhang, Y.; Wilson, J.M. “Stealth” adenoviruses blunt cell-mediated and humoral immune responses against the virus and allow for significant gene expression upon readministration in the lung. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 4792–4801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croyle, M.A.; Chirmule, N.; Zhang, Y.; Wilson, J.M. Pegylation of e1-deleted adenovirus vectors allows significant gene expression on readministration to liver. Hum. Gene Ther. 2002, 13, 1887–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mok, H.; Palmer, D.J.; Ng, P.; Barry, M.A. Evaluation of polyethylene glycol modification of first-generation and helper-dependent adenoviral vectors to reduce innate immune responses. Mol. Ther. 2005, 11, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croyle, M.A.; Le, H.T.; Linse, K.D.; Cerullo, V.; Toietta, G.; Beaudet, A.; Pastore, L. Pegylated helper-dependent adenoviral vectors: Highly efficient vectors with an enhanced safety profile. Gene Ther. 2005, 12, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofherr, S.E.; Mok, H.; Gushiken, F.C.; Lopez, J.A.; Barry, M.A. Polyethylene glycol modification of adenovirus reduces platelet activation, endothelial cell activation, and thrombocytopenia. Hum. Gene Ther. 2007, 18, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bischoff, J.R.; Kirn, D.H.; Williams, A.; Heise, C.; Horn, S.; Muna, M.; Ng, L.; Nye, J.A.; Sampson-Johannes, A.; Fattaey, A.; et al. An adenovirus mutant that replicates selectively in p53-deficient human tumor cells. Science 1996, 274, 373–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fueyo, J.; Gomez-Manzano, C.; Alemany, R.; Lee, P.S.; McDonnell, T.J.; Mitlianga, P.; Shi, Y.X.; Levin, V.A.; Yung, W.K.; Kyritsis, A.P. A mutant oncolytic adenovirus targeting the rb pathway produces anti-glioma effect in vivo. Oncogene 2000, 19, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doronin, K.; Kuppuswamy, M.; Toth, K.; Tollefson, A.E.; Krajcsi, P.; Krougliak, V.; Wold, W.S. Tissue-specific, tumor-selective, replication-competent adenovirus vector for cancer gene therapy. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 3314–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauerschmitz, G.J.; Guse, K.; Kanerva, A.; Menzel, A.; Herrmann, I.; Desmond, R.A.; Yamamoto, M.; Nettelbeck, D.M.; Hakkarainen, T.; Dall, P.; et al. Triple-targeted oncolytic adenoviruses featuring the cox2 promoter, e1a transcomplementation, and serotype chimerism for enhanced selectivity for ovarian cancer cells. Mol. Ther. 2006, 14, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doronin, K.; Toth, K.; Kuppuswamy, M.; Ward, P.; Tollefson, A.E.; Wold, W.S. Tumor-specific, replication-competent adenovirus vectors overexpressing the adenovirus death protein. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 6147–6155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, S.K.; Barry, M.A. Rapid construction of capsid-modified adenoviral vectors through bacteriophage lambda red recombination. Hum. Gene Ther. 2004, 15, 1125–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, S.K.; Barry, M.A. Comparison of adenovirus fiber, protein ix, and hexon capsomeres as scaffolds for vector purification and cell targeting. Virology 2006, 349, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, M.A.; Spencer, J.F.; Wold, W.S. Use of the syrian hamster as an animal model for oncolytic adenovirus vectors. Methods Mol. Med. 2007, 130, 169–183. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lichtenstein, D.L.; Spencer, J.F.; Doronin, K.; Patra, D.; Meyer, J.M.; Shashkova, E.V.; Kuppuswamy, M.; Dhar, D.; Thomas, M.A.; Tollefson, A.E.; et al. An acute toxicology study with ingn 007, an oncolytic adenovirus vector, in mice and permissive syrian hamsters; comparisons with wild-type ad5 and a replication-defective adenovirus vector. Cancer Gene Ther. 2009, 16, 644–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, B.; Toth, K.; Spencer, J.F.; Meyer, J.; Tollefson, A.E.; Patra, D.; Dhar, D.; Shashkova, E.V.; Kuppuswamy, M.; Doronin, K.; et al. Ingn 007, an oncolytic adenovirus vector, replicates in syrian hamsters but not mice: Comparison of biodistribution studies. Cancer Gene Ther. 2009, 16, 625–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.Y.; Weaver, E.A.; Khare, R.; May, S.M.; Barry, M.A. Mining the adenovirus virome for oncolytics against multiple solid tumor types. Cancer Gene Ther. 2011, 18, 744–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhar, D.; Spencer, J.F.; Toth, K.; Wold, W.S. Effect of preexisting immunity on oncolytic adenovirus vector ingn 007 antitumor efficacy in immunocompetent and immunosuppressed syrian hamsters. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 2130–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khare, R.; Reddy, V.S.; Nemerow, G.R.; Barry, M.A. Identification of adenovirus serotype 5 hexon regions that interact with scavenger receptors. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 2293–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.V.; Heller, G.J.; Barry, M.E.; Crosby, C.M.; Turner, M.A.; Barry, M.A. Evaluation of polymer shielding for adenovirus serotype 6 (Ad6) for systemic virotherapy against human prostate cancers. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2016, 3, 15021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofherr, S.E.; Shashkova, E.V.; Weaver, E.A.; Khare, R.; Barry, M.A. Modification of adenoviral vectors with polyethylene glycol modulates in vivo tissue tropism and gene expression. Mol. Ther. 2008, 16, 1276–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crosby, C.M.; Barry, M.A. Iiia deleted adenovirus as a single-cycle genome replicating vector. Virology 2014, 462–463, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cines, D.B.; Pollak, E.S.; Buck, C.A.; Loscalzo, J.; Zimmerman, G.A.; McEver, R.P.; Pober, J.S.; Wick, T.M.; Konkle, B.A.; Schwartz, B.S.; et al. Endothelial cells in physiology and in the pathophysiology of vascular disorders. Blood 1998, 91, 3527–3561. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Di Paolo, N.C.; van Rooijen, N.; Shayakhmetov, D.M. Redundant and synergistic mechanisms control the sequestration of blood-born adenovirus in the liver. Mol. Ther. 2009, 17, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Q.; Xu, Z.; Tian, J.; Moitra, R.; Gunti, S.; Notkins, A.L.; Byrnes, A.P. Impact of natural igm concentration on gene therapy with adenovirus type 5 vectors. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 3412–3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Qiu, Q.; Tian, J.; Smith, J.S.; Conenello, G.M.; Morita, T.; Byrnes, A.P. Coagulation factor x shields adenovirus type 5 from attack by natural antibodies and complement. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, T.V.; Barry, M.E.; Turner, M.A.; Crosby, C.M.; Trujillo, M.A.; Morris, J.C., III; Barry, M.A. Comparison of Liver Detargeting Strategies for Systemic Therapy with Oncolytic Adenovirus Serotype 5. Biomedicines 2017, 5, 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines5030046
Nguyen TV, Barry ME, Turner MA, Crosby CM, Trujillo MA, Morris JC III, Barry MA. Comparison of Liver Detargeting Strategies for Systemic Therapy with Oncolytic Adenovirus Serotype 5. Biomedicines. 2017; 5(3):46. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines5030046
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Tien V., Mary E. Barry, Mallory A. Turner, Catherine M. Crosby, Miguel A. Trujillo, John C. Morris, III, and Michael A. Barry. 2017. "Comparison of Liver Detargeting Strategies for Systemic Therapy with Oncolytic Adenovirus Serotype 5" Biomedicines 5, no. 3: 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines5030046
APA StyleNguyen, T. V., Barry, M. E., Turner, M. A., Crosby, C. M., Trujillo, M. A., Morris, J. C., III, & Barry, M. A. (2017). Comparison of Liver Detargeting Strategies for Systemic Therapy with Oncolytic Adenovirus Serotype 5. Biomedicines, 5(3), 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines5030046