Abstract
The detection of phospholipase A2 receptor (PLA2R) and thrombospondin domain containing 7A THSD7A among primary membranous glomerulonephritis (MGN) patients transformed the diagnosis, treatment monitoring, and prognosis. Anti-PLA2R can be detected in 70–90% of primary MGN patients while anti-THSD7A in 2–3% of anti-PLA2R negative primary MGN patients depending on the technique used. Serum and urine samples are less invasive and non-invasive, respectively, and thus can detect the presence of anti-PLA2R and anti-THSD7A with higher sensitivity and specificity, which is significant in patient monitoring and prognosis. It is better than exposing patients to a frequent biopsy, which is an invasive procedure. Different techniques of detection of PLA2R and THSD7A in patients’ urine and sera were reviewed to provide newer and alternative techniques. We proposed the use of biomarkers (PLA2R and THSD7A) in the diagnosis, treatment decision, and follow-up of patients with primary MGN. In addition, other prognostic renal biomarkers like retinol binding protein (RBP) and beta-2 microglobulin were reviewed to detect the progression of renal damage for early intervention.
1. Introduction
Membranous glomerulonephritis (MGN) is characterized by the deposit of the immune complex at the subepithelial region of the glomerular membrane and the formation of perpendicular projection similar to the glomerular basement membrane (GBM) found between podocyte cytoplasm and GBM [1]. The histological characteristics of MGN include GBM thickening, staining of the C3 complement along the periphery of glomerular capillaries, granular staining for immunoglobulin G subtype, and deposition of the immune complex at the subepithelium found exclusively in primary MGN [2].
Studies have shown that MGN is the most common cause of nephrotic syndrome among adults, consisting of up to 20% of cases among Hispanic and African Americans. Whites are the most affected, followed by Asians, Africans, and Hispanics [3,4]. MGN accounts for 1.5–9% of the nephrotic syndrome among children and 21–35% in adults. The disease is predominantly seen among adults aged 40–50 years, with a male to female ratio of (2:1)–(3:1) [5].
Idiopathic or primary MGN is the commonest type seen in about 75% of the patients with MGN while the remaining 25% manifest as a secondary disease to other conditions, mainly infection [6,7,8,9].
It is very difficult to differentiate between primary and secondary MGN based on their clinical presentations and laboratory evaluations. Therefore, good leading history, clinical, and laboratory findings (including renal biopsy) are crucial in differentiating the two types of MGN [10]. Diagnosis of MGN is traditionally made through electron microscopy, light microscopy, and immunofluorescence techniques from renal biopsy [11].
There are a lot of attempts to use less invasive methods, like serum samples, or non-invasive methods, like urine samples, to make a diagnosis and monitor MGN patients immediately following the detection of anti-phospholipase A2 receptor (PLA2R) and anti-thrombospondin domain containing 7A (THSD7A) in the serum of primary MGN patients. Despite these tremendous achievements, making a diagnosis using serum alone is still difficult due to the lack of a cut-off point value universally agreed on for diagnosis and follow-up. Moreover, certain forms of secondary diseases are associated with these biomarkers.
Hence, this review aims at highlighting the newer techniques used in making a diagnosis of MGN by detecting biomarkers in serum and urine samples of MGN and the importance of those biomarkers in patient management.
2. Pathogenesis
Immune complex formation in the subepithelial surface of the glomerular complex membrane is central to the formation of membranous glomerulonephritis [12]. Three major mechanisms have been proposed so far [1,2].
The first hypothesis emphasizes on passive entrapment of preformed immune complex due to higher intraglomerular pressure and negatively charged capillary which force the protein across the glomerular capillary wall. An example is in lupus nephritis [13,14].
The second hypothesis involves the localization of the circulating antigens in the subepithelial aspect of the glomerular basement membrane, as such, the antigen forms in-situ immune complex deposit with the antibodies. This is seen in hepatitis B [15,16], hepatitis C [17,18], Helicobacter pylori [19], and patients diagnosed with MGN [20,21].
The third mechanism focuses on the binding of autoantibodies to antigens, as well as to podocyte membrane, leading to immune complex deposition. Numerous studies were conducted to describe the pathogenesis of MGN, ranging from the Heymann rat model of 1959 where membranous glomerulonephritis was induced using Lewis rats with crude kidney extract [22]. The use of megalin in the 1980s by Kerjaschki and Farquhar showed oxygen radicals responsible for glomerular damage resulting in proteinuria [23]. No anti-megalin antibody was recorded to have been found in patients with MGN. Therefore, megalin cannot be associated with proteinuria in human [12,24].
3. Materials and Methods
Pubmed, Google Scholar, Springer, and Science Direct were searched for manuscripts published in English using keywords, such as “primary OR idiopathic membranous nephropathy” alone or in combination with “prognosis” or “clinical features”. Review articles were cited to provide more details and additional references.
3.1. The Biomarkers
Neutral endopeptidase (NEP) is the first human biomarker for MGN identified in early 2000s and is seen in patients with alloimmune neonatal MGN. This involves vertical transmission from a mother to her offspring following sensitization during previous pregnancy [25]. Therefore, it is very important to screen families with a history of membranous nephropathy as part of their antenatal care [25,26].
Beck et al. (2009) conducted a breakthrough study where a M-type phospholipase A2 receptor (PLA2R) was detected as a biomarker for MGN using Western blot technique. More recently, another biomarker, thrombospondin domain containing 7A (THSD7A) was discovered to complement PLA2R. This biomarker is detected in seronegative anti-PLA2R primary MGN patients except for some rare conditions where anti-PLA2R and anti-THSD7A can be detected [27,28]. Anti-THSD7A cannot be detected in a normal individual or patients with secondary MGN [29,30].
Anti-THSD7A occur in 2.5–5% of patients with idiopathic MGN and does not appear in secondary MGN. Except for few where both PLA2R and THSD7A were found positive, THSD7A is only detected among those MGN patients who are PLA2R negative [31,32].
3.1.1. Clinical Feature
Nephrotic range proteinuria is the commonest presentation among MGN patients. It occurs in 70–80% of patients associated with edema, hypoalbuminemia, and hyperlipidemia, while the remaining patients present with subnephrotic range proteinuria [3,4,33,34,35,36]. The renal function may be normal or slightly impaired at diagnosis. An abrupt change in renal functions may call for a prompt investigation to look for possible superimposed conditions like bilateral renal thrombosis, drug toxicity, and crescentic glomerulonephritis [37]. Other features include hematuria; hypertension is mostly not specific to idiopathic membranous nephropathy [38].
A study involved the administration of THSD7A-specific IgG to mice, thereby leading to massive proteinuria and histomorphological changes of MGN. The above findings showed that anti-THSD7A antibodies might interfere with the integrity of podocyte resulting in damage of cells and subsequently proteinuria [39].
Most of the patients presenting with subnephrotic proteinuria are asymptomatic and have a natural history different from those with nephrotic range proteinuria. About 40% will have spontaneous remission, needing just conservative management while the remaining 60% may develop nephrotic range proteinuria within 2 years of presentation, especially when the anti-PLA2R antibody is still present [40,41]. The progression of the disease is four times accelerated, which becomes synonymous to those that presented with nephrotic syndrome ab initio [42]. This is another scenario in which anti-PLA2R measurement may be important [5].
3.1.2. PLA2R-Related Sarcoidosis and Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Infection
Sarcoidosis is rarely seen in glomerular diseases. However, when it occurs, it is frequently associated with MGN [43,44]. The pathogenesis linking MGN to sarcoidosis remains unclear due to the inability to identify a target antigen or specific antibody linking the two diseases. Notably, while MGN resulted from an autoimmune reaction involving type-2 helper (Th2) cells, sarcoidosis is associated with type-1 helper (Th1) cells [45,46]. Stehle et al. (2015) demonstrated a high prevalence of anti-PLA2R antibodies in the serum of MGN patients with sarcoidosis [44].
In addition to sarcoidosis, PLA2R was detected in 64% hepatitis B virus (HBV) related MGN [47]. This may be due to co-localization of PLA2R and HBsAg in HBV-related MGN due to chronic HBV infection [48,49].
3.1.3. THSD7A and Malignancy
Patients with anti-THSD7A were found to be at risk of reoccurrence after transplant [50]. It has been observed that the messenger RNA for THSD7A was detected in gall bladder carcinoma and not in the normal gall bladder [51]. Serum samples of 1276 patients with MGN were screened for anti-THSD7A. Forty of them tested positive for anti-THSD7A and 8 out of the 40 developed malignancy within an average follow-up period of 3 months. Thus, this finding denoted that THSD7A is associated with malignancy [52]. In another study involving 81 patients with breast cancer and 20 with colorectal cancer, THS7A expression was detected by immunohistochemical stains in 100% and 97.5% of breast cancer and colorectal cancer, respectively [53].
3.1.4. Role of Biomarkers in Kidney Transplant
The discovery of PLA2R does not only help in differentiating primary and secondary MGN but also helps in pre- and post-kidney transplantation by identifying those at risk of post-transplantation failure for intensive therapy and monitoring [54,55,56]. About 30–50% of primary MGN patients are at risk of reoccurrence following kidney transplant especially among those with very high anti-PLA2R antibodies titer [57,58]. Anti-PLA2R titer should be considered post-transplantation, even though the threshold of anti-PLA2R level determining the reoccurrence is not clear [59] (Figure 1).
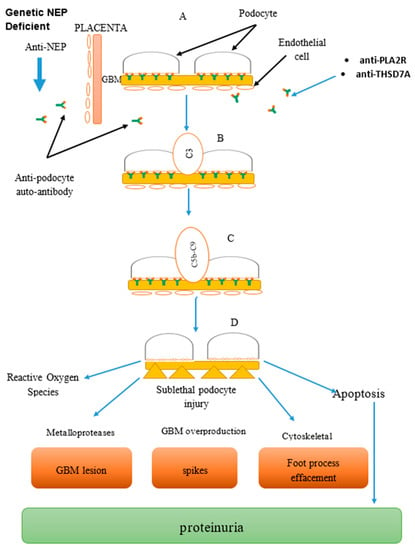
Figure 1.
Combined image: Mechanism of anti-podocyte (anti-neutral endopeptidase (NEP), anti-phospholipase A2 receptor (PLA2R), anti-thrombospondin domain containing 7A (THSD7A)) antibody-mediated disease in membranous glomerulonephritis (MGN), part of glomerular basement membrane (GBM). Formation of complexes: (A) Antigen–antibody reacts to form complexes at the podocyte. (B) Complement activation system via the classical and alternative pathway. (C) Formation of complement membrane attack complex leading to cell injury. (D) Podocyte injury leading to proteinuria and cell death.
3.2. Detection of Biomarkers
The following methods can be used in detecting PLA2R and THSD7A antibodies in the patients’ sera: Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) method, Laser Bead Immunoassay (ALBIA), Luciferase Immunoprecipitation System (LIPS) [60]. Recently, different methods of detecting anti-PLA2R and THSD7A are available commercially due to the rise in their clinical applications in patient management.
3.2.1. Western Blot Technique
Western blot technique is the first method used to detect the expression of anti-PLA2R in the patient’s serum with primary MGN [61]. In the Western blot technique, proteins are separated based on their molecular weight through gel electrophoresis [62]. The technique was first reported to have a sensitivity of about 70% with up to 96% specificity [61]. There were also reports on an improved variant of the Western blot technique (specially designed to detect very low anti-PLA2R) with sensitivity even greater than 90% [63]. However, the method is only suitable for a smaller sample size and also requires expertise [64].
3.2.2. Recombinant Cell-Indirect Immunoassay (RC-IFA)
In this case, the substrate is human cell-line HEK293-overexpressing the full-length PLA2R1 [65]. RC-IFA can be used to make a diagnosis and monitor primary MGN patients. It was shown to have a sensitivity of 75% and a specificity of nearly 100% [66]. RC-IFA has been considered the most suitable method for the detection of anti-PLA2R1 [67]. It can also be used as a reference technique to determine several antibodies against the membrane proteins of the outer surface like NMDR in autoimmune encephalitis [68], aquaporin 4 in neuromyelitis optica [69], and Crohn’s disease [70].
Despite all the advantages mentioned above, it has its limitations. RC-IFA requires technical know-how and special equipment like fluorescence microscopy. It is liable to subjective interpretation and it can only give a semi-quantitative variable.
3.2.3. Time-Resolved Fluoroimmunoassay (TRFIA)
This is a highly specific antigen–antibody binding reaction by measuring light-emission from labels conjugated from protein [71,72]. This assay has high sensitivity, used in the quantitative measurement of serum PLA2R-Ab immunoglobulin (IgG4) [73].
3.2.4. Laser Bead Immunoassay (ALBIA)
Behnert et al. (2013) reported the use of Laser Bead Immunoassay (ALBIA) using an in vivo expressed recombinant human PLA2R to take care of limitations of RC-IFA (quantitative assay, high objectivity in assessment) [74]. Further study was carried out to compare with two other commercially available immunoassays. It was proved that ALBIA correlates better with RC-IFA than with ELISA (p = 0.003) and the overall result showed sensitivity and specificity of 60%/98.6%, and 56.2%/100% for ALBIA and RC-IFA, respectively [75]. Despite this remarkable result for ALBIA, it is not available commercially.
3.2.5. Luciferase Immunoprecipitation System (LIPS)
Another technique is the LIPS assay that makes use of light-emitting proteins. This can detect different types of antibodies, including anti-PLA2R [76]. The PLA2R LIPS assay is quantitative and highly sensitive. It has a sensitivity of nearly 100% and a specificity of 100% and is better than most of these methods of detecting PLA2R. It can also positively correlate with proteinuria and disease process (p < 0.005) [60]. More studies are needed to prove the above claim, and its uses are limited to research only (not yet available commercially).
3.2.6. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
There is an urgent need to develop a standardized ELISA to overcome the above-mentioned shortcomings and to give identical diagnostic accuracy for better clinical importance. This involves the expression of PLA2R1 in HEK293. This technique was used to analyze sera from 200 primary MGN patients, 27 secondary MGN, and 291 healthy individuals. The results indicated a remarkable sensitivity of 78% and a specificity of 91%. The result has correlated significantly well with clinical findings of patients and the results obtained from RC-IFA [64].
A comparative study involving different methods of detecting PLA2R antibody among 158 patients was conducted of which 142 were primary and 16 were secondary MGN. Western blot, ELISA, and IIFT techniques were compared, and the results showed a specificity of 97% for all techniques, a sensitivity of 68% for IIFT, and 72% for both ELISA and the Western blot technique. The ELISA technique may be the preferred method because it can be used for a larger sample size, both qualitative and quantitative measurements. It is less time consuming, requires less technical know-how, and can be interpreted objectively. This clearly showed the superiority of the ELISA method in terms of commercial availability and clinical application [77].
Western blot, ELISA, and RC-IFA are widely used due to their commercial availability and technically. The ELISA technique is widely used compared to other methods due to its ability to measure both qualitative and quantitative assays, and also for its affordability. Table 1 below shows the superiority of the ELISA technique over other methods.

Table 1.
Showing various techniques used in detecting PLA2R antibody.
3.2.7. Detection of Anti-PLA2R and Anti-THSD7A in Serum
A meta-analysis involving 19 studies and 1160 patients was conducted to investigate the clinical importance and the accuracy of histological and serological PLA2R in differentiating primary and secondary MGN. The overall results showed a sensitivity of 0.68, specificity of 0.97, and the diagnostic odds ratio (DOR) was 3.75, while the area under the receiver operating curve (AUROC) was 0.82 for serum anti-PLA2R with a substantial heterogenicity (I2 = 86.42%). In the case of PLA2R staining, the overall sensitivity was 0.78, specificity was 0.91, and DOR (34.70) and AUROC (0.84) without heterogenicity (I2 = 0%). Thus, serum anti-PLA2R can be used to make a diagnosis of primary MGN, but in the case of serum anti-PLA2R negative patients, clinical presentation and biopsy must be considered before making the diagnosis [78,79].
Another study involved 57 biopsy-proven primary MGN, 62 non-MGN, and 22 healthy individuals using the ELISA technique to quantify anti-PLA2R in the serum. The results obtained show that at a cut-off value of 2.0 RU/mL, the sensitivity and specificity were 75% and 82.5%, respectively. At 2.6 RU/mL, the sensitivity and specificity were 78.9% and 91.7%, respectively, while the sensitivity and specificity at 20 RU/mL were found to be 50.9% and 96.4%, respectively. As the cut-off value increases, the sensitivity and specificity also increase [80].
THSD7A is a form of membrane-associated N-glycoprotein found within endothelial cells of the human umbilical vein and also expressed in blood vesicles of the placenta [81].
A study conducted in 154 primary MGN patients demonstrated that 15 of the 154 patients have antibodies for only anti-THSD7A [58]. Subsequently, more researches were conducted to detect the level of anti-THSD7A in the serum of MGN patients. Anti-THSD7A can be detected in serum and tissue of primary MGN patients with THSD7A [82]. Unlike PLA2R, THSD7A does not show any significant preference for serum creatinine, albumin, and proteinuria levels [83]. No significant correlation was found between THSD7A and proteinuria [52].
In a meta-analysis of 10 different studies involving 4121 patients with primary MGN and based on sample size, race, and detection method, it was found that anti-THSD7A was 3% in all patients and 10% among those without anti-PLA2R. Thus, this clearly showed a significant difference in the prevalence of anti-THSD7A based on the sample size but not many differences were observed among the races [39].
In a study conducted on 1318 biopsy-proven primary MGN, 31 stained positives for THS7A showed a strong correlation with IIFT results (p < 0.001) [82].
3.2.8. Detection of Anti-PLA2R and Anti-THSD7A in Urine
A urine sample is non-invasive and can detect renal damage more than serum. Therefore, it is important to demonstrate whether anti-PLA2R can be detected in urine. To do this, a study was conducted on 28 primary MGN and 12 secondary MGN patients in China using ELISA and IIFT. The result showed that 18 of the 28 (64.3%) primary MGN patients tested positive for IIFT serum PLA2R, while 19 of the 28 (67.9%) had IIFT positive urinary anti-PLA2R. The antibody titer of anti-PLA2R from primary MGN patients in urine and serum is higher than the corresponding titers from secondary MGN (p < 0.05). Statistical analysis indicated a positive correlation between urinary anti-PLA2R and serum anti-PLA2R. More studies needed to prove that anti-PLA2R can be detected in the urine of primary MGN patients [84].
Despite several studies involved in the detection of THSD7A in tissue and serum, no known published study is regarding its detection in the patients’ urine.
3.3. Diagnosis
Previous studies showed that anti-PLA2R is now an established parameter for diagnosing primary MGN, differentiating it from secondary type, monitoring treatment, and prognosis [85]. The antibody titer helps in monitoring treatment more than proteinuria as the change in titer is immunological, so it precedes the change in proteinuria [11].
All patients with biopsy-proven MGN should be screened for anti-PLA2R/THSD7A, as well as hepatitis C, hepatitis B, lupus nephritis antigens, and malignancies to rule out secondary causes [86,87,88].
Most ELISA authors define positivity of anti-PLA2R using a cut-off point of 20 RU/mL, some use 14 RU/mL, 2.6 RU/mL, or 2 RU/mL as their cut-off point value to define positivity [89,90,91,92]. In some cases, the cut-off point value is obtained by measuring the anti-PLA2R of apparently normal subjects without any renal compromised [93].
Though detection of anti-PLA2R and anti-THSD7A in serum were found to be reliable, biopsy remains the best option in the diagnosis of primary MGN. A study conducted on 42 biopsies has proven primary MGN with serum samples collected at the time of biopsy. The resultant sensitivities and specificities were 0.74 and 0.57 for renal glomerular deposit and circulating anti-PLA2R in serum, respectively, with 3 patients who had no PLA2R but detectable anti-PLA2R in their serum. Furthermore, 18 patients who were serum anti-PLA2R negative have a glomerular deposit of PLA2R. This study suggested that both biopsy and serum are very important in making the diagnosis of primary MGN [94].
3.4. Treatment of Idiopathic MGN and Further Therapy
Serum and urine biomarkers (PLA2R and THSD7A) are now used in monitoring the efficiency of immunosuppressive therapy. The biomarkers can also be used to compare two immunosuppressive drugs by measuring the serum level of PLA2R and THSD7A before, during, and after treatment [95,96,97,98]. Rituximab can be used to reduce PLA2R. However, the total dose needed to clear anti-PLA2R remains unclear and may be patient dependent [99].
Another suggestion was the use of drugs that inhibit the factors that activate autoreactive B cells. In this case, Belimumab acts by reducing the production of autoantibodies by binding to a B-lymphocyte Stimulator (BLyS) [100]. In a study involving 14 patients, it was found that Belimumab caused significant reduction in anti-PLA2R and proteinuria and normalized the serum albumin level [101].
3.5. Prognosis
Recent studies conducted within 5 years have shown that anti-PLA2R concentration is correlated with urinary protein and disease activities; the antibodies are usually undetectable in spontaneous or drug-induced remission patients and reappear when there is relapse [102,103,104,105,106].
Toronto risk score has been used to predict the prognosis of MGN patients. It is calculated based on creatinine clearance at diagnosis, highest sustained 6 months period of proteinuria, and slope of creatinine clearance over 6 months with an accuracy level of up to 90%. However, there are challenges associated with this method which include complex calculation and prolonged observation of up to 18 months which may delay treatment [107]. Recently, biomarkers like PLA2R, retinol binding protein (RBP), and beta-2 microglobulin can be used to predict prognosis among patients with MGN [108].
RBP is considered to be a prognostic biomarker for MGN and other chronic kidney diseases. The high value of RBP is associated with poor prognosis [109,110].
β2-microglobulin can predict the prognosis of MGN [111,112]. β2-microglobulin has 88% sensitivity and 91% specificity in determining the prognosis in renal failure with the threshold level at 40 mg/min [111]. However, when re-evaluated, both biomarkers show low sensitivity and specificity compared to the initial result. This may be due to conservative therapy. There are no significant differences between prognostic accuracies from β2-microglobulin and Toronto risk score [107].
A retrospective study involving 33 non-nephrotic MGN patients showed that anti-PLA2R positive patients (48%) were more at risk of progressing towards a nephrotic syndrome compared to anti-PLA2R negative patients. In addition, patients with high anti-PLA2R titer are more at risk of adverse effects of immunosuppressive drugs and end-stage renal disease compared to those with no anti-PLA2R by the end of the follow-up [105]. More studies involving a large number of patients are needed to confirm the above claim, as the small number of patients in this study and the too short follow-up duration rendered it hard to categorically determine the outcome.
To accurately predict the progression of MGN, the watchful waiting method was adopted. This involves 24 h urinary protein and creatinine clearance monitoring for at least 6 months and comparing the result with nephrotic range proteinuria [108].
It is important to know that the presenting proteinuria is inversely proportional to the rate of spontaneous remission [112]. Further, it was observed that there is a high chance of spontaneous remission if a 50% reduction in proteinuria is achieved within the first year irrespective of the initial level of proteinuria. About 32% can undergo spontaneous remission within 14 months and up to 62% in 5 years especially among MGN patients with decreased (low) anti-PLA2R and anti-THSD7A [29,41,113].
More recent studies support a watchful waiting approach and also indicated that spontaneous remission can occur even when the presenting proteinuria is greater than 12 g/day [113].
Further studies involving natural history and spontaneous remission in Southeast Asia and Malaysia are needed.
4. Conclusions
The standardized ELISA method is the best so far considering its ability to measure both qualitative and quantitative variables, it requires less time, it is easier to perform, it has high sensitivity and specificity, and is also readily available and affordable commercially.
Serum or urine samples should be used to determine the level of anti-PLA2R/anti-THSD7A to make a diagnosis, monitor patients’ treatment, and to determine the prognosis especially among patients who cannot withstand renal biopsy. Serum and urine samples can determine when to commence or stop immunosuppressive therapy.
Funding
The review was sponsored by Universiti Putra Malaysia (UPM) grant.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Larsen, C.P.; Messias, N.C.; Silva, F.G.; Messias, E.; Walker, P.D. Determination of primary versus secondary membranous glomerulopathy utilizing phospholipase A2 receptor staining in renal biopsies. Modern Pathol. 2012, 26, 709–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogo, A.B.; Lusco, M.A.; Najafian, B. AJKD atlas of renal pathology: Membranous nephropathy. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 26, 3425–3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salant, D.J. Membranous nephropathy. Port. J. Nephrol. Hypert. 2015, 33, 239–251. [Google Scholar]
- Cattran, D.C.; Brenchley, P.E. Membranous nephropathy: Integrating basic science into improved clinical management. Kidney Int. 2017, 566–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattran, D.; Brenchley, P. Membranous nephropathy: Thinking through the therapeutic options. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2017, 32, i22–i29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Seitz-Polski, B.; Dolla, G.; Payre, C.; Girard, C.A.; Polidori, J.; Zorzi, K.; Birgy-Barelli, E.; Jullien, P.; Courivaud, C.; Krummel, T.; et al. Epitope Spreading of Autoantibody Response to PLA2R Associates with Poor Prognosis in Membranous Nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 27, 1517–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Wang, S.; Huang, Y.; Liang, X.; Shi, W.; Zhang, B. A follow-up analysis of positron emission tomography/computed tomography in detecting hidden malignancies at the time of diagnosis of membranous nephropathy. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 9645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.H.; Chen, H.M.; Wang, R.S.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, S.H.; Liu, L.; Li, L.S.; Liu, Z.H. Etiology and Clinical Characteristics of Membranous Nephropathy in Chinese Patients. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2008, 52, 691–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefaucheur, C.; Stengel, B.; Nochy, D.; Martel, P.; Hill, G.S.; Jacquot, C.; Rossert, J. Membranous nephropathy and cancer: Epidemiologic evidence and determinants of high-risk cancer association. Kidney Int. 2006, 70, 1510–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for Glomerulonephritis. Available online: https://www.theisn.org/education-home/gop-articles/item/594-kdigogn (accessed on 28 March 2014).
- Mastroianni-Kirsztajn, G.; Hornig, N.; Schlumberger, W. Autoantibodies in renal diseases-clinical significance and recent developments in serological detection. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, W.; Hao, T.; Chen, P.M.; Chan, C.K.; Chiang, W.C.; Chen, Y.M.; Wu, K.D. Science Direct Membranous nephropathy: A review on the pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2015, 114, 102–111. [Google Scholar]
- Shlomchik, M.J.; Madaio, M.P. The role of antibodies and B cells in the pathogenesis of lupus nephritis. Springer Semin. Immunopathol. 2003, 24, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilcox, T.; Hirshkowitz, A. The role of B cells in Lupus pathogenesis. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2010, 42, 543–550. [Google Scholar]
- Bhimma, R.; Coovadia, H.M. Hepatitis B virus-associated nephropathy. Am. J. Nephrol. 2004, 24, 198–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.Y.; Lee, S.H. Treatment of Hepatitis B Virus-Associated Membranous Nephropathy: Lamivudine Era versus Post-Lamivudine Era. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2012, 27, 394–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandri, A.M.; Elewa, U.; Poterucha, J.J.; Fervenza, F.C. Treatment of hepatitis C-mediated glomerular disease. Nephron. Clin. Pract. 2011, 119, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, J.M.; Kamar, N.; Rostaing, L. Hepatitis C and renal disease: Epidemiology, diagnosis, pathogenesis. Hepat. C Ren. Dis. Hemodial. Transplant. 2012, 176, 10–23. [Google Scholar]
- Dede, F.; Ayli, D.; Gonul, I.; Yuksel, O.; Ozturk, R.; Yildiz, A.; Yenigun, E.; Piskinpasa, S.; Turgut, D.; Koc, E.; et al. The effect of Helicobacter pylori eradication on proteinuria in patients with primary glomerulonephritis. Arch. Med. Sci. 2015, 11, 764–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, Y.H. Pathogenesis, diagnosis and management of paraneoplastic glomerulonephritis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2011, 7, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, L.H.; Salant, D.J. Membranous nephropathy: Recent travels and new roads ahead. Kidney Int. 2010, 77, 765–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heymann, W.; Hackel, D.B.; Harwood, S.; Wilson, S.G. Production of nephrotic syndrome in rats by Freund’s adjuvants and rat kidney suspensions. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1959, 100, 660–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farquhar, M.G.; Saito, A.; Kerjaschki, D. The Heymann nephritis antigenic complex: Megalin (gp330) and RAP. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1995, 6, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronco, P.; Debiec, H. Pathophysiological advances in membranous nephropathy: Time for a shift in patient’s care. Lancet 2015, 385, 1983–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Xuan, Q.; Hu, B.; Lu, L.; Qin, Y.H. Anti-neutral endopeptidase natriuretic peptides, disarrangement and proteinuria onset in membranous nephropathy. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2013, 40, 2963–2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debiec, H.; Nauta, J.; Coulet, F.; van der, B.M.; Guigonis, V.; Schurmans, T. Role of truncating mutations in MME gene in fetomaternal alloimmunisation and antenatal glomerulopathies. Lancet 2004, 364, 1252–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, C.P.; Cossey, L.N.; Beck, L.H. THSD7A staining of membranous glomerulopathy in clinical practice reveals cases with dual autoantibody positivity. Mod. Pathol. 2016, 29, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gödel, M.; Grahammer, F.; Huber, T.B. Thrombospondin Type-1 Domain-Containing 7A in Idiopathic Membranous Nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1073–1075. [Google Scholar]
- Hofstra, J.M.; Beck, L.H.; Beck, D.M.; Wetzels, J.F.; Salant, D.J. Anti-phospholipase a2 receptor antibodies correlatewith clinical status in idiopathic membranous nephropathy. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 6, 1286–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prunotto, M.; Carnevali, M.L.; Candiano, G.; Murtas, C.; Bruschi, M.; Corradini, E.; Trivelli, A.; Magnasco, A.; Petretto, A.; Santucci, L.; et al. Autoimmunity in membranous nephropathy targets aldose reductase and SOD2. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.Y.; Lin, M.; Lai, Z.; Jiang, J.; Huang, Y.; Jao, L. Motor neuron-derived Thsd7a is essential for zebrafish vascular development via the Notch-dll4 signaling pathway. J. Biomed. Sci. 2016, 23, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novel Nephrological Markers: Anti-PLA2R, anti-THSD7A and Uromodulin. Available online: https://www.google.com.hk/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=1&ved=2ahUKEwj2gt-M88XlAhUXA4gKHR_cAcAQFjAAegQIABAC&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.euroimmun.com%2Ffileadmin%2Feuroimmun%2Fpdf%2Fnews%2Farticle%2FHA_1254_L_UK_B18.pdf&usg=AOvVaw32W_ClcC3eRyofbMQM4anO (accessed on June 2016).
- Kemp, W.L.; Burns, D.K.; Brown, T.G. Pathology of the Kidney and Bladder. In Pathology: The Big Picture; McGraw-Hill Medical: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, A.; Cattran, D.C.; Blank, M. Complete and partial remission as surrogate end points in membranous nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 2930–2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbour, S.; Reich, H. Short-term complication of membranous nephropathy. Contrib. Nephrol. 2013, 143–151. [Google Scholar]
- Ponticelli, C.; Passerini, P. A randomized pilot trial comparing methylprednisolone plus a cytotoxic agent versus synthetic adrenocorticotropic hormone in idiopathic membranous nephropathy. Am. J. Kidney 2006, 47, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nachman, P.H.; Jennette, J.C. Primary glomerular disease. In Brenner and Rector’s the Kidney, 9th ed.; Elsevier: London, UK, 2012; pp. 1100–1191. [Google Scholar]
- 5 rd Report of the Malaysian Registry of Renal Biopsy. Available online: https://www.google.com.hk/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=1&ved=2ahUKEwiqmMae68flAhVUw4sBHfHyCFwQFjAAegQIAxAC&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.msn.org.my%2Fmsn%2FDoc%2FPublicDoc_PB%2FPublication%2Fmrrb_report2012%2FFULL_5th_2012.pdf&usg=AOvVaw0nKLz64bns7kA7epTCeYeO (accessed on June 2012).
- Ren, S.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, A.Y.; Li, G.; Wang, L.; Hong, D. An update on clinical significance of use of THSD7A in diagnosing idiopathic membranous nephropathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis of THSD7A in IMN. Ren. Fail. 2018, 40, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerry, M.J.; Vanhille, P.; Ronco, P. Serum anti-PLA2R antibodies may be present before clinical manifestations of membranous nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2016, 89, 1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanescu, H.C.; Arcos-Burgos, M.; Medlar, A.; Bockenhauer, D.; Kottgen, A.; Ragomirescu, L. Risk HLA-DQA1 and PLA2R1 alleles in idiopathic membranous nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 616–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hladunewich, M.A.; Troyanov, S.; Calafati, J. The natural history of the non-nephrotic membranous nephropathy patient. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 4, 1417–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stehlé, T.; Joly, D.; Vanhille, P.; Boffa, J.J.; Rémy, P.; Mesnard, L.; Hoffmann, M.; Grimbert, P.; Choukroun, G.; Vrtovsnik, F.; et al. Clinicopathological study of glomerular diseases associated with sarcoidosis: A multicenter study. Orphanet. J. Rare. Dis. 2013, 8, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stehlé, T.; Audard, V.; Ronco, P.; Debiec, H. Phospholipase A2 receptor and sarcoidosis-associated membranous nephropathy. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2015, 30, 1047–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannuzzi, M.C.; Rybicki, B.A. Sarcoidosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 2153–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debiec, H.; Ronco, P. Immunopathogenesis of membranous nephropathy: An update. Semin. Immunopathol. 2014, 36, 381–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Q.; Li, Y.; Xue, J.; Xiong, Z.; Wang, L.; Sun, Z.; Ren, Y.; Zhu, X.; Hao, C.M. Renal Phospholipase A2 Receptor in Hepatitis B Virus-Associated Membranous Nephropathy. Am. J. Nephrol. 2015, 41, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, Y.; Nagai, Y.; Mikami, T.; Akasaka, Y.; Shibuya, K.; Urita, Y. Anti-phospholipase A2 receptor antibody positive hepatitis B virus-associated membranous nephropathy remitted with entecavir after relapse with lamivudine. J. Nephropathol. 2018, 7, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Xu, X.; Zhu, X.; Yuan, S.; Jiang, W.; Xia, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, J.; Sun, L.; Peng, Y.; Liu, F. Role of M-Type phospholipase A2 receptor and its antibody in hepatitis B virus-Associated membranous nephropathy. J. Cent. South. Univ. Med. Sci. 2016, 41, 1064–1068. [Google Scholar]
- Tomas, N.M. Autoantibodies against thrombospondin type 1 domain–containing 7A induce membranous nephropathy. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 2519–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoxha, E.; Wiech, T.; Stahl, P.R. A mechanism for cancer-associated membranous nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 1995–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoxha, E.; Beck, L.H.; Wiech, T. An indirect immunofluorescence method facilitates detection of thrombospondin type 1 domain-containing 7A-specific antibodies in membranous nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 28, 520–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, L.; Dong, D.; Luo, J.; Zhuo, L.; Li, K.; Zhang, P.; Wang, W.; Xu, Y.; Xu, G.; Wang, L.; et al. Expression of THSD7A in neoplasm tissues and its relationship with proteinuria. BMC Nephrol. 2019, 20, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana, L.F.; Miguel, B.; Miguel, S.; Perez, N.S.; Lopez-Hoyos, M.; Patricia, V.; Emillio, R.; Odette, V.; Guadalupe, E.; Fritz, D.; et al. Antiphospholipase A2 antibody predict the risk of post transplantation recurrence of membranous nephropathy. Transplantation 2015, 99, 1709–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, G.; Fattah, H.; Ayalon, R.; Kidd, J.; Gehr, T.; Quintana, L.F. Pretransplant phospholipase A2 receptor autoantibody concentration is associated with clinically significant recurrence of membranous nephropathy post-kidney transplantation. Clin. Transpl. 2016, 30, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon, J.; Pérez-Sáez, M.J.; Batal, I.; Beck, L.H.; Rennke, H.G.; Canaud, G.; Legendre, C.; Pascual, J.; Riella, L.V. Membranous Nephropathy Post-Transplantation. Transplantation 2019, 103, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Debiec, H.; Lefeu, F.; Kemper, M.J.; Niaudet, P.; Deschênes, G.; Remuzzi, G.; Ulinski, T.; Ronco, P. Early-childhood membranous nephropathy due to cationic bovine serum albumin. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 2101–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomas, N.M.; Beck, L.H.; Meyer-Schwesinger, C.; Seitz-Polski, B.; Ma, H.; Zahner, G.; Dolla, G.; Hoxha, E.; Helmchen, U.; Dabert-Gay, A.-S.; et al. Thrombospondin Type-1 Domain-Containing 7A in Idiopathic Membranous Nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 2277–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wai, H.; Lim, M.S.G.W. Recurrent and de novo glomerulonephritis after kidney transplantation. Core Concepts Ren. Transplant. 2019, 10, 211–231. [Google Scholar]
- Peter, D.B.; Beck Jr, L.H.; Waldman, M. Detection and Monitoring PLA2R Autoantibodies by LIPS in Membranous Nephropathy. J. Immunol. Methods 2017, 20, 48–55. [Google Scholar]
- Beck Jr, L.H.; Bonegio, R.G.; Lambeau, G.; Beck, D.M.; Powell, D.W.; Cummins, T.D.; Klein, J.B. M-type Phospholipase A2 receptor as target antigen in idiopathic membranous nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, T.; Yang, P.C. Western blot: Technique, Theory and Trouble shooting. N. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2012, 4, 429–434. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, W.; Beck Jr, L.H.; Zeng, C.; Chen, Z.; Li, S.; Zuo, K.; Salant, D.J. Anti-phospholipase A2 receptor antibody in membranous nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 1137–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahnrich, C.; Komowski, L.; Probst, C.; Seitz-Polski, B.; Esnault, V.; Wetzels, J.F.; Hofstra, J.M.; Hoxha, E.; Stahl, R.A.; Lambeau, G.; et al. Development of standarzed ELISA for the determination of autoantibodies against human M-type phospholipase A2 receptor in primary membranous nephropathy. Clin. Chim. Acta 2013, 421, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoxha, E.; Blöcker, I.M.; Probst, C. Detection of PLA2R specific autoantibodies in patients with idiopathic membranous nephropathy using PLA2R producing HEK293 cells. In Proceedings of the 7th Congress on Autoimmunity, Ljubljana, Slovenia, 5–9 May 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Hofstra, J.M.; Debiec, H.; Short, C.D. Antiphospholipase A2 receptor antibody titer and subclass in idiopathic membranous nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 23, 1735–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debiec, H. Nephrotic syndrome: A new specific test for idiopathic mem- branous nephropathy. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2011, 7, 496–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wandinger, K.P.; Saschenbrecker, S.; Stoecker, W. Anti-NMDA-receptor en- cephalitis: A severe, multistage, treatable disorder presenting with psychosis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2011, 231, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waters, P.J.; McKeon, A.; Leite, M.I. Serologic diagnosis of NMO: A multicenter comparison of aquaporin-4-IgG assays. Neurology 2012, 78, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komorowski, L.; Teegen, B.; Probst, C. Autoantibodies against exocrine pancreas in Crohn’s disease are directed against two antigens: The glycoproteins CUZD1 and GP2. J. Crohns Colitis 2013, 7, 780–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemmilä, I.; Dakubu, S.; Mukkala, V.M.; Siitari, H.; Lövgren, T. Europium as a label in time-resolved immunofluorometric assays. Anal. Biochem. 1984, 137, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soini, E.; Hemmila, I. Flouroimmunoassay: Present status and key problems. Clin. Chem. 1979, 353–362. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Huang, B.; Liu, X.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Hua, J.; Fan, Y.; Hu, L.; Meng, M.; et al. Ultrasensitive Quantitation of Anti-Phospholipase A2 Receptor Antibody as A Diagnostic and Prognostic Indicator of Idiopathic Membranous Nephropathy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnert, A.; Fritzler, M.J.; Teng, B.; Zhang, M.; Bollig, F.; Haller, H.; Skoberne, A.; Mahler, M.; Schiffer, M. An Anti-Phospholipase A2Receptor Quantitative Immunoassay and Epitope Analysis in Membranous Nephropathy Reveals Different Antigenic Domains of the Receptor. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnert, A.; Schiffer, M.; Müller-Deile, J.; Beck, L.H.; Mahler, M.; Fritzler, M.J. Antiphospholipase A2receptor autoantibodies: A comparison of three different immunoassays for the diagnosis of idiopathic membranous nephropathy. J. Immunol. Res. 2014, 2014, 143274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burbelo, P.D.; Lebovitz, E.E.; Notkins, A.L. Luciferase immunoprecipitation systems for measuring antibodies in autoimmune and infectious diseases. Transl. Res. 2015, 165, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayalon, R.; Beck, L.H., Jr.; Schlumberger, W. Evaluation of Anti-PLA2R1 as Measured by a Novel ELISA in Patients with Idiopathic Membranous Nephropathy a Cohort Study. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2014, 142, 29–34. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, H.; Zhang, H.; He, Y. Diagnostic accuracy of PLA2R autoantibodies and glomerular staining for the differentiation of idiopathic and secondary membranous nephropathy: An updated meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.Y. Diagnostic test accuracy of Serum anti-PLa2R autoantibodies and Glomerular PLa2R antigen for diagnosing idiopathic membranous Nephropathy: An Updated meta-analysis. Front. Med. 2018, 5, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Ma, C.; Wang, P.; Liu, J.; Su, H.; Zhuo, H.; Kong, X.; Xu, D.; Xu, D. Serum anti-PLA2R antibody as a diagnostic biomarker of idiopathic membranous nephropathy: The optimal cut-off value for Chinese patients. Clin. Chim. Acta 2018, 476, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.H.; Su, P.T.; Du, X.Y.; Kuo, M.W.; Lin, C.Y.; Yang, C.C.; Chan, H.S.; Chang, S.J.; Kuo, C.; Seo, K.; et al. Thrombospondin type I domain containing 7A (THSD7A) mediates endothelial cell migration and tube formation. J. Cell. Physiol. 2010, 222, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.G. Tissue staining for THSD7A in glomeruli correlates with serum antibodies in primary membranous nephropathy: A clinicopathological study. Mod. Pathol. 2018, 31, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwakura, T.; Ohashi, N.; Kato, A. Prevalence of enhanced granular expression of thrombospondin type-1 domain-containing 7A in the glomeruli of Japanese patients with idiopathic membranous nephr-opathy. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; He, Y.X.; Diao, T.T.; Wei, S.Y.; Qi, W.R.; Wang, C.C.; Song, S.M.; Bi, M.; Li, C.M.; Zhang, C.X.; et al. Urine anti-PLA2R antibody is a novel biomarker of idiopathic membranous nephropathy. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourcine, F.; Dahan, K.; Mihout, F.; Cachanado, M.; Brocheriou, I.; Debiec, H.; Ronco, P. Prognostic value of PLA2R autoimmunity detected by measurement of anti-PLA2R antibodies combined with detection of PLA2R antigen in membranous nephropathy: A single-centre study over 14 years. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vriese, A.S.; Glassock, R.J.; Nath, K.A.; Sethi, S.; Fervenza, F.C. A Proposal for a Serology-Based Approach to Membranous Nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, J.M.; Beck LHJr, S.D. Membranous nephropathy: A journey from bench to bedside. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2011, 616–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debiec, H. Immune response against autoantigen PLA2R is not gambling: Implications for pathophysiology, prognosis and therapy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 1275–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Z.; Zhang, M.F.; Cui, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Y.M.; Wang, F.; Wang, X.; Meng, L.Q.; Cheng, X.Y.; et al. Antibodies against M-type phospholipase A2 receptor may predict treatment response and outcome in membranous nephropathy. Am. J. Nephrol. 2018, 48, 438–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tampoia, M. Definition of a new cut-off for the anti-phospholipase A2 receptor (PLA2R) autoantibody immunoassay in patients affected by idiopathic membranous nephropathy. J. Nephrol. 2018, 31, 899–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Liu, L.; Guo, Y.; Yang, L. Clinical value of a serum anti-PLA2R antibody in the diagnosis and monitoring of primary membranous nephropathy in adults. Int. J. Nephrol. Renovasc. Dis. 2018, 11, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobart, S.A.; De Vriese, A.S.; Pawar, A.S.; Zand, L.; Sethi, S.; Giesen, C.; Lieske, J.C.; Fervenza, F.C. Noninvasive diagnosis of primary membranous nephropathy using phospholipase A2 receptor antibodies. Kidney Int. 2019, 95, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jullien, P.; Polski, B.S.; Maillard, N.; Thibaudin, D.; Laurent, B.; Ollier, E.; Alamartine, E.; Lambeau, G.; Mariat, C. Anti-phospholipase A2 receptor antibody levels at diagnosis predicts spontaneous remission of idiopathic membranous nephropathy. Clin. Kidney J. 2017, 10, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debiec, H.; Ronco, P. PLA2R autoantibodies and PLA2R glomerular deposits in membranous nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 689–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hladunewich, M.A.; Cattran, D.; Beck, L.H.; Odutayo, A.; Sethi, S.; Ayalon, R.; Leung, N.R. A pilot study to determine the dose and effectiveness of adrenocortico- trophic hormone (H.P. Acthar® Gel) in ne- phrotic syndrome due to idiopathic membra- nous nephropathy. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2014, 29, 1570–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahan, K.; Debiec, H.; Plaisier, E.; Cachanado, M.; Rousseau, A.; Wakselman, L.; Michel, P.-A.; Mihout, F.; Dussol, B.; Matignon, M.; et al. Rituximab for Severe Membranous Nephropathy: A 6-Month Trial with Extended Follow-Up. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggenenti, P.; Debiec, H.; Ruggiero, B.; Chianca, A.; Pelle, T.; Gaspari, F.; Suardi, F.; Gagliardini, E.; Orisio, S.; Benigni, A.; et al. Anti-Phospholipase A2 Receptor Antibody Titer Predicts Post-Rituximab Outcome of Membranous Nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 2545–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, L.H.; Fervenza, F.C.; Beck, D.M.; Bonegio, R.G.B.; Malik, F.A.; Erickson, S.B.; Cosio, F.G.; Cattran, D.C.; Salant, D.J. Rituximab-Induced Depletion of Anti-PLA2R Autoantibodies Predicts Response in Membranous Nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 1543–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahan, K.; Gillion, V.; Johanet, C.; Debiec, H.; Ronco, P. The Role of PLA2R Antibody in Treatment of Membranous Nephropathy. Kidney Int. Rep. 2018, 3, 498–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stohl, W.; Hiepe, F.; Latinis, K.M. Belimumab reduces autoantibodies normalizes low complement levels, and reduces select B cell populations in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 2328–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willcocks, L.; Barrett, C.; Brenchley, P.; Schmidt, T.; Gisbert, S.; Cai, G.; Savage, C. Effect of belimumab on proteinuria and anti-PLA2R autoantibody in idiopathic membranous ne-phropathy—6 months data. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2015, 30, 32–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lv, J.; Hou, W.; Zhou, X. Interaction between PLA2R1 and HLA-DQA1 variants associates with anti-PLA2R antibodies and membranous nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 24, 1323–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.J.; Yang, S.H.; Kim, D.K.; Kang, S.W. Autoantibodies against phospholipase A2 receptor in Korean patients with membranous nephropathy. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bech, A.P.; Hofstra, J.M.; Brenchley, P.E. Association of anti-PLA2R antibodies with outcomes after immunosuppressive therapy in idiopathic membraneous nephropathy. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 9, 1386–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoxha, E.; Thiele, I.; Zahner, G.; Panzer, U.; Harendza, S. Phospholipase A2 receptor autoantibodies and clinical outcome in patients with primary membranous nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 25, 1357–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoxha, E.; Harendza, S.; Pinnschmidt, H.; Panzer, U. PLA2R antibody level and clinical outcome in patients with membranous nephropathy and non-nephrotic range proteinuria under treatment with inhibitors of the renin-angiotensin system. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Brand, J.A.; Hofstra, J.M.; We, J. Prognostic value of risk score and urinary markers in idiopathic membranous nephropathy. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 7, 1242–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cattran, D.C.; Kim, E.D.; Reich, H.; Hladunewich, M.; Kim, S.J. Toronto Glomerulonephritis Registry group, and for the T.G.R. Membranous Nephropathy: Quantifying Remission Duration on Outcome. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 995–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domingos, M.A.M.; Moreira, S.R.; Gomez, L.; Goulart, A.; Lotufo, P.A.; Benseñor, I.; Titan, S. Urinary Retinol-Binding Protein: Relationship to Renal Function and Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Chronic Kidney Disease. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Ming Wang, W.; Xia Pan, X.; Xu, J.; Ni Gao, C.; Zhang, W.; Ren, H.; Yuan Xie, J.; Yan Shen, P.; Wen Xu, Y.; et al. Biomarkers to detect membranous nephropathy in Chinese patients. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 67868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branten, A.J.; du Buf-Vereijken, P.W.; Klasen, I.S.; Bosch, F.H.; Feith, G.W.; Hollander, D.A. Urinary excretion of beta-2 microglobulin and IgG predict prognosis in idiopathic membranous nephropathy: A validation study. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005, 16, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Brand, J.A.; van Dijk, P.R.; Hofstra, J.M. Long-term outcomes in idiopathic membranous nephropathy using a restrictive treatment strategy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 25, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polanco, N.; Gutiérrez, E.; Covarsí, A. Spontaneous remission of nephrotic syndrome in idiopathic membranous nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).