Anti-c-myc RNAi-Based Onconanotherapeutics
Abstract
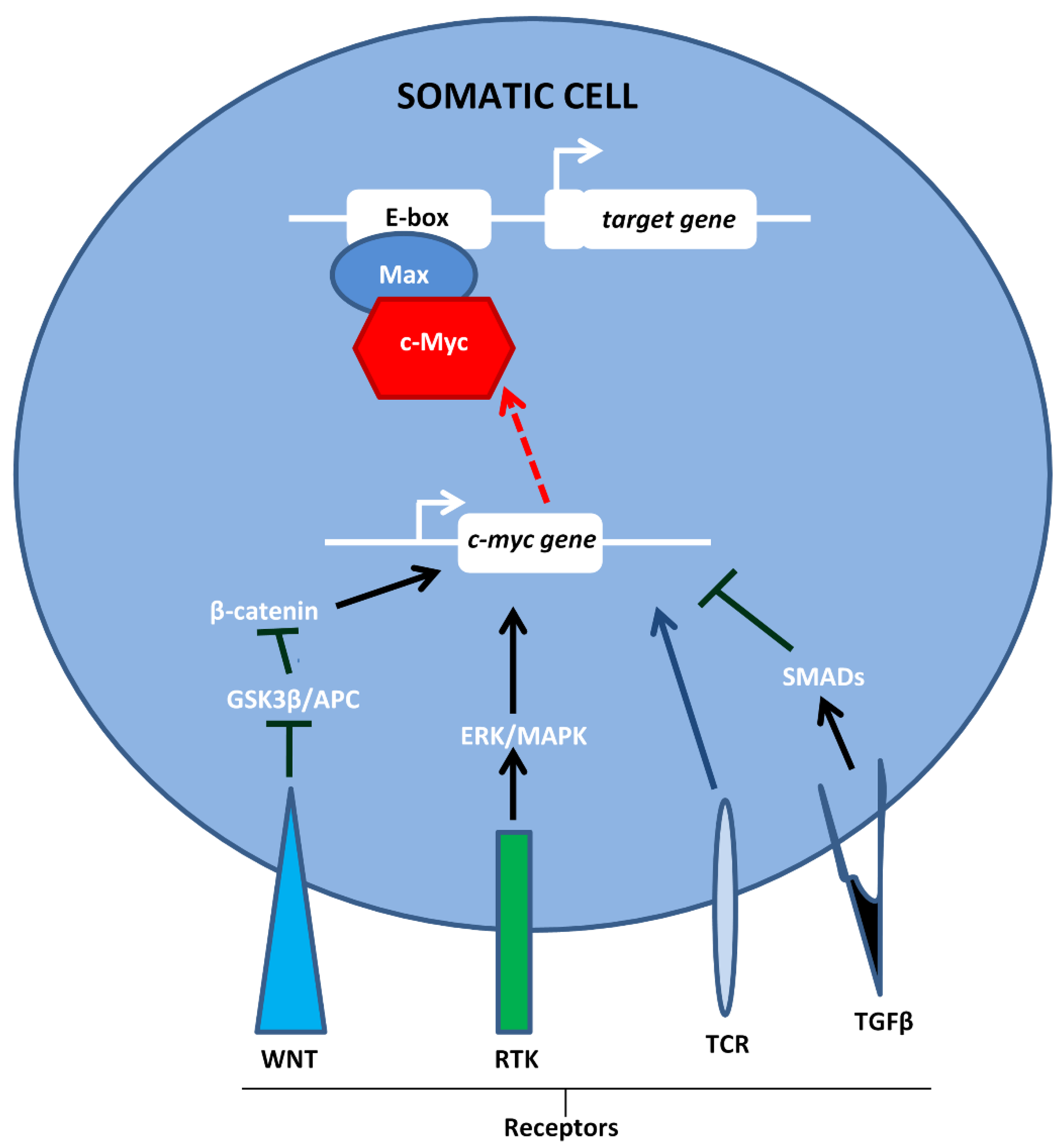
1. Introduction
2. Anti-c-myc-siRNA
2.1. Lipid-Based Nanosystems
2.2. Miscellaneous Organic Nanosystems
2.3. Inorganic Nanosystems
3. DsiRNA
4. Anti-c-myc-shRNA
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zeller, K.I.; Zhao, X.; Lee, C.W.H.; Chiu, K.P.; Yao, F.; Yustein, J.T.; Ooi, H.S.; Orlov, Y.L.; Shahab, A.; Yong, H.C.; et al. Global mapping of c-Myc binding sites and target gene networks in human B cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 17834–17839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berns, K.; Hijmans, E.M.; Bernards, R. Repression of c-Myc responsive genes in cycling cells causes G1 arrest through reduction of cyclin E/CDK2 kinase activity. Oncogene 1997, 15, 1347–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermeking, H.; Rago, C.; Schuhmacher, M.; Li, Q.; Barrett, J.F.; Obaya, A.; O’Connell, B.C.; Mateyak, M.K.; Tam, W.; Kohlhuber, F.; et al. Identification of CDK4 as a target of c-MYC. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 2229–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-W.; Zeller, K.I.; Wang, Y.; Jegga, A.G.; Aronow, B.J.; O’Donnell, K.A.; Dang, C.V. Evaluation of Myc E-Box Phylogenetic Footprints in Glycolytic Genes by Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Assays. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 5923–5936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.-C.; Li, F.; Handler, J.; Huang, C.R.L.; Xiang, Y.; Neretti, N.; Sedivy, J.M.; I Zeller, K.; Dang, C.V. Global Regulation of Nucleotide Biosynthetic Genes by c-Myc. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuhmacher, M.; Staege, M.S.; Pajic, A.; Polack, A.; Weidle, U.H.; Bornkamm, G.W.; Eick, D.; Kohlhuber, F. Control of cell growth by c-Myc in the absence of cell division. Curr. Biol. 1999, 9, 1255–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Riggelen, J.; Alper, S.L.; Felsher, D.W. MYC as a regulator of ribosome biogenesis and protein synthesis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, A.; Murphy, M.J.; Oskarsson, T.; Kaloulis, K.; Bettess, M.D.; Oser, G.M.; Pasche, A.-C.; Knabenhans, C.; Macdonald, H.R.; Trumpp, A. c-Myc controls the balance between hematopoietic stem cell self-renewal and differentiation. Genes Dev. 2004, 18, 2747–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebhardt, A.; Frye, M.; Herold, S.; Benitah, S.A.; Braun, K.; Samans, B.; Watt, F.M.; Elsässer, H.-P.; Eilers, M. Myc regulates keratinocyte adhesion and differentiation via complex formation with Miz1. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 172, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrish, F.; Giedt, C.; Hockenbery, D. c-MYC apoptotic function is mediated by NRF-1 target genes. Genes Dev. 2003, 17, 240–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eick, D.; Bornkamm, G.W. Transcriptional arrest within the first exon is a fast control mechanism in c-myc gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986, 14, 8331–8346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bentley, D.L.; Groudine, M. Novel promoter upstream of the human c-myc gene and regulation of c-myc expression in B-cell lymphomas. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1986, 6, 3481–3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Culjkovic, B.; Topisirovic, I.; Skrabanek, L.; Ruiz-Gutierrez, M.; Borden, K.L.B. eIF4E is a central node of an RNA regulon that governs cellular proliferation. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 175, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dani, C.; Blanchard, J.M.; Piechaczyk, M.; El Sabouty, S.; Marty, L.; Jeanteur, P. Extreme instability of myc mRNA in normal and transformed human cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 7046–7050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vervoorts, J.; Lüscher-Firzlaff, J.; Lüscher, B. The Ins and Outs of MYC Regulation by Posttranslational Mechanisms. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 34725–34729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, M.-S.; Arnold, H.; Sun, X.-X.; Sears, R.; Lü, H. Inhibition of c-Myc activity by ribosomal protein L11. EMBO J. 2009, 28, 993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Grandori, C.; Cowley, S.M.; James, L.P.; Eisenman, R.N. The Myc/Max/Mad Network and the Transcriptional Control of Cell Behavior. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2000, 16, 653–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, C.V. MYC on the Path to Cancer. Cell 2012, 149, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battey, J.; Moulding, C.; Taub, R.; Murphy, W.; Stewart, T.; Potter, H.; Lenoir, G.; Leder, P. The human c-myc oncogene: Structural consequences of translocation into the igh locus in Burkitt lymphoma. Cell 1983, 34, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalla-Favera, R.; Martinotti, S.; Gallo, R.C.; Erikson, J.; Croce, C.M. Translocation and rearrangements of the c-myc oncogene locus in human undifferentiated B-cell lymphomas. Science 1983, 219, 963–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treszl, A.; Ádány, R.; Rákosy, Z.; Kardos, L.; Bégány, Á.; Gilde, K.; Balazs, M. Extra copies of c-mycare more pronounced in nodular melanomas than in superficial spreading melanomas as revealed by fluorescence in situ hybridisation. Cytom. Part B Clin. Cytom. 2004, 60, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.R.; Myint, T.; Goh, H.S. Over-expression of the c-myc proto-oncogene in colorectal carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 1993, 68, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Adams, J.M.; Harris, A.W.; Pinkert, C.A.; Corcoran, L.M.; Alexander, W.S.; Cory, S.; Palmiter, R.D.; Brinster, R.L. The c-myc oncogene driven by immunoglobulin enhancers induces lymphoid malignancy in transgenic mice. Nat. Cell Biol. 1985, 318, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leder, A.; Pattengale, P.K.; Kuo, A.; Stewart, T.A.; Leder, P. Consequences of widespread deregulation of the c-myc gene in transgenic mice: Multiple neoplasms and normal development. Cell 1986, 45, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Dang, C.V. c-Myc Overexpression Uncouples DNA Replication from Mitosis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999, 19, 5339–5351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, J.J.; Kerai, P.P.; Lleonart, M.M.; Bernard, D.; Cigudosa, J.C.J.; Peters, G.G.; Carnero, A.; Beach, D.D. Immortalization of Primary Human Prostate Epithelial Cells by c-Myc. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 2179–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzyk, A.; Mai, S. c-MYC-Induced Genomic Instability. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2014, 4, a014373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaux, D.L.; Cory, S.; Adams, J.M. Bcl-2 gene promotes haemopoietic cell survival and cooperates with c-myc to immortalize pre-B cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 1988, 335, 440–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Lisanti, M.P.; Liao, D.J. Reviewing once more the c-myc and Ras collaboration. Cell Cycle 2011, 10, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvanitis, C.; Felsher, D.W. Conditional transgenic models define how MYC initiates and maintains tumorigenesis. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2006, 16, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felsher, D.W. MYC Inactivation Elicits Oncogene Addiction through Both Tumor Cell-Intrinsic and Host-Dependent Mechanisms. Genes Cancer 2010, 1, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soucek, L.; Whitfield, J.R.; Martins, C.P.; Finch, A.J.; Murphy, D.J.; Sodir, N.M.; Karnezis, A.N.; Swigart, L.B.; Nasi, S.; Evan, G.I. Modelling Myc inhibition as a cancer therapy. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 455, 679–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holt, J.T.; Redner, R.L.; Nienhuis, A.W. An oligomer complementary to c-myc mRNA inhibits proliferation of HL-60 promyelocytic cells and induces differentiation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1988, 8, 963–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loke, S.L.; Stein, C.; Zhang, X.; Avigan, M.; Cohen, J.; Neckers, L.M. Delivery of c-myc Antisense Phosphorothioate Oligodeoxynucleotides to Hematopoietic Cells in Culture by Liposome Fusion: Specific Reduction in c-myc Protein Expression Correlates with Inhibition of Cell Growth and DNA Synthesis. Endogenous ADP-Ribosylation 1988, 141, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickstrom, E.L.; Bacon, T.A.; Gonzalez, A.; Freeman, D.L.; Lyman, G.H.; Wickstrom, E. Human promyelocytic leukemia HL-60 cell proliferation and c-myc protein expression are inhibited by an antisense pentadecadeoxynucleotide targeted against c-myc mRNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 1028–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutrona, G.; Carpaneto, E.M.; Ponzanelli, A.; Ulivi, M.; Millo, E.; Scarfì, S.; Ferrarini, M. Inhibition of the translocated c-myc in Burkitt’s lymphoma by a PNA Complementary to the Eμ Enhancer. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 6144–6148. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hudziak, R.M.; Summerton, J.; Weller, D.D.; Iversen, P.L. Antiproliferative Effects of Steric Blocking Phosphorodiamidate Morpholino Antisense Agents Directed against c-myc. Antisense Nucleic Acid Drug Dev. 2000, 10, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fire, A.; Xu, S.; Montgomery, M.K.; Kostas, S.A.; Driver, S.E.; Mello, C.C. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 1998, 391, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbashir, S.M.; Lendeckel, W.; Tuschl, T. RNA interference is mediated by 21- and 22-nucleotide RNAs. Genes Dev. 2001, 15, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-H.; Behlke, M.A.; Rose, S.D.; Chang, M.-S.; Choi, S.; Rossi, J.J. Synthetic dsRNA Dicer substrates enhance RNAi potency and efficacy. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambesajir, A.; Kaushik, A.; Kaushik, J.J.; Petros, S.T. RNA interference: A futuristic tool and its therapeutic applications. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2012, 19, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taxman, D.J.; Moore, C.B.; Guthrie, E.H.; Huang, M.T.-H. Short Hairpin RNA (shRNA): Design, Delivery, and Assessment of Gene Knockdown. In Structural Genomics and Drug Discovery; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2010; Volume 629, pp. 139–156. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, B.; Ji, A.-M. Construction of small interfering RNA targeting mouse vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2: Its serum stability and gene silencing efficiency in vitro. J. South. Med. Univ. 2009, 29, 864–867. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Hong, J.; Zheng, S.; Ding, Y.; Guo, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Du, Q.; Liang, Z. Elimination Pathways of Systemically Delivered siRNA. Mol. Ther. 2011, 19, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoerter, J.A.H.; Walter, N.G. Chemical modification resolves the asymmetry of siRNA strand degradation in human blood serum. RNA 2007, 13, 1887–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allison, S.J.; Milner, J. RNA Interference by Single- and Double-stranded siRNA with a DNA Extension Containing a 3′ Nuclease-resistant Mini-hairpin Structure. Mol. Ther. Nucl. Acids 2014, 2, e141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Akhtar, S.; Benter, I. Toxicogenomics of non-viral drug delivery systems for RNAi: Potential impact on siRNA-mediated gene silencing activity and specificity. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 164–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lu, Z.; Wientjes, M.G.; Au, J.L.-S. Delivery of siRNA Therapeutics: Barriers and Carriers. AAPS J. 2010, 12, 492–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batzri, S.; Korn, E.D. Single bilayer liposomes prepared without sonication. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Biomembr. 1973, 298, 1015–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-González, J.M.; Armaiz-Peña, G.N.; Mangala, L.S.; Valiyeva, F.; Ivan, C.; Pradeep, S.; Echevarría-Vargas, I.M.; Rivera-Reyes, A.; Sood, A.K.; Vivas-Mejía, P.E. Targeting c-MYC in Platinum-Resistant Ovarian Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2015, 14, 2260–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suk, J.S.; Xu, Q.; Kim, N.; Hanes, J.; Ensign, L.M. PEGylation as a strategy for improving nanoparticle-based drug and gene delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 99, 28–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivas-Mejia, P.E.; Gonzalez, J.M.R.; Sood, A.K. Nanoliposomal c-MYC-siRNA Inhibits In Vivo Tumor Growth of Cisplatin-Resistant Ovarian Cancer. U.S. Patent No. 10,548,842, 4 February 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Felgner, P.L.; Gadek, T.R.; Holm, M.; Roman, R.; Chan, H.W.; Wenz, M.; Northrop, J.P.; Ringold, G.M.; Danielsen, M. Lipofection: A highly efficient, lipid-mediated DNA-transfection procedure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 7413–7417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatri, N.; Baradia, D.; Vhora, I.; Rathi, M.; Misra, A. Development and Characterization of siRNA Lipoplexes: Effect of Different Lipids, In Vitro Evaluation in Cancerous Cell Lines and In Vivo Toxicity Study. AAPS PharmSciTech 2014, 15, 1630–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Ge, Y.; Tian, R.-H. The knockdown of c-myc expression by RNAi inhibits cell proliferation in human colon cancer HT-29 cells in vitro and in vivo. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2009, 14, 305–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habib, S.; Daniels, A.; Ariatti, M.; Singh, M. Anti-c-myc cholesterol based lipoplexes as onco-nanotherapeutic agents in vitro. F1000Research 2020, 9, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wu, J.J.; Huang, L. Nanoparticles Targeted With NGR Motif Deliver c-myc siRNA and Doxorubicin for Anticancer Therapy. Mol. Ther. 2010, 18, 828–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Peng, L.; Mumper, R.J.; Huang, L. Combinational delivery of c-myc siRNA and nucleoside analogs in a single, synthetic nanocarrier for targeted cancer therapy. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 8459–8468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xie, X.; Wang, Z.; Gong, W.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Yu, F.; Li, Z.; Mei, X. Dual-modified liposomes with a two-photon-sensitive cell penetrating peptide and NGR ligand for siRNA targeting delivery. Biomaterials 2015, 48, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Lin, W.; Li, M.; Yang, Y.; Deng, J.; Liu, H.; Chen, Y.; Fu, X.; Liu, H.; Yang, Y. Efficient siRNA Delivery Using Novel Cell-Penetrating Peptide-siRNA Conjugate-Loaded Nanobubbles and Ultrasound. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2016, 42, 1362–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, E.; Zhu, P.; Lee, S.-K.; Chowdhury, D.; Kussman, S.; Dykxhoorn, D.M.; Feng, Y.; Palliser, D.; Weiner, D.B.; Shankar, P.; et al. Antibody mediated in vivo delivery of small interfering RNAs via cell-surface receptors. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.-D.; Chono, S.; Huang, L. Efficient Oncogene Silencing and Metastasis Inhibition via Systemic Delivery of siRNA. Mol. Ther. 2008, 16, 942–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, F.; Huang, L. Systemic Delivery of siRNA via LCP Nanoparticle Efficiently Inhibits Lung Metastasis. Mol. Ther. 2012, 20, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, F.; Huang, L. Nanoparticle Delivery of Pooled siRNA for Effective Treatment of Non-Small Cell Lung Caner. Mol. Pharm. 2012, 9, 2280–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, D.; Yang, N.; Nadithe, V. Exosomes as therapeutic drug carriers and delivery vehicles across biological membranes: Current perspectives and future challenges. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2016, 6, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lunavat, T.R.; Jang, S.C.; Nilsson, L.; Park, H.T.; Repiska, G.; Lässer, C.; Nilsson, J.A.; Gho, Y.S.; Lötvall, J. RNAi delivery by exosome-mimetic nanovesicles–Implications for targeting c-Myc in cancer. Biomaterials 2016, 102, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Hu, X.; Zhang, M.; Ma, S.; Yu, F.; Zhao, S.; Liu, N.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Guan, H.; et al. Dual Tumor-Targeting Nanocarrier System for siRNA Delivery Based on pRNA and Modified Chitosan. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2017, 8, 169–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raichur, A.; Nakajima, Y.; Nagaoka, Y.; Matsumoto, K.; Mizuki, T.; Kato, K.; Maekawa, T.; Kumar, D.S. Strategist PLGA Nano-capsules to Deliver siRNA for Inhibition of Carcinoma and Neuroblastoma Cell Lines by Knockdown of MYC Proto-oncogene using CPPs and PNA. NanoWorld J. 2015, 1, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, S.K.; Kampert, T.L.; Pan, D. Nano-Assembly of Pamitoyl-Bioconjugated Coenzyme-A for Combinatorial Chemo-Biologics in Transcriptional Therapy. Bioconjugate Chem. 2018, 29, 1419–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, R.; Chen, M.; Sun, S.; Wei, P.; Zou, L.; Liu, J.; Gao, D.; Wen, L.; Ding, W. Topical and Targeted Delivery of siRNAs to Melanoma Cells Using a Fusion Peptide Carrier. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjorge, J.D.; Pang, A.; Fujita, D.J. Delivery of gene targeting siRNAs to breast cancer cells using a multifunctional peptide complex that promotes both targeted delivery and endosomal release. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xie, X.; Xu, X.; Xia, X.; Wang, H.; Li, L.; Dong, W.; Ma, P.; Liu, Y. Dual stimulus of hyperthermia and intracellular redox environment triggered release of siRNA for tumor-specific therapy. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 506, 158–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Xie, X.; Xu, X.; Xia, X.; Wang, H.; Li, L.; Dong, W.; Ma, P.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; et al. Thermal and magnetic dual-responsive liposomes with a cell-penetrating peptide-siRNA conjugate for enhanced and targeted cancer therapy. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 146, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, S.; Umar, A.; Mehta, S.K. Surface functionalized selenium nanoparticles for biomedical applications. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2014, 10, 3004–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraga, S.; Brandão, A.; Soares, M.E.; Morais, T.; Duarte, J.A.; Pereira, L.; Soares, L.; Neves, C.S.; Pereira, E.; Bastos, M.D.L.; et al. Short- and long-term distribution and toxicity of gold nanoparticles in the rat after a single-dose intravenous administration. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2014, 10, 1757–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Ralston, J.; Sedev, R.; Beattie, D.A. Functionalized gold nanoparticles: Synthesis, structure and colloid stability. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 331, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiyo, F.; Singh, M. Polymerized Selenium Nanoparticles for Folate-Receptor-Targeted Delivery of Anti-Luc-siRNA: Potential for Gene Silencing. Biomaterials 2020, 8, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbatha, L.S.; Maiyo, F.C.; Singh, M. Dendrimer functionalized folate-targeted gold nanoparticles for luciferase gene silencing in vitro: A proof of principle study. Acta Pharm. 2019, 69, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conde, J.; Ambrosone, A.; Sanz, V.; Hernandez, Y.; Marchesano, V.; Tian, F.; Child, B.H.; Berry, C.C.; Ibarra, M.R.; Baptista, P.V.; et al. Design of Multifunctional Gold Nanoparticles for In Vitro and In Vivo Gene Silencing. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 8316–8324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Guo, M.; Xu, T.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Lin, Z.; Zhao, M.; Zhu, B. siRNA-loaded selenium nanoparticle modified with hyaluronic acid for enhanced hepatocellular carcinoma therapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 1539–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCully, M.; Hernandez, Y.; Conde, J.; Baptista, P.V.; De La Fuente, J.M.; Hursthouse, A.; Stirling, D.; Berry, C.C. Significance of the balance between intracellular glutathione and polyethylene glycol for successful release of small interfering RNA from gold nanoparticles. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 3281–3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaat, H.; Mostafa, A.; Moustafa, M.; Gamal-Eldeen, A.; Emam, A.; El-Hussieny, E.; Elhefnawi, M. Modified gold nanoparticles for intracellular delivery of anti-liver cancer siRNA. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 504, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniels, A.N.; Singh, M. Sterically stabilized siRNA:gold nanocomplexes enhance c-MYC silencing in a breast cancer cell model. Nanomedicine 2019, 14, 1387–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.S.; Son, Y.J.; Mao, W.; Leong, K.W.; Yoo, H.S. Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization of Multishelled Cationic Corona for the Systemic Delivery of siRNA. Nano Lett. 2017, 18, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, W.; Lee, S.; Shin, J.U.; Yoo, H.S. Surface-Initiated Atom Transfer Polymerized Anionic Corona on Gold Nanoparticles for Anti-Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conde, J.; Tian, F.; Hernandez, Y.; Bao, C.; Baptista, P.V.; Cui, D.; Stoeger, T.; De La Fuente, J.M. RNAi-based glyconanoparticles trigger apoptotic pathways for in vitro and in vivo enhanced cancer-cell killing. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 9083–9091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conde, J.; Tian, F.; Hernández, Y.; Bao, C.; Cui, D.; Janssen, K.-P.; Ibarra, M.R.; Baptista, P.V.; Stoeger, T.; De La Fuente, J.M. In vivo tumor targeting via nanoparticle-mediated therapeutic siRNA coupled to inflammatory response in lung cancer mouse models. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 7744–7753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Liang, Y.; Sang, C.; Mei, C.; Li, X.; Chen, T. Therapeutic nanosystems co-deliver anticancer drugs and oncogene SiRNA to achieve synergetic precise cancer chemo-gene therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 3013–3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imani, R.; Prakash, S.; Vali, H.; Faghihi, S. Polyethylene glycol and octa-arginine dual-functionalized nanographene oxide: An optimization for efficient nucleic acid delivery. Biomater. Sci. 2018, 6, 1636–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nundkumar, N.; Singh, S.; Singh, M. Amino Acid Functionalized Hydrotalcites for Gene Silencing. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2020, 20, 3387–3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolcher, A.W.; Papadopoulos, K.P.; Patnaik, A.; Rasco, D.W.; Martinez, D.; Wood, D.L.; Fielman, B.; Sharma, M.; Janisch, L.A.; Brown, B.D.; et al. Safety and activity of DCR-MYC, a first-in-class Dicer-substrate small interfering RNA (DsiRNA) targeting MYC, in a phase I study in patients with advanced solid tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 11006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield, J.R.; Beaulieu, M.-E.; Soucek, L. Strategies to Inhibit Myc and Their Clinical Applicability. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, G.; Zhou, C.-Q.; Zhu, H.-X.; Zhou, X.-B.; Quan, L.-P.; Bai, J.-F.; Xu, N. Knockdown of c-Myc expression by RNAi inhibits MCF-7 breast tumor cells growth in vitro and in vivo. Breast Cancer Res. 2004, 7, R220–R228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Gao, W.; Zheng, Y.-X.; Wang, Y.-K.; Zhou, Z.-Q.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.-J. RNAi silencing of c-Myc inhibits cell migration, invasion, and proliferation in HepG2 human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line: C-Myc silencing in hepatocellular carcinoma cell. Cancer Cell Int. 2013, 13, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Nancai, Y.; Lei, F.; Xiong, W.; Wen, S.; Guofu, H.; Yanxia, W.; Hanju, H.; Qian, L.; Hong, X. siRNA directed against c-Myc inhibits proliferation and downregulates human telomerase reverse transcriptase in human colon cancer Colo 320 cells. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 27, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Dong, M.-M.; Yang, H.-F. Effects of RNA interference targeting four different genes on the growth and proliferation of nasopharyngeal carcinoma CNE-2Z cells. Cancer Gene Ther. 2011, 18, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Tai, J.; Wang, G.; Liu, T.; Wang, L.; Lin, C.; Li, F. Effects of siRNA Targeting c-Myc and VEGF on Human Colorectal Cancer Volo Cells. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2012, 26, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Ma, D.; Lu, L.; Ouyang, D.; Xi, Z. Building Customizable Multisite-Targeting c-Myc shRNA Array into Branch-PCR-Constructed DNA Nanovectors for Enhanced Tumor Cell Suppression. ChemistrySelect 2020, 5, 10250–10255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangudu, N.K.; Verma, V.K.; Clemons, T.D.; Beevi, S.S.; Hay, T.; Mahidhara, G.; Raja, M.; Nair, R.A.; Alexander, L.E.; Patel, A.B.; et al. RNA Interference Using c-Myc-Conjugated Nanoparticles Suppresses Breast and Colorectal Cancer Models. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2015, 14, 1259–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moodley, T.; Singh, M. Polymeric Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Enhanced Delivery of 5-Fluorouracil In Vitro. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moodley, T.; Singh, M. Sterically Stabilised Polymeric Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Improve Doxorubicin Efficiency: Tailored Cancer Therapy. Molecules 2020, 25, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mngadi, S.; Mokhosi, S.; Singh, M.; Mdlalose, W. Chitosan-Functionalized Mg0.5Co0.5Fe2O4 Magnetic Nanoparticles Enhance Delivery of 5-Fluorouracil In Vitro. Coatings 2020, 10, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Synthesis and characterization of magnetic nanoparticles of cobalt ferrite coated with silica. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2019, 10, 4908–4913. [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, Y.; Yamaoka, K.; Nishikawa, M.; Takakura, Y. Quantitative and Temporal Analysis of Gene Silencing in Tumor Cells Induced by Small Interfering RNA or Short Hairpin RNA Expressed from Plasmid Vectors. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 98, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.-F.; Wang, J. Delivery systems for siRNA drug development in cancer therapy. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boettcher, M.; McManus, M.T. Choosing the Right Tool for the Job: RNAi, TALEN, or CRISPR. Mol. Cell 2015, 58, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unniyampurath, U.; Pilankatta, R.; Krishnan, M.N. RNA Interference in the Age of CRISPR: Will CRISPR Interfere with RNAi? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabay, M.; Li, Y.; Felsher, D.W. MYC Activation Is a Hallmark of Cancer Initiation and Maintenance. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2014, 4, a014241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanamaru, T.; Takagi, T.; Takakura, Y.; Hashida, M. Biological Effects and Cellular Uptake of c-mycAntisense Oligonucleotides and Their Cationic Liposome Complexes. J. Drug Target. 1998, 5, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putney, S.D.; Brown, J.; Cucco, C.; Lee, R.; Skorski, T.; Leonetti, C.; Geiser, T.; Calabretta, B.; Zupi, G.; Zon, G. Enhanced Anti-Tumor Effects with Microencapsulated c-mycAntisense Oligonucleotide. Antisense Nucleic Acid Drug Dev. 1999, 9, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, J.S.; Swarbrick, A.; Musgrove, E.A.; Sutherland, R.L. Mechanisms of growth arrest by c-myc antisense oligonucleotides in MCF-7 breast cancer cells: Implications for the antiproliferative effects of antiestrogens. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 3126–3131. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, D.; Kim, B.; Hu, G.; Gupta, D.S.; Senpan, A.; Yang, X.; Schmieder, A.; Swain, C.; A Wickline, S.; Tomasson, M.H.; et al. A strategy for combating melanoma with oncogenic c-Myc inhibitors and targeted nanotherapy. Nanomedicine 2015, 10, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soodgupta, D.; Pan, D.; Cui, G.; Senpan, A.; Yang, X.; Lu, L.; Weilbaecher, K.N.; Prochownik, E.V.; Lanza, G.M.; Tomasson, M.H. Small Molecule MYC Inhibitor Conjugated to Integrin-Targeted Nanoparticles Extends Survival in a Mouse Model of Disseminated Multiple Myeloma. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2015, 14, 1286–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esser, A.K.; Ross, M.H.; Fontana, F.; Su, X.; Gabay, A.; Fox, G.C.; Xu, Y.; Xiang, J.; Schmieder, A.H.; Yang, X.; et al. Nanotherapy delivery of c-myc inhibitor targets Protumor Macrophages and preserves Antitumor Macrophages in Breast Cancer. Theranostics 2020, 10, 7510–7526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sajid, M.I.; Moazzam, M.; Kato, S.; Cho, K.Y.; Tiwari, R.K. Overcoming Barriers for siRNA Therapeutics: From Bench to Bedside. Pharmaceutics 2020, 13, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Nucleic Acid | Carrier | Polymer Modification (✓/✗) | Ligand-Targeting Modification (✓/✗) | Disease State | Test System | Advantages | Disadvantages | Clinical Trial (✓/✗) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| siRNA | neutral liposome | ✓ | ✗ | Ovarian cancer | Xenograft tumors | High encapsulation efficiency Good biocompatibility Low toxicity Weak immunogenicity | Low transfection efficiency High production cost | ✗ | [50,52] |
| cationic liposome | ✗ | ✗ | Colon cancer Breast cancer | HT-29 cells MCF-7 cells | High encapsulation efficiency Good biocompatibility Low toxicity Weak immunogenicity | Low transfection efficiency High production cost | ✗ | [55,56] | |
| liposome-polycation-DNA nanoparticle | ✓ | ✓ | Fibrosarcoma | HT-1080 cells Xenograft tumors | High transfection efficiency Good biocompatibility | Complex structure and synthesis | ✗ | [57] | |
| lipid calcium phosphate nanoparticle | ✓ | ✓ | Non-small cell lung cancer | Xenograft tumors | High transfection efficiency Good biocompatibility Low toxicity | Complex structure and synthesis | ✗ | [58] | |
| exosomes | ✗ | ✗ | - | Mouse λ820 cells | High encapsulation efficiency Natural carriers Good biocompatibility Steady release profile | Lack of standardized techniques for isolation and purification | ✗ | [66] | |
| chitosan nanoparticles | ✓ | ✓ | Breast cancer | MCF-7 cells Xenograft tumors | Small particle size Good biocompatibility | Low transfection efficiency | ✗ | [67] | |
| poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanocapsule | ✗ | ✗ | Neuroblastoma | - | High stability Biodegradability FDA-approved material Sustained release | Low transfection efficiency | ✗ | [68] | |
| siNozyme | ✗ | ✗ | melanoma | - | Biocompatibility Good bioavailability | Complex structure and synthesis | ✗ | [69] | |
| cell-penetrating peptide | ✗ | ✓ | melanoma | B16 cells Xenograft tumors | High transfection efficiency Low toxicity | The possible need for covalent conjugation Low cell specificity | ✗ | [70] | |
| multi-peptide complex | ✗ | ✓ | Breast cancer | MDA-MB-231 | High transfection efficiency Low toxicity | Complex structure and synthesis | ✗ | [71] | |
| gold nanoparticles | ✓ | ✓ | Cervical cancer Breast cancer Lung cancer | HeLa cells MCF-7 cells Xenograft tumors A549 cells CMT/167 cells | Large surface area-high loading capacity Amenable to chemical manipulation | Toxicity | ✗ | [81,82,83,84,85,86,87] | |
| selenium nanoparticles | ✓ | ✓ | Glioblastoma | U251 tumor spheroids | Large surface area-high loading capacity Amenable to chemical manipulation | Toxicity | ✗ | [88] | |
| nano-graphene oxide | ✓ | ✗ | Breast cancer | MCF-7 cells MDA-MB-231 cells | High surface area to volume ratio Flexibility for cargo loading Amenable to functionalization | Adverse interactions with proteins Toxicity Immunogenicity | ✗ | [89] | |
| DsiRNA | EnCore™ lipid nanoparticle | ✗ | ✗ | Advanced solid tumors Multiple myeloma Lymphoma | -Patients | High carrying capacity Good biocompatibility | Poor tumor penetration Unsatisfactory knockdown efficiency Expensive Labor intensive | ✓ | [91] |
| shRNA expression plasmid | cationic liposome | ✗ | ✗ | Breast cancer Liver cancer Colon cancer Nasopharyngeal cancer | MCF-7 cells Xenograft tumors HepG2 cells Colo320 cells CNE-2Z | High encapsulation efficiency Good biocompatibility Low toxicity Weak immunogenicity | Low transfection efficiency High production cost | ✗ | [93,94,95,96] |
| polyglycidal methacrylate nanoparticle | ✓ | ✗ | Breast cancer Colorectal cancer | - | Low toxicity at high concentrations | Low transfection efficiency Complex structure and synthesis | ✗ | [99] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Habib, S.; Ariatti, M.; Singh, M. Anti-c-myc RNAi-Based Onconanotherapeutics. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 612. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8120612
Habib S, Ariatti M, Singh M. Anti-c-myc RNAi-Based Onconanotherapeutics. Biomedicines. 2020; 8(12):612. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8120612
Chicago/Turabian StyleHabib, Saffiya, Mario Ariatti, and Moganavelli Singh. 2020. "Anti-c-myc RNAi-Based Onconanotherapeutics" Biomedicines 8, no. 12: 612. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8120612
APA StyleHabib, S., Ariatti, M., & Singh, M. (2020). Anti-c-myc RNAi-Based Onconanotherapeutics. Biomedicines, 8(12), 612. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8120612






