Cytocompatibility of Bilayer Scaffolds Electrospun from Chitosan/Alginate-Chitin Nanowhiskers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Characterization of Polysaccharides
2.2. Polymer Solutions
2.3. Electrospinning
2.4. Film Preparation
2.5. General Methods
2.6. Cell Culture and In Vitro Tests
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation and Morphology of CS and CS–ALG&CNW Scaffolds
3.2. X-Ray Diffraction Structure
3.3. Swelling
3.4. Porosity
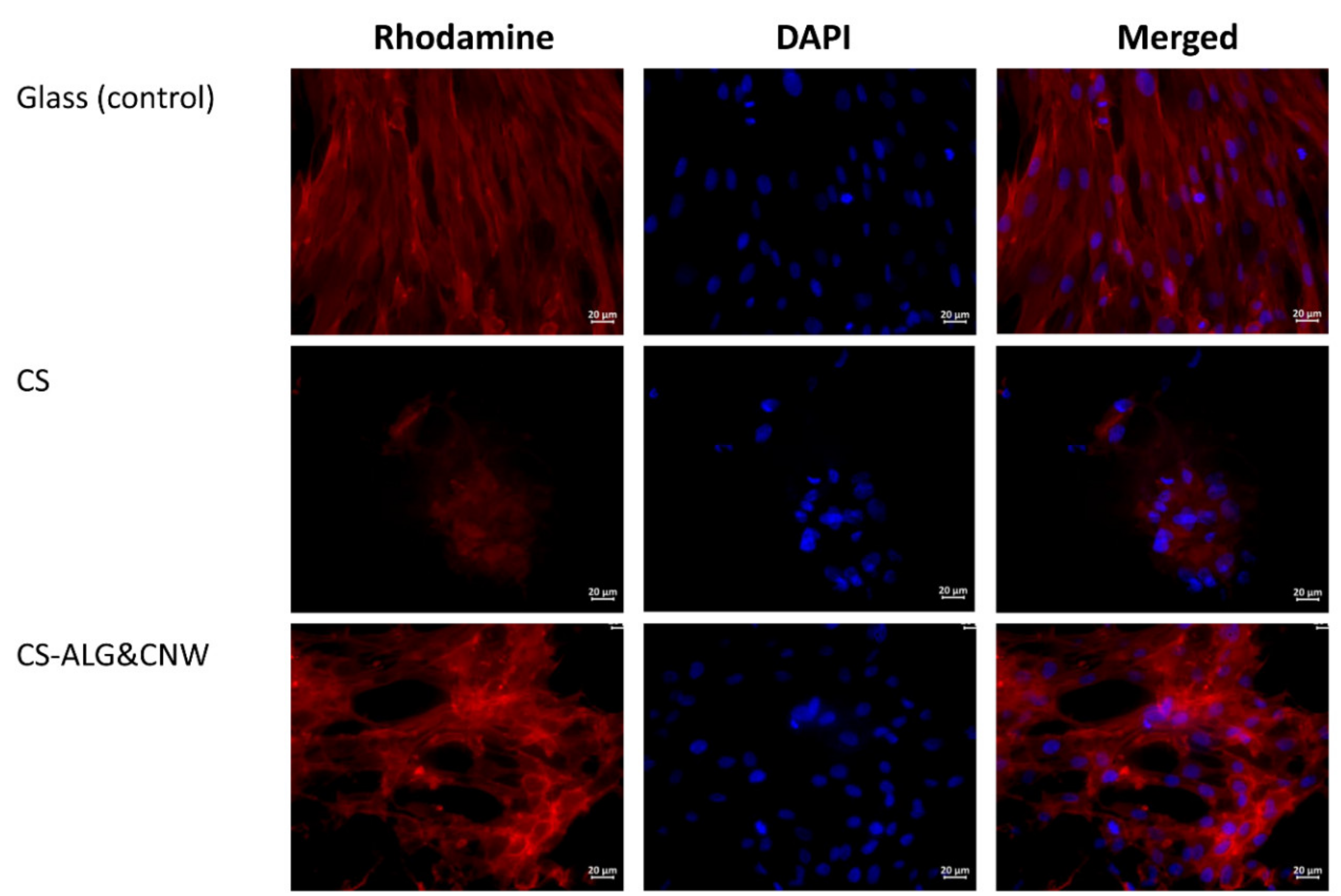
3.5. Testing of Cell Adhesion Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al-Enizi, A.M.; Zagho, M.M.; Elzatahry, A.A. Polymer-based electrospun nanofibers for biomedical applications. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naeimirad, M.; Zadhoush, A.; Kotek, R.; Neisiany, R.E.; Khorasani, S.N.; Ramakrishna, S. Recent advances in core/shell bicomponent fibers and nanofibers: A review. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norouzi, M. Recent advances in brain tumor therapy: Application of electrospun nanofibers. Drug Discov. Today 2018, 23, 912–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, I.; Han, H.-S.; Edwards, J.R.; Jeon, H. Electrospun Fibrous Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering: Viewpoints on Architecture and Fabrication. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paim, Á.; Tessaro, I.C.; Cardozo, N.S.M.; Pranke, P. Mesenchymal stem cell cultivation in electrospun scaffolds: Mechanistic modeling for tissue engineering. J. Biol. Phys. 2018, 44, 245–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steffens, D.; Braghirolli, D.I.; Maurmann, N.; Pranke, P. Update on the main use of biomaterials and techniques associated with tissue engineering. Drug Discov. Today 2018, 23, 1474–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Wendorff, J.H.; Greiner, A. Use of electrospinning technique for biomedical applications. Polymer 2008, 49, 5603–5621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y.; Jeong, L.; Kang, Y.O.; Lee, S.J.; Park, W.H. Electrospinning of polysaccharides for regenerative medicine. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 1020–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, T.; Rath, G.; Goyal, A.K. Biomaterials-based nanofiber scaffold: Targeted and controlled carrier for cell and drug delivery. J. Drug Target. 2015, 23, 202–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saquing, C.D.; Tang, C.; Monian, B.; Bonino, C.A.; Manasco, J.L.; Alsberg, E.; Khan, S.A. Alginate–Polyethylene Oxide Blend Nanofibers and the Role of the Carrier Polymer in Electrospinning. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 8692–8704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseri, N.; Mathew, A.P.; Oksman, K. Electrospinnability of bionanocomposites with high nanocrystal loadings: The effect of nanocrystal surface characteristics. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 147, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gizaw, M.; Thompson, J.; Faglie, A.; Lee, S.-Y.; Neuenschwander, P.; Chou, S.-F. Electrospun fibers as a dressing material for drug and biological agent delivery in wound healing applications. Bioengineering 2018, 5, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrova, V.A.; Chernyakov, D.D.; Poshina, D.N.; Gofman, I.V.; Romanov, D.P.; Mishanin, A.I.; Golovkin, A.S.; Skorik, Y.A. Electrospun bilayer chitosan/hyaluronan material and its compatibility with mesenchymal stem cells. Materials 2019, 12, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ifuku, S. Chitin and chitosan nanofibers: Preparation and chemical modifications. Molecules 2014, 19, 18367–18380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, H.; Furuike, T.; Nair, S.; Jayakumar, R. Biomedical applications of chitin hydrogel membranes and scaffolds. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 84, 820–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaudo, M. Chitin and chitosan: Properties and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2006, 31, 603–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzzarelli, R.A. Biomedical Exploitation of Chitin and Chitosan via Mechano-Chemical Disassembly, Electrospinning, Dissolution in Imidazolium Ionic Liquids, and Supercritical Drying. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1510–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitha, A.; Sowmya, S.; Jayakumar, R.; Deepthi, S.; Chennazhi, K.; Ehrlich, H.; Tsurkan, M.V.; Jayakumar, R. Chitin and chitosan in selected biomedical applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 1644–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mincea, M.; Negrulescu, A.; Ostafe, V. Preparation, modification, and applications of chitin nanowhiskers: A review. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2012, 30, 225–242. [Google Scholar]
- Jayakumar, R.; Prabaharan, M.; Kumar, P.S.; Nair, S.; Tamura, H. Biomaterials based on chitin and chitosan in wound dressing applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2011, 29, 322–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, L.; Zhu, L.; Thielemans, W. Chitin nanowhisker aerogels. ChemSusChem 2013, 6, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naseri, N.; Algan, C.; Jacobs, V.; John, M.; Oksman, K.; Mathew, A.P. Electrospun chitosan-based nanocomposite mats reinforced with chitin nanocrystals for wound dressing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 109, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, X.; Zheng, J.; Zhao, X.; Liu, M. Chemically Cross-Linked Chitin Nanocrystal Scaffolds for Drug Delivery. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 6790–6799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pangon, A.; Saesoo, S.; Saengkrit, N.; Ruktanonchai, U.R.; Intasanta, V. Hydroxyapatite-hybridized chitosan/chitin whisker bionanocomposite fibers for bone tissue engineering applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 144, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrova, V.A.; Elokhovskiy, V.Y.; Raik, S.V.; Poshina, D.N.; Romanov, D.P.; Skorik, Y.A. Alginate gel reinforcement with chitin nanowhiskers modulates rheological properties and drug release profile. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiroshka, V.V.; Petrova, V.A.; Chernyakov, D.D.; Bozhkova, Y.O.; Kiroshka, K.V.; Baklagina, Y.G.; Romanov, D.P.; Kremnev, R.V.; Skorik, Y.A. Influence of chitosan-chitin nanofiber composites on cytoskeleton structure and the proliferation of rat bone marrow stromal cells. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2016, 28, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakumar, R.; Prabaharan, M.; Nair, S.; Tamura, H. Novel chitin and chitosan nanofibers in biomedical applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rejinold, N.S.; Nair, A.; Sabitha, M.; Chennazhi, K.P.; Tamura, H.; Nair, S.; Jayakumar, R. Synthesis, characterization and in vitro cytocompatibility studies of chitin nanogels for biomedical applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 943–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.F. There is no such thing as a biocompatible material. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 10009–10014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifpanah, F.; Reinhardt, M.; Schonleben, J.; Meyer, C.; Richter, M.; Schnabelrauch, M.; Rode, C.; Wartenberg, A.; Bekhite, M.; Sauer, H.; et al. Embryonic stem cells for tissue biocompatibility, angiogenesis, and inflammation testing. Cells Tissues Organs 2017, 204, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, K.H.; Park, K.-M.; Kang, K.-S.; Woo, H.-M. Biocompatibility evaluation of tissue-engineered decellularized scaffolds for biomedical application. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 67, 766–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Yang, L.; Wang, G.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, B.; Qi, N. Biocompatibility Evaluation of Chitosan-based Injectable Hydrogels for the Culturing Mice Mesenchymal Stem Cells In Vitro. J. Biomater. Appl. 2009, 24, 625–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, S.-J.; Driscoll, T.P.; Thorpe, S.D.; Nerurkar, N.L.; Baker, B.M.; Yang, M.T.; Chen, C.S.; Lee, D.A.; Mauck, R.L. Differentiation alters stem cell nuclear architecture, mechanics, and mechano-sensitivity. eLife 2016, 5, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolbasov, E.; Goreninskii, S.; Tverdokhlebov, S.; Mishanin, A.; Viknianshchuk, A.; Bezuidenhout, D.; Golovkin, A. Comparative Study of the Physical, Topographical and Biological Properties of Electrospinning PCL, PLLA, their Blend and Copolymer Scaffolds. IOP Conf. Series Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 350, 012012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Saito, T.; Isogai, A. Individual chitin nano-whiskers prepared from partially deacetylated α-chitin by fibril surface cationization. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 79, 1046–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrova, V.A.; Panevin, A.; Zhuravskii, S.G.; Gasilova, E.R.; Vlasova, E.N.; Romanov, D.P.; Poshina, D.N.; Skorik, Y.A. Preparation of N-succinyl-chitin nanoparticles and their applications in otoneurological pathology. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 1023–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrovolskaya, I.P.; Yudin, V.E.; Popryadukhin, P.V.; Ivan’Kova, E.M.; Shabunin, A.S.; Kasatkin, I.; Morgantie, P. Effect of chitin nanofibrils on electrospinning of chitosan-based composite nanofibers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 194, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semnani, D.; Naghashzargar, E.; Hadjianfar, M.; Manshadi, F.D.; Mohammadi, S.; Karbasi, S.; Effaty, F. Evaluation of PCL/Chitosan Electrospun Nanofibers for Liver Tissue Engineering. Int. J. Polym. Mater. 2016, 66, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milleret, V.; Hefti, T.; Hall, H.; Vogel, V.; Eberli, D. Influence of the fiber diameter and surface roughness of electrospun vascular grafts on blood activation. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 4349–4356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, D.; Chen, S.; Jeong, Y.; Joo, Y.L. Surface hydro-properties of electrospun fiber mats. Fibers Polym. 2015, 16, 1578–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denchai, A.; Tartarini, D.; Mele, E. Cellular Response to Surface Morphology: Electrospinning and Computational Modeling. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2018, 6, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sashina, E.S.; Vnuchkin, A.V.; Novoselov, N.P. A study of the thermodynamics of chitosan interaction with polyvinyl alcohol and polyethylene oxide by differential scanning calorimetry. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2006, 79, 1643–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakravan, M.; Heuzey, M.-C.; Ajji, A. A fundamental study of chitosan/peo electrospinning. Polymer 2011, 52, 4813–4824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zotkin, M.A.; Vikhoreva, G.A.; Kechek’yan, A.S. Thermal modification of chitosan films in the form of salts with various acids. Polym. Sci. Ser. B 2004, 46, 39–42. [Google Scholar]
- Cesarz, Z.; Tamama, K. Spheroid Culture of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Stem Cells Int. 2016, 2016, 9176357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.S.; Dai, L.G.; Yen, B.L.; Hsu, S.H. Spheroid formation of mesenchymal stem cells on chitosan and chitosan-hyaluronan membranes. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 6929–6945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, H.Y.; Liu, B.H.; Sieber, M.; Hsu, S.H. Substrate-dependent gene regulation of self-assembled human msc spheroids on chitosan membranes. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartosh, T.J.; Ylostalo, J.H.; Mohammadipoor, A.; Bazhanov, N.; Coble, K.; Claypool, K.; Lee, R.H.; Choi, H.; Prockop, D.J. Aggregation of human mesenchymal stromal cells (mscs) into 3d spheroids enhances their antiinflammatory properties. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 13724–13729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumura, K.; Nakamura, K.; Hisatomi, Y.; Nagano, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Terada, K.; Sugiyama, T.; Umeyama, K.; Matsumoto, K.; Yamamoto, T.; et al. Salivary gland progenitor cells induced by duct ligation differentiate into hepatic and pancreatic lineages. Hepatology 2003, 38, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
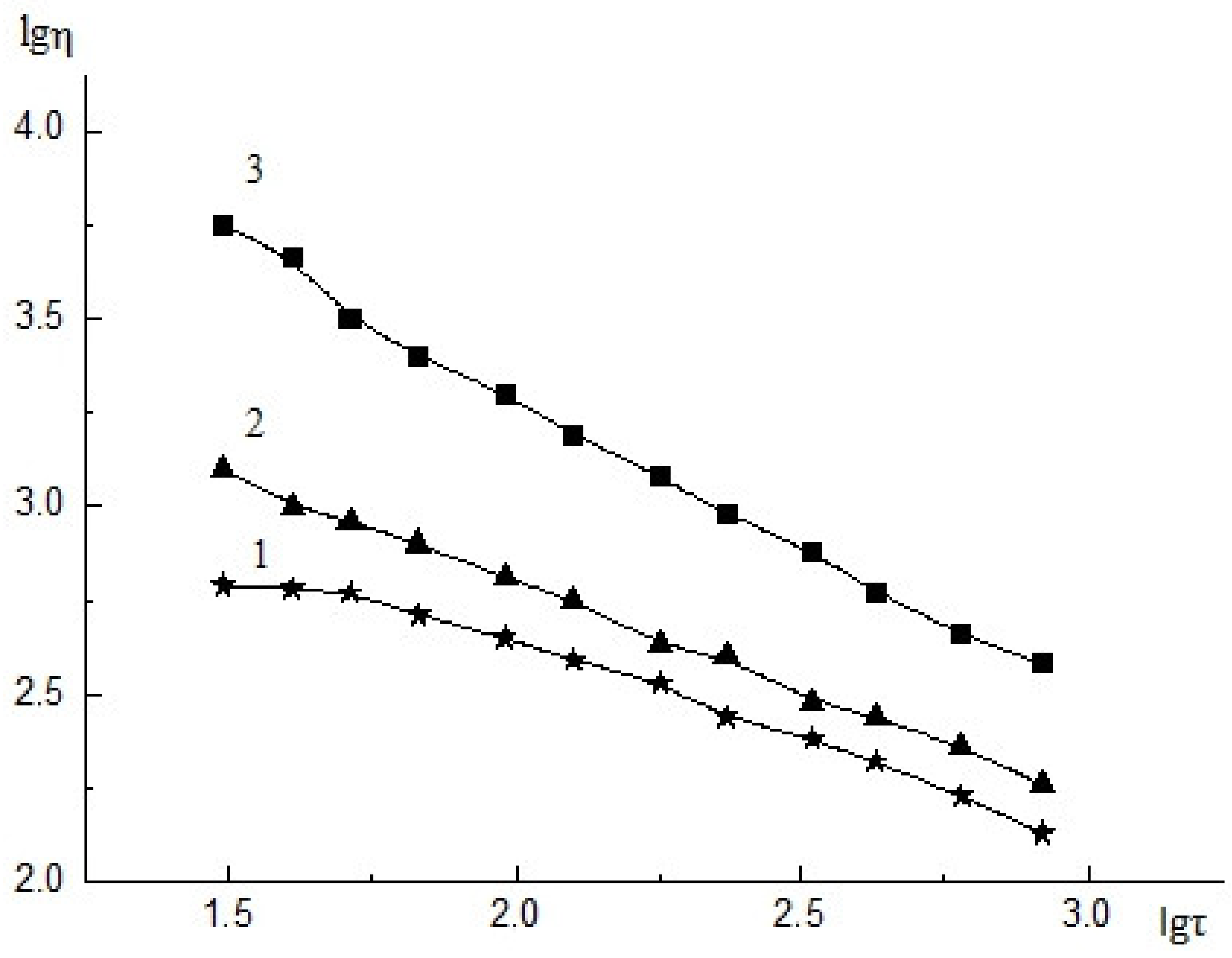





| Roughness Parameter | CS Surface | ALG&CNW Surface |
|---|---|---|
| Peak-to-peak roughness, µm | 6.13 | 4.76 |
| Average roughness, µm | 0.39 | 0.27 |
| Root mean square roughness, µm | 0.50 | 0.25 |
| Sample | Treatment | Swelling in Water, g/g | Swelling in 0.9% NaCl, g/g |
|---|---|---|---|
| CS | 80 °C, 4 h | 5.3 ± 0.3 | 2.2 ± 0.2 |
| ALG&CNW | - | partially dissolved | partially dissolved |
| CS-ALG&CNW | 80 °C, 4 h | 2.5 ± 0.2 | 2.0 ± 0.2 |
| Parameter | CS [13] | CS-ALG&CNW |
|---|---|---|
| Average logarithmic pore radius (nm) | 1.62 | 2.26 |
| Average pore radius, nm | 489 | 2193 |
| Porosity over weight, cm3/g | 9.36 | 8.48 |
| Porosity over volume, cm3/cm3 | 0.976 | 0.861 |
| Meso- and macro-pore surface over weight, m2/g | 878 | 878 |
| Meso- and macro-pore surface over volume, m2/cm3 | 89.1 | 89.1 |
| Total pore surface over weight, m2/g | 2464 | 1463 |
| Total pore surface over volume, m2/cm3 | 257 | 149 |
| Sample | Non-Adhered Cells | Adhered Cells | Prevailing Type of Colony | The Average Size of MMSC Spheroids, µm (mean ± SD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glass (control) | - | multiple | monolayer | |
| CS | isolated | multiple | spheroids | 70±37 |
| CS-ALG&CNW | isolated | multiple | monolayer + spheroids | 109±43* |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Petrova, V.A.; Golovkin, A.S.; Mishanin, A.I.; Romanov, D.P.; Chernyakov, D.D.; Poshina, D.N.; Skorik, Y.A. Cytocompatibility of Bilayer Scaffolds Electrospun from Chitosan/Alginate-Chitin Nanowhiskers. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8090305
Petrova VA, Golovkin AS, Mishanin AI, Romanov DP, Chernyakov DD, Poshina DN, Skorik YA. Cytocompatibility of Bilayer Scaffolds Electrospun from Chitosan/Alginate-Chitin Nanowhiskers. Biomedicines. 2020; 8(9):305. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8090305
Chicago/Turabian StylePetrova, Valentina A., Alexey S. Golovkin, Alexander I. Mishanin, Dmitry P. Romanov, Daniil D. Chernyakov, Daria N. Poshina, and Yury A. Skorik. 2020. "Cytocompatibility of Bilayer Scaffolds Electrospun from Chitosan/Alginate-Chitin Nanowhiskers" Biomedicines 8, no. 9: 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8090305
APA StylePetrova, V. A., Golovkin, A. S., Mishanin, A. I., Romanov, D. P., Chernyakov, D. D., Poshina, D. N., & Skorik, Y. A. (2020). Cytocompatibility of Bilayer Scaffolds Electrospun from Chitosan/Alginate-Chitin Nanowhiskers. Biomedicines, 8(9), 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8090305







