The Inhibition of Complement System in Formal and Emerging Indications: Results from Parallel One-Stage Pairwise and Network Meta-Analyses of Clinical Trials and Real-Life Data Studies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
Hypothesis and Study Objective
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Systematic Narrative Synthesis
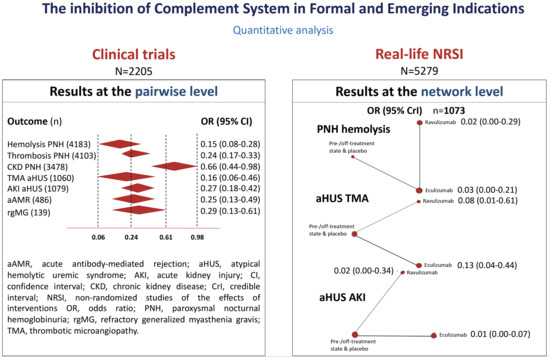
3.2. Quantitative Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Important Messages
4.2. Findings in Context
4.3. Study Limitations
4.4. Future Research
4.5. Conclusions and Regulatory Considerations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ricklin, D.; Hajishengallis, G.; Yang, K.; Lambris, J.D. Complement: A key system for immune surveillance and homeostasis. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 785–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheridan, D.; Yu, Z.-X.; Zhang, Y.; Patel, R.; Sun, F.; Lasaro, M.A.; Bouchard, K.; Andrien, B.; Marozsan, A.; Wang, Y.; et al. Design and preclinical characterization of ALXN1210: A novel anti-C5 antibody with extended duration of action. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berger, M.; Lefaucheur, C.; Jordan, S.C. Update on C1 Esterase Inhibitor in Human Solid Organ Transplantation. Transplant 2019, 103, 1763–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, Y.D.; Harr, T.; Dayer, E.; Seebach, J.D. C1 esterase inhibitor concentrates and attenuated androgens. Lancet 2018, 391, 1355–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricklin, D.; Mastellos, D.C.; Reis, E.S.; Lambris, J.D. The renaissance of complement therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2018, 14, 26–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ricklin, D.; Reis, E.S.; Lambris, J.D. Complement in disease: A defence system turning offensive. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2016, 12, 383–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reis, E.S.; Mastellos, D.C.; Yancopoulou, D.; Risitano, A.M.; Ricklin, D.; Lambris, J.D. Applying complement therapeutics to rare diseases. Clin. Immunol. 2015, 161, 225–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ricklin, D.; Barratt-Due, A.; Mollnes, T.E. Complement in clinical medicine: Clinical trials, case reports and therapy monitoring. Mol. Immunol. 2017, 89, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oneil, M.E.; Berkman, N.D.; Hartling, L.; Chang, S.M.; Anderson, J.; Motu’Apuaka, M.; Guise, J.-M.; McDonagh, M.S. Observational evidence and strength of evidence domains: Case examples. Syst. Rev. 2014, 3, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herrera-Gómez, F.; Chimeno, M.M.; García, D.M.; Lizaraso-Soto, F.; Maurtua-Briseño-Meiggs, Á.; Grande-Villoria, J.; Bustamante-Munguira, J.; Alamartine, E.; Vilardell, M.; Sangrador, C.O.; et al. Cholesterol-Lowering Treatment in Chronic Kidney Disease: Multistage Pairwise and Network Meta-Analyses. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Green, S. (Eds.) Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions—Version 5.1.0.; The Cochrane Collaboration: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Hernán, M.A.; Reeves, B.C.; Savović, J.; Berkman, N.D.; Viswanathan, M.; Henry, D.; Altman, D.G.; Ansari, M.T.; Boutron, I.; et al. ROBINS-I: A tool for assessing risk of bias in non-randomised studies of interventions. BMJ 2016, 355, i4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brown, S.; Hutton, B.; Clifford, T.J.; Coyle, D.; Grima, D.T.; Wells, G.A.; Cameron, C. A Microsoft-Excel-based tool for running and critically appraising network meta-analyses—An overview and application of NetMetaXL. Syst. Rev. 2014, 3, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Systematic Reviews: Centre for Reviews and Dissemination’s (CRD) Guidance for Undertaking Reviews in Health Care; University of York: York, UK, 2008.
- Shamseer, L.; Moher, D.; Clarke, M.; Ghersi, D.; Liberati, A.; Petticrew, M.; Shekelle, P.; Stewart, L.A. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015: Elaboration and explanation. BMJ 2015, 350, g7647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hutton, B.; Salanti, G.; Caldwell, D.M.; Chaimani, A.; Schmid, C.H.; Cameron, C.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Straus, S.; Thorlund, K.; Jansen, J.P.; et al. The PRISMA Extension Statement for Reporting of Systematic Reviews Incorporating Network Meta-analyses of Health Care Interventions: Checklist and Explanations. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 162, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hillmen, P.; Hall, C.; Marsh, J.C.; Elebute, M.; Bombara, M.P.; Petro, B.E.; Cullen, M.J.; Richards, S.J.; Rollins, S.A.; Mojcik, C.F.; et al. Effect of Eculizumab on Hemolysis and Transfusion Requirements in Patients with Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 552–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hill, A.; Hillmen, P.; Richards, S.J.; Elebute, D.; Marsh, J.C.; Chan, J.; Mojcik, C.F.; Rother, R.P. Sustained response and long-term safety of eculizumab in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Blood 2005, 106, 2559–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hillmen, P.; Young, N.S.; Schubert, J.; Brodsky, R.A.; Socié, G.; Muus, P.; Röth, A.; Szer, J.; Elebute, M.O.; Nakamura, R.; et al. The Complement Inhibitor Eculizumab in Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 1233–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodsky, R.A.; Young, N.S.; Antonioli, E.; Risitano, A.M.; Schrezenmeier, H.; Schubert, J.; Gaya, A.; Coyle, L.; De Castro, C.; Fu, C.-L.; et al. Multicenter phase 3 study of the complement inhibitor eculizumab for the treatment of patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Blood 2008, 111, 1840–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillmen, P.; Muus, P.; Roth, A.; Elebute, M.O.; Risitano, A.M.; Schrezenmeier, H.; Szer, J.; Browne, P.; Maciejewski, J.P.; Schubert, J.; et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of sustained eculizumab treatment in patients with paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria. Br. J. Haematol. 2013, 162, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillmen, P.; Muus, P.; Dührsen, U.; Risitano, A.; Schubert, J.; Luzzatto, L.; Schrezenmeier, H.; Szer, J.; Brodsky, R.A.; Hill, A.; et al. Effect of the complement inhibitor eculizumab on thromboembolism in patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Blood 2007, 110, 4123–4128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hillmen, P.; Elebute, M.; Kelly, R.; Urbano-Ispizua, A.; Hill, A.; Rother, R.P.; Khursigara, G.; Fu, C.-L.; Omine, M.; Browne, P.; et al. Long-term effect of the complement inhibitor eculizumab on kidney function in patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Am. J. Hematol. 2010, 85, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanakura, Y.; Ohyashiki, K.; Shichishima, T.; Okamoto, S.; Ando, K.; Ninomiya, H.; Kawaguchi, T.; Nakao, S.; Nakakuma, H.; Nishimura, J.-I.; et al. Safety and efficacy of the terminal complement inhibitor eculizumab in Japanese patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: The AEGIS Clinical Trial. Int. J. Hematol. 2011, 93, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanakura, Y.; Ohyashiki, K.; Shichishima, T.; Okamoto, S.; Ando, K.; Ninomiya, H.; Kawaguchi, T.; Nakao, S.; Nakakuma, H.; Nishimura, J.-I.; et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of eculizumab in Japanese patients with PNH: AEGIS trial. Int. J. Hematol. 2013, 98, 406–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; De Fontbrune, F.S.; Lee, L.W.L.; Pessoa, V.; Gualandro, S.; Füreder, W.; Ptushkin, V.; Rottinghaus, S.T.; Volles, L.; Shafner, L.; et al. Ravulizumab (ALXN1210) vs. eculizumab in adult patients with PNH naive to complement inhibitors: The 301 study. Blood 2019, 133, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kulasekararaj, A.G.; Hill, A.; Rottinghaus, S.T.; Langemeijer, S.; Wells, R.; Gonzalez-Fernandez, F.A.; Gaya, A.; Lee, J.W.; Gutierrez, E.O.; Piatek, C.I.; et al. Ravulizumab (ALXN1210) vs. eculizumab in C5-inhibitor–experienced adult patients with PNH: The 302 study. Blood 2019, 133, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrezenmeier, H.; Muus, P.; Socié, G.; Szer, J.; Urbano-Ispizua, A.; Maciejewski, J.P.; Brodsky, R.A.; Bessler, M.; Kanakura, Y.; Rosse, W.; et al. Baseline characteristics and disease burden in patients in the International Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria Registry. Haematologica 2014, 99, 922–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Socié, G.; Schrezenmeier, H.; Muus, P.; Lisukov, I.; Röth, A.; Kulasekararaj, A.; Lee, J.W.; Araten, D.; Hill, A.; Brodsky, R.; et al. Changing prognosis in Paroxysmal Nocturnal Haemoglobinuria disease subcategories; an analysis of International PNH Registry. Intern. Med. J. 2016, 46, 1044–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Urbano-Ispizua, A.; Muus, P.; Schrezenmeier, H.; Almeida, A.; Wilson, A.; Ware, R.E. Different clinical characteristics of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria in pediatric and adult patients. Haematologica 2016, 102, e76–e79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.W.; De Latour, R.P.; Brodsky, R.A.; Jang, J.H.; Hill, A.; Röth, A.; Schrezenmeier, H.; Wilson, A.; Marantz, J.L.; Maciejewski, J.P. Effectiveness of eculizumab in patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) with or without aplastic anemia in the International PNH Registry. Am. J. Hematol. 2019, 94, E37–E41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakurai, M.; Jang, J.H.; Chou, W.-C.; Kim, J.S.; Wilson, A.; Nishimura, J.-I.; Chiou, T.-J.; Kanakura, Y.; Lee, J.W.; Okamoto, S. Comparative study on baseline clinical characteristics of Asian versus non-Asian patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Int. J. Hematol. 2019, 110, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninomiya, H.; Obara, N.; Chiba, S.; Usuki, K.; Nishiwaki, K.; Matsumura, I.; Shichishima, T.; Okamoto, S.; Nishimura, J.-I.; Ohyashiki, K.; et al. Interim analysis of post-marketing surveillance of eculizumab for paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria in Japan. Int. J. Hematol. 2016, 104, 548–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.W.; Jang, J.H.; Kim, J.S.; Jo, D.-Y.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, S.-H.; Kim, Y.-K.; Won, J.-H.; Chung, J.S.; Kim, H.; et al. Efficacy of eculizumab in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria patients with or without aplastic anemia: Prospective study of a Korean PNH cohort. Blood Res. 2017, 52, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.H.; Kim, J.S.; Yoon, S.-S.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, Y.-K.; Jo, D.-Y.; Chung, J.S.; Sohn, S.K.; Lee, J.W. Predictive Factors of Mortality in Population of Patients with Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria (PNH): Results from a Korean PNH Registry. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2016, 31, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Jang, J.H.; Yoon, S.-S.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, Y.-K.; Jo, D.-Y.; Chung, J.S.; Sohn, S.K.; Lee, J.W. Distinct subgroups of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) with cytopenia: Results from South Korean National PNH Registry. Ann. Hematol. 2016, 95, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Cheong, J.-W.; Mun, Y.-C.; Jang, J.H.; Jo, D.-Y.; Lee, J.W.; Hematology, A.A.W.P.O.T.K.S.O.; Hematology, O.B.O.A.A.W.P.O.T.K.S.O. Clinical implication of renal dysfunction during the clinical course in patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: A longitudinal analysis. Ann. Hematol. 2019, 98, 2273–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loschi, M.; Porcher, R.; Barraco, F.; Terriou, L.; Mohty, M.; De Guibert, S.; Mahe, B.; Lemal, R.; Dumas, P.; Etienne, G.; et al. Impact of eculizumab treatment on paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: A treatment versus no-treatment study. Am. J. Hematol. 2016, 91, 366–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Latour, R.P.; Mary, J.Y.; Salanoubat, C.; Terriou, L.; Etienne, G.; Mohty, M.; Roth, S.; De Guibert, S.; Maury, S.; Cahn, J.Y.; et al. Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: Natural history of disease subcategories. Blood 2008, 112, 3099–3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villegas, A.; Núñez, R.; Gaya, A.; Cuevas-Ruiz, M.V.; Carral, A.; Arrizabalaga, B.; Gómez-Roncero, M.I.; Mora, A.; Bravo, P.; Lavilla, E.; et al. Presence of acute and chronic renal failure in patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: Results of a retrospective analysis from the Spanish PNH Registry. Ann. Hematol. 2017, 96, 1727–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Linares, C.; Ojeda, E.; Forés, R.; Pastrana, M.; Cabero, M.; Morillo, D.; Bautista, G.; Baños, I.; Monteserin, C.; Bravo, P.; et al. Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: A single Spanish center’s experience over the last 40 yr. Eur. J. Haematol. 2014, 93, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, M.L.; Morado, M.; Gaya, A.; Rosa, D.A.; Ojeda, E.; Muñoz, J.A.; De Mendiguren, B.P.; Monteagudo, M.D.; Durán, J.M.; Fisac, R.M.; et al. Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria therapy with eculizumab: Spanish experience. Med. Clin. Barc. 2011, 137, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-C.; Kuo, C.-Y.; Liu, I.-T.; Chen, T.-Y.; Chang, Y.-H.; Lin, S.-J.; Cho, S.-F.; Liu, Y.-C.; Liu, T.-C.; Lin, S.-F.; et al. Distinct clinical characteristics of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria in patients in Southern Taiwan: A multicenter investigation. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2017, 33, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, R.J.; Hill, A.; Arnold, L.M.; Brooksbank, G.L.; Richards, S.J.; Cullen, M.; Mitchell, L.D.; Cohen, D.R.; Gregory, W.M.; Hillmen, P. Long-term treatment with eculizumab in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: Sustained efficacy and improved survival. Blood 2011, 117, 6786–6792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Legendre, C.; Licht, C.; Muus, P.; Greenbaum, L.; Babu, S.; Bedrosian, C.; Bingham, C.; Cohen, D.; Delmas, Y.; Douglas, K.; et al. Terminal Complement Inhibitor Eculizumab in Atypical Hemolytic–Uremic Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 2169–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Licht, C.; Greenbaum, L.A.; Muus, P.; Babu, S.; Bedrosian, C.L.; Cohen, D.J.; Delmas, Y.; Douglas, K.; Furman, R.R.; Gaber, O.A.; et al. Efficacy and safety of eculizumab in atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome from 2-year extensions of phase 2 studies. Kidney Int. 2015, 87, 1061–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walle, J.V.; Delmas, Y.; Ardissino, G.; Wang, J.; Kincaid, J.F.; Haller, H. Improved renal recovery in patients with atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome following rapid initiation of eculizumab treatment. J. Nephrol. 2017, 30, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greenbaum, L.A.; Fila, M.; Ardissino, G.; Al-Akash, S.I.; Evans, J.; Henning, P.; Lieberman, K.V.; Maringhini, S.; Pape, L.; Rees, L.; et al. Eculizumab is a safe and effective treatment in pediatric patients with atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome. Kidney Int. 2016, 89, 701–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fakhouri, F.; Hourmant, M.; Campistol, J.M.; Cataland, S.R.; Espinosa, M.; Gaber, A.O.; Menne, J.; Minetti, E.E.; Provot, F.; Rondeau, E.; et al. Terminal Complement Inhibitor Eculizumab in Adult Patients With Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome: A Single-Arm, Open-Label Trial. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2016, 68, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Menne, J.; Delmas, Y.; Fakhouri, F.; Licht, C.; Lommelé, Å.; Minetti, E.E.; Provôt, F.; Rondeau, E.; Sheerin, N.S.; Wang, J.; et al. Outcomes in patients with atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome treated with eculizumab in a long-term observational study. BMC Nephrol. 2019, 20, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Menne, J.; Delmas, Y.; Fakhouri, F.; Kincaid, J.F.; Licht, C.; Minetti, E.E.; Mix, C.; Provôt, F.; Rondeau, É.; Sheerin, N.S.; et al. Eculizumab prevents thrombotic microangiopathy in patients with atypical haemolytic uraemic syndrome in a long-term observational study. Clin. Kidney J. 2018, 12, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondeau, E.; Scully, M.; Ariceta, G.; Barbour, T.D.; Cataland, S.R.; Heyne, N.; Miyakawa, Y.; Ortiz, D.; Swenson, E.D.; Vallee, M.; et al. TH-PO800: Efficacy and safety of the Long-acting C5-inhibitor ravulizumab in adult patients with atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS). In Proceedings of the American Society of Nephrology (ASN) Kidney Week 2019, Washington, DC, USA, 5–10 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Licht, C.; Ardissino, G.; Ariceta, G.; Cohen, D.; Cole, J.A.; Gasteyger, C.; Greenbaum, L.A.; Johnson, S.; Ogawa, M.; Schaefer, F.; et al. The global aHUS registry: Methodology and initial patient characteristics. BMC Nephrol. 2015, 16, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rondeau, E.; Cataland, S.R.; Al-Dakkak, I.; Miller, B.; Webb, N.J.; Landau, D. Eculizumab Safety: Five-Year Experience From the Global Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome Registry. Kidney Int. Rep. 2019, 4, 1568–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schaefer, F.; Ardissino, G.; Ariceta, G.; Fakhouri, F.; Scully, M.; Isbel, N.; Lommelé, Å.; Kupelian, V.; Gasteyger, C.; Greenbaum, L.A.; et al. Clinical and genetic predictors of atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome phenotype and outcome. Kidney Int. 2018, 94, 408–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leanne, C.; Rondeau, E.; Ardissino, G.; Caby-Tosi, M.-P.; Al-Dakkak, I.; Fakhouri, F.; Miller, B.; Scully, M. SP075: Pregnancy outcomes in patients enrolled in the Global aHUS Registry. In Proceedings of the 56th European Renal Association—European Dialysis and Transplant Association (ERA-EDTA) Congress, Budapest, Hungary, 13–16 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, S.; Hidaka, Y.; Inoue, N.; Kaname, S.; Kato, H.; Matsumoto, M.; Miyakawa, Y.; Mizuno, M.; Okada, H.; Shimono, A.; et al. Safety and effectiveness of eculizumab for pediatric patients with atypical hemolytic-uremic syndrome in Japan: Interim analysis of post-marketing surveillance. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2019, 23, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kato, H.; Miyakawa, Y.; Hidaka, Y.; Inoue, N.; Ito, S.; Kagami, S.; Kaname, S.; Matsumoto, M.; Mizuno, M.; Matsuda, T.; et al. Safety and effectiveness of eculizumab for adult patients with atypical hemolytic-uremic syndrome in Japan: Interim analysis of post-marketing surveillance. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2019, 23, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ito, N.; Hataya, H.; Saida, K.; Amano, Y.; Hidaka, Y.; Motoyoshi, Y.; Ohta, T.; Yoshida, Y.; Terano, C.; Iwasa, T.; et al. Efficacy and safety of eculizumab in childhood atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome in Japan. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2016, 20, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallett, A.; Hughes, P.; Szer, J.; Tuckfield, A.; Van Eps, C.L.; Cambell, S.B.; Hawley, C.M.; Burke, J.; Kausman, J.; Hewitt, I.; et al. Atypical Haemolytic Uraemic Syndrome treated with the complement inhibitor Eculizumab: The experience of the Australian compassionate access cohort. Intern. Med. J. 2015, 45, 1054–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Andrade, L.G.M.; Contti, M.M.; Nga, H.S.; Bravin, A.M.; Takase, H.M.; Viero, R.M.; Da Silva, T.N.; Chagas, K.D.N.; Palma, L.M.P. Long-term outcomes of the Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome after kidney transplantation treated with eculizumab as first choice. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Besbas, N.; Gulhan, B.; Soylemezoglu, O.; Özçakar, Z.B.; Korkmaz, E.; Hayran, M.; Ozaltin, F. Turkish pediatric atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome registry: Initial analysis of 146 patients. BMC Nephrol. 2017, 18, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gediz, F.; Payzin, B.K.; Ecemis, S.; Güler, N.; Yilmaz, A.F.; Topcugil, F.; Berdeli, A.; Yılmaz, A.F. Efficacy and safety of eculizumab in adult patients with atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome: A single center experience from Turkey. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2016, 55, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yenerel, M.N.; Aktan, M.; Yildiz, A.; Caliskan, Y.; Nalcaci, M. 311-II-4: The importance of Eculizumab in patients with atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome: Single center experience. In Proceedings of the 56th American Society of Hematology (ASH) Annual Meeting, San Francisco, CA, USA, 6–9 December 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Le Clech, A.; Simon-Tillaux, N.; Provôt, F.; Delmas, Y.; Vieira-Martins, P.; Limou, S.; Halimi, J.-M.; Le Quintrec, M.; Lebourg, L.; Grangé, S.; et al. Atypical and secondary hemolytic uremic syndromes have a distinct presentation and no common genetic risk factors. Kidney Int. 2019, 95, 1443–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhouri, F.; Delmas, Y.; Provot, F.; Barbet, C.; Karras, A.; Makdassi, R.; Courivaud, C.; Rifard, K.; Servais, A.; Allard, C.; et al. Insights From the Use in Clinical Practice of Eculizumab in Adult Patients With Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome Affecting the Native Kidneys: An Analysis of 19 Cases. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2014, 63, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fremeaux-Bacchi, V.; Fakhouri, F.; Garnier, A.; Bienaimé, F.; Dragon-Durey, M.-A.; Ngo, S.; Moulin, B.; Servais, A.; Provot, F.; Rostaing, L.; et al. Genetics and Outcome of Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome: A Nationwide French Series Comparing Children and Adults. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 8, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Fontbrune, F.S.; Galambrun, C.; Sirvent, A.; Huynh, A.; Faguer, S.; Nguyen, S.; Bay, J.-O.; Neven, B.; Moussi, J.; Simon, L.; et al. Use of Eculizumab in Patients With Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplant-Associated Thrombotic Microangiopathy: A study from the SFGM-TC. Transplantation 2015, 99, 1953–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Quintrec, M.; Lionet, A.; Kamar, N.; Karras, A.; Barbier, S.; Büchler, M.; Fakhouri, F.; Provost, F.; Fridman, W.H.; Thervet, E.; et al. Complement Mutation-AssociatedDe NovoThrombotic Microangiopathy Following Kidney Transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2008, 8, 1694–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuber, J.; Le Quintrec, M.; Krid, S.; Bertoye, C.; Gueutin, V.; Lahoche, A.; Heyne, N.; Ardissino, G.; Chatelet, V.; Noël, L.-H.; et al. Eculizumab for atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome recurrence in renal transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2012, 12, 3337–3354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servais, A.; Noël, L.-H.; Roumenina, L.T.; Le Quintrec, M.; Ngo, S.; Dragon-Durey, M.-A.; Macher, M.-A.; Zuber, J.; Karras, A.; Provot, F.; et al. Acquired and genetic complement abnormalities play a critical role in dense deposit disease and other C3 glomerulopathies. Kidney Int. 2012, 82, 454–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cavero, T.; Rabasco, C.; López, A.; Román, E.; Avila, A.; Sevillano, A.; Huerta, A.; Rojas-Rivera, J.; Fuentes, C.; Blasco, M.; et al. Eculizumab in secondary atypical haemolytic uraemic syndrome. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2017, 32, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huerta, A.; Arjona, E.; Portoles, J.; Lopez, P.; Rabasco, C.; Espinosa, M.; Cavero, T.; Blasco, M.; Cao, M.; Manrique, J.; et al. A retrospective study of pregnancy-associated atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome. Kidney Int. 2018, 93, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavero, T.; de Córdoba, S.R.; Praga, M. 121: ¿Microangiopatía trombótica asociada a hipertensión o a hiperactividad del complemento? Implicaciones diagnósticas y terapéuticas. In Proceedings of the XLVIII Congreso de la Sociedad Española de Nefrología y IX Congreso Iberoamericano de Nefrología, Madrid, Spain, 16–19 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sheerin, N.S.; Kavanagh, D.; Goodship, T.H.J.; Johnson, S. A national specialized service in England for atypical haemolytic uraemic syndrome-the first year’s experience. QJM 2016, 109, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brocklebank, V.; Johnson, S.; Sheerin, T.P.; Marks, S.D.; Gilbert, R.D.; Tyerman, K.S.; Kinoshita, M.; Awan, A.; Kaur, A.; Webb, N.; et al. Factor H autoantibody is associated with atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome in children in the United Kingdom and Ireland. Kidney Int. 2017, 92, 1261–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Howard, J.F.; Barohn, R.J.; Cutter, G.R.; Freimer, M.; Juel, V.C.; Mozaffar, T.; Mellion, M.L.; Benatar, M.; Farrugia, M.E.; Wang, J.; et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase II study of eculizumab in patients with refractory generalized myasthenia gravis. Muscle Nerve 2013, 48, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, J.F.; Utsugisawa, K.; Benatar, M.; Murai, H.; Barohn, R.J.; Illa, I.; Jacob, S.; Vissing, J.; Burns, T.M.; Kissel, J.T.; et al. Safety and efficacy of eculizumab in anti-acetylcholine receptor antibody-positive refractory generalised myasthenia gravis (REGAIN): A phase 3, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre study. Lancet Neurol. 2017, 16, 976–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muppidi, S.; Utsugisawa, K.; Benatar, M.; Murai, H.; Barohn, R.J.; Illa, I.; Jacob, S.; Vissing, J.; Burns, T.M.; Kissel, J.T.; et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of eculizumab in generalized myasthenia gravis. Muscle Nerve 2019, 60, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Viglietti, D.; Gosset, C.; Loupy, A.; Deville, L.; Verine, J.; Zeevi, A.; Glotz, D.; Lefaucheur, C. C1 Inhibitor in Acute Antibody-Mediated Rejection Nonresponsive to Conventional Therapy in Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Pilot Study. Am. J. Transplant. 2016, 16, 1596–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Montgomery, R.A.; Orandi, B.J.; Racusen, L.; Jackson, A.M.; Garonzik-Wang, J.M.; Shah, T.; Woodle, E.S.; Sommerer, C.; Fitts, D.; Rockich, K.; et al. Plasma-Derived C1 Esterase Inhibitor for Acute Antibody Mediated Rejection Following Kidney Transplantation: Results of a Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Pilot Study. Am. J. Transplant. 2016, 16, 3468–3478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stegall, M.; Diwan, T.; Raghavaiah, S.; Cornell, L.D.; Burns, J.; Dean, P.G.; Cosio, F.G.; Gandhi, M.J.; Kremers, W.; Gloor, J.M. Terminal Complement Inhibition Decreases Antibody-Mediated Rejection in Sensitized Renal Transplant Recipients. Am. J. Transplant. 2011, 11, 2405–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vo, A.A.; Zeevi, A.; Choi, J.; Cisneros, K.; Toyoda, M.; Kahwaji, J.; Peng, A.; Villicana, R.; Puliyanda, D.; Reinsmoen, N.; et al. A Phase I/II Placebo-Controlled Trial of C1-Inhibitor for Prevention of Antibody-Mediated Rejection in HLA Sensitized Patients. Transplantation 2015, 99, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, A.A.; Choi, J.; Kahwaji, J.; Puliyanda, D.; Peng, A.; Villicana, R.; Jordan, S. A194: Long-term analysis of a placebo-controlled trial of C1-INH for prevention of antibody-mediated rejection. In Proceedings of the 2015 American Transplant Congress, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 3–6 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Vo, A.A.; Choi, J.; Peng, A.; Lim, K.; Varanasi, L.; Najjar, R.; Huang, E.; Puliyanda, D.; Jordan, S. A50: Update of a placebo-controlled trial of C1 esterase inhibitor for prevention of antibody mediated rejection (ABMR) in highly-HLA sensitized patients. In Proceedings of the 2017 American Transplant Congress, Chicago, IL, USA, 29 April–3 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Marks, W.H.; Mamode, N.; Montgomery, R.A.; Stegall, M.D.; Ratner, L.E.; Cornell, L.D.; Rowshani, A.T.; Colvin, R.B.; Dain, B.; Boice, J.A.; et al. Safety and efficacy of eculizumab in the prevention of antibody-mediated rejection in living-donor kidney transplant recipients requiring desensitization therapy: A randomized trial. Am. J. Transplant. 2019, 19, 2876–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Glotz, D.; Russ, G.; Rostaing, L.; Legendre, C.; Tufveson, G.; Chadban, S.; Grinyó, J.; Mamode, N.; Rigotti, P.; Couzi, L.; et al. Safety and efficacy of eculizumab for the prevention of antibody-mediated rejection after deceased-donor kidney transplantation in patients with preformed donor-specific antibodies. Am. J. Transplant. 2019, 19, 2865–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaabak, M.M.; Babenko, N.; Shapiro, R.; Zokoyev, A.; Dymova, O.; Kim, E. A prospective randomized, controlled trial of eculizumab to prevent ischemia-reperfusion injury in pediatric kidney transplantation. Pediatr. Transplant. 2018, 22, e13129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, S.C.; Choi, J.; Aubert, O.; Haas, M.; Loupy, A.; Huang, E.; Peng, A.; Kim, I.; Louie, S.; Ammerman, N.; et al. A phase I/II, double-blind, placebo-controlled study assessing safety and efficacy of C1 esterase inhibitor for prevention of delayed graft function in deceased donor kidney transplant recipients. Am. J. Transplant. 2018, 18, 2955–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schröppel, B.; Akalin, E.; Baweja, M.; Bloom, R.D.; Florman, S.; Goldstein, M.; Haydel, B.; Hricik, D.E.; Kulkarni, S.; Levine, M.; et al. Peritransplant eculizumab does not prevent delayed graft function in deceased donor kidney transplant recipients: Results of two randomized controlled pilot trials. Am. J. Transplant. 2019, 20, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prevention of Delayed Graft Function Using Eculizumab Therapy (PROTECT Study). ClinicalTrials.gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02145182 (accessed on 29 April 2020).
- Kim, M.S.; Prasad, V. The Clinical Trials Portfolio for On-label and Off-label Studies of Eculizumab. JAMA Intern. Med. 2019, 180, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suarez, M.L.G.; Thongprayoon, C.; Mao, M.A.; Leeaphorn, N.; Bathini, T.; Cheungpasitporn, W. Outcomes of Kidney Transplant Patients with Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome Treated with Eculizumab: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moher, D.; Tetzlaff, J.; Tricco, A.C.; Sampson, M.; Altman, D.G. Epidemiology and Reporting Characteristics of Systematic Reviews. PLoS Med. 2007, 4, e78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Study of ALXN1210 in Children and Adolescents with Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome (aHUS). ClinicalTrials.gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03131219?term=NCT03131219&draw=2&rank=1 (accessed on 29 April 2020).
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sterne, J.A.; Gavaghan, D.; Egger, M. Publication and related bias in meta-analysis: Power of statistical tests and prevalence in the literature. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2000, 53, 1119–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, S.; Kirkiles-Smith, N.C.; Deng, Y.H.; Formica, R.N.; Moeckel, G.; Broecker, V.; Bow, L.; Tomlin, R.; Pober, J.S. Eculizumab Therapy for Chronic Antibody-Mediated Injury in Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial. Am. J. Transplant. 2016, 17, 682–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]









| Criteria | |
|---|---|
| Participants | Adult and pediatric individuals affected by or at higher risk of developing PNH attacks, aHUS, rgMG, aAMR episodes, or DGF. |
| Interventions | Commercial C5 inhibitors (e.g., eculizumab, ravulizumab) and C1-inhibitors (e.g., Berinert®, Cinryze®, Haegarda®, Ruconest®). |
| Comparisons | Placebo, pre-/off-treatment state, historical cohorts that did not receive the interventions, and any other therapeutic strategy (e.g., SOC) including active drugs when it was considered as comparators in the eligible studies. |
| Type of study | RCT including their extension follow-up studies/post-hoc analyses, in addition to historically controlled interventional studies and other non-randomized (single arm) clinical trials. |
| Real-life NRSI (e.g., registry studies and other real-world data studies). |
| Clinical Trials | Real-Life NRSI | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C5 Inhibition | C1 Inhibition | Controls | C5 Inhibition | C1 Inhibition | Controls | |
| PNH | 665 | - | 86 | 1338 | - | 2851 |
| aHUS | 137 | - | 185 | 463 | - | 627 |
| rgMG | 69 | - | 70 | - | - | - |
| aAMR | 186 | 60 | 285 | - | - | - |
| DGF | 187 | 45 | 230 | - | - | - |
| Total | 1244 | 105 | 856 | 1801 | - | 3478 |
| Drug Intervention † C5 Inhibitors | SUCRA ‡ Outcomes: A/B/C § |
|---|---|
| Eculizumab | 0.637/0.642/0.797 |
| Ravulizumab | 0.860/0.850/0.700 |
| Pre-treatment/off-treatment states or placebo | 0.002/0.007/0.003 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bernuy-Guevara, C.; Chehade, H.; Muller, Y.D.; Vionnet, J.; Cachat, F.; Guzzo, G.; Ochoa-Sangrador, C.; Álvarez, F.J.; Teta, D.; Martín-García, D.; et al. The Inhibition of Complement System in Formal and Emerging Indications: Results from Parallel One-Stage Pairwise and Network Meta-Analyses of Clinical Trials and Real-Life Data Studies. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8090355
Bernuy-Guevara C, Chehade H, Muller YD, Vionnet J, Cachat F, Guzzo G, Ochoa-Sangrador C, Álvarez FJ, Teta D, Martín-García D, et al. The Inhibition of Complement System in Formal and Emerging Indications: Results from Parallel One-Stage Pairwise and Network Meta-Analyses of Clinical Trials and Real-Life Data Studies. Biomedicines. 2020; 8(9):355. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8090355
Chicago/Turabian StyleBernuy-Guevara, Coralina, Hassib Chehade, Yannick D. Muller, Julien Vionnet, François Cachat, Gabriella Guzzo, Carlos Ochoa-Sangrador, F. Javier Álvarez, Daniel Teta, Débora Martín-García, and et al. 2020. "The Inhibition of Complement System in Formal and Emerging Indications: Results from Parallel One-Stage Pairwise and Network Meta-Analyses of Clinical Trials and Real-Life Data Studies" Biomedicines 8, no. 9: 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8090355
APA StyleBernuy-Guevara, C., Chehade, H., Muller, Y. D., Vionnet, J., Cachat, F., Guzzo, G., Ochoa-Sangrador, C., Álvarez, F. J., Teta, D., Martín-García, D., Adler, M., de Paz, F. J., Lizaraso-Soto, F., Pascual, M., & Herrera-Gómez, F. (2020). The Inhibition of Complement System in Formal and Emerging Indications: Results from Parallel One-Stage Pairwise and Network Meta-Analyses of Clinical Trials and Real-Life Data Studies. Biomedicines, 8(9), 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8090355