Exosomal let-7e, miR-21-5p, miR-145, miR-146a and miR-155 in Predicting Antidepressants Response in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Treatment
2.3. Serum Exosomes Isolation
2.4. Exosomal RNA Extraction
2.4.1. Quantitative Reverse-Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
2.4.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographics
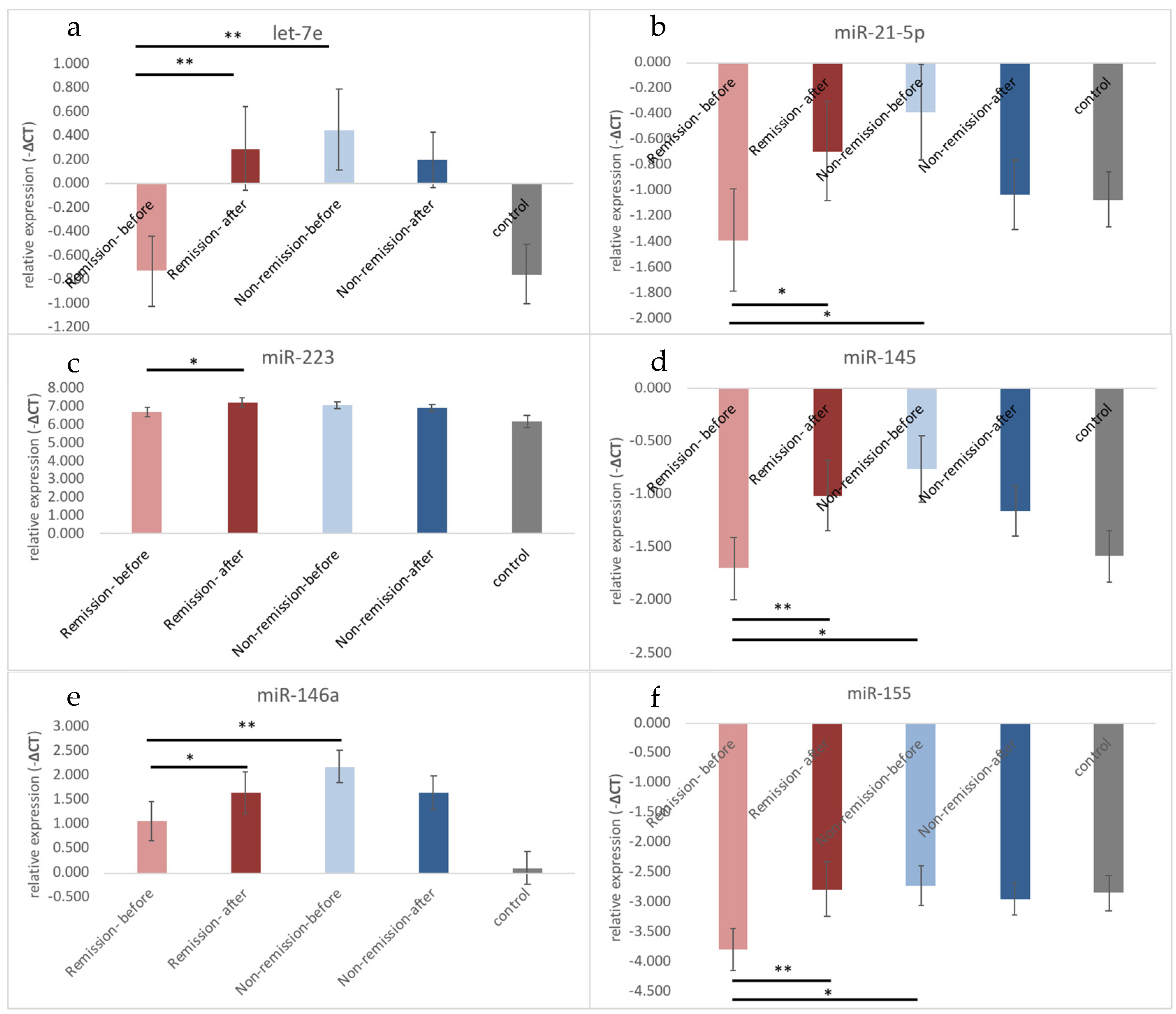
3.2. Different Expression Profiles of Exosomal microRNA between Remission and Non-Remission
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Labermaier, C.; Masana, M.; Muller, M.B. Biomarkers predicting antidepressant treatment response: How can we advance the field? Dis. Markers 2013, 35, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fleshner, M.; Frank, M.; Maier, S.F. Danger Signals and Inflammasomes: Stress-Evoked Sterile Inflammation in Mood Disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology 2017, 42, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, G.N.; Rizavi, H.S.; Bhaumik, R.; Ren, X. Innate immunity in the postmortem brain of depressed and suicide subjects: Role of Toll-like receptors. Brain Behav. Immun. 2019, 75, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, Y.Y.; Kang, H.Y.; Huang, K.W.; Huang, T.L. Association between toll-like receptors expression and major depressive disorder. Psychiatry Res. 2014, 220, 283–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, Y.Y.; Lin, C.C.; Kang, H.Y.; Huang, T.L. TNFAIP3, a negative regulator of the TLR signaling pathway, is a potential predictive biomarker of response to antidepressant treatment in major depressive disorder. Brain Behav. Immun. 2017, 59, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hung, Y.Y.; Wu, M.K.; Tsai, M.C.; Huang, Y.L.; Kang, H.Y. Aberrant Expression of Intracellular let-7e, miR-146a, and miR-155 Correlates with Severity of Depression in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder and Is Ameliorated after Antidepressant Treatment. Cells 2019, 8, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsilioni, I.; Panagiotidou, S.; Theoharides, T.C. Exosomes in neurologic and psychiatric disorders. Clin. Ther. 2014, 36, 882–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Dinkins, M.; He, Q.; Zhu, G.; Poirier, C.; Campbell, A.; Mayer-Proschel, M.; Bieberich, E. Astrocytes secrete exosomes enriched with proapoptotic ceramide and prostate apoptosis response 4 (PAR-4): Potential mechanism of apoptosis induction in Alzheimer disease (AD). J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 21384–21395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, C.; Gao, T.; Zhao, L.; Zhu, S.; Guo, L. Plasma exosomes from depression ameliorate inflammation-induced depressive-like behaviors via sigma-1 receptor delivery. Brain Behav. Immun. 2021, 94, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, K.; Xu, J.X.; Chen, X.X.; Gao, X.R.; Huang, L.L.; Du, A.Q.; Jiang, C.; Ge, J.F. Differential serum exosome microRNA profile in a stress-induced depression rat model. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 274, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, M.; Hu, R.; Runtsch, M.C.; Kagele, D.A.; Mosbruger, T.L.; Tolmachova, T.; Seabra, M.C.; Round, J.L.; Ward, D.M.; O’Connell, R.M. Exosome-delivered microRNAs modulate the inflammatory response to endotoxin. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.; Zong, S.; Wang, Z.; Lu, J.; Zhu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Cui, Y. Visualization and intracellular dynamic tracking of exosomes and exosomal miRNAs using single molecule localization microscopy. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 5154–5162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Wu, J.; Liu, K.; Zhou, J.; Liu, L.; Zhang, C. Identification of differential microRNAs in cerebrospinal fluid and serum of patients with major depressive disorder. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.K.; Tyryshkin, K.; Elmi, N.; Dharsee, M.; Evans, K.R.; Good, J.; Javadi, M.; McCormack, S.; Vaccarino, A.L.; Zhang, X.; et al. Plasma microRNA expression levels and their targeted pathways in patients with major depressive disorder who are responsive to duloxetine treatment. J. Psychiatr Res. 2019, 110, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, J.; Pan, J.Y.; Liao, N.; Shi, J.; Zeng, Q.; Huang, L.; Chen, L.P. Influence of miR-155 on behaviors of depression mice through regulating Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Eur Rev. Med. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 24, 1398–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, J.P.; Fiori, L.M.; Cruceanu, C.; Lin, R.; Labonte, B.; Cates, H.M.; Heller, E.A.; Vialou, V.; Ku, S.M.; Gerald, C.; et al. MicroRNAs 146a/b-5 and 425-3p and 24-3p are markers of antidepressant response and regulate MAPK/Wnt-system genes. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Li, S.; Li, L.; Li, M.; Guo, C.; Yao, J.; Mi, S. Exosome and exosomal microRNA: Trafficking, sorting, and function. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2015, 13, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, Y.; Dou, H.; Li, X.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, D.; Ji, J.; Liu, F.; Ding, L.; Ni, Y.; et al. Exosomal miR-146a Contributes to the Enhanced Therapeutic Efficacy of Interleukin-1beta-Primed Mesenchymal Stem Cells Against Sepsis. Stem Cells 2017, 35, 1208–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Androulidaki, A.; Iliopoulos, D.; Arranz, A.; Doxaki, C.; Schworer, S.; Zacharioudaki, V.; Margioris, A.N.; Tsichlis, P.N.; Tsatsanis, C. The kinase Akt1 controls macrophage response to lipopolysaccharide by regulating microRNAs. Immunity 2009, 31, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mahesh, G.; Biswas, R. MicroRNA-155: A Master Regulator of Inflammation. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2019, 39, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, J.P.; Lim, R.; Cruceanu, C.; Crapper, L.; Fasano, C.; Labonte, B.; Maussion, G.; Yang, J.P.; Yerko, V.; Vigneault, E.; et al. miR-1202 is a primate-specific and brain-enriched microRNA involved in major depression and antidepressant treatment. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 764–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bocchio-Chiavetto, L.; Maffioletti, E.; Bettinsoli, P.; Giovannini, C.; Bignotti, S.; Tardito, D.; Corrada, D.; Milanesi, L.; Gennarelli, M. Blood microRNA changes in depressed patients during antidepressant treatment. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013, 23, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, W.H.; Dong, Z.Q.; Tian, L.T.; Li, J. MicroRNA-451a, microRNA-34a-5p, and microRNA-221-3p as predictors of response to antidepressant treatment. Braz J. Med. Biol Res. 2018, 51, e7212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liang, J.Q.; Liao, H.R.; Xu, C.X.; Li, X.L.; Wei, Z.X.; Xie, G.J.; Cheng, Y. Serum Exosome-Derived miR-139-5p as a Potential Biomarker for Major Depressive Disorder. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2020, 16, 2689–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Assay ID | Assay Name | Mature microRNA Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| 002406 | hsa-let-7e | UGAGGUAGGAGGUUGUAUAGUU |
| 000397 | hsa-miR-21-5P | UGAGGUAGUAGGUUGUAUGGUU |
| 002198 | hsa-miR-125a-5p | UCCCUGAGACCCUUUAACCUGUGA |
| 002278 | hsa-miR-145 | GUCCAGUUUUCCCAGGAAUCCCU |
| 000468 | hsa-miR-146a | UGAGAACUGAAUUCCAUGGGUU |
| 002623 | hsa-miR-155 | UUAAUGCUAAUCGUGAUAGGGGU |
| 002285 | hsa-miR-186 | CAAAGAAUUCUCCUUUUGGGCU |
| 002295 | hsa-miR-223 | UGUCAGUUUGUCAAAUACCCCA |
| 001973 | U6 snRNA | GTGCTCGCTTCGGCAGCACATATACTAAAATTGGAACGATACAGAGAAGATTAGCATGGCCCCTGCGCAAGGATGACACGCAAATTCGTGAAGCGTTCCATATTTT |
| Depression before Treatment (n = 52) | Health Control (n = 31) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 42.52 ± 13.51 | 39.06 ± 7.95 | 0.199 |
| Sex (M/F) | 18/34 | 9/22 | 0.637 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 24.57 ± 4.56 | 23.24 ± 2.61 | 0.142 |
| Smoking (yes/no) | 20/32 | 2/29 | 0.002 ** |
| HAMD before treatment | 23.35 ± 4.76 | - | - |
| HAMD after treatment | 7.53 ± 4.27 | - | - |
| I | II | III | I vs III | I vs II | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Depression before treatment n = 52 | Depression after treatment n = 39 | Health control n = 31 | p-value | p-value | |
| let-7e | −0.243 ± 1.466 | 0.258 ± 1.268 | −0.752 ± 1.351 | 0.443 | 0.044 * |
| Remission | −0.727 ± 1.160 | 0.295 ± 1.390 | 0.900 | 0.002 §§ | |
| Non-remission | 0.452 ± 1.611 | 0.205 ± 1.112 | 0.009 ¶,¶ | 0.278 | |
| miR-21-5p | −0.977 ± 1.730 | −0.823 ± 1.459 | −1.07 ± 1.18 | 0.605 | 0.581 |
| Remission | −1.390 ± 1.594 | −0.690 ± 1.571 | 0.396 | 0.036 § | |
| Non-remission | −0.384 ± 1.794 | −1.036 ± 1.302 | 0.122 | 0.098 | |
| miR-223 | 6.86 ± 1.019 | 7.140 ± 0.964 | 6.19 ± 1.68 | 0.127 | 0.102 |
| Remission | 6.704 ± 1.081 | 7.254 ± 1.025 | 0.416 | 0.014 § | |
| Non-remission | 7.084 ± 0.910 | 6.976 ± 0.874 | 0.007 ¶,¶ | 0.278 | |
| miR-145 | −1.316 ± 1.394 | −1.068 ± 1.230 | −1.58 ± 1.32 | 0.765 | 0.274 |
| Remission | −1.700 ± 1.190 | −1.009 ± 1.308 | 0.693 | 0.003 §§ | |
| Non-remission | −0.763 ± 1.514 | −1.154 ± 1.145 | 0.149 | 0.179 | |
| miR-146a | 1.515 ± 1.685 | 1.639 ± 1.681 | 0.10 ± 1.83 | 0.007 * | 0.592 |
| Remission | 1.051 ± 1.627 | 1.642 ± 1.756 | 0.062 | 0.048 § | |
| Non-remission | 2.181 ± 1.583 | 1.635 ± 1.624 | 0.000 ¶¶ | 0.079 | |
| miR-155 | −3.353 ± 1.554 | −2.849 ± 1.627 | −2.85 ± 1.67 | 0.126 | 0.048 * |
| Remission | −3.794 ± 1.408 | −2.780 ± 1.840 | 0.081 | 0.004 §§ | |
| Non-remission | −2.719 ± 1.576 | −2.949 ± 1.311 | 0.995 | 0.408 |
| Remission (n = 16) | Non-Remission (n = 23) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| let-7e | −0.727 ± 1.160 | 0.452 ± 1.611 | 0.001 ** |
| miR-21-5p | −1.390 ± 1.594 | −0.384 ± 1.794 | 0.038 * |
| miR-125a | −4.706 ± 1.411 | −3.545 ± 1.493 | 0.018 * |
| miR-223 | 6.704 ± 1.081 | 7.084 ± 0.910 | 0.093 |
| miR-145 | −1.700 ± 1.190 | −0.763 ± 1.514 | 0.018 * |
| miR-146a | 1.051 ± 1.627 | 2.181 ± 1.583 | 0.004 ** |
| miR-155 | −3.794 ± 1.408 | −2.719 ± 1.576 | 0.042 * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hung, Y.-Y.; Chou, C.-K.; Yang, Y.-C.; Fu, H.-C.; Loh, E.-W.; Kang, H.-Y. Exosomal let-7e, miR-21-5p, miR-145, miR-146a and miR-155 in Predicting Antidepressants Response in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1428. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9101428
Hung Y-Y, Chou C-K, Yang Y-C, Fu H-C, Loh E-W, Kang H-Y. Exosomal let-7e, miR-21-5p, miR-145, miR-146a and miR-155 in Predicting Antidepressants Response in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder. Biomedicines. 2021; 9(10):1428. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9101428
Chicago/Turabian StyleHung, Yi-Yung, Chen-Kai Chou, Yi-Chien Yang, Hung-Chun Fu, El-Wui Loh, and Hong-Yo Kang. 2021. "Exosomal let-7e, miR-21-5p, miR-145, miR-146a and miR-155 in Predicting Antidepressants Response in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder" Biomedicines 9, no. 10: 1428. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9101428
APA StyleHung, Y.-Y., Chou, C.-K., Yang, Y.-C., Fu, H.-C., Loh, E.-W., & Kang, H.-Y. (2021). Exosomal let-7e, miR-21-5p, miR-145, miR-146a and miR-155 in Predicting Antidepressants Response in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder. Biomedicines, 9(10), 1428. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9101428







