In Silico Drug Repurposing by Structural Alteration after Induced Fit: Discovery of a Candidate Agent for Recovery of Nucleotide Excision Repair in Xeroderma Pigmentosum Group D Mutant (R683W)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Preparation of Compounds for DR and Construction of the 3D Structure of XPD R683W
2.2. Docking Analysis of Compounds with XPD R683W and Optimizing the Structures of the Complexes
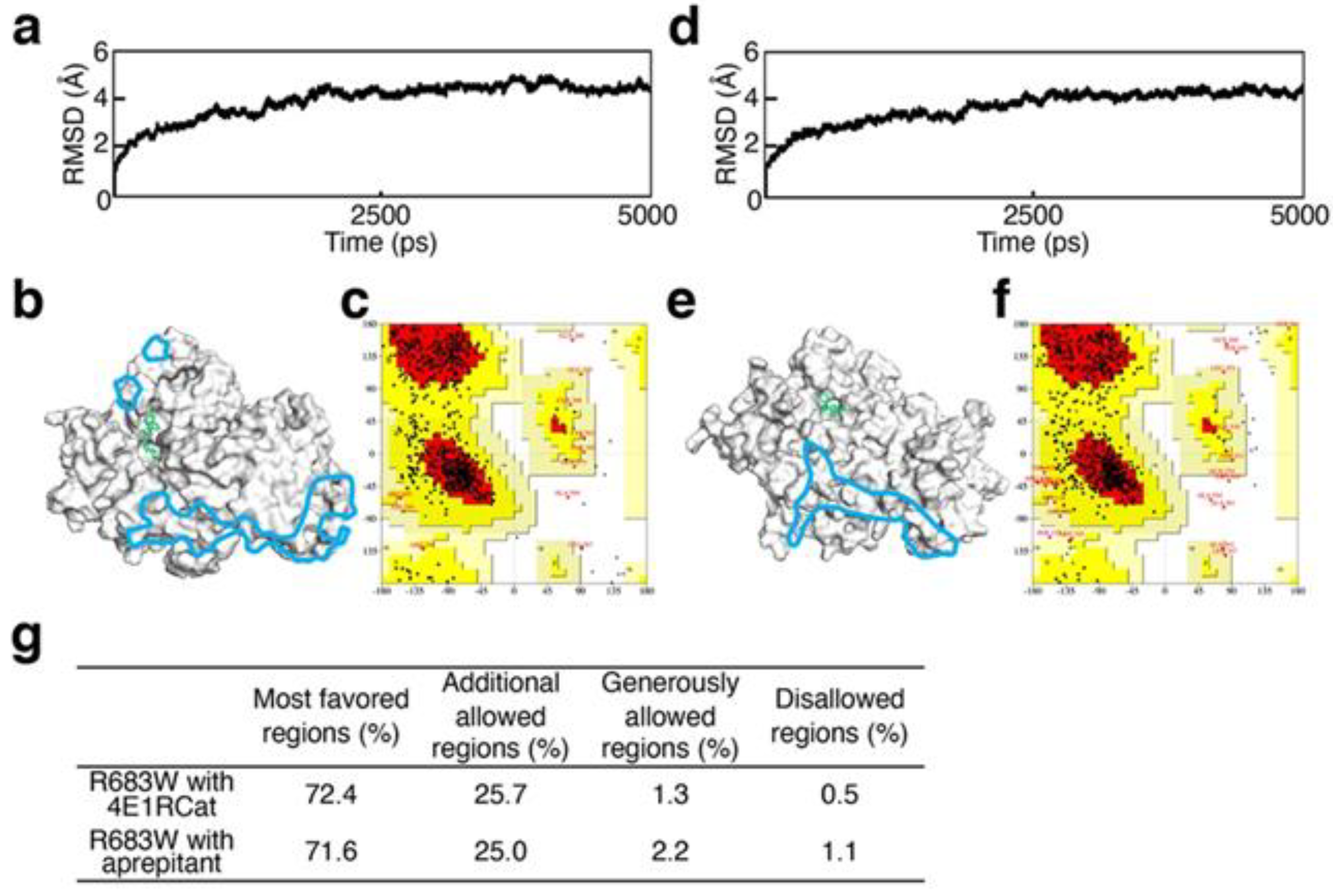
2.3. Validation of Structural Optimization
2.4. Evaluation of the Recovery of ATP-Binding Activity
2.5. Evaluation of the Agents In Vitro: UV-Induced UDS Measurement in Primery Human Fibroblasts by Using EdU Incorporation
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Validation of Structural Optimization
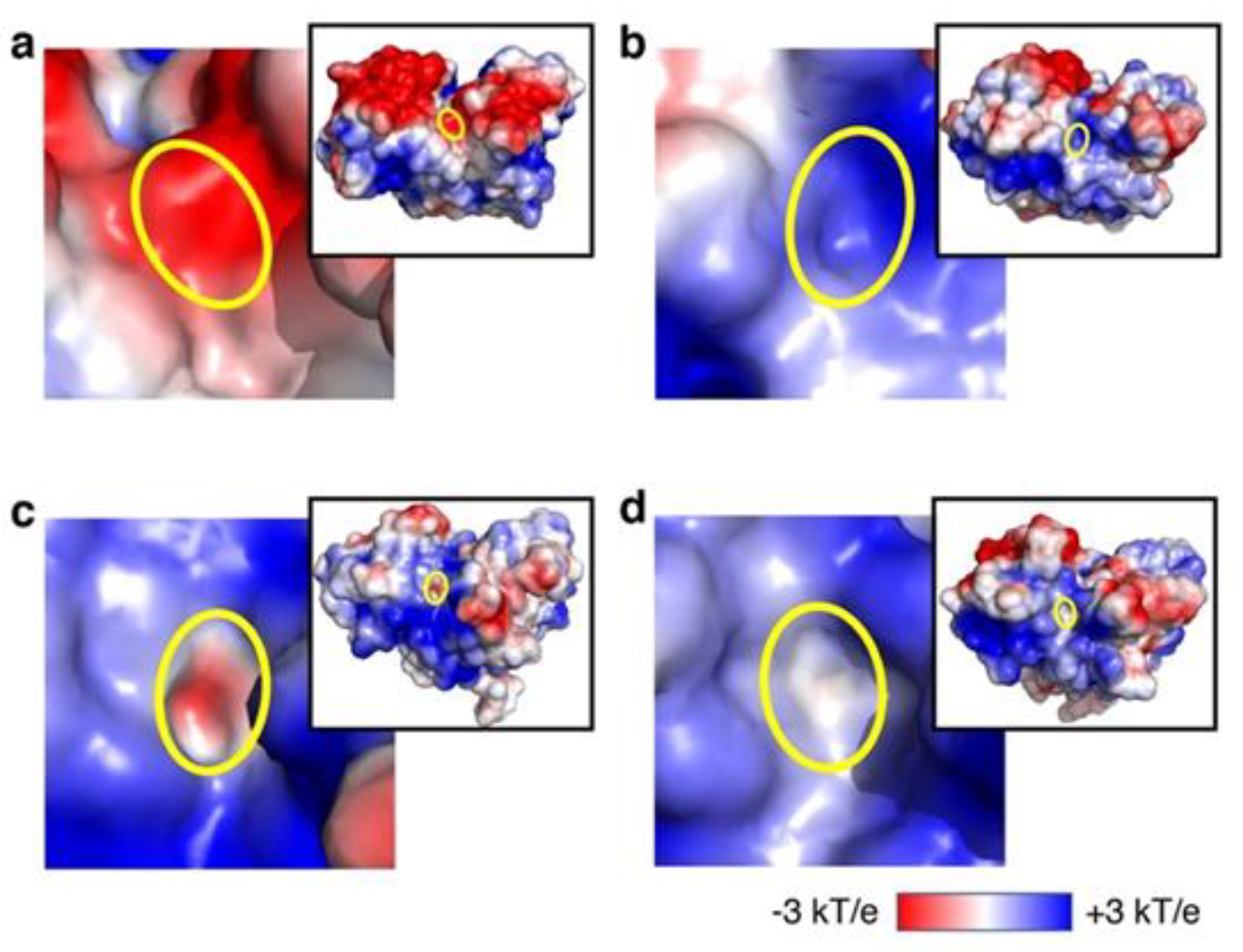
3.2. Analysis of Recovery of ATP-Binding Activity In Silico
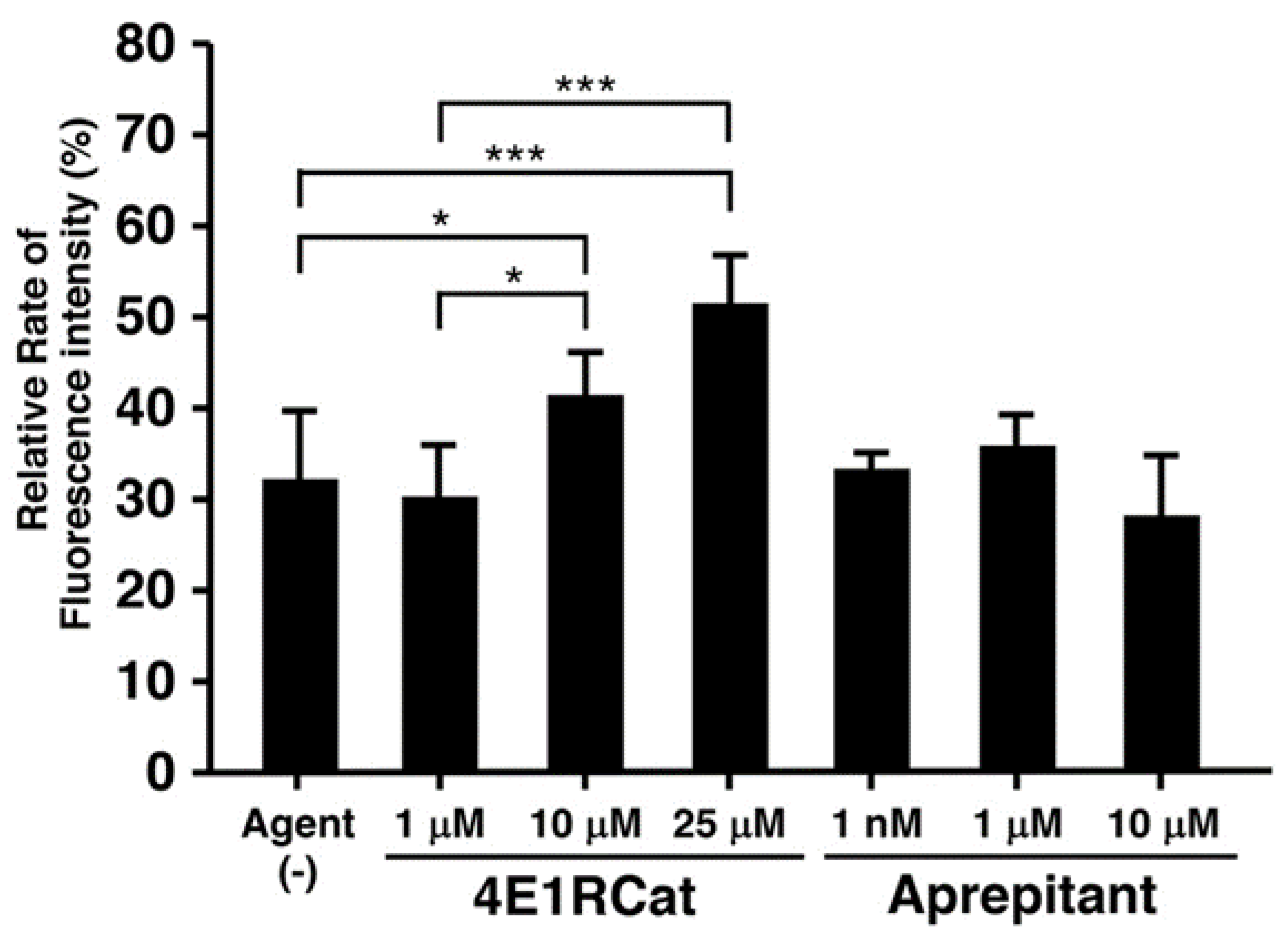
3.3. Effect of Candidate Agents on NER Recovery as Determined via the EdU-Based UDS Assay
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Itoh, T.; Fujiwara, Y.; Yamaizumi, M. UVs syndrome, a new general category of photosensitive disorder with defective DNA repair, is distinct from xeroderma pigmentosum variant and rodent complementation group I. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1995, 56, 1267–1276. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nishigori, C.; Nakano, E.; Masaki, T.; Ono, R.; Takeuchi, S.; Tsujimoto, M.; Ueda, T. Characteristics of xeroderma pigmentosum in Japan: Lessons from two clinical surveys and measures for patient care. Photochem. Photobiol. 2019, 95, 140–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bradford, P.T.; Goldstein, A.M.; Tamura, D.; Khan, S.G.; Ueda, T.; Boyle, J.; Oh, K.S.; Imoto, K.; Inui, H.; Moriwaki, S.; et al. Cancer and neurologic degeneration in xeroderma pigmentosum: Long term follow-up characterises the role of DNA repair. J. Med. Genet. 2011, 48, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraemer, K.H.; Lee, M.M.; Scotto, J. Xeroderma pigmentosum. Cutaneous, ocular, and neurologic abnormalities in 830 published cases. Arch. Dermatol. 1987, 123, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fassihi, H.; Sethi, M.; Fawcett, H.; Wing, J.; Chandler, N.; Mohammed, S.; Craythorne, E.; Morley, A.M.; Lim, R.; Turner, S.; et al. Deep phenotyping of 89 xeroderma pigmentosum patients reveals unexpected heterogeneity dependent on the precise molecular defect. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E1236–E1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moriwaki, S.; Kraemer, K.H. Xeroderma pigmentosum-bridging a gap between clinic and laboratory. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 2001, 17, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takayama, K.; Salazar, E.P.; Lehmann, A.; Stefanini, M.; Thompson, L.H.; Weber, C.A. Defects in the DNA repair and transcription gene ERCC2 in the cancer-prone disorder xeroderma pigmentosum group D. Cancer Res. 1995, 55, 5656–5663. [Google Scholar]
- Houten, B.V.; Kuper, J.; Kisker, C. Role of XPD in cellular functions: To TFIIH and beyond. DNA Repair Amst. 2016, 44, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, E.; Ono, R.; Masaki, T.; Takeuchi, S.; Takaoka, Y.; Maeda, E.; Nishigori, C. Differences in clinical phenotype among patients with XP complementation group D: 3D structure and ATP-docking of XPD in silico. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 1775–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hartenfeller, M.; Schneider, G. De novo drug design. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 672, 299–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashburn, T.T.; Thor, K.B. Drug repositioning: Identifying and developing new uses for existing drugs. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 673–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaoka, Y.; Sugano, A.; Miura, K.; Nakano, E.; Ohta, M.; Nishigori, C. In silico drug repositioning for treatment of xeroderma pigmentosum group D. HPCI Res. Rep. 2018, 3, 39–45. [Google Scholar]
- Limsirichaikul, S.; Niimi, A.; Fawcett, H.; Lehmann, A.; Yamashita, S.; Ogi, T. A rapid non-radioactive technique for measurement of repair synthesis in primary human fibroblasts by incorporation of ethynyl deoxyuridine (EdU). Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PyMOL by Schrödinger. Available online: https://pymol.org/2/ (accessed on 16 November 2017).
- Abraham, M.J.; Murtola, T.; Schulz, R.; Pll, S.; Smith, J.C.; Hess, B.; Lindahl, E. GROMACS: High performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. SoftwareX 2015, 1, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jorgensen, W.; Chandrasekhar, J.; Madura, J.; Impey, R.; Klein, M. Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water. J. Chem. Phys. 1983, 79, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendsen, H.J.C.; Postma, J.P.M.; Gunsteren, W.F.; DiNola, A.; Haak, J.R. Molecular dynamics with coupling to an external bath. J. Chem. Phys. 1984, 81, 3684–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hess, B.; Bekker, H.; Berendsen, H.J.C.; Fraaije, J.G.E.M. LINCS: A linear constraint solver for molecular simulations. J. Comput. Chem. 1997, 18, 1463–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskowski, R.A.; MacArthur, M.W.; Moss, D.S.; Thornton, J.M. PROCHECK: A program to check the stereochemical quality of protein structures. J. Appl. Cryst. 1993, 26, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuss, J.O.; Tainer, J.A. XPB and XPD helicases in TFIIH orchestrate DNA duplex opening and damage verification to coordinate repair with transcription and cell cycle via CAK kinase. DNA Repair Amst. 2011, 10, 697–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogasawara, M.; Nakamura, Y.; Morikawa, N.; Nitanai, H.; Moriguchi, S.; Chiba, R.; Saito, H.; Ohta, M.; Tanita, T.; Sugai, T.; et al. Analysis of a single-codon E746 deletion in exon 19 of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2016, 77, 1019–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, N.A.; Sept, D.; Joseph, S.; Holst, M.J.; McCammon, J.A. Electrostatics of nanosystems: Application to microtubules and the ribosome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 10037–10041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cencic, R.; Hall, D.R.; Robert, F.; Du, Y.; Min, J.; Li, L.; Qui, M.; Lewis, I.; Kurtkaya, S.; Dingledine, R.; et al. Reversing chemoresistance by small molecule inhibition of the translation initiation complex eIF4F. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 1046–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamaguchi, R.; Yamamoto, T.; Sakamoto, A.; Ishimaru, Y.; Narahara, S.; Sugiuchi, H.; Yamaguchi, Y. Substance P enhances tissue factor release from granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor-dependent macrophages via the p22phox/β-arrestin 2/Rho A signaling pathway. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2016, 57, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz, M.; Rosso, M. The NK-1 receptor antagonist aprepitant as a broad spectrum antitumor drug. Investig. New Drugs 2010, 28, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakazawa, Y.; Sasaki, K.; Mitsutake, N.; Matsusel, M.; Shimada, M.; Nardo, T.; Takahashi, Y.; Ohyama, K.; Ito, K.; Mishima, H.; et al. Mutations in UVSSA cause UV-sensitive syndrome and impair RNA polymerase IIo processing in transcription-coupled nucleotide-excision repair. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 586–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Itoh, T.; Ono, T.; Yamaizumi, M. A simple method for diagnosing xeroderma pigmentosum variant. J. Investig. Derm. 1996, 107, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, S.; Tyagi, C.; Grover, A.; Goswami, S.K. Molecular modeling and molecular dynamics simulations based structural analysis of the SG2NA protein variants. BMC Res. Notes 2014, 7, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, G.; Hu, M.; Li, C.; Lee, J.; Yuan, K.; Zhu, G.; Che, C. Osteopontin contributes to effective neutrophil recruitment, IL-1β production and apoptosis in Aspergillus fumigatus keratitis. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2018, 96, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Liu, C.; Hu, X.; Shang, Y.; Wu, L. MicroRNA-21: A positive regulator for optimal production of type I and type III interferon by plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cencic, R.; Desforges, M.; Hall, D.R.; Kozakov, D.; Du, Y.; Min, J.; Dingledine, R.; Fu, H.; Vajda, S.; Talbot, P.J.; et al. Blocking eIF4E-eIF4G interaction as a strategy to impair coronavirus replication. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 6381–6389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jeeva, S.; Cheng, E.; Ganaie, S.S.; Mir, M.A. Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus nucleocapsid protein augments mRNA translation. J. Virol. 2017, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kolupaeva, V.; Katsara, O.; Attur, M. Translational control maintains cartilage homeostasis and regulates osteoarthritis progression. In Proceedings of the OARSI World Congress on Osteoarthritis: Promoting Clinical and Basic Research in Osteoarthritis, Toronto, ON, Canada, 2–5 May 2019; p. S187. [Google Scholar]


| Candidate Agents Tested with R683W | Correct Binding of ATP (per 10 Runs) | ATP in the Binding Region (per 100 Runs) | Docing Scores of XPD R683W and Agents | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Docking Score | n | Docking Score | ||
| Wild-type (no agent) | 6 | −5.59 ± 0.35 | 1 | −4.08 | NA |
| 4E1RCat | 8 | −6.26 ± 0.72 | 2 | −6.22 ± 0.49 | −6.80 ± 2.17 |
| Aprepitant | 4 | −5.16 ± 0.70 | 1 | −6.18 | −6.35 ± 0.86 |
| ABT-737 | 4 | −6.44 ± 0.56 | 0 | NA | −8.36 ± 1.39 |
| Bromosporine | 3 | −5.87 ± 0.55 | 1 | 4.82 | −6.43 ± 1.55 |
| 17-AAG | 3 | −4.96 ± 3.07 | 0 | NA | −6.42 ± 1.10 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Takaoka, Y.; Ohta, M.; Tateishi, S.; Sugano, A.; Nakano, E.; Miura, K.; Suzuki, T.; Nishigori, C. In Silico Drug Repurposing by Structural Alteration after Induced Fit: Discovery of a Candidate Agent for Recovery of Nucleotide Excision Repair in Xeroderma Pigmentosum Group D Mutant (R683W). Biomedicines 2021, 9, 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9030249
Takaoka Y, Ohta M, Tateishi S, Sugano A, Nakano E, Miura K, Suzuki T, Nishigori C. In Silico Drug Repurposing by Structural Alteration after Induced Fit: Discovery of a Candidate Agent for Recovery of Nucleotide Excision Repair in Xeroderma Pigmentosum Group D Mutant (R683W). Biomedicines. 2021; 9(3):249. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9030249
Chicago/Turabian StyleTakaoka, Yutaka, Mika Ohta, Satoshi Tateishi, Aki Sugano, Eiji Nakano, Kenji Miura, Takashi Suzuki, and Chikako Nishigori. 2021. "In Silico Drug Repurposing by Structural Alteration after Induced Fit: Discovery of a Candidate Agent for Recovery of Nucleotide Excision Repair in Xeroderma Pigmentosum Group D Mutant (R683W)" Biomedicines 9, no. 3: 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9030249
APA StyleTakaoka, Y., Ohta, M., Tateishi, S., Sugano, A., Nakano, E., Miura, K., Suzuki, T., & Nishigori, C. (2021). In Silico Drug Repurposing by Structural Alteration after Induced Fit: Discovery of a Candidate Agent for Recovery of Nucleotide Excision Repair in Xeroderma Pigmentosum Group D Mutant (R683W). Biomedicines, 9(3), 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9030249






