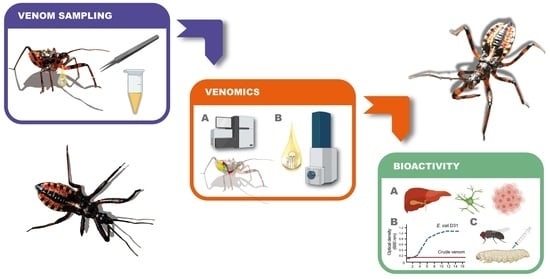
Hexapod Assassins’ Potion: Venom Composition and Bioactivity from the Eurasian Assassin Bug Rhynocoris iracundus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Assassin Bug Collection, Rearing, and Venom Collection
2.2. Cell Lines and Cell Viability Assay
2.3. Antibacterial Assay
2.4. Injection of Venom in Galleria Mellonella
2.5. Venom Gland Transcriptome Analysis
2.5.1. RNA Isolation, Library Preparation and Illumina Sequencing
2.5.2. Transcriptome Assembly, Annotation, and Venom Protein Prediction
2.6. Venom Proteome Analysis
2.6.1. SDS-PAGE, Protein Digestion and LC–MS Analysis of R. iracundus Venom
2.6.2. Data Processing and Protein Identification
2.7. Protein Sequence Alignment
2.8. Phylogenetic Tree
3. Results
3.1. Venom Activity Against Mouse Cancer Cells and Healthy Mouse Cells
3.2. Venom Activity Against Bacteria
3.3. Venom Activity Against Insect Cells and G. mellonella Pupae and Larvae
3.4. Molecular Components of the Venom
3.4.1. Overview of R. iracundus Venom-Gland Transcriptome
3.4.2. Venom Proteome of the Assassin Bug R. iracundus
3.5. Selected Toxins with Potential Cytotoxic and Antibacterial Activities
3.5.1. Redulysins
3.5.2. Kininogens
3.5.3. Chitinases
3.5.4. Hemolysins
3.5.5. Ptu1 Family Peptides
4. Discussion
4.1. Primary Functions of Reduviid Venom: Capturing and Feeding on Arthropod Prey
4.2. Versatility of Assassin Bug Venom towards Defense Purposes
4.3. Keeping the Glands Clean: The Antibacterial Activity of Assassin Bug Venom
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schendel, V.; Rash, L.D.; Jenner, R.A.; Undheim, E.A.B. The Diversity of Venom: The Importance of Behavior and Venom System Morphology in Understanding Its Ecology and Evolution. Toxins 2019, 11, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y. Why Do We Study Animal Toxins? Zool. Res. 2015, 36, 183–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, S.L.; Rowan, E.G.; Albericio, F.; Stábeli, R.G.; Calderon, L.A.; Soares, A.M. Animal Toxins and Their Advantages in Biotechnology and Pharmacology. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 951561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McDermott, A. News Feature: Venom Back in Vogue as a Wellspring for Drug Candidates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 10100–10104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McGivern, J.G. Ziconotide: A Review of Its Pharmacology and Use in the Treatment of Pain. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2007, 3, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, Y.; Wei, L.; Ma, L.; Huang, X.; Tao, A.; Liu, Z.; Yuan, W. Long-Acting Preparations of Exenatide. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2013, 7, 963–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosendorff, C. Captopril—An Overview. South Afr. Med. J. Suid-Afr. Tydskr. Vir Geneeskd. 1982, 62, 593–599. [Google Scholar]
- Waheed, H.; Moin, S.F.; Choudhary, M.I. Snake Venom: From Deadly Toxins to Life-Saving Therapeutics. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 24, 1874–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, Y.; Wu, C.; Ling, E.-A. Animal Venom Peptides as a Treasure Trove for New Therapeutics Against Neurodegenerative Disorders. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 4749–4774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderon, L.A.; Sobrinho, J.C.; Zaqueo, K.D.; de Moura, A.A.; Grabner, A.N.; Mazzi, M.V.; Marcussi, S.; Nomizo, A.; Fernandes, C.F.C.; Zuliani, J.P.; et al. Antitumoral Activity of Snake Venom Proteins: New Trends in Cancer Therapy. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 203639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arruda Macêdo, J.K.; Fox, J.W.; de Souza Castro, M. Disintegrins from Snake Venoms and Their Applications in Cancer Research and Therapy. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2015, 16, 532–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Windley, M.J.; Herzig, V.; Dziemborowicz, S.A.; Hardy, M.C.; King, G.F.; Nicholson, G.M. Spider-Venom Peptides as Bioinsecticides. Toxins 2012, 4, 191–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Juichi, H.; Miyashita, M.; Nakagawa, Y.; Miyagawa, H. Isolation and Characterization of the Insecticidal, Two-Domain Toxin LaIT3 from the Liocheles Australasiae Scorpion Venom. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2019, 83, 2183–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escoubas, P.; King, G.F. Venomics as a Drug Discovery Platform. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2009, 6, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennington, M.W.; Czerwinski, A.; Norton, R.S. Peptide Therapeutics from Venom: Current Status and Potential. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 2738–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahayaraj, K.; Muthukumar, S. Zootoxic Effects of Reduviid Rhynocoris Marginatus (Fab.) (Hemiptera: Reduviidae) Venomous Saliva on Spodoptera Litura (Fab.). Toxicon 2011, 58, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weirauch, C.; Schuh, R.T. Systematics and Evolution of Heteroptera: 25 Years of Progress. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2011, 56, 487–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuh, R.T.; Slater, J.A. True Bugs of the World (Hemiptera:Heteroptera): Classification and Natural History; Cornell University Press: Ithaca, NY, USA, 1995; ISBN 9780801420665. [Google Scholar]
- Dan, A.; Pereira, M.H.; Pesquero, J.L.; Diotaiuti, L.; Beirão, P.S. Action of the Saliva of Triatoma Infestans (Heteroptera: Reduviidae) on Sodium Channels. J. Med. Entomol. 1999, 36, 875–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, R.; Soares, A.C.; Alves, C.L.; Lorosa, E.S.; Pereira, M.H.; Diotaiuti, L. Feeding Behavior of Triatoma Vitticeps (Reduviidae: Triatominae) in the State of Minas Gerais, Brazil. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2011, 106, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santos, H.P.; Rost-Roszkowska, M.; Vilimova, J.; Serrão, J.E. Ultrastructure of the Midgut in Heteroptera (Hemiptera) with Different Feeding Habits. Protoplasma 2017, 254, 1743–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Dai, W. Fine Morphology of the Mouthparts in Cheilocapsus Nigrescens (Hemiptera: Heteroptera: Miridae) Reflects Adaptation for Phytophagous Habits. Insects 2019, 10, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edwards, J.S.A. The Action and Composition of the Saliva of an Assassin Bug Platymeris Rhadamanthus Gaerst. (Hemiptera, Reduviidae). J. Exp. Biol. 1961, 38, 61–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerachia, T.; Bergmann, F.; Shulov, A. Pharmacological Activities of the Venom of the Predaceous Bug Holotrichius Innesi (Heteroptera, Reduviidae). Int. Symp. Anim. Plant Toxins 3d Darnstadt 1972, 143–146. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, A.A.; Mayhew, M.L.; Jin, J.; Herzig, V.; Undheim, E.A.B.; Sombke, A.; Fry, B.G.; Meritt, D.J.; King, G.F. The Assassin Bug Pristhesancus Plagipennis Produces Two Distinct Venoms in Separate Gland Lumens. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Walker, A.A.; Madio, B.; Jin, J.; Undheim, E.A.B.; Fry, B.G.; King, G.F. Melt With This Kiss: Paralyzing and Liquefying Venom of The Assassin Bug Pristhesancus Plagipennis (Hemiptera: Reduviidae). Mol. Cell. Proteom. MCP 2017, 16, 552–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Walker, A.A.; Robinson, S.D.; Undheim, E.A.B.; Jin, J.; Han, X.; Fry, B.G.; Vetter, I.; King, G.F. Missiles of Mass Disruption: Composition and Glandular Origin of Venom Used as a Projectile Defensive Weapon by the Assassin Bug Platymeris Rhadamanthus. Toxins 2019, 11, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haridass, E.T.; Ananthakrishnan, T.N. Functional Morphology of Pylorus and Rectal Glands in Reduviidae (Insecta—Heteroptera). Proc. Anim. Sci. 1981, 90, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira Dos Santos, C.E.; de Souza, J.R.; Zanette, R.A.; da Silva, F.J.; Strussmann, C. Bite Caused by the Assassin Bug Zelus Fabricius, 1803 (Hemiptera; Heteroptera: Reduviidae) in a Human. Wilderness Environ. Med. 2019, 30, 63–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tonk, M.; Vilcinskas, A.; Grevelding, C.G.; Haeberlein, S. Anthelminthic Activity of Assassin Bug Venom against the Blood Fluke Schistosoma Mansoni. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonk, M.; Cabezas-Cruz, A.; Valdés, J.J.; Rego, R.O.M.; Chrudimská, T.; Strnad, M.; Šíma, R.; Bell-Sakyi, L.; Franta, Z.; Vilcinskas, A.; et al. Defensins from the Tick Ixodes Scapularis Are Effective against Phytopathogenic Fungi and the Human Bacterial Pathogen Listeria Grayi. Parasit. Vectors 2014, 7, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, K.; Hain, T.; Fischer, R.; Chakraborty, T.; Vilcinskas, A. Brain Infection and Activation of Neuronal Repair Mechanisms by the Human Pathogen Listeria Monocytogenes in the Lepidopteran Model Host Galleria Mellonella. Virulence 2013, 4, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Götz, S.; García-Gómez, J.M.; Terol, J.; Williams, T.D.; Nagaraj, S.H.; Nueda, M.J.; Robles, M.; Talón, M.; Dopazo, J.; Conesa, A. High-Throughput Functional Annotation and Data Mining with the Blast2GO Suite. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 3420–3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterhouse, R.M.; Seppey, M.; Simão, F.A.; Manni, M.; Ioannidis, P.; Klioutchnikov, G.; Kriventseva, E.V.; Zdobnov, E.M. BUSCO Applications from Quality Assessments to Gene Prediction and Phylogenomics. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacobs, C.G.C.; Steiger, S.; Heckel, D.G.; Wielsch, N.; Vilcinskas, A.; Vogel, H. Sex, Offspring and Carcass Determine Antimicrobial Peptide Expression in the Burying Beetle. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shevchenko, A.; Tomas, H.; Havli, J.; Olsen, J.V.; Mann, M. In-Gel Digestion for Mass Spectrometric Characterization of Proteins and Proteomes. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 2856–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevchenko, A.; Sunyaev, S.; Loboda, A.; Shevchenko, A.; Bork, P.; Ens, W.; Standing, K.G. Charting the Proteomes of Organisms with Unsequenced Genomes by MALDI-Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry and BLAST Homology Searching. Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 1917–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT Multiple Sequence Alignment Software Version 7: Improvements in Performance and Usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuraku, S.; Zmasek, C.M.; Nishimura, O.; Katoh, K. ALeaves Facilitates On-Demand Exploration of Metazoan Gene Family Trees on MAFFT Sequence Alignment Server with Enhanced Interactivity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, W22–W28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crooks, G.E.; Hon, G.; Chandonia, J.-M.; Brenner, S.E. WebLogo: A Sequence Logo Generator. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 1188–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castresana, J. Selection of Conserved Blocks from Multiple Alignments for Their Use in Phylogenetic Analysis. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2000, 17, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hempel, B.F.; Damm, M.; Göçmen, B.; Karis, M.; Oguz, M.A.; Nalbantsoy, A.; Süssmuth, R.D. Comparative Venomics of the Vipera ammodytes transcaucasiana and Vipera ammodytes montandoni from Turkey Provides Insights into Kinship. Toxins 2018, 1, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petras, D.; Hempel, B.F.; Göçmen, B.; Karis, M.; Whiteley, G.; Wagstaff, S.C.; Heiss, P.; Casewell, N.R.; Nalbantsoy, A.; Süssmuth, R.D. Intact protein mass spectrometry reveals intraspecies variations in venom composition of a local population of Vipera kaznakovi in Northeastern Turkey. J. Proteom. 2019, 199, 31–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amino, R.; Martins, R.M.; Procopio, J.; Hirata, I.Y.; Juliano, M.A.; Schenkman, S. Trialysin, a Novel Pore-Forming Protein from Saliva of Hematophagous Insects Activated by Limited Proteolysis. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 6207–6213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Le, S.Q.; Gascuel, O. An Improved General Amino Acid Replacement Matrix. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2008, 25, 1307–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Perrakis, A.; Tews, I.; Dauter, Z.; Oppenheim, A.B.; Chet, I.; Wilson, K.S.; Vorgias, C.E. Crystal Structure of a Bacterial Chitinase at 2.3 Å Resolution. Structure 1994, 2, 1169–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bernard, C.; Corzo, G.; Mosbah, A.; Nakajima, T.; Darbon, H. Solution Structure of Ptu1, a Toxin from the Assassin Bug Peirates Turpis That Blocks the Voltage-Sensitive Calcium Channel N-Type. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 12795–12800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, S.R.; McArthur, J.R.; Brust, A.; Bhola, R.F.; Rosengren, K.J.; Ragnarsson, L.; Dutertre, S.; Alewood, P.F.; Christie, M.J.; Adams, D.J.; et al. Novel Analgesic ω-Conotoxins from the Vermivorous Cone Snail Conus Moncuri Provide New Insights into the Evolution of Conopeptides. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, D.J.; Smith, A.B.; Schroeder, C.I.; Yasuda, T.; Lewis, R.J. ω-Conotoxin CVID Inhibits a Pharmacologically Distinct Voltage-Sensitive Calcium Channel Associated with Transmitter Release from Preganglionic Nerve Terminals. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 4057–4062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Evans, D.L.; Schmid, J.O. Insect Defense: Adaptive Mechanisms and Strategies of Prey and Predators; State University of New York Press: Albany, NY, USA, 1990; ISBN 9780887068966. [Google Scholar]
- Moret, Y.; Moreau, J. The Immune Role of the Arthropod Exoskeleton. Invertebr. Surviv. J. 2012, 9, 200–206. [Google Scholar]
- Moreau, S.J.M. “It Stings a Bit but It Cleans Well”: Venoms of Hymenoptera and Their Antimicrobial Potential. J. Insect Physiol. 2013, 59, 186–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villas-Boas, I.M.; Bonfá, G.; Tambourgi, D.V. Venomous Caterpillars: From Inoculation Apparatus to Venom Composition and Envenomation. Toxicon 2018, 153, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaik, H.A.; Mishra, A.; Kodrík, D. Beneficial Effect of Adipokinetic Hormone on Neuromuscular Paralysis in Insect Body Elicited by Braconid Wasp Venom. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Toxicol. Pharmacol. CBP 2017, 196, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Geer, C. Memoires Pour Servir a l’Histoire Des Insectes; Pierre Hesselberg: Stockholm, Sweden, 1773; Volume III. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, M.L.; Wielsch, N.; Heckel, D.G.; Vilcinskas, A.; Vogel, H. Context-Dependent Venom Deployment and Protein Composition in Two Assassin Bugs. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 10, 9932–9947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corzo, G.; Adachi-Akahane, S.; Nagao, T.; Kusui, Y.; Nakajima, T. Novel Peptides from Assassin Bugs (Hemiptera: Reduviidae): Isolation, Chemical and Biological Characterization. FEBS Lett. 2001, 499, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sollod, B.L.; Wilson, D.; Zhaxybayeva, O.; Gogarten, J.P.; Drinkwater, R.; King, G.F. Were Arachnids the First to Use Combinatorial Peptide Libraries? Peptides 2005, 26, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaji, R.A.; Ohtake, A.; Sato, K.; Gopalakrishnakone, P.; Kini, R.M.; Seow, K.T.; Bay, B.-H. λ-Conotoxins, a New Family of Conotoxins with Unique Disulfide Pattern and Protein Folding: Isolation and Characterization from the Venom of Conus Marmoreus. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 39516–39522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deer, T.R.; Pope, J.E.; Hanes, M.C.; McDowell, G.C. Intrathecal Therapy for Chronic Pain: A Review of Morphine and Ziconotide as Firstline Options. Pain Med. Off. J. Am. Acad. Pain Med. 2019, 20, 784–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayakumar, N.; Nalini, M.; Rajkuberan, C.; Faruck, L.H.; Bakshi, H.; Sangilimuthu, A.Y. Genotoxic and Cytotoxic Effect of Chitinase against Corcyra Cephalonica Larvae under Laboratory Conditions. Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, J.M.C.; Assumpção, T.C.; Francischetti, I.M.B. An Insight into the Sialomes of Bloodsucking Heteroptera. Psyche 2012, 2012, e470436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ribeiro, J.M.C.; Genta, F.A.; Sorgine, M.H.F.; Logullo, R.; Mesquita, R.D.; Paiva-Silva, G.O.; Majerowicz, D.; Medeiros, M.; Koerich, L.; Terra, W.R.; et al. An Insight into the Transcriptome of the Digestive Tract of the Bloodsucking Bug, Rhodnius Prolixus. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andre, F. Notes on the Biology of Oncopeltus Fasciatus (Dallas). Iowa State Coll. J. Sci. 1934, 9, 73–88. [Google Scholar]
- Lazzari, C.R.; Fauquet, A.; Lahondère, C. Keeping Cool: Kissing Bugs Avoid Cannibalism by Thermoregulating. J. Insect Physiol. 2018, 107, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royer, V.; Fraichard, S.; Bouhin, H. A Novel Putative Insect Chitinase with Multiple Catalytic Domains: Hormonal Regulation during Metamorphosis. Biochem. J. 2002, 366, 921–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arakane, Y.; Muthukrishnan, S. Insect Chitinase and Chitinase-like Proteins. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2010, 67, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kzhyshkowska, J.; Yin, S.; Liu, T.; Riabov, V.; Mitrofanova, I. Role of Chitinase-Like Proteins in Cancer. Biol. Chem. 2016, 397, 231–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakhleh, J.; El Moussawi, L.; Osta, M.A. Chapter Three—The Melanization Response in Insect Immunity. In Advances in Insect Physiology; Ligoxygakis, P., Ed.; Insect Immunity; Academic Press: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2017; Volume 52, pp. 83–109. [Google Scholar]
- Cabezas-Cruz, A.; Valdés, J.J. Are Ticks Venomous Animals? Front. Zool. 2014, 11, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pineda, S.S.; Sollod, B.L.; Wilson, D.; Darling, A.; Sunagar, K.; Undheim, E.A.B.; Kely, L.; Antunes, A.; Fry, B.G.; King, G.F. Diversification of a Single Ancestral Gene into a Successful Toxin Superfamily in Highly Venomous Australian Funnel-Web Spiders. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klint, J.K.; Senff, S.; Rupasinghe, D.B.; Er, S.Y.; Herzig, V.; Nicholson, G.M.; King, G.F. Spider-Venom Peptides That Target Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels: Pharmacological Tools and Potential Therapeutic Leads. Toxicon 2012, 60, 478–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hertle, R.; Hilger, M.; Weingardt-Kocher, S.; Walev, I. Cytotoxic Action of Serratia Marcescens Hemolysin on Human Epithelial Cells. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 817–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, J.; Fang, J.; Cheng, Z.; Fan, L.; Hu, W.; Zhou, F.; Shen, H. Overexpression of the Kininogen-1 Inhibits Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis of Glioma Cells. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bhakdi, S.; Weller, U.; Walev, I.; Martin, E.; Jonas, D.; Palmer, M. A Guide to the Use of Pore-Forming Toxins for Controlled Permeabilization of Cell Membranes. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 1993, 182, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, A.P.; Green, B.J.; Beezhold, D.H. Fungal Hemolysins. Med. Mycol. 2013, 51, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rawlings, N.D.; Barrett, A.J. Evolution of Proteins of the Cystatin Superfamily. J. Mol. Evol. 1990, 30, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turk, V.; Bode, W. The Cystatins: Protein Inhibitors of Cysteine Proteinases. FEBS Lett. 1991, 285, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kamiyama, F.; Maeda, T.; Yamane, T.; Li, Y.H.; Ogukubo, O.; Otsuka, T.; Ueyama, H.; Takahashi, S.; Ohkubo, I.; Matsui, N. Inhibition of Vitronectin-Mediated Haptotaxis and Haptoinvasion of MG-63 Cells by Domain 5 (D5(H)) of Human High-Molecular-Weight Kininogen and Identification of a Minimal Amino Acid Sequence. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 288, 975–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet-Gely, I.; Lemaitre, B.; Boccard, F. Bacterial Strategies to Overcome Insect Defences. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, L.; Bohra, N.; Rajput, V.D.; Quiroz-Figueroa, F.R.; Singh, R.K.; Marques, G. Advances in Entomopathogen Isolation: A Case of Bacteria and Fungi. Microorganisms 2020, 9, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilcinskas, A.; Stoecker, K.; Schmidtberg, H.; Röhrich, C.R.; Vogel, H. Invasive Harlequin Ladybird Carries Biological Weapons against Native Competitors. Science 2013, 340, 862–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldiviezo, L.V.; Pedrini, N.; Santana, M.; Mannino, M.C.; Nieva, L.B.; Gentile, A.; Cardozo, R.M. Isolation of Beauveria Bassiana from the Chagas Disease Vector Triatoma Infestans in the Gran Chaco Region of Argentina: Assessment of Gene Expression during Host–Pathogen Interaction. J. Fungi 2020, 6, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurat-Fuentes, J.L.; Jackson, T.A. Bacterial Entomopathogens—Chapter 8. In Insect Pathology, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2012; pp. 265–349. ISBN 9780123849847. [Google Scholar]













| Galleria mellonella Stages | Venom Dose (%) | Incubation after Injection | Replicates | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 min | 30 min | 1 h | 4 h | 24 h | ||||||
| Paralysis | Paralysis | Paralysis | Melanization (%) | Paralysis | Melanization (%) | Paralysis | Melanization (%) | |||
| Pupae | 140 | none | n.a. | none | 0 | full | 70 | full | 100 | 4 |
| full | n.a. | full | 0 | full | 70 | full | 100 | 1 | ||
| 50 | full | n.a. | full | 0 | full | 40 | full | 90 | 7 | |
| PBS only | none | none | none | 0 | none | 5 | none | 5 | 12 | |
| No injection | none | none | none | 0 | none | 0 | none | 0 | 12 | |
| Larvae | 50 | none | partial | n.a. | n.a. | full | 60 | full | 100 | 5 |
| full | full | n.a. | n.a. | full | 30 | full | 100 | 3 | ||
| full | full | n.a. | n.a. | partial | 20 | partial | 100 | 1 | ||
| full | full | n.a. | n.a. | partial | 20 | full | 100 | 1 | ||
| full | full | n.a. | n.a. | partial | 20 | n.a. | 0 | 1 | ||
| PBS only | none | none | n.a. | n.a. | none | 5 | none | 5 | 12 | |
| No injection | none | none | n.a. | n.a. | none | 0 | none | 0 | 12 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rügen, N.; Jenkins, T.P.; Wielsch, N.; Vogel, H.; Hempel, B.-F.; Süssmuth, R.D.; Ainsworth, S.; Cabezas-Cruz, A.; Vilcinskas, A.; Tonk, M. Hexapod Assassins’ Potion: Venom Composition and Bioactivity from the Eurasian Assassin Bug Rhynocoris iracundus. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 819. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9070819
Rügen N, Jenkins TP, Wielsch N, Vogel H, Hempel B-F, Süssmuth RD, Ainsworth S, Cabezas-Cruz A, Vilcinskas A, Tonk M. Hexapod Assassins’ Potion: Venom Composition and Bioactivity from the Eurasian Assassin Bug Rhynocoris iracundus. Biomedicines. 2021; 9(7):819. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9070819
Chicago/Turabian StyleRügen, Nicolai, Timothy P. Jenkins, Natalie Wielsch, Heiko Vogel, Benjamin-Florian Hempel, Roderich D. Süssmuth, Stuart Ainsworth, Alejandro Cabezas-Cruz, Andreas Vilcinskas, and Miray Tonk. 2021. "Hexapod Assassins’ Potion: Venom Composition and Bioactivity from the Eurasian Assassin Bug Rhynocoris iracundus" Biomedicines 9, no. 7: 819. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9070819
APA StyleRügen, N., Jenkins, T. P., Wielsch, N., Vogel, H., Hempel, B.-F., Süssmuth, R. D., Ainsworth, S., Cabezas-Cruz, A., Vilcinskas, A., & Tonk, M. (2021). Hexapod Assassins’ Potion: Venom Composition and Bioactivity from the Eurasian Assassin Bug Rhynocoris iracundus. Biomedicines, 9(7), 819. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9070819