Immune Assessment of BNT162b2 m-RNA-Spike Based Vaccine Response in Adults
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Flow Cytometry for B and T Cell Subsets
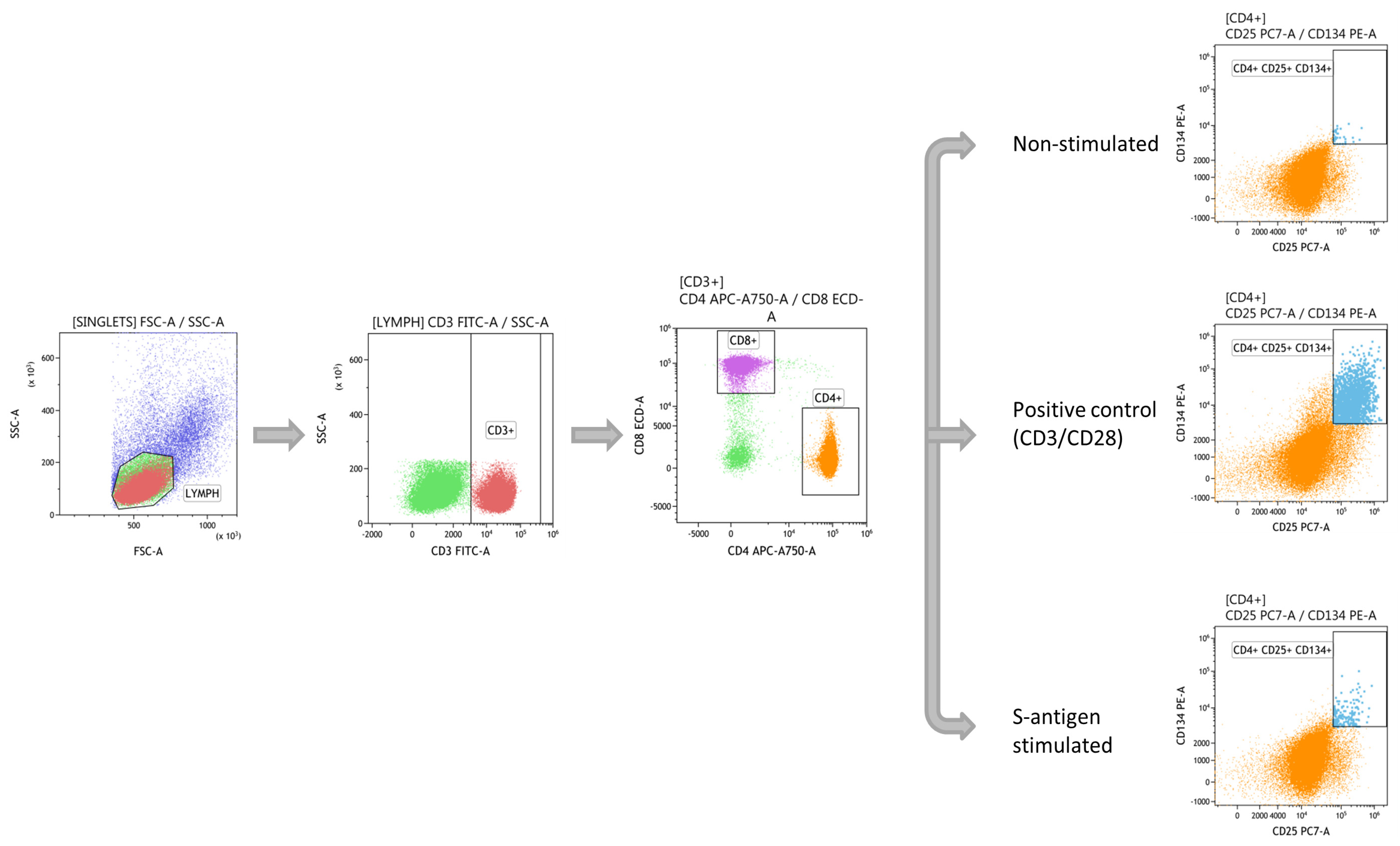
2.3. SARS-CoV-2 T-Specific Response Assessment by Flow Cytometry
2.4. SARS-CoV-2 Anti-S Antibodies Detection
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. T-Cell Immune Response after Vaccination
3.2. Specific T-Cell Immune Response
3.3. B Cell and Antibody Response
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baden, L.R.; El Sahly, H.M.; Essink, B. Efficacy and safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folegatti, P.M.; Ewer, K.J.; Aley, P.K. Safety and immunogenicity of the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine against SARS-CoV-2: A preliminary report of a phase 1/2, single-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2020, 396, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logunov, D.Y.; Dolzhikova, I.V.; Shcheblyakov, D.V. Safety and efficacy of an rAd26 and rAd5 vector-based heterologous prime-boost COVID-19 vaccine: An interim analysis of a randomised controlled phase 3 trial in Russia. Lancet 2021, 397, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polack, F.P.; Thomas, S.J.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Pérez Marc, G.; Moreira, E.D.; Zerbini, C.; et al. Safety and efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2603–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, J.M.; Mateus, J.; Kato, Y.; Hastie, K.M.; Yu, E.D.; Faliti, C.E.; Grifoni, A.; Ramirez, S.I.; Haupt, S.; Frazier, A.; et al. Immunological memory to SARS-CoV-2 assessed for up to 8 months after infection. Science 2021, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawat, K.; Kumari, P.; Saha, L. COVID-19 vaccine: A recent update in pipeline vaccines, their design and development strategies. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, J.; Ge, J.; Yu, J. Structure of the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain bound to the ACE2 receptor. Nature 2020, 581, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Victora, G.D.; Nussenzweig, M.C. Germinal centers. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 30, 429–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.S.; Kim, W.; Kalaidina, E.; Goss, C.W.; Rauseo, A.M.; Schmitz, A.J.; Hansen, L.; Haile, A.; Klebert, M.K.; Pusic, I.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection induces long-lived bone marrow plasma cells in humans. Nature 2021, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgson, S.H.; Mansatta, K.; Mallett, G. What defines an efficacious COVID-19 vaccine? A review of the challenges assessing the clinical efficacy of vaccines against SARS-CoV-2. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, e26–e35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekine, T.; Perez-Potti, A.; Rivera-Ballesteros, O. Robust T cell immunity in convalescent individuals with asymptomatic or mild COVID-19. Cell 2020, 183, 158–168.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irure-Ventura, J.; Segundo, D.S.; Rodrigo, E. High pretransplant BAFF levels and B-cell subset polarized towards a memory phenotype as predictive biomarkers for antibody-mediated rejection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suàrez-Fernández, P.; Utrero-Rico, A.; Sandonis, V.; García-Ríos, E.; Arroyo-Sánchez, D.; Fernández-Ruiz, M.; Andrés, A.; Polanco, N.; González-Cuadrado, C.; Almendro-Vázquez, P.; et al. Circulatory follicular helper T lymphocytes associate with lower incidence of CMV infection in kidney transplant recipients. Am. J. Transplant. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, N.; Bentebibel, S.E.; Ueno, H. Phenotype and functions of memory Tfh cells in human blood. Trends Immunol. 2014, 35, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grifoni, A.; Weiskopf, D.; Ramirez, S.I. Targets of T cell responses to SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus in humans with COVID-19 disease and unexposed individuals. Cell 2020, 181, 1489–1501.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradenas, E.; Trinité, B.; Urrea, V. Stable neutralizing antibody levels 6 months after mild and severe COVID-19 episodes. Medicine 2021, 2, 313–320.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, E.J.; Angulo, F.J.; McLaughlin, J.M.; Anis, E.; Singer, S.R.; Khan, F.; Brooks, N.; Smaja, M.; Mircus, G.; Pan, K.; et al. Impact and effectiveness of mRNA BNT162b2 vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 infections and COVID-19 cases, hospitalisations, and deaths following a nationwide vaccination campaign in Israel: An observational study using national surveillance data. Lancet 2021, 397, 1819–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentebibel, S.E.; Lopez, S.; Obermoser, G. Induction of ICOS + CXCR3 + CXCR5 + T H cells correlates with antibody responses to influenza vaccination. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morita, R.; Schmitt, N.; Bentebibel, S.E.; Ranganathan, R.; Bourdery, L.; Zurawski, G.; Foucat, E.; Dullaers, M.; Oh, S.K.; Sabzghabaei, N.; et al. Human Blood CXCR5 + CD4+ T cells are counterparts of T Follicular cells and contain specific subsets that differentially support antibody secretion. Immunity 2011, 34, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lindgren, G.; Ols, S.; Liang, F. Induction of robust B cell responses after influenza mRNA vaccination is accompanied by circulating hemagglutinin-specific ICOS+ PD-1+ CXCR3+ T follicular helper cells. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gobbi, F.; Buonfrate, D.; Moro, L. Antibody response to the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine in subjects with prior SARS-CoV-2 infection. Viruses 2021, 13, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo, J.; Izquierdo-Useros, N.; Ávila-Nieto, C. Humoral immune responses and neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2; implications in pathogenesis and protective immunity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 538, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Fresnedo, G.; Ramos, M.A.; González-Pardo, M.C.; De Francisco, A.L.M.; López-Hoyos, M.; Arias, M. B lymphopenia in uraemia is related to an accelerated in vitro apoptosis and dysregulation of Bcl-2. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2000, 15, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grupper, A.; Sharon, N.; Finn, T. Humoral Response to the Pfizer BNT162b2 Vaccine in Patients Undergoing Maintenance Hemodialysis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockman, M.A.; Mwimanzi, F.; Sang, Y. Weak humoral immune reactivity among residents of long-term care facilities following one dose of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine. medRxiv Prepr. Serv. Health Sci. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashokkumar, C.; Rohan, V.; Kroemer, A.H.; Rao, S.; Mazariegos, G.; Higgs, B.W.; Nadig, S.; Almeda, J.; Dhani, H.; Khan, K.; et al. Impaired T-cell and antibody immunity after COVID-19 infection in chronically immunosuppressed transplant recipients. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heldman, M.R.; Limaye, A.P. SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines in kidney transplant recipients: Will they be safe and effective and how will we know? J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 32, 1021–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero-Marcos, A.; Salcedo, M.; Alonso-Fernández, R.; Rodríguez-Perálvarez, M.; Olmedo, M.; Graus Morales, J.; Cuervas-Mons, V.; Cachero, A.; Loinaz-Segurola, C.; Iñarrairaegui, M.; et al. Changes in humoral immune response after SARS-CoV-2 infection in liver transplant recipients compared to immunocompetent patients. Am. J. Transplant. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alp Ikizler, T.; Coates, P.T.; Rovin, B.H.; Ronco, P. Immune response to SARS-CoV-2 infection and vaccination in patients receiving kidney replacement therapy. Kidney Int. 2021, 99, 1275–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinowich, L.; Grupper, A.; Baruch, R.; Ben-Yehoyada, M.; Halperin, T.; Turner, D.; Katchman, E.; Levi, S.; Houri, I.; Lubezky, N.; et al. Low immunogenicity to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination among liver transplant recipients. J. Hepatol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Cell Subsets | Phenotypic CD Markers |
|---|---|
| T cell subsets | |
| T helper 1 (Th1) | CD45+CD3+CD4+CXCR3+CCR6− |
| Th memory (ThMEM) | CD45+CD3+CD4+CD45RO+ |
| Th1 memory (Th1MEM) | CD45+CD3+CD4+CD45RO+CXCR3+CCR6− |
| Memory T follicular helper (TFH) | CD45+CD3+CD4+CD45RO+CXCR5+ |
| Memory T follicular helper 1(TFH1) | CD45+CD3+CD4+CD45RO+CXCR5+CXCR3+CCR6− |
| Memory T follicular helper 1(TFH2) | CD45+CD3+CD4+CD45RO+CXCR5+CXCR3−CCR6− |
| Memory T follicular helper 1(TFH17) | CD45+CD3+CD4+CD45RO+CXCR5+CXCR3−CCR6+ |
| B cell subsets | |
| Switched memory B (SwM) | CD45+CD19+CD27+IgD− |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
San Segundo, D.; Comins-Boo, A.; Irure-Ventura, J.; Renuncio-García, M.; Roa-Bautista, A.; González-López, E.; Merino-Fernández, D.; Lamadrid-Perojo, P.; Alonso-Peña, M.; Ocejo-Vinyals, J.G.; et al. Immune Assessment of BNT162b2 m-RNA-Spike Based Vaccine Response in Adults. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 868. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9080868
San Segundo D, Comins-Boo A, Irure-Ventura J, Renuncio-García M, Roa-Bautista A, González-López E, Merino-Fernández D, Lamadrid-Perojo P, Alonso-Peña M, Ocejo-Vinyals JG, et al. Immune Assessment of BNT162b2 m-RNA-Spike Based Vaccine Response in Adults. Biomedicines. 2021; 9(8):868. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9080868
Chicago/Turabian StyleSan Segundo, David, Alejandra Comins-Boo, Juan Irure-Ventura, Mónica Renuncio-García, Adriel Roa-Bautista, Elena González-López, David Merino-Fernández, Patricia Lamadrid-Perojo, Marta Alonso-Peña, Javier Gonzalo Ocejo-Vinyals, and et al. 2021. "Immune Assessment of BNT162b2 m-RNA-Spike Based Vaccine Response in Adults" Biomedicines 9, no. 8: 868. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9080868
APA StyleSan Segundo, D., Comins-Boo, A., Irure-Ventura, J., Renuncio-García, M., Roa-Bautista, A., González-López, E., Merino-Fernández, D., Lamadrid-Perojo, P., Alonso-Peña, M., Ocejo-Vinyals, J. G., Gutiérrez-Larrañaga, M., Guiral-Foz, S., & López-Hoyos, M. (2021). Immune Assessment of BNT162b2 m-RNA-Spike Based Vaccine Response in Adults. Biomedicines, 9(8), 868. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9080868









