Hepatic and Extrahepatic Insulin Clearance in Mice with Double Deletion of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 and Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide Receptors
Abstract
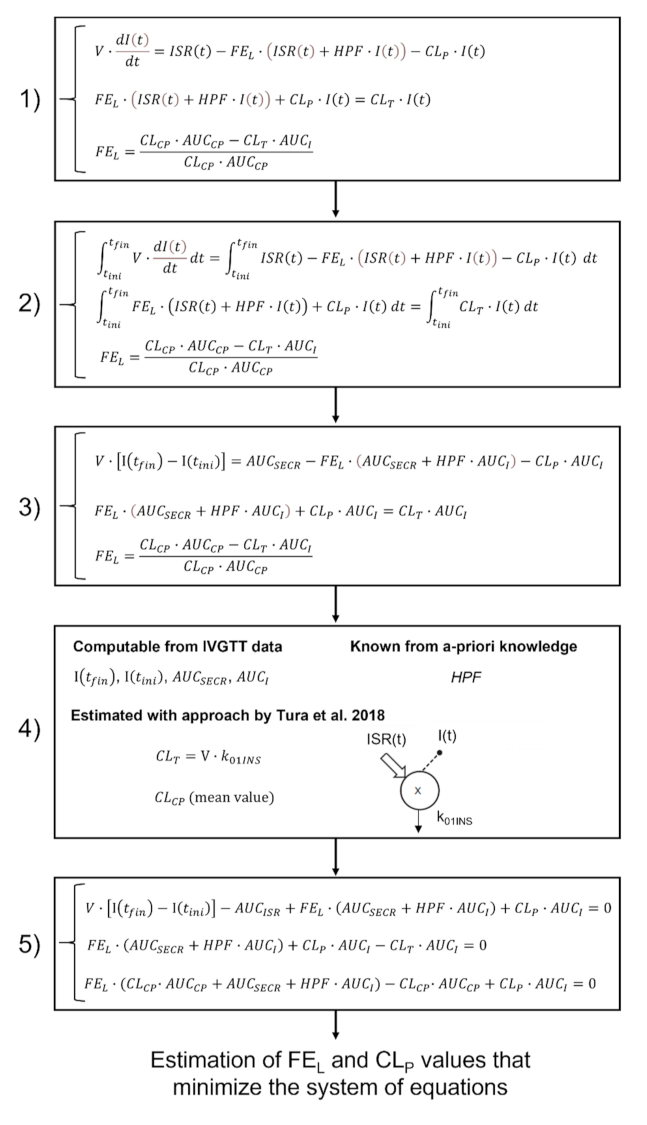
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Assessment of Hepatic and Extrahepatic Insulin Clearance
2.3. Assessment of Other Parameters of Glucose Metabolism
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AIRG | Acute Insulin Response to glucose |
| AUCCP | Area Under the Curve of C-peptide |
| AUCI | Area Under the Curve of insulin |
| AUCSECR | Area Under the Curve of insulin secretion rate |
| CEACAM1 | Carcinoembryonic Antigen-related Cell Adhesion Molecule 1 |
| CLCP | C-peptide clearance during IVGTT |
| CLP-P1 | Extrahepatic insulin clearance in the first phase of IVGTT |
| CLP-P2 | Extrahepatic insulin clearance in the second phase of IVGTT |
| CLT-P1 | Total insulin clearance in the first phase of IVGTT |
| CLT-P2 | Total insulin clearance in the second phase of IVGTT |
| DI | Disposition Index |
| DIRKO | Double Incretin Receptor KnockOut |
| EICR(t) | Extrahepatic Insulin Clearance Rate |
| FEL-P1 | Hepatic insulin clearance in the first phase of IVGTT |
| FEL-P2 | Hepatic insulin clearance in the second phase of IVGTT |
| GIP | Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide |
| GLP-1 | Glucagon-like Peptide 1 |
| HICR(t) | Hepatic Insulin Clearance Rate |
| HPF | Hepatic Plasma Flow |
| I(t) | Plasma insulin concentration |
| IDE | Insulin-Degrading Enzyme |
| ISR(t) | Insulin Secretion Rate |
| IVGTT | Intravenous Glucose Tolerance Test |
| KG | Glucose tolerance |
| QUICKI | Quantitative Insulin Sensitivity Check Index |
| SI | Insulin sensitivity during the IVGTT |
| SG | Glucose effectiveness |
| SNX | Sorting Nexin |
| tfin | Final time of IVGTT |
| tini | Initial time of IVGTT |
| V | Distribution volume |
| WT | Wild-Type |
References
- Dupre, J.; Ross, S.A.; Watson, D.; Brown, J.C. Stimulation of insulin secretion by gastric inhibitory polypeptide in man. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1973, 37, 826–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreymann, B.; Williams, G.; Ghatei, M.A.; Bloom, S.R. Glucagon-like peptide-1 7-36: A physiological incretin in man. Lancet (London, England) 1987, 2, 1300–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boer, G.A.; Holst, J.J. Incretin hormones and type 2 diabetes—mechanistic insights and therapeutic approaches. Biology (Basel) 2020, 9, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drucker, D.J. The biology of incretin hormones. Cell Metab. 2006, 3, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Svegliati-Baroni, G.; Saccomanno, S.; Rychlicki, C.; Agostinelli, L.; De Minicis, S.; Candelaresi, C.; Faraci, G.; Pacetti, D.; Vivarelli, M.; Nicolini, D.; et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor activation stimulates hepatic lipid oxidation and restores hepatic signalling alteration induced by a high-fat diet in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Liver Int. 2011, 31, 1285–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holst, J.J. The incretin system in healthy humans: The role of GIP and GLP-1. Metabolism 2019, 96, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pacini, G.; Thomaseth, K.; Ahrén, B. Dissociated effects of glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide vs glucagon-like peptide-1 on β-cell secretion and insulin clearance in mice. Metabolism 2010, 59, 988–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrén, B.; Thomaseth, K.; Pacini, G. Reduced insulin clearance contributes to the increased insulin levels after administration of glucagon-like peptide 1 in mice. Diabetologia 2005, 48, 2140–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rudovich, N.N.; Rochlitz, H.J.; Pfeiffer, A.F.H. Reduced hepatic insulin extraction in response to gastric inhibitory polypeptide compensates for reduced insulin secretion in normal-weight and normal glucose tolerant first-degree relatives of type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes 2004, 53, 2359–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meier, J.J.; Gallwitz, B.; Siepmann, N.; Holst, J.J.; Deacon, C.F.; Schmidt, W.E.; Nauck, M.A. The reduction in hepatic insulin clearance after oral glucose is not mediated by Gastric inhibitory polypeptide (GIP). Regul. Pept. 2003, 113, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, J.J.; Holst, J.J.; Schmidt, W.E.; Nauck, M.A. Reduction of hepatic insulin clearance after oral glucose ingestion is not mediated by glucagon-like peptide 1 or gastric inhibitory polypeptide in humans. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2007, 293, E849–E856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tura, A.; Bizzotto, R.; Yamada, Y.; Seino, Y.; Pacini, G.; Ahrén, B. Increased insulin clearance in mice with double deletion of glucagon-like peptide-1 and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptors. Am. J. Physiol. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2018, 314, R639–R646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansotia, T.; Baggio, L.L.; Delmeire, D.; Hinke, S.A.; Yamada, Y.; Tsukiyama, K.; Seino, Y.; Holst, J.J.; Schuit, F.; Drucker, D.J. Double incretin receptor knockout (DIRKO) mice reveal an essential role for the enteroinsular axis in transducing the glucoregulatory actions of DPP-IV inhibitors. Diabetes 2004, 53, 1326–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Polidori, D.C.; Bergman, R.N.; Chung, S.T.; Sumner, A.E. Hepatic and extrahepatic insulin clearance are differentially regulated: Results from a novel model-based analysis of intravenous glucose tolerance data. Diabetes 2016, 65, 1556–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cauter, E.V.; Mestrez, F.; Sturis, J.; Polonsky, K.S. Estimation of insulin secretion rates from C-peptide levels: Comparison of individual and standard kinetic parameters for C-peptide clearance. Diabetes 1992, 41, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, D.; Lin, L.; Jiao, H.; Cai, X.; Duan, J.-X.; Matteucci, M. Pharmacokinetics of TH-302: A hypoxically activated prodrug of bromo-isophosphoramide mustard in mice, rats, dogs and monkeys. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2012, 69, 643–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camilo, D.F.; Vasques, A.C.J.; Hayashi, K.; Tura, A.; da Silva, C.d.C.; Zambon, M.P.; Antônio, M.Â.R.d.G.M.; Geloneze, B. Adiposity and family history of type 2 diabetes in an admixed population of adolescents: Associations with insulin sensitivity, beta-cell function, and hepatic insulin extraction in BRAMS study. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 137, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacini, G.; Ahrén, M.; Ahrén, B. Reappraisal of the intravenous glucose tolerance index for a simple assessment of insulin sensitivity in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2009, 296, R1316–R1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pacini, G.; Thomaseth, K.; Ahrén, B. Contribution to glucose tolerance of insulin-independent vs. insulin-dependent mechanisms in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2001, 281, E693–E703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, A.; Nambi, S.S.; Mather, K.; Baron, A.D.; Follmann, D.A.; Sullivan, G.; Quon, M.J. Quantitative insulin sensitivity check index: A simple, accurate method for assessing insulin sensitivity in humans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 85, 2402–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahn, S.E.; Prigeon, R.L.; McCulloch, D.K.; Boyko, E.J.; Bergman, R.N.; Schwartz, M.W.; Neifing, J.L.; Ward, W.K.; Beard, J.C.; Palmer, J.P.; et al. Quantification of the relationship between insulin sensitivity and beta-cell function in human subjects. Evidence for a hyperbolic function. Diabetes 1993, 42, 1663–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tura, A.; Kautzky-Willer, A.; Pacini, G. Insulinogenic indices from insulin and C-peptide: Comparison of beta-cell function from OGTT and IVGTT. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2006, 72, 298–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, B.; Ahlkvist, L.; Yamada, Y.; Seino, Y.; Ahrén, B. Incretin hormone receptors are required for normal beta cell development and function in female mice. Peptides 2016, 79, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahrén, B.; Yamada, Y.; Seino, Y. The incretin effect in female mice with double deletion of GLP-1 and GIP receptors. J. Endocr. Soc. 2020, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansotia, T.; Maida, A.; Flock, G.; Yamada, Y.; Tsukiyama, K.; Seino, Y.; Drucker, D.J. Extrapancreatic incretin receptors modulate glucose homeostasis, body weight, and energy expenditure. J. Clin. Invest. 2007, 117, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flock, G.; Baggio, L.L.; Longuet, C.; Drucker, D.J. Incretin receptors for glucagon-like peptide 1 and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide are essential for the sustained metabolic actions of vildagliptin in mice. Diabetes 2007, 56, 3006–3013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najjar, S.M.; Perdomo, G. Hepatic insulin clearance: Mechanism and physiology. Physiology 2019, 34, 198–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramakrishnan, S.K.; Khuder, S.S.; Al-Share, Q.Y.; Russo, L.; Abdallah, S.L.; Patel, P.R.; Heinrich, G.; Muturi, H.T.; Mopidevi, B.R.; Oyarce, A.M.; et al. PPARα (peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α) activation reduces hepatic CEACAM1 protein expression to regulate fatty acid oxidation during fasting-refeeding transition. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 8121–8129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghadieh, H.E.; Muturi, H.T.; Russo, L.; Marino, C.C.; Ghanem, S.S.; Khuder, S.S.; Hanna, J.C.; Jash, S.; Puri, V.; Heinrich, G.; et al. Exenatide induces carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 1 expression to prevent hepatic steatosis. Hepatol. Commun. 2018, 2, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrannini, E.; Wahren, J.; Faber, O.K.; Felig, P.; Binder, C.; DeFronzo, R.A. Splanchnic and renal metabolism of insulin in human subjects: A dose-response study. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 1983, 244, E517–E527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pina, A.F.; Borges, D.O.; Meneses, M.J.; Branco, P.; Birne, R.; Vilasi, A.; Macedo, M.P. Insulin: Trigger and target of renal functions. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Yang, J.; Villar, V.A.M.; Asico, L.D.; Ma, X.; Armando, I.; Sanada, H.; Yoneda, M.; Felder, R.A.; Jose, P.A.; et al. Loss of renal SNX5 results in impaired IDE activity and insulin resistance in mice. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buenaventura, T.; Kanda, N.; Douzenis, P.C.; Jones, B.; Bloom, S.R.; Chabosseau, P.; Corrêa, I.R.; Bosco, D.; Piemonti, L.; Marchetti, P.; et al. A targeted RNAi screen identifies endocytic trafficking factors that control GLP-1 receptor signaling in pancreatic β-Cells. Diabetes 2018, 67, 385–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tura, A.; Pacini, G.; Yamada, Y.; Seino, Y.; Ahrén, B. Glucagon and insulin secretion, insulin clearance, and fasting glucose in GIP receptor and GLP-1 receptor knockout mice. Am. J. Physiol. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2019, 316, R27–R37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tura, A.; Göbl, C.; Morettini, M.; Burattini, L.; Kautzky-Willer, A.; Pacini, G. Insulin clearance is altered in women with a history of gestational diabetes progressing to type 2 diabetes. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2020, 30, 1272–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okura, T.; Fujioka, Y.; Nakamura, R.; Anno, M.; Ito, Y.; Kitao, S.; Matsumoto, K.; Shoji, K.; Sumi, K.; Matsuzawa, K.; et al. Hepatic insulin clearance is increased in patients with high HbA1c type 2 diabetes: A preliminary report. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2020, 8, e001149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| WT | DIRKO | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| First phase | FEL-P1 (%) | 28.9 [25.7–32.0] | 29.7 [26.7–34.9] | 0.18 |
| CLP-P1 (10−3 l∙min−1) | 0.15 [0.11–0.22] | 0.18 [0.13–0.27] * | 0.04 | |
| CLT-P1 (10−3 l∙min−1) | 0.51 [0.46–0.65] | 0.61 [0.48–0.82] * | 0.02 | |
| Second phase | FEL-P2 (%) | 39.8 [35.8–44.2] | 37.8 [35.1–43.1] | 0.46 |
| CLP-P2 (10−3 l∙min−1) | 0.79 [0.69–0.87] | 0.72 [0.64–0.81] | 0.27 | |
| CLT-P2 (10−3 l∙min−1) | 1.69 [1.48–1.87] | 1.38 [1.13–1.75] | 0.10 |
| WT | DIRKO | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| KG (%/min) | 2.49 [1.85–3.14] | 1.98 [0.96–2.41] * | <0.01 |
| SI (10−4 min−1/pmol/l) | 1.37 [0.97–1.78] | 0.85 [0.77–1.39] * | <0.01 |
| QUICKI (dimensionless) | 0.123 [0.119–0.126] | 0.120 [0.116–0.123] | 0.07 |
| SG (min−1) | 0.052 [0.037–0.063] | 0.037 [0.028–0.055] * | 0.02 |
| AIRG (pmol/l) | 445 [288–635] | 426 [195–634] | 0.16 |
| DI (10−3 min−1) | 1.17 [0.70–1.64] | 0.72 [0.34–1.03] * | 0.02 |
| AUCSECR (pmol) | 13.0 [12.0–16.8] | 17.0 [14.3–21.0] * | <0.01 |
| β-cell sensitivity (mmol C-peptide/mmol Glucose) | 0.022 [0.018–0.027] | 0.025 [0.021–0.030] | 0.05 |
| First Phase | Second Phase | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FEL-P1 | CLP-P1 | CLT-P1 | FEL-P2 | CLP-P2 | CLT-P2 | ||
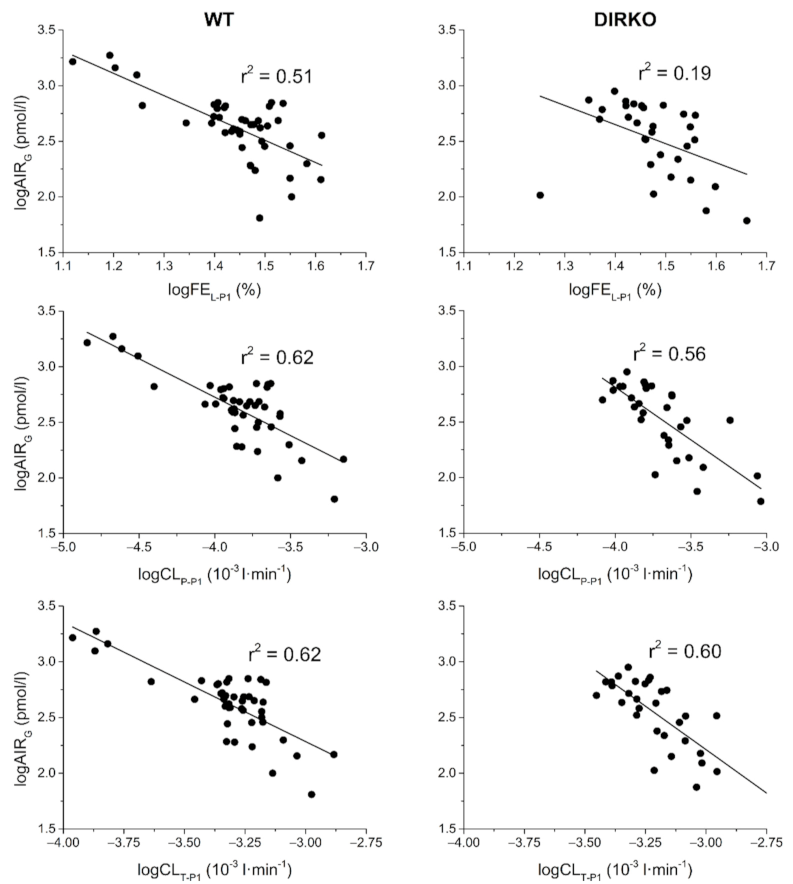
| WT + DIRKO | KG | n.s. | 0.08 (0.01) | 0.08 (0.01) | 0.08 (0.01) | n.s. | 0.07 (0.03) |
| SI | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | |
| QUICKI | 0.06 (0.02) | 0.10 (<0.01) | 0.12 (<0.01) | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | |
| SG | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | 0.06 (0.03) | n.s. | n.s. | |
| AIRG | 0.37 (<0.001) | 0.59 (<0.001) | 0.60 (<0.001) | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | |
| DI | 0.23 (<0.001) | 0.38 (<0.001) | 0.39 (<0.01) | 0.07 (0.02) | n.s. | n.s. | |
| AUCSECR | 0.07 (0.02) | 0.13 (<0.01) | 0.12 (<0.01) | 0.17 (<0.001) | n.s. | n.s. | |
| β-cell sensitivity | 0.06 (0.03) | 0.11 (<0.01) | 0.11 (<0.01) | n.s. | n.s. | 0.11 (<0.01) | |
| WT | KG | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
| SI | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | |
| QUICKI | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | |
| SG | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | |
| AIRG | 0.51 (<0.001) | 0.62 (<0.001) | 0.62 (<0.001) | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | |
| DI | 0.33 (<0.001) | 0.40 (<0.001) | 0.40 (<0.001) | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | |
| AUCSECR | 0.15 (<0.01) | 0.14 (0.01) | 0.15 (<0.01) | 0.15 (<0.01) | n.s. | n.s. | |
| β-cell sensitivity | 0.16 (<0.01) | 0.22 (<0.01) | 0.23 (<0.001) | n.s. | n.s. | 0.11 (0.03) | |
| DIRKO | KG | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | 0.14 (0.04) |
| SI | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | |
| QUICKI | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | |
| SG | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | |
| AIRG | 0.19 (0.01) | 0.56 (<0.001) | 0.60 (<0.001) | n.s. | n.s. | 0.19 (0.01) | |
| DI | n.s. | 0.29 (<0.01) | 0.31 (<0.01) | n.s. | n.s. | 0.26 (<0.01) | |
| AUCSECR | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | 0.37 (<0.001) | n.s. | 0.15 (0.03) | |
| β-cell sensitivity | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Morettini, M.; Piersanti, A.; Burattini, L.; Pacini, G.; Göbl, C.; Ahrén, B.; Tura, A. Hepatic and Extrahepatic Insulin Clearance in Mice with Double Deletion of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 and Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide Receptors. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 973. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9080973
Morettini M, Piersanti A, Burattini L, Pacini G, Göbl C, Ahrén B, Tura A. Hepatic and Extrahepatic Insulin Clearance in Mice with Double Deletion of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 and Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide Receptors. Biomedicines. 2021; 9(8):973. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9080973
Chicago/Turabian StyleMorettini, Micaela, Agnese Piersanti, Laura Burattini, Giovanni Pacini, Christian Göbl, Bo Ahrén, and Andrea Tura. 2021. "Hepatic and Extrahepatic Insulin Clearance in Mice with Double Deletion of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 and Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide Receptors" Biomedicines 9, no. 8: 973. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9080973
APA StyleMorettini, M., Piersanti, A., Burattini, L., Pacini, G., Göbl, C., Ahrén, B., & Tura, A. (2021). Hepatic and Extrahepatic Insulin Clearance in Mice with Double Deletion of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 and Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide Receptors. Biomedicines, 9(8), 973. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9080973









