Ozonated Olive Oil Dressing for Pediatric Hypospadias Repair: A Prospective Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Enrolment
2.2. Sample Size Calculation
2.3. Data Collection and Outcomes Measurement
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Dressing Composition
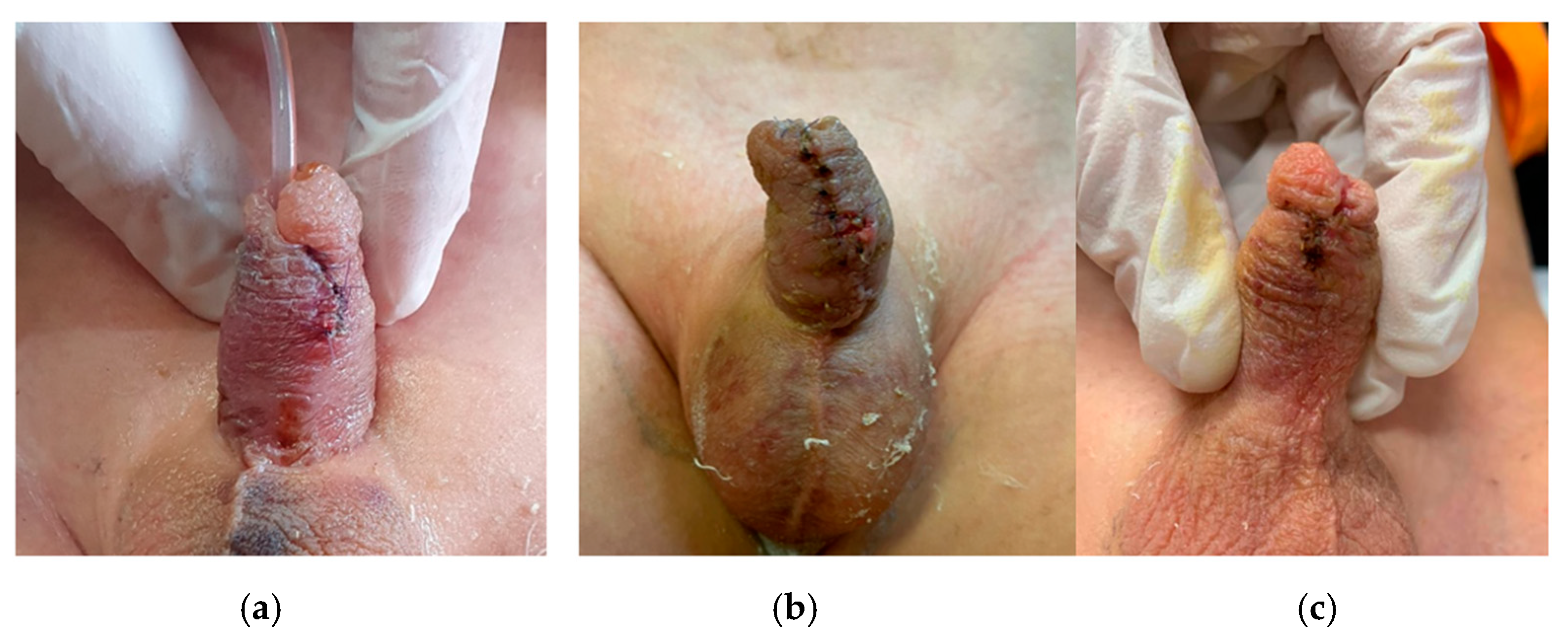
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TIPU | Tubularized Incised Plate Urethroplasty |
| SWAS | Southampton Wound Assessment Scale |
| FLACC | Face, Legs, Activity, Cry, Consolability Scale |
References
- Patil, J.D.; Mohamed, Y.M.; Farhan, A.; Corbally, M.; Patil, J.; Mohamed, Y. Outcomes Assessment of Hypospadias Repair. Cureus 2023, 15, e48808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLorie, G.; Joyner, B.; Herz, D.; McCallum, J.; Bagli, D.; Merguerian, P.; Khoury, A. A prospective randomized clinical trial to evaluate methods of postoperative care of hypospadias. J. Urol. 2001, 165, 1669–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirmer, J.; Fawzy, M.; Sennert, M.; Hadidi, A.T. Should we correct hypospadias during childhood? Decision Regret And Quality of Life Assessment (DRAQULA) study. J. Pediatr. Urol. 2024, 20, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beland, L.E.; Reifsnyder, J.E.; Palmer, L.S. The diversity of hypospadias management in North America: A survey of pediatric urologists. World J. Urol. 2023, 41, 2775–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceccarelli, P.L.; Lucaccioni, L.; Poluzzi, F.; Bianchini, A.; Biondini, D.; Iughetti, L.; Predieri, B. Hypospadias: Clinical approach, surgical technique, and long-term outcome. BMC Pediatr. 2021, 21, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimador, M.; Vallasciani, S.; Manzoni, G.; Rigamonti, W.; De Grazia, E.; Castagnetti, M. Failed hypospadias in paediatric patients. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2013, 10, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Savage, J.G.; Palanca, L.G.; Slaughenhoupt, B.L. A prospective randomized trial of dressing versus no dressings for hypospadias repair. J. Urol. 2000, 164, 981–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangopadhyay, A.N.; Sharma, S. Peha-haft bandage as a new dressing for pediatric hypospadias repair. Indian J. Plast. Surg. 2005, 38, 162–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.M.V.; Rasekhi, A.R.; Zarenezhad, M.; Hedjazi, A. Cyanoacrylate Glue Dressing for Hypospadias Surgery. N. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2012, 4, 320–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.K.; Reid, C.D. A simple penile dressing following hypospadias surgery. Br. J. Plast. Surg. 1990, 43, 628–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narci, A.; Embleton, D.B.; Boyaci, E.O.; Mingir, S.; Cetinkurşun, S. A practical offer for hypospadias dressing: Allevyn. Afr. J. Paediatr. Surg. 2011, 8, 272–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gormley, A.; Fishwick, J.; Whitnall, B. Home dressing removal following hypospadias repair. J. Child Health Care 2007, 11, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertuccio, M.P.; Rizzo, V.; Arena, S.; Trainito, A.; Montalto, A.S.; Caccamo, D.; Currò, M.; Romeo, C.; Impellizzeri, P. Ozoile Reduces the LPS-Induced Inflammatory Response in Colonic Epithelial Cells and THP-1 Monocytes. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 1333–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khafaji, S.S. Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-reprotoxic effects of kaempferol and vitamin E on lead acetate-induced testicular toxicity in male rats. J. Control Release 2015, 207, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, T.; Currò, M.; Ferlazzo, N.; Caccamo, D.; Perrone, P.; Arena, S.; Antonelli, E.; Antonuccio, P.; Ientile, R.; Romeo, C.; et al. Stable Ozonides with Vitamin E Acetate versus Corticosteroid in the Treatment of Lichen Sclerosus in Foreskin: Evaluation of Effects on Inflammation. Urol. Int. 2019, 103, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babl, F.E.; Crellin, D.; Cheng, J.; Sullivan, T.P.; O’Sullivan, R.; Hutchinson, A. The use of the faces, legs, activity, cry and consolability scale to assess procedural pain and distress in young children. Pediatr. Emerg. Care. 2012, 28, 1281–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chua, M.; Welsh, C.; Amir, B.; Silangcruz, J.M.; Ming, J.; Gnech, M.; Sanger, S.; Lorenzo, A.; Braga, L.H.; Bägli, D. Non-stented versus stented urethroplasty for distal hypospadias repair: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Pediatr. Urol. 2018, 14, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, C. Comparison of dressing removal following hypospadias repair. Br. J. Nurs. 2003, 12, S21–S28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redman, J.F. A dressing technique that facilitates outpatient hypospadias surgery. Urology 1991, 37, 248–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Han, C.; Zhou, H.X.; Li, P.; Ma, L.F.; Tao, T.; Zhou, X.G.; Tao, Y.D.; Zhu, W.W.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Clinical evaluation of compound chamomile and lidocaine hydrochloride gel for postoperative hypospadias in children. Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue 2021, 27, 815–818. [Google Scholar]
- Doluoglu, O.G.; Yıldız, Y.; Tokat, E.; Ozgur, B.C.; Kılınc, M.F.; Inan, M.A.; Gonul, I.I.; Hoscan, M.B. The histopathological effect of aloe vera on the wound healing process in a surgically created tubularized incised plate urethroplasty model on rats. J. Investig. Surg. 2022, 35, 1062–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valacchi, G.; Fortino, V.; Bocci, V. The dual action of ozone on the skin. Br. J. Dermatol. 2005, 153, 1096–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Noh, S.U.; Han, Y.W.; Kim, K.M.; Kang, H.; Kim, H.O.; Park, Y.M. Therapeutic effects of topical application of ozone on acute cutaneous wound healing. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2009, 24, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzolin, A.P.; da Silveira-Kaross, N.L.; Bertol, C.D. Ozonated oil in wound healing: What has already been proven? Med. Gas Res. 2020, 10, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, E.; Holland, O.J.; Vanderlelie, J.J. Ozone therapy for the treatment of chronic wounds: A systematic review. Int. Wound J. 2018, 15, 633–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springer, A.; Krois, W.; Horcher, E. Trends in hypospadias surgery: Results of a worldwide survey. Eur. Urol. 2011, 60, 1184–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| G1 N = 43 | G2 N = 43 | Adjusted Treatment Effect (+/−) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median patients age (months) | 19 ± 4.5 | 18 ± 5.2 | n/a | n/a |
| Coronal Hypospadias, n (%) | 37/43 (86%) | 35/43 (81%) | +5% | >0.05 |
| Subcoronal Hypospadia, n (%) | 6/43 (14%) | 8/43 (19%) | −5% | >0.05 |
| Hospital stays (days) | 6 ± 0.6 | 6 ± 0.6 | 0 | >0.05 |
| Follow-up (months) | 15.0 ± 3.9 | 17.0 ± 6.3 | −15.2% | <0.05 |
| Indwelling bladder catheter (days) | 4.3 ± 0.3 | 6.3 ± 0.7 | −4.6% | >0.05 |
| Wound healing time, (days) | 17.2 ± 5.1 | 31.3 ± 16.9 | −32.8% | <0.05 |
| Postoperative complications, n (%) | 2/43 (4.6%) | 7/43 (16.3%) | −12.3% | >0.05 |
| Urethrocutaneous fistula, n (%) | 0 | 2/43 (4.6%) | −4.6% | >0.05 |
| Foreskin dehiscence, n (%) | 2/43 (4.6%) | 2/43 (4.6%) | 0 | >0.05 |
| Meatal stenosis, n (%) | 0 | 1/43 (2.3%) | −2.3% | >0.05 |
| Wound infection, n (%) | 0 | 2/43 (4.6%) | −4.6% | >0.05 |
| Total re-operations, n (%) | 2/43 (4.6%) | 5/43 (11.6%) | −7% | >0.05 |
| Adverse skin reaction, n (%) | 0 | 0 | n/a | n/a |
| No./Total No. (%) G1 | No./Total No. (%) G2 | Absolute Risk Difference (95% CI), % | Relative Risk (95% CI) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wound Healing Complication | |||||
| Red and inflamed | 7/47 (14.9) | 18/47 (38.3) | −23.4% (−38.6 to −8.1) | 0.39 (0.18 to 0.83) | <0.05 |
| Swollen | 6/47 (12.7) | 12/47 (25.5) | −12.8 (−28.4 to 2.8) | 0.50 (0.20 to 1.24) | >0.05 |
| Fever > 38 °C | 3/47 (6.4) | 4/47 (8.5) | −2.1 (−13.3 to 9.1) | 0.75 0.17 to 3.26) | >0.05 |
| Fluid Leaking (not pus) | 12/47 (25.5) | 14/47 (29.8) | −4.3 (−21.1 to 12.5) | 0.86 (0.44 to 1.69) | >0.05 |
| G1 n = 43 | G2 n = 43 | p (X2) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Evaluation of the dressing used | |||
| Easy of Application | 0.0006 | ||
| Excellent | 29 (67.5%) | 13 (30.2%) | |
| Good | 9 (21%) | 9 (21%) | |
| Fair | 5 (11.6%) | 20 (46.5%) | |
| Poor | 0 (0%) | 1 (2.3%) | |
| Time Spent | 0.0087 | ||
| Excellent | 31 (72%) | 19 (44.2%) | |
| Good | 10 (23.2%) | 12 (28%) | |
| Fair | 2 (4.6%) | 7 (16.2%) | |
| Poor | 0 | 5 (11.6%) | |
| Status and Cleanliness | 0.56 | ||
| Excellent | 35 (81.4%) | 37 (86%) | |
| Good | 8 (18.6%) | 5 (11.6%) | |
| Fair | 0 | 1 (2.3%) | |
| Poor | 0 | 0 | |
| Comfort and Safety | 0.66 | ||
| Excellent | 18 (41.8%) | 20 (46.5%) | |
| Good | 15 (34.9%) | 11 (25.6%) | |
| Fair | 10 (23.2%) | 12 (28%) | |
| Poor | 0 | 0 | |
| Reliability | 0.0006 | ||
| Excellent | 28 (65.1%) | 12 (28%) | |
| Good | 11 (25.6%) | 18 (41.9%) | |
| Fair | 5 (11.6%) | 12 (27.9%) | |
| Poor | 0 | 2 (4.6%) | |
| Cost | 0.0001 | ||
| Excellent | 33 (76.7%) | 3 (6.9%) | |
| Good | 9 (20.9%) | 8 (18.6%) | |
| Fair | 1 (2.3%) | 13 (30.2%) | |
| Poor | 0 | 19 (44.1%) | |
| Face, Legs, Activity, Cry, Consolability (FLACC) Scale | P (t) | ||
| FLACC Scale at t.1 | 8 (6–10) | 6–7 (4–9) | 0.0001 |
| 0: relaxed and comfortable | |||
| 1–3: mild discomfort | |||
| 4–6: moderate pain | |||
| 7–10: severe discomfort of pain or both | |||
| FLACC Scale at t.3 | 4 (3–5) | 5–6 (4–7) | 0.01 |
| FLACC Scale at t.7 | 1 (0–2) | 3 (1–5) | 0.0001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Coppola, V.; Escolino, M.; Del Conte, F.; Di Mento, C.; Carraturo, F.; Esposito, G.; Tedesco, F.; Guglielmini, R.; Esposito, C. Ozonated Olive Oil Dressing for Pediatric Hypospadias Repair: A Prospective Randomized Clinical Trial. Children 2025, 12, 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12050549
Coppola V, Escolino M, Del Conte F, Di Mento C, Carraturo F, Esposito G, Tedesco F, Guglielmini R, Esposito C. Ozonated Olive Oil Dressing for Pediatric Hypospadias Repair: A Prospective Randomized Clinical Trial. Children. 2025; 12(5):549. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12050549
Chicago/Turabian StyleCoppola, Vincenzo, Maria Escolino, Fulvia Del Conte, Claudia Di Mento, Francesca Carraturo, Giovanni Esposito, Francesco Tedesco, Roberta Guglielmini, and Ciro Esposito. 2025. "Ozonated Olive Oil Dressing for Pediatric Hypospadias Repair: A Prospective Randomized Clinical Trial" Children 12, no. 5: 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12050549
APA StyleCoppola, V., Escolino, M., Del Conte, F., Di Mento, C., Carraturo, F., Esposito, G., Tedesco, F., Guglielmini, R., & Esposito, C. (2025). Ozonated Olive Oil Dressing for Pediatric Hypospadias Repair: A Prospective Randomized Clinical Trial. Children, 12(5), 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12050549









