Nitinol Type Alloys General Characteristics and Applications in Endodontics
Abstract
:1. Endodontic Treatment Social Significance and General Objectives of the Paper
2. The Importance of Tools Made of Ni–Ti Alloy of the Nitinol Type in Endodontic Treatment
- ✓
- Correct selection of filling material.
- ✓
- Choosing the right obturation technique.
3. Chemical Composition, Methods of Nitinol Manufacturing, and Conventional Technologies for the Endodontic Tools Manufacturing
4. Shape Memory Effect and Superelasticity of Nitinol
- One-way shape memory effect.
- Superelasticity.
- Bidirectional shape memory effect.
5. The Importance of Heat Treatment and Other Technological Processes of Shaping the Structure and Properties of Nitinol Alloys Used in the Production of Endodontic Tools
6. The Influence of Sterilization on the Possibility of Using Nitinol Endodontic Tools
7. SWOT Analysis of Strengths and Weaknesses as Well as Opportunities and Threats of Using Nitinol Tools in Endodontics and Forecast of Their Strategic Development
8. Recapitulation and Final Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oxilia, G.; Peresani, M.; Romandini, M.; Matteucci, C.; Debono Spiteri, C.; Henry, A.G.; Schulz, D.; Archer, W.; Crezzini, J.; Boschin, F.; et al. Earliest evidence of dental caries manipulation in the Late Upper Palaeolithic. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobrzański, L.A.; Dobrzański, L.B.; Dobrzańska-Danikiewicz, A.D.; Dobrzańska, J. The Concept of Sustainable Development of Modern Dentistry. Processes 2020, 8, 1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J.P. The Art of Medicine in Ancient Egypt; The Metropolitan Museum of Art: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Frayer, D.W.; Gatti, J.; Monge, J.; Radovčic, D. Prehistoric dentistry? P4 rotation, partial M3 impaction, toothpick grooves and other signs of manipulation in krapina dental person 20. Bull. Int. Assoc. Paleodont. 2017, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Caldas, A.F., Jr. Reason for tooth extraction in a Brazilian population. Int. Dent. J. 2000, 50, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chestnutt, I.G.; Binnie, V.I.; Taylor, M.M. Reason for tooth extraction in Scotland. J. Dent. 2000, 28, 295–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, M.; Kimura, T.; Kanegae, M.; Ishikawa, A.; Watanobe, T. Reasons for extraction of permanent teeth in Japan. Community Dent. Oral. Epidemiol. 1994, 22, 303–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelillo, I.F.; Nobile, C.G.A.; Pavia, M. Survey of reasons for extraction of permanent teeth in Italy. Community Dent. Oral. Epidemiol. 1996, 24, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shammari, K.F.; Al-Arsari, J.M.; Al-Melh, M.A.; Al-Khabhaz, A.K. Reasons for tooth extraction in Kuwait. Med. Princ. Pract. 2006, 15, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollandra, A.C.B.; de Alencar, A.H.G.; de Estrela, C.R.A.; Bueno, M.R.; Estrela, C. Prevalance of Endodontically Trale Teeth in a Brazilian Adult Population. Braz. Dent. J. 2008, 19, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fejerskov, O. Concepts of dental caries and their consequences for understanding the disease. Community Dent. Oral Epidemiol. 1997, 25, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reisine, S.; Litt, M. Social and psychological theories and their use for dental practice. Int. Dent. J. 1993, 43 (Suppl. 1), 279–287. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Selwitz, R.H.; Ismail, A.I.; Pitts, N.B. Dental caries. Lancet 2007, 369, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Abbott, P.V. An overview of the dental pulp: Its functions and responses to injury. Aust. Dent. J. 2007, 52, S4–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harumi Miyagi, S.P.; Kerkis, I.; da Costa Maranduba, C.M.; Gomes, C.M.; Martinis, M.D.; Marques, M.M. Expression of extracellular matrix proteins in human dental pulp stem cells depends on the donor tooth conditions. J. Endod. 2010, 36, 826–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, C.L.Z.; Caramelli, B. The history of dentistry and medicine relationship: Could the mounth finally return to the body? Oral Dis. 2009, 15, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallasch, T.J.; Wahl, M.J. Focal infection: New age or ancient history? Endod. Top. 2003, 4, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mueller, A.A.; Saldami, B.; Stübinger, S.; Walter, C.; Flückiger, U.; Merlo, A.; Schwenzer-Zimmerer, K.; Zeilhofer, H.F.; Zimmerer, S. Oral bacterial cultures in nontraumatic brain abscesses: Results of a first line study. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2009, 107, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buset, S.L.; Walter, C.; Friedmann, A.; Weiger, R.; Borgnakke, W.S.; Zitzmann, N.U. Are periodontal diseases really silent? A systematic review of their effect on quality of life. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2016, 43, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierpinska, T.; Golebiewska, M.; Dlugosz, J.W.; Kemona, A.; Laszewicz, W. Connection between masticatory efficiency and pathomorphologic changes in gastric mucosa. Quint. Int. 2007, 38, 31–37. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Nawas, B.; Maeurer, M. Severe versus local odontogenic bacterial infections: Comparision of microbial isolates. Eur. Surg. Res. 2008, 40, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Pablo, P.; Dietrich, T.; McAlindon, T.E. Association of periodontal disease and tooth loss with rheumatoid arthritis in the US population. J. Rheumatol. 2008, 35, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Felton, D.A. Edentualism and comorbid factors. J. Prosthodont. 2009, 18, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volzke, H.; Schwahn, C.; Hummel, A.; Wolff, B.; Kleine, V.; Robinson, D.M.; Dahm, J.B.; Felix, S.B.; John, U.; Kocher, T. Tooth loss is independently associated with the risk of acquired aortic valve sclerosis. Am. Heart J. 2005, 150, 1198–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagchi, S.; Tripathi, A.; Tripathi, S.; Kar, S.; Tiwari, S.C.; Singh, J. Obstructive sleep apnea and neurocognitive dysfunction in edentulous patients. J. Prosthodont. 2019, 28, e837–e842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagpal, R.; Yamashiro, Y.; Izumi, Y. The two-way association of periodontal infection with systemic disorders: An overview. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 793898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abnet, C.C.; Qiao, Y.L.; Dawsey, S.M.; Dong, Z.W.; Taylor, P.R.; Mark, S.D. Tooth loss is associated with increased risk of total death and death from upper gastrointestinal cancer, heart disease, and stroke in a Chinese population-based cohort. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2005, 34, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burzyńska, B.; Mierzwińska-Nastalska, E. Rehabilitacja protetyczna pacjentów bezzębnych. Nowa Stomatol. 2011, 4, 167–199. [Google Scholar]
- Bui, F.Q.; Almeida-da-Silva, C.L.C.; Huynh, B.; Trinh, A.; Liu, J.; Woodward, J.; Asadi, H.; Ojcius, D.M. Association between periodontal pathogens and systemic disease. Biomed. J. 2019, 42, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmlund, A.; Holm, G.; Lind, L. Number of teeth as a predictor of cardiovascular mortality in a cohort of 7674 subjects followed for 12 years. J. Periodontol. 2010, 81, 870–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takata, Y.; Ansai, T.; Matsumura, K.; Awano, S.; Hamasaki, T.; Sonoki, K.; Kusaba, A.; Akifusa, S.; Takehara, T. Relationship between tooth loss and electrocardiographic abnormalities in octogenarians. J. Dent. Res. 2001, 80, 1648–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felton, D.A. Complete edentulism and comorbid diseases: An update. J. Prosthodont. 2016, 25, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Iinuma, M.; Onozuka, M.; Kubo, K.-Y. Chewing maintains hippocampus-dependent cognitive. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2015, 12, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stein, P.S.; Desrosiers, M.; Donegan, S.J.; Yepes, J.F.; Kryscio, R.J. Tooth loss, dementia and neuropathology in the Nun study. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2007, 138, 1314–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henke, K. A model for memory systems based on processing modes rather than consciousness. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2010, 11, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lexomboon, D.; Trulsson, M.; Wårdh, I.; Parker, W.G. Chewing ability and tooth loss: Association with cognitive impairment in an elderly population study. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2012, 60, 1951–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, Y.; Obata, T.; Takahashi, H.; Tachibana, A.; Kuroiwa, D.; Takahashi, T.; Ikehira, H.; Onozuka, M. Effects of chewing on cognitive processing speed. Brain Cognit. 2013, 81, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onishi, M.; Iinuma, M.; Tamura, Y.; Kubo, K.Y. Learning deficits and suppression of the cell proliferation in the hippocampal dentate gyrus of offspring are attenuated by maternal chewing during prenatal stress. Neurosci. Lett. 2014, 560, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawahata, M.; Ono, Y.; Ohno, A.; Kawamoto, S.; Kimoto, K.; Onozuka, M. Loss of molars early in life develops behavioral lateralization and impairs hippocampus-dependent recognition memory. BMC Neurosci. 2014, 15, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Tornstad, L.; Olsen, I. Brain abscesses caused by oral infection. Dent. Traumatol. 1999, 15, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scannapieco, F.A.; Bush, R.B.; Paju, S. Associations between periodontal disease and risk for nosocomial bacterial pneumonia and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. A systemic review. Ann. Periodontol. 2003, 8, 54–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dobrzański, L.A.; Dobrzański, L.B.; Dobrzańska-Danikiewicz, A.D.; Dobrzańska, J.; Rudziarczyk, K.; Achtelik-Franczak, A. Non-antagonistic contradictoriness of the progress of advanced digitized production with SARS-CoV-2 virus transmission in the area of dental engineering. Processes 2020, 8, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksander, M.; Krishnan, B.; Shenoy, N. Diabetes mellitus and odontogenic infections-an exaggerated risk? Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2008, 12, 129–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scannapieco, F.A. Role of oral bacteria in respiratory infection. J. Periodontol. 1999, 70, 793–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Peres, K.G.; Peres, M.A. Retention of teeth and oral health-related quality of life. J. Dent. Res. 2016, 95, 1350–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, C.J.L.; Lopez, A.D. The Global Burden of Disease: A Comprehensive Assessment of Mortality and Disability from Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors in 1990 and Projected to 2020; University Press on behalf of the World Health Organization and The World Bank: Boston, MA, USA; Harvard: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1996; Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/41864 (accessed on 17 August 2021).
- Dobrzańska, J.; Dobrzański, L.B.; Gołombek, K.; Dobrzański, L.A.; Dobrzańska-Danikiewicz, A.D. Virtual approach to the comparative analysis of biomaterials used in endodontic treatment. Processes 2021, 9, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellucci, A. Endodontics; Il Tridente Edizioni Odontolatriche: Bologna, Italy, 2005; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Alwadani, M.; Mashyakhy, M.H.; Jali, A.; Hakami, A.O.; Areshi, A.; Daghriri, A.A.; Shaabi, F.I.; Al Moaleem, M.M. Dentists and Dental Intern’s Preferences of Root Canal Treatment with Restoration Versus Extraction then Implant-Supported Crown Treatment Plan. Open Dent. J. 2019, 13, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrela, C.; Holland, R.; Estrela, C.R.; Alencar, A.H.; Sousa-Neto, M.D.; Pécora, J.D. Characterization of successful root canal treatment. Braz. Dent. J. 2014, 25, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dental Consumables Market by Product [Dental Implants (Root Form Dental Implants and Plate Form Dental Implants), Dental Prosthetics (Crowns, Bridges, Dentures, Abutments, Veneers, and Inlays & Onlays), Endodontics (Endodontic Files, Obturators, and Permanent Endodontic Sealers), Orthodontics (Brackets, Archwires, Anchorage Appliances, and Ligatures), Periodontics (Dental Sutures and Dental Hemostats), Retail Dental Care Essentials (Specialized Dental Pastes, Dental Brushes, Dental Wash Solutions, Whitening Agents, and Dental Floss), and Other Dental Consumables (Dental Splints, Dental Sealants, Dental Burs, Dental Impression Materials, Dental Disposables, Bonding Agents, Patient Bibs, and Aspirator Tubes & Saliva Ejectors)]—Global Opportunity Analysis and Industry Forecast, 2017–2023. Available online: https://www.alliedmarketresearch.com/dental-consumables-market (accessed on 7 May 2021).
- Endodontic Devices Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report by Type (Instruments, Consumables), by End Use (Hospitals, Clinics, Dental Academic & Research Institutes), and Segment Forecasts, 2019–2026. Available online: https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/endodontic-devices-market (accessed on 7 May 2021).
- Dental Endodontics Market (Product—Instruments (Endodontic Scalers & Lasers, Motors, Apex Locators, and Machine Assisted Obturation Systems) and Consumables (Obturation, Shaping and Cleaning, and Access Cavity Preparation); End User: Dental Hospitals, Dental Clinics, and Dental Academic & Research Institutes)—Global Industry Analysis, Size, Share, Growth, Trends, and Forecast 2017–2025. Available online: https://www.transparencymarketresearch.com/dental-endodontics-market.html (accessed on 7 May 2021).
- Dobrzański, L.A.; Dobrzańska-Danikiewicz, A.D.; Dobrzański, L.B. Effect of Biomedical Materials in the implementation of a long and healthy life policy. Processes 2021, 9, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrzański, L.A.; Dobrzańska-Danikiewicz, A.D.; Dobrzański, L.B.; Dobrzańska, J. The Importance of Synthesis and Characterization of Biomedical Materials for the Current State of Medicine and Dentistry. Processes 2021, 9, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrzański, L.A.; Dobrzański, L.B. Dentistry 4.0 Concept in the Design and Manufacturing of Prosthetic Dental Restorations. Processes 2020, 8, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrzański, L.A.; Dobrzański, L.B.; Achtelik-Franczak, A.; Dobrzańska, J. Application Solid Laser-Sintered or Machined Ti6Al4V Alloy in Manufacturing of Dental Implants and Dental Prosthetic Restorations According to Dentistry 4.0 Concept. Processes 2020, 8, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peres, M.A.; Macpherson, L.M.D.; Weyant, R.J.; Daly, B.; Venturelli, R.; Mathur, M.R.; Listl, S.; Celeste, R.K.; Guarnizo-Herreño, C.C.; Kearns, C.; et al. Oral diseases: A global public health challenge. Lancet 2019, 394, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watt, R.G.; Daly, B.; Allison, P.; Macpherson, L.M.D.; Venturelli, R.; Listl, S.; Weyant, R.J.; Mathur, M.R.; Guarnizo-Herreño, C.C.; Celeste, R.K.; et al. Ending the neglect of global oral health: Time for radical action. Lancet 2019, 394, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrotte, P. Endodontics: Part 1. The modern concept of root canal treatment. Br. Dent. J. 2004, 197, 181–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siqueira, J.F.; Rocas, I.N.; Lopes, H.P.; de Uzeda, M. Coronal leakage of two root canal sealers containing calcium hydroxide after exposure to human saliva. J. Endod. 1999, 25, 14–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, J.M.; Ahlstrom, U.; Henrikson, P.A.; Peterson, L.E. Periapical surgery. Int. J. Oral Surg. 1979, 8, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundqvist, G.; Figdor, D.; Persson, S.; Sjörgren, U. Microbiological analysis of teeth with failed endodontic treatment and the outcome of conservative re-treatment. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 1998, 85, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ǿstravik, D. Materials used for root canal obturation: Technical, biological and clinical testing. Endod. Top. 2005, 12, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrzańska, J.; Dobrzański, L.B.; Gołombek, K.; Dobrzański, L.A. Is gutta-percha still the “gold standard” among filling materials in endodontic treatment? Processes 2021, 9, 1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrzański, L.A.; Dobrzańska, J.; Dobrzański, L.B.; Dobrzańska-Danikiewicz, A.D.; Gołombek, K. Development Strategy of Endodontic Filling Materials Based on Engineering and Medical Approaches. Processes 2021, 9, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrzańska, J.; Dobrzański, L.B.; Dobrzański, L.A.; Dobrzańska-Danikiewicz, A.D.; Gołombek, K. What Are the Chances of Resilon to Dominate the Market Filling Materials for Endodontics? Metals 2021, 11, 1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stabholz, A.; Sahar-Helft, S.; Moshonov, J. Lasers in endodontics. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 2004, 48, 809–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, Y.; Wilder-Smith, P.; Matsumoto, K. Lasers in endodontics: A review. Int. Endod. J. 2000, 33, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Sluis, L.W.M.; Versluis, M.; Wu, M.K.; Wasserlink, P.R. Passive ultrasonic irrigation of the root canal: A review of the literature. Int. Endod. J. 2007, 40, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, R.A.; Ahmad, M.; Crum, L.A. Physical mechanisms governing the hydrodynamic response of an oscillating ultrasonic file. Int. Endod. J. 1994, 27, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huque, J.; Kota, K.; Yamaga, M.; Iwaku, M.; Hoshino, E. Bacterial eradication from root dentine by ultrasonic irrigation with sodium hypochloride. Int. Endod. J. 1998, 31, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hülsmann, M.; Paters, O.A.; Dummer, P.M.H. Mechanical preparation of root canals: Shaping goals, techniques and means. Endod. Top. 2005, 10, 30–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walia, H.M.; Brantley, W.A.; Gerstein, H. An initial investigation of the bending and torsional properties of Nitinol root canal files. J. Endod. 1988, 14, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.E.; Price, J.H.W.; Parashos, P. Fracture resistance of electropolished rotary Nickel-Titanium endodontic instruments. J. Endod. 2007, 33, 1212–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duerig, T.; Pelton, A.; Stöckel, D. An overview of nitinol medical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1999, 273–275, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fife, D.; Gambarini, G.; Britto, L.R. Cyclic fatigue testing of ProTaper NiTi rotary instruments after clinical use. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2004, 97, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutmann, J.L.; Gao, Y. Alteration in the inherent metallic and surface properties of nickel-titanium root canal instruments to enhance performance, durability and safety: A focused review. Int. Endod. J. 2012, 45, 113–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruett, J.P.; Clement, D.J.; Carnes, D.L., Jr. Cyclic fatigue testing of nickel-titanium endodontic instruments. J. Endod. 1997, 23, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metallurgy: The Alloy That Remembers. Available online: http://content.time.com/time/subscriber/article/0,33009,838687,00.html (accessed on 10 May 2021).
- Buehler, W.J.; Gilfrich, J.W.; Wiley, R.C. Effects of Low-Temperature Phase Changes on the Mechanical Properties of Alloys Near Composition TiNi. J. App. Phys. 1963, 34, 1475–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.E.; Buehler, W.J.; Pickart, S.J. Crystal Structure and a Unique Martensitic Transition of TiNi. J. App. Phys. 1965, 36, 3232–3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauffman, G.B.; Mayo, I. The Story of Nitinol: The Serendipitous Discovery of the Memory Metal and Its Applications. Chem Edu. 1997, 2, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Withers, N. Nitinol. Available online: https://www.chemistryworld.com/podcasts/nitinol/6710.article (accessed on 10 May 2021).
- Ölander, A. An Electrochemical Investigation of Solid Cadmium-Gold Alloys. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1932, 54, 3819–3833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornbogen, E.; Wassermann, G. Über den Einfluβ von Spannungen und das Auftreten von Umwandlungsplastizität bei β1-β-Umwandlung des Messings. Z. Metalkd. 1956, 47, 427–433. [Google Scholar]
- Tamburrino, F.; Apicella, A.; Aversa, R.; Petrescu, F.I.T. Advanced Manufacturing for Novel Materials in Industrial Design Applications. Am. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2018, 11, 932–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, H.; Wu, M.H.; Zhou, F.; McMeeking, R.M.; Ritchie, R.O. The influence of mean strain on the high-cycle fatigue of Nitinol with application to medical devices. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2020, 143, 104057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoeckel, D.; Pelton, A.; Duerig, T. Self-expanding nitinol stents: Material and design considerations. Eur. Radiol. 2004, 14, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanz, J.; Kim, W.-K.; Walther, T.; Burgdorf, C.; Möllmann, H.; Linke, A.; Redwood, S.; Thilo, C.; Hilker, M.; Joner, M.; et al. Safety and efficacy of a self-expanding versus a balloon-expandable bioprosthesis for transcatheter aortic valve replacement in patients with symptomatic severe aortic stenosis: A randomised non-inferiority trial. Lancet 2019, 394, 1619–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelton, A.R.; Schroeder, V.; Mitchell, M.R.; Gong, X.Y.; Barney, M.; Robertson, S.W. Fatigue and durability of Nitinol stents. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2008, 1, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassi, C.J. Inferior vena caval filters: Analysis of five currently available devices. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1991, 156, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hull, J.E.; Robertson, S.W. Bard Recovery filter: Evaluation and management of vena cava limb perforation, fracture, and migration. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2009, 20, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, S.W.; Pelton, A.R.; Ritchie, R.O. Mechanical fatigue and fracture of Nitinol. Int. Mater. Rev. 2012, 57, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, S. Fatigue of Materials, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1998; pp. 1–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.P.; Wilson, N.M.; Hallett, R.L.; Herfkens, R.J.; Taylor, C.A. In vivo MR angiographic quantification of axial and twisting deformations of the superficial femoral artery resulting from maximum hip and knee flexion. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2006, 17, 979–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, E.H.; Johnson, E.D.; Arko, F.R. Evaluation of wall motion and dynamic geometry of the inferior vena cava using intravascular ultrasound: Implications for future device design. J. Endovasc. Ther. 2008, 15, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milnor, W.R. Hemodynamics; Williams & Wilkins: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1982; pp. 1–390. [Google Scholar]
- Laborda, A.; Sierre, S.; Malvé, M.; De Blas, I.; Ioakeim, I.; Kuo, W.T.; De Gregorio, M.A. Influence of breathing movements and Valsalva maneuver on vena caval dynamics. World J. Radiol. 2014, 6, 833–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dobrzański, L.A.; Dobrzański, L.B.; Dobrzańska-Danikiewicz, A.D.; Dobrzańska, J.; Kraszewska, M. The synergistic ethics interaction with nanoengineering, dentistry, and dental engineering. In Ethics in Nanotechnology; Emerging Technologies Aspects; Van de Voorde, M., Jeswani, G., Eds.; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2021; Volume I, pp. 119–189. [Google Scholar]
- Brantley, W.A. Evolution, clinical applications, and prospects of nickel-titanium alloys for orthodontic purposes. J. World Fed. Orthod. 2020, 9, S19–S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harshavardhan, J.M.; Dhanavel, C.; Vijayaraja, S.; Manoj, K.T.; Bakkiyalakshmi, A.; Kavimalar, S. Metallurgy of Rotary Files—A Review. J. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2021, 4, 975–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, L.; Bronnec, F.; Machtou, P. Endodontic Instruments and Canal Preparation Techniques. In Endodontic Materials in Clinical Practice; Camilleri, J., Ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 81–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlicka, H.; Ebert, J.; Prociów, A. Systematyka rotacyjnych narzędzi niklowo-tytanowych. Czas. Stomatol. 2005, 58, 709–713. [Google Scholar]
- Hryniewicz, T.; Rokosz, K.; Rokicki, R. Magnetoelectropolishing process improves characteristics of finished metal surfaces: Intensity of externally applied magnetic field, plus oxygen control, manipulates rate of dissolution in electropolishing. Met. Finish. 2006, 104, 26–31, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hryniewicz, T. Wstęp do Obróbki Powierzchniowej Biomateriałów Metalowych; Wyd. Politechniki Koszalińskiej: Koszalin, Poland, 2007; pp. 1–155. [Google Scholar]
- Rokicki, R.; Hryniewicz, T. Nitinol Surface Finishing by Magnetoelectropolishing. Trans. Inst. Met. Finish. 2008, 86, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hryniewicz, T.; Rokicki, R.; Rokosz, K. Modifying Metallic Implants with Magnetoelectropolishing. Med. Dev. Diagn. Indust. 2008, 30, 102–111. [Google Scholar]
- Mtwo. The Efficient NiTi Sytem. Available online: https://www.vdw-dental.com/en/products/detail/mtwo/ (accessed on 7 May 2021).
- Hryniewicz, T.; Rokosz, K. On the wear inspection and endurance recovery of Nitinol endodontic files. PAK 2009, 55, 247–250. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, P.; Cheng, F.T.; Man, H.C. Improvement in corrosion resistance of NiTi by anodization in acetic acid. Mater. Lett. 2007, 61, 2385–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibris, N.; Rosca, J.C.M. EIS study of Ti and its alloys in biological media. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2002, 526, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Dodd, R.A.; Crone, W.C. Corrosion and wear-corrosion behaviour of NiTi modified by plasma source implantation. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 3931–3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.T.; Shi, P.; Man, H.C. A preliminary study of TiO2 deposition on NiTi by a hydrothermal method. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2004, 187, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueira, N.; Silva, T.M.; Carmezim, M.J.; Fernandes, J.C.S. Corrosion behaviour of NiTi alloy. Electrochim. Acta 2009, 54, 921–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabalovskaya, S.A. Surface, corrosion and biocompatibility aspects of Nitinol as an implant material. Biomed. Mater. Eng. 2002, 12, 69–109. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Venugopalan, R.; Trépanier, C. Assessing the corrosion behaviour of Nitinol for minimally-invasive device design. Min. Invas. Therap. Allied Technol. 2000, 9, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondelli, G.; Brunella, M.F.; De Nardo, L.; Cigada, A. Corrosion Behaviour of Nitinol Vascular Stents. Adv. Sci. Technol. 2006, 49, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInnes, P.M.; Wendt, S.L., Jr.; Retief, D.H.; Weinberg, R. Effect of dentin surface roughness on shear bond strength. Dent. Mater. 1990, 6, 204–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, S.A. An overview of nickel–titanium alloys used in dentistry. Int. Endod. J. 2000, 33, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Himel, V.T.; Ahmed, K.M.; Wood, D.M.; Alhadainy, H.A. An evaluation of nitinol and stainless steel files used by dental students during a laboratory proficiency exam. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 1995, 79, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelton, A.R.; Stöckel, D.; Duerig, T.W. Medical Uses of Nitinol. MSF 2000, 327–328, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Civjan, S.; Huget, E.F.; DeSimon, L.B. Potential applications of certain nickel-titanium (nitinol) alloys. J. Dent. Res. 1975, 54, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karacay, S.; Akin, E.; Olmez, H.; Gurton, A.U.; Sagdic, D. Forsus Nitinol Flat Spring and Jasper Jumper corrections of Class II division 1 malocclusions. Angle Orthod. 2006, 76, 666–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.H.; Park, B.; Saxena, A.; Serene, T.P. Enhanced surface hardness by boron implantation in Nitinol alloy. J. Endod. 1996, 22, 543–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadood, A. Brief Overview on Nitinol as Biomaterial. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2016, 4173138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cutright, D.E.; Bhaskar, S.N.; Perez, B.; Johnson, R.M.; Cowan, G.S., Jr. Tissue reaction to nitinol wire alloy. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. 1973, 35, 578–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, O.T.; Jansen, C.E.; Seo, Y.; Yellich, G. Guided Nitinol-Retained (Smileloc) Single-Tooth Dental Restorations. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 31, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glossen, C.R.; Haller, R.H.; Dove, S.B.; del Rio, C.E. A comparison of root canal preparations using Ni-Ti hand, Ni-Ti engine-driven, and K-Flex endodontic instruments. J. Endod. 1995, 21, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, J.A.; Morgan, L.A.; Baumgartner, J.C. A comparison of canal centering ability of four instrumentation techniques. J. Endod. 1997, 23, 503–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, E. Shaping ability of Hero 642 rotary nickel-titanium instruments and stainless steel hand K-Flexofiles in simulated curved root canals. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2001, 92, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schäfer, E.; Lohmann, D. Efficiency of rotary nickel-titanium FlexMaster instruments compared with stainless steel hand K-Flexofile—Part 1. Shaping ability in simulated curved canals. Int. Endod. J. 2002, 35, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, R.G.; McIlwain, E.D.; Peyton, F.A. Bending and torsion properties of endodontic instruments. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. 1968, 25, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, A.C.; Chaves Craveiro de Melo, M.; Guiomar de Azevedo Bahia, M.; Lopes Buono, V.T. Relationship between flexibility and physical, chemical, and geometric characteristics of rotary nickel-titanium instruments. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2010, 110, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zupanc, J.; Vahdat-Pajouh, N.; Schäfer, E. New thermomechanically treated NiTi alloys—A review. Int. Endod. J. 2018, 51, 1088–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tabassum, S.; Zafar, K.; Umer, F. Nickel-Titanium Rotary File Systems: What’s New? Eur. Endod. J. 2019, 4, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dioguardi, M.; Laneve, E.; Di Cosola, M.; Cazzolla, A.P.; Sovereto, D.; Aiuto, R.; Laino, L.; Leanza, T.; Alovisi, M.; Troiano, G.; et al. The Effects of Sterilization Procedures on the Cutting Efficiency of Endodontic Instruments: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Materials 2021, 14, 1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dioguardi, M.; Sovereto, D.; Aiuto, R.; Laino, L.; Illuzzi, G.; Laneve, E.; Raddato, B.; Caponio, V.C.A.; Dioguardi, A.; Zhurakivska, K.; et al. Effects of Hot Sterilization on Torsional Properties of Endodontic Instruments: Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Materials 2019, 12, 2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dioguardi, M.; Sovereto, D.; Illuzzi, G.; Laneve, E.; Raddato, B.; Arena, C.; Caponio, V.C.A.; Caloro, G.A.; Zhurakivska, K.; Troiano, G.; et al. Management of Instrument Sterilization Workflow in Endodontics: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Dent. 2020, 2020, 5824369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lo Russo, G.; Spolveri, F.; Ciancio, F.; Mori, A. Mendeley: An easy way to manage, share, and synchronize papers and citations. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2013, 131, 946e–947e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Green, S. Cochrane Collaboration. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions; Wiley-Blackwell: Chichester, UK; Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; p. 649. [Google Scholar]
- Lo, C.K.-L.; Mertz, D.; Loeb, M. Newcastle-Ottawa Scale: Comparing reviewers’ to authors’ assessments. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2014, 14, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- La Rosa, G.R.M.; Shumakova, V.; Isola, G.; Indelicato, F.; Bugea, C.; Pedullà, E. Evaluation of the Cyclic Fatigue of Two Single Files at Body and Room Temperature with Different Radii of Curvature. Materials 2021, 14, 2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Kum, K.-Y.; Perinpanayagam, H.; Kim, C.; Kum, D.J.; Lim, S.-M.; Chang, S.-W.; Baek, S.-H.; Zhu, Q.; Yoo, Y.-J. Various heat-treated nickel–titanium rotary instruments evaluated in S-shaped simulated resin canals. J. Dent. Sci. 2017, 12, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dobrzański, L.A. Materiały Inżynierskie i Projektowanie Materiałowe: Podstawy Nauki o Materiałach i Metaloznawstwo, 2nd ed.; WNT: Warszawa, Poland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Dobrzański, L.A. Significance of materials science for the future development of societies. J. Mater. Proc. Technol. 2006, 175, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrzański, L.A. Podstawy Metodologii Projektowania Materiałowego; Wydawnictwo Politechniki Śląskiej: Gliwice, Poland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Rahim, M.; Frenzel, J.; Frotscher, M.; Pfetzing-Micklich, J.; Steegmüller, R.; Wohlschlögel, M.; Mughrabi, H.; Eggeler, G. Impurity levels and fatigue lives of pseudoelastic NiTi shape memory alloys. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 3667–3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmans, L.; van Cleynenbreugel, J.; Wevers, M.; Lambrechts, P. Mechanical root canal preparation with NiTi rotary instruments: Rationale, performance and safety. Status report for the American Journal of Dentistry. Am. J. Dent. 2001, 14, 324–333. [Google Scholar]
- Sattapan, B.; Nervo, G.J.; Palamara, J.E.; Messer, H.H. Defects in rotary nickel-titanium files after clinical use. J. Endod. 2000, 26, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martín, B.; Zelada, G.; Varela, P.; Bahillo, J.G.; Magán, F.; Ahn, S.; Rodríguez, C. Factors influencing the fracture of nickel-titanium rotary instruments. Int. Endod. J. 2003, 36, 262–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, M.C.; Pereira, E.S.; Viana, A.C.; Fonseca, A.M.; Buono, V.T.; Bahia, M.G. Dimensional characterization and mechanical behaviour of K3 rotary instruments. Int. Endod. J. 2008, 41, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vasconcelos, R.A.; Murphy, S.; Carvalho, C.A.; Govindjee, R.G.; Govindjee, S.; Peters, O.A. Evidence for Reduced Fatigue Resistance of Contemporary Rotary Instruments Exposed to Body Temperature. J. Endod. 2016, 42, 782–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dosanjh, A.; Paurazas, S.; Askar, M. The Effect of Temperature on Cyclic Fatigue of Nickel-titanium Rotary Endodontic Instruments. J. Endod. 2017, 43, 823–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grande, N.M.; Plotino, G.; Silla, E.; Pedullà, E.; DeDeus, G.; Gambarini, G.; Somma, F. Environmental Temperature Drastically Affects Flexural Fatigue Resistance of Nickel-titanium Rotary Files. J. Endod. 2017, 43, 1157–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotino, G.; Grande, N.M.; Mercadé Bellido, M.; Testarelli, L.; Gambarini, G. Influence of Temperature on Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of ProTaper Gold and ProTaper Universal Rotary Files. J. Endod. 2017, 43, 200–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedullà, E.; Grande, N.M.; Plotino, G.; Gambarini, G.; Rapisarda, E. Influence of continuous or reciprocating motion on cyclic fatigue resistance of 4 different nickel-titanium rotary instruments. J. Endod. 2013, 39, 258–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Higueras, J.J.; Arias, A.; de la Macorra, J.C. Cyclic fatigue resistance of K3, K3XF, and twisted file nickel-titanium files under continuous rotation or reciprocating motion. J. Endod. 2013, 39, 1585–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ninan, E.; Berzins, D.W. Torsion and bending properties of shape memory and superelastic nickel-titanium rotary instruments. J. Endod. 2013, 39, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahia, M.G.; Buono, V.T. Decrease in the fatigue resistance of nickel-titanium rotary instruments after clinical use in curved root canals. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2005, 100, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobrzański, L.A. Podstawy Nauki o Materiałach; Wydawnictwo Politechniki Śląskiej: Gliwice, Poland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Shotton, V.; Wilkinson, K.; Phillips, G.; Johnson, W.B. Effects of raw material and rotational speed on the cyclic fatigue of ProFile Vortex rotary instruments. J. Endod. 2010, 36, 1205–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bojarski, Z.; Morawiec, H. Metale z Pamięcią Kształtu; PWN: Warsaw, Poland, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Launey, M.; Robertson, S.W.; Vien, L.; Senthilnathan, K.; Chintapalli, P.; Pelton, A.R. Influence of microstructural purity on the bending fatigue behavior of VAR-melted superelastic Nitinol. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2014, 34, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbano, M.F.; Coda, A.; Beretta, S.; Cadelli, A.; Sczerzenie, F. The Effect of Inclusions on Fatigue Properties for Nitinol. In Fatigue and Fracture Metallic Medical Materials and Devices; Mitchell, M., Smith, S., Woods, T., Berg, B., Eds.; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2013; pp. 18–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Pike, K.; Schlun, M.; Zipse, A.; Draper, J. Nitinol Fatigue Life for Variable Strain Amplitude Fatigue. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2012, 21, 2628–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Pike, K.; Zipse, A.; Schlun, M. Nitinol Fatigue Investigation on Stent-Finish Specimens Using Tension-Tension Method. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2011, 20, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanalp, J.; Kaplan, F.; Sert, S.; Kayahan, B.; Bayirl, G. Quantitative evaluation of the amount of apically extruded debris using 3 different rotary instrumentation systems. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2006, 101, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuolo, M.L.; Walton, R.E. Instrument deterioration with usage: Nickel-titanium versus stainless steel. Quint. Int. 1997, 28, 397–402. [Google Scholar]
- Guelzow, A.; Stamm, O.; Martus, P.; Kielbassa, A.M. Comparative study of six rotary nickel-titanium systems and hand instrumentation for root canal preparation. Int. Endod. J. 2005, 38, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bechelli, C.; Orlandini, S.Z.; Colafranceschi, M. Scanning electron microscope study on the efficacy of root canal wall debridement of hand versus Lightspeed instrumentation. Int. Endod. J. 1999, 32, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tucker, D.M.; Wenckus, C.S.; Bentkover, S.K. Canal wall planning by engine-driven nickel-titanium instruments, compared with stainless steel hand instrumentation. J. Endod. 1997, 23, 170–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hryniewicz, T.; Rokicki, R. Improved surface properties of nitinol after magnetoelectropolishing. In Proceedings of the 16th Annual International Conference on Composites/Nano-Engineering “ICCE-16”, Kunming, China, 20–26 July 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Hryniewicz, T. Biomaterials surface improvement by magnetoelectropolishing. In Proceedings of the BIT Life Sciences’ 1st Annual World Congress of IBIO2008, New Starting Line for Decision Makers in Bioeconomy Era, Hangzhou, China, 18–22 May 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Product Catalog Dentsply Maillefer. Available online: https://www.maillefer.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/2016-Maillefer-Catalog.pdf (accessed on 31 May 2021).
- Schrader, C.; Ackermann, M.; Barbakow, F. Step-by-step description of a rotary root canals preparation technique. Int. Endod. J. 1999, 32, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM F2063-18. Standard Specification for Wrought Nickel-Titanium Shape Memory Alloys for Medical Devices and Surgical Implants; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Otsuka, K.; Ren, X. Physical Metallurgy of Ti-Ni-based Shape Memory Alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2005, 50, 511–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chluba, C.; Ge, W.; Lima de Miranda, R.; Strobel, J.; Kienle, L.; Quandt, E.; Wuttig, M. Shape memory alloys. Ultralow-fatigue shape memory alloy films. Science 2015, 348, 1004–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spini, T.S.; Valarelli, F.P.; Cançado, R.H.; Freitas, K.M.; Villarinho, D.J. Transition temperature range of thermally activated nickel-titanium archwires. J. Appl. Oral. Sci. 2014, 22, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- GT Rotary Files 20/.06 Yellow 25 mm. Available online: https://www.dentsplysirona.com/en-ca/products/endodontics/glide-path-shaping.html/Endodontics/Glide-Path-%26-Shaping/Rotary-%26-Reciprocating-Files/Shaping/GT-Rotary-Files/p/TUL-GTR0602025/c/1000671.html (accessed on 7 May 2021).
- ASTM 2063 Shape Memory Ni Ti Alloy Nitinol 55 Nitinol 60 Wire. Available online: https://www.nitinolcn.com/showroom/astm-2063-shape-memory-ni-ti-alloy-nitinol-55-nitinol-60-wire.html (accessed on 7 May 2021).
- Andreasen, G.F.; Barrett, R.D. An evaluation of cobalt-substituted nitinol wire in orthodontics. Am. J. Orthod. 1973, 63, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreasen, G.F.; Hilleman, T.B. An evaluation of 55 cobalt substituted Nitinol wire for use in orthodontics. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 1971, 82, 1373–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massalski, T.B.; Okamoto, H.; Subramanian, P.R.; Kacprzak, L. (Eds.) Binary Alloy Phase Diagrams, 2nd ed.; ASM International: Cleveland, OH, USA, 1990; Volume 3, pp. 1–2875. [Google Scholar]
- Honma, T.; Matsumoto, T.; Shugo, Y.; Nishida, M. Annual Research Report. Res. Rep. Nucl. Sci. Lab. Tohoku Univ. 1979, 12, 183–190. [Google Scholar]
- Nishida, M.; Wayman, C.M.; Honma, T. Electron microscopy studies of the Ti11Ni14 phase in an aged Ti-52.0at%Ni shape memory alloy. Scr. Metall. 1985, 19, 983–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadaki, T.; Nakata, Y.; Shimizu, K.; Otsuka, K. Crystal Structure, Composition and Morphology of a Precipitate in an Aged Ti-51 at%Ni Shape Memory Alloy. Trans. JIM 1986, 27, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saburi, T.; Nenno, S.; Fukuda, T. Crystal structure and morphology of the metastable X phase in shape memory Ti-Ni alloys. J. Less Com. Met. 1986, 125, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, K.; Ren, X. Martensitic transformations in nonferrous shape memory alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1999, 273–275, 89–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batalu, D.; Guoqiu, H.; Aloman, A.; Cosmeleata, G.; Xiaoshan, L.; Zhihua, Z. A Review on TiNi Shape Memory Alloys (SMA) Used for Medical Applications. Recycling Aspects. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Dan_Batalu/publication/268338951_A_review_on_TiNi_shape_memory_alloys_SMA_used_for_medical_applications_Recycling_aspects/links/5471047a0cf216f8cfad0bd7/A-review-on-TiNi-shape-memory-alloys-SMA-used-for-medical-applications-Recycling-aspects.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2021).
- Cascadan, D.; Grandini, C.R. Structure, Microstructure, and Some Selected Mechanical Properties of Ti-Ni Alloys. In Recent Advancements in the Metallurgical Engineering and Electrodeposition; Al-Naib, U.B., Vikraman, D., Karuppasamy, K., Eds.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2020; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanlon, J.E.; Butler, S.R.; Wasilewski, R.J. Effect of martensitic transformation on the electrical and magnetic properties of NiTi. Trans. Metall. Soc. AIME 1967, 239, 1323–1327. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, J.D.; Hodgson, D.E. Use of TiNi in Mechanical and Electrical Connectors. In Shape Memory Effects in Alloys; Perkins, J., Ed.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1975; pp. 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffer, J.E.; Plumley, D.L. Fatigue Performance of Nitinol Round Wire with Varying Cold Work Reductions. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2009, 18, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ASTM F2004-05. Standard Test Method for Transformation Temperature of Nickel-Titanium Alloys by Thermal Analysis; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Andreasen, G.F.; Morrow, R.E. Laboratory and clinical analyses of nitinol wire. Am. J. Orthod. 1978, 73, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreasen, G.; Wass, K.; Chan, K.C. A review of superelastic and thermodynamic nitinol wire. Quint. Int. 1985, 16, 623–626. [Google Scholar]
- Bryant, S.T.; Thompson, S.A.; al-Omari, M.A.; Dummer, P.M. Shaping ability of Profile rotary nickel-titanium instruments with ISO sized tips in simulated root canals: Part 1. Int. Endod. J. 1998, 31, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, S.T.; Thompson, S.A.; al-Omari, M.A.; Dummer, P.M. Shaping ability of ProFile rotary nickel-titanium instruments with ISO sized tips in simulated root canals: Part 2. Int. Endod. J. 1998, 31, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buehler, W.J.; Wang, F.E. A summary of recent research on the Nitinol alloys and their potential application in ocean engineering. Ocean Eng. 1968, 1, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buehler, W.J.; Cross, W.B. 55-Nitinol unique wire alloy with a memory. Wire J. 1969, 2, 41–49. [Google Scholar]
- Burstone, C.J.; Goldberg, A.J. Beta titanium: A new orthodontic alloy. Am. J. Orthod. 1980, 77, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burstone, C.J. Variable-modulus orthodontics. Am. J. Orthod. 1981, 80, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinard, K.; von Fraunhofer, J.A.; Kuftinec, M.M. The corrosion susceptibility of modern orthodontic spring wires. J. Dent. Res. 1981, 60A, 628–Abstract 1277. [Google Scholar]
- Drake, S.R.; Wayne, D.M.; Powers, J.M.; Asgar, K. Mechanical properties of orthodontic wires in tension, bending, and torsion. Am. J. Orthod. 1982, 82, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duerig, W. Applications of shape memory. Mater. Sci. Forum 1990, 56–58, 679–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edie, J.; Andreasen, G. Surface corrosion of Nitinol and stainless wires. J. Dent. Res. 1980, 59A, 528. [Google Scholar]
- Edie, J.W.; Andreasen, G.F.; Zaytoun, M.P. Surface corrosion of nitinol and stainless steel under clinical conditions. Angle Orthod. 1981, 51, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, P.T.; Cunningham, C.J. A comparison of canal preparation with nickel-titanium and stainless steel instruments. J. Endod. 1995, 21, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, T.J.; Durning, P. Aligning archwires, the shape of things to come?—A fourth and fifth phase of force delivery. Br. J. Orthod. 1996, 23, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, J.V. Machinability of Nickel–Titanium Alloys; Metcut Research Associates, Report No. 573–4062–1, Report No. AD-419009; Office of Technical Services, U.S. Deptartment of Commerce: Washington, DC, USA, 1963.
- Hamanaka, H.; Doi, H.; Kohno, O.; Miura, I. Dental castings of NiTi alloys. Part 2. New casting techniques for NiTi alloys. J. Dent. Mater. 1985, 4, 573–579. [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa, K. Ti-Ni shape memory alloy for dental use. Trial production of prefabricated straight-slit type posts by electric discharge machining. J. Dent. Mater. 1989, 8, 388–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, K. The studies of Ti-Ni shape memory alloy for dental use—The influence of shape memory alloy post on the stress of post hole. J. Dent. Mater. 1991, 10, 509–517. [Google Scholar]
- Kapila, S.; Haugen, J.W.; Watanabe, L.G. Load-deflection characteristics of nickel-titanium alloy wires after clinical recycling and dry heat sterilization. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofacial Orthop. 1992, 102, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, H.; Sohmura, T. Pure Ti thermal spray coating on Ti-Ni shape memory alloys and Ti. J. Osaka Univ. Dent. School 1987, 6, 672–678. [Google Scholar]
- Kimura, H.; Sohmura, T. Improvement in corrosion resistance of Ti-Ni shape memory alloy by oxide film coating. J. Dent. Mater. 1988, 7, 106–110. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, P.; Yang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H.; Yu, Y.; Dai, K.; Hong, W.Q.; Ke, M.Z.; Cai, T.D.; Tao, J.C. The use of nickel–titanium alloy in orthopaedic surgery in China. Orthopaedics 1989, 12, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusy, R.P.; Stush, A.M. Geometric and material parameters of a nickel-titanium and a beta titanium orthodontic arch wire alloy. Dent. Mater. 1987, 3, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusy, R.P. A review of contemporary archwires: Their properties and characteristics. Angle Orthod. 1997, 67, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Park, J.B.; Andreasen, G.F.; Lakes, R.S. Thermomechanical study of Ni-Ti alloys. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1988, 22, 573–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsicovetere, E.S.; Clement, D.J.; del Rio, C.E. Morphometric video analysis of the engine-driven nickel-titanium Lightspeed instrument system. J. Endod. 1996, 22, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayhew, M.J.; Kusy, R.P. Effects of sterilization on the mechanical properties and the surface topography of nickel-titanium arch wires. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofacial Orthop. 1988, 93, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercier, O.; Torok, E. Mechanical properties of the coldworked martensitic NiTi type alloys. J. Phys. 1982, 43, C4-267–C4-272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, F.; Mogi, M.; Ohura, Y.; Hamanaka, H. The super-elastic property of the Japanese NiTi alloy wire for use in orthodontics. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofacial Orthop. 1986, 90, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, F.; Mogi, M.; Okamoto, Y. New application of superelastic NiTi rectangular wire. J. Clin. Orthod. 1990, 24, 544–548. [Google Scholar]
- Saburi, T.; Tatsumi, T.; Nenno, S. Effects of heat treatment on mechanical behaviour of Ti-Ni alloys. J. Phys. 1982, 43, C4-261–C4-266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachdeva, R.; Fukuyo, S.; Suzuki, K.; Oshida, Y.; Miyazaki, S. Shape memory NiTi alloys—Applications in dentistry. Mater. Sci. Forum 1990, 56–58, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, N.K.; Redmond, W.; Schwaninger, B.; Goldberg, A.J. The chloride corrosion behaviour of four orthodontic wires. J. Oral Rehabil. 1983, 10, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, N.K.; Schwaninger, B. The in vivo corrosion of Nitinol wire. J. Dent. Res. 1980, 59A, 528–Abstract 1035. [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer, E. Root canal instruments for manual use: A review. Dent. Traumatol. 1997, 13, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, E.; Tepel, J.; Hoppe, W. Properties of endodontic hand instruments used in rotary motion. Part 2. Instrumentation of curved canals. J. Endod. 1995, 21, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schettler, D.; Baumgart, F.; Bensmann, G.; Haasters, J. Method of alveolar bracing in mandibular fractures using a new form of fixation made from memory alloy (preliminary report). J. Maxillofac. Surg. 1979, 7, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serene, T.P.; Adams, J.D.; Saxena, A. Nickel–Titanium Instruments: Applications in Endodontics; Ishiyaku Euro America, Inc.: St. Louis, MO, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, G.A.; von Fraunhofer, J.A.; Casey, G.R. The effect of clinical use and sterilization on selected orthodontic arch wires. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofacial Orthop. 1992, 102, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoeckel, D.; Yu, W. Superelastic Ni-Ti wire. Wire J. Int. 1991, 45–50. Available online: https://www.nitinol.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/01/056.pdf (accessed on 25 November 2021).
- Thompson, S.A.; Dummer, P.M. Shaping ability of Lightspeed rotary nickel-titanium instruments in simulated root canals. Part 1. J. Endod. 1997, 23, 698–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, S.A.; Dummer, P.M. Shaping ability of Lightspeed rotary nickel-titanium instruments in simulated root canals. Part 2. J. Endod. 1997, 23, 742–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, S.A.; Dummer, P.M. Shaping ability of ProFile.04 Taper Series 29 rotary nickel-titanium instruments in simulated root canals. Part 1. Int. Endod. J. 1997, 30, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, S.A.; Dummer, P.M. Shaping ability of ProFile.04 Taper Series 29 rotary nickel-titanium instruments in simulated root canals. Part 2. Int. Endod. J. 1997, 30, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, S.A.; Dummer, P.M. Shaping ability of NT Engine and McXim rotary nickel-titanium instruments in simulated root canals. Part 1. Int. Endod. J. 1997, 30, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, S.A.; Dummer, P.M. Shaping ability of NT Engine and McXim rotary nickel-titanium instruments in simulated root canals. Part 2. Int. Endod. J. 1997, 30, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, S.A.; Dummer, P.M. Shaping ability of Mity Roto 360 degrees and Naviflex rotary nickel-titanium instruments in simulated root canals. Part 1. J. Endod. 1998, 24, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, S.A.; Dummer, P.M. Shaping ability of Mity Roto 360 degrees and Naviflex rotary nickel-titanium instruments in simulated root canals. Part 2. J. Endod. 1998, 24, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, S.A.; Dummer, P.M. Shaping ability of Quantec Series 2000 rotary nickel-titanium instruments in simulated root canals: Part 1. Int. Endod. J. 1998, 31, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, S.A.; Dummer, P.M. Shaping ability of Quantec Series 2000 rotary nickel-titanium instruments in simulated root canals: Part 2. Int. Endod. J. 1998, 31, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walia, H.; Costas, J.; Brantley, W.; Gerstein, H. Torsional ductility and cutting efficiency of the Nitinol file. J. Endod. 1989, 15, 174–Abstract 22. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.E.; Pickart, S.J.; Alperin, H.A. Mechanism of the TiNi martensitic transformation and the crystal structures of TiNi-II and TiNi-III phases. J. Appl. Phys. 1972, 43, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoneyama, T.; Doi, H.; Hamanaka, H.; Okamoto, Y.; Mogi, M.; Miura, F. Super-elasticity and thermal behavior of Ni-Ti alloy orthodontic arch wires. Dent. Mater. J. 1992, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, S.W.; Launey, M.; Shelley, O.; Ong, I.; Vien, L.; Senthilnathan, K.; Saffari, P.; Schlegel, S.; Pelton, A.R. A statistical approach to understand the role of inclusions on the fatigue resistance of superelastic Nitinol wire and tubing. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2015, 51, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoj Samson, R.; Prakash, M.; Nirmal, R.; Vajpayee, G. Vibration Analysis of Nitinol Shape Memory Alloy in Carbon Fibre Reinforced Polymer Composites. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 912, 052029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, G.S.; Shen, Y.; Darvell, B.W. Does electropolishing improve the low-cycle fatigue behavior of a nickel-titanium rotary instrument in hypochlorite? J. Endod. 2007, 33, 1217–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, G.; Tavernier, B.; Jordan, L. Influence of structure on nickel-titanium endodontic instruments failure. J. Endod. 2001, 27, 516–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, H.P.; Elias, C.N.; Vieira, V.T.; Moreira, E.J.; Marques, R.V.; de Oliveira, J.C.; Debelian, G.; Siqueira, J.F., Jr. Effects of electropolishing surface treatment on the cyclic fatigue resistance of BioRace nickel-titanium rotary instruments. J. Endod. 2010, 36, 1653–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chekotu, J.C.; Groarke, R.; O’Toole, K.; Brabazon, D. Advances in Selective Laser Melting of Nitinol Shape Memory Alloy Part Production. Materials 2019, 12, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zadafiya, K.; Bandhu, D.; Kumari, S.; Chatterjee, S.; Abhishek, K. Recent trends in non-traditional machining of shape memory alloys (SMAs): A review. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 2021, 32, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaccorso, A.; Tripi, T.R.; Rondelli, G.; Condorelli, G.G.; Cantatore, G.; Schäfer, E. Pitting corrosion resistance of nickel-titanium rotary instruments with different surface treatments in seventeen percent ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid and sodium chloride solutions. J. Endod. 2008, 34, 208–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripi, T.R.; Bonaccorso, A.; Condorelli, G.G. Cyclic fatigue of different nickel-titanium endodontic rotary instruments. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2006, 102, e106–e114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, H.P.; Elias, C.N.; Vieira, M.V.; Vieira, V.T.; de Souza, L.C.; Dos Santos, A.L. Influence of Surface Roughness on the Fatigue Life of Nickel-Titanium Rotary Endodontic Instruments. J. Endod. 2016, 42, 965–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, T.B.; Mitchell, J.C.; Baumgartner, J.C. Effect of electropolishing ProFile nickel-titanium rotary instruments on cyclic fatigue resistance, torsional resistance, and cutting efficiency. J. Endod. 2008, 34, 190–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condorelli, G.G.; Bonaccorso, A.; Smecca, E.; Schäfer, E.; Cantatore, G.; Tripi, T.R. Improvement of the fatigue resistance of NiTi endodontic files by surface and bulk modifications. Int. Endod. J. 2010, 43, 866–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praisarnti, C.; Chang, J.W.; Cheung, G.S. Electropolishing enhances the resistance of nickel-titanium rotary files to corrosion-fatigue failure in hypochlorite. J. Endod. 2010, 36, 1354–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herold, K.S.; Johnson, B.R.; Wenckus, C.S. A scanning electron microscopy evaluation of microfractures, deformation and separation in EndoSequence and Profile nickel-titanium rotary files using an extracted molar tooth model. J. Endod. 2007, 33, 712–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwangi, J.W.; Bui, V.D.; Thüsing, K.; Hahn, S.; Wagner, M.F.-X.; Schubert, A. Characterization of the arcing phenomenon in micro-EDM and its effect on key mechanical properties of medical-grade Nitinol. J. Mater. Proc. Tech. 2020, 275, 116334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- COLTENE. HyFlex® Rotary Files. Available online: https://nam.coltene.com/pim/DOC/BRO/docbro03464-h-en-hyflex-cm-8-5-x-11-0senaindv1.pdf (accessed on 16 November 2021).
- Pirani, C.; Iacono, F.; Generali, L.; Sassatelli, P.; Nucci, C.; Lusvarghi, L.; Gandolfi, M.G.; Prati, C. HyFlex EDM: Superficial features, metallurgical analysis and fatigue resistance of innovative electro discharge machined NiTi rotary instruments. Int. Endod. J. 2016, 49, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Maheshwari, S.; Pandey, P.C. Some investigations into the electric discharge machining of hardened tool steel using different electrode materials. J. Mater. Proc. Tech. 2004, 149, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojorquez, B.; Marloth, R.T.; Es-Said, O.S. Formation of a crater in the workpiece on an electrical discharge machine. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2002, 9, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneshmand, S.; Kahrizi, E.F.; Abedi, E.; Abdolhosseini, M.M. Influence of machining parameters on electro discharge machining of NiTi shape memory alloys. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2013, 8, 3095–3104. [Google Scholar]
- Uslu, G.; Özyürek, T.; Yılmaz, K. Comparison of Alterations in the Surface Topographies of HyFlex CM and HyFlex EDM Nickel-titanium Files after Root Canal Preparation: A Three-dimensional Optical Profilometry Study. J. Endod. 2018, 44, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iacono, F.; Pirani, C.; Generali, L.; Bolelli, G.; Sassatelli, P.; Lusvarghi, L.; Gandolfi, M.G.; Giorgini, L.; Prati, C. Structural analysis of HyFlex EDM instruments. Int. Endod. J. 2017, 50, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaval, M.E.; Capar, I.D.; Ertas, H. Evaluation of the Cyclic Fatigue and Torsional Resistance of Novel Nickel-Titanium Rotary Files with Various Alloy Properties. J. Endod. 2016, 42, 1840–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedullà, E.; Lo Savio, F.; Boninelli, S.; Plotino, G.; Grande, N.M.; La Rosa, G.; Rapisarda, E. Torsional and Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of a New Nickel-Titanium Instrument Manufactured by Electrical Discharge Machining. J. Endod. 2016, 42, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelton, A.R.; Russell, S.M.; DiCello, J. The physical metallurgy of nitinol for medical applications. JOM 2003, 55, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brantley, W.A.; Svec, T.A.; Iijima, M.; Powers, J.M.; Grentzer, T.H. Differential scanning calorimetric studies of nickel titanium rotary endodontic instruments. J. Endod. 2002, 28, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, E.S.; Peixoto, I.F.; Viana, A.C.; Oliveira, I.I.; Gonzalez, B.M.; Buono, V.T.; Bahia, M.G. Physical and mechanical properties of a thermomechanically treated NiTi wire used in the manufacture of rotary endodontic instruments. Int. Endod. J. 2012, 45, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurley, A.; Lambert, T.R.; Beale, D.; Broughton, R. Dual measurement self-sensing technique of NiTi actuators for use in robust control. Smart Mater. Struct. 2017, 26, 105050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilibal, S.; Sahin, H.; Dursun, E.; Engeberg, E.D. Nickel–titanium shape memory alloy-actuated thermal overload relay system design. Electr. Eng. 2017, 99, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrpouya, M.; Gisario, A.; Broggiato, G.B.; Puopolo, M.; Vesco, S.; Barletta, M. Effect of welding parameters on functionality of dissimilar laser-welded NiTi superelastic (SE) to shape memory effect (SME) wires. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 103, 1593–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casati, R.; Saghafi, F.; Biffi, C.A.; Vedani, M.; Tuissi, A. Improved functional properties and efficiencies of nitinol wires under high-performance shape memory effect (HP-SME). J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2017, 26, 4964–4969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metale i Ich Stopy; Dobrzański, L.A. (Ed.) Open Access Library VII(2); International OCSCO World Press: Gliwice, Poland, 2017; pp. 1–982. [Google Scholar]
- Tadayyon, G.; Mazinani, M.; Guo, Y.; Zebarjad, S.M.; Tofail, S.A.M.; Biggs, M.J. The effect of annealing on the mechanical properties and microstructural evolution of Ti-rich NiTi shape memory alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 662, 564–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM E8/E8M-21. Standard Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Sadiq, H.; Wong, M.B.; Al-Mahaidi, R.; Zhao, X.L. The effects of heat treatment on the recovery stresses of shape memory alloys. Smart Mater. Struct. 2010, 19, 035021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gall, K.; Sehitoglu, H.; Chumlyakov, Y.I.; Kireeva, I.V.; Maier, H.J. The influence of aging on critical transformation stress levels and martensite start temperatures in NiTi: Part I—Aged microstructure and micro- mechanical modeling. J. Eng. Mater. Technol. 1999, 121, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gall, K.; Sehitoglu, H.; Chumlyakov, Y.I.; Kireeva, I.V.; Maier, H.J. The Influence of Aging on Critical Transformation Stress Levels and Martensite Start Temperatures in NiTi: Part II—Discussion of Experimental Results. J. Eng. Mater. Technol. 1999, 121, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funakubo, H. Shape Memory Alloys; University of Tokyo: Tokyo, Japan, 1984; p. 7. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, X.; Miura, N.; Taniwaki, K.; Otsuka, K.; Suzuki, T.; Tanaka, K.; Chumlyakov, Y.I.; Asai, M. Understanding the martensitic transformations in TiNi-based alloys by elastic constants measurement. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1999, 273–275, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenxi, N.; Xia, L. Research progress on the effect of root canal sealers on root fracture resistance. Int. J. Stomatol. 2020, 47, 711–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faus-Llácer, V.; Pérez, R.L.; Faus-Matoses, I.; Ruiz-Sánchez, C.; Zubizarreta-Macho, Á.; Sauro, S.; Faus-Matoses, V. Efficacy of Removing Thermafil and GuttaCore from Straight Root Canal Systems Using a Novel Non-Surgical Root Canal Re-Treatment System: A Micro-Computed Tomography Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kim, S.; Park, J.-W.; Jung, I.-Y.; Shin, S.-J. Comparison of the Percentage of Voids in the Canal Filling of a Calcium Silicate-Based Sealer and Gutta Percha Cones Using Two Obturation Techniques. Materials 2017, 10, 1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Teoh, Y.-Y.; Walsh, L.J. Residual Endodontic Filling Material after Post Space Preparation: A Confocal Microscopic Study. Materials 2017, 10, 1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Yu, Y.; Joubert, C.; Bruder, G.; Liu, Y.; Chang, C.-C.; Simon, M.; Walker, S.G.; Rafailovich, M. Differentiation of Dental Pulp Stem Cells on Gutta-Percha Scaffolds. Polymers 2016, 8, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ribeiro, M.A.; Queiroz, A.C.F.S.; Silva, P.G.; Yoshinari, G.H.; Guerisoli, D.M.Z.; Pereira, K.F.S. Comparative study of the area filled with gutta-percha in the TC, Thermafil and Lateral Condensation techniques. Rev. Odontol. UNESP 2009, 38, 65–71. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, G.; Chen, W.; Yang, S.; Zhu, J.; Ren, X.; Otsuka, K. Origin of abnormal multi-stage martensitic transformation behavior in aged Ni-rich Ti–Ni shape memory alloys. Acta Mater. 2004, 52, 4351–4362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Everaerts, J.; Salvati, E.; Korsunsky, A.M. Evolution of thermal and mechanical properties of Nitinol wire as a function of ageing treatment conditions. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 819, 153024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chad Hornbuckle, B.; Yu, X.X.; Noebe, R.D.; Martens, R.; Weaver, M.L.; Thompson, G.B. Hardening behavior and phase decomposition in very Ni-rich Nitinol alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 639, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Kustov, S.; Verlinden, B.; Van Humbeeck, J. Fundamental development on utilizing the R-phase transformation in NiTi shape memory alloys. Shap. Mem. Superelasticity 2015, 1, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shamimi, A.; Amin-Ahmadi, B.; Stebner, A.; Duerig, T. The effect of low temperature aging and the evolution of R-phase in Ni-rich NiTi. Shap. Mem. Superelasticity 2018, 4, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Qian, M.; Zhu, X.; Shang, C.; Geng, L. Elastocaloric effects in ultra-fine grained NiTi microwires processed by cold-drawing. APL Mater. 2018, 6, 036102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Świec, P.; Zubko, M.; Lekston, Z.; Stróż, D. Structure and properties of NiTi shape memory alloy after cold rolling in martensitic state. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2016, 130, 1081–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burow, J.; Frenzel, J.; Somsen, C.; Prokofiev, E.; Valiev, R.; Eggeler, G. Grain nucleation and growth in deformed NiTi shape memory alloys: An in situ TEM study. Shap. Mem. Superelast. 2017, 3, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.X.; Hu, K.P.; Chen, F.; Tian, B.; Li, L.; Zheng, Y.F. Multiple-stage transformation behavior of Ti49.2Ni50.8 alloy with different initial microstructure processed by equal channel angular pressing. Intermetallics 2017, 85, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velmurugan, C.; Senthilkumar, V.; Dinesh, S.; Arulkirubakaran, D. Review on phase transformation behavior of NiTi shape memory alloys. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 14597–14606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.I.; Miyazaki, S. Effect of nano-scaled precipitates on shape memory behavior of Ti-50.9at.%Ni alloy. Acta Mater. 2005, 53, 4545–4554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Xiao, F.; Chen, H.; Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Jin, X.; Fukuda, T. Internal friction of the R-phase in single crystalline Ti-50.8Ni (at.%) alloy containing controlled precipitate of Ti3Ni4. Scr. Mater. 2019, 166, 44–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourbabak, S.; Orekhov, A.; Samaee, V.; Verlinden, B.; Van Humbeeck, J.; Schryvers, D. In-Situ TEM stress induced martensitic transformation in Ni50.8Ti49.2 microwires. Shap. Mem. Superelast. 2019, 5, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; VerlinDen, B.; Kustov, S. Multi-stage martensitic transformation in Ni-rich NiTi shape memory alloys. Funct. Mater. Lett. 2017, 10, 1740004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhu, J.; Lin, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, G. Coupling effect of stretch-bending deformation and electric pulse treatment on phase transformation behavior and superelasticity of a Ti-50.8 at.% Ni alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 799, 140164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.L.; Lin, K.L. The microstructure and property variations of metals induced by electric current treatment: A review. Mater. Charact. 2018, 145, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Jiang, Y.; Guan, L.; Li, H.; Tang, G. Difference in recrystallization between electropulsing-treated and furnace-treated NiTi alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 658, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Tyc, O.; Kadeřávek, L.; Molnárová, O.; Heller, L.; Šittner, P. Temperature and microstructure dependence of localized tensile deformation of superelastic NiTi wires. Mater. Des. 2019, 174, 107797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhao, G.; Yang, F. Effect of electric current on nanoindentation of superelastic NiTi alloy. Exp. Mech. 2015, 55, 1503–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delville, R.; Malard, B.; Pilch, J.; Sittner, P.; Schryvers, D. Microstructure changes during non-conventional heat treatment of thin Ni-Ti wires by pulsed electric current studied by transmission electron microscopy. Acta Mater. 2010, 58, 4503–4515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malard, B.; Pilch, J.; Sittner, P.; Delville, R.; Curfs, C. In situ investigation of the fast microstructure evolution during electropulse treatment of cold drawn NiTi wires. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 1542–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malard, B.; Pilch, J.; Sittner, P.; Gartnerova, V.; Delville, R.; Schryvers, D.; Curfs, C. Microstructure and Functional Superelasticity Property Changes in Thin NiTi Wires Heat Treated by Electric Current. ESOMAT 2009, 2009, 06004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Pu, Z.; Yang, Q.; Huang, S.; Wang, Z.; Kustov, S.; Van Humbeeck, J. Improved functional stability of a coarse-grained Ti-50.8 at.% Ni shape memory alloy achieved by precipitation on dislocation networks. Scr. Mater. 2019, 163, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, M.; Wayman, C.M.; Honma, T. Precipitation processes in near-equiatomic TiNi shape memory alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1986, 17, 1505–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adharapurapu, R.R.; Jiang, F.; Vecchio, K.S. Aging effects on hardness and dynamic compressive behavior of Ti-55Ni (at.%) alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 1665–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, C.-H.; Chien, C.; Wu, S.-K. Multistage martensitic transformation in high temperature aged Ti48Ni52 shape memory alloy. Intermetallics 2015, 67, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Liu, Y. Effect of annealing on the transformation behavior and superelasticity of NiTi shape memory alloy. Scr. Mater. 2001, 45, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, D.; Zhou, Y.; Ren, X. The effect of ageing on the B2-R transformation behaviors in Ti-51at%Ni alloy. Intermetallics 2011, 19, 1752–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, L.; Chandrasekaran, M.; Masse, M.M.; Bouquet, G. Study of the phase transformation in Ni-Ti based shape memory alloys. J. Phys. IV France 1995, 5, C2-489–C2-494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allafi, J.K.; Eggeler, G.; Schmahl, W.W. Quantitative phase analysis in microstructures which display multiple step martensitic transformations in Ni-rich NiTi shape memory alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 438–440, 593–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, S.; Otsuka, K. Deformation and transition behavior associated with the R-phase in Ti-Ni alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1986, 17, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, S.; Kimura, S.; Otsuka, K. Shape-memory effect and pseudoelasticity associated with the R-phase transition in Ti-50·5 at.% Ni single crystals. Philos. Mag. A 1988, 57, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dautovich, D.P.; Purdy, G.R. Phase Transformations in TiNi. Canad. Metall. Quart. 1965, 4, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatanayon, S.; Hehemann, R.F. Martensitic Transformations in β Phase Alloys. In Shape Memory Effects in Alloys; Perkins, J., Ed.; Plenum: New York, NY, USA, 1975; pp. 115–145. [Google Scholar]
- Goo, E.; Sinclair, R. The B2 To R Transformation in Ti50Ni47Fe3 and Ti49.5Ni50.5 alloys. Acta Metall. 1985, 33, 1717–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, T.; Ohba, T.; Okunishi, E.; Otsuka, K. Structural Study of R-Phase in Ti-50.23 at.%Ni and Ti-47.75 at.%Ni-1.50 at.%Fe Alloys. Mater. Trans. JIM 1997, 38, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duerig, T.W.; Bhattacharya, K. The Influence of the R-Phase on the Superelastic Behavior of NiTi. Shap. Mem. Superelast. 2015, 1, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šittner, P.; Landa, M.; Lukáš, P.; Novák, V. R-phase transformation phenomena in thermomechanically loaded NiTi polycrystals. Mech. Mater. 2006, 38, 475–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobushi, H.; Kimura, K.; Sawada, T.; Hattori, T.; Lin, P.H. Recovery Stress Associated with R-Phase Transformation in TiNi Shape Memory Alloy: Properties under Constant Residual Strain. JSME Int. J. A 1994, 37, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tobushi, H.; Yamada, S.; Hachisuka, T.; Ikai, A.; Tanaka, K. Thermomechanical properties due to martensitic and R-phase transformations of TiNi shape memory alloy subjected to cyclic loadings. Smart Mater. Struct. 1996, 5, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelton, A.R.; Huang, G.H.; Moine, P.; Sinclair, R. Effects of thermal cycling on microstructure and properties in Nitinol. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 532, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchil, J.; Kumara, K.G.; Mahesh, K.K. Effect of thermal cycling on R-phase stability in a NiTi shape memory alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2002, 332, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, S.; Igo, Y.; Otsuka, K. Effect of thermal cycling on the transformation temperatures of Ti-Ni alloys. Acta Metall. 1986, 34, 2045–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, S.; Otsuka, K. Mechanical behaviour associated with the premartensitic rhombohedral-phase transition in a Ti50Ni47Fe3 alloy. Philos. Mag. A 1985, 50, 393–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, J.H.; Kim, S.K.; Cohenca, N.; Kim, H.C. Effect of R-phase heat treatment on torsional resistance and cyclic fatigue fracture. J. Endod. 2013, 39, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Li, K.; Schryvers, D.; Verlinden, B.; Van Humbeeck, J. R-phase transition and related mechanical properties controlled by low-temperature aging treatment in a Ti–50.8at.% Ni thin wire. Scr. Mater. 2014, 72–73, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lygin, K.; Langbein, S.; Labenda, P.; Sadek, T. A Methodology for the Development, Production, and Validation of R-Phase Actuators. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2012, 21, 2657–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Jiang, F.; Li, L.; Yang, H.; Liu, Y. Effect of ageing treatment on the transformation behaviour of Ti–50.9 at.% Ni alloy. Acta Mater. 2008, 56, 736–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.I.; Liu, Y.; Miyazaki, S. Ageing-induced two-stage R-phase transformation in Ti-50.9at.%Ni. Acta Mater. 2004, 52, 487–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gall, K.; Tyber, J.; Wilkesanders, G.; Robertson, S.W.; Ritchie, R.O.; Maier, H.J. Effect of microstructure on the fatigue of hot-rolled and cold-drawn NiTi shape memory alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 486, 389–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, M.; Wayman, C.M. Electron microscopy studies of the “Premartensitic” transformations in an aged Ti-51 at%Ni shape memory alloy. Metallography 1988, 21, 255–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favier, D.; Liu, Y.; McCormick, P.G. Three stage transformation behaviour in aged NiTi. Scr. Metall. Mater. 1993, 28, 669–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Yang, D.; Qi, M. The effect of ageing treatment on shape-setting and superelasticity of a nitinol stent. Mater. Charact. 2008, 59, 402–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil-Allafi, J.; Eggeler, G.; Dlouhy, A.; Schmahl, W.W.; Somsen, C.H. On the influence of heterogeneous precipitation on martensitic transformations in a Ni-rich NiTi shape memory alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 378, 148–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, H. Appearance of an intermediate phase with thermal cycling on the transformation of NiTi. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 1991, 10, 408–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, H. Transformation behaviour with thermal cycling in NiTi alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2003, 350, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilibal, S.; Hamilton, R.F.; Lanba, A. The effect of employed loading mode on the mechanical cyclic stabilization of NiTi shape memory alloys. Intermetallics 2017, 89, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piekielny, M.; Jarmołowicz, M.; Dobrzyński, M. Odporność na cykliczne zmęczenie wybranych endodontycznych narzędzi maszynowych w świetle piśmiennictwa. Inż. Fiz. Med. 2020, 9, 143–144. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, G.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, W.; Yang, S.; Ren, X.; Otsuka, K. Precipitation kinetics of Ti3Ni4 in polycrystalline Ni-rich TiNi alloys and its relation to abnormal multi-stage transformation behavior. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 438–440, 622–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.Y.; Cao, S.; Li, Y.Y.; Zhao, Z.X.; Yao, X.Y.; Ma, X.; Zhang, X.P. A hidden single-stage martensitic transformation from B2 parent phase to B19′ martensite phase in an aged Ni51Ti49 alloy. Mater. Lett. 2019, 253, 99–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, I.; Tobe, H.; Karaca, H.E.; Nagasako, M.; Kainuma, R.; Chumlyakov, Y. Positive and negative two-way shape memory effect in [111]-oriented Ni51Ti49 single crystals. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 639, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Xiao, F.; Liang, X.; Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Jin, X.; Min, N.; Fukuda, T. Improvement of the stability of superelasticity and elastocaloric effect of a Ni-rich Ti-Ni alloy by precipitation and grain refinement. Scr. Mater. 2019, 162, 230–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poletika, T.M.; Girsova, S.L.; Lotkov, A.I. Ti3Ni4 precipitation features in heat-treated grain/subgrain nanostructure in Ni-rich TiNi alloy. Intermetallics 2020, 127, 106966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhu, J.; Lin, Y.; Wang, G.; Wang, X. Effect of stretching-bending deformation and aging treatment on phase transformation behavior and superelasticity of Ti-50.8 at.% Ni alloy. Intermetallics 2021, 129, 107051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Fukuda, T.; Kakeshita, T. Inverse elastocaloric effect in a Ti-Ni alloy containing aligned coherent particles of Ti3Ni4. Scr. Mater. 2016, 124, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Zeng, C.Y.; Li, Y.Y.; Yao, X.; Ma, X.; Samaee, V.; Schryvers, D.; Zhang, X.P. Quantitative FIB/SEM three-dimensional characterization of a unique Ni4Ti3 network in a porous Ni50.8Ti49.2 alloy undergoing a two-step martensitic transformation. Mater. Charact. 2020, 169, 110595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, I.; Acar, E.; Karaca, H.E. Effects of deformation temperature and amount on the two-way shape memory effect of solutionized Ni50.8Ti49.2 alloys. Intermetallics 2019, 114, 106607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, P.; Howie, A.; Nicholson, R.B.; Pashley, D.W.; Whelan, M.J. Electron Microscopy of Thin Crystals, 2nd ed.; R. E. Krieger Publishing Company: Malabar, FL, USA, 1977; pp. 169, 317. [Google Scholar]
- Honma, T. The effect of aging, on the spontaneous shape change and the all-round shape memory effect in Ni-rich TiNi alloy. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Martensitic Transformations ICOMAT-86, Nara, Japan, 26–30 August 1986; pp. 709–716. [Google Scholar]
- Kainuma, R.; Matsumoto, M.; Honma, T. The mechanism of the all-round shape memory effect in a Ni-rich TiNi alloy. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Martensitic Transformations ICOMAT-86, Nara, Japan, 26–30 August 1986; pp. 717–722. [Google Scholar]
- Koskimaki, D.; Marcinkowski, M.J.; Sastri, A.S. Solid State Diffusional Transformations in the Near Equiatomic Ni-Ti Alloys. Trans. Metall. Soc. AIME 1969, 245, 1883–1890. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Wu, X.F.; Ko, T. The effects of Ti3Ni4 precipitates on the R-phase transformation. Scr. Metall. Mater. 1993, 29, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.Y.; Zhao, L.C.; Lei, T.C. Effect of precipitates on the electrical resistivity-temperature curves in an aged Ti-51.8 at % Ni shape memory alloy. Scr. Metall. 1989, 23, 2131–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.Y.; Zhao, L.C.; Lei, T.C. Effect of Ti3Ni4 precipitates on the phase transitions in an aged Ti-51.8at% Ni shape memory alloy. Scr. Metall. Mater. 1990, 24, 1753–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, M.; Wayman, C.M.; Kainuma, R.; Honma, T. Further electron microscopy studies of the Ti11Ni14 phase in an aged Ti-52at%Ni shape memory alloy. Scr. Metall. 1986, 20, 899–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.H.; Han, X.D.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, W.-Z.; Lai, J.K.L. TEM and HREM study of the interphase interface structure of Ti3Ni4 precipitates and parent phase in an aged TiNi shape memory alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1996, 219, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil-Allafi, J.; Ren, X.; Eggeler, G. The mechanism of multistage martensitic transformations in aged Ni-rich NiTi shape memory alloys. Acta Mater. 2002, 50, 793–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, C.; Verlinden, B.; Van Humbeeck, J. Effect of grain size on aging microstructure as reflected in the transformation behavior of a low-temperature aged Ti–50.8 at.% Ni alloy. Scr. Mater. 2013, 69, 545–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Humbeeck, J. Non-medical applications of shape memory alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1999, 273–275, 134–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Nishida, M.; Schryvers, D. Quantitative three-dimensional analysis of Ni4Ti3 precipitate morphology and distribution in polycrystalline Ni-Ti. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 1780–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushin, V.G.; Stolyarov, V.V.; Valiev, R.Z.; Lowe, T.C.; Zhu, Y.T. Nanostructured TiNi based shape memory alloys processed by severe plastic deformation. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2005, 410–411, 386–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, H.-j.; Chun, S.-j.; Liu, Y.; Yang, H.; Kim, Y.-w.; Nam, T.-h. Effect of alloy composition on the B2–R transformation in rapidly solidified Ti–Ni alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 577, S259–S264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stróż, D.; Kwarciak, J.; Morawiec, H. Effect of ageing on martensitic transformation in NiTi shape memory alloy. J. Mater. Sci. 1988, 23, 4127–4131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stróż, D.; Bojarski, Z.; Ilczuk, J.; Lekston, Z.; Morawiec, H. Effect of thermal cycling on as-quenched and aged nickel-rich Ni-Ti alloy. J. Mater. Sci. 1991, 26, 1741–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meisel, L.V.; Cote, P.J. Transient Phenomena Following Precipitation and Resolution Anneals in a NiTi Alloy; Minerals, Metals and Materials Society: 173; US Army Armament Research, Development and Engineering Center: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1992; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Morawiec, H.; Stróż, D.; Chrobak, D. Effect of Deformation and Thermal Treatment of NiTi Alloy on Transition Sequence. J. Phys. IV France 1995, 5, C2-205–C2-210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bataillard, L.; Gotthardt, R. Influence of Thermal Treatment on the Appearance of a Three Step Martensitic Transformation in NiTi. J. Phys. IV Fr. 1995, 5, C8-647–C8-652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morawiec, H.; Stróż, D.; Goryczka, T.; Chrobak, D. Two-stage martensitic transformation in a deformed and annealed NiTi alloy. Scr. Mater. 1996, 35, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morawiec, H.; Ilczuk, J.; Stróż, D.; Goryczka, T.; Chrobak, D. Two-Stage Martensitic Transformation in NiTi Alloys Caused by Stress Fields. J. Phys. IV Fr. 1997, 7, C5-155–C5-159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bataillard, L.; Bidaux, J.-E.; Gotthardt, R. Interaction between microstructure and multiple-step transformation in binary NiTi alloys using in-situ transmission electron microscopy observations. Philos. Mag. A 1998, 78, 327–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil-Allafi, J.; Dlouhy, A.; Eggeler, G. Ni4Ti3-precipitation during aging of NiTi shape memory alloys and its influence on martensitic phase transformations. Acta Mater. 2002, 50, 4255–4274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dlouhy, A.; Khalil-Allafi, J.; Eggeler, G. Multiple-step martensitic transformations in Ni-rich NiTi alloys—An in-situ transmission electron microscopy investigation. Philos. Mag. A 2003, 83, 339–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitepu, H.; Schmahl, W.W.; Allafi, J.K.; Eggeler, G.; Dlouhy, A.; Toebbens, D.M.; Tovar, M. Neutron diffraction phase analysis during thermal cycling of a Ni-rich NiTi shape memory alloy using the Rietveld method. Scr. Mater. 2002, 46, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, M.; Hara, T.; Ohba, T.; Yamaguchi, K.; Tanaka, K.; Yamauchi, K. Experimental Consideration of Multistage Martensitic Transformation and Precipitation Behavior in Aged Ni-Rich Ti-Ni Shape Memory Alloys. Mater. Trans. 2003, 44, 2631–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frick, C.P.; Ortega, A.M.; Tyber, J.; Gall, K.; Maier, H.J. Multiscale structure and properties of cast and deformation processed polycrystalline NiTi shape-memory alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2004, 35, 2013–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirry, W.; Schryvers, D. Quantitative determination of strain fields around Ni4Ti3 precipitates in NiTi. Acta Mater. 2005, 53, 1041–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaca, H.E.; Kaya, I.; Tobe, H.; Basaran, B.; Nagasako, M.; Kainuma, R.; Chumlyakov, Y. Shape memory behavior of high strength Ni54Ti46 alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 580, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM E8M–91. Standard Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Van Humbeeck, J.; Stalmans, R.; Delaey, L. Some aspects of the properties of NiTi shape memory alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 1997, 247, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y. Detwinning process and its anisotropy in shape memory alloys. Smart Mater. 2001, 4234, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xie, Z.; Van Humbeeck, J.; Delaey, L.; Liu, Y. On the deformation of the Twinned domain in NiTi shape memory alloys. Philos. Mag. A 2000, 80, 1935–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Jiang, H.-c.; Rong, L.-j.; Xiao, L.; Zhao, X.-q. Mechanical behavior in NiTiNb shape memory alloys with low Nb content. Intermetallics 2011, 19, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.X.; Jiang, P.C.; Chen, F.; Tian, B.; Li, L.; Zheng, Y.F.; Gunderov, D.V.; Valiev, R.Z. Microstructure and martensitic transformation of an ultrafine-grained TiNiNb shape memory alloy processed by equal channel angular pressing. Intermetallics 2014, 49, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salje, E.K.H.; Koppensteiner, J.; Reinecker, M.; Schranz, W.; Planes, A. Jerky elasticity: Avalanches and the martensitic transition in Cu74.08Al23.13Be2.79 shape-memory alloy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 95, 231908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gallardo, M.C.; Manchado, J.; Romero, F.J.; del Cerro, J.; Salje, E.K.H.; Planes, A.; Vives, E.; Romero, R.; Stipcich, M. Avalanche criticality in the martensitic transition of Cu67.64Zn16.71Al15.65 shape-memory alloy: A calorimetric and acoustic emission study. Phys. Rev. B 2010, 81, 174102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCormick, P.G.; Liu, Y. Thermodynamic analysis of the martensitic transformation in NiTi—II. Effect of transformation cycling. Acta Metall. Mater. 1994, 42, 2407–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; McCormick, P.G. Thermodynamic analysis of the martensitic transformation in NiTi—I. Effect of heat treatment on transformation behaviour. Acta Metall. Mater. 1994, 42, 2401–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, G.B.; Cohen, M. Reply to “On the equilibrium temperature in thermoelastic martensitic transformations”. Scr. Metall. 1977, 11, 345–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salzbrenner, R.J.; Cohen, M. On the thermodynamics of thermoelastic martensitic transformations. Acta Metall. 1979, 27, 739–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, G.B.; Owen, W.S. Martenite; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Ortin, J.; Planes, A. Thermodynamic analysis of thermal measurements in thermoelastic martensitic transformations. Acta Metall. 1988, 36, 1873–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Peng, B.; Zheng, Y.F. An overview of the mechanical properties of nickel-titanium endodontic instruments. Endod. Top. 2013, 29, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKelvey, A.L.; Ritchie, R.O. Fatigue-crack growth behavior in the superelastic and shape-memory alloy nitinol. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2001, 32, 731–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Zhou, H.M.; Zheng, Y.F.; Peng, B.; Haapasalo, M. Current challenges and concepts of the thermomechanical treatment of nickel-titanium instruments. J. Endod. 2013, 39, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dentsply Sirona. Available online: https://www.dentsplysirona.com/pl-pl/explore/endodontics.html (accessed on 17 November 2021).
- Kim, H.; Jeon, S.J.; Seo, M.S. Comparison of the canal transportation of ProTaper GOLD, WaveOne GOLD, and TruNatomy in simulated double-curved canals. BMC Oral Health 2021, 21, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, É.S.; Viana, A.C.; Buono, V.T.; Peters, O.A.; Bahia, M.G. Behavior of nickel-titanium instruments manufactured with different thermal treatments. J. Endod. 2015, 41, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Whitten, B.; Sedgley, C.; Svec, T. Effect of three NiTi files on transportation of the apical foramen. Int. Endod. J. 2014, 47, 1064–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hieawy, A.; Haapasalo, M.; Zhou, H.; Wang, Z.J.; Shen, Y. Phase Transformation Behavior and Resistance to Bending and Cyclic Fatigue of ProTaper Gold and ProTaper Universal Instruments. J. Endod. 2015, 41, 1134–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Zhou, H.M.; Zheng, Y.F.; Campbell, L.; Peng, B.; Haapasalo, M. Metallurgical characterization of controlled memory wire nickel-titanium rotary instruments. J. Endod. 2011, 37, 1566–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özyürek, T. Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Reciproc, WaveOne, and WaveOne Gold Nickel-Titanium Instruments. J. Endod. 2016, 42, 1536–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotino, G.; Grande, N.M.; Cotti, E.; Testarelli, L.; Gambarini, G. Blue treatment enhances cyclic fatigue resistance of vortex nickel-titanium rotary files. J. Endod. 2014, 40, 1451–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Zhou, H.; Coil, J.M.; Aljazaeri, B.; Buttar, R.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, Y.F.; Haapasalo, M. ProFile Vortex and Vortex Blue Nickel-Titanium Rotary Instruments after Clinical Use. J. Endod. 2015, 41, 937–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De-Deus, G.; Silva, E.J.; Vieira, V.T.; Belladonna, F.G.; Elias, C.N.; Plotino, G.; Grande, N.M. Blue Thermomechanical Treatment Optimizes Fatigue Resistance and Flexibility of the Reciproc Files. J. Endod. 2017, 43, 462–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Gutmann, J.L.; Wilkinson, K.; Maxwell, R.; Ammon, D. Evaluation of the impact of raw materials on the fatigue and mechanical properties of ProFile Vortex rotary instruments. J. Endod. 2012, 38, 398–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagliardi, J.; Versiani, M.A.; de Sousa-Neto, M.D.; Plazas-Garzon, A.; Basrani, B. Evaluation of the shaping characteristics of ProTaper Gold, ProTaper NEXT, and ProTaper Universal in curved canals. J. Endod. 2015, 41, 1718–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adıgüzel, M.; Capar, I.D. Comparison of cyclic fatigue resistance of WaveOne and WaveOne Gold small, primary, and large instruments. J. Endod. 2017, 43, 623–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duke, F.; Shen, Y.; Zhou, H.; Ruse, N.D.; Wang, Z.J.; Hieawy, A.; Haapasalo, M. Cyclic Fatigue of ProFile Vortex and Vortex Blue Nickel-Titanium Files in Single and Double Curvatures. J. Endod. 2015, 41, 1686–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elnaghy, A.M.; Elsaka, S.E. Effect of sodium hypochlorite and saline on cyclic fatigue resistance of WaveOne Gold and Reciproc reciprocating instruments. Int. Endod. J. 2017, 50, 991–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafin, M.; De Biasi, M.; Franco, V.; Generali, L.; Angerame, D. Influence of different motions on the cyclic fatigue resistance of Reciproc and Reciproc Blue endodontic instruments. J. Conserv. Dent. 2019, 22, 449–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keskin, C.; Inan, U.; Demiral, M.; Keleş, A. Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Reciproc Blue, Reciproc, and WaveOne Gold Reciprocating Instruments. J. Endod. 2017, 43, 1360–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.H.; Fong, H.; Paranjpe, A.; Flake, N.M.; Johnson, J.D.; Peters, O.A. Evaluation of the resistance to cyclic fatigue among ProTaper Next, ProTaper Universal, and Vortex Blue rotary instruments. J. Endod. 2014, 40, 1190–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topçuoğlu, H.S.; Düzgün, S.; Aktı, A.; Topçuoğlu, G. Laboratory comparison of cyclic fatigue resistance of WaveOne Gold, Reciproc and WaveOne files in canals with a double curvature. Int. Endod. J. 2017, 50, 713–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topçuoğlu, H.S.; Topçuoğlu, G. Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Reciproc Blue and Reciproc Files in an S-shaped Canal. J. Endod. 2017, 43, 1679–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uygun, A.D.; Kol, E.; Topcu, M.K.; Seckin, F.; Ersoy, I.; Tanriver, M. Variations in cyclic fatigue resistance among ProTaper Gold, ProTaper Next and ProTaper Universal instruments at different levels. Int. Endod. J. 2016, 49, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serafin, M.; De Biasi, M.; Franco, V.; Angerame, D. In vitro comparison of cyclic fatigue resistance of two rotary single-file endodontic systems: OneCurve vs. OneShape. Odontology 2019, 107, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duque, J.A.; Vivan, R.R.; Cavenago, B.C.; Amoroso-Silva, P.A.; Bernardes, R.A.; Vasconcelos, B.C.; Duarte, M.A. Influence of NiTi alloy on the root canal shaping capabilities of the ProTaper Universal and ProTaper Gold rotary instrument systems. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2017, 25, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Elnaghy, A.M.; Elsaka, S.E. Shaping ability of ProTaper Gold and ProTaper Universal files by using cone-beam computed tomography. Indian J. Dent. Res. 2016, 27, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özyürek, T.; Yılmaz, K.; Uslu, G. Shaping Ability of Reciproc, WaveOne GOLD, and HyFlex EDM Single-file Systems in Simulated S-shaped Canals. J. Endod. 2017, 43, 805–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, S.R.; Alcalde, M.P.; Vivacqua-Gomes, N.; Bramante, C.M.; Vivan, R.R.; Duarte, M.A.H.; Vasconcelos, B.C. Evaluation of apical transportation and centring ability of five thermally treated NiTi rotary systems. Int. Endod. J. 2018, 51, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, E.J.; Muniz, B.L.; Pires, F.; Belladonna, F.G.; Neves, A.A.; Souza, E.M.; De-Deus, G. Comparison of canal transportation in simulated curved canals prepared with ProTaper Universal and ProTaper Gold systems. Restor. Dent. Endod. 2016, 41, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasconcelos, R.A.; Arias, A.; Peters, O.A. Lateral and axial cutting efficiency of instruments manufactured with conventional nickel-titanium and novel gold metallurgy. Int. Endod. J. 2018, 51, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dentsply Sirona. TruNatomy Brochure. Available online: https://www.dentsplysirona.com/en/explore/endodontics/trunatomy.html (accessed on 18 November 2021).
- Elnaghy, A.M.; Elsaka, S.E.; Mandorah, A.O. In vitro comparison of cyclic fatigue resistance of TruNatomy in single and double curvature canals compared with different nickel-titanium rotary instruments. BMC Oral Health 2020, 20, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- FKG Swiss Endo. Catalogue. Available online: https://www.fkg.ch/sites/default/files/FKG_Catalogue%202019_EN_WEB.pdf (accessed on 17 November 2021).
- Gambarini, G.; Grande, N.M.; Plotino, G.; Somma, F.; Garala, M.; De Luca, M.; Testarelli, L. Fatigue resistance of engine-driven rotary nickel-titanium instruments produced by new manufacturing methods. J. Endod. 2008, 34, 1003–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendt, C. US Patent 20070072147A1: Method of Preparing Nitinol for Use in Manufacturing Instruments with Improved Fatigue Resistance. 2007. Available online: https://patentimages.storage.googleapis.com/24/b9/52/82a5ccc8031262/US20070072147A1.pdf (accessed on 19 November 2021).
- Alapati, S.B.; Brantley, W.A.; Iijima, M.; Clark, W.A.; Kovarik, L.; Buie, C.; Liu, J.; Johnson, W.B. Metallurgical characterization of a new nickel-titanium wire for rotary endodontic instruments. J. Endod. 2009, 35, 1589–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, L.C.; Faria Silva, A.C.; Buono, V.T.; de Azevedo Bahia, M.G. Impact of heat treatments on the fatigue resistance of different rotary nickel-titanium instruments. J. Endod. 2014, 40, 1494–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Gao, Y. Metallurgical characterization of M-Wire nickel-titanium shape memory alloy used for endodontic rotary instruments during low-cycle fatigue. J. Endod. 2012, 38, 105–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, E.; Lloyd, A.; Kuttler, S.; Namerow, K. Comparison between a novel nickel-titanium alloy and 508 nitinol on the cyclic fatigue life of ProFile 25/.04 rotary instruments. J. Endod. 2008, 34, 1406–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, E.S.; Gomes, R.O.; Leroy, A.M.; Singh, R.; Peters, O.A.; Bahia, M.G.; Buono, V.T. Mechanical behavior of M-Wire and conventional NiTi wire used to manufacture rotary endodontic instruments. Dent. Mater. 2013, 29, e318–e324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalvão, D.; Alçada, F.S. Numeric comparison of the static mechanical behavior between ProFile GT and ProFile GT series X rotary nickel-titanium files. J. Endod. 2011, 37, 1158–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Hadlaq, S.M.; Aljarbou, F.A.; AlThumairy, R.I. Evaluation of cyclic flexural fatigue of M-wire nickel-titanium rotary instruments. J. Endod. 2010, 36, 305–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, C.M.; Watanabe, I.; Glickman, G.N.; He, J. Cyclic fatigue analysis of a new generation of nickel titanium rotary instruments. J. Endod. 2009, 35, 401–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramkowski, T.R.; Bahcall, J. An in vitro comparison of torsional stress and cyclic fatigue resistance of ProFile GT and ProFile GT Series X rotary nickel-titanium files. J. Endod. 2009, 35, 404–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Coil, J.M.; Zhou, H.; Zheng, Y.; Haapasalo, M. HyFlex nickel-titanium rotary instruments after clinical use: Metallurgical properties. Int. Endod. J. 2013, 46, 720–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, H.M.; Shen, Y.; Zheng, W.; Li, L.; Zheng, Y.F.; Haapasalo, M. Mechanical properties of controlled memory and superelastic nickel-titanium wires used in the manufacture of rotary endodontic instruments. J. Endod. 2012, 38, 1535–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saber, S.E.; Nagy, M.M.; Schäfer, E. Comparative evaluation of the shaping ability of ProTaper Next, iRaCe and Hyflex CM rotary NiTi files in severely curved root canals. Int. Endod. J. 2015, 48, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marceliano-Alves, M.F.; Sousa-Neto, M.D.; Fidel, S.R.; Steier, L.; Robinson, J.P.; Pécora, J.D.; Versiani, M.A. Shaping ability of single-file reciprocating and heat-treated multifile rotary systems: A micro-CT study. Int. Endod. J. 2015, 48, 1129–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bürklein, S.; Börjes, L.; Schäfer, E. Comparison of preparation of curved root canals with Hyflex CM and Revo-S rotary nickel-titanium instruments. Int. Endod. J. 2014, 47, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, B.S.; Pattanshetty, S.; Prasad, M.; Soni, S.; Pattanshetty, K.S.; Prasad, S. An in-vitro Evaluation of canal transportation and centering ability of two rotary Nickel Titanium systems (Twisted Files and Hyflex files) with conventional stainless Steel hand K-flexofiles by using Spiral Computed Tomography. J. Int. Oral Health 2013, 5, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rubio, J.; Zarzosa, J.I.; Pallarés, A. A Comparative Study of Shaping Ability of four Rotary Systems. Acta Stomatol. Croat. 2015, 49, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- COLTENE. Nowa Generacja Pilników NiTi, HyFlex™ CM & EDM. Available online: https://global.coltene.com/pim/DOC/BRO/docbro60013831-03-18-pl-hyflex-cm-edm-a4splaindv1.pdf (accessed on 19 November 2021).
- Morgental, R.D.; Vier-Pelisser, F.V.; Kopper, P.M.; de Figueiredo, J.A.; Peters, O.A. Cutting efficiency of conventional and martensitic nickel-titanium instruments for coronal flaring. J. Endod. 2013, 39, 1634–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, O.A.; Morgental, R.D.; Schulze, K.A.; Paqué, F.; Kopper, P.M.; Vier-Pelisser, F.V. Determining cutting efficiency of nickel-titanium coronal flaring instruments used in lateral action. Int. Endod. J. 2014, 47, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, R.G.; Lopes, H.P.; Elias, C.N.; Viera, M.V.B.; Vieira, V.T.L.; de Paula, C.B.; Alves, F.R.F. Comparative study of the mechanical properties of instruments made of conventional, M-wire, R-phase, and controlled memory nickel-titanium alloys. ENDO—Endod. Pract. Today 2017, 11, 271–277. [Google Scholar]
- Testarelli, L.; Plotino, G.; Al-Sudani, D.; Vincenzi, V.; Giansiracusa, A.; Grande, N.M.; Gambarini, G. Bending properties of a new nickel-titanium alloy with a lower percent by weight of nickel. J. Endod. 2011, 37, 1293–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goo, H.J.; Kwak, S.W.; Ha, J.H.; Pedullà, E.; Kim, H.C. Mechanical Properties of Various Heat-treated Nickel-titanium Rotary Instruments. J. Endod. 2017, 43, 1872–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pongione, G.; Pompa, G.; Milana, V.; Di Carlo, S.; Giansiracusa, A.; Nicolini, E.; De Angelis, F. Flexibility and resistance to cyclic fatigue of endodontic instruments made with different nickel-titanium alloys: A comparative test. Ann. Stomatol. 2012, 3, 119–122. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, L.A.; de Azevedo Bahia, M.G.; Las Casas, E.B.; Buono, V.T. Comparison of the mechanical behavior between controlled memory and superelastic nickel-titanium files via finite element analysis. J. Endod. 2013, 39, 1444–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlShwaimi, E. Cyclic fatigue resistance of a novel rotary file manufactured using controlled memory Ni-Ti technology compared to a file made from M-wire file. Int. Endod. J. 2018, 51, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capar, I.D.; Ertas, H.; Arslan, H. Comparison of cyclic fatigue resistance of novel nickel-titanium rotary instruments. Aust. Endod. J. 2015, 41, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Qian, W.; Abtin, H.; Gao, Y.; Haapasalo, M. Fatigue testing of controlled memory wire nickel-titanium rotary instruments. J. Endod. 2011, 37, 997–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casper, R.B.; Roberts, H.W.; Roberts, M.D.; Himel, V.T.; Bergeron, B.E. Comparison of autoclaving effects on torsional deformation and fracture resistance of three innovative endodontic file systems. J. Endod. 2011, 37, 1572–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.W.; Shim, K.S.; Kim, Y.C.; Jee, K.K.; Zhu, Q.; Perinpanayagam, H.; Kum, K.Y. Cyclic fatigue resistance, torsional resistance, and metallurgical characteristics of V taper 2 and V taper 2H rotary NiTi files. Scanning 2016, 38, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peters, O.A.; Gluskin, A.K.; Weiss, R.A.; Han, J.T. An in vitro assessment of the physical properties of novel Hyflex nickel-titanium rotary instruments. Int. Endod. J. 2012, 45, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouska, J.; Justman, B.; Williamson, A.; DeLong, C.; Qian, F. Resistance to cyclic fatigue failure of a new endodontic rotary file. J. Endod. 2012, 38, 667–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulem, Ü.K.; Kececi, A.D.; Guldas, H.E. Experimental evaluation of cyclic fatigue resistance of four different nickel-titanium instruments after immersion in sodium hypochlorite and/or sterilization. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2013, 21, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aminsobhani, M.; Meraji, N.; Sadri, E. Comparison of Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Five Nickel Titanium Rotary File Systems with Different Manufacturing Techniques. J. Dent. 2015, 12, 636–646. [Google Scholar]
- Bhagabati, N.; Yadav, S.; Talwar, S. An in vitro cyclic fatigue analysis of different endodontic nickel-titanium rotary instruments. J. Endod. 2012, 38, 515–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersoy, I.; Kol, E.; Uygun, A.D.; Tanriver, M.; Seckin, F. Comparison of cyclic fatigue resistance between different NiTi instruments with 4% taper. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2016, 79, 345–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.C.; Yum, J.; Hur, B.; Cheung, G.S. Cyclic fatigue and fracture characteristics of ground and twisted nickel-titanium rotary files. J. Endod. 2010, 36, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedullà, E.; Plotino, G.; Grande, N.M.; Pappalardo, A.; Rapisarda, E. Cyclic fatigue resistance of four nickel-titanium rotary instruments: A comparative study. Ann. Stomatol. 2012, 3, 59–63. [Google Scholar]
- Pedullà, E.; Grande, N.M.; Plotino, G.; Pappalardo, A.; Rapisarda, E. Cyclic fatigue resistance of three different nickel-titanium instruments after immersion in sodium hypochlorite. J. Endod. 2011, 37, 1139–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, R.C.; Lopes, H.P.; Elias, C.N.; Amaral, G.; Vieira, V.T.; De Martin, A.S. Influence of different manufacturing methods on the cyclic fatigue of rotary nickel-titanium endodontic instruments. J. Endod. 2011, 37, 1553–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Oh, S.; Kim, Y.C.; Jee, K.K.; Kum, K.; Chang, S. Fracture Resistance of K3 Nickel-Titanium Files Made from Different Thermal Treatments. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2016, 2016, 6374721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hou, X.; Yahata, Y.; Hayashi, Y.; Ebihara, A.; Hanawa, T.; Suda, H. Phase transformation behaviour and bending property of twisted nickel-titanium endodontic instruments. Int. Endod. J. 2011, 44, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Zhou, H.M.; Wang, Z.; Campbell, L.; Zheng, Y.F.; Haapasalo, M. Phase transformation behavior and mechanical properties of thermomechanically treated K3XF nickel-titanium instruments. J. Endod. 2013, 39, 919–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gambarini, G.; Pongione, G.; Rizzo, F.; Testarelli, L.; Cavalleri, G.; Gerosa, R. Bending properties of nickel-titanium instruments: A comparative study. Minerva Stomatol. 2008, 57, 393–398. [Google Scholar]
- Gambarini, G.; Gerosa, R.; De Luca, M.; Garala, M.; Testarelli, L. Mechanical properties of a new and improved nickel-titanium alloy for endodontic use: An evaluation of file flexibility. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2008, 105, 798–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, K.; Wayman, C.M. Shape Memory Alloys, 1st ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1998; pp. 1–284. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.K.; Lin, H.C.; Chou, T.S. A study of electrical resistivity, internal friction and shear modulus on an aged Ti49Ni51 alloy. Acta Metall. Mater. 1990, 38, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaw, Y.C.; Su, Y.Y.; Lai, Y.L.; Lee, S.Y. Stiffness and frictional resistance of a superelastic nickel-titanium orthodontic wire with low-stress hysteresis. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofacial Orthop. 2007, 131, 578.E12–578.E18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Batouty, K.M.; Elmallah, W.E. Comparison of canal transportation and changes in canal curvature of two nickel-titanium rotary instruments. J. Endod. 2011, 37, 1290–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashem, A.A.; Ghoneim, A.G.; Lutfy, R.A.; Foda, M.Y.; Omar, G.A. Geometric analysis of root canals prepared by four rotary NiTi shaping systems. J. Endod. 2012, 38, 996–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rejula, F.; Christalin, R.; Ahmed, W.; Dinakaran, S.; Gopinathan, A.S.; Babu, A. Measure and compare the Degree of Root Canal Transportation and Canal-centering ability of Twisted, ProTaper, and Conventional Stainless Steel K Files using Spiral Computed Tomography: An in vitro Study. J. Contemp. Dent. Pract. 2017, 18, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, P.J.; Kumar, V.S.; Aravind, K.; Kumar, H.T.; Vishal, M.B.; Vizaikumar, V.N.; Das, R.; Vamsilatha, K. Canal shaping with one shape file and twisted files: A comparative study. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2014, 8, ZF01–ZF03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, L.C.; Magalhães, R.R.; Nakagawa, R.K.; Puente, C.G.; Buono, V.T.; Bahia, M.G. Physical and mechanical properties of twisted or ground nickel-titanium instruments. Int. Endod. J. 2013, 46, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higuera, O.; Plotino, G.; Tocci, L.; Carrillo, G.; Gambarini, G.; Jaramillo, D.E. Cyclic fatigue resistance of 3 different nickel-titanium reciprocating instruments in artificial canals. J. Endod. 2015, 41, 913–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsaka, S.E.; Elnaghy, A.M.; Badr, A.E. Torsional and bending resistance of WaveOne Gold, Reciproc and Twisted File Adaptive instruments. Int. Endod. J. 2017, 50, 1077–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wycoff, R.C.; Berzins, D.W. An in vitro comparison of torsional stress properties of three different rotary nickel-titanium files with a similar cross-sectional design. J. Endod. 2012, 38, 1118–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapisarda, E.; Bonaccorso, A.; Tripi, T.R.; Condorelli, G.G. Effect of sterilization on the cutting efficiency of rotary nickel-titanium endodontic files. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 1999, 88, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotino, G.; Costanzo, A.; Grande, N.M.; Petrovic, R.; Testarelli, L.; Gambarini, G. Experimental Evaluation on the Influence of Autoclave Sterilization on the Cyclic Fatigue of New Nickel-Titanium Rotary Instruments. J. Endod. 2012, 38, 222–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Chapelle, C.F.; Veersema, S.; Brölmann, H.A.M.; Jansen, F.W. Effectiveness and feasibility of hysteroscopic sterilization techniques: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Fertil. Steril. 2015, 103, 1516–1525.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haïkel, Y.; Serfaty, R.; Bleicher, P.; Lwin, T.-T.C.; Allemann, C. Effects of cleaning, disinfection, and sterilization procedures on the cutting efficiency of endodontic files. J. Endod. 1996, 22, 657–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laneve, E.; Raddato, B.; Dioguardi, M.; Di Gioia, G.; Troiano, G.; Lo Muzio, L. Sterilisation in Dentistry: A Review of the Literature. Int. J. Dent. 2019, 2019, 6507286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raju, T.B.; Garapati, S.; Agrawal, R.; Reddy, S.; Razdan, A.; Kumar, S.K. Sterilizing Endodontic Files by four different sterilization methods to prevent cross-infection—An In-vitro Study. J. Int. Oral. Health 2013, 5, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Venkatasubramanian, R.; Jayanthi; Das, U.M.; Bhatnagar, S. Comparison of the effectiveness of sterilizing endodontic files by 4 different methods: An in vitro study. J. Indian Soc. Pedod. Prev. Dent. 2010, 28, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheth, N.C.; Rathod, Y.V.; Shenoi, P.R.; Shori, D.D.; Khode, R.T.; Khadse, A.P. Evaluation of new technique of sterilization using biological indicator. J. Conserv. Dent. 2017, 20, 346–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgeois, D.; Dussart, C.; Saliasi, I.; Laforest, L.; Tramini, P.; Carrouel, F. Observance of Sterilization Protocol Guideline Procedures of Critical Instruments for Preventing Iatrogenic Transmission of Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease in Dental Practice in France, 2017. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schafer, E. Effect of sterilization on the cutting efficiency of PVD-coated nickel-titanium endodontic instruments. Int. Endod. J. 2002, 35, 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seago, S.T.; Bergeron, B.E.; Kirkpatrick, T.C.; Roberts, M.D.; Roberts, H.W.; Himel, V.T.; Sabey, K.A. Effect of Repeated Simulated Clinical Use and Sterilization on the Cutting Efficiency and Flexibility of Hyflex CM Nickel-Titanium Rotary Files. J. Endod. 2015, 41, 725–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haïkel, Y.; Serfaty, R.; Wilson, P.; Speisser, J.M.; Allemann, C. Cutting efficiency of nickel-titanium endodontic instruments and the effect of sodium hypochlorite treatment. J. Endod. 1998, 24, 736–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, R.G.; Craig, R.G.; Powers, J.M. Effect of sterilization and irrigants on the cutting ability of stainless steel files. J. Endod. 1983, 9, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, S.W.; Newton, C.W.; Brown, C.E. The effects of steam sterilization and usage on cutting efficiency of endodontic instruments. J. Endod. 1989, 15, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haïkel, Y.; Serfaty, R.; Lwin, T.T.; Allemann, C. Measurement of the cutting efficiency of endodontic instruments: A new concept. J. Endod. 1996, 22, 651–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webber, J.; Moser, J.B.; Heuer, M.A. A method to determine the cutting efficiency of root canal instruments in linear motion. J. Endod. 1980, 6, 829–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalobos, R.L.; Moser, J.B.; Heuer, M.A. A method to determine the cutting efficiency of root canal instruments in rotary motion. J. Endod. 1980, 6, 667–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molven, O. A comparison of the dentin-removing ability of five root canal instruments. Scand. J. Dent. Res. 1970, 78, 500–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliet, S.; Sorin, S.M. Cutting efficiency of endodontic reamers. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. 1973, 36, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fromme, H.G.; Riedel, H. Treatment of Dental Root Canals and the Marginal Contact between Filling Material and Tooth, studied by Scanning Electronic Microscopy. Int. Endod. J. 1972, 6, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanescu, T.; Popovici, R.A.; Antoniac, I.V.; Galuscan, A.; Tirca, T. Ni-Ti Rotary Instrument Fracture Analysis after Clinical Use. Structure Changes in Used Instruments. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2016, 15, 981–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matei, A.; Pencea, I.; Stanciu, S.; Hristu, R.; Antoniac, I.; Coman, E.C.; Sfat, C.; Stanciu, G. Structural characterization and adhesion appraisal of TiN and TiCN coatings deposited by CAE-PVD technique on a new carbide composite cutting tool. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2015, 29, 2576–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inan, U.; Keskin, C. Torsional Resistance of ProGlider, Hyflex EDM, and One G Glide Path Instruments. J. Endod. 2019, 45, 1253–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spagnuolo, G.; Ametrano, G.; d’Antò, V.; Rengo, C.; Simeone, M.; Riccitiello, F.; Amato, M. Effect of autoclaving on the surfaces of TiN-coated and conventional nickel-titanium rotary instruments. Int. Endod. J. 2012, 45, 1148–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavian, H.; Iranmanesh, P.; Mojtahedi, H.; Nazeri, R. Effect of Autoclave Cycles on Surface Characteristics of S-File Evaluated by Scanning Electron Microscopy. Iran. Endod. J. 2015, 11, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, A.S.; Tilakchand, M.; Naik, B.D. The effect of multiple autoclave cycles on the surface of rotary nickel-titanium endodontic files: An in vitro atomic force microscopy investigation. J. Conserv. Dent. 2015, 18, 218–222. [Google Scholar]
- Fayyad, D.M.; Elgendy, A.A.E. Cutting Efficiency of Twisted versus Machined Nickel-Titanium Endodontic Files. J. Endod. 2011, 37, 1143–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilt, B.R.; Cunningham, C.J.; Shen, C.; Richards, N. Torsional Properties of Stainless-Steel and Nickel-Titanium Files After Multiple Autoclave Sterilizations. J. Endod. 2000, 26, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvaggio, J.; Hicks, M.L. Effect of heat sterilization on the torsional properties of rotary nickel-titanium endodontic files. J. Endod. 1997, 23, 731–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khabiri, M.; Ebrahimi, M.; Saei, M.R. The Effect of Autoclave Sterilization on Resistance to Cyclic Fatigue of Hero Endodontic File #642 (6%) at Two Artificial Curvature. J. Dent. 2017, 18, 277–281. [Google Scholar]
- Hilfer, P.B.; Bergeron, B.E.; Mayerchak, M.J.; Roberts, H.W.; Jeansonne, B.G. Multiple Autoclave Cycle Effects on Cyclic Fatigue of Nickel-Titanium Rotary Files Produced by New Manufacturing Methods. J. Endod. 2011, 37, 72–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshwaimi, E.O. Effect of Sterilization on Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Proflexendo Endodontic Rotary Files. Saudi J. Med. Med. Sci. 2019, 7, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testarelli, L.; Gallottini, L.; Gambarini, G. Mechanical properties of nickel-titanium files following multiple heat sterilizations. Minerva Stomatol. 2003, 52, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- King, J.B.; Roberts, H.W.; Bergeron, B.E.; Mayerchak, M.J. The effect of autoclaving on torsional moment of two nickel-titanium endodontic files. Int. Endod. J. 2012, 45, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viana, A.C.; Gonzalez, B.M.; Buono, V.T.; Bahia, M.G. Influence of sterilization on mechanical properties and fatigue resistance of nickel-titanium rotary endodontic instruments. Int. Endod. J. 2006, 39, 709–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfoqom Alazemi, M.; Bryant, S.T.; Dummer, P.M. Deformation of HyFlex CM instruments and their shape recovery following heat sterilization. Int. Endod. J. 2015, 48, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, K.; Uslu, G.; Ozyurek, T. Effect of multiple autoclave cycles on the surface roughness of HyFlex CM and HyFlex EDM files: An atomic force microscopy study. Clin. Oral. Investig. 2018, 22, 2975–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Shen, Y.; Peng, B.; Haapasalo, M. Effect of autoclave sterilization on the cyclic fatigue resistance of thermally treated Nickel-Titanium instruments. Int. Endod. J. 2016, 49, 990–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valois, C.R.; Silva, L.P.; Azevedo, R.B. Multiple autoclave cycles affect the surface of rotary nickel-titanium files: An atomic force microscopy study. J. Endod. 2008, 34, 859–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canalda-Sahli, C.; Brau-Aguadé, E.; Sentís-Vilalta, J. The effect of sterilization on bending and torsional properties of K-files manufactured with different metallic alloys. Int. Endod. J. 1998, 31, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.F.; Zheng, P.; Xu, L.; Su, Q. The influence of autoclave sterilization on surface characteristics and cyclic fatigue resistance of 3 nickel-titanium rotary instruments. Shanghai Kou Qiang Yi Xue 2015, 24, 690–695. [Google Scholar]
- Mize, S.B.; Clement, D.J.; Pruett, J.P.; Carnes, D.L., Jr. Effect of sterilization on cyclic fatigue of rotary nickel-titanium endodontic instruments. J. Endod. 1998, 24, 843–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özyürek, T.; Yılmaz, K.; Uslu, G. The effects of autoclave sterilization on the cyclic fatigue resistance of ProTaper Universal, ProTaper Next, and ProTaper Gold nickel-titanium instruments. Restor. Dent. Endod. 2017, 42, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alexandrou, G.; Chrissafis, K.; Vasiliadis, L.; Pavlidou, E.; Polychroniadis, E.K. Effect of heat sterilization on surface characteristics and microstructure of Mani NRT rotary nickel-titanium instruments. Int. Endod. J. 2006, 39, 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


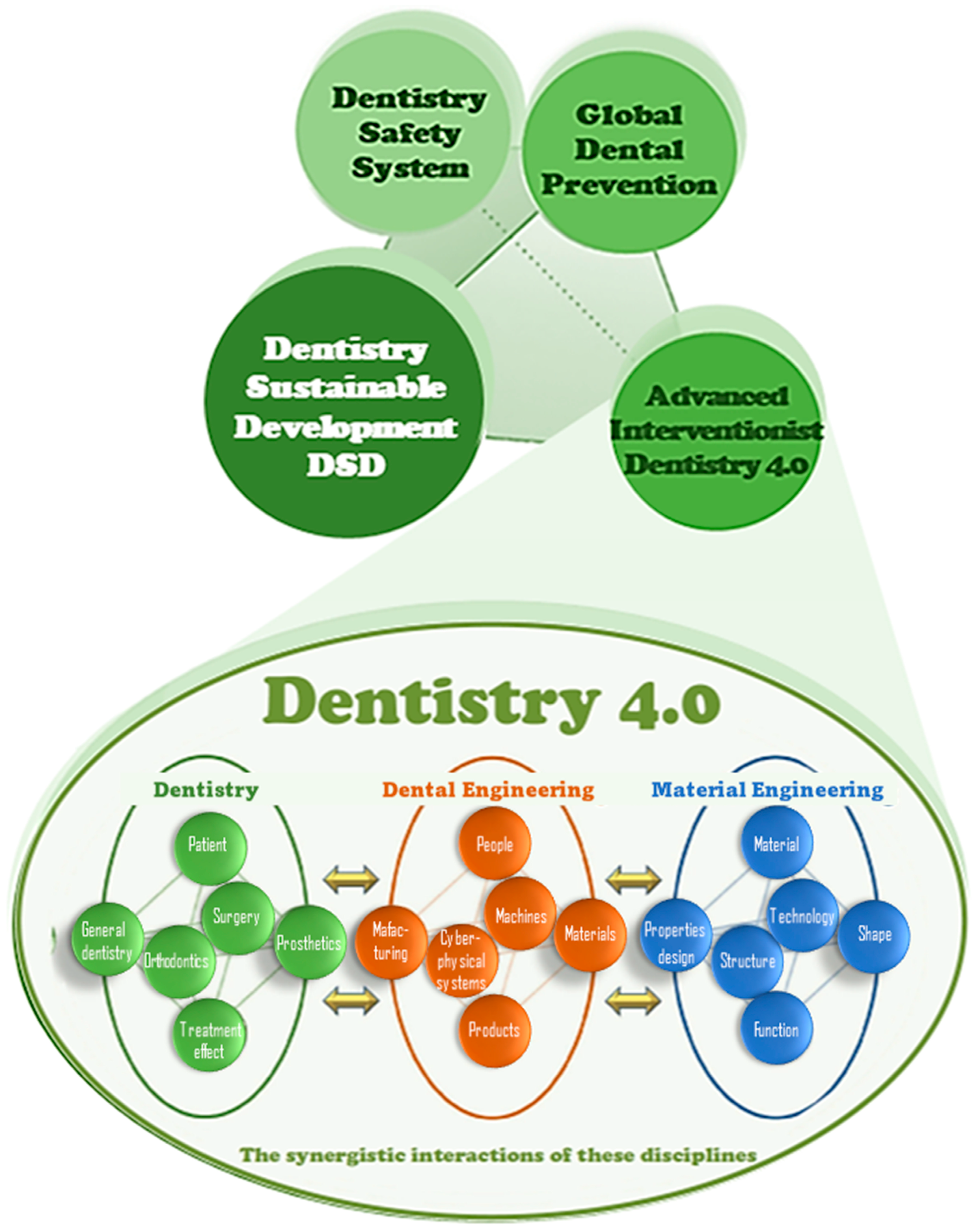
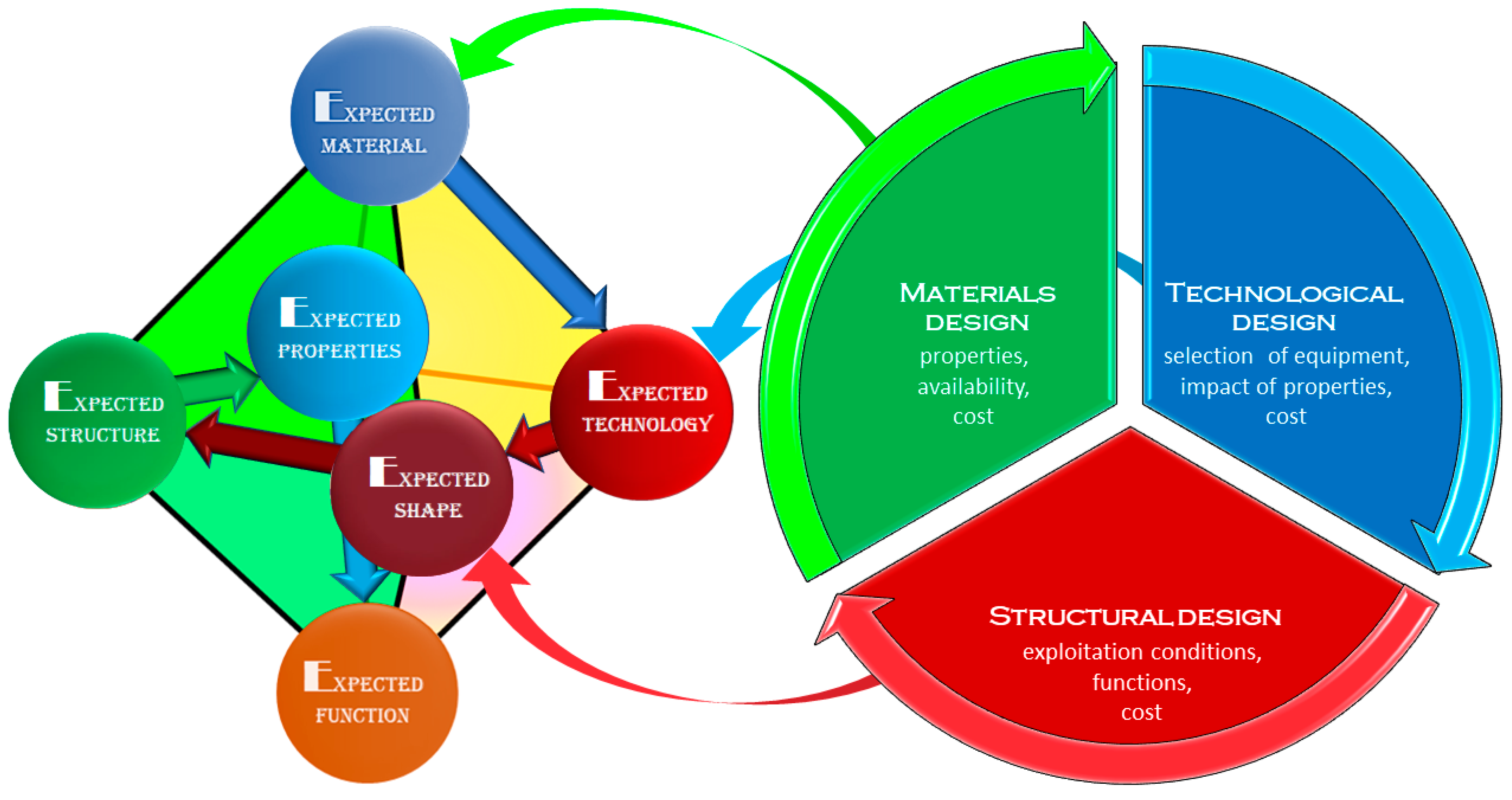

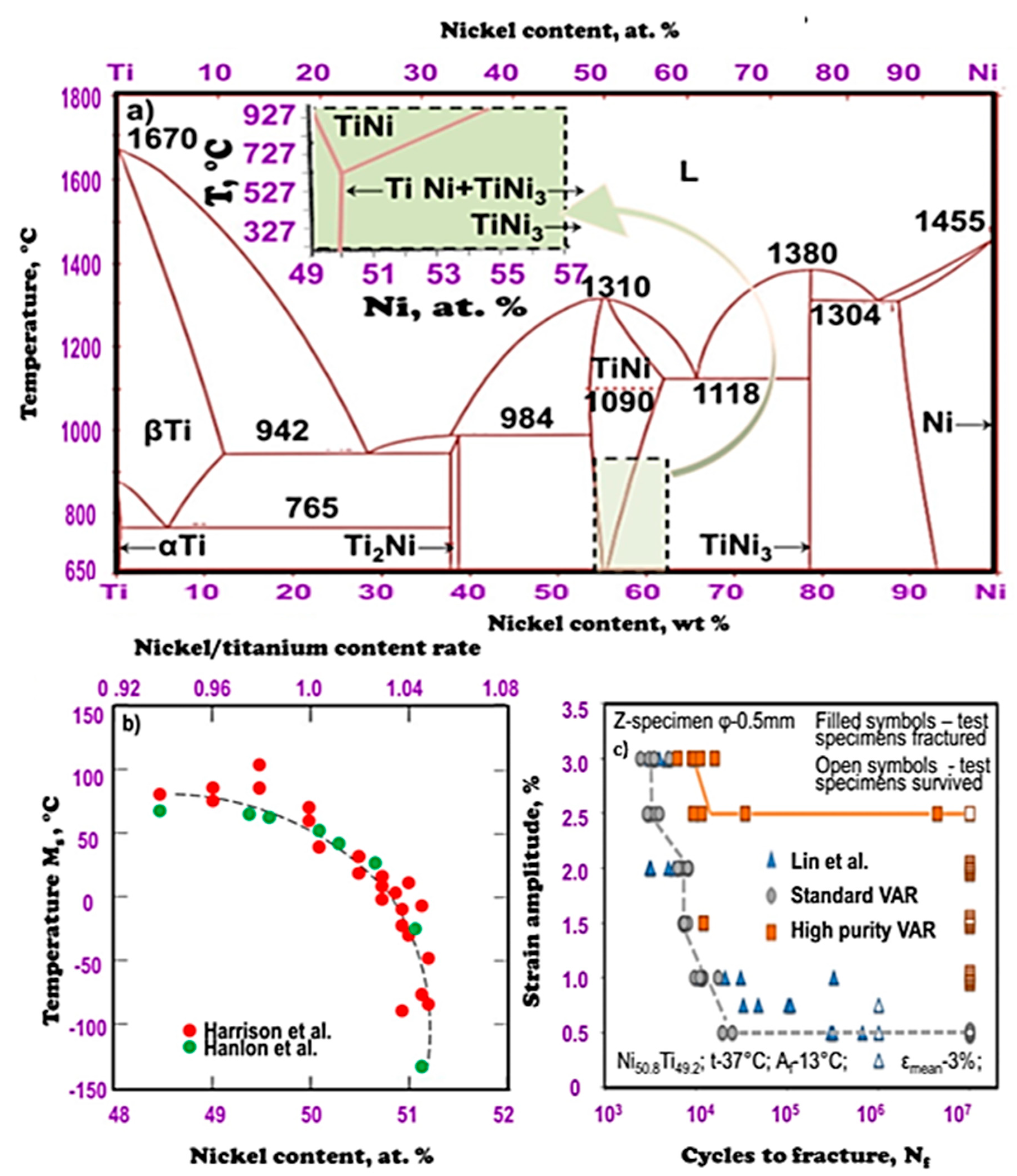

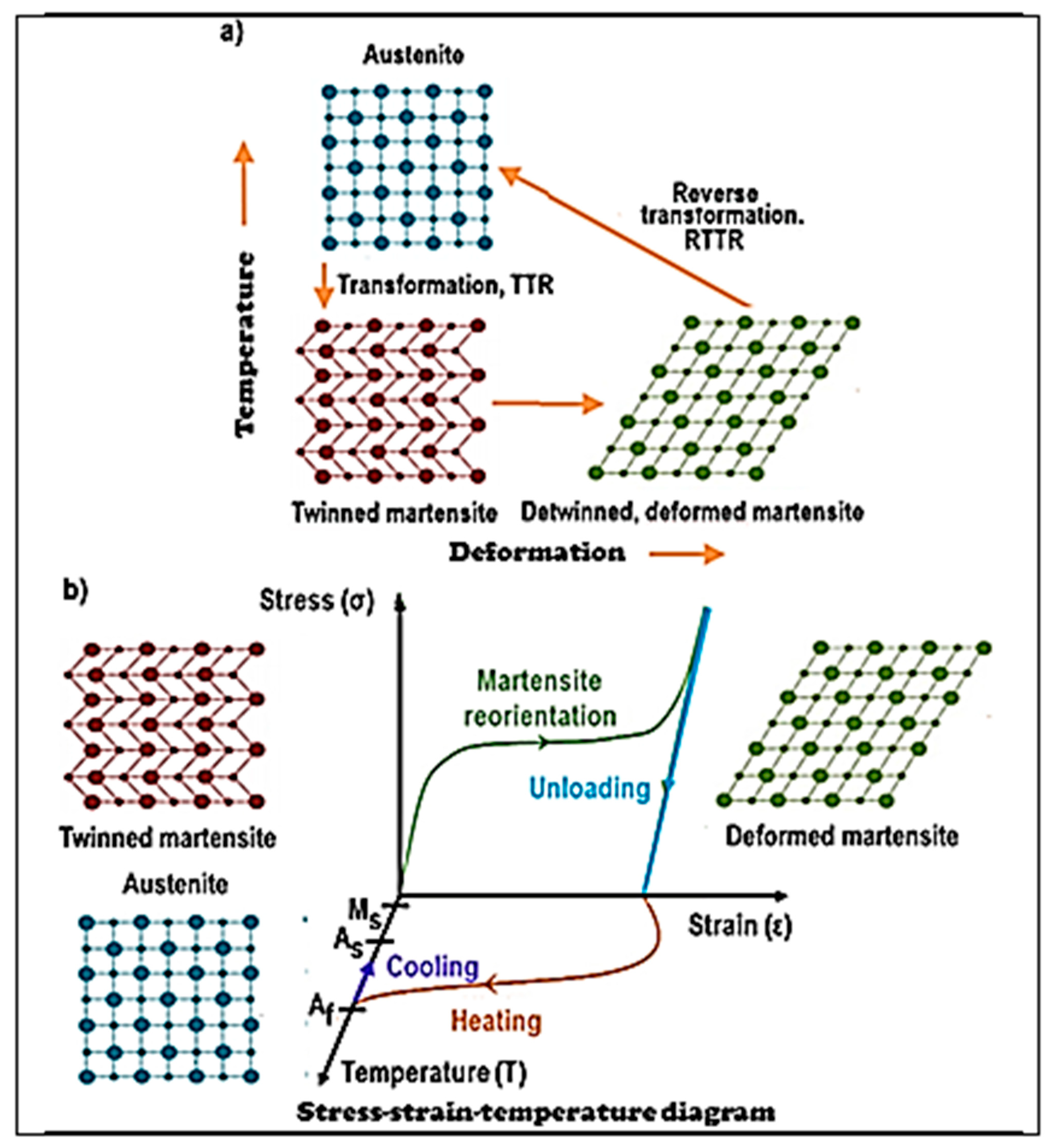
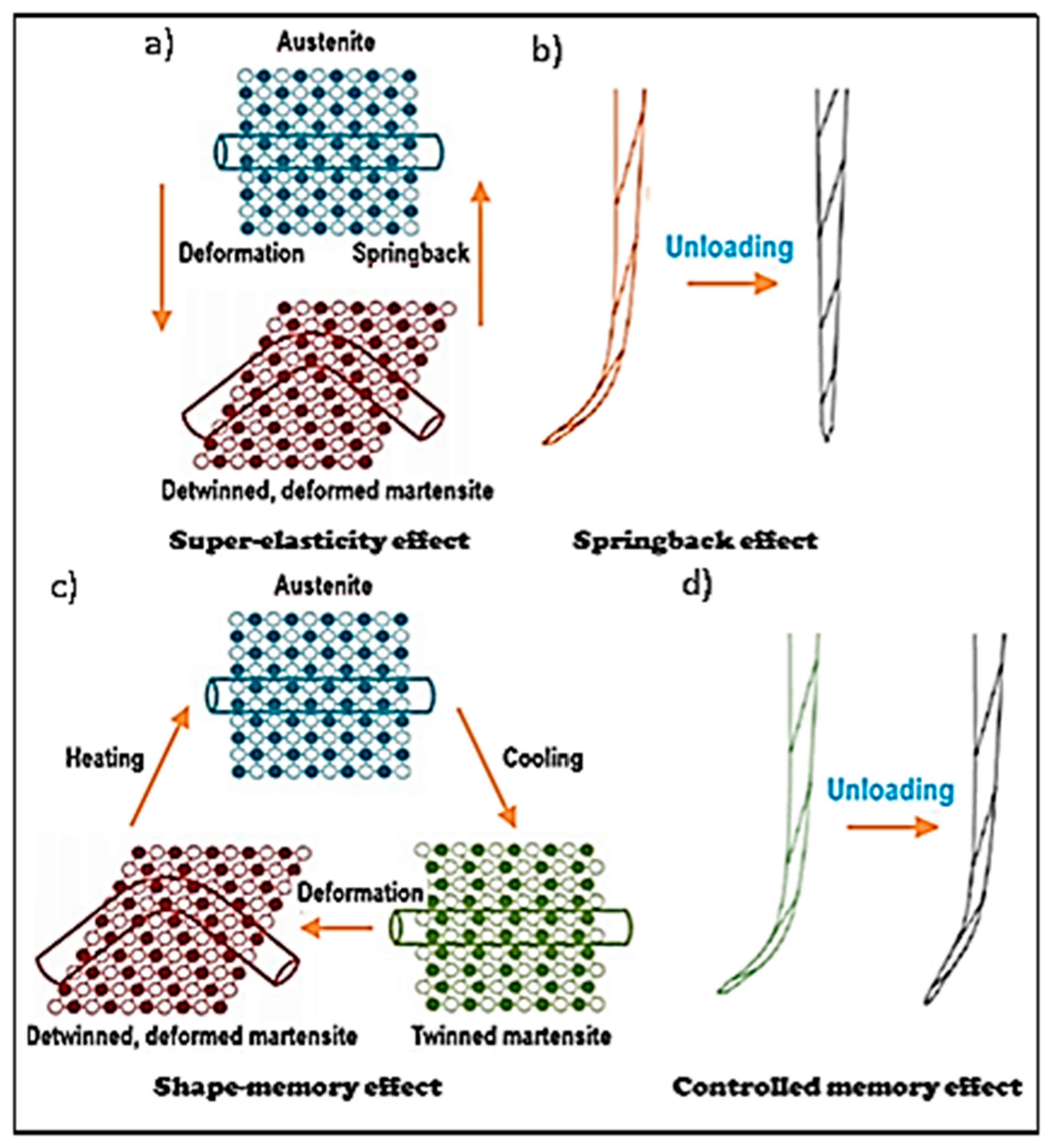

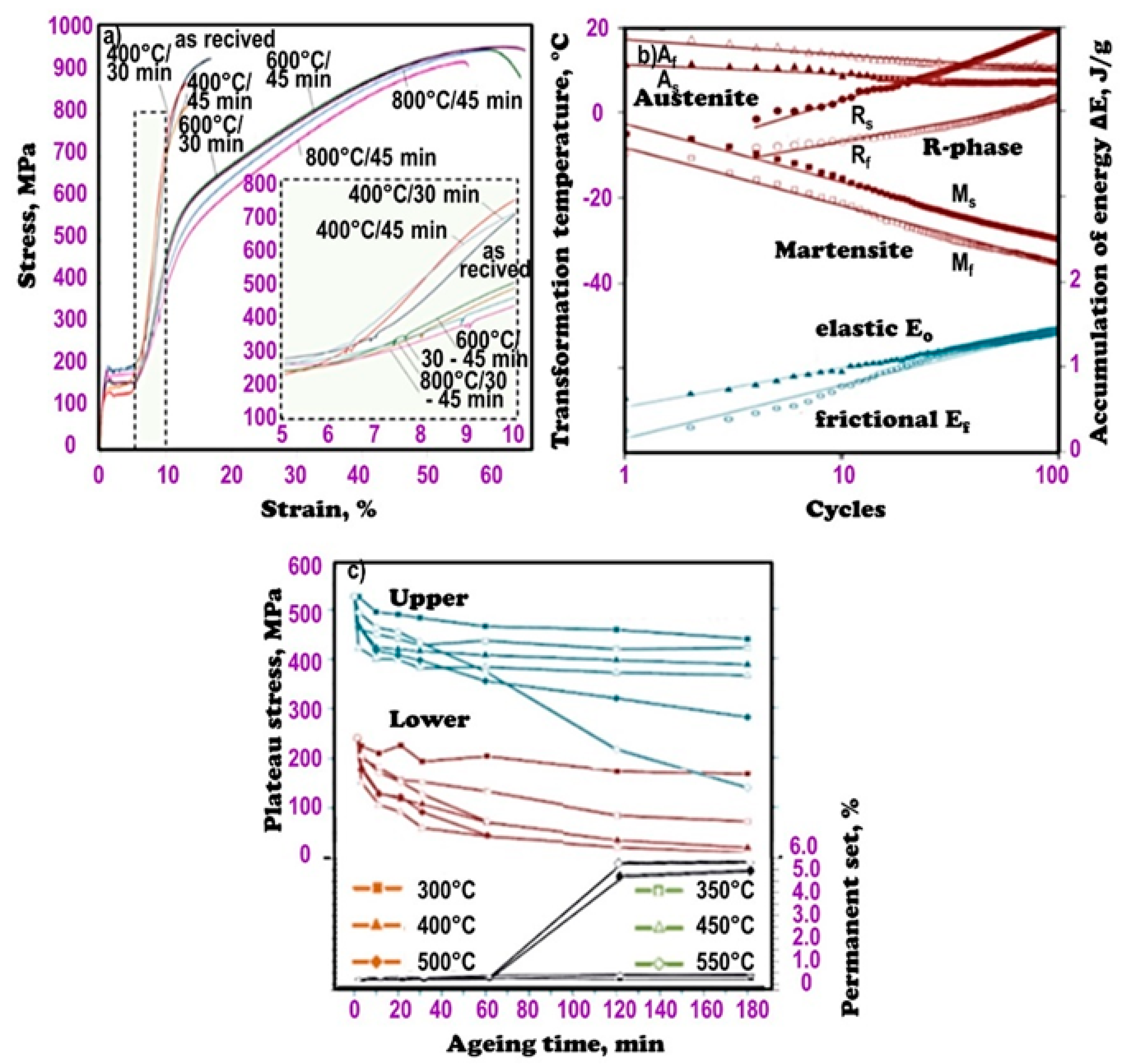





| Alloy No | Weight Concentration, % | Temperature, °C | σ0,2, MPa | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni | Ti | Ms | Mf | As | Af | ||
| 1 | 54.8 | 45.2 | 20 | −20 | 39 | 77 | 115 |
| 2 | 55.5 | 44.5 | −30 | −53 | −12 | 0 | 75 |
| Alloy | Chemical Composition, wt. % | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni | Ti | O + N max | C max | Al. max | Each of Co, Fe max | Each of Cu, Cr max | H max | Each of Mn, Mo, W max | Nb max | Si max | S max | Sn max | |
| Standard | 55.6 | Balance | 0.0252 | 0.0020 | 0.0057 | 0.0050 | 0.0050 | 0.0015 | 0.0050 | 0.0050 | 0.0025 | 0.0010 | 0.0100 |
| High purity | 56.0 | 0.0060 | 0.0050 | 0.0012 | |||||||||
| ASTM [178] requirement | 54.5 - 57.0 | 0.050 | 0.050 | - | 0.050 | 0.010 | - | - | 0.025 | - | - | - | |
| Alloy | Transformation Temperature 1, At, °C | Longitudinal Length, µm | Area Fraction, % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard | −12 | −11 | - |
| High purity | 35 | 17 | ≤39 |
| ASTM [178] requirement | 1.01 | 0.28 | ≤2.8 |
| No. | Material | Type of Autoclave | Time and Temperature | Autoclave Cycles Number | Reduction of Cutting Efficiency | Comments | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Stainless steel | Steam autoclave | 15 min, 121 °C | 5, 10, and 15 | No results | No significant differences in cutting efficiency. | [512] |
| 2 | Autoclave bags | 30 min, 132 °C | 10 | No results | Autoclave sterilization resulted in a small but significant decrease in cutting ability of the files. | [511] | |
| 3 | Chemiclave | 30 min, 131 °C | 5 | 63.9–77% | A cutting efficiency reduction in range of 50% to 77%. | [502] | |
| 10 | 50.4–73% | ||||||
| 4 | Nitinol | Euroclave | 30 min, 121 °C | 7 | 20% | The number of sterilization cycles is a determining factor as to cutting efficiency. | [499] |
| 14 | 50% | ||||||
| 5 | Aesculap Automat 356 | 30 min, 134 °C | 5 | 16.1% | Sterilization resulted in a significant decrease in cutting ability. | [508] | |
| 10 | 50.6% | ||||||
| 6 | STATIM 5000 | 6 min, 132 °C | 2,3,7,8, and 9 | No results | A statistically significant decrease in cutting efficiency. | [509] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dobrzański, L.A.; Dobrzański, L.B.; Dobrzańska-Danikiewicz, A.D.; Dobrzańska, J. Nitinol Type Alloys General Characteristics and Applications in Endodontics. Processes 2022, 10, 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10010101
Dobrzański LA, Dobrzański LB, Dobrzańska-Danikiewicz AD, Dobrzańska J. Nitinol Type Alloys General Characteristics and Applications in Endodontics. Processes. 2022; 10(1):101. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10010101
Chicago/Turabian StyleDobrzański, Leszek A., Lech B. Dobrzański, Anna D. Dobrzańska-Danikiewicz, and Joanna Dobrzańska. 2022. "Nitinol Type Alloys General Characteristics and Applications in Endodontics" Processes 10, no. 1: 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10010101
APA StyleDobrzański, L. A., Dobrzański, L. B., Dobrzańska-Danikiewicz, A. D., & Dobrzańska, J. (2022). Nitinol Type Alloys General Characteristics and Applications in Endodontics. Processes, 10(1), 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10010101









