Chemical Recycling of Mixed Plastics in Electronic Waste Using Solvent-Based Processing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Hansen Solubility Parameters (HSPs)
2.3. Designing Solvents and Anti-Solvents Based on HSPs
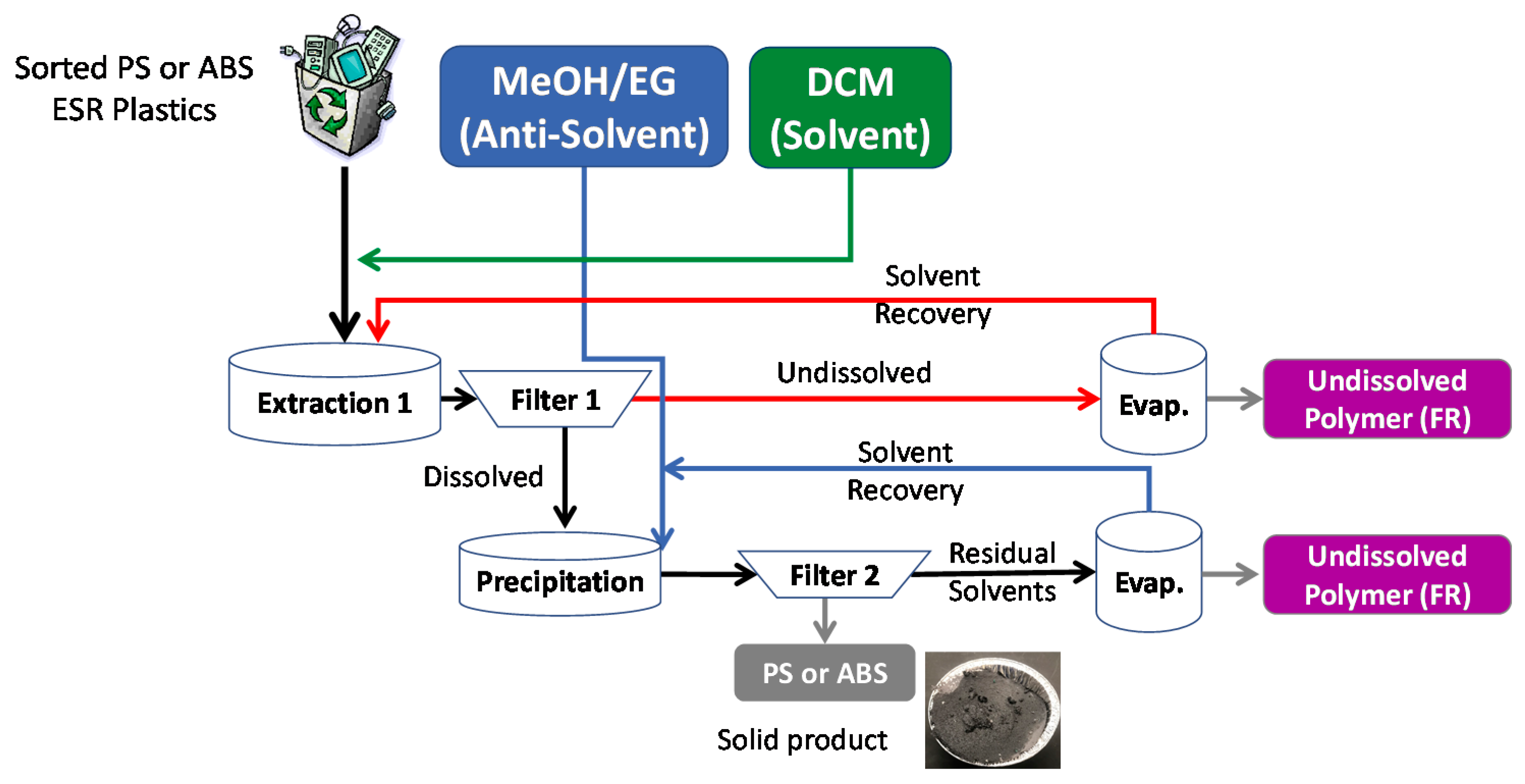
2.4. Dissolution-Precipitation of ESR
2.5. Characterization
2.5.1. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectrometry
2.5.2. Elemental Analysis
2.5.3. Thermogravimetric Analysis
2.5.4. Differential Scanning Calorimetry
2.5.5. Thermal Desorption Gas Chromatography Mass Spectrometry
2.5.6. Gel Permeation Chromatography
3. Results
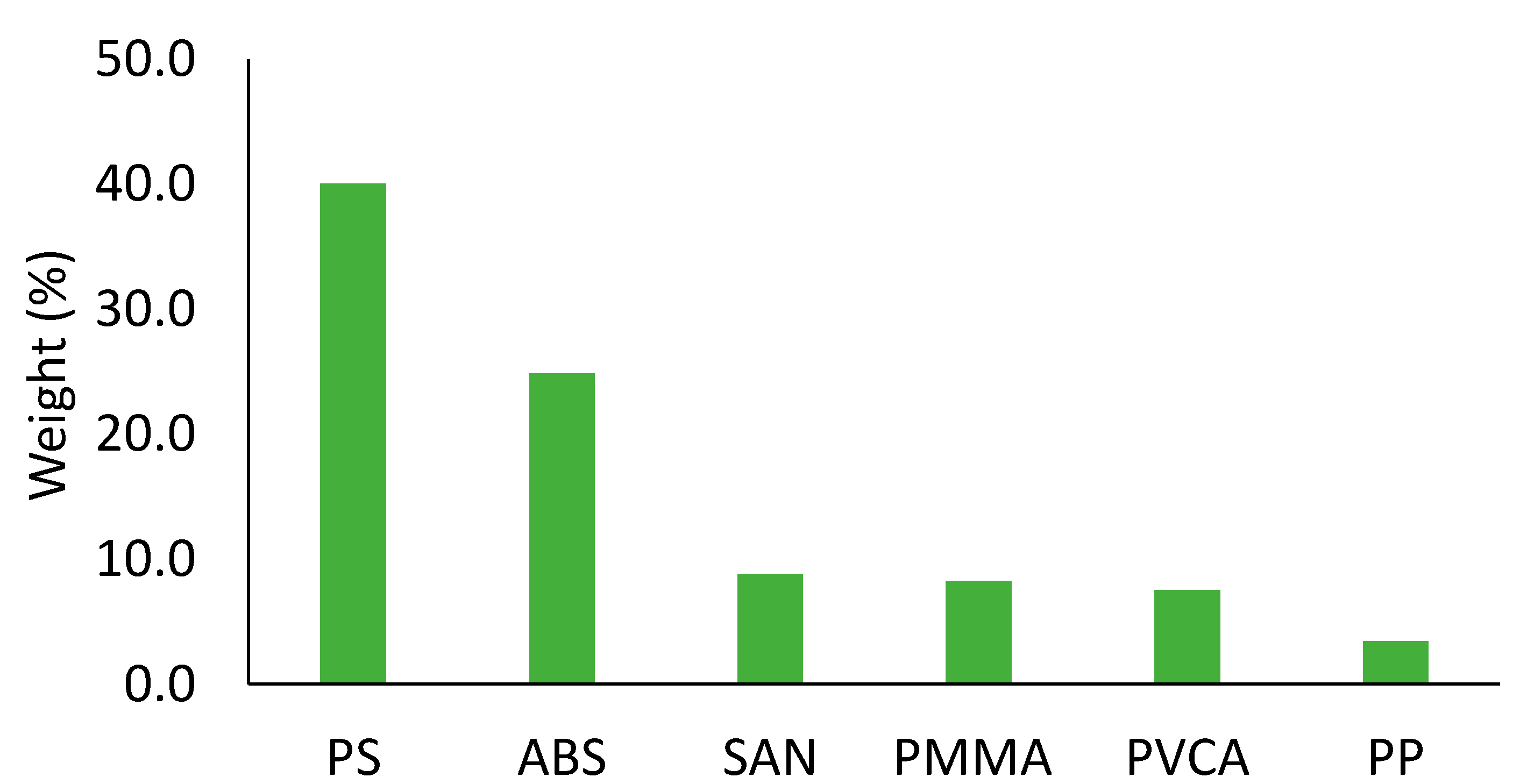
3.1. Composition of ESR Feedstock
3.2. Solvent Screening Process
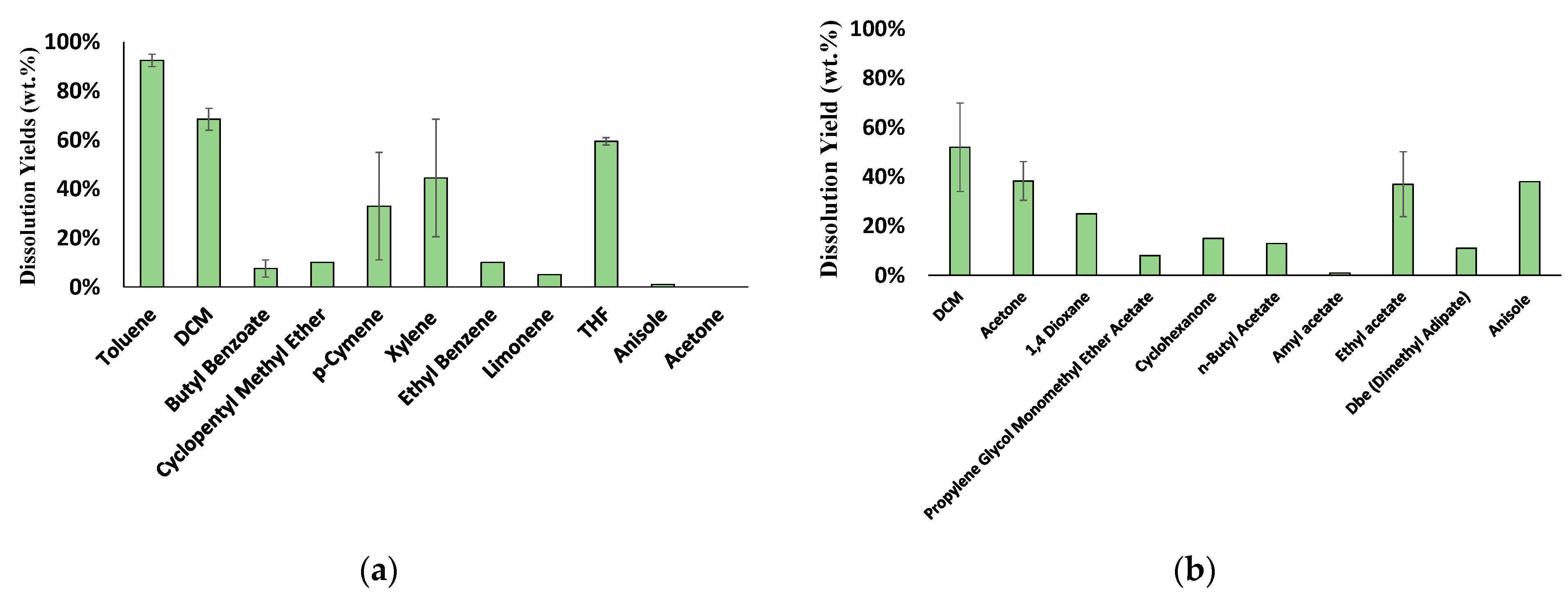
3.2.1. Solvent Screening for PS and ABS
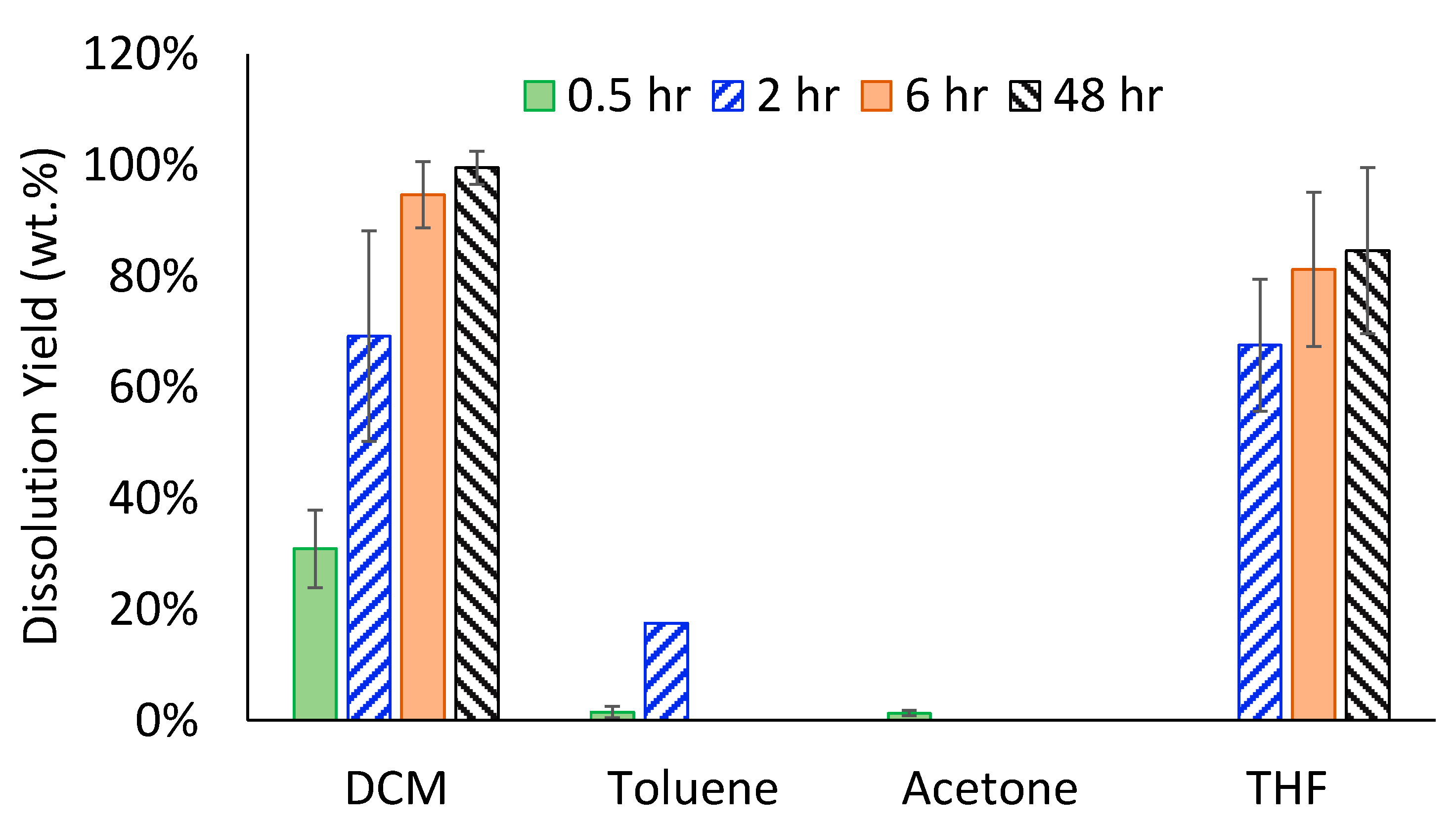
3.2.2. Optimizing Solvents for Dissolving ESR Waste
3.2.3. Solvent Screening Results for the Anti-Solvents
3.2.4. Optimization Results for Precipitating ESR Using Anti-Solvents
3.3. Charactarization of Recycled Products
3.3.1. Molecular Weight Analysis
3.3.2. Polymeric Composition Analysis by FTIR
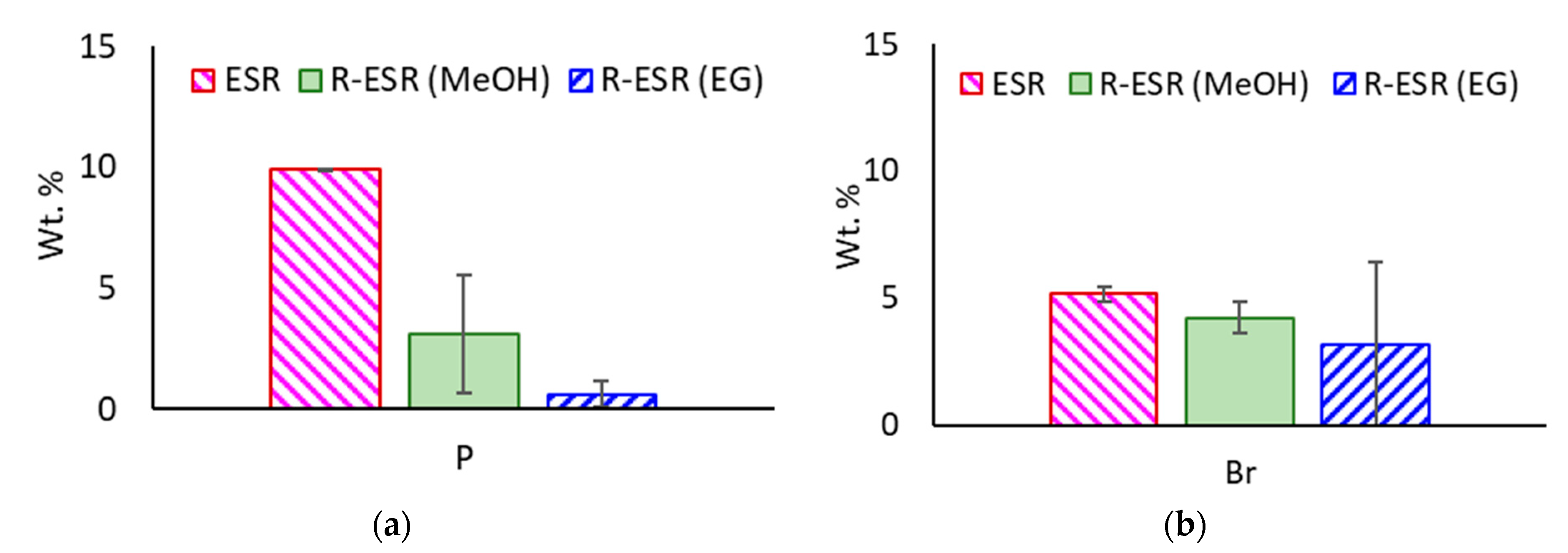
3.3.3. Halogen Content
3.3.4. Thermal Gravimetric Analysis
3.3.5. Differential Scanning Calorimetry
3.3.6. Implications and Improvement for Future E-Waste Recycling
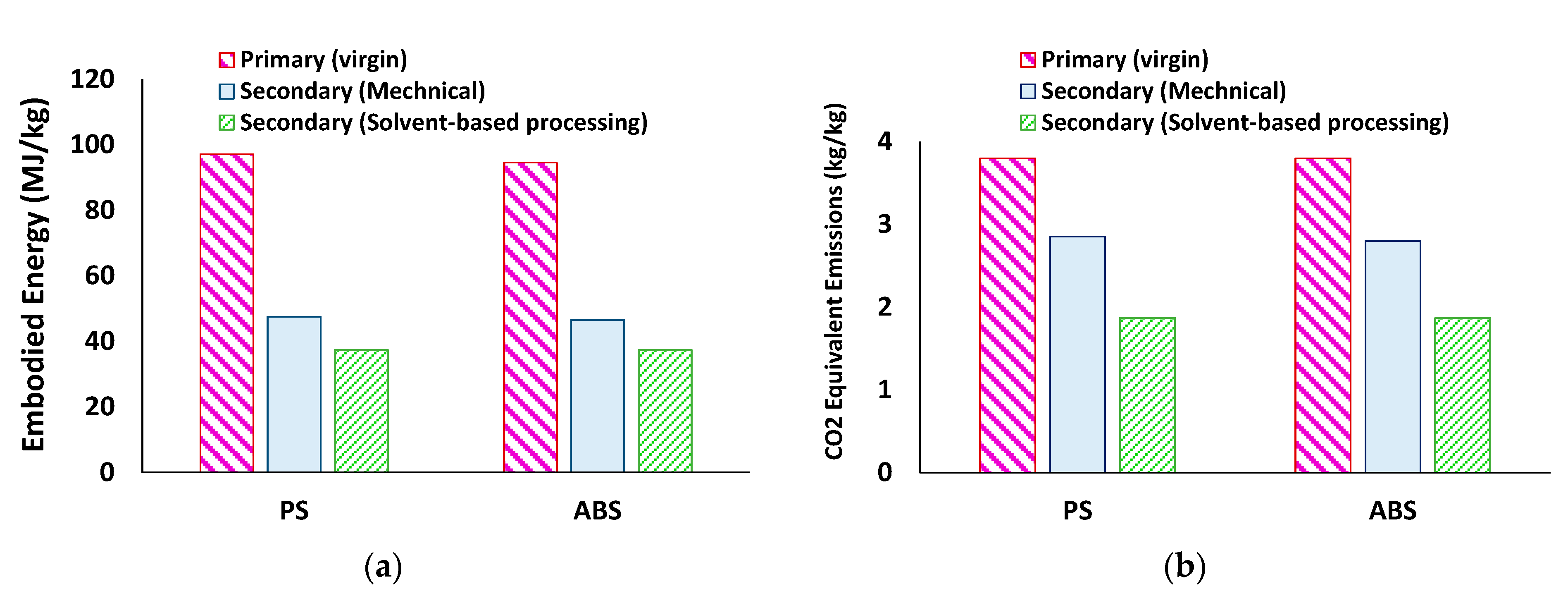
3.4. Energy Analysis
3.5. Economics of the Solvent-Based Recycling of E-Waste
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ning, C.; Lin, C.S.K.; Hui, D.C.W.; McKay, G.J. Waste Printed Circuit Board (PCB) Recycling Techniques. Top. Curr. Chem. 2017, 375, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakolbinger, T.; Toyasaki, F.; Nowak, T.; Nagurney, A. When and for whom would e-waste be a treasure trove? Insights from a network equilibrium model of e-waste flows. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2014, 154, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- USEPA. Durable Goods: Product-Specific Data; EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2018.
- Suresh, S.S.; Bonda, S.; Mohanty, S.; Nayak, S.K. A review on computer waste with its special insight to toxic elements, segregation and recycling techniques. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2018, 116, 477–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PINFA, the Phosphorus, Inorganic and Nitrogen Flame Retardants Association. In Flame Retardants in Electric and Electronic Applications; PINFA: Brussels, Belgium, 2017.
- Evangelopoulos, P.; Arato, S.; Persson, H.; Kantarelis, E.; Yang, W. Reduction of brominated flame retardants (BFRs) in plastics from waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE) by solvent extraction and the influence on their thermal decomposition. Waste Manag. 2019, 94, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riise, B. Recovering plastics from electronics waste. In Energy Technology 2020: Recycling, Carbon Dioxide Management, and Other Technologies; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 295–305. [Google Scholar]
- Gohatre, O.K.; Biswal, M.; Mohanty, S.; Nayak, S.K. An effective sustainable approach towards recycling and value addition of waste poly (vinyl chloride) and acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) recovered from electronic waste (e-waste). J. Polym. Res. 2021, 28, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balart, R.; Lopez, J.; García, D.; Salvador, M.D. Recycling of ABS and PC from electrical and electronic waste. Effect of miscibility and previous degradation on final performance of industrial blends. Eur. Polym. J. 2005, 41, 2150–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopewell, J.; Dvorak, R.; Kosior, E. Plastics recycling: Challenges and opportunities. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 2115–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, H.-Y.; Schoenung, J.M. Economic Analysis of Electronic Waste Recycling: Modeling the Cost and Revenue of a Materials Recovery Facility in California. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 1672–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fromme, H.; Becher, G.; Hilger, B.; Völkel, W. Brominated flame retardants—Exposure and risk assessment for the general population. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2016, 219, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Brominated Flame Retardants (BFRs): Hazard/Risk Information Sheets; OECD: Paris, France, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Xiu, F.-R.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, F.-S. Co-treatment of waste printed circuit boards and polyvinyl chloride by subcritical water oxidation: Removal of brominated flame retardants and recovery of Cu and Pb. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 237, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Yu, J.; Wang, B.; Song, Z.; Xiang, J.; Hu, S.; Su, S.; Sun, L. Chemical recycling of brominated flame retarded plastics from e-waste for clean fuels production: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 61, 433–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayyam Nekouei, R.; Maroufi, S.; Assefi, M.; Pahlevani, F.; Sahajwalla, V. Thermal isolation of a clean alloy from waste slag and polymeric residue of electronic waste. Processes 2020, 8, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chandrasekaran, S.R.; Avasarala, S.; Murali, D.; Rajagopalan, N.; Sharma, B.K. Materials and Energy Recovery from E-Waste Plastics. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 4594–4602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollmer, I.; Jenks, M.J.F.; Roelands, M.C.P.; White, R.J.; van Harmelen, T.; de Wild, P.; van der Laan, G.P.; Meirer, F.; Keurentjes, J.T.F.; Weckhuysen, B.M. Beyond Mechanical Recycling: Giving New Life to Plastic Waste. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 15402–15423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gandhi, N.; Farfaras, N.; Wang, N.-H.-L.; Chen, W.-T. Life Cycle Assessment of Recycling High-Density Polyethylene Plastic Waste. J. Renew. Mater. 2021, 9, 1463–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achilias, D.S.; Roupakias, C.; Megalokonomos, P.; Lappas, A.A.; Antonakou, E.V. Chemical recycling of plastic wastes made from polyethylene (LDPE and HDPE) and polypropylene (PP). J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 149, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cella, R.F.; Mumbach, G.D.; Andrade, K.L.; Oliveira, P.; Marangoni, C.; Bolzan, A.; Bernard, S.; Machado, R.A.F. Polystyrene recycling processes by dissolution in ethyl acetate. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi, A.J.; Najmuldeen, G.F.; Yusoh, K.B. Dissolution/reprecipitation technique for waste polyolefin recycling using new pure and blend organic solvents. J. Polym. Eng. 2013, 33, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ügdüler, S.; Van Geem, K.M.; Roosen, M.; Delbeke, E.I.P.; De Meester, S. Challenges and opportunities of solvent-based additive extraction methods for plastic recycling. Waste Manag. 2020, 104, 148–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reimonn, G.; Lu, T.; Gandhi, N.; Chen, W.-T.J. Review of Microplastic Pollution in the Environment and Emerging Recycling Solutions. J. Renew. Mater. 2019, 7, 1251–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weeden, G.S.; Soepriatna, N.H.; Wang, N.H.L. Method for efficient recovery of high-purity polycarbonates from electronic waste. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 2425–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilaplana, F.; Ribes-Greus, A.; Karlsson, S. Microwave-assisted extraction for qualitative and quantitative determination of brominated flame retardants in styrenic plastic fractions from waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE). Talanta 2009, 78, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-T.; Nien-hwa, L.W.; Jin, K. Method of Converting Plastic Waste into Useful Stock. U.S. Patent No. 10,894,870, 19 January 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, T.; Reimonn, G.; Morose, G.; Yu, E.; Chen, W.-T. Removing Acrylic Conformal Coating with Safer Solvents for Re-Manufacturing Electronics. Polymers 2021, 13, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, J. Solubility parameters: Theory and application; AIC Book and Paper Group: Washington, DC, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Lengeling, B.; Roch, L.M.; Perea, J.D.; Langner, S.; Brabec, C.J.; Aspuru-Guzik, A. A Bayesian Approach to Predict Solubility Parameters. Adv. Theory Simul. 2019, 2, 1800069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Yu, E.; Morose, G.; Nguyen, D.T.; Chen, W.-T. Designing Safer Solvents to Replace Methylene Chloride for Liquid Chromatography Applications Using Thin-Layer Chromatography as a Screening Tool. Separations 2021, 8, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, C.M. Hansen Solubility Parameters: A User’s Handbook; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.-B.; Lv, X.-D.; Yang, W.-D.; Ni, H.-G. Laboratory simulations of the mixed solvent extraction recovery of dominate polymers in electronic waste. Waste Manag. 2017, 69, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achilias, D.S.; Giannoulis, A.; Papageorgiou, G.Z. Recycling of polymers from plastic packaging materials using the dissolution–reprecipitation technique. Polym. Bull. 2009, 63, 449–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Microlab, M. Bromine Determination via Schoniger Combustion. Available online: https://midwestlab.com/elemental-analysis-services/bromine-testing/ (accessed on 2 June 2021).
- Microlab, M. Analysis of Phosphorus with Spectrophotometry. Available online: https://midwestlab.com/elemental-analysis-services/phosphorus-testing/ (accessed on 2 June 2021).
- Puype, F.; Samsonek, J.; Knoop, J.; Egelkraut-Holtus, M.; Ortlieb, M. Evidence of waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE) relevant substances in polymeric food-contact articles sold on the European market. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2015, 32, 410–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Zhao, R.; Wang, J.; Chen, X.; Ge, X.; Chen, M. Waste-to-energy: Dehalogenation of plastic-containing wastes. Waste Manag. 2016, 49, 287–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackadder, D.; Le Poidevin, G. Dissolution of polypropylene in organic solvents: 1. Partial dissolution. Polymer 1976, 17, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackadder, D.; Le Poidevin, G. Dissolution of polypropylene in organic solvents: 2. The steady state dissolution process. Polymer 1976, 17, 768–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackadder, D.; Le Poidevin, G. Dissolution of polypropylene in organic solvents: 4. Nature of the solvent. Polymer 1978, 19, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackadder, D.; Le Poidevin, G. Dissolution of polypropylene in organic solvents: 3. Effect of molecular weight of polymer. Polymer 1977, 18, 547–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, C.; Lundberg, P.; Tang, S.; Ràfols-Ribé, J.; Sandström, A.; Mattias Lindh, E.; Wang, J.; Edman, L. A tool for identifying green solvents for printed electronics. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weeden, G.S.; Ling, L.; Soepriatna, N.H.; Wang, N.H.L. Size-exclusion simulated moving bed for separating organophosphorus flame retardants from a polymer. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1422, 99–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, G.-M.; Wang, L.-S.; Sun, J.; Jiang, L.-K. Solubilities of Three Phosphorus Flame Retardants in Selected Organic Solvents. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2015, 60, 1803–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altwaiq, A.m.; Wolf, M.; van Eldik, R. Extraction of brominated flame retardants from polymeric waste material using different solvents and supercritical carbon dioxide. Anal. Chim. Acta 2003, 491, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashby, M.F. Materials and the Environment: Eco-Informed Material Choice; Elsevier Science: Waltham, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- The REMADE Institute, REMADE Project Impact Caculator. Available online: https://remadeinstitute.org/project-impact-calculator (accessed on 5 November 2021).
- Althaus, H.; Chudacoff, M.; Hischier, R.; Jungbluth, N.; Osses, M.; Primas, A. Life Cycle Inventories of Chemicals; Swiss Center for Life Cycle Inventories: Dübendorf, Switzerland, 2007; Available online: www.ecoinvent.org (accessed on 5 November 2021).
- Tatariants, M.; Yousef, S.; Denafas, G.; Tichonovas, M.; Bendikiene, R. Recovery of gold, other metallic and non-metallic components of full-size waste random access memory. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 2811–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anderson, L.; Yu, E.; Chen, W.-T. Chemical Recycling of Mixed Plastics in Electronic Waste Using Solvent-Based Processing. Processes 2022, 10, 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10010066
Anderson L, Yu E, Chen W-T. Chemical Recycling of Mixed Plastics in Electronic Waste Using Solvent-Based Processing. Processes. 2022; 10(1):66. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10010066
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnderson, Lester, Evan Yu, and Wan-Ting Chen. 2022. "Chemical Recycling of Mixed Plastics in Electronic Waste Using Solvent-Based Processing" Processes 10, no. 1: 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10010066
APA StyleAnderson, L., Yu, E., & Chen, W.-T. (2022). Chemical Recycling of Mixed Plastics in Electronic Waste Using Solvent-Based Processing. Processes, 10(1), 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10010066






