Tilt Angle’s Effects on Free Convection Heat Transfer Coefficient inside a Water-Filled Rectangular Parallelepiped Enclosure
Abstract
:1. Introduction
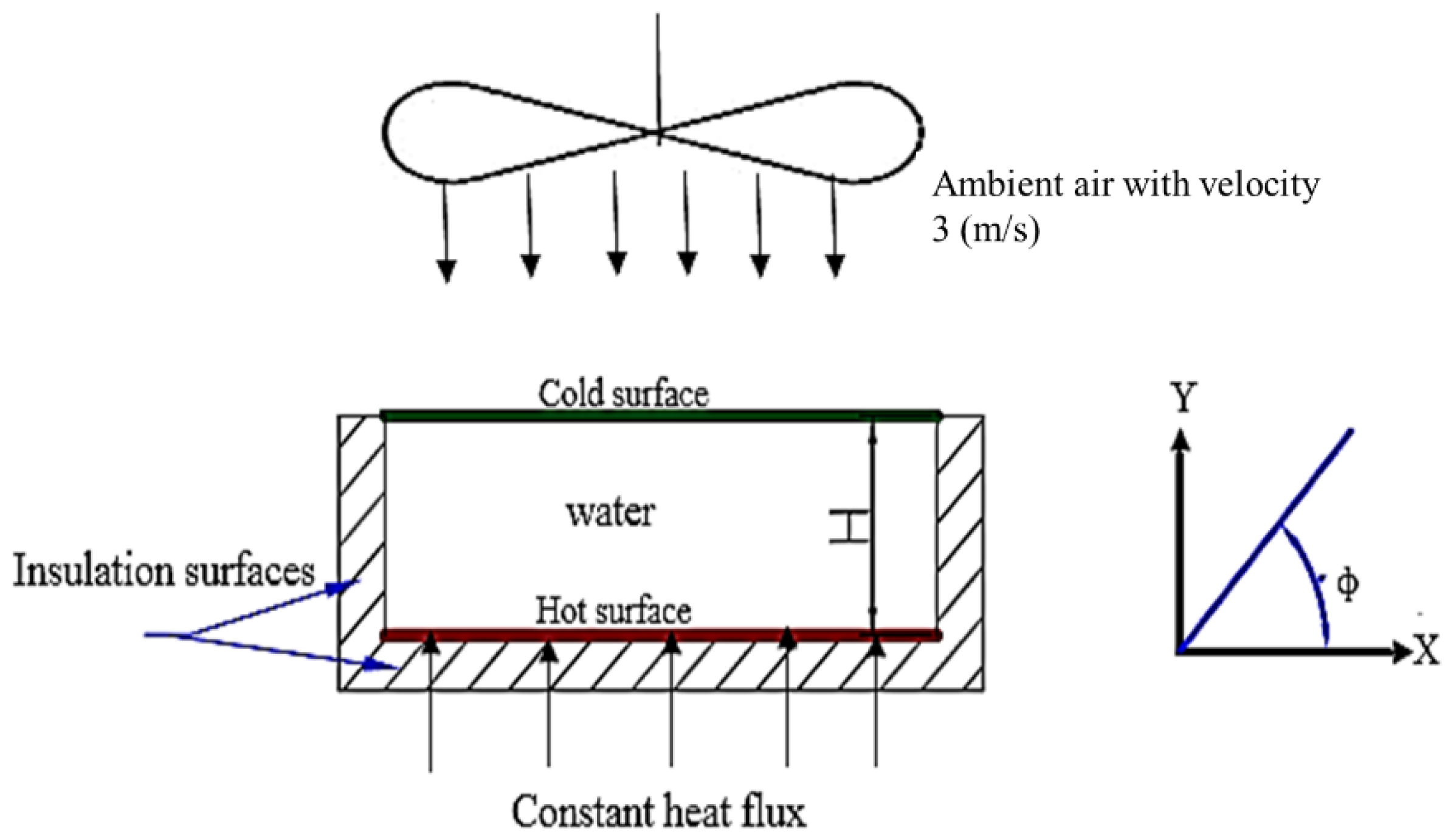
2. Experimental Setup
3. Experimental Procedure
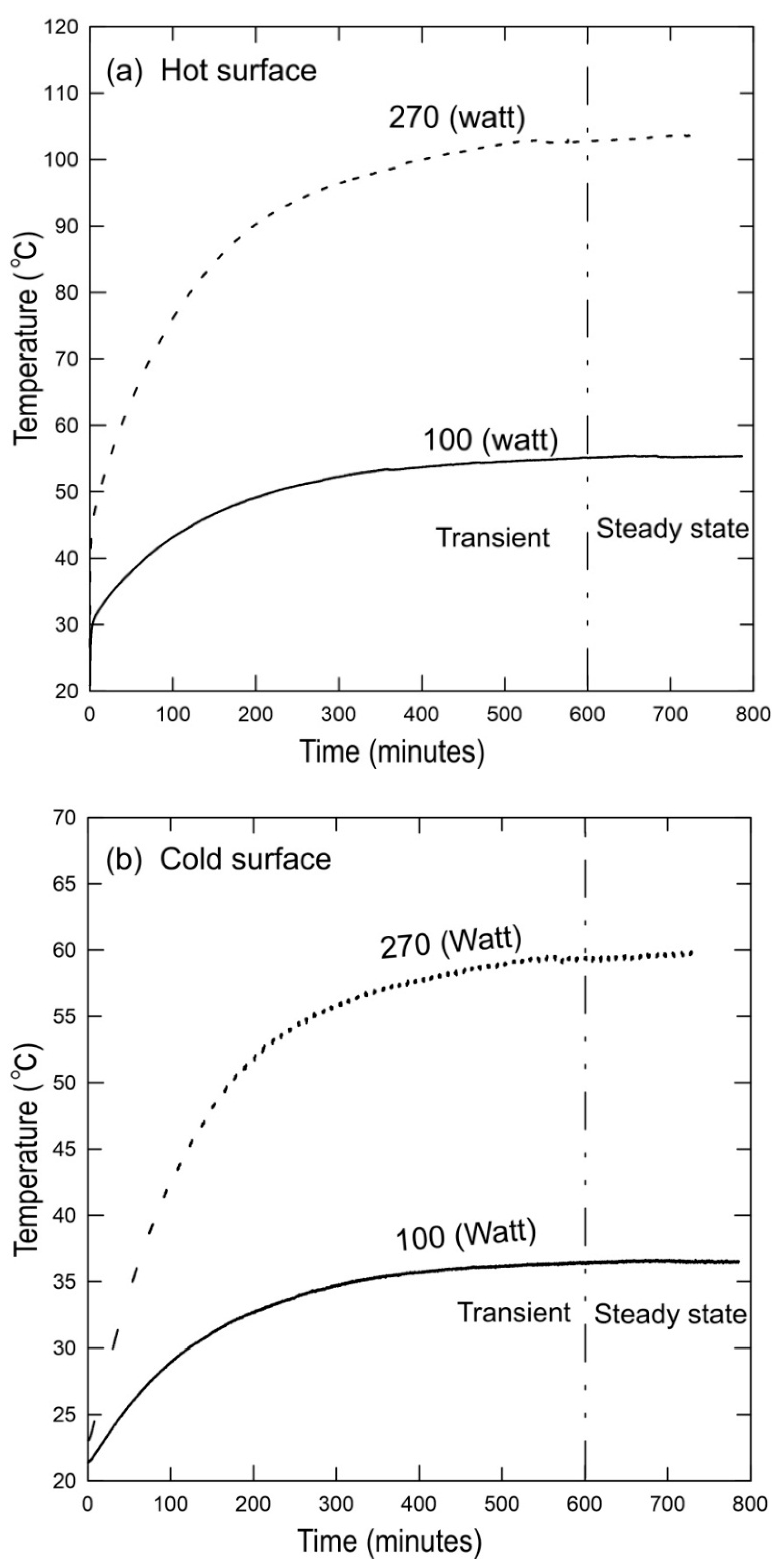
4. Experimental Analyses
5. Uncertainty Calculations
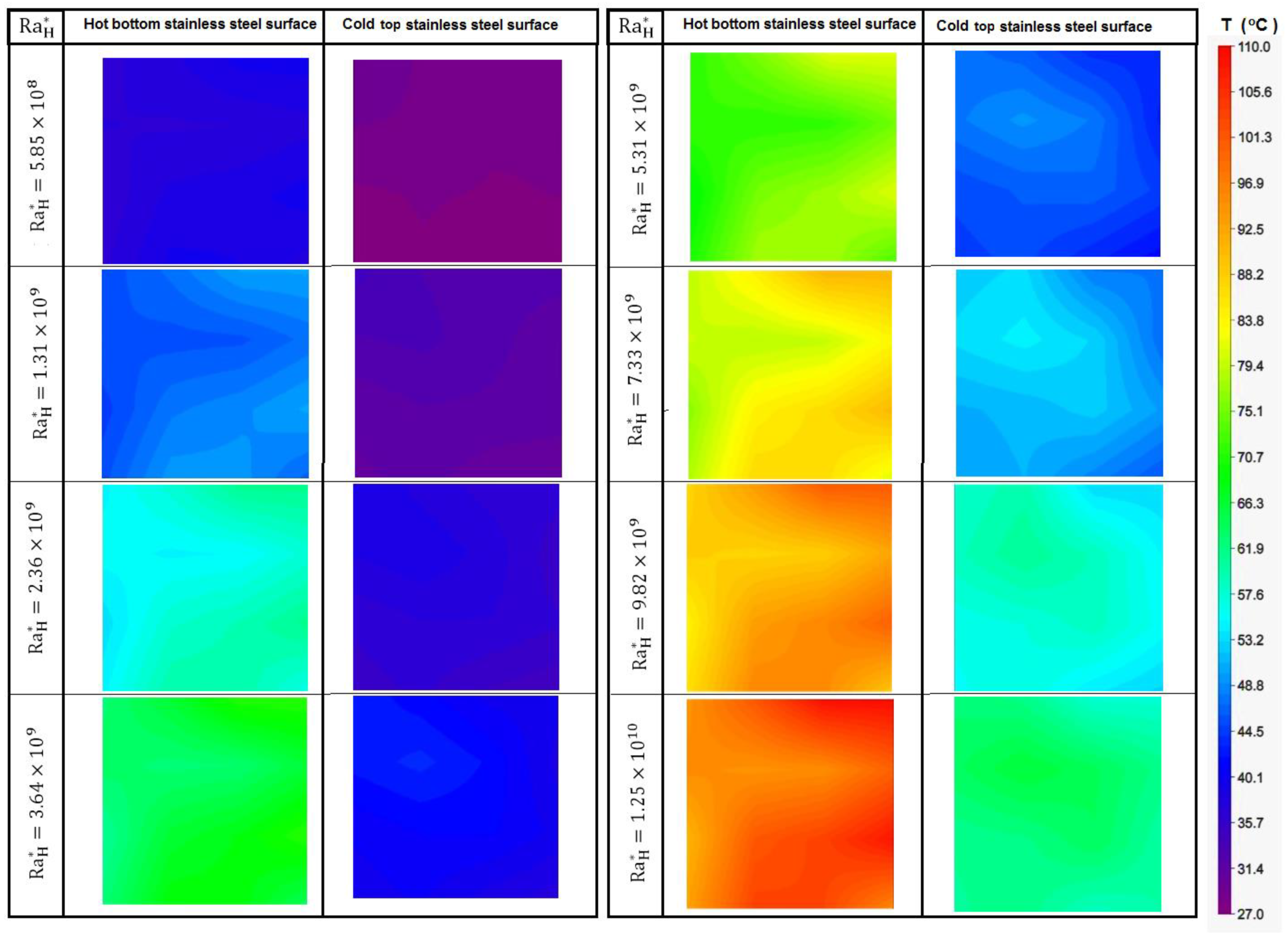
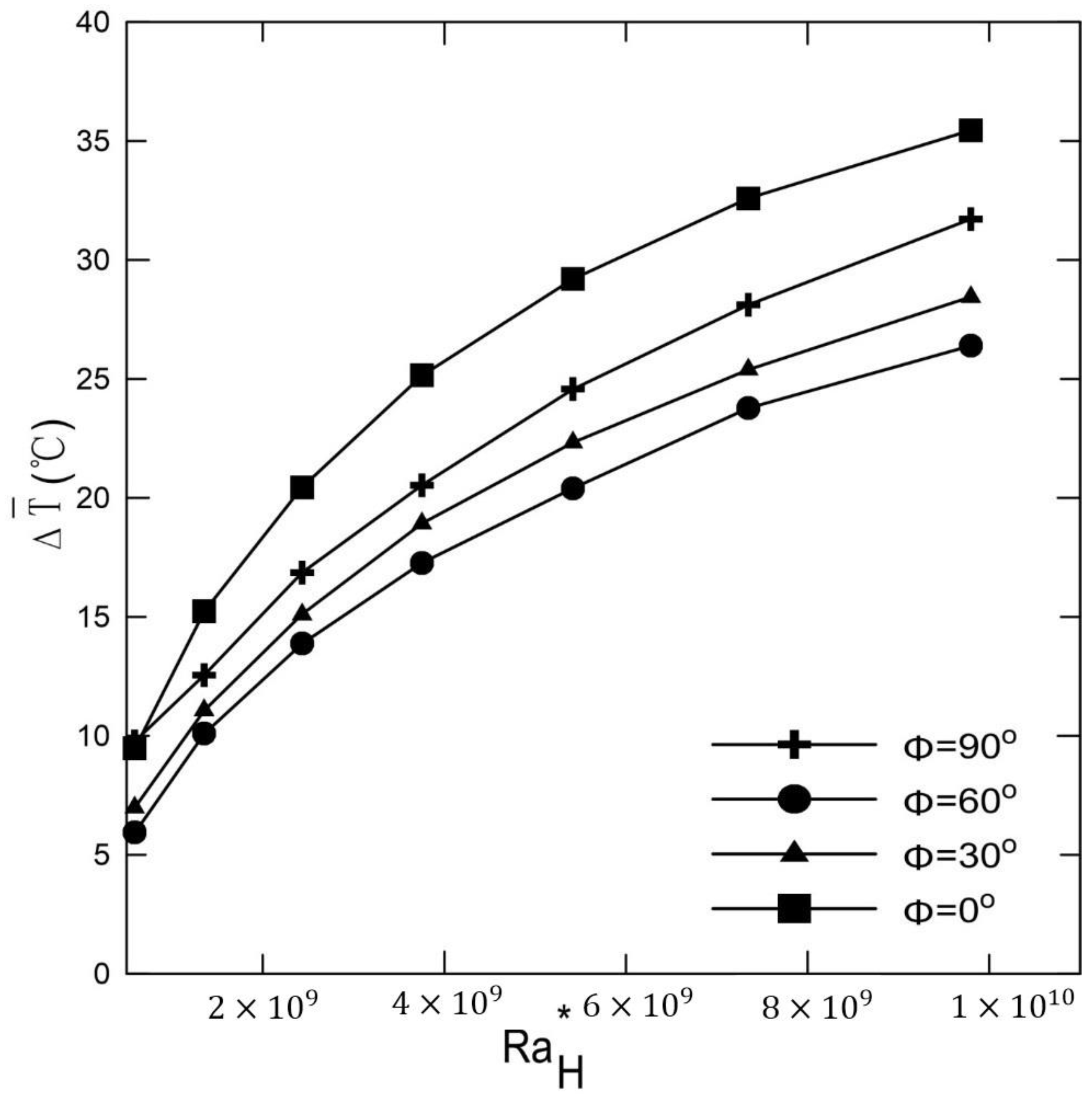
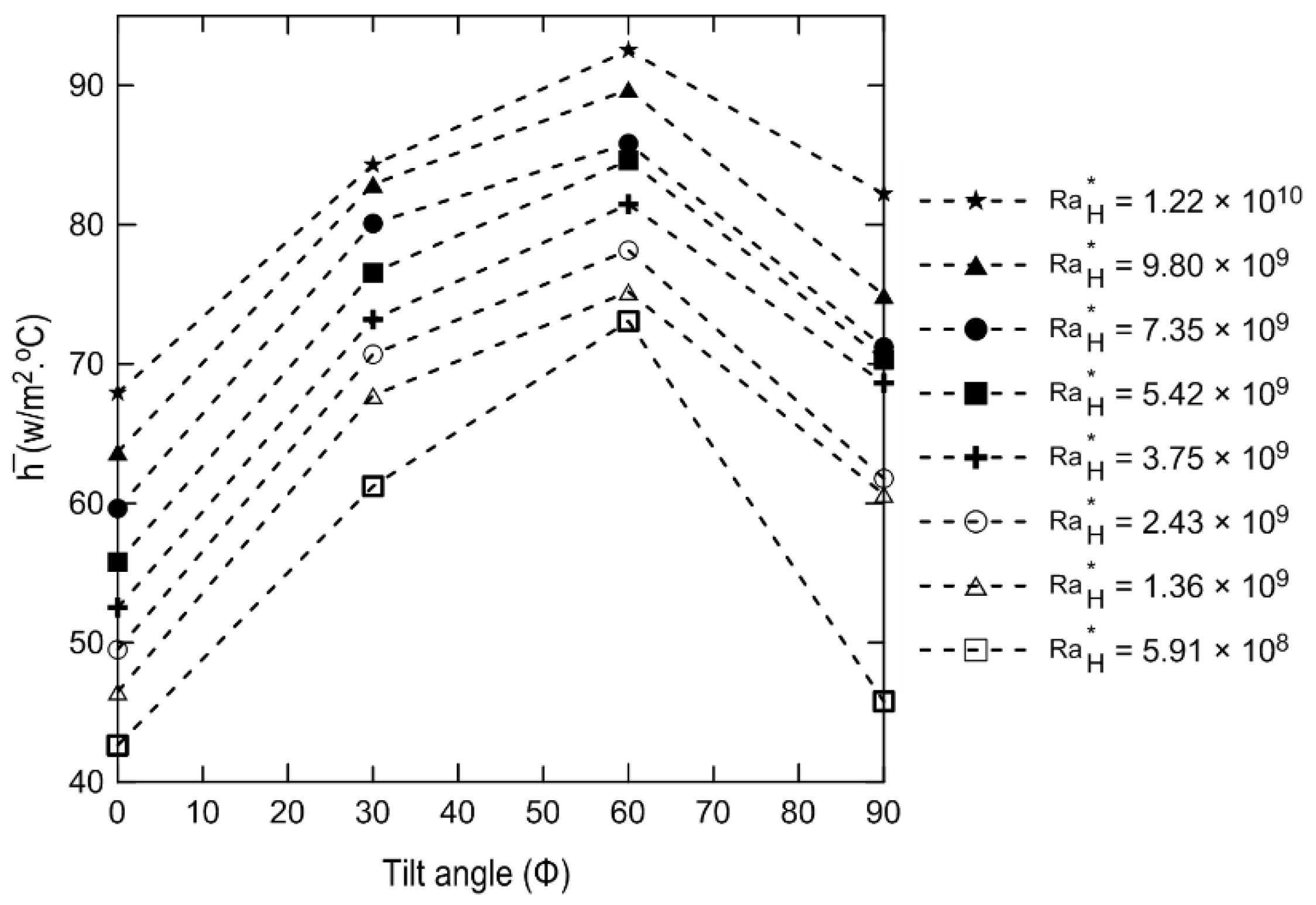
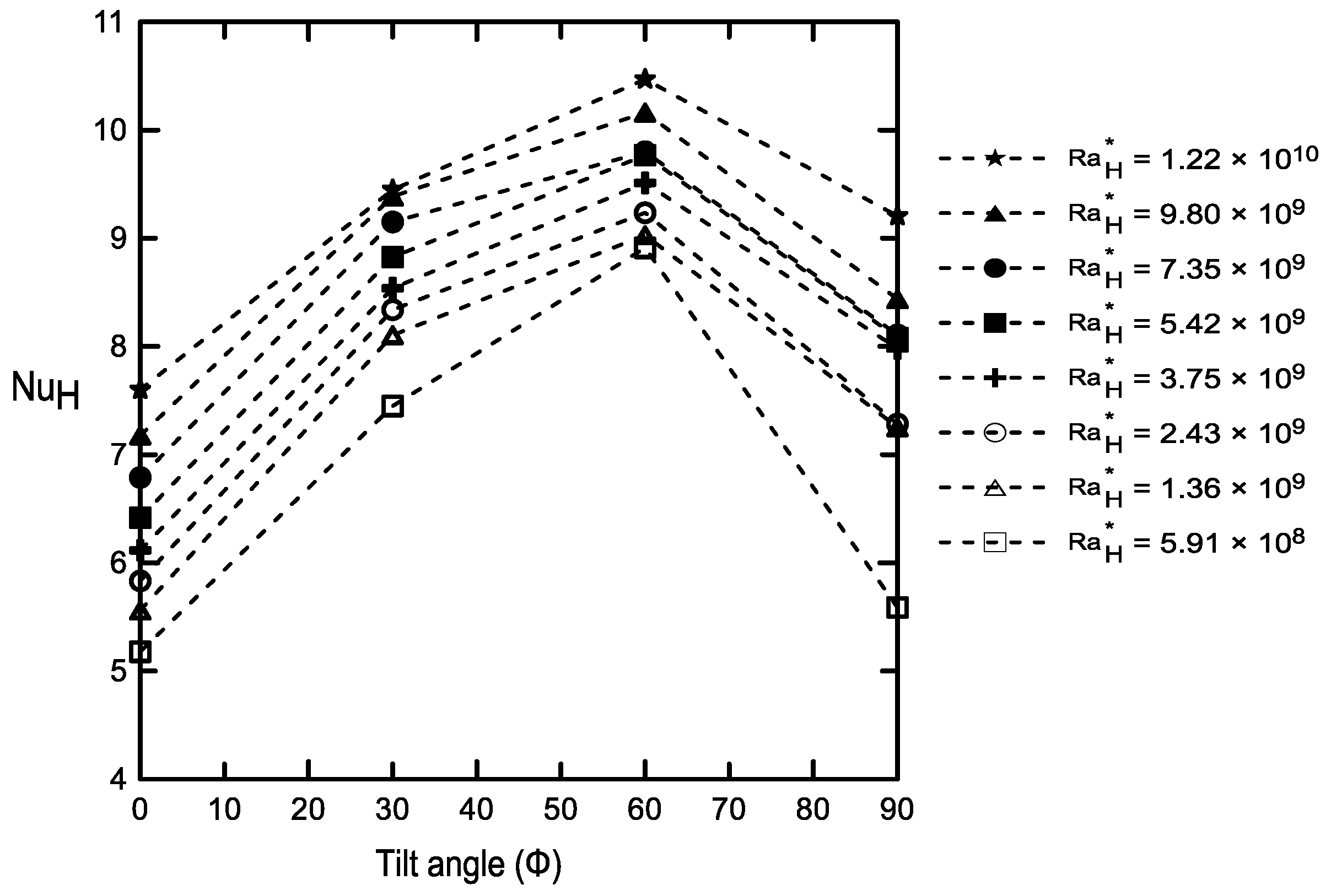
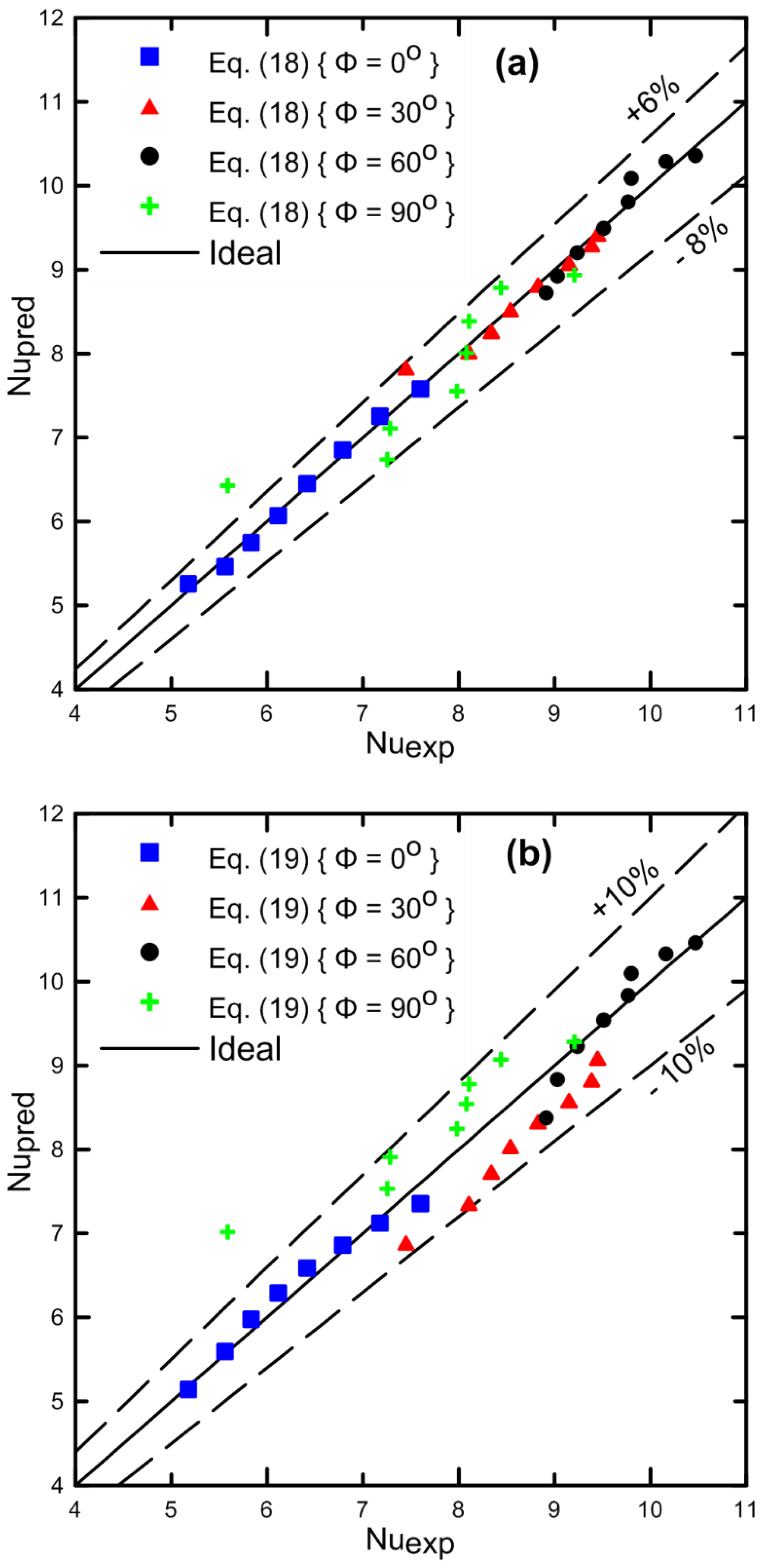
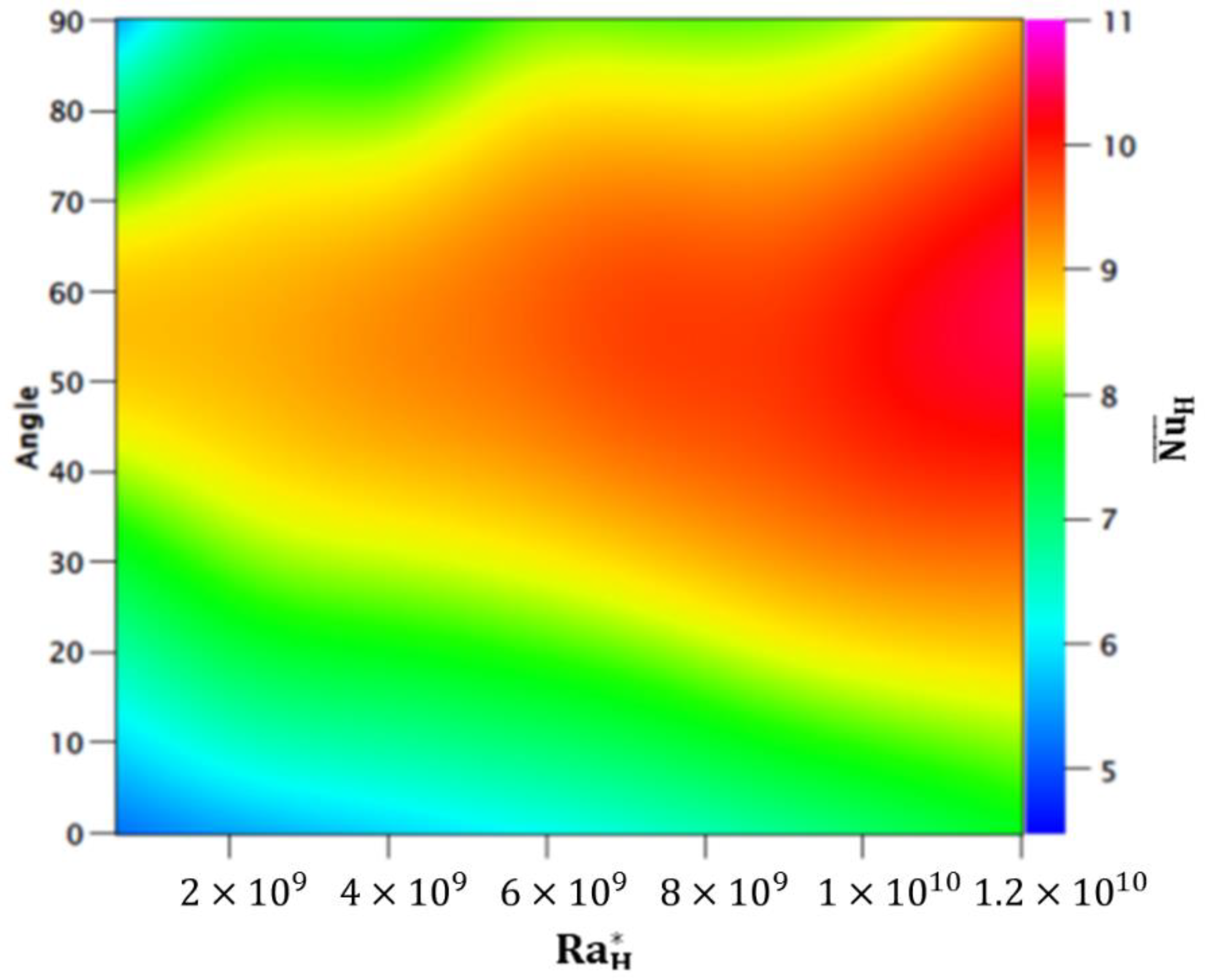
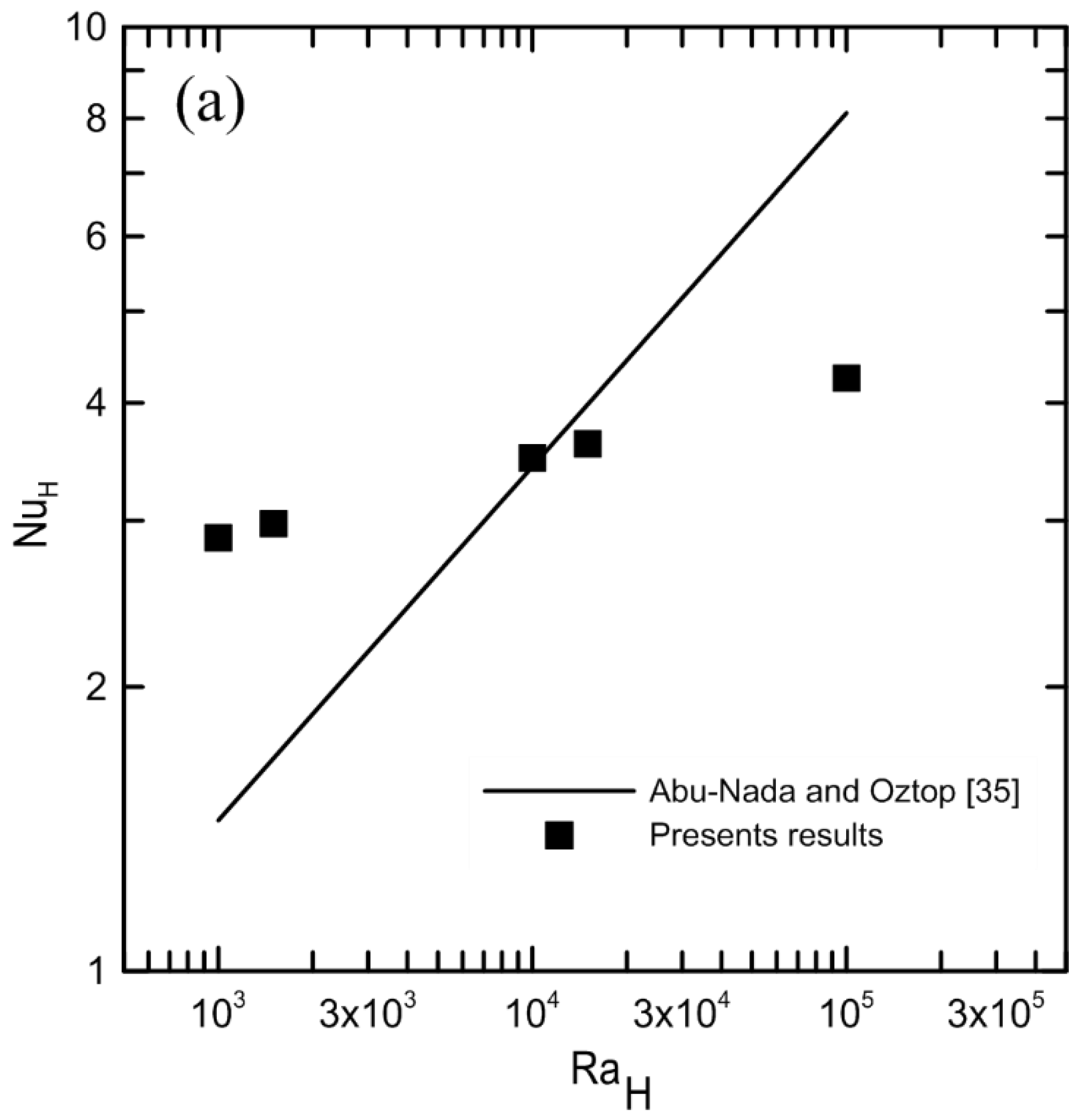
6. Results and Dissuasion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| A | Enclosure surface area, m2 |
| Surface area of the Bakelite plate above the heater, m2 | |
| Surface area of the Bakelite sides, m2 | |
| H | Inside height of the cavity, m |
| h | Heat transfer coefficient, W m−2 k−1 |
| I | Electrical current, Ampere |
| k | Thermal conductivity, W m−2 k−1 |
| Nu | Nusselt number, h H/k |
| Qtotal | Input power electrical, W |
| Heat lost by conduction through the lower Bakelite plate, W | |
| Heat lost by conduction through the Bakelite sides, W | |
| Heat transfer by convection through the fluid, W | |
| R | Overall enclosure thermal resistances, K/W |
| Rss | Stainless-steel thermal resistances, K/W |
| Fluid thermal resistances, K/W | |
| Ra | |
| S | Inside length of the cavity, m |
| T | Temperature, °C |
| ∆T | , °C |
| U | Uncertainty |
| V | Voltage, volt |
| Greek symbols | |
| α | Thermal diffusivity, m−2 s−1 |
| β | Coefficient for thermal expansion, K−1 |
| δ | Bakelite thickness |
| ν | Kinematics viscosity, m−2 s−1 |
| Δx | Thickness of stainless steel, m |
| φ | Tilt angle of the cavity |
| Aspect ratio, | |
| Subscripts | |
| Bakelite plate | |
| Bks | Bakelite side |
| cs | Cold surface |
| exp | Experimental data |
| H | Characteristic length |
| hs | Hot surface |
| Inside Bakelite surface | |
| pred | Predicted data |
| ss | Stainless steel |
| Superscripts | |
| - | Averaged quantity |
References
- Ostrach, S. Natural Convection in Enclosures. J. Heat Transf. 1988, 110, 1175–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeng, D.Z.; Yang, C.S.; Gau, C. Experimental and numerical study of transient natural convection due to mass transfer in inclined enclosures. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2009, 52, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfahani, J.A.; Alinejad, J. Entropy generation of conjugate natural convection in enclusures: The lattice Boltzmann method. J. Thermophys. Heat Transf. 2013, 27, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasoul, J.; Prinos, P. Natural convection in an inclined enclosure. Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow 1997, 7, 438–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Park, Y.G.; Ha, M.Y. An exhaustive review of studies on natural convection in enclosures with and without internal bodies of various shapes. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 138, 762–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.E.-S.; Nuhait, A.O.; Alabdulkarem, A.; Almuzaiqer, R. Free convection heat transfer inside square water-filled shallow enclosures. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Imberger, J. Natural convection in a shallow cavity with differentially heated end walls. Part 3. Experimental results. J. Fluid Mech. 1974, 65, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejan, A.; Al-Homoud, A.A.; Imberger, J. Experimental study of high-Rayleigh-number convection in a horizontal cavity with different end temperatures. J. Fluid Mech. 1981, 109, 283–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiroyuki, O.; Akira, M.; Masaru, O.; Churchill, S.W.; Lior, N. Numerical calculations of laminar and turbulent natural convection in water in rectangular channels heated and cooled isothermally on the opposing vertical walls. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1985, 28, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valencia, L.; Pallares, J.; Cuesta, I.; Grau, F.X. Turbulent Rayleigh–Bénard convection of water in cubical cavities: A numerical and experimental study. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2007, 50, 3203–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavi, M.; Sharifpur, M.; Ghodsinezhad, H.; Meyer, J.P. Experimental and numerical investigation on a water-filled cavity natural convection to find the proper thermal boundary conditions for simulations. Heat Transf. Eng. 2018, 39, 359–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuznetsov, G.V.; Sheremet, M.A. Conjugate natural convection with radiation in an enclosure. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2009, 52, 2215–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.; Saury, D.; Lemonnier, D. Coupling of turbulent natural convection with radiation in an air-filled differentially-heated cavity at Ra = 1.5 × 109. Comput. Fluids 2013, 88, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salat, J.; Xin, S.; Joubert, P.; Sergent, A.; Penot, F.; Le Quere, P. Experimental and numerical investigation of turbulent natural convection in a large air-filled cavity. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2004, 25, 824–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuyper, R.; Van Der Meer, T.H.; Hoogendoorn, C.; Henkes, R. Numerical study of laminar and turbulent natural convection in an inclined square cavity. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1993, 36, 2899–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markatos, N.C.; Pericleous, K. Laminar and turbulent natural convection in an enclosed cavity. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1984, 27, 755–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ampofo, F.; Karayiannis, T. Experimental benchmark data for turbulent natural convection in an air filled square cavity. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2003, 46, 3551–3572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Viskanta, R. Study of the effects of wall conductance on natural convection in differently oriented square cavities. J. Fluid Mech. 1984, 144, 153–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saglam, M.; Sarper, B.; Aydin, O. Natural Convection in an Enclosure with a Pair of Discrete Heat Sources. J. Thermophys. Heat Transf. 2019, 33, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahoosh, R.; Mohamadi, F.; Karimi, M. Numerical investigation of natural convection in a square cavity with tilting walls. J. Thermophys. Heat Transf. 2015, 29, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasnaoui, M.; Bilgen, E.; Vasseur, P. Natural convection heat transfer in rectangular cavities partially heated from below. J. Thermophys. Heat Transf. 1992, 6, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varol, Y.; Oztop, H.F.; Koca, A.; Avci, E. Forecasting of entropy production due to buoyant convection using support vector machines (SVM) in a partially cooled square cross-sectional room. Expert Syst. Appl. 2009, 36, 5813–5821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.-H. Fluid flow and heat transfer characteristics of natural convection in square cavities due to discrete source–sink pairs. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2008, 51, 5949–5957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcione, M. Effects of the thermal boundary conditions at the sidewalls upon natural convection in rectangular enclosures heated from below and cooled from above. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2003, 42, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calcagni, B.; Marsili, F.; Paroncini, M. Natural convective heat transfer in square enclosures heated from below. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2005, 25, 2522–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callister, W.D.; Rethwisch, D.G. Materials Science and Engineering; John Wiley & Sons NY: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Siegel, R.; Howell, J. Thermal Radiation Heat Transfer; Mcgraw-Hill Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Bejan, A. Convection Heat Transfer; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, S.A.; Alvarado, F. Engineering Equation Solver (EES); FChart Software: Madison, WI, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, B.N.; Kuyatt, C.E. NIST technical note 1297. In Guidelines for Evaluating and Expressing the Uncertainty of NIST Measurement Results; United States Department of Commerce Technology Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 1994; Volume 1, pp. 14571–14577. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.; Sharif, M. Numerical study of laminar natural convection in inclined rectangular enclosures of various aspect ratios. Numer. Heat Transf. Part A Appl. 2003, 44, 355–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, B.; Aminossadati, S. Natural convection heat transfer in an inclined enclosure filled with a water-CuO nanofluid. Numer. Heat Transf. Part A Appl. 2009, 55, 807–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.H.; Hussein, A.K.; Mahdi, M.M. Natural convection in a square inclined enclosure with vee-corrugated sidewalls subjected to constant flux heating from below. Nonlinear Anal. Model. Control 2011, 16, 152–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inam, M.I. Direct Numerical Simulation of Laminar Natural Convection in a Square Cavity at Different Inclination Angle. J. Eng. Adv. 2020, 1, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Nada, E.; Oztop, H.F. Effects of inclination angle on natural convection in enclosures filled with Cu–water nanofluid. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2009, 30, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sert, Z.; Tekkalmaz, M.; Timuralp, C. Combined natural convection and thermal radiation in an inclined cubical cavity with a rectangular pins attached to its active wall. Period. Eng. Nat. Sci. 2017, 5, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ravnik, J.; Škerget, L.; Žunič, Z. Velocity–vorticity formulation for 3D natural convection in an inclined enclosure by BEM. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2008, 51, 4517–4527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
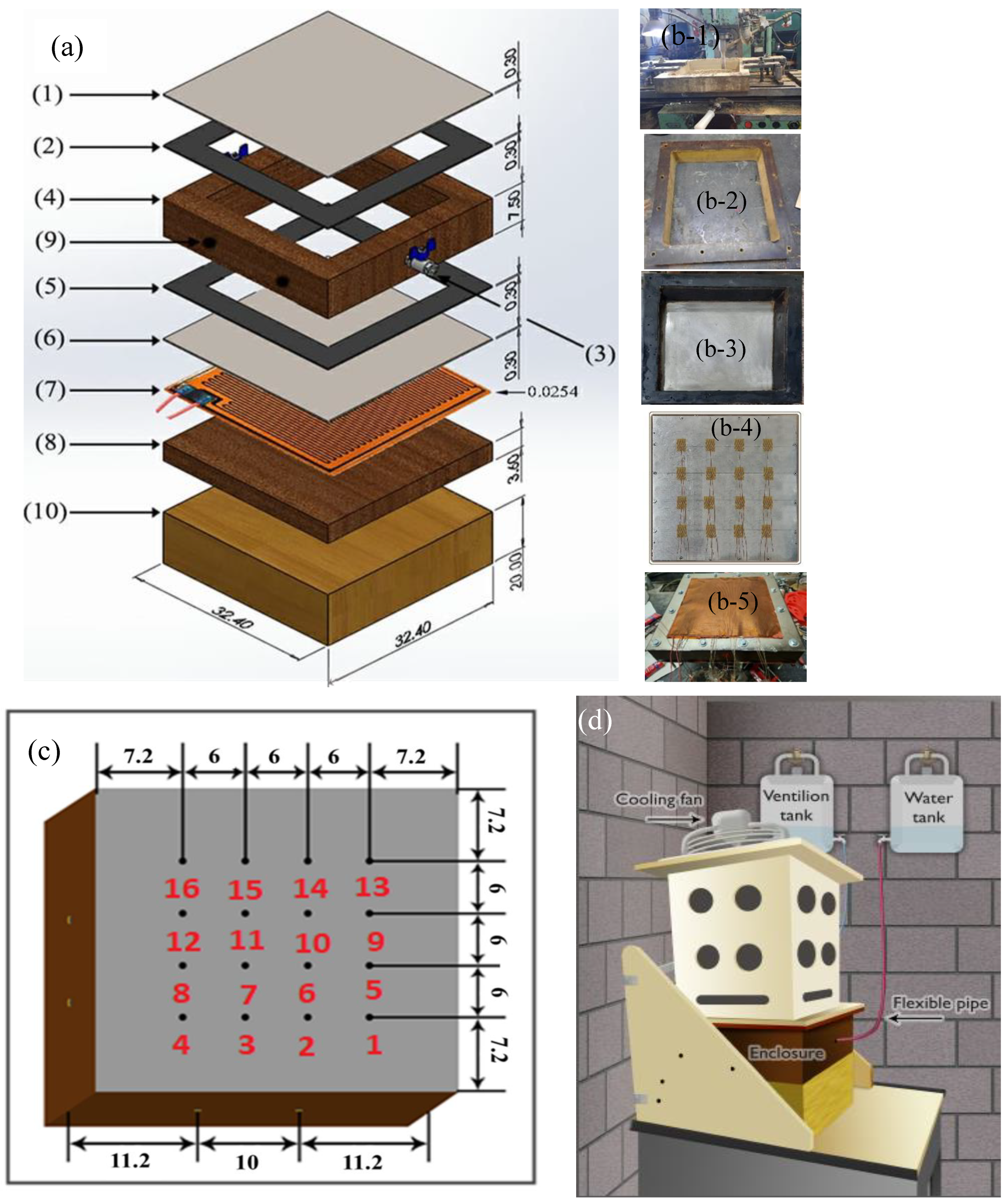



| Parts Number | Part Description | Material | Dimensions (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Enclosure cover (cold surface) | Stainless steel | |
| 2 | Gasket | Polyurethane | |
| 3 | Two-way valve | Steel | Diameter = 0.635 |
| 4 | Enclosure | Bakelite | |
| 5 | Gasket | Polyurethane | |
| 6 | Enclosure cover (hot surface) | Stainless steel | |
| 7 | Electrical heater | Polyimide | |
| 8 | Insulation cover | Bakelite | |
| 9 | Thermocouple | Type-K, self-adhesive | |
| 10 | Insulation cover | Fiber glass |
| Quantity | Uncertainty (%) |
|---|---|
| 3.00 | |
| QBkp | 8.07 |
| QBks | 12.11 |
| Qcon | 3.53 |
| havg | 3.90 |
| 3.91 | |
| 3.55 |
| Enhancement (%) at φ = 30° | Enhancement (%) at φ = 60° | Enhancement (%) at φ = 90° | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 43.86 | 72.10 | 7.92 | |
| 45.75 | 62.38 | 30.45 | |
| 42.99 | 58.36 | 24.87 | |
| 39.63 | 55.55 | 30.52 | |
| 37.52 | 52.19 | 25.88 | |
| 34.80 | 44.37 | 19.42 | |
| 30.78 | 41.59 | 17.57 | |
| 24.33 | 37.76 | 21.13 |
| a | b | R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| φ = 0o | 0.4303 | 0.1218 | 96% |
| φ = 30o | 1.54 | 0.782 | 98% |
| φ = 60o | 3.0198 | 0.0526 | 90% |
| φ = 90o | 9.5179 | 0.2691 | 93% |
| c | 5.084 |
| d | 0.09781 |
| e | 3.00 × 10−10 |
| f | −0.0001 |
| g | −2.18 × 10−12 |
| h | −8.04 × 10−21 |
| i | −9.38 × 10−6 |
| j | 3.62 × 10−14 |
| k | −7.11×10−23 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Almuzaiqer, R.; Ali, M.E.; Al-Salem, K. Tilt Angle’s Effects on Free Convection Heat Transfer Coefficient inside a Water-Filled Rectangular Parallelepiped Enclosure. Processes 2022, 10, 396. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10020396
Almuzaiqer R, Ali ME, Al-Salem K. Tilt Angle’s Effects on Free Convection Heat Transfer Coefficient inside a Water-Filled Rectangular Parallelepiped Enclosure. Processes. 2022; 10(2):396. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10020396
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlmuzaiqer, Redhwan, Mohamed Elsayed Ali, and Khaled Al-Salem. 2022. "Tilt Angle’s Effects on Free Convection Heat Transfer Coefficient inside a Water-Filled Rectangular Parallelepiped Enclosure" Processes 10, no. 2: 396. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10020396
APA StyleAlmuzaiqer, R., Ali, M. E., & Al-Salem, K. (2022). Tilt Angle’s Effects on Free Convection Heat Transfer Coefficient inside a Water-Filled Rectangular Parallelepiped Enclosure. Processes, 10(2), 396. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10020396







