Changes in Protein and Non-Protein Nitrogen Compounds during Fishmeal Processing—Identification of Unoptimized Processing Steps
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Raw Material and Sampling
2.1.1. Raw Materials
2.1.2. Sampling during Industrial Fishmeal and Oil Processing
2.1.3. Chemicals
2.2. Proximate Composition Changes during Processing
2.3. Mass Balances during Processing
2.4. Protein Changes during Processing
2.4.1. Salt Soluble Protein Content (SSP)
2.4.2. Biogenic Amines (BA)
2.4.3. Total Volatile Basic Nitrogen (TVB-N), Trimethylamine (TMA) and Dimethylamine (DMA)
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
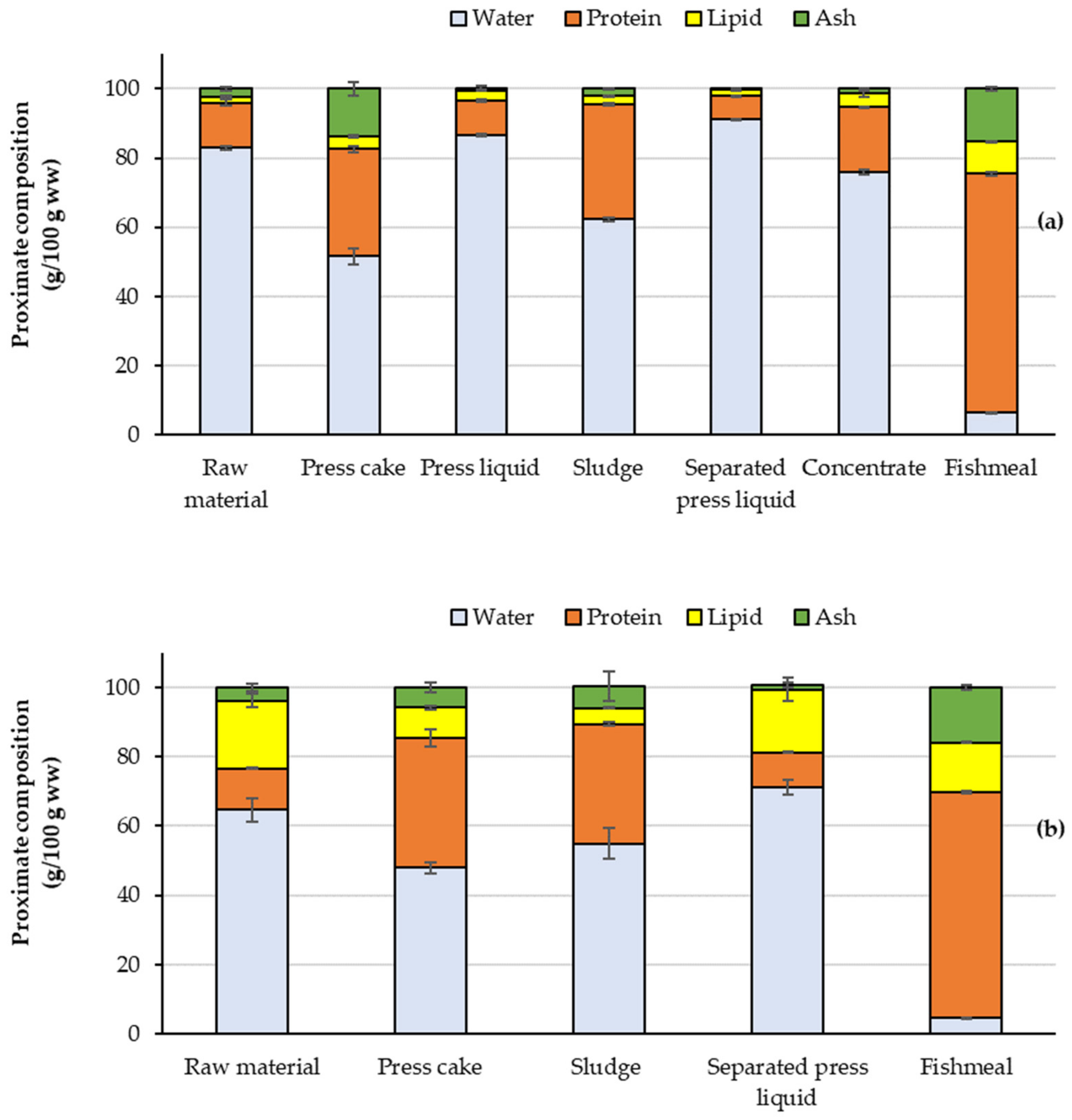
3.1. Changes in Proximate Composition during Processing
3.2. Mass Balances during Processing
3.3. Protein Quality Changes during Processing
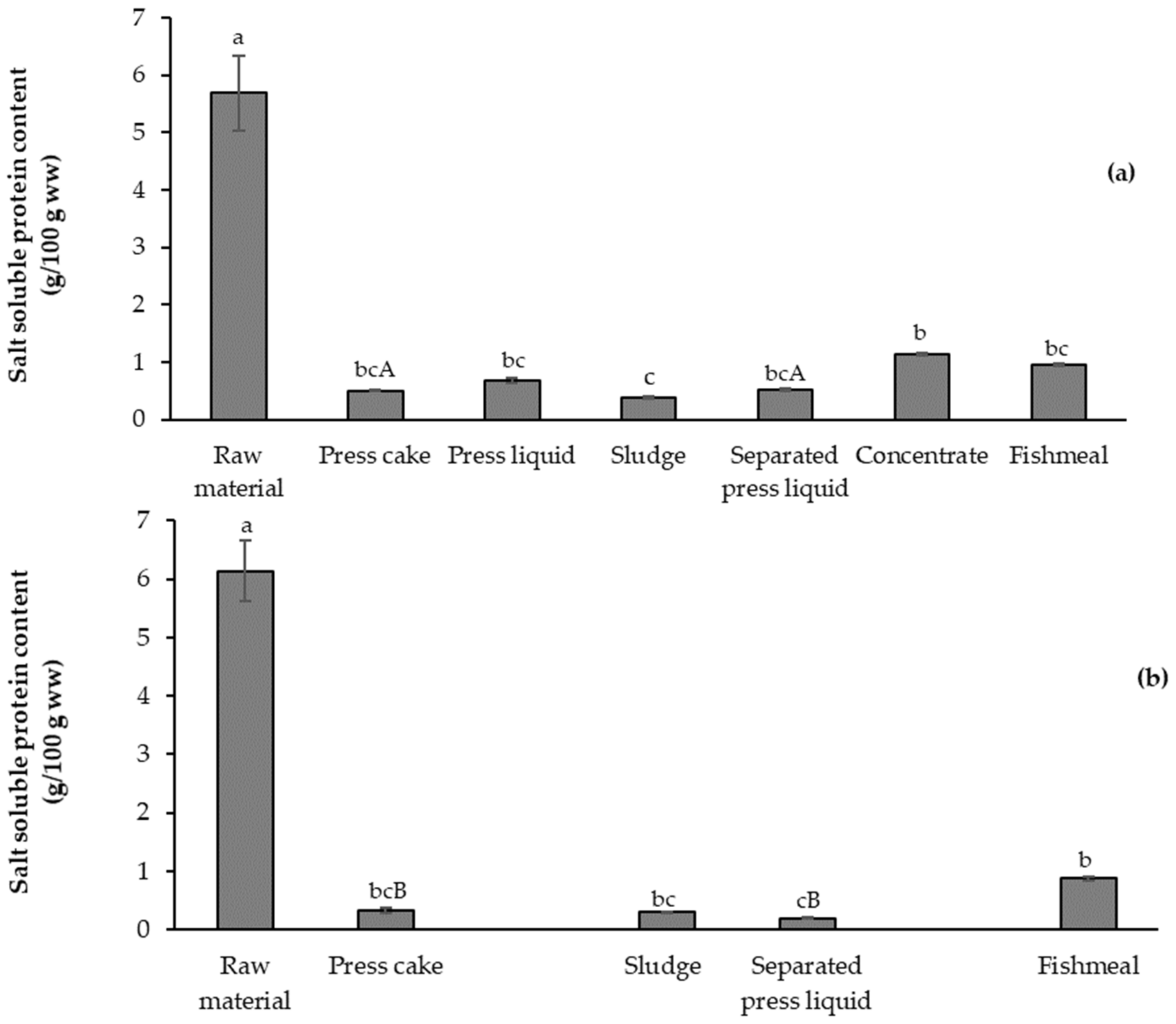
3.3.1. Salt Soluble Protein Content (SSP)
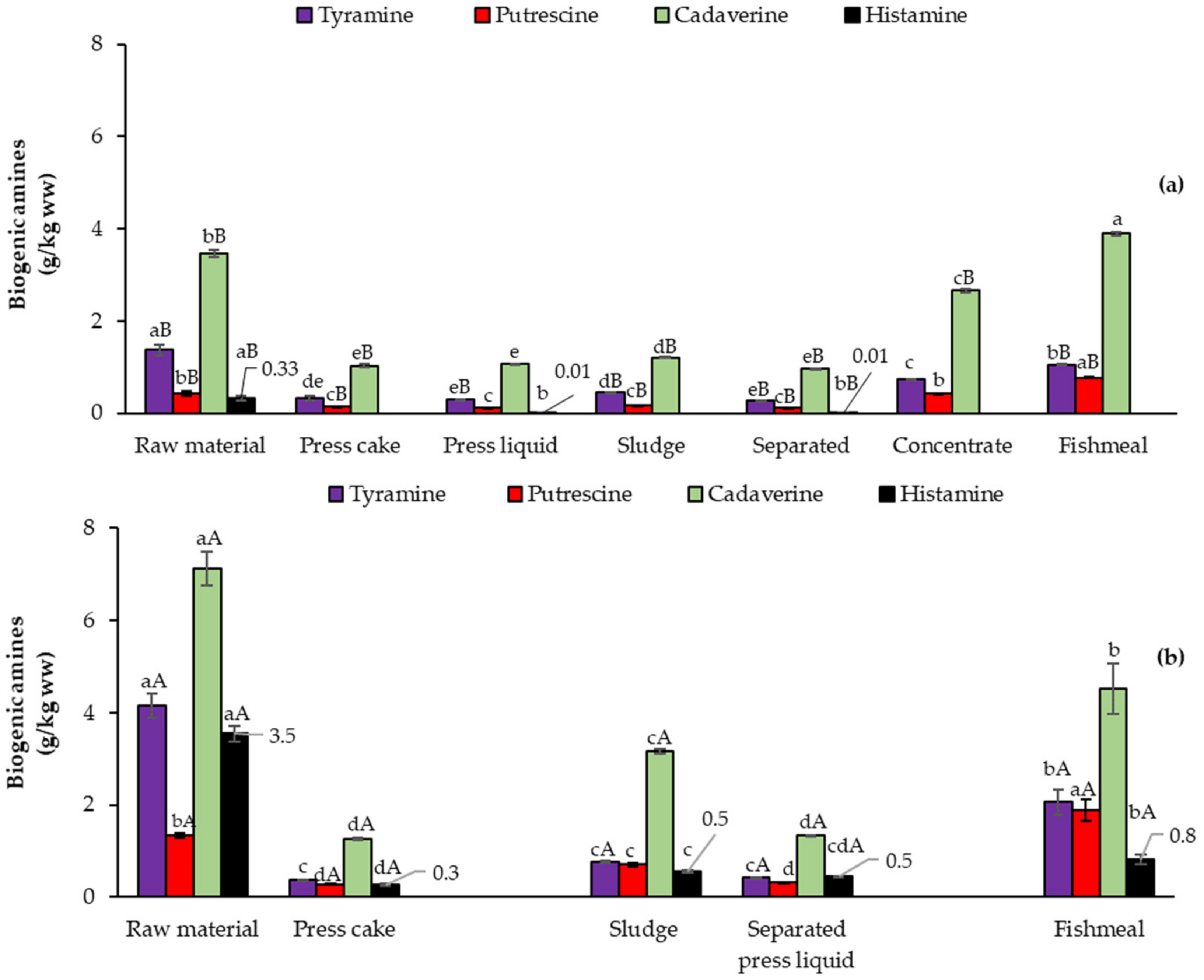
3.3.2. Biogenic Amines (BA)
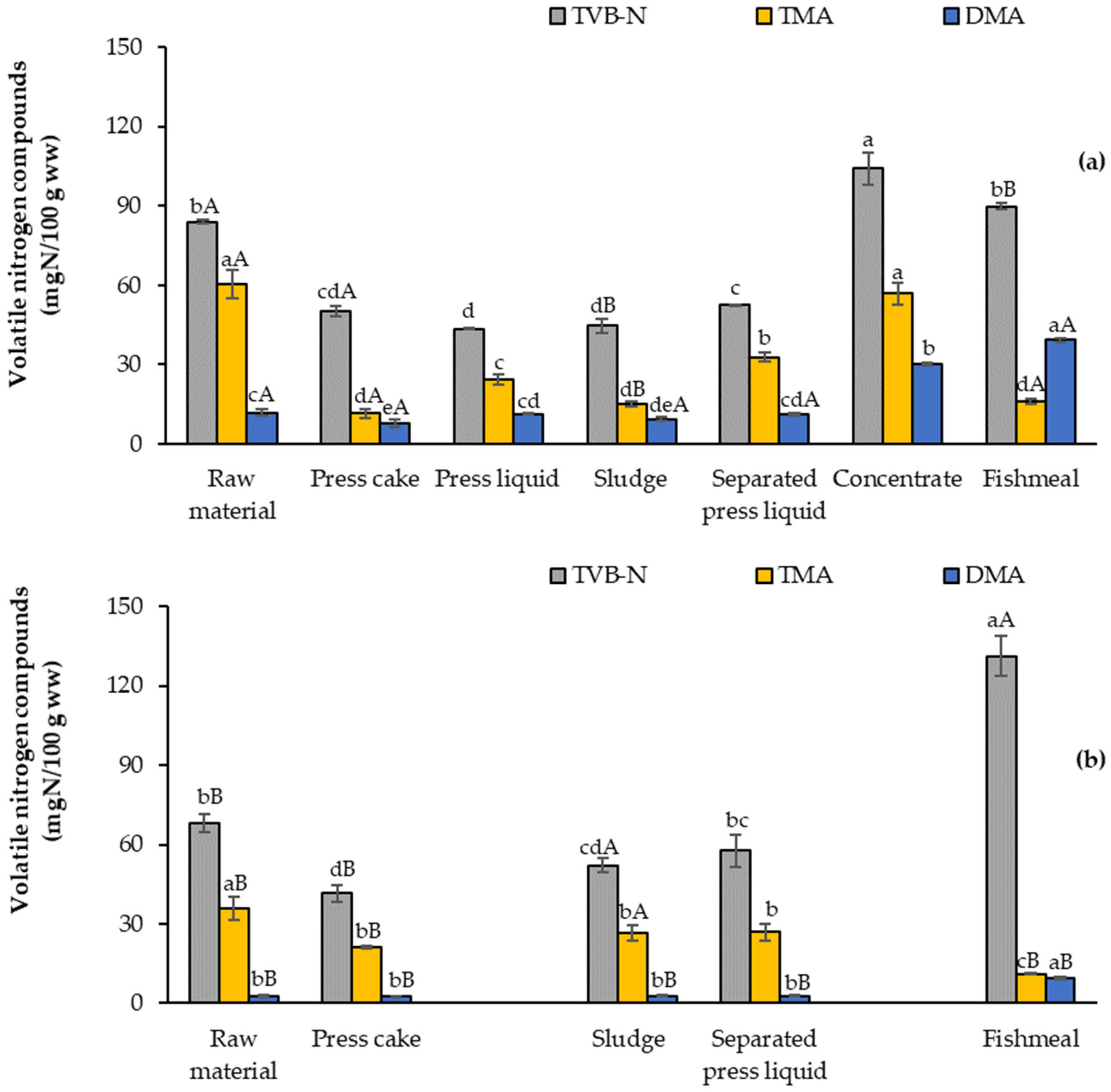
3.3.3. Total Volatile Basic Nitrogen (TVB-N), Trimethylamine, and Dimethylamine
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Golden, C.D.; Allison, E.H.; Cheung, W.W.L.; Dey, M.M.; Halpern, B.S.; McCauley, D.J.; Smith, M.; Vaitla, B.; Zeller, D.; Myers, S.S. Nutrition: Fall in fish catch threatens human health. Nature 2016, 534, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikorski, Z.E.; Bonnie, S.P.; Fereidoon, S. Seafood Proteins; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2020: Sustainability in Action; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Merino, G.; Barange, M.; Blanchard, J.L.; Harle, J.; Holmes, R.; Allen, I.; Allison, E.H.; Badjeck, M.C.; Dulvy, N.K.; Holt, J.; et al. Can marine fisheries and aquaculture meet fish demand from a growing human population in a changing climate? Glob. Environ. Change 2012, 22, 795–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béné, C.; Barange, M.; Subasinghe, R.; Pinstrup-Andersen, P.; Merino, G.; Hemre, G.I.; Williams, M. Feeding 9 billion by 2050—Putting fish back on the menu. Food Secur. 2015, 7, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cashion, T.; Le Manach, F.; Zeller, D.; Pauly, D. Most fish destined for fishmeal production are food-grade fish. Fish Fish. 2017, 18, 837–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbey, L.; Glover-Amengor, M.; Atikpo, M.O.; Atter, A.; Toppe, J. Nutrient content of fish powder from low value fish and fish byproducts. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 5, 374–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaviklo, A.R. Development of fish protein powder as an ingredient for food applications: A review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 648–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chalamaiah, M.; Dinesh kumar, B.; Hemalatha, R.; Jyothirmayi, T. Fish protein hydrolysates: Proximate composition, amino acid composition, antioxidant activities and applications: A review. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 3020–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barraza, F.A.A.; León, R.A.Q.; Álvarez, P.X.L. Kinetics of protein and textural changes in Atlantic salmon under frozen storage. Food Chem. 2015, 182, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soladoye, O.P.; Juárez, M.L.; Aalhus, J.L.; Shand, P.; Estévez, M. Protein oxidation in processed meat: Mechanisms and potential implications on human health. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2015, 14, 106–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikorski, Z.E.; Kolakowska, A. Changes in protein in frozen stored fish. In Seafood Proteins; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1994; pp. 99–112. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. The Production of Fishmeal and Oil; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, M.V.; Thorarinsdottir, K.A.; Gudmundsdottir, A.; Thorkelsson, G.; Arason, S. The effects of salt concentration on conformational changes in cod (Gadus morhua) proteins during brine salting. Food Chem. 2011, 125, 1013–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, G.; Hardisson, A. Fish|Fish as Food. In Encyclopedia of Food Sciences and Nutrition, 2nd ed.; Caballero, B., Ed.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2003; pp. 2417–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilmarsdottir, G.S.; Ogmundarson, Ó.; Arason, S.; Gudjónsdóttir, M. Efficiency of fishmeal and fish oil processing of different pelagic fish species: Identification of processing steps for potential optimization toward protein production for human consumption. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2021, 45, e15294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistics Iceland. Profitability in Fishing and Fish Processing 2020; Statistics Iceland: Reykjavik, Iceland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Hilmarsdottir, G.S.; Ogmundarson, O.; Arason, S.; Gudjónsdóttir, M. The effects of varying heat treatments on lipid composition during pelagic fishmeal production. Processes 2020, 8, 1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sveinsdóttir, H.I.; Karlsdóttir, M.G.; Arason, S.; Stefánsson, G.; Sone, I.; Skåra, T.; Rustad, T.; Larsson, K.; Undeland, I.; Gudjonsdottir, M. Effect of antioxidants on the sensory quality and physicochemical stability of Atlantic mackerel (Scomber scombrus) fillets during frozen storage. Food Chem. 2020, 321, 126744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karovičová, J.; Kohajdová, Z. Biogenic amines in food. Chem. Pap. 2005, 59, 70–79. [Google Scholar]
- Klausen, N.K.; Lund, E. Formation of biogenic amines in herring and mackerel. Z. Lebensm. Unters. Forsch. 1986, 182, 459–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Capillas, C.; Herrero, A.M. Impact of biogenic amines on food quality and safety. Foods 2019, 8, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Visciano, P.; Schirone, M.; Paparella, A. An overview of histamine and other biogenic amines in fish and fish products. Foods 2020, 9, 1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey-Mansilla, M.; Sotelo, C.G.; Gallardo, J.M. Decomposition of trimethylamine oxide during iced storage of blue whiting (Micromesistius poutassou). Z. Lebensm. Unters. Forsch. 1999, 208, 267–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einarsson, M.I.; Jokumsen, A.; Bæk, A.; Jacobsen, C.; Pedersen, S.A.; Samuelsen, T.A.; Pálsson, J.; Eliasen, O.; Flesland, O. Nordic Centre of Excellence Network in Fishmeal and Fish Oil, 1670–7192; Matís Ohf/Matis—Food Research, Innovation & Safety: Reykjavik, Iceland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bligh, E.G.; Dyer, W.J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 1959, 37, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentas, K.J.; Rotstein, E.; Singh, R.P. Handbook of Food Engineering Practice; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Fellows, P.J. Food Processing Technology: Principles and Practice; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kelleher, S.D.; Hultin, H.O. Lithium chloride as a preferred extractant of fish muscle proteins. J. Food Sci. 1991, 56, 315–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olajos, I. Implementation and Verification of an Analytical Method for the Quantification of Biogenic Amines in Seafood Products. Master’s Thesis, University of Iceland, Reykjavik, Iceland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Malle, P.; Poumeyrol, M. A new chemical criterion for the quality control of fish: Trimethylamine/total volatile basic nitrogen (%). J. Food Prot. 1989, 52, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baliño-Zuazo, L.; Barranco, A. A novel liquid chromatography–mass spectrometric method for the simultaneous determination of trimethylamine, dimethylamine and methylamine in fishery products. Food Chem. 2016, 196, 1207–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egerton, S.; Mannion, D.; Culloty, S.; Whooley, J.; Stanton, C.; Ross, R.P. The proximate composition of three marine pelagic fish: Blue whiting (Micromesistius poutassou), boarfish (Capros aper) and Atlantic herring (Clupea harengus). Irish J. Agric. Food Res. 2020, 185–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeannes, M.I.; Almandos, M.E. Estimation of fish proximate composition starting from water content. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2003, 16, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romotowska, P.E.; Karlsdóttir, M.G.; Gudjónsdóttir, M.; Kristinsson, H.G.; Arason, S. Seasonal and geographical variation in chemical composition and lipid stability of Atlantic mackerel (Scomber scombrus) caught in Icelandic waters. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2016, 49, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Senecal, A.; Chinachoti, P.; Faustman, C. Effect of water activity on lipid oxidation and protein solubility in freeze-dried beef during storage. J. Food Sci. 2002, 67, 2512–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariyawansa, S. The Evaluation of Functional Properties of Fish Meal; United Nations University, Fisheries Training Programme: Reykjavik, Iceland, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Ween, O.; Stangeland, J.K.; Fylling, T.S.; Aas, G.H. Nutritional and functional properties of fishmeal produced from fresh by-products of cod (Gadus morhua L.) and saithe (Pollachius virens). Heliyon 2017, 3, e00343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cozzolino, D.; Chree, A.; Scaife, J.R.; Murray, I. Usefulness of near-infrared reflectance (NIR) spectroscopy and chemometrics to discriminate fishmeal batches made with different fish species. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 4459–4463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.H.; Kim, I.H. Fish meal–nutritive value. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2011, 95, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Koning, A.J. Quantitative quality tests for fish meal. II. An investigation of the quality of South African fish meals and the validity of a number of chemical quality indices. Int. J. Food Prop. 2002, 5, 495–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasmiran, B.; Suvveb, N.V.; Jónsson, A. Comparison and Evaluation of the Quality of Fish Oil and Fishmeal Extracted from the Heads of Yellowfin Tuna (Thunnus albacares) and Albacore Tuna (Thunnus alalunga); Final Project; Nations University Fisheries Training Programme: Reykjavik, Iceland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ustunol, Z. Applied Food Protein Chemistry; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zayas, J.F. Functionality of Proteins in Food; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Derkach, S.R.; Grokhovsky, V.A.; Kuranova, L.K.; Volchenko, V.I. Nutrient analysis of underutilized fish species for the production of protein food. Foods Raw Mater. 2017, 5, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yada, R.Y. Proteins in Food Processing; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Gulati, P.; Li, A.; Holding, D.; Santra, D.; Zhang, Y.; Rose, D.J. Heating reduces proso millet protein digestibility via formation of hydrophobic aggregates. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 1952–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skipnes, D.; Van der Plancken, I.; Van Loey, A.; Hendrickx, M.E. Kinetics of heat denaturation of proteins from farmed Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua). J. Food Eng. 2008, 85, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Llave, Y.; Fukuoka, M.; Sakai, N. Estimation of color changes in fish surface at the beginning of grilling based on the degree of protein denaturation. J. Food Eng. 2014, 129, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, S.; Franco, A.R.; Fernandes, E.M.; Amorim, S.; Ferreira, H.; Pires, R.A.; Reis, R.L.; Martins, A.; Neves, N.M. Fish sarcoplasmic proteins as a high value marine material for wound dressing applications. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 167, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghelichpour, M.; Shabanpour, B. The investigation of proximate composition and protein solubility in processed mullet fillets. Int. Food Res. J. 2011, 18, 1343. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Obielodan, M.; Sismour, E.; Arnett, A.; Alzahrani, S.; Zhang, B. Physicochemical, functional, thermal and structural properties of isolated Kabuli chickpea proteins as affected by processing approaches. Int. J. Food Sci. 2017, 52, 1147–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Kumar, M.; Mittal, A.; Mehta, P.K. Microbial enzymes: Industrial progress in 21st century. 3 Biotech 2016, 6, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clemente, A. Enzymatic protein hydrolysates in human nutrition. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2000, 11, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, P. Enzymes in fish and seafood processing. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2016, 4, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nilsang, S.; Lertsiri, S.; Suphantharika, M.; Assavanig, A. Optimization of enzymatic hydrolysis of fish soluble concentrate by commercial proteases. J. Food Eng. 2005, 70, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikorski, Z.E.; Kotakowski, E. Endogenous enzyme activity and seafood quality: Influence of chilling, freezing, and other environmental factors. In Seafood Enzymes Utilization and Influence on Postharvest Seafood Quality; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 451–488. [Google Scholar]
- Bulushi, I.A.; Poole, S.; Deeth, H.C.; Dykes, G.A. Biogenic amines in fish: Roles in intoxication, spoilage, and nitrosamine formation—A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2009, 49, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halász, A.; Baráth, A.; Simon-Sarkadi, L.; Holzapfel, W. Biogenic amines and their production by microorganisms in food. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 1994, 5, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pike, I.H.; Hardy, R.W. Standards for assessing quality of feed ingredients. In Crustacean Nutrition—Advances in World Aquaculture; D’Abramo, L., Conclin, D., Akiyama, D., Eds.; World Aquaculture Society: Sorrento, LA, USA, 1997; Volume 6, pp. 473–492. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, T.H.; Nigg, J.D.; Stine, J.J.; Bechtel, P.J. Nutritional and chemical composition of by-product fractions produced from wet reduction of individual red salmon (Oncorhynchus nerka) heads and viscera. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2011, 20, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prester, L. Biogenic amines in fish, fish products and shellfish: A review. Food Addit. Contam. 2011, 28, 1547–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, M.H.S. Biogenic amines: Their importance in foods. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1996, 29, 213–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Capillas, C.; Moral, A. Free amino acids and biogenic amines in red and white muscle of tuna stored in controlled atmospheres. Amino Acids 2004, 26, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naila, A.; Flint, S.; Fletcher, G.; Bremer, P.; Meerdink, G. Control of biogenic amines in food—Existing and emerging approaches. J. Food Sci. 2010, 75, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Köse, S.; Quantick, P.; Hall, G. Changes in the levels of histamine during processing and storage of fish meal. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2003, 107, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mih, H.; Lacherai, A. Nutritional properties of fish meal produced from fresh by-products of Sardina pilchardus. J. Fish. Environ. 2020, 44, 16–23. [Google Scholar]
- Aubourg, S.P.; Medina, I.; Gallardo, J.M. Quality assessment of blue whiting (Micromesistius poutassou) during chilled storage by monitoring lipid damages. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 3662–3666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mizuguchi, T.; Kumazawa, K.; Yamashita, S.; Safey, J. Factors that accelerate dimethylamine formation in dark muscle of three gadoid species during frozen storage. Fish Sci. 2011, 77, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howgate, P. A critical review of total volatile bases and trimethylamine as indices of freshness of fish. Part 2. Formation of the bases, and application in quality assurance. Electron. J. Environ. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 9, 58–88. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, T.H.; Bechtel, P.J. Ammonia, dimethylamine, trimethylamine, and trimethylamine oxide from raw and processed fish by-products. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2008, 17, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.K.; Hurng, D.C. Thermal conversion of trimethylamine-N-oxide to trimethylamine and dimethylamine in squids. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1985, 23, 579–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinelli, J.; Koury, B. Nonenzymic formation of dimethylamine in dried fishery products. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1979, 27, 1104–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, M.; Ho, C.T. Ammonia generation during thermal degradation of amino acids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1995, 43, 3001–3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswal, B.K.; Huang, H.; Dai, J.; Chen, G.H.; Wu, D. Impact of low-thermal pretreatment on physicochemical properties of saline waste activated sludge, hydrolysis of organics and methane yield in anaerobic digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 297, 122423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, H.T.; Hilmarsdóttir, G.S.; Tómasson, T.; Arason, S.; Gudjónsdóttir, M. Changes in Protein and Non-Protein Nitrogen Compounds during Fishmeal Processing—Identification of Unoptimized Processing Steps. Processes 2022, 10, 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10040621
Nguyen HT, Hilmarsdóttir GS, Tómasson T, Arason S, Gudjónsdóttir M. Changes in Protein and Non-Protein Nitrogen Compounds during Fishmeal Processing—Identification of Unoptimized Processing Steps. Processes. 2022; 10(4):621. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10040621
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Hang Thi, Gudrún Svana Hilmarsdóttir, Tumi Tómasson, Sigurjón Arason, and María Gudjónsdóttir. 2022. "Changes in Protein and Non-Protein Nitrogen Compounds during Fishmeal Processing—Identification of Unoptimized Processing Steps" Processes 10, no. 4: 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10040621
APA StyleNguyen, H. T., Hilmarsdóttir, G. S., Tómasson, T., Arason, S., & Gudjónsdóttir, M. (2022). Changes in Protein and Non-Protein Nitrogen Compounds during Fishmeal Processing—Identification of Unoptimized Processing Steps. Processes, 10(4), 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10040621






