Evaluation of Porcine and Aspergillus oryzae α-Amylases as Possible Model for the Human Enzyme
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Modelling
2.2. Chemicals and Enzymatic Activity
3. Results
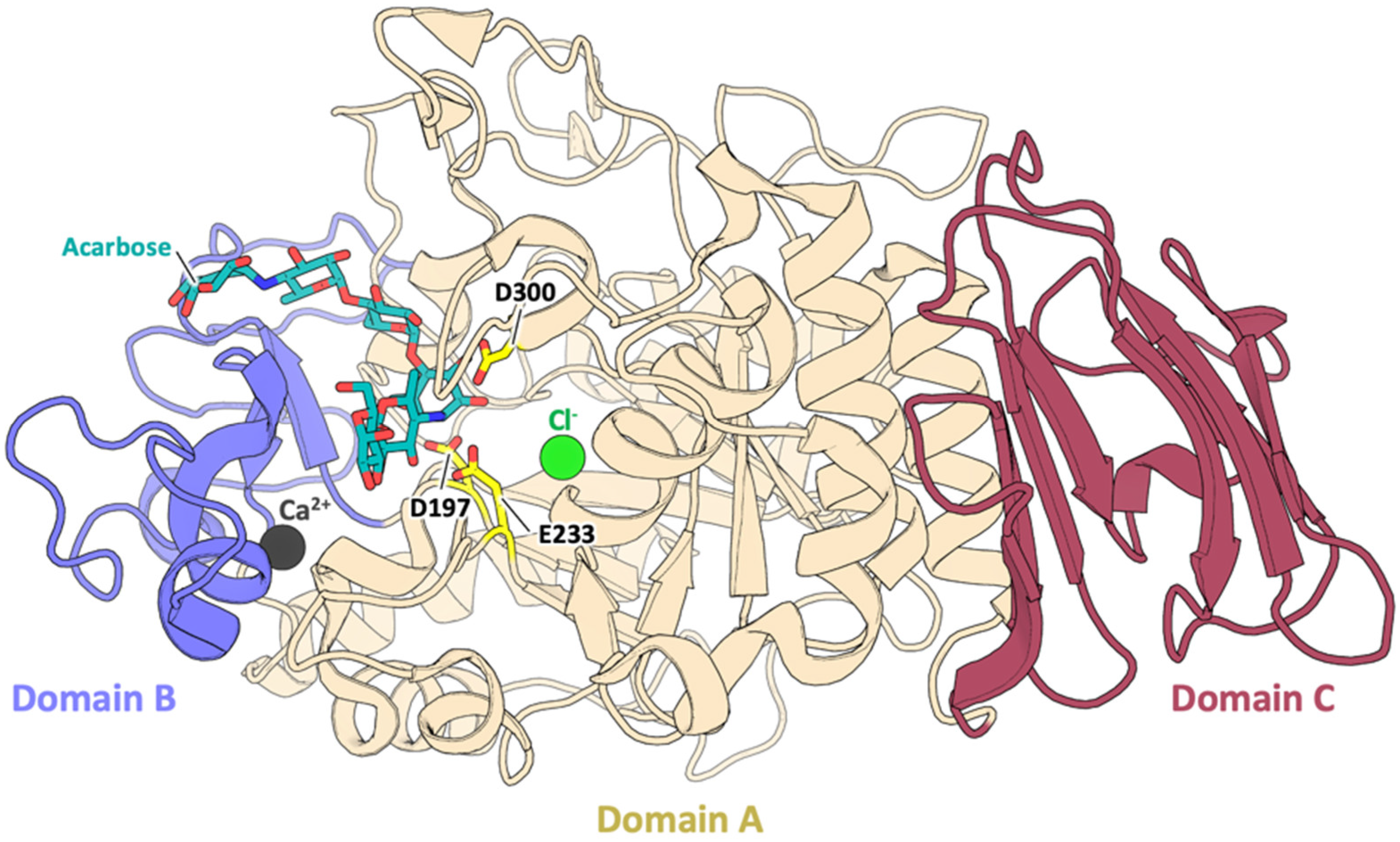
3.1. Sequence and Structural Comparison
3.2. Enzymatic Activity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- D’Amico, S.; Gerday, C.; Feller, G. Structural Similarities and Evolutionary Relationships in Chloride-Dependent α-Amylases. Gene 2000, 253, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henrissat, B.; Bairoch, A. Updating the Sequence-Based Classification of Glycosyl Hydrolases. Biochem. J. 1996, 316, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Henrissat, B.; Davies, G. Structural and Sequence-Based Classification of Glycoside Hydrolases. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 1997, 7, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombard, V.; Golaconda Ramulu, H.; Drula, E.; Coutinho, P.M.; Henrissat, B. The Carbohydrate-Active Enzymes Database (CAZy) in 2013. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D490–D495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janeček, Š.; Svensson, B.; MacGregor, E.A. α-Amylase: An Enzyme Specificity Found in Various Families of Glycoside Hydrolases. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2014, 71, 1149–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazur, A.K.; Haser, R.; Payan, F. The Catalytic Mechanism of α-Amylases Based upon Enzyme Crystal Structures and Model Building Calculations. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1994, 204, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriško, M. Evolutionary History of Eukaryotic α-Glucosidases from the α-Amylase Family. J. Mol. Evol. 2013, 76, 129–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzozowski, A.M.; Davies, G.J. Structure of the Aspergillus Oryzae α-Amylase Complexed with the Inhibitor Acarbose at 2.0 Å Resolution. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 10837–10845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasubbu, N.; Paloth, V.; Luo, Y.; Brayer, G.D.; Levine, M.J. Structure of Human Salivary α-Amylase at 1.6 A Resolution: Implications for Its Role in the Oral Cavity. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 1996, 52, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boel, E.; Brady, L.; Brzozowski, A.M.; Derewenda, Z.; Dodson, G.G.; Jensen, V.J.; Petersen, S.B.; Swift, H.; Thim, L.; Woldike, H.F. Calcium Binding in α-Amylases: An x-Ray Diffraction Study at 2.1-.ANG. Resolution of Two Enzymes from Aspergillus. Biochemistry 2002, 29, 6244–6249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linden, A.; Mayans, O.; Meyer-Klaucke, W.; Antranikian, G.; Wilmanns, M. Differential Regulation of a Hyperthermophilic α-Amylase with a Novel (Ca,Zn) Two-Metal Center by Zinc. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 9875–9884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qian, M.; Haser, R.; Payan, F. Structure and Molecular Model Refinement of Pig Pancreatic α-Amylase at 2.1 A Resolution. J. Mol. Biol. 1993, 231, 785–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feller, G.; Bussy, O.L.; Houssier, C.; Gerday, C. Structural and Functional Aspects of Chloride Binding to Alteromonas Haloplanctis α-Amylase. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 23836–23841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Larson, S.B.; Greenwood, A.; Cascio, D.; Day, J.; McPherson, A. Refined Molecular Structure of Pig Pancreatic α-Amylase at 2.1 A Resolution. J. Mol. Biol. 1994, 235, 1560–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghajari, N.; Feller, G.; Gerday, C.; Haser, R. Crystal Structures of the Psychrophilic α-Amylase from Alteromonas Haloplanctis in Its Native Form and Complexed with an Inhibitor. Protein Sci. Publ. Protein Soc. 1998, 7, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qian, M.; Ajandouz, E.H.; Payan, F.; Nahoum, V. Molecular Basis of the Effects of Chloride Ion on the Acid-Base Catalyst in the Mechanism of Pancreatic α-Amylase. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 3194–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numao, S.; Maurus, R.; Sidhu, G.; Wang, Y.; Overall, C.M.; Brayer, G.D.; Withers, S.G. Probing the Role of the Chloride Ion in the Mechanism of Human Pancreatic α-Amylase. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCleary, B.V.; McNally, M.; Monaghan, D.; Mugford, D.C.; Black, C.; Broadbent, R.; Chin, M.; Cormack, M.; Fox, R.; Gaines, C.; et al. Measurement of α-Amylase Activity in White Wheat Flour, Milled Malt, and Microbial Enzyme Preparations, Using the Ceralpha Assay: Collaborative Study. J. AOAC Int. 2002, 85, 1096–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brayer, G.D.; Luo, Y.; Withers, S.G. The Structure of Human Pancreatic α-Amylase at 1.8 A Resolution and Comparisons with Related Enzymes. Protein Sci. Publ. Protein Soc. 1995, 4, 1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rydberg, E.H.; Li, C.; Maurus, R.; Overall, C.M.; Brayer, G.D.; Withers, S.G. Mechanistic Analyses of Catalysis in Human Pancreatic α-Amylase: Detailed Kinetic and Structural Studies of Mutants of Three Conserved Carboxylic Acids. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 4492–4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurus, R.; Begum, A.; Williams, L.K.; Fredriksen, J.R.; Zhang, R.; Withers, S.G.; Brayer, G.D. Alternative Catalytic Anions Differentially Modulate Human α-Amylase Activity and Specificity. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 3332–3344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattio, L.M.; Marengo, M.; Parravicini, C.; Eberini, I.; Dallavalle, S.; Bonomi, F.; Iametti, S.; Pinto, A. Inhibition of Pancreatic α-Amylase by Resveratrol Derivatives: Biological Activity and Molecular Modelling Evidence for Cooperativity between Viniferin Enantiomers. Molecules 2019, 24, 3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aghajari, N.; Feller, G.; Gerday, C.; Haser, R. Structural Basis of α-Amylase Activation by Chloride. Protein Sci. Publ. Protein Soc. 2002, 11, 1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, A.; Rosenkranz, T.; Kayastha, A.M.; Fitter, J. The Effect of Calcium Binding on the Unfolding Barrier: A Kinetic Study on Homologous α-Amylases. Biophys. Chem. 2010, 151, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marengo, M.; Pezzilli, D.; Gianquinto, E.; Fissore, A.; Oliaro-Bosso, S.; Sgorbini, B.; Spyrakis, F.; Adinolfi, S. Evaluation of Porcine and Aspergillus oryzae α-Amylases as Possible Model for the Human Enzyme. Processes 2022, 10, 780. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10040780
Marengo M, Pezzilli D, Gianquinto E, Fissore A, Oliaro-Bosso S, Sgorbini B, Spyrakis F, Adinolfi S. Evaluation of Porcine and Aspergillus oryzae α-Amylases as Possible Model for the Human Enzyme. Processes. 2022; 10(4):780. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10040780
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarengo, Mauro, Davide Pezzilli, Eleonora Gianquinto, Alex Fissore, Simonetta Oliaro-Bosso, Barbara Sgorbini, Francesca Spyrakis, and Salvatore Adinolfi. 2022. "Evaluation of Porcine and Aspergillus oryzae α-Amylases as Possible Model for the Human Enzyme" Processes 10, no. 4: 780. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10040780
APA StyleMarengo, M., Pezzilli, D., Gianquinto, E., Fissore, A., Oliaro-Bosso, S., Sgorbini, B., Spyrakis, F., & Adinolfi, S. (2022). Evaluation of Porcine and Aspergillus oryzae α-Amylases as Possible Model for the Human Enzyme. Processes, 10(4), 780. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10040780









