A Review of Digital Transformation on Supply Chain Process Management Using Text Mining
Abstract
:1. Introduction
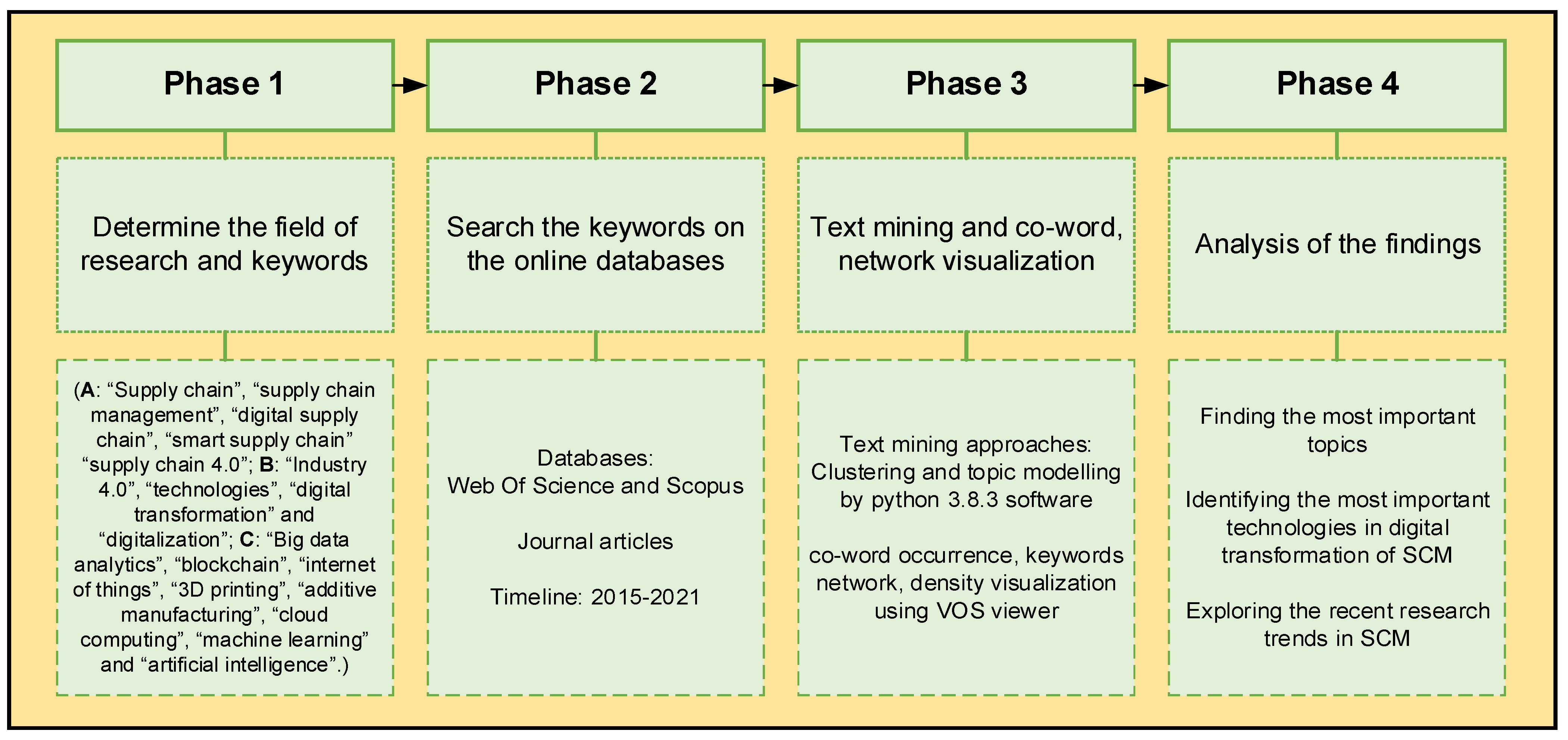
2. Research Framework
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Text Mining
2.2.1. Clustering and Topic Modeling Techniques
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Limitations of the Study
- Managerial implications
- Scope for future research
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abedi, M.; Fathi, M.S.; Rawai, N.M. The impact of cloud computing technology to precast supply chain management. Int. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2013, 2, 13–16. [Google Scholar]
- Abeyratne, S.A.; Monfared, R.P. Blockchain ready manufacturing supply chain using distributed ledger. Int. J. Res. Eng. Technol. 2016, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addo-Tenkorang, R.; Helo, P.T. Big data applications in operations/supply-chain management: A literature review. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2016, 101, 528–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, P.; Narain, R.; Ullah, I. Analysis of barriers in implementation of digital transformation of supply chain using interpretive structural modelling approach. J. Model. Manag. 2019, 15, 297–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinade, O.O.; Oyedele, L.O. Integrating construction supply chains within a circular economy: An ANFIS-based waste analytics system (A-WAS). J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 229, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqahtani, A.Y.; Gupta, S.M.; Nakashima, K. Warranty and maintenance analysis of sensor embedded products using internet of things in industry 4.0. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2019, 208, 483–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunachalam, D.; Kumar, N.; Kawalek, J.P. Understanding big data analytics capabilities in supply chain management: Unravelling the issues, challenges and implications for practice. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2018, 114, 416–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awwad, M.; Kulkarni, P.; Bapna, R.; Marathe, A. Big data analytics in supply chain: A literature review. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Operations Management, Paris, France, 27–29 September 2018; pp. 418–425. [Google Scholar]
- Barnes, S.; Rutter, R.N.; La Paz, A.I.; Scornavacca, E. Empirical identification of skills gaps between chief information officer supply and demand: A resource-based view using machine learning. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2021, 121, 1749–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, L.; Bourlakis, M.; Smart, P.; Maull, R. In search of a circular supply chain archetype—a content-analysis-based literature review. Prod. Plan. Control 2018, 29, 438–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, L.; Dora, M.; Garza-Reyes, J.A.; Kumar, V. Improving the sustainability of food supply chains through circular economy practices—A qualitative mapping approach. Manag. Environ. Qual. Int. J. 2021, 32, 752–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechtsis, D.; Tsolakis, N.; Vlachos, D.; Srai, J.S. Intelligent Autonomous Vehicles in digital supply chains: A framework for integrating innovations towards sustainable value networks. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 181, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blei, D.M.; Ng, A.Y.; Jordan, M.I. Latent dirichlet allocation. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2003, 3, 993–1022. [Google Scholar]
- Bose, R. Advanced analytics: Opportunities and challenges. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2009, 109, 155–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brereton, P.; Kitchenham, B.; Budgen, D.; Turner, M.; Khalil, M. Lessons from applying the systematic literature review process within the software engineering domain. J. Syst. Softw. 2006, 80, 571–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brinch, M. Understanding the value of big data in supply chain management and its business processes: Towards a conceptual framework. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2018, 38, 1589–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Büyüközkan, G.; Göçer, F. Digital Supply Chain: Literature review and a proposed framework for future research. Comput. Ind. 2018, 97, 157–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büyüközkan, G.; Tüfekçi, G.; Uztürk, D. Evaluating Blockchain requirements for effective digital supply chain management. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2021, 242, 108309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.E.; Chen, Y. When Blockchain Meets Supply Chain: A Systematic Literature Review on Current Development and Potential Applications. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 62478–62494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiarello, F.; Belingheri, P.; Bonaccorsi, A.; Fantoni, G.; Martini, A. Value creation in emerging technologies through text mining: The case of blockchain. Technol. Anal. Strat. Manag. 2021, 33, 1404–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.-Y.; Park, K.; Kremer, G.E. A global supply chain risk management framework: An application of text-mining to identify region-specific supply chain risks. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2020, 45, 101053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, R.; Stevenson, M.; Aitken, J. Blockchain technology: Implications for operations and supply chain management. Supply Chain Manag. Int. J. 2019, 24, 469–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallasega, P.; Rauch, E.; Linder, C. Industry 4.0 as an enabler of proximity for construction supply chains: A systematic literature review. Comput. Ind. 2018, 99, 205–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gölcük, I. An interval type-2 fuzzy reasoning model for digital transformation project risk assessment. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 159, 113579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Giovanni, P.; Cariola, A. Process innovation through industry 4.0 technologies, lean practices and green supply chains. Res. Transp. Econ. 2020, 90, 100869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dev, N.K.; Shankar, R.; Qaiser, F.H. Industry 4.0 and circular economy: Operational excellence for sustainable reverse supply chain performance. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 153, 104583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, R.; Nallapati, R.; Xiang, B. Coherence-Aware Neural Topic Modeling. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Brussels, Belgium, 2–4 November 2018; pp. 830–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolgui, A.; Ivanov, D.; Sethi, S.; Sokolov, B. Control theory applications to operations systems, supply chain management and Industry 4.0 networks. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2018, 51, 1536–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltsov, T.; Yutkin, M.; Patzek, T.W. Text Analysis Reveals Major Trends in Exploration Geophysics. Energies 2020, 13, 4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, A.G.; Dalenogare, L.S.; Ayala, N.F. Industry 4.0 technologies: Implementation patterns in manufacturing companies. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2019, 210, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gezdur, A.; Bhattacharjya, J. Digitization in the Oil and Gas Industry: Challenges and Opportunities for Supply Chain Partners. In IFIP Advances in Information and Communication Technology; Springer: Zurich, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 506, pp. 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghadimi, P.; Wang, C.; Lim, M.K.; Heavey, C. Intelligent sustainable supplier selection using multi-agent technology: Theory and application for Industry 4.0 supply chains. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2018, 127, 588–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, H.; Kusi-Sarpong, S.; Rezaei, J. Barriers and overcoming strategies to supply chain sustainability innovation. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 161, 104819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackius, N.; Petersen, M. Blockchain in logistics and supply chain: Trick or treat? In Proceedings of the Hamburg International Conference of Logistics (HICL), Hamburg, Germant, 12–13 October 2017; pp. 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HaddadPajouh, H.; Dehghantanha, A.; Parizi, R.M.; Aledhari, M.; Karimipour, H. A survey on internet of things security: Requirements, challenges, and solutions. Internet Things 2021, 14, 100129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hald, K.S.; Kinra, A. How the blockchain enables and constrains supply chain performance. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2019, 49, 376–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamble, S.S.; Gunasekaran, A.; Parekh, H.; Joshi, S. Modeling the internet of things adoption barriers in food retail supply chains. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2019, 48, 154–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamble, S.S.; Gunasekaran, A.; Sharma, R. Analysis of the driving and dependence power of barriers to adopt industry 4.0 in Indian manufacturing industry. Comput. Ind. 2018, 101, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamble, S.S.; Gunasekaran, A.; Gawankar, S.A. Achieving sustainable performance in a data-driven agriculture supply chain: A review for research and applications. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2019, 219, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, D.; Khodaverdi, R.; Olfat, L.; Jafarian, A.; Diabat, A. Integrated fuzzy multi criteria decision making method and multi-objective programming approach for supplier selection and order allocation in a green supply chain. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 47, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, A.; Lundy, M.; Webb, F.; Dwivedi, Y.K. Twitter and Research: A Systematic Literature Review through Text Mining. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 67698–67717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshavarz-Ghorabaee, M.; Amiri, M.; Hashemi-Tabatabaei, M.; Ghahremanloo, M. Prioritizing the Barriers and Challenges of Big Data Analytics in Logistics and Supply Chain Management Using MCDM Method. In Big Data Analytics in Supply Chain Management: Theory and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020; pp. 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittipanya-Ngam, P.; Tan, K.H. A framework for food supply chain digitalization: Lessons from Thailand. Prod. Plan. Control 2019, 31, 158–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korpela, K.; Hallikas, J.; Dahlberg, T. Digital supply chain transformation toward blockchain integration. In Proceedings of the 50th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Waikoloa, Hawaii, 4–7 January 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Leminen, S.; Rajahonka, M.; Wendelin, R.; Westerlund, M. Industrial internet of things business models in the machine-to-machine context. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2019, 84, 298–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luthra, S.; Mangla, S.K. Evaluating challenges to Industry 4.0 initiatives for supply chain sustainability in emerging economies. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2018, 117, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ly, P.T.M.; Lai, W.-H.; Hsu, C.-W.; Shih, F.-Y. Fuzzy AHP analysis of Internet of Things (IoT) in enterprises. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2018, 136, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, J.C.; Luli, G.K. Understanding the Public Discussion about the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention During the COVID-19 Pandemic Using Twitter Data: Text Mining Analysis Study. J. Med. Internet Res. 2021, 23, e25108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majeed, M.A.A.; Rupasinghe, T.D. Internet of things (IoT) embedded future supply chains for industry 4.0: An assessment from an ERP-based fashion apparel and footwear industry. Int. J. Supply Chain. Manag. 2017, 6, 25–40. [Google Scholar]
- Manavalan, E.; Jayakrishna, K. A review of Internet of Things (IoT) embedded sustainable supply chain for industry 4.0 requirements. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2018, 127, 925–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matt, C.; Hess, T.; Benlian, A. Digital Transformation Strategies. Bus. Inf. Syst. Eng. 2015, 57, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mergel, I.; Edelmann, N.; Haug, N. Defining digital transformation: Results from expert interviews. Gov. Inf. Q. 2019, 36, 101385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, J.M.; Voigt, K.-I. The Impact of Industry 4.0 on Supply Chains in Engineer-to-Order Industries—An Exploratory Case Study. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2018, 51, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagar, D.; Raghav, S.; Bhardwaj, A.; Kumar, R.; Singh, P.L.; Sindhwani, R. Machine learning: Best way to sustain the supply chain in the era of industry 4.0. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 47, 3676–3682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiri, M.; Ukko, J.; Saunila, M.; Rantala, T. Managing the digital supply chain: The role of smart technologies. Technovation 2020, 96–97, 102121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Nguyen, T.; Zhou, L.; Spiegler, V.; Ieromonachou, P.; Lin, Y. Big data analytics in supply chain management: A state-of-the-art literature review. Comput. Oper. Res. 2018, 98, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Novais, L.; Maqueira, J.M.; Ortiz-Bas, A. A systematic literature review of cloud computing use in supply chain integration. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2019, 129, 296–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Mara-Eves, A.; Thomas, J.; McNaught, J.; Miwa, M.; Ananiadou, S. Using text mining for study identification in systematic reviews: A systematic review of current approaches. Syst. Rev. 2015, 4, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Park, C.; Kim, Y.; Jeong, M. Influencing factors on risk perception of IoT-based home energy management services. Telematics Informatics 2018, 35, 2355–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pflaum, A.; Prockl, G.; Bodendorf, F.; Chen, H. Introduction to the Minitrack on The Digital Supply Chain of the Future: Technologies, Applications and Business Models. In Proceedings of the 51st Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Waikoloa, Hawaii, 3–6 January 2018; pp. 4179–4181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Queiroz, M.M.; Pereira, S.C.F.; Telles, R.; Machado, M.C. Industry 4.0 and digital supply chain capabilities. Benchmark. Int. J. 2019, 28, 1761–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Peña, M.; Sotano, A.J.S.; Pérez-Fernandez, V.; Abad, F.J.; Batista, M. Achieving a sustainable shipbuilding supply chain under I4.0 perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 244, 118789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, E.H.D.R.; Shinohara, A.C.; de Lima, E.P.; Angelis, J.; Machado, C. Reviewing Digital Manufacturing concept in the Industry 4.0 paradigm. Procedia CIRP 2019, 81, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saberi, S.; Kouhizadeh, M.; Sarkis, J. Blockchains and the Supply Chain: Findings from a Broad Study of Practitioners. IEEE Eng. Manag. Rev. 2019, 47, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyedghorban, Z.; Tahernejad, H.; Meriton, R.; Graham, G. Supply chain digitalization: Past, present and future. Prod. Plan. Control 2019, 31, 96–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.D.S.; Mehta, I.; Mitra, J.; Agrawal, S. Application of Big Data in Supply Chain Management. Mater. Today Proc. 2017, 4, 1106–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohrabi, B.; Vanani, I.R.; Gooyavar, A.; Naderi, N. Predicting the Readmission of Heart Failure Patients through Data Analytics. J. Inf. Knowl. Manag. 2019, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, D.; Yang, P.; Feng, H. Utilization of text mining as a big data analysis tool for food science and nutrition. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 875–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Taghikhah, F.; Voinov, A.; Shukla, N. Extending the supply chain to address sustainability. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 229, 652–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavana, M.; Shaabani, A.; Santos-Arteaga, F.J.; Vanani, I.R. A Review of Uncertain Decision-Making Methods in Energy Management Using Text Mining and Data Analytics. Energies 2020, 13, 3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjahjono, B.; Esplugues, C.; Ares, E.; Pelaez, G. What does Industry 4.0 mean to Supply Chain? Procedia Manuf. 2017, 13, 1175–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, Y.-C. Managing default risk under trade credit: Who should implement Big-Data analytics in supply chains? Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2017, 106, 276–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Maaten, L.; Hinton, G. Visualizing data using t-SNE. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2008, 9, 2579–2605. [Google Scholar]
- Vemula, R.; Zsifkovits, H. Cloud Computing im Supply Chain Management. BHM Berg-Und Hüttenmännische Mon. 2016, 161, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Han, J.H.; Beynon-Davies, P. Understanding blockchain technology for future supply chains: A systematic literature review and research agenda. Supply Chain Manag. 2019, 24, 62–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhong, Y. What were residents’ petitions in Beijing- based on text mining. J. Urban Manag. 2019, 9, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannah, W.; Daniel, S.; Saskia, S. A literature review on machine learning in supply chain management. In Proceedings of the Hamburg International Conference of Logistics (HICL), Hamburg, Germany, 26–27 September 2019; epubli GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2019; Volume 27, pp. 413–441, ISBN 978-3-7502-4947-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, G.; Luthra, S.; Jakhar, S.K.; Mangla, S.K.; Rai, D.P. A framework to overcome sustainable supply chain challenges through solution measures of industry 4.0 and circular economy: An automotive case. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 254, 120112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Singh, S.P. Blockchain critical success factors for sustainable supply chain. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 152, 104505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Tan, K.H. An analytic infrastructure for harvesting big data to enhance supply chain performance. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2018, 281, 559–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Kim, M.C.; Chen, C. An investigation of the intellectual structure of opinion mining research. Inf. Res. Int. Electron. J. 2017, 22, n1. [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann, M.; Rosca, E.; Antons, O.; Bendul, J.C. Supply chain risks in times of Industry 4.0: Insights from German cases. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2019, 52, 1755–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Journal Name | Number | H-Index | Impact Factor | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Journal of Cleaner Production | 28 | 173 | 7.246 |
| 2 | International Journal of Production Economics | 26 | 93 | 3.954 |
| 3 | Computers in Industry | 24 | 172 | 5.134 |
| 4 | Technological Forecasting and Social Change | 23 | 70 | 3.605 |
| 5 | Production Planning and Control | 21 | 103 | 5.846 |
| 6 | Computers in Industry | 19 | 100 | 3.954 |
| 7 | International Journal of Production Research | 18 | 125 | 4.577 |
| 8 | Sustainability | 18 | 85 | 2.798 |
| 9 | Computers and Industrial Engineering | 18 | 121 | 4.135 |
| 10 | Resources, Conservation, and Recycling | 17 | 119 | 8.086 |
| 11 | International Journal of Information Management | 14 | 99 | 8.210 |
| 12 | Industrial Marketing Management | 8 | 125 | 4.695 |
| 13 | Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review | 8 | 110 | 4.690 |
| 14 | Journal of Manufacturing Technology Management | 5 | 70 | 3.385 |
| 15 | Supply Chain Management: An International Journal | 5 | 115 | 4.725 |
| 16 | Journal of Purchasing and Supply Management | 4 | 80 | 4.640 |
| 17 | Business Horizons | 4 | 87 | 3.444 |
| 18 | European Journal of Operational Research | 3 | 243 | 3.806 |
| 19 | Future Generation Computer Systems | 3 | 119 | 5.387 |
| 20 | Applied Soft Computing Journal | 3 | 143 | 5.472 |
| 21 | Computers and Chemical Engineering | 2 | 139 | 4.000 |
| 22 | Expert Systems with Applications | 2 | 184 | 4.292 |
| 23 | other | 124 | ||
| Total | 395 |
| Component | Cluster Number | Automatic Cluster Label Extraction Using Word Embedding Technique | Manual Interpretation | LDA Output on Each Cluster |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | TC1 | Supply chain management integration using systematic literature reviews | Systematic reviews in the area of sustainable supply chain management | [‘0.568 * “Literature” + 0.415 * “review” + “0.027 * “sustainable” + 0.014 * “management” + ”0.016* “supply” + 0.012 * “chain” + “0.009 * “application”, “0.007 * “systematic” + “0.007* “circular” + “0.003 * “research”’] |
| TC2 | Big supply chain management service industry using blockchain big data analytics | Big data, blockchain research in supply chain management | [“0.412 * Big data”, “0.267 * manufacturing”, “0.051 * blockchain”, “0.046*model”, “0.026 * adoption”, “0.021 * performance”, “0.019 * industry”, “0.007 * supply”, “0.004 * chain”, “0.004 * management”]” | |
| TC3 | Impact digital manufacturing supply chain framework research | Digital manufacturing and supply chain management | [“0.018 * digital”, “0.018 * food”, “0.016 * industry”, “0.012 * technology”, “0.009 * management”, “0.008 * framework”, “0.007 * impact”, “0.006 * smart”, “0.004 * model”, “0.004 * analytics”] | |
| Abstract | AC1 | Estimate challenges supply chain | Practical approaches to sustainable supply chain management | [‘0.023 * “provide” + 0.215 * “develop” + “0.119 * “technology” + 0.014 * “sustainability” + ”0.009 * “practice” + 0.007 * “model” + “0.006 * “company”, “0.006 * “study” + “0.004 * “industry” + “0.003 * “approach”’] |
| AC2 | Forecast serve basic planning | Information systems and digital transformation models | [‘0.016 * “application” + 0.011 * “digital” + “0.011 * “supply_chain” + 0.009 * “information” + ”0.009 * “system” + 0.008 * “trust” + “0.008 * “cost”, “0.008 * “firm” + “0.006 * “measurement” + “0.003 * “model”’] | |
| AC3 | Identify blockchain literature | Blockchain, strategy applications in supply chain management | [‘0.030 * “block_chain” + 0.219 * “traceability” + “0.018 * “use” + 0.016 * “system” + ”0.014 * “product” + 0.012 * “purpose” + “0.008 * “application”, “0.007 * “stratergy”+ “0.006 * “provide” + “0.005 * “market”’] | |
| AC4 | Firm access big data analysis | Big data research in supply chain | [‘0.028 * “technology” + 0.020 * “supply_chain” + “0.018 * “big_data” + 0.012 * “impact” + ”0.012 * “research” + 0.011 * “identify” + “0.009 * “paper”, “0.009 * “industry” + “0.008 * “issue” + “0.006 * “metric”’] | |
| AC5 | Purpose paper aim identify literature blockchain supply chain. | Literature reviews in supply chain | [‘0.568 * “review” + 0.415 * “field” + “0.027 * “paper” + 0.014 * “article” + ”0.016 * “research” + 0.012 * “challenge” + “0.009 * “supply_chain”, “0.007 * “systematic” + “0.007 * “process” + “0.003 * “concept”’] | |
| Keywords | KC1 | Emerging blockchain research | Blockchain, sustainability-related research | [‘0.294 * “block” + 0.272 * “chain” + “0.117 * “emerge” + 0.109 * “sustainability” + ”0.071 * “supply” + 0.012 * “chain” + “0.008 * “research”, “0.007 * “important” + “0.005 * “article” + “0.002 * “focus”’] |
| KC2 | Analytic infrastructure | Decision support techniques in global emerging markets | [‘0.030 * “decision” + 0.013 * “time” + “0.011 * “read” + 0.011 * “support” + ”0.009* “engineer” + 0.009 * “system” + “0.007 * “global”, “0.007 * “study” + “0.004 * “various” + “0.002 * “market”’] | |
| KC3 | Big service application in supply chain management | Big data-based smart manufacturing | [‘0.036 * “data” + 0.024 * “big” + “0.020* “manage” + 0.017 * “field” + ”0.016 * “application” + 0.010 * “industry” + “0.009 * “manufacturing”, “0.008 * “outer”+ “0.007 * “analysis” + “0.007 * “role”’] | |
| KC4 | Supply chain management | Circular economy and sustainable development in supply chains | [‘0.082 * “evidence” + 0.061 * “supply” + “0.006 * “circular” + 0.006 * “economy” + ”0.006 * “value” + 0.006 * “challenge” + “0.004 * “manage”, “0.004 * “role” + “0.004 * “progress” + “0.003 * “chain”’] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tavana, M.; Shaabani, A.; Raeesi Vanani, I.; Kumar Gangadhari, R. A Review of Digital Transformation on Supply Chain Process Management Using Text Mining. Processes 2022, 10, 842. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10050842
Tavana M, Shaabani A, Raeesi Vanani I, Kumar Gangadhari R. A Review of Digital Transformation on Supply Chain Process Management Using Text Mining. Processes. 2022; 10(5):842. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10050842
Chicago/Turabian StyleTavana, Madjid, Akram Shaabani, Iman Raeesi Vanani, and Rajan Kumar Gangadhari. 2022. "A Review of Digital Transformation on Supply Chain Process Management Using Text Mining" Processes 10, no. 5: 842. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10050842
APA StyleTavana, M., Shaabani, A., Raeesi Vanani, I., & Kumar Gangadhari, R. (2022). A Review of Digital Transformation on Supply Chain Process Management Using Text Mining. Processes, 10(5), 842. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10050842






