Lightweight Design and Experimental Study of Ceramic Composite Armor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Design of Ceramic Monomer Structure
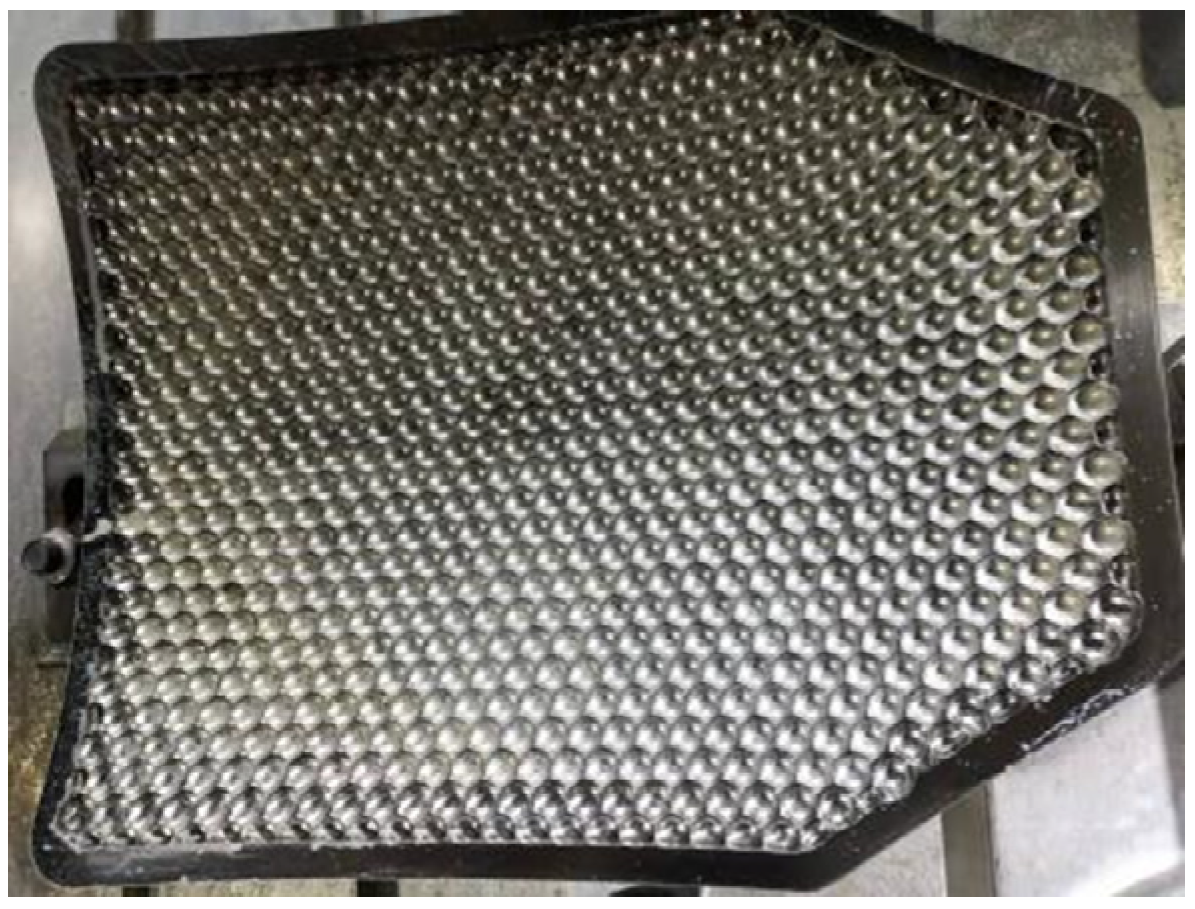
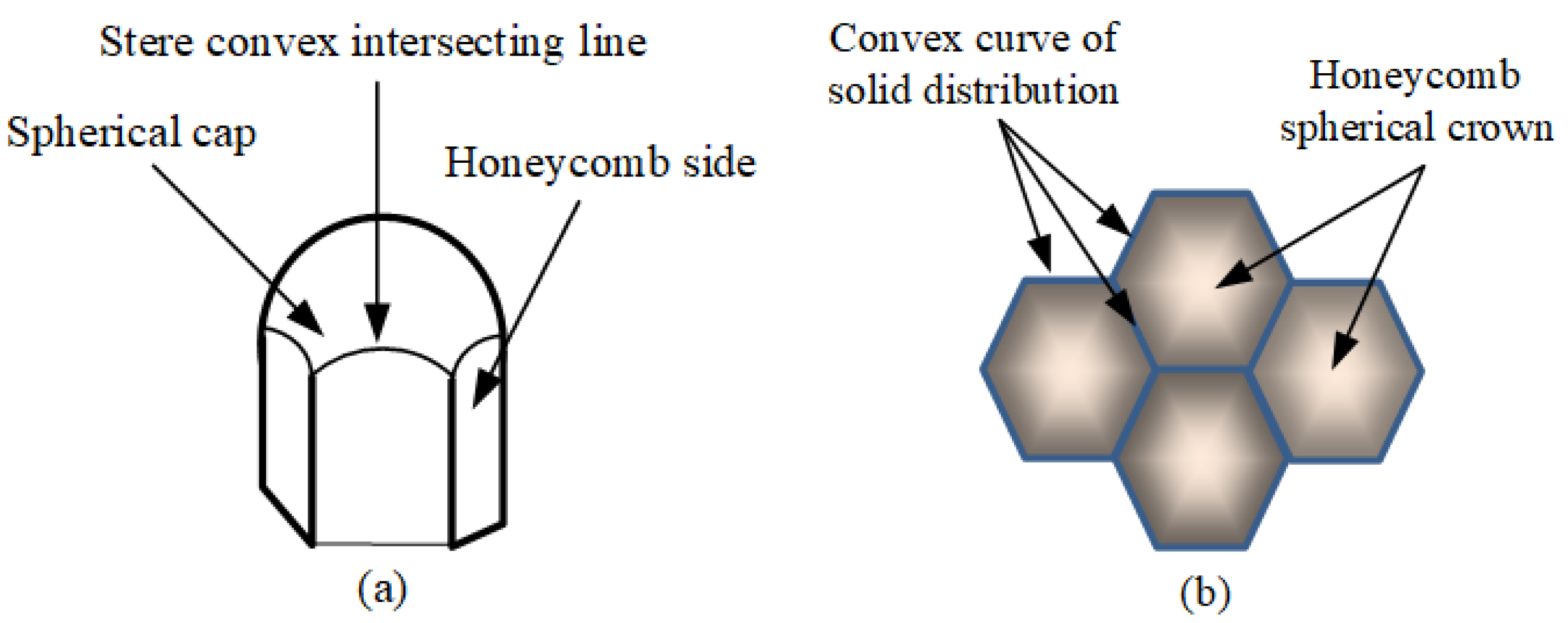
2.1. Structure Form
2.2. Monomer, Splice, and Monolithic Ceramic Structure
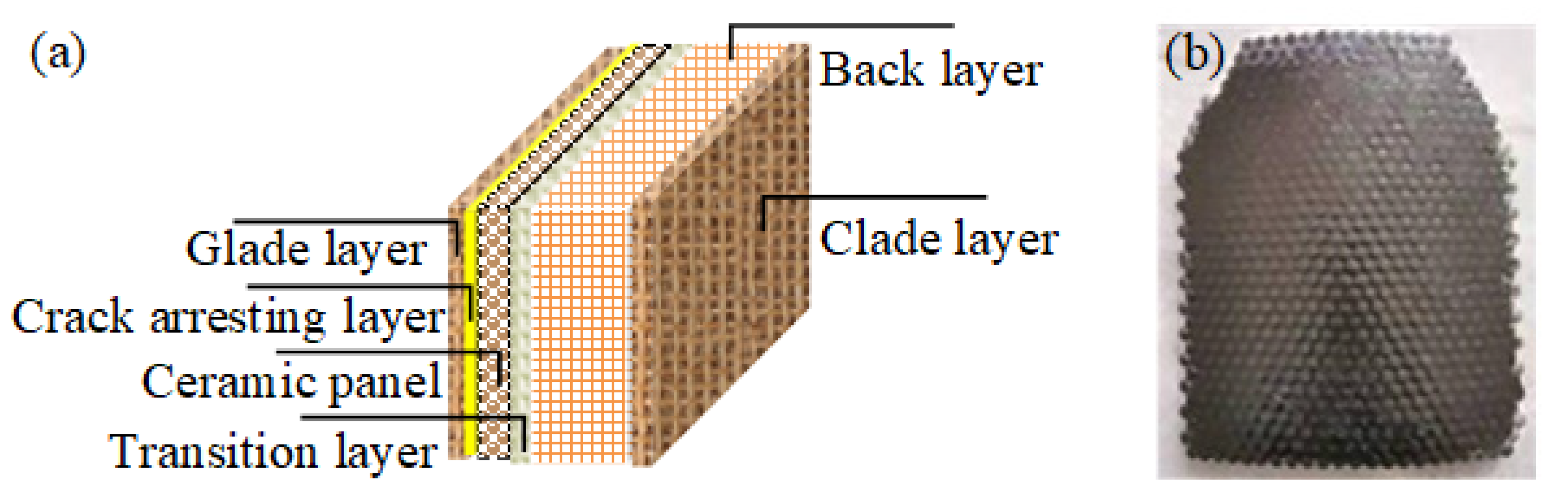
2.3. Material Selection for Panels and Backboards
2.4. Preparation of Ceramic/Fiber Composite Armor
3. Test Conditions and Methods
4. Results and Discussion
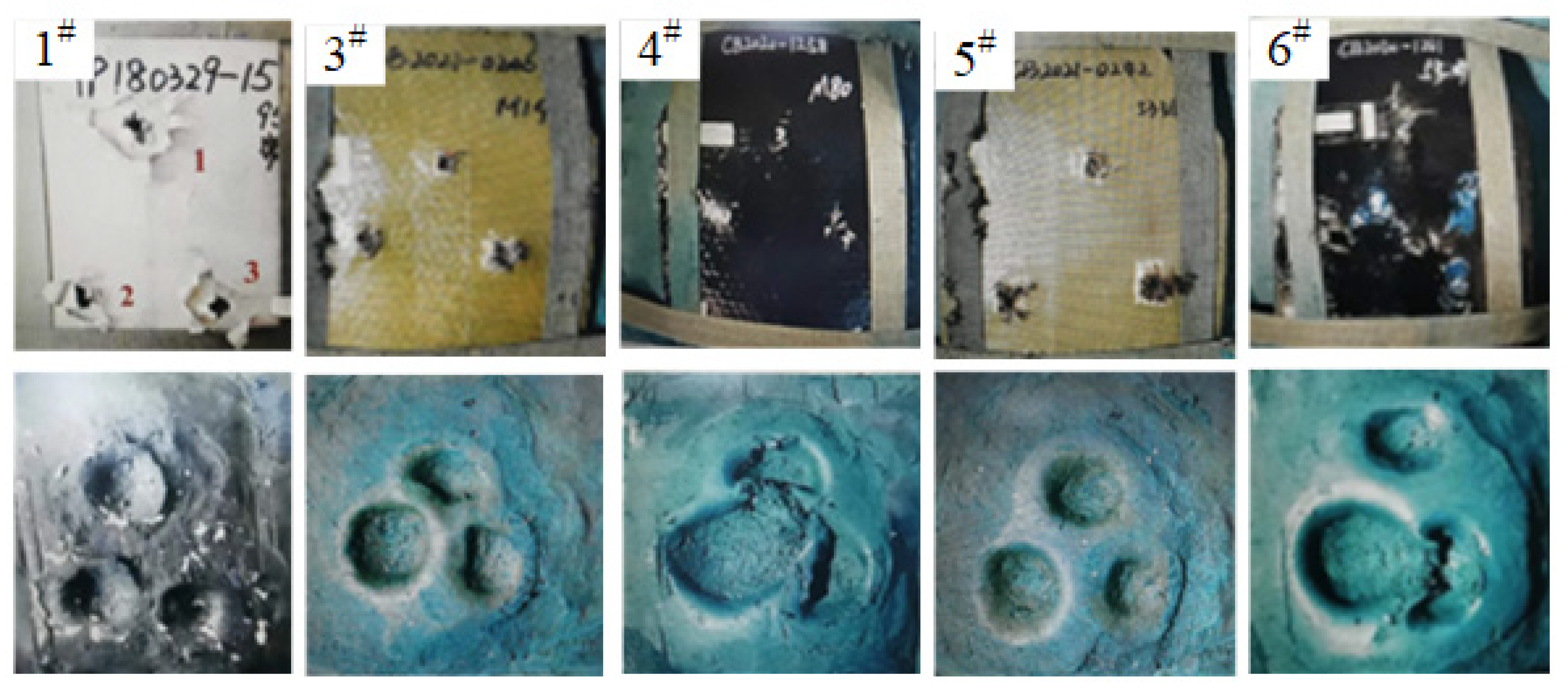
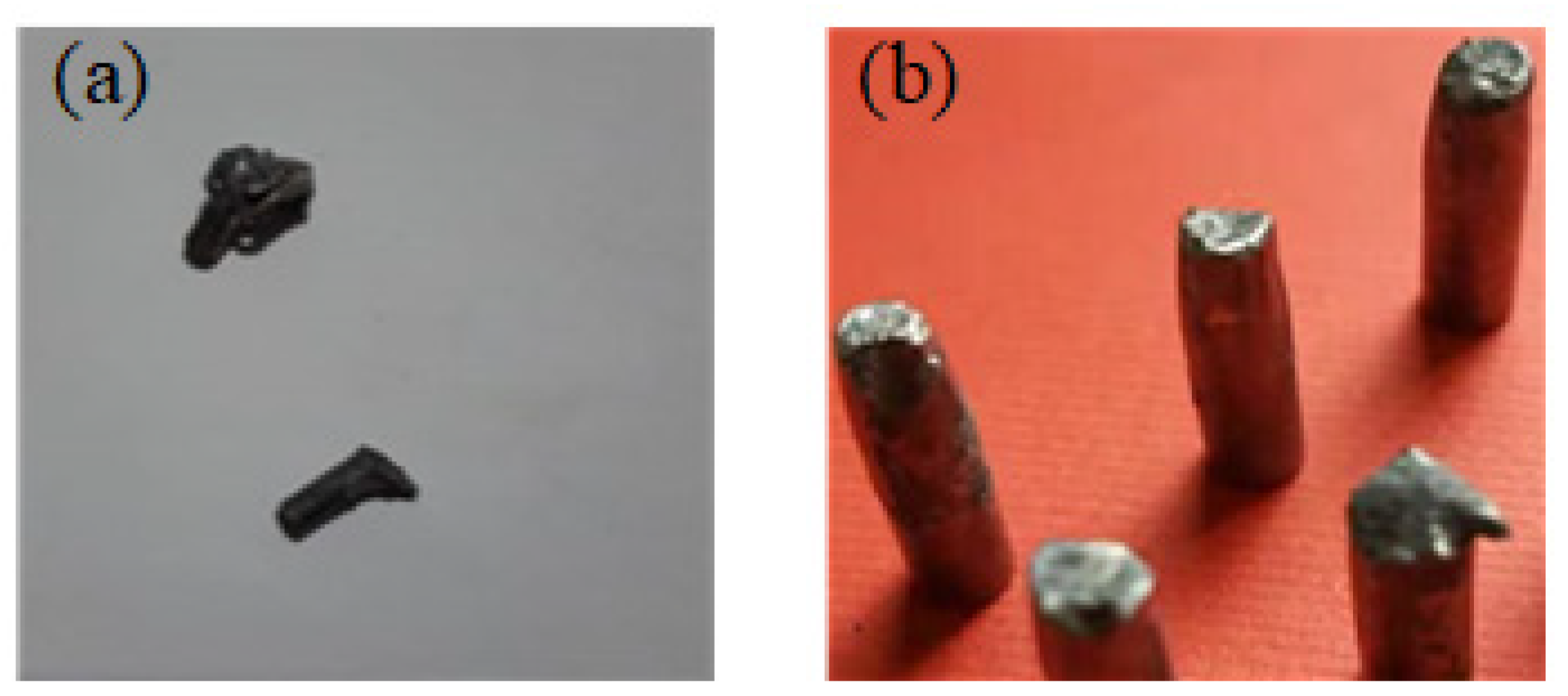
4.1. Analysis of Experimental Results
4.2. Correlation Analysis of the Influencing Factors of Shells Penetrating Ceramic Composite Target Plates
4.2.1. Establishment of the Fuzzy Grey Relational Analysis Model
- (1)
- Determine the analysis sequence
- (2)
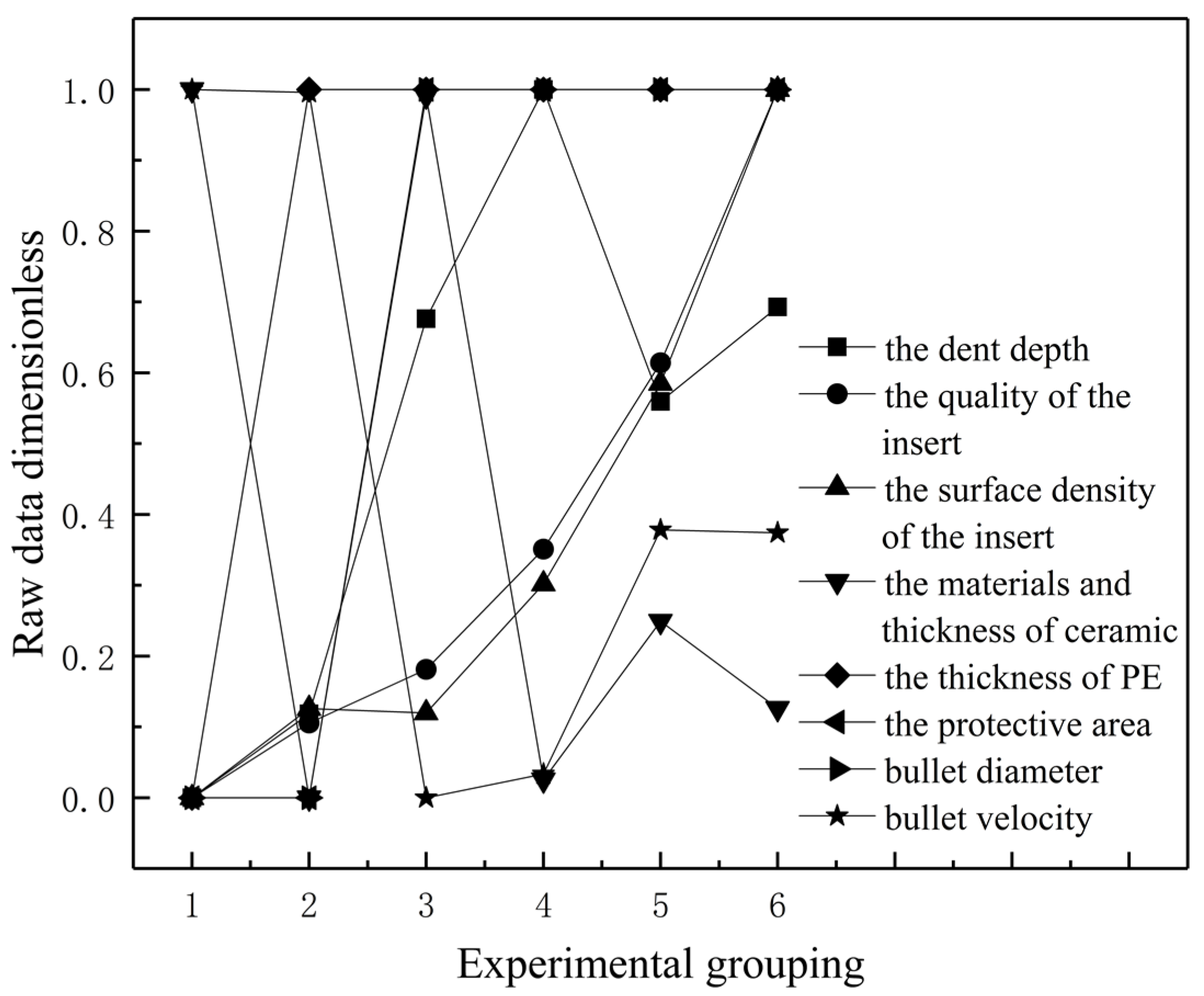
- Dimensionless analysis sequence
- (3)
- Calculation of fuzzy membership
- (4)
- Calculation of the grey correlation coefficient
- Step 1: Calculate the mean of all absolute differences:
- Step 2: Determine the value interval of the resolution coefficient ρ according to the ratio of the mean value of the absolute difference to the maximum absolute difference value; record EΔ = /Δmax. The value interval of the resolution coefficient ρ is: EΔ ≤ ρ ≤ 2EΔ, and it needs satisfy:
- (5)
- Disadvantages of European-style gray correlation
- (6)
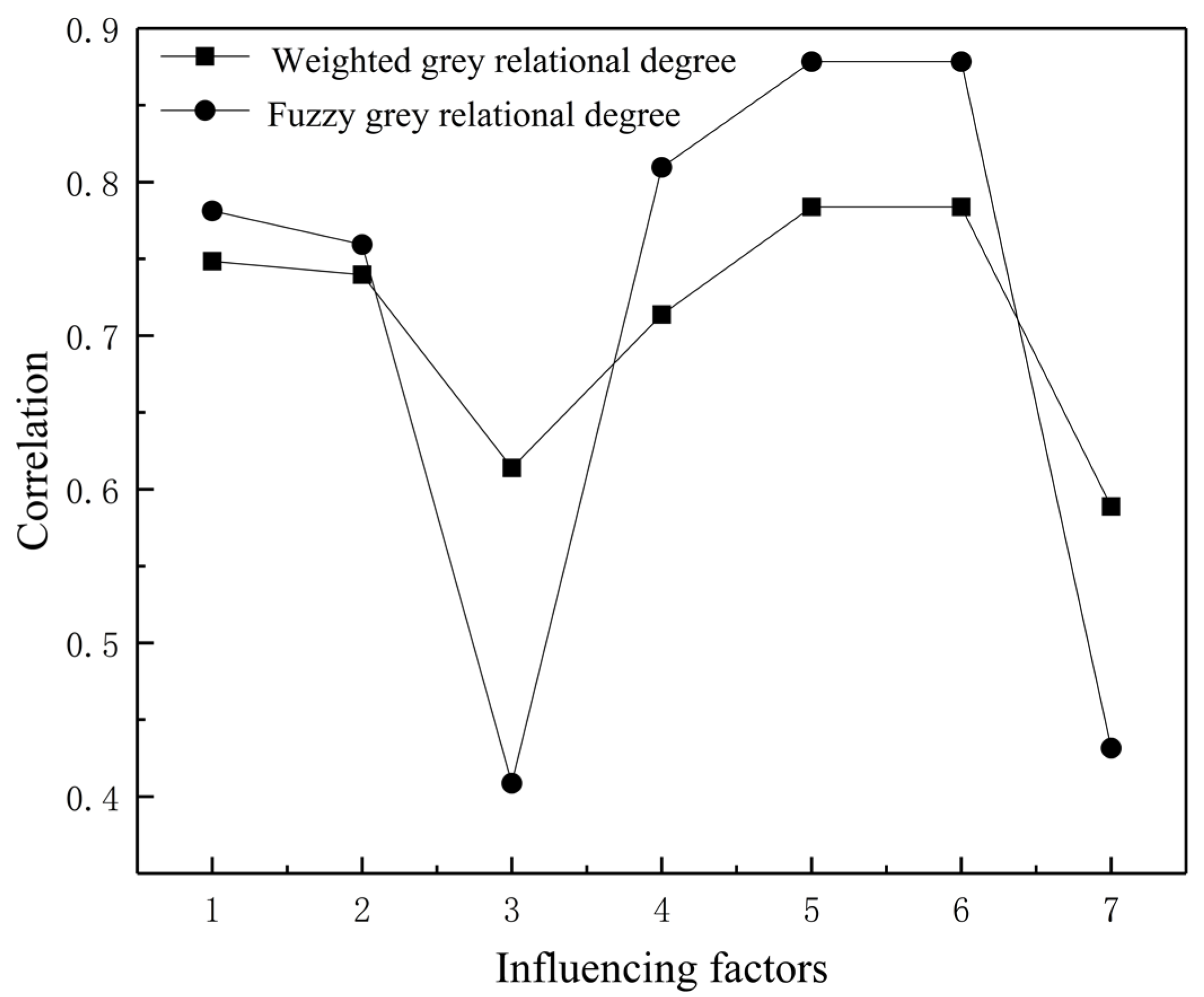
- Calculation of Fuzzy Gray Correlation Degree
4.2.2. Correlation Analysis of the Factors Affecting the Penetration of the Standard Bullet into the Ceramic Composite Target
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The bulletproof performance of the hexagonal prism ball-crown ceramic/fiber composite board was better than that of the conventional ceramic/fiber composite board of the same thickness.
- (2)
- The hexagonal prism spherical cap ceramic panel can transform nominal forward penetration into actual oblique penetration.
- (3)
- The use of a hexagonal prism spherical cap ceramic panel is an effective way to achieve a lightweight design of ceramic/fiber composite armor.
- (4)
- The “protection area” and “bullet type” are the main factors affecting the dent depth of the backing material, while the “ceramic material and thickness” and “bullet velocity” have little effect on it.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shen, Z.; Hu, D.; Yang, G.; Han, X. Ballistic reliability study on SiC/UHMWPE composite armor against armor-piercing bullet. Compos. Struct. 2019, 213, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldin, M.S.; Berendeev, N.N.; Melekhin, N.V.; Popov, A.A.; Nokhrin, A.V.; Chuvildeev, V.N. Review of ballistic performance of alumina: Comparison of alumina with silicon carbide and boron carbide. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 25201–25213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawaz, Z.; Zheng, W.; Behdinan, K. Numerical simulation of normal and oblique ballistic impact on ceramic composite armours. Compos. Struct. 2004, 63, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, J.D. Penetration resistance of armor ceramics: Dimensional analysis and property correlations. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2015, 85, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savio, S.G.; Ramanjaneyulu, K.; Madhu, V.; Bhat, T.B. An experimental study on ballistic performance of boron carbide tiles. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2011, 38, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.X.; Wu, H.; Fang, Q. Interface defeat studies of long-rod projectile impacting on ceramic targets. Def. Technol. 2020, 16, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhu, V.; Ramanjaneyulu, K.; Bhat, T.B.; Gupta, N.K. An experimental study of penetration resistance of ceramic armour subjected to projectile impact. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2005, 32, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokrieh, M.M.; Javadpour, G.H. Penetration analysis of a projectile in ceramic composite armor. Compos. Struct. 2008, 82, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Dong, H.; Liang, K.; Huang, Y. Impact simulation and ballistic analysis of B4C composite armour based on target plate tests—ScienceDirect. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 10035–10049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiusti, J.; Kammer, E.H.; Neckel, L.; Lóh, N.J.; Trindade, W.; Silva, A.O.; Montedo, O.R.K.; de Noni, A. Ballistic performance of Al2O3 mosaic armors with gap-filling materials. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 2697–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, B.K.; Curtin, W.A.; Parthasarathy, T.A.; Dutton, R.E. Criteria for crack deflection/penetration criteria for fiber-reinforced ceramic matrix composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 1998, 58, 1775–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, Y.; Du, S.; Yang, Z.; Cheng, H.; Fan, Q. An analysis of bi-layer ceramic armor and optimization of protection efficiency. Mater. Des. 2021, 203, 109633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, P.; Liu, J.; Yang, H.; Chen, J. A metal/UHMWPE/SiC multi-layered composite armor against ballistic impact of flat-nosed projectile. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 22497–22513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.Q.; Wang, J.R.; Yin, L.K.; Chen, Z.G.; Yi, R.C.; Lu, C.H. Experimental study on the penetration effect of ceramics composite projectile on ceramic/A3 steel compound targets. Def. Technol. 2017, 13, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Baha, T.; Ramazan, K. Ballistic performance of ceramic/composite structures. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 1651–1660. [Google Scholar]
- Zaera, R.; Sanchez-Galvez, V. Analytical modelling of normal and oblique ballistic impact on ceramic/metal lightweight armours. Int. J. Impact Eng. 1998, 21, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahbek, D.B.; Simons, J.W.; Johnsen, B.B.; Kobayashi, T.; Shockey, D.A. Effect of composite covering on ballistic fracture damage development in ceramic plates. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2017, 99, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.Z.; Chen, Z.G.; Feng, S.S.; Zhao, T.Y. Experimental study on ceramic balls impact composite armor. Def. Technol. 2020, 16, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.C.; Chen, X.W. Theoretical analysis of projectile-target interface defeat and transition to penetration by long rods due to oblique impacts of ceramic targets. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2017, 106, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, R.; Serjouei, A.; Sridhar, I.; Geoffrey, T.E. Pre-stress effect on confined ceramic armor ballistic performance. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2015, 84, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Chen, Z.; Cheng, X.; Wang, Y.; Amankwa, A.R.; Xu, J. Design and ballistic penetration of the ceramic composite armor. Compos. Part B Eng. 2016, 84, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chen, S.F.; Yuen, M. Fuzzy Part Family Formation Based on Grey Relational Analysis. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2001, 18, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Jin, Y.; Zhu, N.; Li, X.; Wang, G.; Chen, G. Comprehensive assessment of microbial aggregation characteristics of activated sludge bioreactors using fuzzy clustering analysis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 162, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Ceramic | Density (g·cm−3) | Elasticity-Modulus | Hardness (HK) | Fracture toughness (MPa·m1/2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B4C | 2.50 | 400 | 2900 | 3.55 |
| UHMWPE | Density (g/m3) | Modulus (G/dex) | Strength (G/dex) | Fracture Elongation (%) | Areal Density (g/cm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZT60 | 0.47 | 40 | 1500 | 2.8 | 5 |
| Number | Board Quality (kg) | Board Surface Density (kg/m2) | Ceramic Thickness (mm) | PE Thickness (mm) | Protection Area (m2) | Range (m) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.79 | 23.87 | 6 boron carbide | 10 | 0.075 | 15 | |||
| 2 | 1.97 | 26.37 | 5 Silicon carbide | 12 | 0.075 | 15 | |||
| 3 | 2.1 | 26.25 | 6 boron carbide | 12 | 0.08 | 15 | |||
| 4 | 2.39 | 29.87 | 6 Silicon carbide | 12 | 0.08 | 15 | |||
| 5 | 2.84 | 35.5 | 10 boron carbide | 12 | 0.08 | 15 | |||
| 6 | 3.5 | 43.75 | 10 Silicon carbide | 12 | 0.08 | 15 | |||
| Shot Angle | Ammunition (mm) | Shot Sequence | Warhead Velocity (m/s) | Shooting Situation | Backing Material Recess Depth | ||||
| Require (mm) | Measured Value (mm) | ||||||||
| 0° | Type 87 5.8 | 1 | 926 | No penetration | ≤25 | 18.3 | |||
| 2 | 925 | No penetration | 21.0 | ||||||
| 3 | 923 | No penetration | 17.2 | ||||||
| 0° | Type 87 5.8 | 1 | 925 | No penetration | ≤25 | 15.1 | |||
| 2 | 923 | No penetration | 21.0 | ||||||
| 3 | 925 | Penetration | / | ||||||
| 0° | 7.62 NATO round (M80) | 1 | 845 | No penetration | ≤44 | 28.6 | |||
| 2 | 844 | No penetration | 31.7 | ||||||
| 3 | 847 | No penetration | 36.7 | ||||||
| 0° | 7.62 NATO round (M80) | 1 | 847 | No penetration | ≤44 | 38.5 | |||
| 2 | 852 | No penetration | 36.7 | ||||||
| 3 | 845 | No penetration | 41.2 | ||||||
| 0° | Type 53 piercing bomb 7.62 | 1 | 878 | No penetration | ≤44 | 29.7 | |||
| 2 | 873 | No penetration | 28.4 | ||||||
| 3 | 875 | No penetration | 31.9 | ||||||
| 0° | Type 53 piercing bomb 7.62 | 1 | 877 | No penetration | ≤44 | 26.7 | |||
| 2 | 875 | No penetration | 32.4 | ||||||
| 3 | 873 | No penetration | 38.9 | ||||||
| X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ri | 0.8141 | 0.7788 | 0.2032 | 0.9056 | 0.9731 | 0.9731 | 0.2741 |
| X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.7484 | 0.7397 | 0.6140 | 0.7137 | 0.7837 | 0.7837 | 0.5888 | |
| 0.7813 | 0.7593 | 0.4086 | 0.8096 | 0.8784 | 0.8784 | 0.4315 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, J.; Zeng, Y.; Liang, X.; Hou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Z.; Cui, S. Lightweight Design and Experimental Study of Ceramic Composite Armor. Processes 2022, 10, 1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10061056
Chen J, Zeng Y, Liang X, Hou Y, Wang Y, Sun Z, Cui S. Lightweight Design and Experimental Study of Ceramic Composite Armor. Processes. 2022; 10(6):1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10061056
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Jianmei, Yihui Zeng, Xiaopeng Liang, Yanbin Hou, Yunliang Wang, Zhenqi Sun, and Shuwan Cui. 2022. "Lightweight Design and Experimental Study of Ceramic Composite Armor" Processes 10, no. 6: 1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10061056
APA StyleChen, J., Zeng, Y., Liang, X., Hou, Y., Wang, Y., Sun, Z., & Cui, S. (2022). Lightweight Design and Experimental Study of Ceramic Composite Armor. Processes, 10(6), 1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10061056





