Developing Trusted IoT Healthcare Information-Based AI and Blockchain
Abstract
1. Introduction
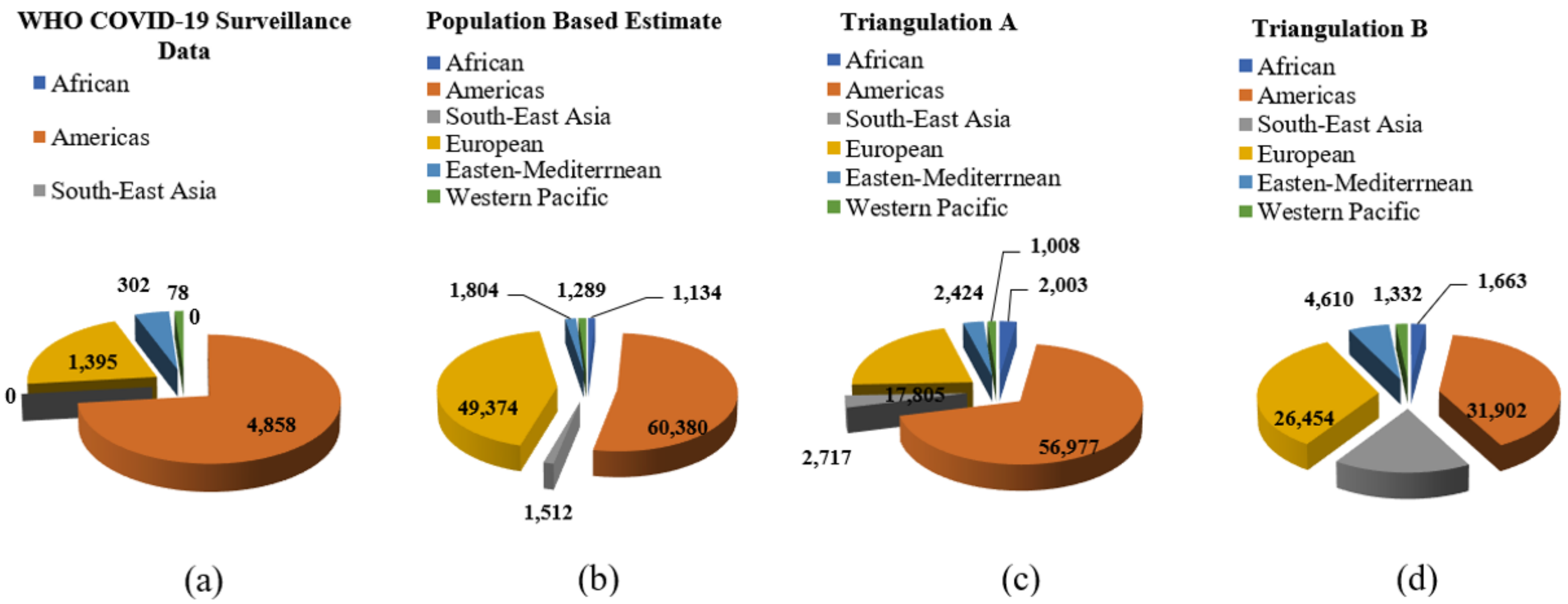
- The first approach, the crude mortality rate from each country, or the total number of fatalities reported to the World Health Organization (WHO) COVID-19 Dashboard divided by population size was applied to simply estimate the number of deaths among HCWs. This evaluation implies that HCWs, regardless of age or gender, have a similar infection risk and risk of mortality to the general population, but a greater risk of infection (both at the workplace and the community, particularly in countries lacking practices, provisions, and guidance on infection prevention and control). Another issue is its poor estimate. Only 6643 of the 3.45 million COVID-19-related deaths reported to WHO were HCWs as shown in Figure 1a.
- The second approach is improving on the first approach by using age- and sex-indirect standardization and age- and sex-specific mortality estimates. The reported COVID-19 fatalities were reallocated within each country based on the age and gender distribution of mortality reported to WHO for chosen countries. The International Labor Organization’s (ILO) estimated number of HCWs (split by gender) was redistributed based on the age and gender mix of the population size in the age range of 25–64 years. According to population estimates, roughly 115,500 HCWs (ranging from 80,000 to 1,600,001) of the 135-million-person global health and care workforce may have died. The age- and gender-specific death rates for each nation were then estimated and applied to the country’s redistributed HCW population. If the anticipated overall mortality in high-burden nations is included, the top range of estimates might exceed 180,000. This strategy disregards any of the potentially increased risks indicated above if HCWs have an exposure risk equivalent to the general population as presented in Figure 1b.
- The third approach is based on the analysis of SARS-CoV-2 infections and deaths among HCWs, which discovered that infections of HCWs accounted for 12.5% (confidence interval 6.2%, 23.5%) of all SARS-CoV-2 infections between March and July 2020. The decreasing proportion of HCW infections among all SARS-CoV-2 illnesses reported to WHO supports the lower bound of 6.2% of all cases (from 5.7% in May 2020 to 1.8% by May 2021). The meta-analysis revealed the prevalence of death among HCWs, which was then multiplied by the estimated infection rate among HCWs, yielding an estimate of 6.2% of all SARS-CoV-2 infections reported by each nation as illustrated in Figure 1c.
- In the fourth approach, a separate estimate based on meta-analysis summary statistics yields a global estimated total of 79,700 HCW fatalities (as shown in Figure 1d), which supports the 83,000 number (with figures falling between 39,900 and 159,500). It may be argued, however, that the lowest estimate in the range—39,900 HCWs—is the least plausible because it combines the lowest infection rate (6.2%) and mortality rate (6.2%) (0.4%).
2. Relevant Literature
2.1. Internet of Things (IoT)
2.2. Introduction to the Blockchain
- Block version: block validation rules.
- Previous block hash: the previous block’s hash value.
- Timestamp: the current block’s creation time.
- Nonce: a 4-byte random field that miners adjust for every hash calculation to solve a PoW mining puzzle.
- Body root hash: the hash value of the Merkle tree root built by transactions in the block body.
- Target hash: target threshold of the hash value of a new valid block. The target hash is used to determine the difficulty of the PoW puzzle.
- Public: A public blockchain, also known as the permissionless blockchain, is one that does not require any permissions. By performing a bitcoin transaction, mining a block, or operating and connecting as a node, anybody may become a participant in this blockchain.
- Permission blockchain: The private blockchain is also known as the permission blockchain. Only members of the organization or chosen persons can participate in the event, which is closed to the public.
- Consortium: This is a somewhat centralized and decentralized system. This type of blockchain is managed by a consortium of companies, whereas others are managed by a single company.
- Time Preservation: Because the certification of the central authority is required for settlements, this procedure is quicker and less expensive.
- Cost Reduction: It does away with third-party verification and direct asset transfer. Sharing a copy of the ledger created by each participant eliminates middlemen and decreases transaction effort. This is how the blockchain helps you save money.
- Increased Security: The client system serves as a deterrent to cybercrime and fraud. It is impossible to tamper with the data on the blockchain since it is shared with millions of people.
- Administration of patient consent
- 2.
- Remote treatment traceability
- 3.
- Traceability of medical kits and devices used at home
- 4.
- Personal health records must be kept secure
- 5.
- Automated payments
- 6.
- Reliable monitoring of elderly care services
- 7.
- Drug delivery and pharmacy refill traceability
- 8.
- Reliable health insurance services
- 9.
- Specialist referral services with a good reputation
- 10.
- Patient follow-up care service automation
3. The Proposed Smart Clinic
3.1. Phase I: The Clinic’s Website
- Registration, data collection, and receiving symptoms of the patient
- Data Collection
- Symptoms of the Patient
- -
- The chronic diseases that the patient suffers from (e.g., diabetes, hypertension, heart disease, obesity, cancer, asthma, etc.).
- -
- The symptoms that the patient is feeling (e.g., fever, cough, tiredness, loss of taste or smell, sore throat, headache, aches and pains, diarrhea, red or irritated eyes).
- -
- Whether the patient is a smoker or not.
- 2.
- QR code generation and determination of the appropriate appointment for the patient
- 3.
- Suggestion of an appropriate treatment protocol
3.2. Phase II: Clinic Visit

3.2.1. Stage 1: Sensing and Measurements
Node MCU Controller
Sensing Elements
- SpO2 Level
- -
- Blood oxygen saturation is calculated using the number of oxygenated and deoxygenated hemoglobin molecules, which is represented as a percentage by the SpO2 parameters. According to medical research, SpO2, or the percentage of oxygen in a healthy human body, should be greater than 94%, or more than 94 hemoglobin in 100 hemoglobin.
- -
- Pulse oximetry technology measures the amount of SpO2 in the body by using infrared and red light. Oxygenated hemoglobin always absorbs infrared light while passing a red light, and deoxygenated hemoglobin always absorbs red light while passing infrared light. The SpO2 data is derived from this pass-through and absorption.
- -
- The pulse rate is also determined using the same data since the heart rate causes the blood pressure to rise because the amplitude of the wave created by the raw data is high and low depending on the heartbeat, which is calculated and shown as the PR value. An adult human being’s typical heart rate ranges between 60 and 100 beats per minute.
- Temperature Sensor MLX90614
- -
- The MLX90614 temperature sensor has been used in the proposed smart clinic; it is a contactless IR temperature sensor that works on the Stefan Boltzmann principle. It states that everybody radiates IR radiation proportional to their temperature. A specific object’s temperature can be measured with the MLX90614 Contactless Infrared (IR) Digital Temperature Sensor between −70 °C and 382.2 °C. The sensor communicates with the microcontroller using the I2C protocol and measures the object’s temperature using IR rays without making any physical contact.
3.2.2. Stage 2: X-ray Image
- Scenario I: Normal case
- -
- The patient is considered negative when he has a normal temperature and normal SpO2 reading or a high temperature and normal SpO2 reading. The patient takes the green path “Path (A)” toward the lobby and leaves the clinic from the side door shown in Figure 7. Then, the sterilization process is carried out.
- -
- In the first state of normal temperature and normal SpO2 reading, the patient can leave and go home.
- -
- In the second state of high temperature and normal SpO2 reading, the patient can visit the medical service rooms to check up on the reason for the high temperature.
- Scenario II: Abnormal case
- -
- The patient is considered negative when he has a high temperature and abnormal SpO2 reading. In this case, the probability of being infected with a virus or being a virus carrier is increased. Therefore, an X-ray check becomes a necessary step.
- -
- The patient is exposed to chest X-ray radiation. ResNet152 model is utilized in the COVID-19 detection system. The result of the X-ray image detection is either a “negative case” or a “positive case”.
- -
- In the negative case, the patient takes the yellow path “Path (B)” toward the lobby and leaves the clinic from the side door as shown in Figure 7. Then, the sterilization process is carried out.
- -
- In the positive case, the patient takes the red path “Path (C)” toward the isolation rooms; according to the patient’s case and registration data, the appropriate treatment protocol is selected.
4. The Proposed COVID-19 Detection from an X-ray Image Using Deep Learning
4.1. Dataset Construction
4.2. Preprocessing
4.3. Training Model
4.4. Classification
ResNet Architecture
- Convolution layer
- 2.
- Activation function
- 3.
- Pooling layer
- 4.
- Batch normalization
5. The Proposed Blockchain-Based Pharmaceutical System
- The blockchain network connects the medical kit with physicians and Health Authority. The blockchain network will use several smart contracts which will be applied to the data passed through it, such as:
- Registration Smart Contract;
- Authentication Smart Contract;
- Patient monitoring Smart Contract;
- Consent Management Smart Contract;
- Drug prescription verification.
- 2.
- The medical kit and sensing devices: the medical kit has sensing devices that read the measurements of the patients. First, the kit sends device registration to the Health Authority through the blockchain network to access the login to the decentralized storage systems connected to the Health Authority. If the login fails, the blockchain network sends an emergency alert; otherwise, the registration succeeds. Next, the medical kit sends the updated measurement reports, which include Temperature value, Pulse Rate, and SpO2, to physicians through the blockchain network when they ask for the reports. Finally, the kit can directly store the final measurements report in the decentralized storage systems.
- 3.
- The physicians: first, the physicians will send the registration to access the data stored in the decentralized storage systems in the Health Authority through the blockchain network. If the registration fails, the blockchain network will return an emergency alert; otherwise, the registration succeeds. Next, the physicians can inquire about measurement reports for any patient; then, they obtain permission for requested reports from the blockchain network; then, they can update reports based on patents’ analysis. Finally, the physicians can directly access the decentralized storage systems in the Health Authority to update the patients’ periodical reports.
- 4.
- The Health Authority: all operations are done on it through the blockchain network by the physicians and the medical kit. The Health Authority receives regular registration from physicians and the medical kit; then, it checks whether to accept or deny these registrations. After accepting the registration, it sends the requested medical protocol and diagnosis report. Next, it receives a request to obtain permission for requested information from the physicians. Finally, it calculates and updates the reputation score.
- 5.
- The Decentralized Storage Systems: it is a storage system to store the patients’ data and different cure protocols. It has several storage protocols such as IPFS, STORJ.IO, SWARM, etc. The medical kit can directly send the measurement reports that include Temperature value, Pulse Rate, and SpO2 to the storage system. In addition, the physicians can directly request or update the patients’ periodical reports.
- Log into the website for registration, then input some personal information and the symptoms. This information is used to determine the appropriate treatment protocol for each person. Then, the patient can choose the appropriate date and time to visit the clinic for the examination. All patient data are now stored in the data storage.
- The patient now can visit the clinic. The clinic structure consists of two essential stages, the sensing and measurements stage, and the X-ray stage. The sensing and measurements stage consists of five components: Node-MCU controller, sensing elements (SpO2 and Temperature Sensor), power supply, O-LED display, and webpage. The readings of the sensors’ measurements can decide whether the patient needs to proceed to the X-ray stage or not. All these measurements are stored in the Decentralized Storage Systems in the patient’s file. The physicians can see or update the patient’s file anytime.
- Now, the patient can obtain treatment and cure protocol due to the readings of the sensing elements. The cure protocol is also stored in the patient’s report in the storage system.
- When the patient visits at another time, their report will have all the symptoms they reported before together with the cure protocol he received, and any new symptoms will be stored in the same report.
6. Experimental Results
7. Result Discussion
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Islam, S.; Islam, T.; Islam, M.R. New coronavirus variants are creating more challenges to global healthcare system: A brief report on the current knowledge. Clin. Pathol. 2022, 15, 2632010X221075584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chemali, S.; Mari-Sáez, A.; El Bcheraoui, C.; Weishaar, H. Health care workers’ experiences during the COVID-19 pandemic: A scoping review. Hum. Resour. Health 2022, 20, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. The Impact of COVID-19 on Health and Care Workers: A Closer Look at Deaths. World Health Organization. 2021. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/345300 (accessed on 17 March 2022).
- Salih, K.O.M.; Rashid, T.A.; Radovanovic, D.; Bacanin, N. A comprehensive survey on the Internet of Things with the industrial marketplace. Sensors 2022, 22, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Zhu, L.; Xu, C.; Lu, R. PPDP: An efficient and privacy-preserving disease prediction scheme in cloud-based e-healthcare system. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2018, 79, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.M.; Liu, J.; Bukhari SA, C.; Rauf, H.T. Planning a secure and reliable IoT-enabled FOG-assisted computing infrastructure for healthcare. Clust. Comput. 2021, 25, 2143–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.M.; Hong, C.S.; Afghah, F.; Manogaran, G.; Yu, K.; Hua, Q.; Gao, J. Clouds proportionate medical data stream analytics for internet of things-based healthcare systems. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2021, 26, 973–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namasudra, S. Fast and secure data accessing by using DNA computing for the cloud environment. IEEE Trans. Serv. Comput. 2020, 15, 2289–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namasudra, S.; Deka, G.C.; Johri, P.; Hosseinpour, M.; Gandomi, A.H. The revolution of blockchain: State-of-the-art and research challenges. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2020, 28, 1497–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Moparthi, N.; Namasudra, S.; Shanmuganathan, V.; Hsu, C. Blockchain-based IoT architecture to secure healthcare system using identity-based encryption. Expert Syst. 2020, 39, e12915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Shetty, S.; Tosh, D.; Kamhoua, C.; Kwiat, K.; Njilla, L. Provchain: A Blockchain-Based Data Provenance Architecture in Cloud Environment with Enhanced Privacy and Availability. In Proceedings of the 2017 17th IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Cluster, Cloud and Grid Computing (CCGRID), Madrid, Spain, 14–17 May 2017; pp. 468–477. [Google Scholar]
- Kish, L.J.; Topol, E.J. Unpatients—Why patients should own their medical data. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, N.; Qamar, A.; Asim, M.; Khan, F. Blockchain and Smart Healthcare Security: A Survey. The 6th International Workshop on Cyber Security and Digital Investigation (CSDI). Procedia Comput. Sci. 2020, 175, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Khan, F.A. A broadcast-based key agreement scheme using set reconciliation for wireless body area networks. J. Med. Syst. 2014, 38, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.A.; Gumaei, A.; Derhab, A.; Hussain, A. A novel two-stage deep learning model for efficient network intrusion detection. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 30373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, N.; Khan, F.A. Match the Sound Captcha. In Information Technology-New Generations; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 803–808. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, X.; Zhao, J.; Shetty, S.; Liu, J.; Li, D. Integrating blockchain for data sharing and collaboration in mobile healthcare applications. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 28th Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor, and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC), Montreal, QC, Canada, 8–13 October 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Khalid, U.; Asim, M.; Baker, T.; Hung, P.C.; Tariq, M.A.; Rafferty, L. Adecentralized lightweight blockchain-based authentication mechanism for iot systems. Clust. Comput. 2020, 23, 2067–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linn, L.A.; Koo, M.B. Blockchain for Healthdata and Its Potential Use in Health IT and Healthcare Related Research. In Proceedings of the ONC/NIST Use of Blockchain for Healthcare and Research Workshop, Gaithersburg, MA, USA, 26–27 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hardin, T.; Kotz, D. Blockchain in Health Data Systems: A Survey. In Proceedings of the 2019 Sixth International Conference on Internet of Things: Systems, Management and Security (IOTSMS), Granada, Spain, 22–25 October 2019; pp. 490–497. [Google Scholar]
- Yaqoob, I.; Salah, K.; Jayaraman, R.; Al-Hammadi, Y. Blockchain for healthcare data management: Opportunities, challenges, and future recommendations. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 34, 11475–11490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamoto, S. Bitcoin: A Peer-To-Peer Electronic Cash System. 2008. Available online: https://bitcoin.org/bitcoin.pdf (accessed on 15 June 2020).
- Dinh, T.T.A.; Liu, R.; Zhang, M.; Chen, G.; Ooi, B.C.; Wang, J. Untangling blockchain: A data processing view of block chain systems. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2018, 30, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallivalappil, A.S.; Ahmad, S.S.; Raju, Y.; Kumar, C.K.; Krishnaiah, N. Applications of Ensuring Security and Privacy Using Block Chain with IoT for Health Record. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Advance Computing and Innovative Technologies in Engineering (ICACITE), Greater Noida, India, 28–29 April 2022; pp. 1911–1917. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, S.; He, D.; Li, L.; Kumar, N.; Khan, M.K.; Choo, K.K.R. Applications of Blockchain in Ensuring the Security and Privacy of Electronic Health Record Systems: A Survey. Comput. Secur. 2020, 97, 101966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, W.J.; Catalini, C. Blockchain Technology for Healthcare: Facilitating the Transition to Patient-Driven Interoperability. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2018, 16, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.C.; Pathirana, P.N.; Ding, M.; Seneviratne, A. E-Healthcare System Using Blockchain for Secure EHRs Sharing of Mobile Cloud Based with Machine Learning. Int. J. Sci. Dev. Res. 2020, 5, 66792–66806. [Google Scholar]
- Solomon, D.H.; Rudin, R.S. Digital health technologies: Opportunities and challenges in rheumatology. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2020, 16, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianfrancesco, M.A.; Goldstein, N.D. A narrative review on the validity of electronic health record-based research in epidemiology. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2021, 21, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.; Rubinstein, S.M.; Nead, K.T.; Wojcieszynski, A.P.; Gabriel, P.E.; Warner, J.L. The Evolving Use of Electronic Health Records (EHR) for Research. In Seminars in Radiation Oncology; WB Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2019; Volume 29, pp. 354–361. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, R.W.; Salah, K.; Jayaraman, R.; Yaqoob, I.; Ellahham, S.; Omar, M. The role of blockchain technology in telehealth and telemedicine. Int. J. Med. Inform. 2021, 148, 104399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassab, M.; DeFranco, J.; Malas, T.; Neto VV, G.; Destefanis, G. Blockchain: A panacea for electronic health records? In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/ACM 1st International Workshop on Software Engineering for Healthcare (SEH), 2019, Montreal, QC, Canada, 27 May 2019; pp. 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, H.S.A.; Tan, T.H.; Tan, Y.F.C.; Tan, C.J.M. Blockchain personal health records: Systematic review. J. Med. Internet Res. 2021, 23, e25094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katal, A.; Sethi, V.; Choudhury, T. Potential of Blockchain in Telemedicine. In Telemedicine: The Computer Transformation of Healthcare; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 167–184. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, M.N.; Desyansah, S.F.; Al-Zubaidi, S.; Yusuf, E. An internet of things-based smart homes and healthcare monitoring and management system. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1450, 012079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cernian, A.; Tiganoaia, B.; Sacala, I.; Pavel, A.; Iftemi, A. PatientDataChain: A blockchain-based approach to integrate personal health records. Sensors 2020, 20, 6538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radiopaedia Web Page. Available online: https://radiopaedia.org/ (accessed on 1 August 2022).
- SIRM Web Page. Available online: https://sirm.org/en/ (accessed on 1 August 2022).
- EURORAD Web Page. Available online: https://www.eurorad.org/ (accessed on 1 August 2022).



















| Country | WHO Rank | IHME Rank | WHO COVID-19 Surveillance | Population- Based Estimated HCW Deaths | Triangulation A Indirect Standardization (by Sex and Age) | Triangulation B Meta-Analysis Based on PCR Testing (at 6.2% Infection) | Based on IHME Estimated Overall Deaths | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Deaths | Share of All Deaths (%) | HCW Deaths | HCW Deaths | HCW Deaths (All) | HCW Deaths (Males) | HCW Deaths (Females) | HCW Deaths (at 0.8%) | HCW Deaths (at 1.6%) | HCW Deaths | |||
| United States of America | 1 | 1 | 578,984 | 17.3 | 59 | 39,925 | 37,633 | 21,950 | 15,683 | 16,137 | 32,274 | 62,426 |
| Brazil | 2 | 4 | 430,417 | 12.8 | 684 | 9769 | 8966 | 5430 | 3536 | 7655 | 15,311 | 13,525 |
| India | 3 | 2 | 266,207 | 7.9 | 0 | 1129 | 2053 | 1378 | 675 | 12,089 | 24,178 | 2775 |
| Mexico | 4 | 3 | 219,901 | 6.6 | 3214 | 2717 | 2870 | 1899 | 971 | 1178 | 2356 | 7625 |
| The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland | 5 | 6 | 127,668 | 3.8 | 0 | 8562 | 3177 | 1586 | 1519 | 2206 | 4411 | 14,061 |
| Italy | 6 | 7 | 123,927 | 3.7 | 269 | 3970 | 1462 | 810 | 652 | 2057 | 4114 | 5633 |
| Russian Federation | 7 | 5 | 115,480 | 3.4 | 0 | 4386 | 1532 | 803 | 729 | 2446 | 4892 | 22,546 |
| France | 8 | 14 | 106,666 | 3.2 | 4 | 6708 | 2545 | 1282 | 1263 | 2854 | 5708 | 8344 |
| Germany | 9 | 16 | 86,025 | 2.6 | 0 | 5809 | 2112 | 1056 | 1056 | 1778 | 3556 | 8152 |
| Colombia | 10 | 79,760 | 2.4 | 0 | 1609 | 1506 | 891 | 615 | 1522 | 3043 | ||
| Spain | 11 | 15 | 79,095 | 2.4 | 148 | 2845 | 998 | 503 | 495 | 1778 | 3556 | 4453 |
| Islamic Republic of Iran | 12 | 8 | 76,433 | 2.3 | 0 | 737 | 877 | 639 | 238 | 1355 | 2710 | 1679 |
| Poland | 13 | 11 | 71,609 | 2.1 | 5 | 2013 | 676 | 318 | 358 | 1415 | 2829 | 4213 |
| Argentina | 14 | 69,254 | 2.1 | 534 | 1814 | 1883 | 1209 | 674 | 1608 | 3216 | ||
| Peru | 15 | 12 | 65,316 | 1.9 | 0 | 896 | 877 | 550 | 327 | 929 | 1858 | 2027 |
| South Africa | 16 | 10 | 55,124 | 1.6 | 0 | 966 | 1620 | 905 | 715 | 798 | 1596 | 2812 |
| Ukraine | 17 | 13 | 47,942 | 1.4 | 615 | 1342 | 448 | 229 | 219 | 1067 | 2133 | 3877 |
| Indonesia | 18 | 17 | 47,823 | 1.4 | 0 | 314 | 534 | 321 | 213 | 860 | 1720 | 760 |
| Turkey | 19 | 44,301 | 1.3 | 0 | 803 | 318 | 178 | 140 | 2527 | 5055 | ||
| Czech Republic | 20 | 29,712 | 0.9 | 87 | 1103 | 367 | 177 | 190 | 816 | 1632 | ||
| Romania | 21 | 19 | 29,413 | 0.9 | 12 | 652 | 214 | 100 | 114 | 531 | 1062 | 1943 |
| Egypt | 34 | 9 | 14,206 | 0.4 | 181 | 129 | 177 | 121 | 56 | 121 | 241 | 1544 |
| Japan | 39 | 18 | 11,365 | 0.3 | 0 | 942 | 745 | 389 | 356 | 333 | 666 | 8978 |
| Kazakhstan | 59 | 20 | 4760 | 0.1 | 0 | 119 | 46 | 24 | 22 | 203 | 406 | 2042 |
| Sub-total | 99,259 | 73,636 | 42,748 | 30,888 | 64,263 | 128,523 | 179,415 | |||||
| Model | Metric Parameter | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training Accuracy | Training Loss | Validation Accuracy | Validation Loss | |
| Linear | 95.7% | 13.8% | 94.3% | 16.4% |
| DensNet121 | 88.5% | 30.3% | 87.4% | 30.5% |
| ResNet152 | 97.5% | 8.6% | 95.2% | 14.9% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
AlGhamdi, R.; Alassafi, M.O.; Alshdadi, A.A.; Dessouky, M.M.; Ramdan, R.A.; Aboshosha, B.W. Developing Trusted IoT Healthcare Information-Based AI and Blockchain. Processes 2023, 11, 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11010034
AlGhamdi R, Alassafi MO, Alshdadi AA, Dessouky MM, Ramdan RA, Aboshosha BW. Developing Trusted IoT Healthcare Information-Based AI and Blockchain. Processes. 2023; 11(1):34. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11010034
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlGhamdi, Rayed, Madini O. Alassafi, Abdulrahman A. Alshdadi, Mohamed M. Dessouky, Rabie A. Ramdan, and Bassam W. Aboshosha. 2023. "Developing Trusted IoT Healthcare Information-Based AI and Blockchain" Processes 11, no. 1: 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11010034
APA StyleAlGhamdi, R., Alassafi, M. O., Alshdadi, A. A., Dessouky, M. M., Ramdan, R. A., & Aboshosha, B. W. (2023). Developing Trusted IoT Healthcare Information-Based AI and Blockchain. Processes, 11(1), 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11010034








