The Influence of Metal–Support Interactions on the Performance of Ni-MoS2/Al2O3 Catalysts for Dibenzothiophene Hydrodesulfurization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Sulfided Supported HDS Catalysts
2.2.1. Preparation of Catalysts and Supports with Different Annealing Temperatures
2.2.2. Catalyst Preparation from Different Alumina Precursors
2.3. Characterizations of Sulfided NiMo Catalysts
2.4. Catalytic Performance of Sulfided NiMo Catalysts
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Effect of Annealing Temperatures on Catalyst Structure
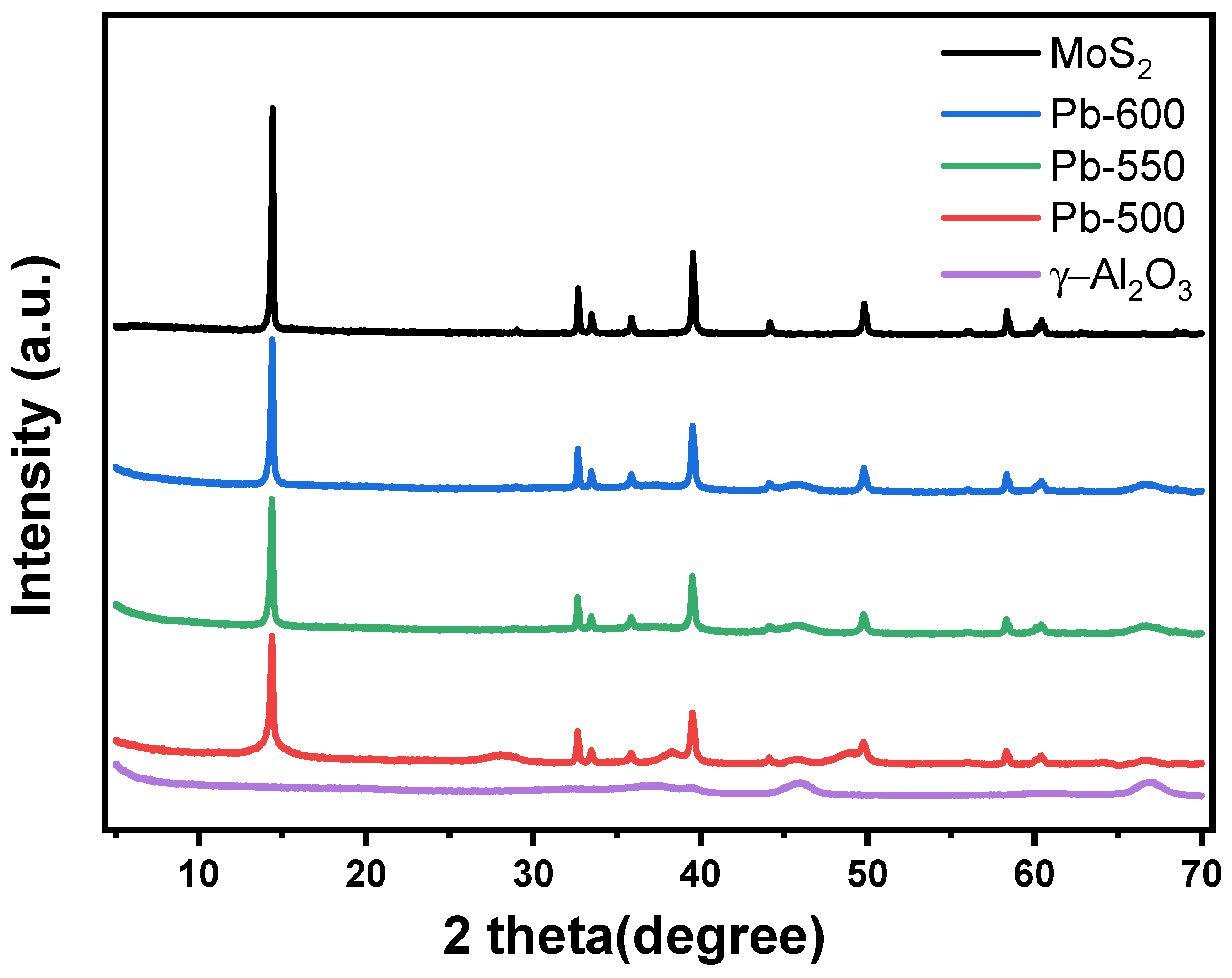
3.1.1. XRD Analysis
3.1.2. N2 Adsorption–Desorption
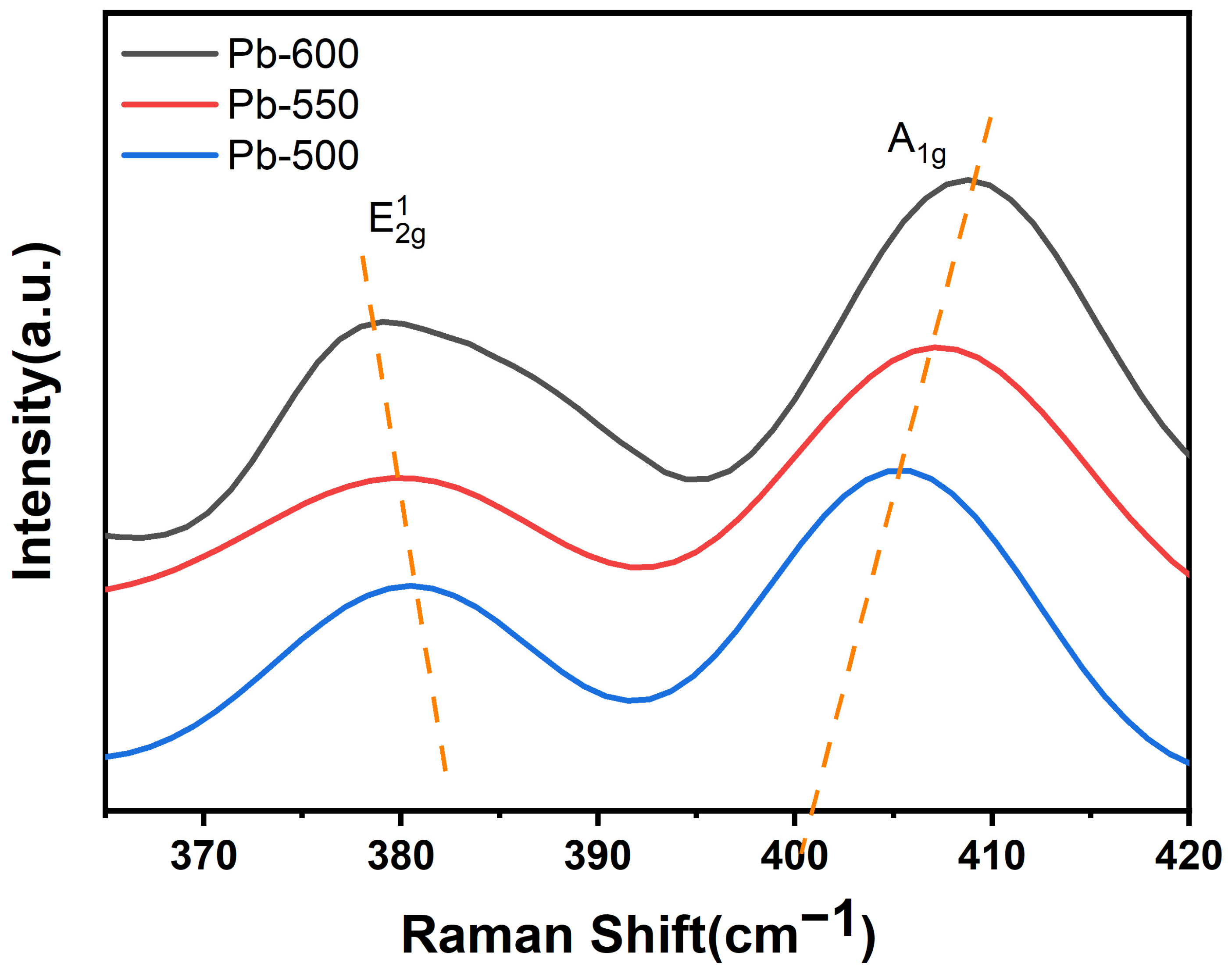
3.1.3. Raman Spectra
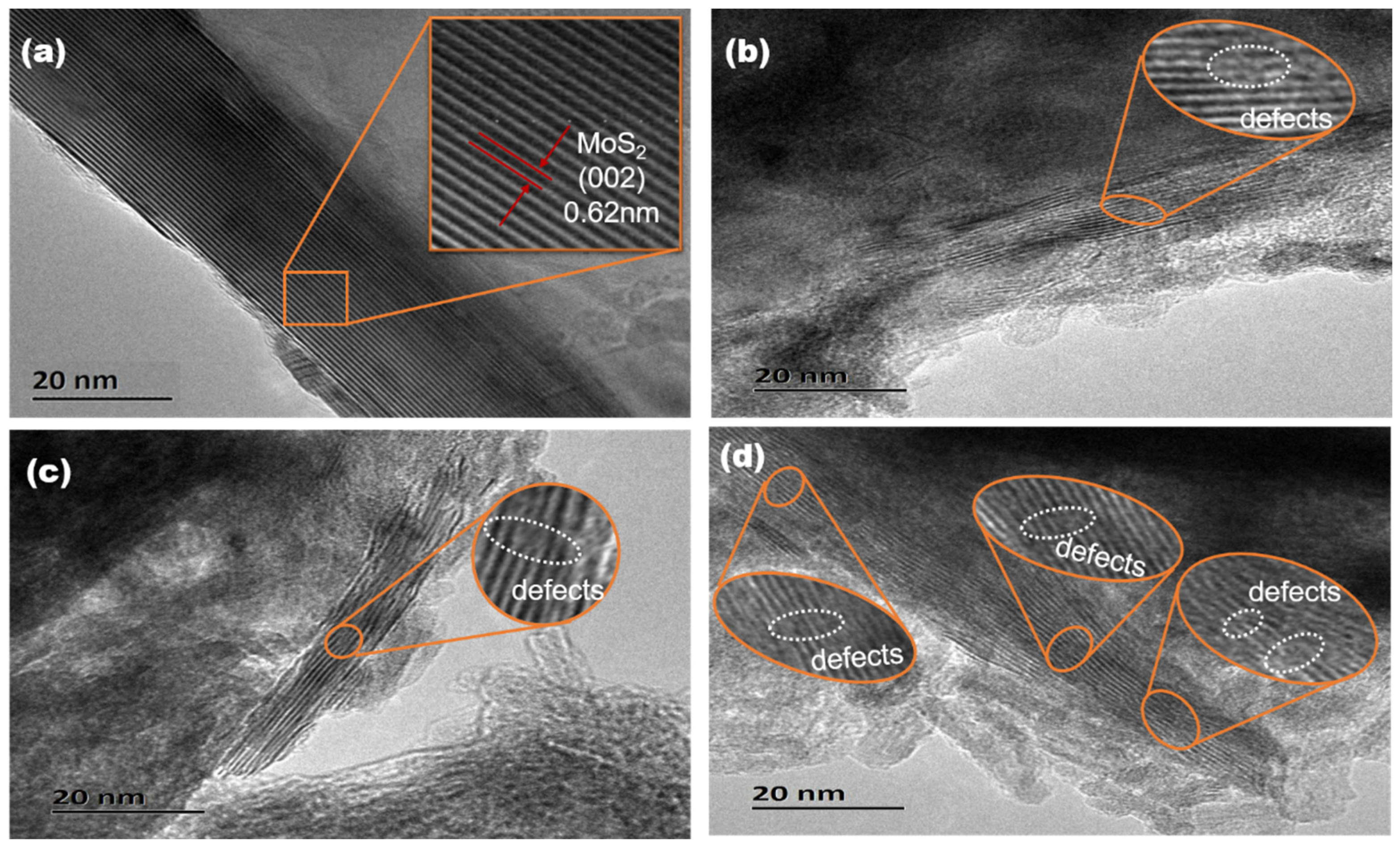
3.1.4. HRTEM Analysis
3.1.5. XPS Analysis
3.2. Effect of Alumina Precursors on Catalyst Structure
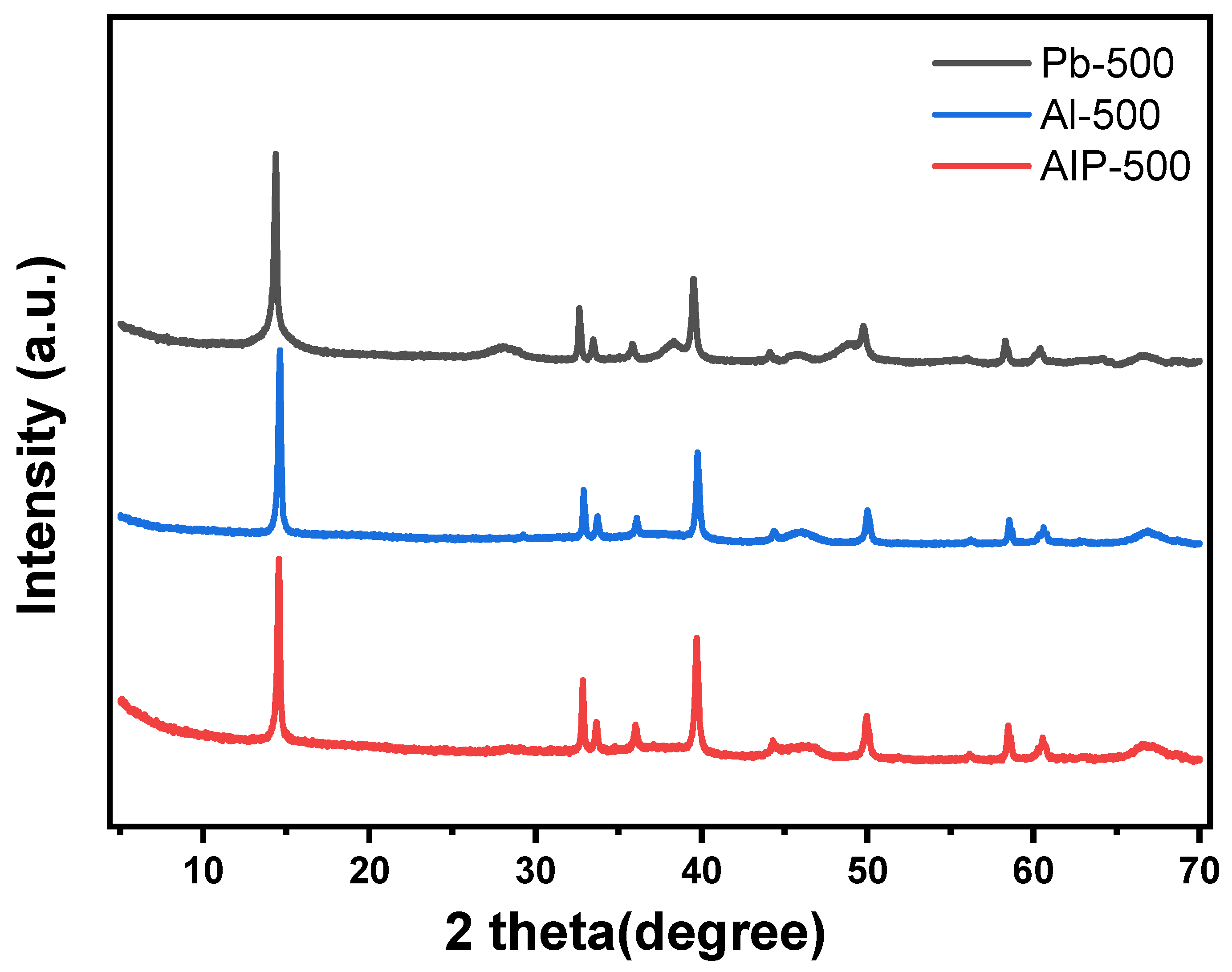
3.2.1. XRD Analysis
3.2.2. Raman Spectra
3.2.3. XPS Analysis
3.3. Activity Evaluation Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, D.; Li, J.; Ma, H.; Yang, C.; Pan, Z.; Qu, W.; Tian, Z. Layer-structure adjustable MoS2 catalysts for the slurry-phase hydrogenation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. J. Energy Chem. 2021, 63, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Han, W.; Long, X.; Nie, H.; Li, D. Preparation of hydrodesulfurization catalysts using MoS3 nanoparticles as a precursor. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 224, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodin, A.; Christoffersen, A.N.; Elkjær, C.F.; Brorson, M.; Kibsgaard, J.; Helveg, S.; Chorkendorff, I. Engineering Ni-Mo-S Nanoparticles for Hydrodesulfurization. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 3454–3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanda, Y.; Kawanishi, K.; Tsujino, T.; Al-Otaibi, A.M.; Uemichi, Y. Catalytic Activities of Noble Metal Phosphides for Hydrogenation and Hydrodesulfurization Reactions. Catalysts 2018, 8, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsalme, A.; Alzaqri, N.; Alsaleh, A.; Siddiqui, M.R.H.; Alotaibi, A.; Kozhevnikova, E.F.; Kozhevnikov, I.V. Efficient Ni–Mo hydrodesulfurization catalyst prepared through Keggin polyoxometalate. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 182, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, A.; Li, T.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, B.; Zhou, X.; Jiang, G.; Liu, J.; Wei, Y.; Pan, H. Synthesis of hierarchically porous L-KIT-6 silica–alumina material and the super catalytic performances for hydrodesulfurization of benzothiophene. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 165, 763–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zepeda, T.A.; de León, J.N.D.; Alonso, G.; Infantes-Molina, A.; Galindo-Ortega, Y.; Huirache-Acuña, R.; Fuentes, S. Hydrodesulfurization activity of Ni-containing unsupported Ga(x)WS2 catalysts. Catal. Commun. 2019, 130, 105760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, L.; Li, G.; Zhang, F.; Chen, L.; Li, X.; Huang, X. Size-dependent activity of unsupported Co–Mo sulfide catalysts for the hydrodesulfurization of dibenzothiophene. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2016, 512, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berhault, G.; Perez De la Rosa, M.; Mehta, A.; Yácaman, M.J.; Chianelli, R.R. The single-layered morphology of supported MoS2-based catalysts—The role of the cobalt promoter and its effects in the hydrodesulfurization of dibenzothiophene. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2008, 345, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauritsen, J.V.; Helveg, S.; Lægsgaard, E.; Stensgaard, I.; Clausen, B.; Topsøe, H.; Besenbacher, F. Atomic-Scale Structure of Co–Mo–S Nanoclusters in Hydrotreating Catalysts. J. Catal. 2001, 197, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besenbacher, F.; Brorson, M.; Clausen, B.; Helveg, S.; Hinnemann, B.; Kibsgaard, J.; Lauritsen, J.; Moses, P.; Nørskov, J.; Topsøe, H. Recent STM, DFT and HAADF-STEM studies of sulfide-based hydrotreating catalysts: Insight into mechanistic, structural and particle size effects. Catal. Today 2008, 130, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topsøe, H.; Clausen, B.S.; Topsøe, N.Y.; Pedersen, E. Recent Basic Research in Hydrodesulfurization Catalysis. Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam. 1986, 25, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Galarza, A.; Gutiérrez-Alejandre, A.; Ramírez, J. Analysis of the promotion of CoMoP/Al2O3 HDS catalysts prepared from a reduced H–P–Mo heteropolyacid Co salt. J. Catal. 2011, 280, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, Y.; Ochiai, K.; Kawano, M.; Kubota, T. Evaluation of the maximum potential activity of Co–Mo/Al2O3 catalysts for hydrodesulfurization. J. Catal. 2004, 222, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Han, W.; Hu, D.; Sun, S.; Hu, A.; Wang, Z.; Jia, Y.; Zhao, X.; Yang, Q. Effects of Ni–Al2O3 interaction on NiMo/Al2O3 hydrodesulfurization catalysts. J. Catal. 2020, 387, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez Garcia, E.; Chen, J.; Oliviero, E.; Oliviero, L.; Maugé, F. New insight into the support effect on HDS catalysts: Evidence for the role of Mo-support interaction on the MoS2 slab morphology. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 260, 117975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, Y.; Ghosh, P.; Daage, M.; Delgass, W. Support effects in HDS catalysts: DFT analysis of thiolysis and hydrolysis energies of metal–support linkages. J. Catal. 2008, 257, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiq, I.; Shafique, S.; Akhter, P.; Yang, W.; Hussain, M. Recent developments in alumina supported hydrodesulfurization catalysts for the production of sulfur-free refinery products: A technical review. Catal. Rev. 2020, 64, 1–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bara, C.; Plais, L.; Larmier, K.; Devers, E.; Digne, M.; Lamic-Humblot, A.-F.; Pirngruber, G.D.; Carrier, X. Aqueous-Phase Preparation of Model HDS Catalysts on Planar Alumina Substrates: Support Effect on Mo Adsorption and Sulfidation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 15915–15928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Xia, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Bai, L.; Xu, J.; Yang, C.-A.; Zheng, S.; Yang, T.; Tang, K.; et al. Influence of the alumina crystal phase on the performance of CoMo/Al2O3 catalysts for the selective hydrodesulfurization of fluid catalytic cracking naphtha. Fuel 2021, 289, 119843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, Z.; Zheng, P.; Chen, Z.; Duan, A.; Xu, C.; Jiao, J.; Zhang, H.; Cao, Z.; Ge, B. Synthesis of NiMo catalysts supported on mesoporous Al2O3 with different crystal forms and superior catalytic performance for the hydrodesulfurization of dibenzothiophene and 4,6-dimethyldibenzothiophene. J. Catal. 2016, 344, 680–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trejo, F.; Rana, M.; Ancheyta, J. CoMo/MgO–Al2O3 supported catalysts: An alternative approach to prepare HDS catalysts. Catal. Today 2008, 130, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zepeda, T.A.; Pawelec, B.; Obeso-Estrella, R.; Díaz de León, J.N.; Fuentes, S.; Alonso-Núñez, G.; Fierro, J.L.G. Competitive HDS and HDN reactions over NiMoS/HMS-Al catalysts: Diminishing of the inhibition of HDS reaction by support modification with P. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 180, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dalama, K.; Stanislaus, A. A comparative study of the influence of chelating agents on the hydrodesulfurization (HDS) activity of alumina and silica-alumina-supported CoMo catalysts. Energy Fuels 2006, 20, 1777–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsyganok, A.I.; Inaba, M.; Tsunoda, T.; Hamakawa, S.; Suzuki, K.; Hayakawa, T. Dry reforming of methane over supported noble metals: A novel approach to preparing catalysts. Catal. Commun. 2003, 4, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, T.; Liu, D.; Liu, B.; Lu, Y.; Chai, Y.; Liu, C. Study of the Promotion Effect of Citric Acid on the Active NiMoS Phase in NiMo/Al2O3 Catalysts. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 17195–17206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-L.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, Z.-T.; Li, J.-M.; Duan, A.-J.; Xu, C.-M.; Gao, D.-W.; Cao, Z.-K.; Zheng, P.; Fan, J.-Y. Effect of synthesis temperature on structure-activity-relationship over NiMo/γ-Al2O3 catalysts for the hydrodesulfurization of DBT and 4,6-DMDBT. Fuel Process. Technol. 2017, 161, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, G.M.; Srinivas, B.; Rana, M.; Kumar, M.; Maity, S. Mixed oxide supported hydrodesulfurization catalysts—A review. Catal. Today 2003, 86, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeina, K.A.; Kazakov, M.O.; Danilova, I.G.; Kovalskaya, A.A.; Stolyarova, E.A.; Dik, P.P.; Gerasimov, E.Y.; Prosvirin, I.P.; Chesalov, Y.A.; Klimov, O.V.; et al. The influence of B and P in the impregnating solution on the properties of NiMo/γ-δ-Al2O3 catalysts for VGO hydrotreating. Catal. Today 2019, 329, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, X.; Yan, Z. Facile route to prepare bimodal mesoporous γ-Al2O3 as support for highly active CoMo-based hydrodesulfurization catalyst. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2012, 121–122, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogica-Betancourt, J.C.; López-Benítez, A.; Montiel-López, J.R.; Massin, L.; Aouine, M.; Vrinat, M.; Berhault, G.; Guevara-Lara, A. Interaction effects of nickel polyoxotungstate with the Al2O3–MgO support for application in dibenzothiophene hydrodesulfurization. J. Catal. 2014, 313, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishan, G.; Van Veen, J.; Niemantsverdriet, J. Realistic surface science models of hydrodesulfurization catalysts on planar thin-film supports: The role of chelating agents in the preparation of CoW/SiO2 catalysts. Top. Catal. 2004, 29, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Wang, Y.; Lu, J.; Lu, H.; He, S.; Song, D.; Luo, Y.; Liu, J. Study of the Metal–Support Interaction and Electronic Effect Induced by Calcination Temperature Regulation and Their Effect on the Catalytic Performance of Glycerol Steam Reforming for Hydrogen Production. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Ding, G.; Shang, Y.; Lv, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, E.; Li, Z.; Ma, X.; Qin, S.; Sun, Q. Effects of MoO3 loading and calcination temperature on the activity of the sulphur-resistant methanation catalyst MoO3/γ-Al2O3. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2012, 431–432, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Ren, Y.; Yue, B.; Tsang, S.C.E.; He, H. Tuning Metal–Support Interactions on Ni/Al2O3 Catalysts to Improve Catalytic Activity and Stability for Dry Reforming of Methane. Processes 2021, 9, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yin, C.; Liu, B.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Chai, Y.; Liu, C. Effect of calcination temperature of unsupported NiMo catalysts on the hydrodesulfurization of dibenzothiophene. Energy Fuels 2014, 28, 2429–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Fan, Q.; Yang, Z.; Tang, S.; Chen, J.; Wu, Y. A novel pre-sulfided hydrotreating catalyst derived from thiomolybdate intercalated NiAl LDHs. Mol. Catal. 2019, 468, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abubakar, U.C.; Alhooshani, K.R.; Adamu, S.; Al Thagfi, J.; Saleh, T.A. The effect of calcination temperature on the activity of hydrodesulfurization catalysts supported on mesoporous activated carbon. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 211, 1567–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujikawa, T. Development of new CoMo HDS catalyst for ultra-low sulfur diesel fuel production. J. Jpn. Pet. Inst. 2007, 50, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergwerff, J.A.; Visser, T.; Leliveld, G.; Rossenaar, B.D.; de Jong, K.P.; Weckhuysen, B.M. Envisaging the physicochemical processes during the preparation of supported catalysts: Raman microscopy on the impregnation of Mo onto Al2O3 extrudates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 14548–14556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolfolk, L.G.; Geantet, C.; Massin, L.; Laurenti, D.; Reyes, J.A.D.L. Solvent effect over the promoter addition for a supported NiWS hydrotreating catalyst. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 201, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, Y.; Hioka, K.; Arakawa, K.; Fujikawa, T.; Ebihara, T.; Kubota, T. Effect of sulfidation atmosphere on the hydrodesulfurization activity of SiO2-supported Co–Mo sulfide catalysts: Local structure and intrinsic activity of the active sites. J. Catal. 2009, 268, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puello-Polo, E.; Gutiérrez-Alejandre, A.; González, G.; Brito, J.L. Relationship Between Sulfidation and HDS Catalytic Activity of Activated Carbon Supported Mo, Fe–Mo, Co–Mo and Ni–Mo Carbides. Catal. Lett. 2010, 135, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, X.; Liu, T.; Jiang, Z.; Li, C. Optimizing both the CoMo/Al2O3 catalyst and the technology for selectivity enhancement in the hydrodesulfurization of FCC gasoline. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2019, 575, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, O.Y.; Singh, S.; Schachtl, E.; Kim, J.; Kondratieva, E.; Hein, J.; Lercher, J.A. Effects of the Support on the Performance and Promotion of (Ni)MoS2 Catalysts for Simultaneous Hydrodenitrogenation and Hydrodesulfurization. ACS Catal. 2014, 4, 1487–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Labruyere, V.; Maugé, F.; Quoineaud, A.-A.; Hugon, A.; Oliviero, L. IR Spectroscopic Evidence for MoS2 Morphology Change with Sulfidation Temperature on MoS2/Al2O3 Catalyst. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 30039–30044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Duan, A.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Z.; Hong, E.; Li, J.; Wang, H. Synthesis of NiMo catalysts supported on mesoporous Al-SBA-15 with different morphologies and their catalytic performance of DBT HDS. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 165, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Xu, H.; Zhang, D.; Chen, S. Synthesis of bilayer MoS2 nanosheets by a facile hydrothermal method and their methyl orange adsorption capacity. Mater. Res. Bull. 2014, 55, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.D.; Ren, L.; Qi, X.; Yang, L.W.; Hao, G.L.; Li, J.; Wei, X.L.; Zhong, J.X. Preparation, characterization and photoelectrochemical property of ultrathin MoS2 nanosheets via hydrothermal intercalation and exfoliation route. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 571, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, X.; Mei, L.; Ma, D.; Liao, Y.; Zu, Y.; Xu, P.; Yin, W.; Gu, Z. A two-step gas/liquid strategy for the production of N-doped defect-rich transition metal dichalcogenide nanosheets and their antibacterial applications. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 8415–8424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendhran, N.; Palanisamy, S.; Periyasamy, P.; Venkatachalam, R. Enhancing of the tribological characteristics of the lubricant oils using Ni-promoted MoS2 nanosheets as nano-additives. Tribol. Int. 2018, 118, 314–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backes, C.; Berner, N.C.; Chen, X.; Lafargue, P.; LaPlace, P.; Freeley, M.; Duesberg, G.S.; Coleman, J.N.; McDonald, A.R. Functionalization of liquid-exfoliated two-dimensional 2H-MoS2. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 2638–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganiyu, S.A.; Alhooshani, K.; Ali, S.A. Single-pot synthesis of Ti-SBA-15-NiMo hydrodesulfurization catalysts: Role of calcination temperature on dispersion and activity. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 203, 428–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Yuan, P.; Fan, Y.; Shi, G.; Liu, H.; Bai, D.; Bao, X. Preparation of supported hydrodesulfurization catalysts with enhanced performance using Mo-based inorganic–organic hybrid nanocrystals as a superior precursor. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 25340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Nie, H.; Long, X.; Li, M.; Yang, Q.; Li, D. A study on the origin of the active sites of HDN catalysts using alumina-supported MoS3 nanoparticles as a precursor. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 3497–3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Bao, X.; Wang, H.; Chen, C.; Shi, G. A surfactant-assisted hydrothermal deposition method for preparing highly dispersed W/γ-Al2O3 hydrodenitrogenation catalyst. J. Catal. 2007, 245, 477–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.-R.; Chan, M.K.Y.; Sun, Y. Edge-terminated molybdenum disulfide with a 9.4-Å interlayer spacing for electrochemical hydrogen production. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Q.; Yap, C.C.R.; Tay, B.K.; Edwin, T.H.T.; Olivier, A.; Baillargeat, D. From Bulk to Monolayer MoS2: Evolution of Raman Scattering. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 1385–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gołasa, K.; Grzeszczyk, M.; Bożek, R.; Leszczyński, P.; Wysmołek, A.; Potemski, M.; Babiński, A. Resonant Raman scattering in MoS2—From bulk to monolayer. Solid State Commun. 2014, 197, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Tang, C.; Zhou, P.; Liu, Z.; Xu, Y.; Wang, D.; Fang, B. Enhanced hydrogen evolution catalysis from osmotically swollen ammoniated MoS2. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 13050–13056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, S.K.; Xiao, B.; Pradhan, A.K. Energy band alignment of high-k oxide heterostructures at MoS2/Al2O3 and MoS2/ZrO2 interfaces. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 120, 125305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Yan, H.; Brus, L.E.; Heinz, T.F.; Hone, J.; Ryu, S. Anomalous lattice vibrations of single-and few-layer MoS2. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 2695–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, J.; Chai, J.; Lu, X.; Wong, L.M.; Wong, T.I.; Pan, J.; Xiong, Q.; Chi, D.; Wang, S. Growth of wafer-scale MoS2 monolayer by magnetron sputtering. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 2497–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Cui, K.; Shen, Q.; Li, P.; Qu, X.; Jiao, L. Molecular Engineering on MoS2 Enables Large Interlayers and Unlocked Basal Planes for High-Performance Aqueous Zn-Ion Storage. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 20286–20293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, J.; Yang, L.; Zheng, J.; Yi, X.; Fang, W. A NiMoS flower-like structure with self-assembled nanosheets as high-performance hydrodesulfurization catalysts. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 3823–3833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; An, C.; Yuan, J. Synthetic Fabrication of Nanoscale MoS2-Based Transition Metal Sulfides. Materials 2010, 3, 401–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Xu, G. Peak overlaps and corresponding solutions in the X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic study of hydrodesulfurization catalysts. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 3413–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Oliviero, L.; Portier, X.; Maugé, F. On the morphology of MoS2slabs on MoS2/Al2O3 catalysts: The influence of Mo loading. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 81038–81044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Jin, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Xiong, G.; Liang, C. Preparation of unsupported Ni–Mo–S catalysts for hydrodesulfurization of dibenzothiophene by thermal decomposition of tetramethylammonium thiomolybdates. Catal. Today 2011, 175, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumbreras, J.A.; Huirache-Acuña, R.; Rivera-Muñoz, E.M.; Berhault, G.; Alonso-Núñez, G. Unsupported Ni/Mo(W)S2 Catalysts from Hexamethylenediammonium Thiometallates Precursors: In Situ Activation During the HDS of DBT. Catal. Lett. 2009, 134, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoosuk, B.; Kim, J.H.; Song, C.; Ngamcharussrivichai, C.; Prasassarakich, P. Highly active MoS2, CoMoS2 and NiMoS2 unsupported catalysts prepared by hydrothermal synthesis for hydrodesulfurization of 4,6-dimethyldibenzothiophene. Catal. Today 2008, 130, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




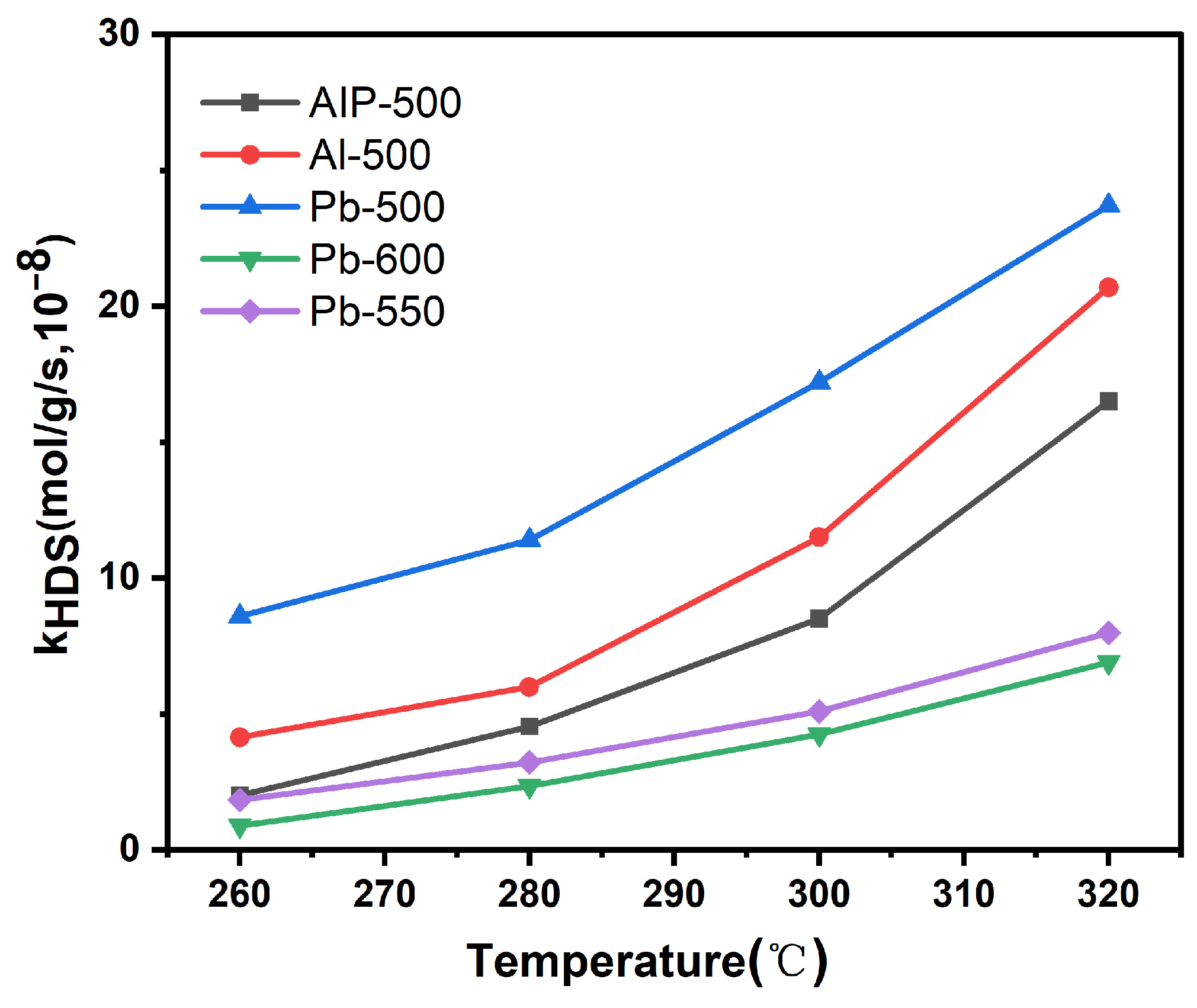
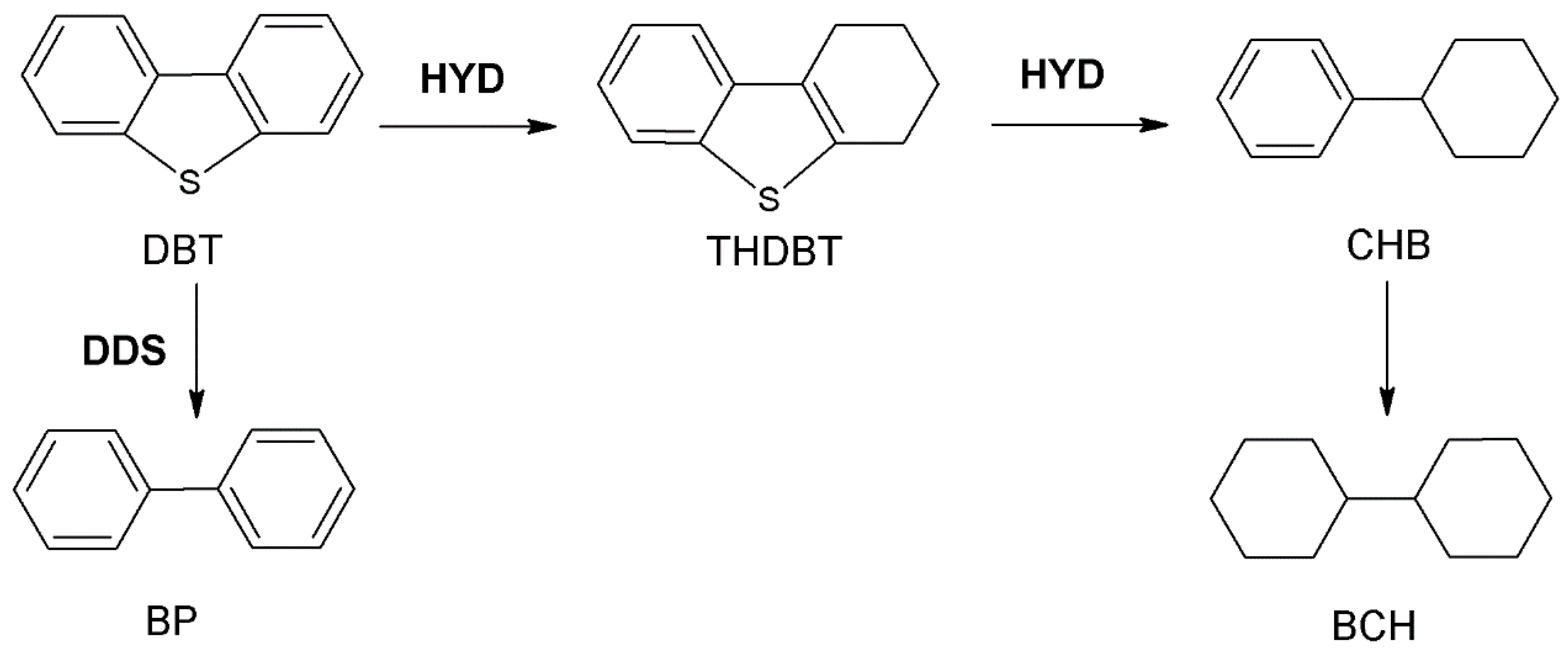
| Samples | XRF Analysis Results | Textual Properties | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MoO3, wt% | NiO, wt% | Sg a, m2·g−1 | Vp b, cm3·g−1 | Dp c, nm | |
| Sup-500 | -- | -- | 222 | 0.47 | 7.4 |
| Sup-550 | -- | -- | 243 | 0.46 | 7.6 |
| Sup-600 | -- | -- | 172 | 0.48 | 9.2 |
| Pb-500 | 14.6 | 6.3 | 218 | 0.43 | 6.4 |
| Pb-550 | 14.7 | 6.3 | 184 | 0.45 | 6.6 |
| Pb-600 | 14.6 | 6.3 | 164 | 0.46 | 8.9 |
| Al-500 | 14.6 | 6.2 | 173 | 0.48 | 9.0 |
| AIP-500 | 14.7 | 6.2 | 183 | 0.47 | 9.3 |
| Catalysts | Lateral Dimension (nm) | Average Number of Layers |
|---|---|---|
| Commercial MoS2 | 153–171 | 33.2 |
| Pb-500 | 43–51 | 7.6 |
| Pb-550 | 50–61 | 8.1 |
| Pb-600 | 60–69 | 8.4 |
| Catalysts | Ni/Al, % | Mo/Al, % | S/Mo, % | Mosul, % | NiNiMoS/Nitotal, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb-500 | 5.061 | 10.570 | 1.823 | 92.8 | 31.6 |
| Pb-550 | 4.710 | 10.937 | 1.789 | 93.2 | 10.9 |
| Pb-600 | 2.183 | 11.846 | 1.807 | 92.0 | 2.58 |
| Al-500 | 4.937 | 10.781 | 1.935 | 92.6 | 26.3 |
| AIP-500 | 4.824 | 10.899 | 1.914 | 91.6 | 20.3 |
| Catalysts | Conversion a,% | THDBT, % | BP, % | CHB, % | BCH, % | SHYD, % | SDDS, % | SHYD/SDDS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb-500 | 16.26 | 3.67 | 67.11 | 26.86 | 2.36 | 32.89 | 67.11 | 0.49 |
| Pb-550 | 15.79 | 7.24 | 70.92 | 20.91 | 0.93 | 29.08 | 70.92 | 0.41 |
| Pb-600 | 14.88 | 8.61 | 71.94 | 18.58 | 0.87 | 28.06 | 71.94 | 0.39 |
| AIP-500 | 14.46 | 4.03 | 68.43 | 27.31 | 0.23 | 31.57 | 68.43 | 0.46 |
| Al-500 | 15.21 | 4.16 | 68.03 | 26.52 | 1.29 | 31.97 | 68.03 | 0.47 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, C.; Dai, Q.; Hu, A.; Yuan, H.; Yang, Q. The Influence of Metal–Support Interactions on the Performance of Ni-MoS2/Al2O3 Catalysts for Dibenzothiophene Hydrodesulfurization. Processes 2023, 11, 3181. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11113181
Yang C, Dai Q, Hu A, Yuan H, Yang Q. The Influence of Metal–Support Interactions on the Performance of Ni-MoS2/Al2O3 Catalysts for Dibenzothiophene Hydrodesulfurization. Processes. 2023; 11(11):3181. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11113181
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Chuangchuang, Qiaoling Dai, Anpeng Hu, Hui Yuan, and Qinghe Yang. 2023. "The Influence of Metal–Support Interactions on the Performance of Ni-MoS2/Al2O3 Catalysts for Dibenzothiophene Hydrodesulfurization" Processes 11, no. 11: 3181. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11113181
APA StyleYang, C., Dai, Q., Hu, A., Yuan, H., & Yang, Q. (2023). The Influence of Metal–Support Interactions on the Performance of Ni-MoS2/Al2O3 Catalysts for Dibenzothiophene Hydrodesulfurization. Processes, 11(11), 3181. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11113181






