A Low-Cost Drive and Detection Scheme for Electrowetting Display
Abstract
1. Introduction
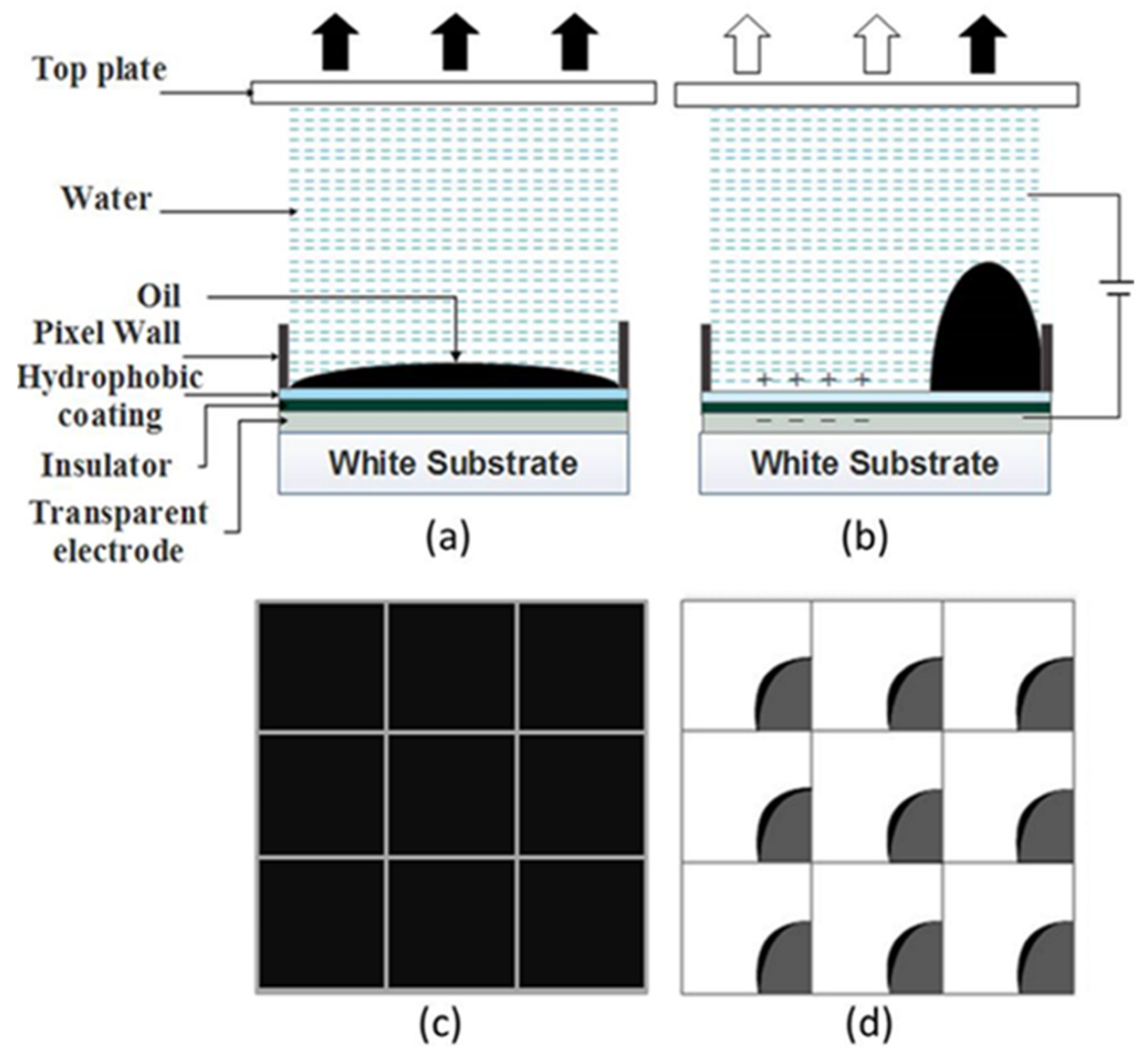
2. Electrowetting Display Structure and Display Principle
3. Proposed Drive and Detection Scheme for EWD
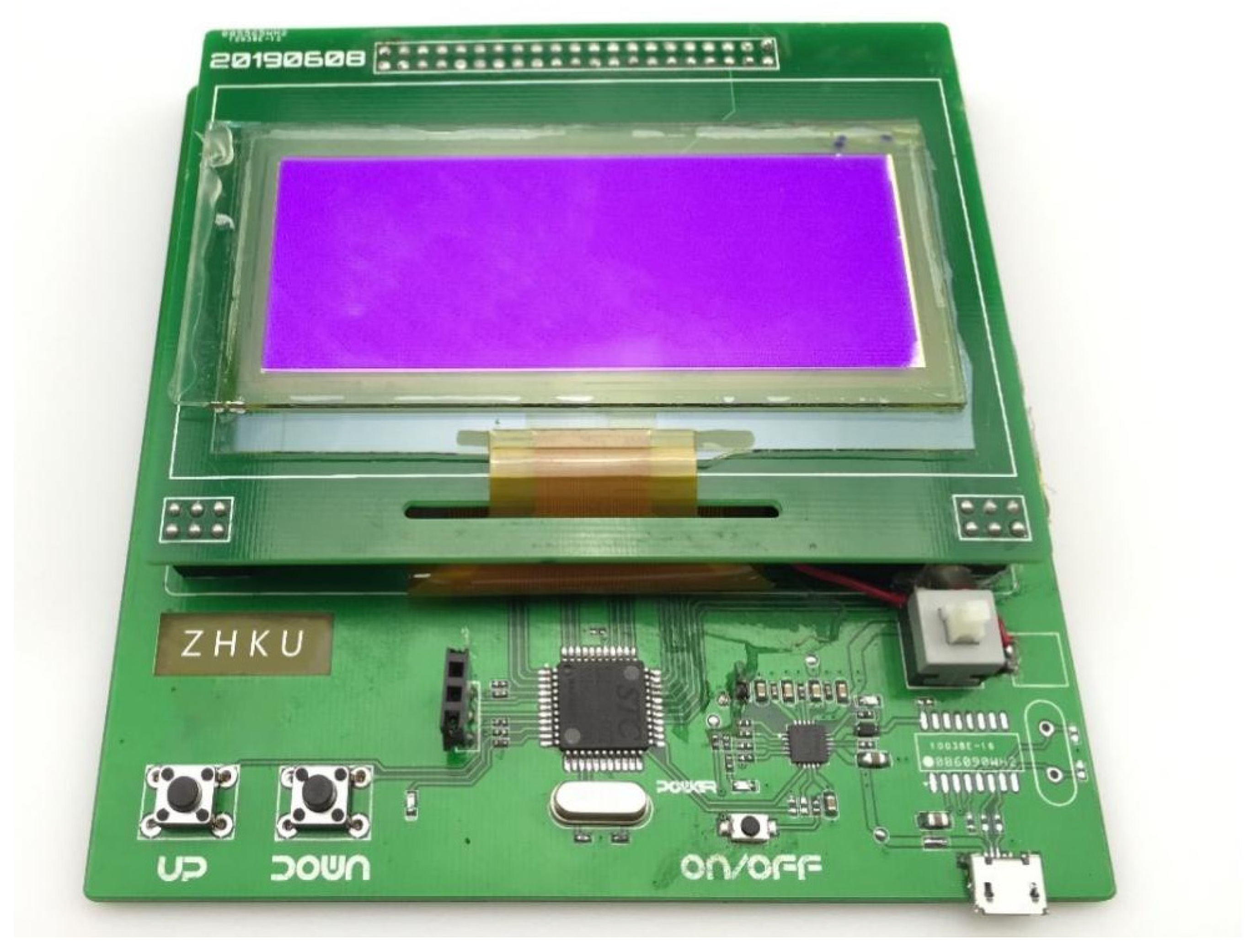
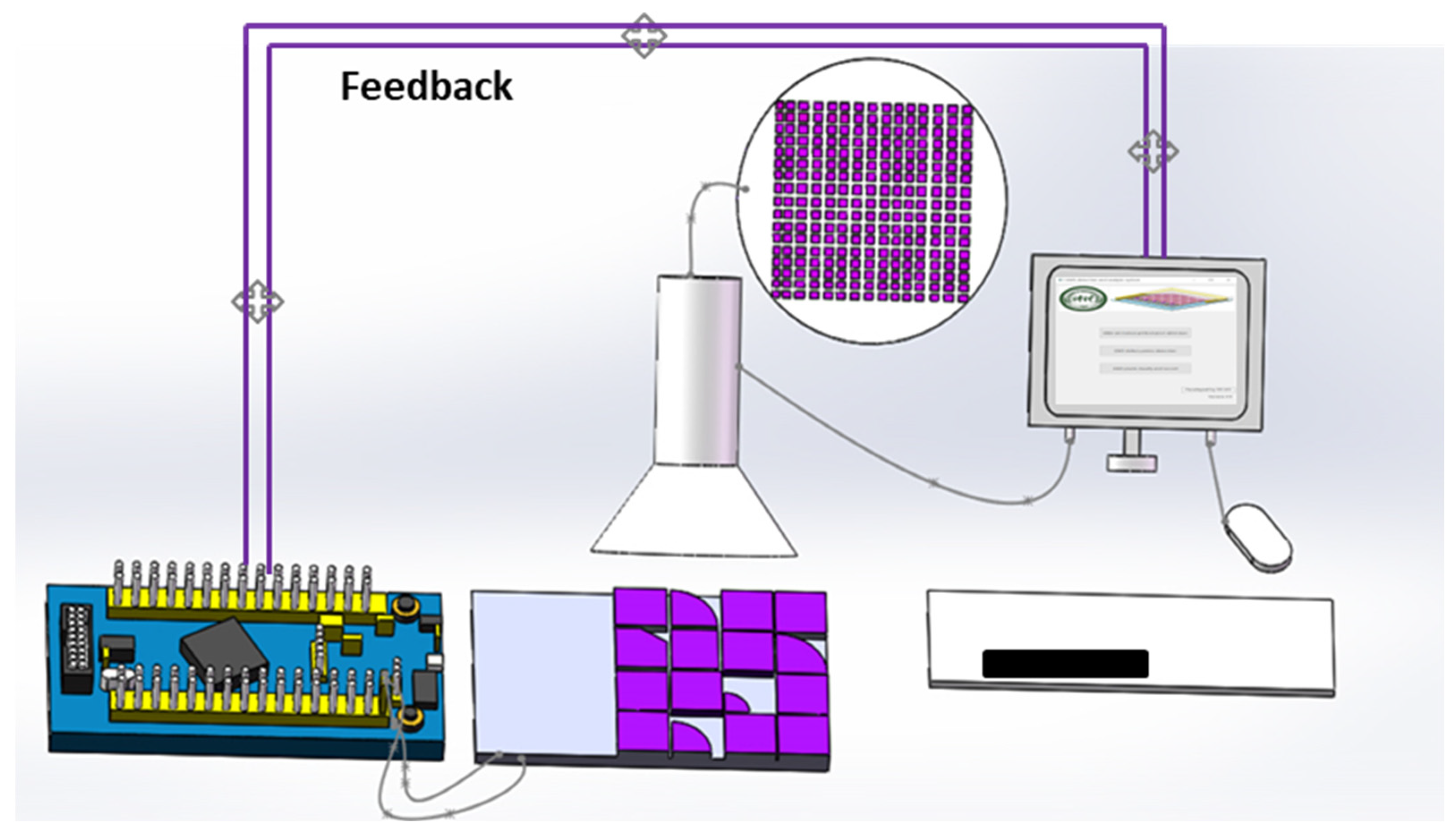
3.1. EWD Device Fabrication
3.2. Machine Vision-Based EWD Detection System
- Use the first-order partial derivative of the Gaussian function to calculate the gradient and detect the local maximum of the gradient modulus;
- Use a low threshold to obtain the weak edge of the EWD defect image and use a high threshold to obtain the strong edge of the EWD defect image; obviously, the weak edge contains a strong edge at this time;
- Take the connected components in the weak edge that are associated with the strong edge as the output edge.
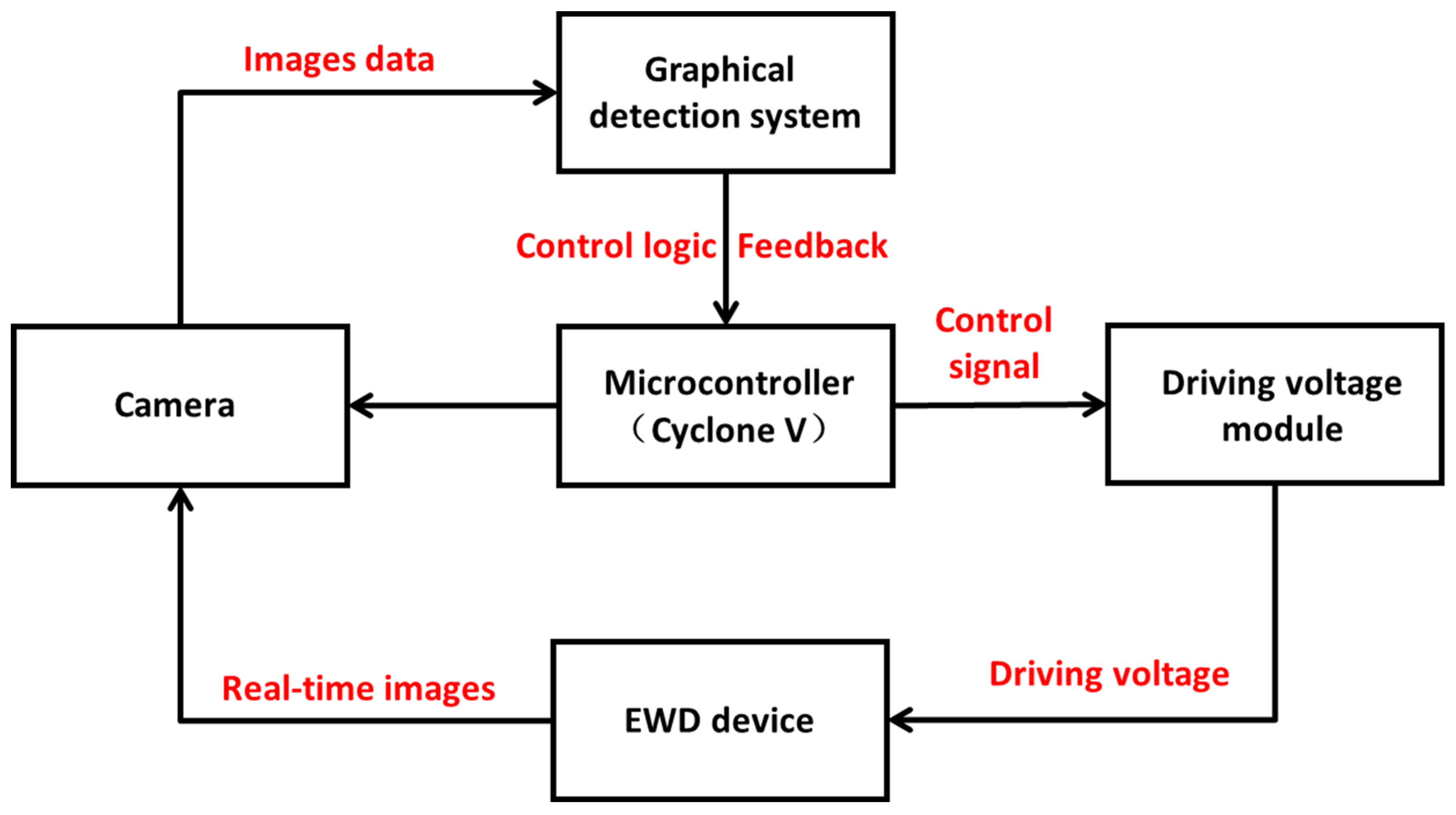
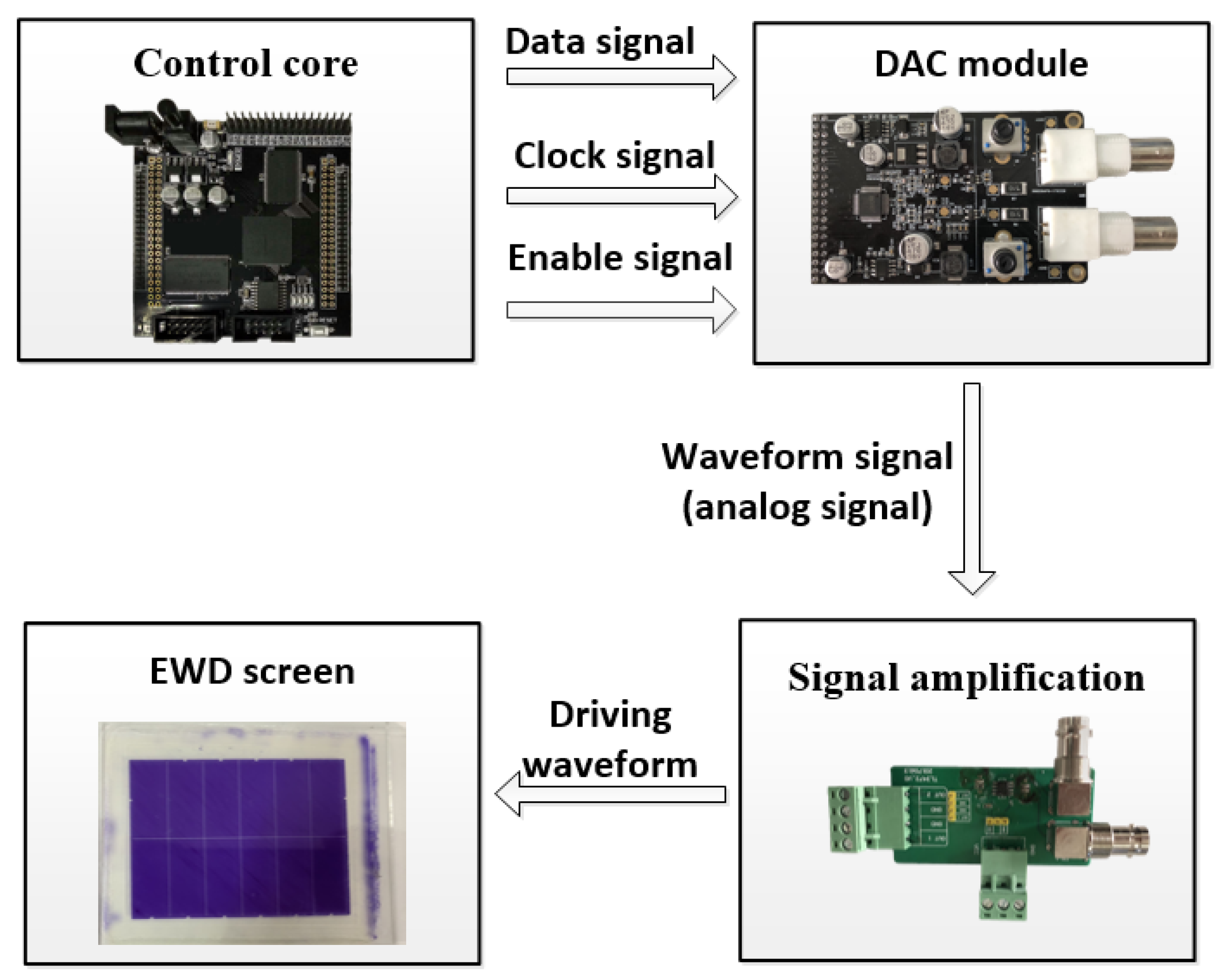
3.3. Driving Control System
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. The Output Verification of Drive Control System
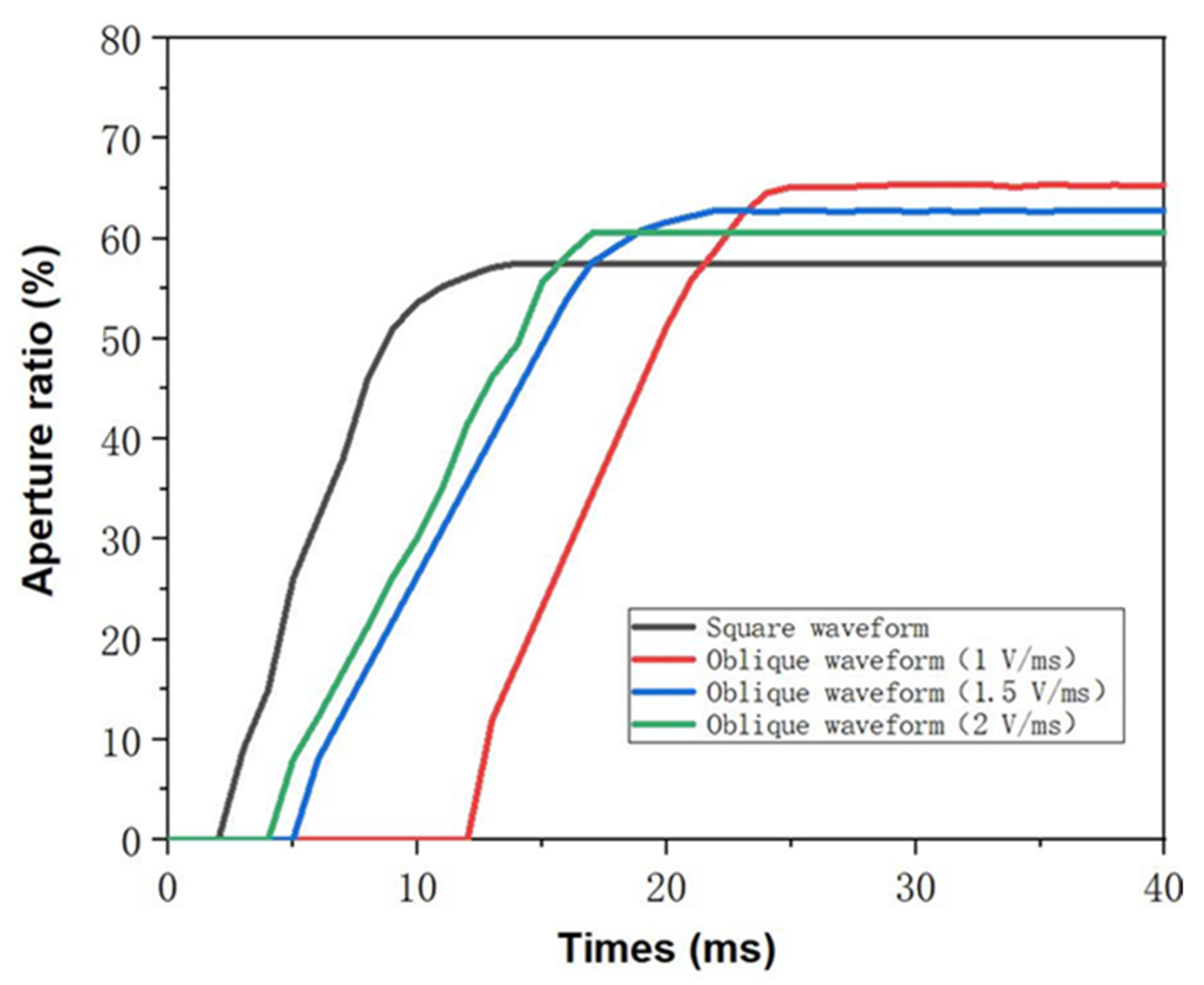
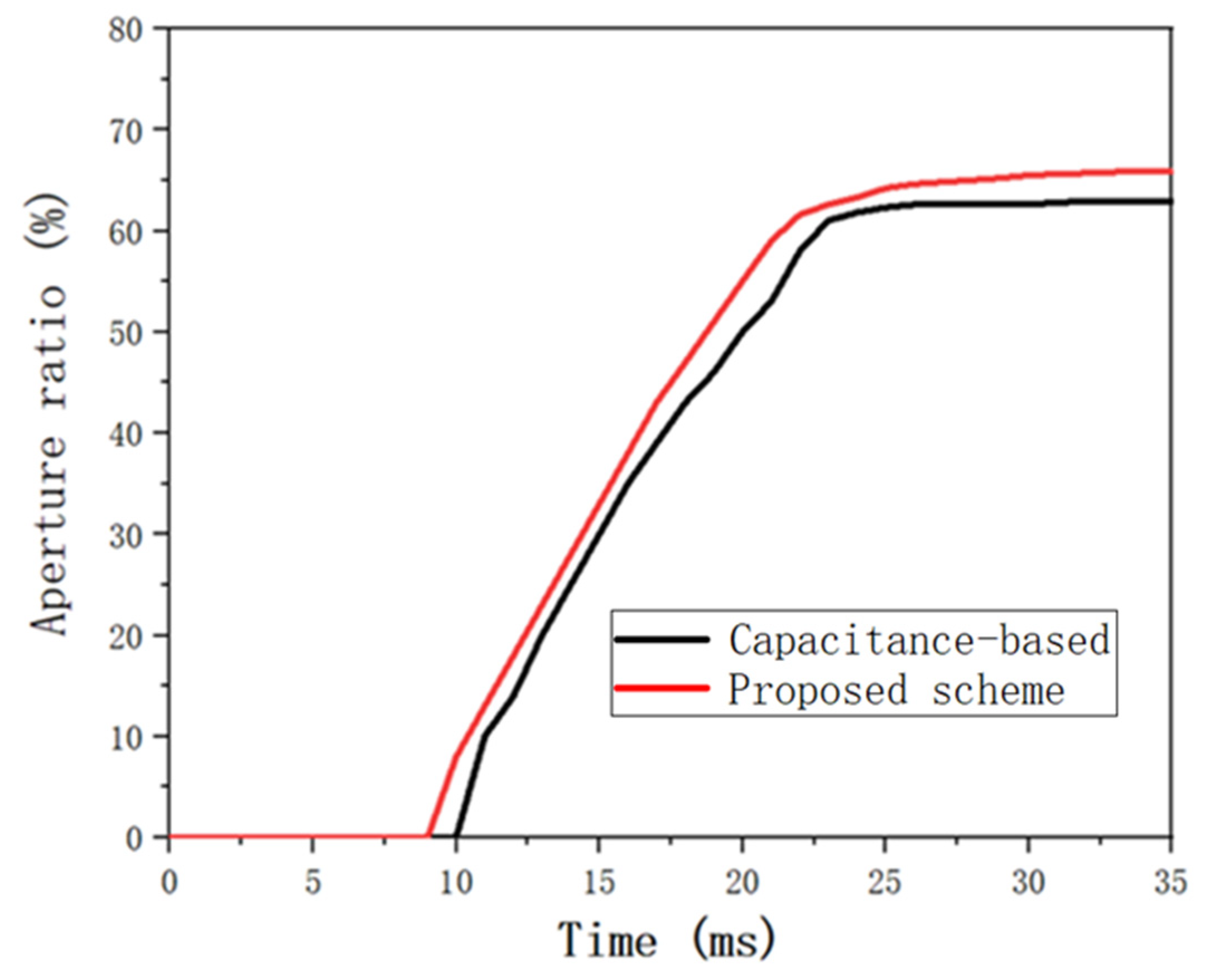
4.2. The Aperture Ratio of EWD Pixel Detection
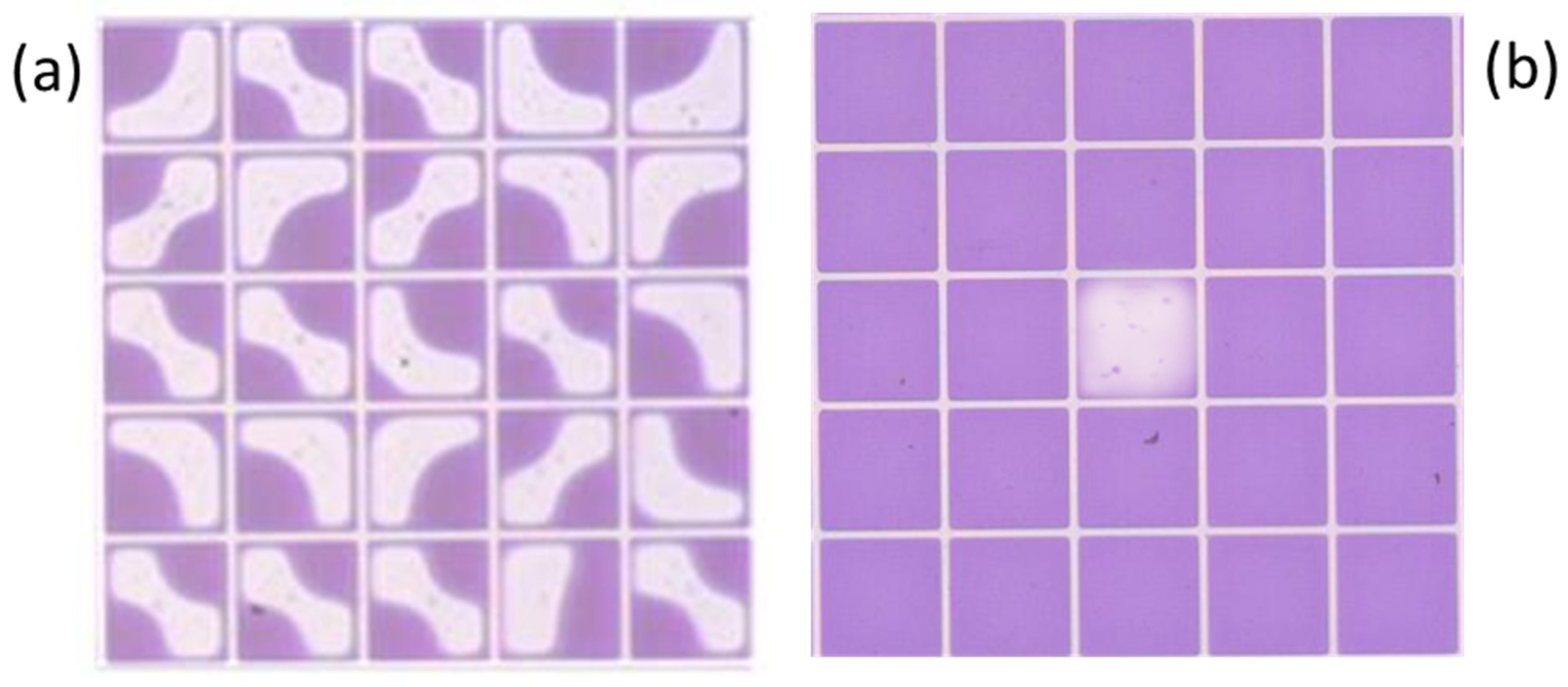
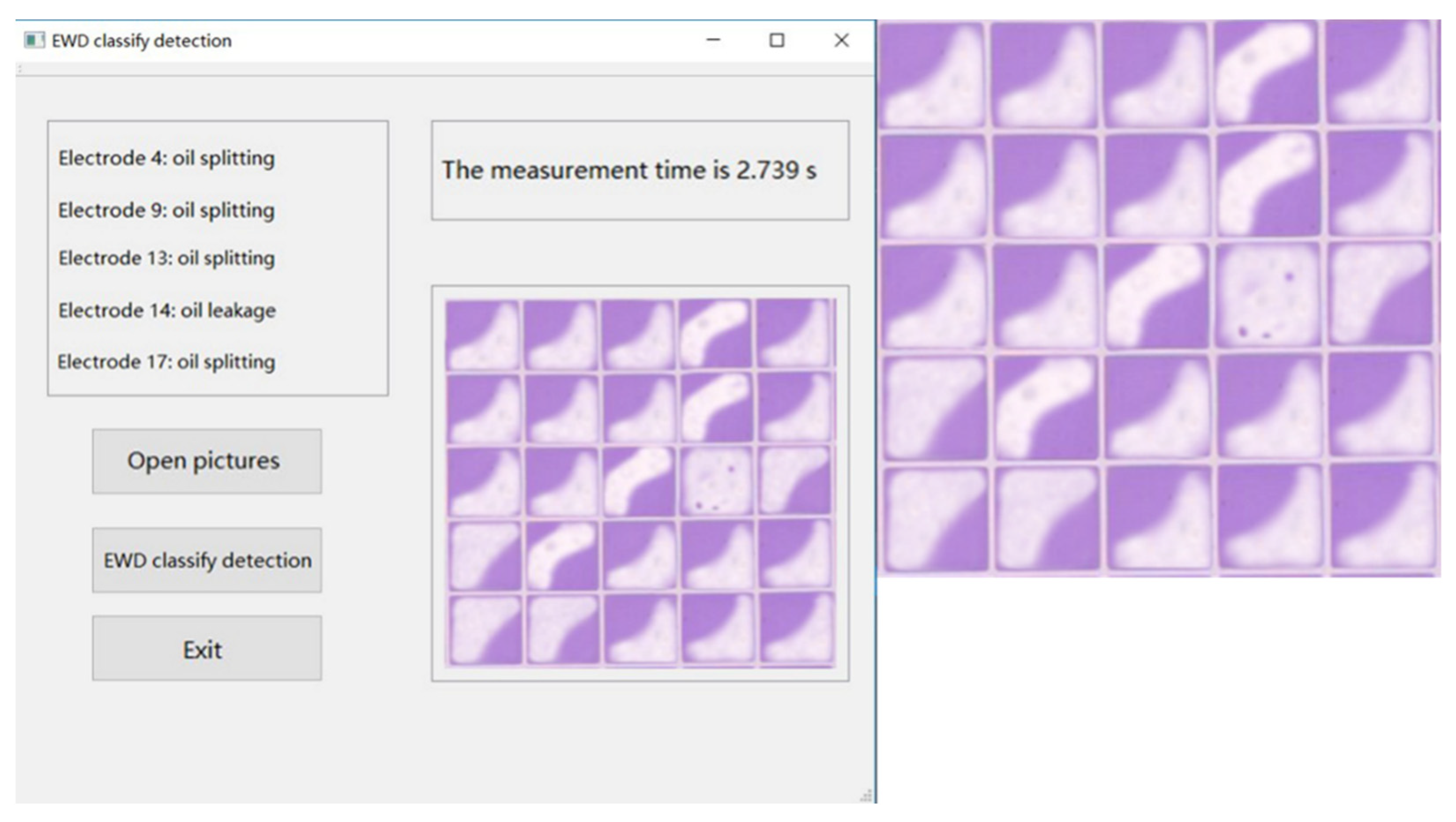
4.3. Oil Motion Defects Detection
4.4. Surface Defects Detection
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature and Abbreviations
| EWD | Electrowetting display |
| PSA | Pressure sensitive adhesive |
| PCB | Printed circuit board |
| KNN | K-nearest neighbor |
| MGWF | Median-based Gaussian weighted filter |
| ROI | Region of interest |
| GUI | Graphical user interface |
| DAC | Digital analog conversion |
| FPGA | Field programmable gate array |
References
- Beni, G.; Hackwood, S. Electro-wetting displays. Apply Phys. Lett. 1981, 38, 207–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, R.A.; Feenstra, B.J. Video-speed electronic paper based on electrowetting. Nature 2003, 425, 383–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shufa, L.; Lixia, T.; Shitao, S.; Dong, Y.; Biao, T. An arc multi-electrode pixel structure for improving the response speed of electrowetting displays. Front. Phys. 2022, 10, 706. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, M.Y.; Zhou, R.; Jiang, H.W.; Zhou, G.F. Effect of liquid conductivity on optical and electric performances of the electrowetting display system with a thick dielectric layer. Results Phys. 2020, 16, 102904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Y.; Chen, L.; Li, H.; Tang, B.; Henzen, A.; Zhou, G. Photolithography Fabricated Spacer Arrays Offering Mechanical Strengthening and Oil Motion Control in Electrowetting Displays. Sensors 2020, 20, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guisong, Y.; Lei, Z.; Pengfei, B.; Biao, T.; Alex, H.; Guofu, Z. Modeling of Oil/Water Interfacial Dynamics in Three-Dimensional Bistable Electrowetting Display Pixels. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 5326–5333. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Q.; Ren, W.Q. A finite element method for electrowetting on dielectric. J. Comput. Phys. 2021, 429, 109998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Zeng, S.Y.; Qian, M.Y.; Lin, Z.X.; Guo, T.L.; Tang, B. Improvement of display performance of electrowetting displays by optimized waveforms and error diffusion. J. Soc. Inf. Disp. 2019, 6, 619–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.M.; Bai, P.F.; Hayes, R.A.; Shui, L.L.; Jin, M.L.; Tang, B.; Zhou, G.F. Novel driving methods for manipulating oil motion in electrofluidic display pixels. J. Disp. Technol. 2016, 12, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Li, W.; Fu, Z.G. Driving Waveform Design for Quick Response Electrowetting Displays Based on Asymmetric Pulse Width Modulation. J. Nanoelectron. Optoelectron. 2020, 15, 1293–1299. [Google Scholar]
- He, T.; Jin, M.; Eijkel, J.C.; Zhou, G.; Shui, L.L. Two-phase microfluidics in electrowetting displays and its effect on optical performance. Biomicrofluidics 2016, 10, 011908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Choi, Y.S.; Choi, K.; Kwon, Y.; Bae, J.; Morozov, A.; Lee, H.S. Measurement of the optical characteristics of electrowetting prism array for three-dimensional display. Proc. SPIE—Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 2013, 8643, 864305. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, M.; Zhao, Q.; Tang, B.; Groenewold, J.; Hayes, R.A.; Zhou, G.F. Simplified dynamical model for optical response of electrofluidic displays. Displays 2017, 49, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Li, S.; Ye, D.C.; Jiang, H.W.; Tang, B.; Zhou, G.F. Synthesis and a photo-stability study of organic dyes for electro-fluidic display. Micromachines 2020, 11, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.J.; Luo, J.K.; Zhao, W.W.; Cao, Y.; Lin, W.J.; Zhou, G.F. A high-resolution and intelligent dead pixel detection scheme for an electrowetting display screen. Opt. Rev. 2018, 25, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Biao, T.; Guisong, Y.; Yuanyuan, G.; Linwei, L.; Alex, H. Progress in Advanced Properties of Electrowetting Displays. Micromachines 2021, 12, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Wang, L.; Zhang, T.Y.; Lai, S.F.; Liu, L.W.; He, W.Y.; Zhou, G.F.; Yi, Z.C. Driving waveform design with rising gradient and sawtooth wave of electrowetting displays for ultra-low power consumption. Micromachines 2020, 11, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, B.; Groenewold, J.; Zhou, M.; Hayes, R.A.; Zhou, G.F. Interfacial electrofluidics in confined systems. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26593–26599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; He, T.; Jiang, H.W.; Wei, B.M.; Chen, G.F.; Fang, X.Z.; Jin, M.L.; Hayes, R.A.; Zhou, G.F.; Shui, L.L. Screen-printing fabrication of electrowetting displays based on poly (imide siloxane) and polyimide. Displays 2014, 37, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Guo, Y.; Barman, J.; Erné, B.H.; Deng, Y.; Zhou, G.; Groenewold, J. Impedance analysis of oil conductivity and pixel non-uniformity in electrowetting displays. Results Phys. 2020, 18, 103223–103230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| FPGA | AD9767 (mA) | First Stage Amplification (V) | Second Stage Amplification (V) | Third Stage Amplification (V) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3FFF | +20 | −1 | +5 | +30 |
| 0 | −20 | +1 | −5 | −30 |
| 2000 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Method | Number of Pixels | Number of Oil Motions Defects | Measurement Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Artificial observation | 25 | 5 | NA |
| 100 | 13 | NA | |
| 225 | 29 | NA | |
| 324 | 50 | NA | |
| Proposed scheme | 25 | 5 | 5 |
| 100 | 12 | 23 | |
| 225 | 25 | 41 | |
| 324 | 42 | 88 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, Z.; Peng, C.; Liu, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhou, G.; Liu, S.; Chen, N. A Low-Cost Drive and Detection Scheme for Electrowetting Display. Processes 2023, 11, 586. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11020586
Luo Z, Peng C, Liu Y, Liu B, Zhou G, Liu S, Chen N. A Low-Cost Drive and Detection Scheme for Electrowetting Display. Processes. 2023; 11(2):586. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11020586
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Zhijie, Cuiling Peng, Yujie Liu, Baoqiang Liu, Guofu Zhou, Shuangyin Liu, and Ningxia Chen. 2023. "A Low-Cost Drive and Detection Scheme for Electrowetting Display" Processes 11, no. 2: 586. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11020586
APA StyleLuo, Z., Peng, C., Liu, Y., Liu, B., Zhou, G., Liu, S., & Chen, N. (2023). A Low-Cost Drive and Detection Scheme for Electrowetting Display. Processes, 11(2), 586. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11020586





