Emissions of Toxic Substances from Biomass Burning: A Review of Methods and Technical Influencing Factors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Applied Methods to Investigate the Biomass Burning Emissions
2.1. Methods of Sampling
2.2. Detection Methods of Toxic Substances
2.2.1. Heavy Metals
2.2.2. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons
2.2.3. Elemental Carbon
2.2.4. Volatile Organic Compounds
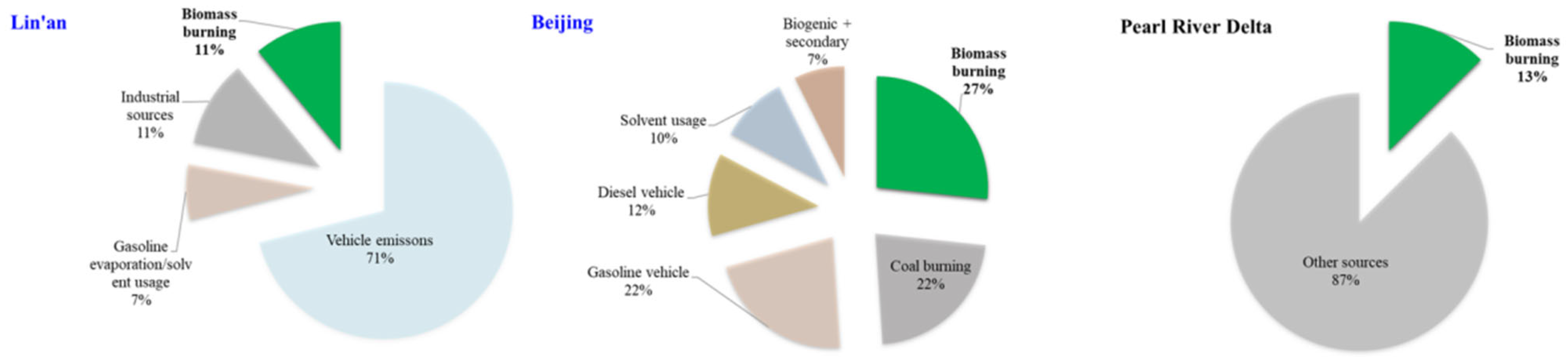
2.3. Source Apportionment
2.4. Emission Inventory
3. Emissions of Toxic Substances
3.1. Emissions of Heavy Metals
3.2. Emissions of PAHs
3.3. Emissions of Elemental Carbon
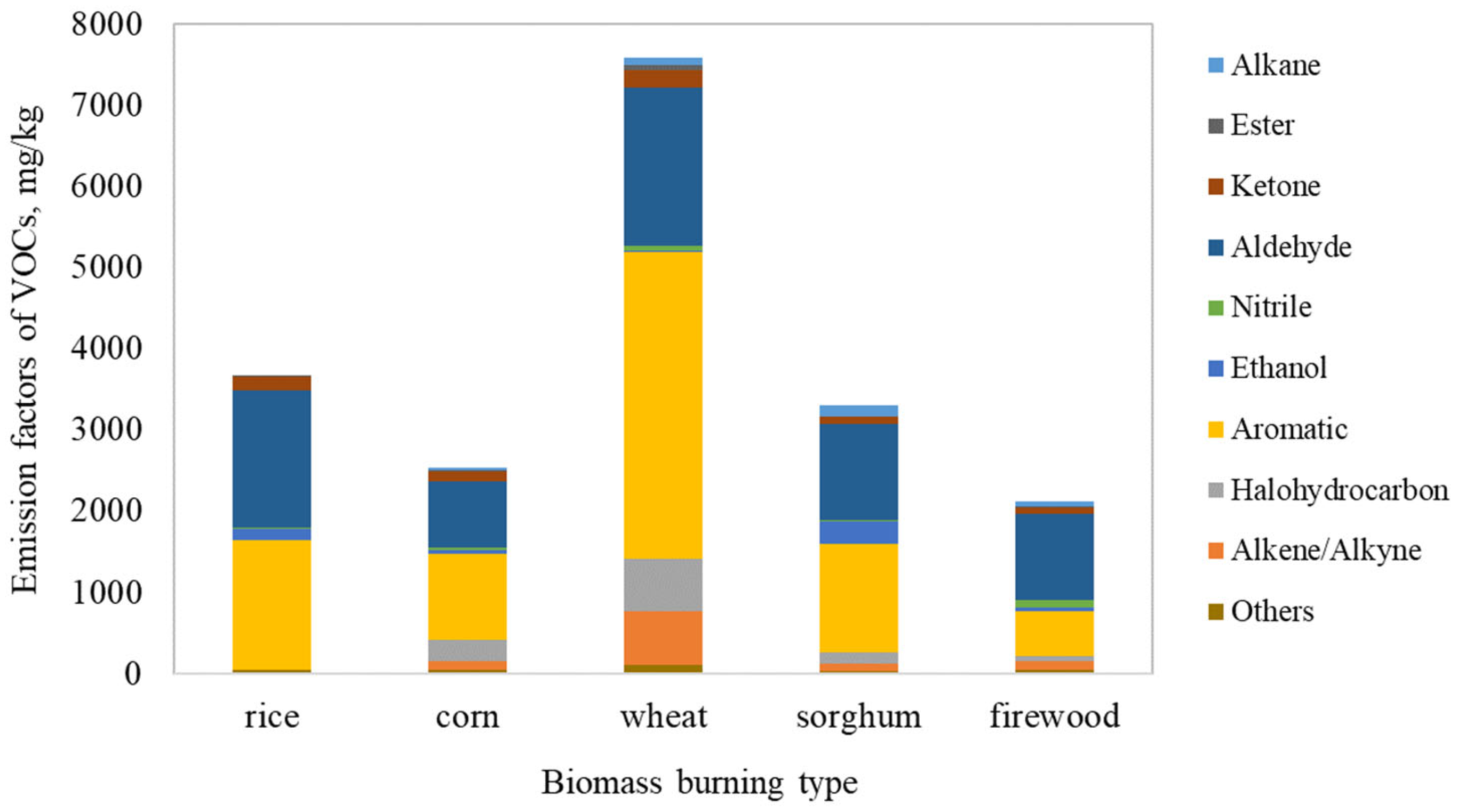
3.4. Emissions of Volatile Organic Compounds
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shen, H.; Luo, Z.; Xiong, R.; Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Du, W.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, H.; Shen, G.; et al. A Critical Review of Pollutant Emission Factors from Fuel Combustion in Home Stoves. Environ. Int. 2021, 157, 106841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Z.; Wang, S.; Fu, X.; Watson, J.G.; Jiang, J.; Fu, Q.; Chen, C.; Xu, B.; Yu, J.; Chow, J.C.; et al. Impact of Biomass Burning on Haze Pollution in the Yangtze River Delta, China: A Case Study in Summer 2011. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 4573–4585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Li, C.; Ristovski, Z.; Milic, A.; Gu, Y.; Islam, M.S.; Wang, S.; Hao, J.; Zhang, H.; He, C.; et al. A Review of Biomass Burning: Emissions and Impacts on Air Quality, Health and Climate in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 1000–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Procházková, B.; Hrubý, J.; Dovrtěl, J.; Dostál, O. Effects of Different Organic Amendment on Winter Wheat Yields under Long-Term Continuous Cropping. Plant Soil Environ. 2003, 49, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palmieri, N.; Forleo, M.B.; Giannoccaro, G.; Suardi, A. Environmental Impact of Cereal Straw Management: An on-Farm Assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 2950–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.K.; Li, J.Q.; Zeng, Y. Advances in the Relationship between Heavy Metal Exposure and Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. (Med. Ed.) 2020, 49, 770–776+783. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Liu, L.L.; Chen, J.B. Research Progress on Effects of Exposure to Heavy Metals on Gut Microbiome and Associations of Gut Microbiome with Related Diseases in Infants and Children. Environ. Occup. Med. 2019, 36, 186–192+195. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, B.; Chi, L.; Mahbub, R.; Bian, X.; Tu, P.; Ru, H.; Lu, K. Multi-Omics Reveals That Lead Exposure Disturbs Gut Microbiome Development, Key Metabolites, and Metabolic Pathways. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2017, 30, 996–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, Y.; Li, S.W.; Ye, S.Z.; Tang, S.; Hu, D.; Wei, L.; Xiao, F. Hexavalent chromium inhibits the formation of neutrophil extracellular traps and promotes the apoptosis of neutrophils via AMPK signaling pathway. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 223, 112614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.S.; Wang, T.J.; Pu, J.; Guo, J.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Jia, G. Multi-element distribution profile in Sprague-Dawley rats: Effects of intratracheal instillation of Cr(VI) and Zn intervention. Toxicol. Lett. 2014, 226, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.R.; Li, N.N.; Jia, G.; Yu, S.F. Progress in Researches on Pulmonary Carcinogenicity of Hexavalent Chromium and Its Mechanism: A Review. Chin. Public Health 2023, 39, 181–185. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.Y.; Wei, F.S. Study on the Relationship between Integrated Exposure to Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Lung Cancer Mortality Rate. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeulen, R.; Downward, G.S.; Zhang, J.; Hu, W.; Portengen, L.; Bassig, B.A.; Hammond, S.K.; Wong, J.Y.Y.; Li, J.; Reiss, B.; et al. Constituents of Household Air Pollution and Risk of Lung Cancer among Never-Smoking Women in Xuanwei and Fuyuan, China. Environ. Health Perspect. 2019, 127, 097001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.; Kong, L.; Yang, K.; Shen, J.; Chen, L.; Jin, S.; Wang, C.; Sha, F.; Wang, L. Characteristics of Air Pollution Episodes Influenced by Biomass Burning Pollution in Shanghai, China. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 238, 117756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Ding, A.; Nie, W.; Mao, H.; Qi, X.; Huang, X.; Xu, Z.; Kerminen, V.-M.; Petäjä, T.; Chi, X.; et al. Enhanced Sulfate Formation by Nitrogen Dioxide: Implications from in Situ Observations at the SORPES Station: Sulfate Formation by Nitrogen Dioxide. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 12679–12694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramanathan, V.; Ramana, M.V.; Roberts, G.; Kim, D.; Corrigan, C.; Chung, C.; Winker, D. Warming trends in Asia amplified by brown cloud solar absorption. Nature 2007, 448, 575–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, A.; Sowlat, M.H.; Lovett, C.; Rauber, M.; Szidat, S.; Boffi, R.; Borgini, A.; De Marco, C.; Ruprecht, A.A.; Sioutas, C. Source Apportionment of Black Carbon (BC) from Fossil Fuel and Biomass Burning in Metropolitan Milan, Italy. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 203, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amnuaylojaroen, T.; Macatangay, R.C.; Khodmanee, S. Modeling the Effect of VOCs from Biomass Burning Emissions on Ozone Pollution in Upper Southeast Asia. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, C.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wang, M.; Jing, X.; Li, G.; Yan, J.; Zhao, L.; Nie, L.; Wang, Y.; et al. Characteristics, Secondary Transformation and Odor Activity Evaluation of VOCs Emitted from Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Power Plant. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 326, 116703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Kong, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Qu, Y.; An, J.; Ma, D.; et al. Characteristics, Secondary Transformation, and Health Risk Assessment of Ambient Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) in Urban Beijing, China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2021, 12, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Kong, S.; Yan, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Yan, Q.; Liu, D.; Wang, S.; Zhang, X.; Qi, S. The Toxicity Emissions and Spatialized Health Risks of Heavy Metals in PM2.5 from Biomass Fuels Burning. Atmos. Environ. 2022, 284, 119178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zosima, A.T.; Tsakanika, L.-A.V.; Ochsenkuhn-Petropoulou, M.T. Particulate Matter Emissions, and Metals and Toxic Elements in Airborne Particulates Emitted from Biomass Combustion: The Importance of Biomass Type and Combustion Conditions. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A-Toxic/Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng. 2017, 52, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, G.; Wang, W.; Yang, Y.; Ding, J.; Xue, M.; Min, Y.; Zhu, C.; Shen, H.; Li, W.; Wang, B.; et al. Emissions of PAHs from Indoor Crop Residue Burning in a Typical Rural Stove: Emission Factors, Size Distributions, and Gas-Particle Partitioning. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 1206–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shen, G.; Tao, S.; Wang, W.; Yang, Y.; Ding, J.; Xue, M.; Min, Y.; Zhu, C.; Shen, H.; Li, W.; et al. Emission of Oxygenated Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons from Indoor Solid Fuel Combustion. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 3459–3465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mohammed, M.O.A.; Song, W.; Ma, Y.; Liu, L.; Ma, W.; Li, W.-L.; Li, Y.-F.; Wang, F.; Qi, M.; Lv, N.; et al. Distribution Patterns, Infiltration and Health Risk Assessment of PM2.5-Bound PAHs in Indoor and Outdoor Air in Cold Zone. Chemosphere 2016, 155, 70–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Hu, D.; Chen, J.; Ye, X.; Wang, S.X.; Hao, J.M.; Wang, L.; Zhang, R.; An, Z. Particle Size Distribution and Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons Emissions from Agricultural Crop Residue Burning. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 5477–5482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Dou, H.; Chang, B.; Wei, Z.; Qiu, W.; Liu, S.; Liu, W.; Tao, S. Emission of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons from Indoor Straw Burning and Emission Inventory Updating in China. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 2008, 1140, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jetter, J.; Zhao, Y.; Smith, K.R.; Khan, B.; Yelverton, T.; DeCarlo, P.; Hays, M.D. Pollutant Emissions and Energy Efficiency under Controlled Conditions for Household Biomass Cookstoves and Implications for Metrics Useful in Setting International Test Standards. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 10827–10834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutlu, E.; Warren, S.H.; Ebersviller, S.M.; Kooter, I.M.; Schmid, J.E.; Dye, J.A.; Linak, W.P.; Gilmour, M.I.; Jetter, J.J.; Higuchi, M.; et al. Mutagenicity and Pollutant Emission Factors of Solid-Fuel Cookstoves: Comparison with Other Combustion Sources. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 974–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oanh, N.T.K.; Reutergårdh, L.B.; Dung, N.T. Emission of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Particulate Matter from Domestic Combustion of Selected Fuels. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 2703–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.; Gaddam, C.K.; Ebersviller, S.M.; Vander Wal, R.L.; Williams, C.; Faircloth, J.W.; Jetter, J.J.; Hays, M.D. A Laboratory Comparison of Emission Factors, Number Size Distributions, and Morphology of Ultrafine Particles from 11 Different Household Cookstove-Fuel Systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 6522–6532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.; Preston, W.; Ebersviller, S.M.; Williams, C.; Faircloth, J.W.; Jetter, J.J.; Hays, M.D. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Fine Particulate Matter Emitted from Burning Kerosene, Liquid Petroleum Gas, and Wood Fuels in Household Cookstoves. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 3081–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Lou, S.; Huang, C.; Qiao, L.; Tang, X.; Chen, C.; Zeng, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, M.; Lu, S.; et al. Source Profiles of Volatile Organic Compounds from Biomass Burning in Yangtze River Delta, China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2014, 14, 818–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, S.; Shen, G.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, M.; Xie, H.; Lin, P.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Tao, S. Field Measurement on the Emissions of PM, OC, EC and PAHs from Indoor Crop Straw Burning in Rural China. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 184, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Wei, W.; Hu, D.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, X. Emission of Speciated Mercury from Residential Biomass Fuel Combustion in China. Energy Fuels 2013, 27, 6792–6800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G. Quantification of Emission Reduction Potentials of Primary Air Pollutants from Residential Solid Fuel Combustion by Adopting Cleaner Fuels in China. J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 37, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Huang, Y.; Wang, R.; Zhu, D.; Li, W.; Shen, G.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Lu, Y.; et al. Global Atmospheric Emissions of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons from 1960 to 2008 and Future Predictions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 6415–6424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roden, C.A.; Bond, T.C.; Conway, S.; Pinel, A.B.O.; MacCarty, N.; Still, D. Laboratory and Field Investigations of Particulate and Carbon Monoxide Emissions from Traditional and Improved Cookstoves. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 1170–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Shen, G.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, X.; Zhuo, S.; Zhong, Q.; Qi, M.; Xue, C.; Liu, G.; Zeng, E.; et al. Comparison of Air Pollutant Emissions and Household Air Quality in Rural Homes Using Improved Wood and Coal Stoves. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 166, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyant, C.L.; Chen, P.; Vaidya, A.; Li, C.; Zhang, Q.; Thompson, R.; Ellis, J.; Chen, Y.; Kang, S.; Shrestha, G.R.; et al. Emission Measurements from Traditional Biomass Cookstoves in South Asia and Tibet. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 3306–3314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Shen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, F.; Wang, T.; Chang, X.; Lei, Y.; Xu, H.; Cao, J.; et al. Effects of Biomass Briquetting and Carbonization on PM2.5 Emission from Residential Burning in Guanzhong Plain, China. Fuel 2019, 244, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, S.; Duan, L.; Hao, J.; Nie, Y. Carbonaceous Aerosol Emissions from Household Biofuel Combustion in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 6076–6081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, J.; Li, Q.; Wu, J.; Jiang, J.; Miao, Z.; Li, D. Biocoal Briquettes Combusted in a Household Cooking Stove: Improved Thermal Efficiencies and Reduced Pollutant Emissions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 1886–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, L.B. The Fate of Trace Elements during Coal Combustion and Gasification: An Overview. Fuel 1993, 72, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Zhong, Z.; Xue, H.; Zhong, D. Migration and Distribution of Heavy Metals During Co-Combustion of Sedum Plumbizincicola and Coal. Waste Biomass Valor. 2018, 9, 2203–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladoye, P.O.; Olowe, O.M.; Asemoloye, M.D. Phytoremediation Technology and Food Security Impacts of Heavy Metal Contaminated Soils: A Review of Literature. Chemosphere 2022, 288, 132555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ye, X.; Zhou, B.; Tian, Z.; Liu, C.; Li, K. Potentially Toxic Elements in Smoke Particles and Residual Ashes by Biomass Combustion from Huangshi National Mine Park, China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2022, 44, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, L.; Peng, L.; Liu, X.; Bai, H.; Song, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z. Emission Characteristics of Heavy Metals and Their Behavior During Coking Processes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 6425–6430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hou, D.; Xiong, G.; Duan, Y.; Cai, C.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Tao, S.; Liu, W. Structural Equation Modeling of PAHs in Ambient Air, Dust Fall, Soil, and Cabbage in Vegetable Bases of Northern China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 239, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, L.C.; George, M.; Gallagher, J.E.; Lewtas, J. Separation of 32P-Postlabeled DNA Adducts of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Nitrated Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons by HPLC. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 1994, 7, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.-R.; Choi, K.-M. Analytical Characteristics of GC/MS and HPLC According to the Concentration Distribution of PAHs. J. Korean Soc. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2015, 25, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phillips, D.L.; Tebbett, I.R.; Bertholf, R.L. Comparison of HPLC and GC-MS for Measurement of Cocaine and Metabolites in Human Urine. J. Anal. Toxicol. 1996, 20, 305–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.H.; Kim, K.H. A Simple Methodological Validation of the Gas/Particle Fractionation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Ambient Air. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.P.; Moon, K.-C.; Lee, J.H. Organic and Elemental Carbon in fine Particles at Kosan, Korea. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 3309–3317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, K.F.; Lee, S.C.; Louie, P.K.K.; Zou, S.C. Seasonal Variation of Carbonyl Compound Concentrations in Urban Area of Hong Kong. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 1259–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mader, B. Sampling Methods Used for the Collection of Particle-Phase Organic and Elemental Carbon during ACE-Asia. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 1435–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleefeld, S.; Hoffer, A.; Krivácsy, Z.; Jennings, S.G. Importance of Organic and Black Carbon in Atmospheric Aerosols at Mace Head, on the West Coast of Ireland (53°19′ N, 9°54′ W). Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 4479–4490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, K.; Hayano, T.; Uematsu, M. Positive Artifact in the Measurement of Particulate Carbonaceous Substances Using an Ambient Carbon Particulate Monitor. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 4713–4717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.; Robles, J.; Wang, X.; Chen, L.-W.; Trimble, D.L.; Kohl, S.D.; Tropp, R.J.; Fung, K.K. Quality assurance and quality control for thermal/optical analysis of aerosol samples for organic and elemental carbon. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 401, 3141–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yau, P.S.; Lee, S.C.; Cheng, Y.; Huang, Y.; Lai, S.C.; Xu, X.H. Contribution of Ship Emissions to the Fine Particulate in the Community near an International Port in Hong Kong. Atmos. Res. 2013, 124, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccioli, P.; Brancaleoni, E.; Frattoni, M.; Cecinato, A.; Pinciarelli, L. Determination of Volatile Organic Compounds (VOC) Emitted from Biomass Burning of Mediterranean Vegetation Species by GC-MS. Anal. Lett. 2001, 34, 937–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Beg, K.R.; Al-Otaiba, Y. A Comparison Study of Sampling and Analyzing Volatile Organic Compounds in Air in Kuwait by Using Tedlar Bags/Canisters and GC-MS with a Cryogenic Trap. Sci. World J. 2006, 6, 551–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikemori, F.; Uranishi, K.; Asakawa, D.; Nakatsubo, R.; Makino, M.; Kido, M.; Mitamura, N.; Asano, K.; Nonaka, S.; Nishimura, R.; et al. Source Apportionment in PM2.5 in Central Japan Using Positive Matrix Factorization Focusing on Small-Scale Local Biomass Burning. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2021, 12, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, J.G.; Chow, J.C.; Fujita, E.M. Review of Volatile Organic Compound Source Apportionment by Chemical Mass Balance. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 1567–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.-H.; Huang, Y.-C.; Pipal, A.S.; Jian, M.-Y.; Liu, Z.-S. Source Apportionment of Black Carbon Using Light Absorption Measurement and Impact of Biomass Burning Smoke on Air Quality over Rural Central Taiwan: A Yearlong Study. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2022, 13, 101264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.-L.; Li, X.; Feng, Y.-C.; Wang, Y.-Q.; Wu, J.-H.; Li, J.; Zhu, T. Combined Source Apportionment, Using Positive Matrix Factorization–Chemical Mass Balance and Principal Component Analysis/Multiple Linear Regression–Chemical Mass Balance Models. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 2929–2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, C.; Yang, W.; Sun, X.; Wang, X.; Bai, Z.; Zhang, X. Emission Factors, Ozone and Secondary Organic Aerosol Formation Potential of Volatile Organic Compounds Emitted from Industrial Biomass Boilers. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 83, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirithian, D.; Thepanondh, S.; Sattler, M.L.; Laowagul, W. Emissions of Volatile Organic Compounds from Maize Residue Open Burning in the Northern Region of Thailand. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 176, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreae, M.O.; Merlet, P. Emission of Trace Gases and Aerosols from Biomass Burning. Global Biogeochem. Cycles 2001, 15, 955–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Warneke, C.; Roberts, J.M.; Veres, P.; Gilman, J.; Kuster, W.C.; Burling, I.; Yokelson, R.; de Gouw, J.A. VOC Identification and Inter-Comparison from Laboratory Biomass Burning Using PTR-MS and PIT-MS. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 303, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chen, Y.; Zeng, L.; Shao, M.; Xie, S.; Chen, W.; Lu, S.; Wu, Y.; Cao, W. Biomass Burning Contribution to Ambient Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) in the Chengdu–Chongqing Region (CCR), China. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 99, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Kong, S.; Zeng, X.; Cheng, Y.; Yan, Q.; Zheng, H.; Yan, Y.; Zheng, S.; Liu, D.; Zhang, X.; et al. First High-Resolution Emission Inventory of Levoglucosan for Biomass Burning and Non-Biomass Burning Sources in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 1497–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tham, J.; Sarkar, S.; Jia, S.; Reid, J.S.; Mishra, S.; Sudiana, I.M.; Swarup, S.; Ong, C.N.; Yu, L.E. Impacts of Peat-Forest Smoke on Urban PM2.5 in the Maritime Continent during 2012–2015: Carbonaceous Profiles and Indicators. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 248, 496–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winiger, P.; Barrett, T.E.; Sheesley, R.J.; Huang, L.; Sharma, S.; Barrie, L.A.; Yttri, K.E.; Evangeliou, N.; Eckhardt, S.; Stohl, A.; et al. Source Apportionment of Circum-Arctic Atmospheric Black Carbon from Isotopes and Modeling. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaau8052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gustafsson, Ö.; Kruså, M.; Zencak, Z.; Sheesley, R.J.; Granat, L.; Engström, E.; Praveen, P.S.; Rao, P.S.P.; Leck, C.; Rodhe, H. Brown Clouds over South Asia: Biomass or Fossil Fuel Combustion? Science 2009, 323, 495–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaustov, A.P.; Redina, M.M. Geochemical Markers Based on Concentration Ratios of PAH in Oils and Oil-Polluted Areas. Geochem. Int. 2017, 55, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, M.O.A.; Song, W.; Liu, L.; Ma, W.; Li, Y.-F.; Wang, F.; Ibrahim, M.A.E.M.; Qi, M.; Elzaki, A.A.; Lv, N. Distribution Patterns and Characterization of Outdoor Fine and Coarse Particles. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2016, 7, 903–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klimont, Z.; Streets, D.G.; Gupta, S.; Cofala, J.; Lixin, F.; Ichikawa, Y. Anthropogenic Emissions of Non-Methane Volatile Organic Compounds in China. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 1309–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Streets, D.G.; He, K.B.; Klimont, Z. Major components of China’s anthropogenic primary particulate emissions. Environ. Res. Lett. 2007, 2, 045027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Nielsen, C.; He, K. An Inventory of Primary Air Pollutants and CO2 Emissions from Cement Production in China, 1990–2020. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jangirh, R.; Ahlawat, S.; Arya, R.; Mondal, A.; Yadav, L.; Kotnala, G.; Yadav, P.; Choudhary, N.; Rani, M.; Banoo, R.; et al. Gridded Distribution of Total Suspended Particulate Matter (TSP) and Their Chemical Characterization over Delhi during Winter. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 17892–17918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Li, J.L.; Chen, N.N.; Cheng, J.J.; Ye, X.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Q.Y. Emission Characteristics of PM2.5 from Domestic Biomass in Rural Areas of Wuhan. J. Jianghan Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2019, 47, 345–350. [Google Scholar]
- Kistler, M.; Schmidl, C.; Padouvas, E.; Giebl, H.; Lohninger, J.; Ellinger, R.; Bauer, H.; Puxbaum, H. Odor, Gaseous and PM10 Emissions from Small Scale Combustion of Wood Types Indigenous to Central Europe. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 51, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Loo, S.; Koppejan, J. (Eds.) The Handbook of Biomass Combustion and Co-Firing; Earthscan: London, UK; Washington, DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs, H.; Szemmelveisz, K.; Palotas, A.B. Solubility Analysis and Disposal Options of Combustion Residues from Plants Grown on Contaminated Mining Area. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 7917–7925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obernberger, I.; Brunner, T.; Barnthaler, G. Chemical Properties of Solid Biofuels—Significance and Impact. Biomass Bioenergy 2006, 30, 973–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirbas, A. Combustion Characteristics of Different Biomass Fuels. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2004, 30, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirbaş, A. Heavy Metal Contents of Fly Ashes from Selected Biomass Samples. Energy Sources 2005, 27, 1269–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obernberger, I.; Biedermann, F.; Widmann, W.; Riedl, R. Concentrations of Inorganic Elements in Biomass Fuels and Recovery in the Different Ash Fractions. Biomass Bioenergy 1997, 12, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Yuan, W.; Wang, T.; Cao, W.; Wang, Y.; Lin, C.; Yang, L.; Guo, J.; Ni, H.; Wu, F. Chemical Signature and Fractionation of Trace Elements in Fine Particles from Anthropogenic and Natural Sources. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 114, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Huang, M.; Zhong, B.; Wang, X.; Tu, Q.; Sun, H.; Wang, C.; Wu, L.; Chang, M. Wet and Dry Deposition Fluxes of Heavy Metals in Pearl River Delta Region (China): Characteristics, Ecological Risk Assessment, and Source Apportionment. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 70, 106–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhao, A.; Matsunaga, T.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Zang, S.; Li, Z.; Yu, T.; Gu, X. High-Resolution Inventory of Mercury Emissions from Biomass Burning in Tropical Continents during 2001–2017. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 653, 638–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obrist, D.; Moosmüller, H.; Schürmann, R.; Chen, L.-W.A.; Kreidenweis, S.M. Particulate-Phase and Gaseous Elemental Mercury Emissions During Biomass Combustion: Controlling Factors and Correlation with Particulate Matter Emissions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.Y.; Zhong, Z.P. Investigation of Transfer Characteristics and Emission Control of Alkali Metals and Heavy Metals in Co-combustion of Coal and Biomass in Fluidized Bed. Ph.D. Thesis, SEU (Southeast University), Nanjing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tao, S. Global Atmospheric Emission Inventory of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) for 2004. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 812–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhao, X.; Shen, G.; Cao, S.; Huang, N.; Qian, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L. Household Fuel Use for Cooking and Heating in China: Results from the First Chinese Environmental Exposure-Related Human Activity Patterns Survey (CEERHAPS). Appl. Energy 2014, 136, 692–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Wang, J.; Zhuo, S.; Zhong, Q.; Wang, W.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Mao, K.; Huang, Y.; Shen, G.; et al. Emissions of Particulate PAHs from Solid Fuel Combustion in Indoor Cookstoves. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 771, 145411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riva, G.; Pedretti, E.F.; Toscano, G.; Duca, D.; Pizzi, A. Determination of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Domestic Pellet Stove Emissions. Biomass Bioenergy 2011, 35, 4261–4267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidur, R.; Abdelaziz, E.A.; Demirbas, A.; Hossain, M.S.; Mekhilef, S. A Review on Biomass as a Fuel for Boilers. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 2262–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Liu, W.; Tao, S. Emission of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 702–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.; Chen, Y.; Xue, C.; Lin, N.; Huang, Y.; Shen, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, T.; Zhang, Y.; Su, S.; et al. Pollutant Emissions from Improved Coal- and Wood-Fuelled Cookstoves in Rural Households. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 6590–6598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Yun, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhong, Q.; Wang, W.; Wang, L.; Qi, M.; Shen, G.; Tao, S. PAHs Emissions from Residential Biomass Burning in Real-World Cooking Stoves in Rural China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Shen, G.; Liu, W.; Du, W.; Su, S.; Duan, Y.; Lin, N.; Zhuo, S.; Wang, X.; Xing, B.; et al. Field Measurement and Estimate of Gaseous and Particle Pollutant Emissions from Cooking and Space Heating Processes in Rural Households, Northern China. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 125, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Bai, P.; Hayakawa, K.; Zhang, L.; Tang, N. Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons Emitted from Open Burning and Stove Burning of Biomass: A Brief Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rejdak, M.; Czardybon, A.; Ignasiak, K.; Robak, J. Utilization of Waste Forest Biomass: Pelletization Studies of Torrefied Sawmill Wood Chips. E3S Web Conf. 2019, 100, 00068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, G.; Tao, S.; Wei, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, R.; Wang, B.; Li, W.; Shen, H.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Y.; et al. Reductions in Emissions of Carbonaceous Particulate Matter and Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons from Combustion of Biomass Pellets in Comparison with Raw Fuel Burning. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 6409–6416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grahame, T.J.; Klemm, R.; Schlesinger, R.B. Public Health and Components of Particulate Matter: The Changing Assessment of Black Carbon. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2014, 64, 620–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bond, T.C. A Technology-Based Global Inventory of Black and Organic Carbon Emissions from Combustion. J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109, D14203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Tian, C.; Feng, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, G. Characterization of Fine and Carbonaceous Particles Emissions from Pelletized Biomass-Coal Blends Combustion: Implications on Residential Crop Residue Utilization in China. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 141, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Ho, S.S.H.; Gong, S.; Ni, J.; Li, H.; Han, L.; Yang, Y.; Qi, Y.; Zhao, D. Characterization of VOCs and Their Related Atmospheric Processes in a Central Chinese City during Severe Ozone Pollution Periods. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 617–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Xing, X.; Lang, J.; Chen, D.; Cheng, S.; Wei, L.; Wei, X.; Liu, C. A Comprehensive Biomass Burning Emission Inventory with High Spatial and Temporal Resolution in China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 2839–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Streets, D.G.; Yarber, K.F.; Woo, J.-H.; Carmichael, G.R. Biomass Burning in Asia: Annual and Seasonal Estimates and Atmospheric Emissions. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2003, 17, 1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiu, H.; Bai, C.-H.; Chuang, K.-J.; Fan, Y.-C.; Chang, T.-P.; Yim, S.H.-L.; Ho, K.-F. Association of Cardiorespiratory Hospital Admissions with Ambient Volatile Organic Compounds: Evidence from a Time-Series Study in Taipei, Taiwan. Chemosphere 2021, 276, 130172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, R. Atmospheric Chemistry of VOCs and NOV. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 2063–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wei, Y.; Fang, Z. Ozone Pollution: A Major Health Hazard Worldwide. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, H.; Wang, T.; Simpson, I.J.; Blake, D.R.; Yu, X.M.; Kwok, Y.H.; Li, Y.S. Source Contributions to Ambient VOCs and CO at a Rural Site in Eastern China. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 4551–4560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- An, J.; Zhu, B.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Lin, X.; Yang, H. Characteristics and Source Apportionment of VOCs Measured in an Industrial Area of Nanjing, Yangtze River Delta, China. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 97, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Liang, D.; Yang, J.; Dai, Q.; Bi, X.; Feng, Y.; Yuan, J.; Xiao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, H. Characterization and Source Apportionment of Volatile Organic Compounds Based on 1-Year of Observational Data in Tianjin, China. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 757–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Yang, L.; Chen, J.; Wang, X.; Xue, L.; Sui, X.; Wen, L.; Xu, C.; Yao, L.; Zhang, J.; et al. Characteristics of Ambient Volatile Organic Compounds and the Influence of Biomass Burning at a Rural Site in Northern China during Summer 2013. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 124, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Jiang, J.; Wang, S.; Rumchev, K.; Mead-Hunter, R.; Morawska, L.; Hao, J. Impacts of Household Coal and Biomass Combustion on Indoor and Ambient Air Quality in China: Current Status and Implication. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 576, 347–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, H.; Yang, G.; Xiu, A.; Zhang, X. A High Resolution Emission Inventory of Domestic Burning in Rural Region of Northeast China Based on Household Consumption. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2020, 30, 921–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Wang, S.X.; Hao, J.M. Characteristics of Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) Emitted from Biofuel Combustion in China. Environ. Sci. 2011, 32, 3515–3521. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, W.; Wang, S.; Chatani, S.; Klimont, Z.; Cofala, J.; Hao, J. Emission and Speciation of Non-Methane Volatile Organic Compounds from Anthropogenic Sources in China. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 4976–4988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, L.J.; Wu, C.Q.; Sun, Z.P.; Liu, X.M. Monitoring of Straw Burning Based on Satellite Remote Sensing and Analysis of Its Influence on Air Quality. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2009, 25, 32–37. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Wei, W.; Du, L.; Li, G.; Hao, J. Characteristics of Gaseous Pollutants from Biofuel-Stoves in Rural China. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 4148–4154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
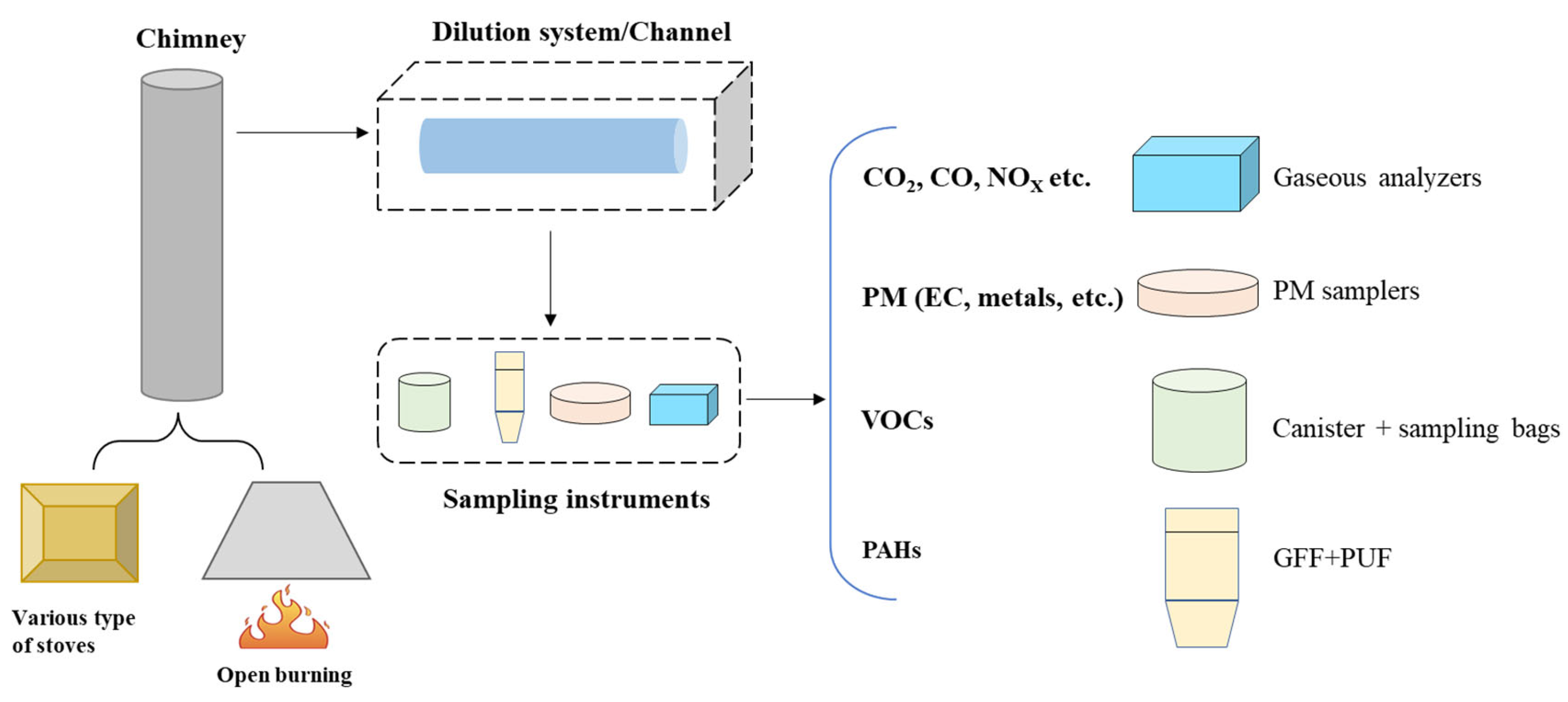
| Combustion Technologies | Types of Biomass | Measurement Facilities |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional stoves (Three stones) [28] | Rice straw [33,34] | Dilution and sampling Systems [1] |
| Brick wok stove [35] | Bean straw [33] | Water boiling test (WBT) protocol [28] |
| Modern cooking stoves [36] | Wheat straw [33,34] | Feasible experimental designs [37] |
| Stoves with chimney [38] | Cotton straw [34] | Lab-based full-capture dilution system [38] |
| Wood gasifier stoves [39] | Rape straw [33,34] | Simulated rural kitchen chamber [35] |
| Traditional clay stoves [40] | Maize straw [41,42] | Kitchen Performance Test (KPT) [39] |
| Open fire burning | Wood [33] | Burning chamber for open fire burning [33] |
| Animal dung [40] | ||
| Biomass briquet [43] |
| EF | Wheat Straw | Corn Straw | Rice Straw | Wood | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb (mg kg−1) | 1.30 ± 0.50 | 0.5 | 2.72 ± 1.71 | 0.99 ± 0.35 | 2.66 ± 0.13 | 1.44 ± 0.51 | 1.69 ± 0.66 | |
| Cr (mg kg−1) | 0.42 ± 0.17 | 7.5 | 0.24 ± 0.03 | 0.29 ± 0.09 | 0.33 ± 0.12 | 0.60 ± 0.21 | 0.19 ± 0.05 | |
| Cd (mg kg−1) | 1.91 ± 1.33 | 0.04 | - | 0.75 ± 0.53 | - | 2.38 ± 2.27 | - | |
| As (mg kg−1) | 0.01 ± 0.06 | 0.2 | - | 0.02 ± 0.04 | - | 0.99 ± 0.12 | - | |
| Mn (mg kg−1) | 1.25 ± 0.61 | 2.4 | 0.50 ± 0.33 | 0.99 ± 0.31 | 0.83 ± 0.78 | 2.14 ± 1.10 | 0.24 ± 0.04 | |
| Fe (mg kg−1) | 3.53 ± 1.20 | 113 | 2.13 ± 0.94 | 2.28 ± 0.44 | 2.42 ± 1.15 | 3.78 ± 1.51 | 1.32 ± 0.53 | |
| Cu (mg kg−1) | 0.93 ± 0.28 | 2.2 | 1.62 ± 0.35 | 0.73 ± 0.26 | 0.81 ± 0.31 | 1.18 ± 0.38 | 0.43 ± 0.04 | |
| Zn (mg kg−1) | 1.00 ± 0.37 | 4.5 | 4.19 ± 2.17 | 0.62 ± 0.18 | 0.81 ± 0.31 | 1.54 ± 0.77 | 3.12 ± 2.27 | |
| Hg (μg kg−1) | 11.09 [91] | 11 [35,92] | 7.94 [91] | 5.56 [91] | 9 [92,93] | |||
 Wu et al., 2022; Wu et al., 2022;  Huang et al., 2022; Huang et al., 2022;  Sun et al., 2019 Sun et al., 2019 | ||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yao, W.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, R.; Wang, M.; Song, W.; Yu, D. Emissions of Toxic Substances from Biomass Burning: A Review of Methods and Technical Influencing Factors. Processes 2023, 11, 853. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11030853
Yao W, Zhao Y, Chen R, Wang M, Song W, Yu D. Emissions of Toxic Substances from Biomass Burning: A Review of Methods and Technical Influencing Factors. Processes. 2023; 11(3):853. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11030853
Chicago/Turabian StyleYao, Wanying, Yixuan Zhao, Ruihan Chen, Mengying Wang, Weiwei Song, and Dajiang Yu. 2023. "Emissions of Toxic Substances from Biomass Burning: A Review of Methods and Technical Influencing Factors" Processes 11, no. 3: 853. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11030853
APA StyleYao, W., Zhao, Y., Chen, R., Wang, M., Song, W., & Yu, D. (2023). Emissions of Toxic Substances from Biomass Burning: A Review of Methods and Technical Influencing Factors. Processes, 11(3), 853. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11030853